The relationship between the thermohaline circulation and climate variability
|
|
|
- Vivian Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The relationship between the thermohaline circulation and climate variability ZHOU Tianjun 1, ZHANG Xuehong 1 & WANG Shaowu 2 1. State Key Laboratory of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG), Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing , China; 2. Geophysical Department, Peking University, Beijing , China Correspondence should be addressed to Zhou Tianjun ( zhou@lasgsgi8.iap.ac.cn) Abstract The long-term integration with the Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land System model of the State Key Laboratory of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG), Institute of Atmospheric Physics(IAP), Chinese Academy of Sciences has been used in the investigations on the relationship between the thermohaline circulation and climate variability. The results show that the strength of the North Atlantic Thermohaline circulation (THC) is negatively correlated with the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO). Based on this kind of relationship, and also the instrumentmeasured climate record such as air pressure and sea surface temperature, the activity of the thermohaline circulation during the 20th century has been evaluated. The inferred variations of the strength of the THC is that, during two multi-decadal periods of and , the THC is estimated to have been running stronger, whereas during the two periods of and , it appears to have been weaker. Keywords: thermohaline circulation, North Atlantic Oscillation climate variability. The climate system of the Earth can be broken down into a number of components: the ocean, the atmosphere, the lithosphere, the cryosphere, and the biosphere. The ultimate forcing mechanism of oceanic and atmospheric motions is the pole-to-equator gradient of radiative heating of the planet. There exists surplus of heat in the equatorial region and deficit of heat in the polar region. In order to keep the thermal balance of the Earth, the excessive heat collected in the equatorial regions must be transported to the polar regions. The transport is taken up by the meridional circulation branch of the climate system, which is mainly made up of the atmospheric components of the famous Hadley cell, the Ferrel cell, and the polar cell, and also its ocean component of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation. About 90% of the water in the world ocean are involved in the thermohalien circulation, which is located beneath the wind driven surface currents and at great depths. The power for this slower, deeper circulation comes from the action of gravity on adjacent water masses of different densities. Since density is largely a function of temperature and salinity, the circulation due to density difference is called thermohaline circulation. The contemporary thermohaline circulation is characterized as the Atlantic Great Ocean Conveyor Belt. Intense radiative cooling of the polar ocean surface during the winter causes the formation or extension of sea ice. Cooling and brine rejection (i.e. salt ejection during ice formation) produces an unstable density gradient in the upper ocean allowing the cool and saline dense water to mix down convectively. Just as the tropical ascent is the rising part of the atmospheric direct circulation (i.e. warm air rising), the sinking motion of the ocean is the thermally direct part of the ocean circulation (i.e. cold water sinking). The thermodynamically direct circulation converts potential energy into kinetic energy. These processes lead to the formation of the deep ocean water, which spreads out away from the poles until it slowly ascends toward the equator. At last, the water moves back to the poles from the equator in the form of shallow warm water circulation [1,2]. The Atlantic meridional overturning (hereafter referred to as the thermohaline circulation (THC)) plays an important role in the pole-ward oceanic heat transport. The variability of the THC and also the accompanied change of pole-ward heat transport have strong impacts on the regional or global climate. Thus, the activity of the THC on the decadal to centennial time scales is highlighted both in the recently produced Science Plan of the World Climate Research Program (WCRP) Climate Variability and Predictability (CLIVAR) Program [3] and in the International Geosphere-Biosphere Program (IGBP) Past Global Changes (PAGES) Core Project [4]. Recognition on the important role of the THC in the climate system is regarded as one of the important developments in the climate research 1052 Chinese Science Bulletin Vol. 45 No. 11 June 2000
2 community in the 1990s. The incompleteness of the observational record makes it extremely difficult to study the variations of THC and associated processes based solely on the observational data. Thus, as a complementary approach, numerical models are effectively used. The authors once reviewed the international research work on THC systematically, and pointed out that most of the former studies focused mainly on the internally variability of THC in single oceanic general circulation models (OGCM), and could not link closely with the widely cared problems of contemporary climate variability [5]1). The relationship between the THC and contemporary climate is therefore of direct interest to current study. The output from a multi-century integration of a coupled Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land System model (hereafter referred to as GOALS), developed at IAP s State Key Laboratory of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics, forms the basis of the analyses presented here. Based on the physical connections between the THC and regional climate revealed by the model, and also the instrumentmeasured climate record such as air pressure and sea surface temperature, the activity of the THC during the 20th century has been evaluated. 