Science of Compact X-Ray and Gamma-ray Objects: MAXI and GLAST
|
|
|
- Alvin McDowell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science of Compact X-Ray and Gamma-ray Objects: MAXI and GLAST D. J. Thompson, 1 on behalf of the GLAST LAT Collaboration 1 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD USA (DJT): David.J.Thompson@nasa.gov Abstract The Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image (MAXI) and Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST) observatories will be surveying the sky simultaneously. Compact objects that may show variability will be excellent targets for coordinated multiwavelength studies. Gamma-ray bursts (and afterglows), pulsars, high-mass X-ray binaries, microquasars, and active galactic nuclei are all objects whose X- and gammaray relationship can be explored by such observations. Of particular interest will be variable unidentified gamma-ray sources, whose contemporaneous observations by MAXI may prove decisive in identifying the source of the high-energy emission. Key words: X-rays gamma rays variability 1. Introduction One of the clearest characteristics of the high-energy (Xray and gamma-ray) sky is variability. Bursting, flaring, and periodic variability are seen on timescales ranging from milliseconds to years. Monitoring the changing cosmos therefore provides a valuable resource for scientific analysis and interpretation. With the launch of GLAST, which took place during the MAXI workshop, and the upcoming launch of MAXI itself, the scientific community will have for the first time sensitive all-sky monitors covering a broad portion of the high-energy electromagnetic spectrum. The goal of this paper is to outline some of the scientific topics that can be addressed by cooperative efforts between these two missions. 2. GLAST Mission and Operating Plans GLAST (Figure 1) is a successor to the successful Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) that operated during the 1990 s. GLAST is an international mission, involving the U.S. NASA and Department of Energy as well as contributions from many astrophysics and particle physics institutions and agencies in Japan, France, Germany, Italy, and Sweden. The GLAST Observatory (Michelson, 2003) includes two scientific instruments: The GLAST Burst Monitor (GBM) is a successor to BATSE on the Compton Observatory. It uses sodium iodide (NaI) and bismuth germanate (BGO) wide-field detectors to monitor the sky for transients in the 10 kev 30 MeV energy range (Meegan et al 2008). The GBM field of view is large enough to view the entire sky except for the part occulted by the Earth. The Large Area Telescope (LAT) is a pairproduction high-energy telescope successor to EGRET on CGRO. It uses a combination of detector subsystems (silicon strip tracker, cesium iodide calorimeter, plastic scintillator anticoincidence detector) to measure the properties of gamma-ray pair production events and to separate such events from the much larger background of charged particle cosmic rays (Atwood et al 2008). Some important characteristics of the GLAST LAT are: Huge field of view (approximately 2.4 steradians). Broad energy range (20 MeV - >300 GeV, including the largely unexplored GeV range). Good source location accuracy (1 arcmin for bright sources). Large effective area (factor >4 better than EGRET). Single photon absolute time accuracy better than 10 microseconds. This combination of improvements results in a factor >30 improvement in sensitivity compared to EGRET, with an even larger factor at energies above 10 GeV. GLAST was launched on June 11, 2008, into a 565 km circular orbit with inclination For comparison with MAXI, the most important operating feature
2 Fig. 1. GLAST on its launch vehicle. of GLAST is its planned scanning mode. Taking advantage of the large instrument fields of view, the spacecraft will continually point away from the Earth. By rocking 35 north of the zenith for one orbit and 35 south of the zenith on the following orbit, both the LAT and the GBM will survey the entire gamma-ray sky every two orbits (192 minutes). For the first time, high-energy gamma-ray astrophysics will have an all-sky monitor. Following a checkout period of about 60 days, GLAST will spend most of the next year in scanning mode, with a few exceptions for pointing mode operation triggered by unusual phenomena such as bright gamma-ray bursts. Results from bright sources and transients will be made public quickly, including Gamma-ray Burst Coordination Network (GCN) notices. At the end of approximately one year of normal science operations, all the data, including the first-year data, will become public as quickly as they can be processed. The GLAST Science Support Center (GSSC) at Goddard Space Flight Center ( will be providing software and support for analysis of both GBM and LAT data. 3. GLAST, MAXI, and Multiwavelength Studies Modern astrophysics has become a multiwavelength enterprise, reflecting the realization that many astrophysical sources reveal their properties across