1 Descriptions of the coupled global ocean-atmosphere-land system model The atmospheric component of GOALS is a global spectral AGCM, which is rhomboidally truncated at zonal wave number 15 (L9R15). There are nine unevenly spaced levels in the vertical σ coordinate. For the purpose of reducing truncation errors, a standard stratification of temperature is introduced into the dynamical framework and the scheme of the reduction of a standard atmosphere is used to improve the model performance. A new k-distribution radiation scheme is implemented into the model. Cloud processes are treated more rationally in this scheme [6]. A diagnosed cloud cover and liquid water path scheme is introduced into the model [7]. To get more insight into the impacts of land surface processes on climate, a simplified biosphere model (SSiB) developed by Sellers and Xue is implemented into the AGCM. There is 1 vegetation layer, 3 soil layers and 11 types of vegetation in SSIB [8]. The oceanic component of GOALS is an OGCM with 20 unevenly spaced layers in the vertical η coordinate. The horizontal resolution is 4 in latitude by 5 in longitude on B-grid. The depth of the maximum flat-bottom is m. Domain of the OGCM covers the global scope except the North Pole. The continental outlines are fairly realistic. Both the Drake and Indonesian Passages are opened, and no attempt was made to broaden the Drake Passage gap artificially [9]. A simple thermodynamic seaice model formulated based on ref. [10] is incorporated into the ocean model. The Prediction-Correction coupling scheme for monthly mean anomaly has been chosen for the ocean-atmosphere coupling process [11]. The ocean and the atmosphere exchange heat flux and momentum through their interface. The model sea surface salinity was restored to the observational field seasonally. The coupled model (i.e. GOALS) has been integrated for 200 years, preliminary analysis shows that it controls sea surface climate drift successfully and can reproduce the basic characteristics of atmospheric and oceanic circulation reasonably. The output of annual mean physical variables from the 200-year integration forms the basis of the forthcoming analyses. 2 Variability of the thermohaline circulation in GOALS As shown in fig. 1, the stream-function (200-year mean) is used in describing the meridional thermohaline circulation in the Atlantic Basin. Note the positive values mean anticlockwise direction, and negative values mean clockwise direction. It is apparent that the model can successfully reproduce two major members of the global scale water masses, i.e. the North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) and the Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW). The southward outflow of NADW is notable, which can cross the equator and reach 30 S. In this study, the intensity of the THC in the North Atlantic is defined each year as the maximum value of the sinking branch around 60 N of the stream- function representing the annual mean meridional thermohaline circulation. The time series of the index, which represents the fluctuations in the intensity of the annual mean THC, is shown in fig. 2(a). Visual inspection of the figure reveals 1) Zhou Tianjun, Modeling studies on the variability of the thermohaline circulation and its link to climate, Ph. D. Thesis of Peking University, 1999, Chinese Science Bulletin Vol. 45 No. 11 June
3 robust variability on inter-annual time scale. The THC oscillated around the annual mean state of m 3 /s or so in all 200 years of the integration, the difference between the highest and lowest values is about m 3 /s. Superposed on the inter-annual variability, there also exists prominent fluctuations on decadal scale. As shown in fig. 2(b), spectral analysis of the time series from the total 200 years demonstrates the dominant period of 24 years. In order to reveal the variation of sea surface temperature (SST) associated with the fluctuations of the THC, correlation coefficients between the THC index shown in fig. 2(a) and annual-mean SST over the North Atlantic region are calculated and the result is shown in fig. 3(a). The pattern of the correlation field is characterized by an anti-symmetric dipole mode, with a negative core over the sea southeast to the Newfoundland and a positive core off western coast of the Northern African continent. This implies that when THC is stronger than normal, the western part of North Atlantic is cooler than normal, and the eastern part is warmer than normal. Fig. 1. Modeled annual mean stream-function of the meridional overturning in the Atlantic Basin (unit: 10 6 m 3 /s). Fig. 2. (a) Time series of the annual mean intensity of the index of the meridional overturning in the North Atlantic. (b) Solid line denotes spectrum of the 200-year THC index time series shown in fig. 1. Dashed line denotes 95% confidence level for accepting the red noise null hypothesis. The spatial pattern of the anomalies of model SST associated with fluctuations in the intensity of the THC is shown in fig. 3(b). These differences are computed by subtracting the mean of two decades Fig. 3. (a) The pattern of correlation field between the annual mean model sea surface temperature and THC index. (b) Differences in annual mean model sea surface temperature between two decades with anomalous large THC index values and two decades with anomalous small THC index values (unit: ) Chinese Science Bulletin Vol. 45 No. 11 June 2000
4 with anomalous small values of the THC index from the mean of two decades with anomalous large values of the THC, and thus can reveal the variation of SST associated with the decadal-scale fluctuations of the THC intuitively. Areas with confidence limits of 95% using t-test are shaded. Note that the pattern of SST change bears encouraging resemblance to the pattern of correlation coefficients shown in fig. 3(a), with anomalies of negative polarity southeast to the Newfoundland and anomalies of positive polarity off the western coast of the Northern African continent. The maximum value of positive anomaly is 0.4 and the minimum value of negative anomaly is Connections between the thermohaline circulation and regional climate The spatial pattern of the correlation coefficients between the THC index series and annual mean model sea level pressure is shown in fig. 4(a), revealing the linkage between the THC and regional climate. Note that only part region over the North Atlantic exceeds the test of 95% confidence limits and appears as a pattern similar to the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO). This implies that the intensity of THC is negatively correlated with the NAO. By calculating the correlation between the annual mean model THC index series and the annual mean model NAO index series directly, we get a result of -0.26, which exceeds the test of 95% confidence limits. This confirms that the intensity of the THC is indeed negatively correlated with the NAO in GOALS. Fig. 4. (a) The pattern of correlation field between the annual mean model THC series and annual-mean model sea level pressure, only the values that exceed the 95% confidence level are shown. (b) Annual mean THC composite field of sea level pressure (high THC index minus low index, threshold being one standard deviation) (unit: hpa). Another approach to exhibit the connections between the THC and the associated atmospheric variability is composite analysis. We consider composite differences between THC extreme phases. Ensemble members of positive and negative composites are keyed to index values (taken from fig. 2(a)) greater and smaller than one standard deviation, respectively. The resulting large-scale anomaly is shown in fig. 4(b) and is locally significant at the 95% confidence level according to a t-test. It can be found in fig. 4(b) that the anomalous pressure pattern encountered during a positive THC phase is associated with a negative NAO phase. In fact, fig. 4(b) reconfirms the negative correlation between the intensity of THC and the NAO. 4 Elementary evaluations on activity of the North Atlantic thermohaline circulation during the 20th century The scarcity of observational oceanic data makes it impossible to offer a time series for the intensity of the North Atlantic thermohaline circulation during the 20th century. Contrary to the paucity of observational oceanic data, the observational sea level pressure record is relatively abundant. According to the relationship of negative correlation between the THC and the NAO exposed by the GOALS model as discussed in section 3, we can make an elementary evaluation on the actual variability of the THC in the past 100 years or so. Climate Change 1995 reported the observational NAO index from 1867 to 1995 [12], according to this time series, the activity of the NAO has experienced four phases of weak-robust-weak-robust since the year 1867, and the transition years are 1904, 1934 and 1972, respectively. Therefore, we can infer the variations of the strength of the THC as, during two multi-decadal periods of and , the THC is estimated to have been running stronger, whereas during the two periods of and , it appears to have Chinese Science Bulletin Vol. 45 No. 11 June
5 been weaker. As mentioned above, accompanied by the strengthening of the THC, the associated changes of SST in the North Atlantic domain are the cooling trend southeast to the Newfoundland and the warming in the other regions. The temporal realization of the Atlantic multi-decadal mode computed from temporal amplitude time series and the areaaveraged spatial loading over the rectangular area in the North Atlantic (45 65 N, W) first provided by Enfield and Mestas-Nunez (1998) is shown in fig. 5 [13]. Positive values indicate warm SST anomalies and imply a stronger THC, consequently, negative values mean warm SST anomalies and suggest a weaker THC. SST in the subpolar North Atlantic are warmed during multi-decadal periods when the THC is stronger, and cooled when the THC is weaker. Generally speaking, the inferred trend of the THC from 1860 to 1995 is similar to that evaluated from the actual activity of the North Atlantic Oscillation. Acknowledgements This work was supported by the National Key Project Studies on the Short term Climate Prediction over China (Grant No ), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No ) and the Excellent National Key Laboratory Research Project (Grant No ). References Fig. 5. Time series of the observational area-averaged SST anomalies over the subpolar North Atlantic (45 65 N, W) (given by Enfield and Mestas-Nunez,1998, quoted from Gray, 1998). 1. Broecker,W. S., The great ocean conveyor, Oceanography, 1991, 4: Schmitz, Jr. W. J., On the interbasin-scale thermohaline circulation, Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33: Duplessy, J. C., Overpeck, J., The PAGES/CLIVAR Intersection Providing the paleoclimatic perspective needed to understand climate variability and predictability, Report of a Joint IGBP/WCRP Workshop, Venice, Italy, International CLIVAR Project Office, CLIVAR Initial Implementation Plan, WCRP No. 103, Hamburg, 1999, Zhou, T. J., Wang, S. W., Zhang, X. H., Reviews of the modeling studies on the stability and variability of the thermohaline circulation, Advances in Earth Sciences (in Chinese), 1998, 4: Wu, G. X., Zhang, X. H., Liu, H. et al., Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land system model of LASG (GOALS//LASG) and its performance in simulation study, Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology (in Chinese), 1997, 8(supplement): Liu, H., Zhang, X. H., Wu, G. X., Cloud feedback on variability of SST of western equatorial Pacific in GOALS/LASG model, Adv. Atmos. Sci., 1998, 15: Xue, Y. K., Sellers, P. J. et al., A simplified biosphere model for global climate studies, J. Climate, 1991, 4: Zhang, X. H., Chen, K. M., Jin, X. Z. et al., Simulation of the thermohaline circulation with a twenty-layer oceanic general circulation model, Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 1996, 55: Parkinson, C. L., Washington, W. M., A large-scale numerical model of sea ice, J. Geophys. Res., 1979, 84: Yu, Y. Q., Zhang, X. H., A modified scheme for air-sea coupling, Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1998, 43: Houghton, J. T., Meira, Filho L. G., Callander, B. A. et al., Climate Change 1995: The Science of Climate Change, New York: Cambridge University Press, Gray, W. M., the Atlantic Ocean Thermohaline Circulation as a Driver for Multi-decadal Variations in El Niño Intensity and Frequency, In: Proceedings of the Twenty-third Annual Climate Diagnostic and Prediction Workshop, Florida: American Meteorology Society, 1998, (Received December 9, 1999) 1056 Chinese Science Bulletin Vol. 45 No. 11 June 2000
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Mean Climatic Characteristics in High Northern Latitudes in an Ocean-Sea Ice-Atmosphere Coupled Model
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 21, NO. 2, 24, 236 244 236 Mean Climatic Characteristics in High Northern Latitudes in an Ocean-Sea Ice-Atmosphere Coupled Model LIU Xiying* (4UH), ZHANG Xuehong
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 21, NO. 2, 24, 236 244 236 Mean Climatic Characteristics in High Northern Latitudes in an Ocean-Sea Ice-Atmosphere Coupled Model LIU Xiying* (4UH), ZHANG Xuehong
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change
 Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
Please be ready for today by:
 Please be ready for today by: 1. HW out for a stamp 2. Paper and pencil/pen for notes 3. Be ready to discuss what you know about El Nino after you view the video clip What is El Nino? El Nino Basics El
Please be ready for today by: 1. HW out for a stamp 2. Paper and pencil/pen for notes 3. Be ready to discuss what you know about El Nino after you view the video clip What is El Nino? El Nino Basics El
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY
 MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific subtropical high
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific
 Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
El Niño Seasonal Weather Impacts from the OLR Event Perspective
 Science and Technology Infusion Climate Bulletin NOAA s National Weather Service 41 st NOAA Annual Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop Orono, ME, 3-6 October 2016 2015-16 El Niño Seasonal Weather
Science and Technology Infusion Climate Bulletin NOAA s National Weather Service 41 st NOAA Annual Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop Orono, ME, 3-6 October 2016 2015-16 El Niño Seasonal Weather
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
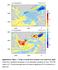 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Weather & Ocean Currents
 Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Winds and Currents in the Oceans
 Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L24701, doi:10.1029/2006gl027655, 2006 Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon Riyu Lu, 1,2 Buwen Dong, 3 and Hui Ding 2,4 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L24701, doi:10.1029/2006gl027655, 2006 Impact of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the Asian summer monsoon Riyu Lu, 1,2 Buwen Dong, 3 and Hui Ding 2,4 Received
MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation
 1 MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation Ocean Climate Temperature Zones The pattern of approximately parallel oceanic surface isotherms (lines of constant temperature)
1 MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation Ocean Climate Temperature Zones The pattern of approximately parallel oceanic surface isotherms (lines of constant temperature)
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Lecture 2
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 2 Ocean basins and relation to climate Learning objectives: (1)What are the similarities and differences among different ocean basins? (2) How does
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 2 Ocean basins and relation to climate Learning objectives: (1)What are the similarities and differences among different ocean basins? (2) How does
Pathways in the ocean
 Pathways Pathways in the in the ocean by Sybren Drijfhout Introduction The properties of water masses in the ocean are set by air-sea interactions at the surface and convective overturning. As direct transfer
Pathways Pathways in the in the ocean by Sybren Drijfhout Introduction The properties of water masses in the ocean are set by air-sea interactions at the surface and convective overturning. As direct transfer
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Chapter 4. Understanding the Weather. Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations
 Video: Meteorologist Paul Douglas April 2013 Understanding the Weather Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations There are natural climate cycle that cause large climate changes
Video: Meteorologist Paul Douglas April 2013 Understanding the Weather Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations There are natural climate cycle that cause large climate changes
Léo Siqueira Ph.D. Meteorology and Physical Oceanography
 Léo Siqueira Ph.D. Meteorology and Physical Oceanography Modular Ocean Model (Griffies 2009) from GFDL version MOM4p1: Includes the Sea Ice Simulator (SIS) built-in ice model (Winton 2000). Includes TOPAZ
Léo Siqueira Ph.D. Meteorology and Physical Oceanography Modular Ocean Model (Griffies 2009) from GFDL version MOM4p1: Includes the Sea Ice Simulator (SIS) built-in ice model (Winton 2000). Includes TOPAZ
Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium
 Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium Meng Zuo, Wenmin Man, Tianjun Zhou Email: zuomeng@lasg.iap.ac.cn Sixth WMO International
Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium Meng Zuo, Wenmin Man, Tianjun Zhou Email: zuomeng@lasg.iap.ac.cn Sixth WMO International
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Surface Circulation Ocean current Surface Currents:
 All Write Round Robin G1. What makes up the ocean water? G2. What is the source of the salt found in ocean water? G3. How does the water temperature affect the density of ocean water? G4. How does the
All Write Round Robin G1. What makes up the ocean water? G2. What is the source of the salt found in ocean water? G3. How does the water temperature affect the density of ocean water? G4. How does the
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Cat Response
 2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia
 Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia I. Introduction To assess the impact of large-scale environmental conditions on tropical cyclone
Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia I. Introduction To assess the impact of large-scale environmental conditions on tropical cyclone
Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice. (from Our Changing Planet)
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Earth s s Climate System Solar forcing Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Earth s s Climate System Solar forcing Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry
Earth s Climate System. Surface Albedo. Climate Roles of Land Surface. Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Earth s Climate System Solar forcing Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry Cycles (from Our Changing
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Earth s Climate System Solar forcing Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry Cycles (from Our Changing
climate system and its subcomponents: the atmosphere, ocean, land surface, Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A A general description of the Earth
 Earth System Climate () Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 9:30-10:20 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book The Earth System, Kump, Kasting, and Crane, Prentice-Hall Global Physical Climatology, Hartmann; Academic
Earth System Climate () Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 9:30-10:20 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book The Earth System, Kump, Kasting, and Crane, Prentice-Hall Global Physical Climatology, Hartmann; Academic
WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA
 WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA INTRODUCTION A good understanding of the causes of climate variability depend, to the large extend, on the precise knowledge of the functioning of the
WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA INTRODUCTION A good understanding of the causes of climate variability depend, to the large extend, on the precise knowledge of the functioning of the
What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate
 What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA POS/PSMI Joint Breakout Session 2017 US CLIVAR Summit Baltimore, August 9,
What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA POS/PSMI Joint Breakout Session 2017 US CLIVAR Summit Baltimore, August 9,
Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton
 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
AMOC Impacts on Climate
 AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY
 NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani NTU International
NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani NTU International
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global warming?
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042743, 2010 Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042743, 2010 Is the basin wide warming in the North Atlantic Ocean related to atmospheric carbon dioxide and global
Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity?
 Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom. 2 Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, Exeter, United Kingdom.
 9.1 RUNNING A CLIMATE MODEL IN FORECAST MODE TO IDENTIFY THE SOURCE OF TROPICAL CLIMATE ERRORS: WITH SPECIFIC REFERENCE TO THE DRY BIAS OVER THE MARITIME CONTINENT IN AN ATMOSPHERE ONLY GCM 1 Jane Strachan,
9.1 RUNNING A CLIMATE MODEL IN FORECAST MODE TO IDENTIFY THE SOURCE OF TROPICAL CLIMATE ERRORS: WITH SPECIFIC REFERENCE TO THE DRY BIAS OVER THE MARITIME CONTINENT IN AN ATMOSPHERE ONLY GCM 1 Jane Strachan,
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 )
 3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013
 1 Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013 by William Gray and Phil Klotzbach Preliminary Draft - March 2014 (Final draft by early June) ABSTRACT This paper discusses the causes of the unusual dearth
1 Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013 by William Gray and Phil Klotzbach Preliminary Draft - March 2014 (Final draft by early June) ABSTRACT This paper discusses the causes of the unusual dearth
LETTERS. Tropical Stabilization of the Thermohaline Circulation in a Greenhouse Warming Simulation
 VOLUME 13 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 1JUNE 2000 LETTERS Tropical Stabilization of the Thermohaline Circulation in a Greenhouse Warming Simulation M. LATIF, E.ROECKNER, U.MIKOLAJEWICZ, AND R. VOSS Max-Planck-Institut
VOLUME 13 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 1JUNE 2000 LETTERS Tropical Stabilization of the Thermohaline Circulation in a Greenhouse Warming Simulation M. LATIF, E.ROECKNER, U.MIKOLAJEWICZ, AND R. VOSS Max-Planck-Institut
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, :30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used.
 SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, 2003 11:30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used. There are three sections to the exam: multiple choice, short answer, and long problems. Points are given
SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, 2003 11:30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used. There are three sections to the exam: multiple choice, short answer, and long problems. Points are given
Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models
 Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models Robert Marsh, Beverly de Cuevas, Andrew Coward & Simon Josey (+ contributions by
Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models Robert Marsh, Beverly de Cuevas, Andrew Coward & Simon Josey (+ contributions by
East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 91 97 East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model ZENG Xian-Feng 1, 2, LI Bo 1, 2, FENG Lei
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 91 97 East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model ZENG Xian-Feng 1, 2, LI Bo 1, 2, FENG Lei
isopycnal outcrop w < 0 (downwelling), v < 0 L.I. V. P.
 Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation
 Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
1. Oceans. Example 2. oxygen.
 1. Oceans a) Basic facts: There are five oceans on earth, making up about 72% of the planet s surface and holding 97% of the hydrosphere. Oceans supply the planet with most of its oxygen, play a vital
1. Oceans a) Basic facts: There are five oceans on earth, making up about 72% of the planet s surface and holding 97% of the hydrosphere. Oceans supply the planet with most of its oxygen, play a vital
1. Introduction. 3. Climatology of Genesis Potential Index. Figure 1: Genesis potential index climatology annual
 C. ENSO AND GENESIS POTENTIAL INDEX IN REANALYSIS AND AGCMS Suzana J. Camargo, Kerry A. Emanuel, and Adam H. Sobel International Research Institute for Climate and Society, Columbia Earth Institute, Palisades,
C. ENSO AND GENESIS POTENTIAL INDEX IN REANALYSIS AND AGCMS Suzana J. Camargo, Kerry A. Emanuel, and Adam H. Sobel International Research Institute for Climate and Society, Columbia Earth Institute, Palisades,
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: August 2009
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
Reprint 675. Variations of Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South China Sea. Y.K. Leung, M.C. Wu & W.L. Chang
 Reprint 675 Variations of Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South China Sea Y.K. Leung, M.C. Wu & W.L. Chang ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee Annual Review 25 Variations in Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South
Reprint 675 Variations of Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South China Sea Y.K. Leung, M.C. Wu & W.L. Chang ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee Annual Review 25 Variations in Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South
The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system
 The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU), Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht University, The Netherlands
The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU), Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht University, The Netherlands
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS Apr 2006
 Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
Project Retrograde imagine Earth rotated in the opposite direction
 Project Retrograde imagine Earth rotated in the opposite direction The rotation of Earth shapes our climate system in various ways: It controls the major wind directions, lets the weather systems swirl,
Project Retrograde imagine Earth rotated in the opposite direction The rotation of Earth shapes our climate system in various ways: It controls the major wind directions, lets the weather systems swirl,
Climate Outlook for December 2015 May 2016
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for December 2015 May 2016 BUSAN, 25 November 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for December 2015 to May 2016 (DJFMAM) at the APEC Climate Center (APCC),
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for December 2015 May 2016 BUSAN, 25 November 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for December 2015 to May 2016 (DJFMAM) at the APEC Climate Center (APCC),
An Interconnected Planet
 An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 2, 87 92 The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model WEI Chao 1,2 and DUAN Wan-Suo 1 1
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 2, 87 92 The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model WEI Chao 1,2 and DUAN Wan-Suo 1 1
Assessing the Quality of Regional Ocean Reanalysis Data from ENSO Signals
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 55 61 Assessing the Quality of Regional Ocean Reanalysis Data from ENSO Signals WANG Lu 1, 2 and ZHOU Tian-Jun 1 1 State Key Laboratory of
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 55 61 Assessing the Quality of Regional Ocean Reanalysis Data from ENSO Signals WANG Lu 1, 2 and ZHOU Tian-Jun 1 1 State Key Laboratory of
Currents & Gyres Notes
 Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
Decadal variability of the IOD-ENSO relationship
 Chinese Science Bulletin 2008 SCIENCE IN CHINA PRESS ARTICLES Springer Decadal variability of the IOD-ENSO relationship YUAN Yuan 1,2 & LI ChongYin 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric
Chinese Science Bulletin 2008 SCIENCE IN CHINA PRESS ARTICLES Springer Decadal variability of the IOD-ENSO relationship YUAN Yuan 1,2 & LI ChongYin 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric
Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
THE RELATION AMONG SEA ICE, SURFACE TEMPERATURE, AND ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION IN SIMULATIONS OF FUTURE CLIMATE
 THE RELATION AMONG SEA ICE, SURFACE TEMPERATURE, AND ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION IN SIMULATIONS OF FUTURE CLIMATE Bitz, C. M., Polar Science Center, University of Washington, U.S.A. Introduction Observations
THE RELATION AMONG SEA ICE, SURFACE TEMPERATURE, AND ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION IN SIMULATIONS OF FUTURE CLIMATE Bitz, C. M., Polar Science Center, University of Washington, U.S.A. Introduction Observations
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: September 2008
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Analysis Links Pacific Decadal Variability to Drought and Streamflow in United States
 Page 1 of 8 Vol. 80, No. 51, December 21, 1999 Analysis Links Pacific Decadal Variability to Drought and Streamflow in United States Sumant Nigam, Mathew Barlow, and Ernesto H. Berbery For more information,
Page 1 of 8 Vol. 80, No. 51, December 21, 1999 Analysis Links Pacific Decadal Variability to Drought and Streamflow in United States Sumant Nigam, Mathew Barlow, and Ernesto H. Berbery For more information,
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Local versus non-local atmospheric weather noise and the North Pacific SST variability
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L14706, doi:10.1029/2007gl030206, 2007 Local versus non-local atmospheric weather noise and the North Pacific SST variability Sang-Wook
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L14706, doi:10.1029/2007gl030206, 2007 Local versus non-local atmospheric weather noise and the North Pacific SST variability Sang-Wook
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell
 1522 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES VOLUME 60 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell IOANA M. DIMA AND JOHN M. WALLACE Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
1522 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES VOLUME 60 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell IOANA M. DIMA AND JOHN M. WALLACE Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction
 1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
Introduction to climate modeling. ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008
 Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016
 Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016 Date: Dec 17, 2015 1. Advisory Most models are showing the continuation of a strong El-Niño episode towards the latesummer season with the expectation to start
Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016 Date: Dec 17, 2015 1. Advisory Most models are showing the continuation of a strong El-Niño episode towards the latesummer season with the expectation to start
Instability of the East Asian Summer Monsoon-ENSO Relationship in a coupled global atmosphere-ocean GCM
 Instability of the East Asian Summer Monsoon-ENSO Relationship in a coupled global atmosphere-ocean GCM JIANG Dabang 1 WANG Huijun 1 DRANGE Helge 2 LANG Xianmei 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling
Instability of the East Asian Summer Monsoon-ENSO Relationship in a coupled global atmosphere-ocean GCM JIANG Dabang 1 WANG Huijun 1 DRANGE Helge 2 LANG Xianmei 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling
Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components
 Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM Workshop, Miami, February 2011 Overview Introduction
Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM Workshop, Miami, February 2011 Overview Introduction
Global Atmospheric Circulation
 Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Climatology & Climate Variability Lecture 11 Nov. 22, 2010 Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation The Polar Vortex
Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Climatology & Climate Variability Lecture 11 Nov. 22, 2010 Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation The Polar Vortex
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228)
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Climate Outlook for March August 2017
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for March August 2017 BUSAN, 24 February 2017 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for March to August 2017 (MAMJJA) at the APEC Climate Center (APCC), located
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for March August 2017 BUSAN, 24 February 2017 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for March to August 2017 (MAMJJA) at the APEC Climate Center (APCC), located
Curriculum Vitae. Jianhua Lu
 Curriculum Vitae Jianhua Lu Research Faculty I Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies Florida State University Tallahassee, FL32306 Phone: (850) 345-7299; Fax: (850) 644-4841 Email: jlu@coaps.fsu.edu
Curriculum Vitae Jianhua Lu Research Faculty I Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies Florida State University Tallahassee, FL32306 Phone: (850) 345-7299; Fax: (850) 644-4841 Email: jlu@coaps.fsu.edu
Recent anomalously cold Central Eurasian winters forced by Arctic sea ice retreat in an atmospheric model
 Recent anomalously cold Central Eurasian winters forced by Arctic sea ice retreat in an atmospheric model Vladimir A. Semenov A.M. Obukhov Institute of Atmospheric Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia and Helmholtz
Recent anomalously cold Central Eurasian winters forced by Arctic sea ice retreat in an atmospheric model Vladimir A. Semenov A.M. Obukhov Institute of Atmospheric Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia and Helmholtz
Climate 1: The Climate System
 Climate 1: The Climate System Prof. Franco Prodi Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate National Research Council Via P. Gobetti, 101 40129 BOLOGNA SIF, School of Energy, Varenna, July 2014 CLIMATE
Climate 1: The Climate System Prof. Franco Prodi Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate National Research Council Via P. Gobetti, 101 40129 BOLOGNA SIF, School of Energy, Varenna, July 2014 CLIMATE
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Climate System. Sophie Zechmeister-Boltenstern
 Climate System Sophie Zechmeister-Boltenstern Reference: Chapin F. St., Matson P., Mooney Harold A. 2002 Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology. Springer, Berlin, 490 p. Structure of this lecture
Climate System Sophie Zechmeister-Boltenstern Reference: Chapin F. St., Matson P., Mooney Harold A. 2002 Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology. Springer, Berlin, 490 p. Structure of this lecture
Weakening relationship between East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO after mid-1970s
 Article Progress of Projects Supported by NSFC Atmospheric Science doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5285-x Weakening relationship between East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO after mid-1970s WANG HuiJun 1,2* & HE
Article Progress of Projects Supported by NSFC Atmospheric Science doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5285-x Weakening relationship between East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO after mid-1970s WANG HuiJun 1,2* & HE
THE INFLUENCE OF CLIMATE TELECONNECTIONS ON WINTER TEMPERATURES IN WESTERN NEW YORK INTRODUCTION
 Middle States Geographer, 2014, 47: 60-67 THE INFLUENCE OF CLIMATE TELECONNECTIONS ON WINTER TEMPERATURES IN WESTERN NEW YORK Frederick J. Bloom and Stephen J. Vermette Department of Geography and Planning
Middle States Geographer, 2014, 47: 60-67 THE INFLUENCE OF CLIMATE TELECONNECTIONS ON WINTER TEMPERATURES IN WESTERN NEW YORK Frederick J. Bloom and Stephen J. Vermette Department of Geography and Planning
Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 6, 515 520 Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3 XUE Feng 1, SUN Dan 2,3, and ZHOU Tian-Jun
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 6, 515 520 Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3 XUE Feng 1, SUN Dan 2,3, and ZHOU Tian-Jun
The Global Monsoon Response to Volcanic Eruptions in the CMIP5 Past1000 Simulations and Model Simulations of FGOALS
 The Global Monsoon Response to Volcanic Eruptions in the CMIP5 Past1000 Simulations and Model Simulations of FGOALS Wenmin Man, Tianjun Zhou Email: manwenmin@mail.iap.ac.cn PAGES2k-PMIP3 Hydroclimate Workshop,
The Global Monsoon Response to Volcanic Eruptions in the CMIP5 Past1000 Simulations and Model Simulations of FGOALS Wenmin Man, Tianjun Zhou Email: manwenmin@mail.iap.ac.cn PAGES2k-PMIP3 Hydroclimate Workshop,
Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring
 Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring 1 Typical flow of making one month forecast Textbook P.66 Observed data Atmospheric and Oceanic conditions Analysis Numerical model Ensemble forecast
Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring 1 Typical flow of making one month forecast Textbook P.66 Observed data Atmospheric and Oceanic conditions Analysis Numerical model Ensemble forecast
Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis
 Extended abstract for the 3 rd WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis held in Tokyo, Japan, on Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis Yan Xue,
Extended abstract for the 3 rd WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis held in Tokyo, Japan, on Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis Yan Xue,
Respective impacts of the East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO on winter rainfall in China
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012502, 2010 Respective impacts of the East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO on winter rainfall in China Lian-Tong
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012502, 2010 Respective impacts of the East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO on winter rainfall in China Lian-Tong
Tropical drivers of the Antarctic atmosphere
 Tropical drivers of the Antarctic atmosphere Bradford S. Barrett Gina R. Henderson Oceanography Department U. S. Naval Academy Acknowledge support of: NSF awards ARC-1203843 and AGS-1240143 ONR award N1416WX01752
Tropical drivers of the Antarctic atmosphere Bradford S. Barrett Gina R. Henderson Oceanography Department U. S. Naval Academy Acknowledge support of: NSF awards ARC-1203843 and AGS-1240143 ONR award N1416WX01752
Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere Coupling and Their Potential Use in Seasonal to Decadal Climate Predictions
 US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Test Bed Joint Seminar Series NCEP, Camp Springs, Maryland, 22 June 2011 Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere
US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Test Bed Joint Seminar Series NCEP, Camp Springs, Maryland, 22 June 2011 Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere
Prediction Research of Climate Change Trends over North China in the Future 30 Years
 42 ACTA METEOROLOGICA SINICA VOL.22 Prediction Research of Climate Change Trends over North China in the Future 30 Years LIU Yanxiang 1,2,3 ( ), YAN Jinghui 1 ( ), WU Tongwen 1 ( ), GUO Yufu 2 ( ), CHEN
42 ACTA METEOROLOGICA SINICA VOL.22 Prediction Research of Climate Change Trends over North China in the Future 30 Years LIU Yanxiang 1,2,3 ( ), YAN Jinghui 1 ( ), WU Tongwen 1 ( ), GUO Yufu 2 ( ), CHEN
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences. Changes of the tropical Pacific Walker circulation simulated by two versions of FGOALS model
 SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4902-8 Changes of the tropical Pacific Walker circulation simulated by two versions of FGOALS model MA ShuangMei 1,2 & ZHOU TianJun 1,3*
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4902-8 Changes of the tropical Pacific Walker circulation simulated by two versions of FGOALS model MA ShuangMei 1,2 & ZHOU TianJun 1,3*