broad ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma-ray telescopes, for example, provide little or no information about distances, composition, velocities, magnetic fields, or polarization of detected objects. Determining these other parameters requires identification and study at other wavelengths. For this reason, GLAST scientists are strongly interested in cooperative efforts with other observatories such as MAXI. MAXI and GLAST have enough similarities that they have a particularly strong potential for working together: Both MAXI and GLAST survey the whole sky regularly. Both have good time resolution. Both cover a wide range of energies. Two likely areas of cooperation between MAXI and GLAST are: Construction of broad-band Spectral Energy Distributions (SEDs) to help determine physical processes (such as particle acceleration and interaction) that are important in specific sources; and Study of correlated time variability to help examine relationships between the X-ray and gamma-ray emission processes. 4. Sensitivities and Potential Targets Although MAXI and GLAST are in principle good candidates for cooperative efforts, the practical question is whether the time-dependent sensitivities of the two instruments are matched to potential sources. One way to address this question is shown in Figure 2, which plots the SED for the Crab along with the approximate energy ranges and sensitivities of the MAXI SSC, the MAXI GSC, and the GLAST LAT for a one week observation in their standard operating modes. These values are approximate because performance is estimated based
3 Fig. 2. Data points: Broadband energy spectrum of the Crab (nebula and pulsar). MAXI open rectangle upper left: SSC sensitivity in one week. MAXI open rectangle lower right: GSC sensitivity in one week. See other MAXI papers in these proceedings for details. GLAST LAT bowtie : sensitivity in one week. on pre-launch calibrations, not from in-flight conditions. The GLAST GBM is primarily sensitive to shorter transients and so is not shown on this figure. It is clear from this figure that a source like the Crab would be easily visible to both MAXI and GLAST in less than one week. Both telescopes can add data to gain sensitivity. For weaker sources, the integration time required for a measurement would be longer. The horizontal dashed line on this figure provides a useful reference for comparing MAXI and GLAST LAT sensitivities. The level erg cm 2 s 1 or JyHz is one that can be reached by either MAXI or GLAST LAT in one to two weeks. Other than the Crab, what sorts of sources might be of interest to both MAXI and GLAST? Thermal sources are not good candidates; they might be visible to MAXI but not to GLAST. Conversely, nuclear sources would be more likely to be gamma-ray sources than X-ray sources. The best possibilities would seem to be nonthermal sources (involving accelerated particles) with some combination of synchrotron radiation (more likely in X-rays) and Compton radiation (more likely in gamma rays). Sources that combine both types of emission may yield information about the particle populations and acceleration processes, the magnetic fields, and photon fields in and around the source. Those with pronounced time variability (i.e. compact objects) are clearly of greatest interest, in order to take advantage of the monitoring capability of the two observatories. Some examples of potential astrophysical targets are discussed below Blazars and Other Active Galactic Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN), particular blazars, in which the jet is pointed toward the Earth, are primary targets for both X-ray and gamma-ray telescopes. They can have broad, nonthermal spectra and strong time variability. Figure 3 illustrates one example, blazar 3C279 as observed in 1993 during a moderately bright state. The data require time-dependent modeling, and this example from Hartman et al (2001) shows some possible components to the emission. If observed simultaneously, the MAXI data would constrain the synchrotron self-compton component, while the GLAST LAT data would measure the Compton components arising from interactions of the same particles with external photon sources. Optical and radio observations would help constrain the synchrotron contribution, allowing a fairly complete model of the source as a function of time. Note that for this 1993 observation no X-ray data were available. Blazars in particular are seen with a wide distribution of luminosities and spectra. 3C279 is a Flat Spectrum Radio Quasar with high luminosity and SED peaks at relatively low energies. High-Peaked BL Lac objects such as Mkn 421 have lower luminosities but SED peaks at higher energies. For such sources, MAXI would measure
4 Fig. 3. Data and models for the 3C279 SED, adapted from Hartman et al (2001). The approximate one-week sensitivities of MAXI and GLAST LAT are shown by their names. the synchrotron component directly, while GLAST LAT would measure the synchrotron self-compoton component Gamma-ray Bursts The GLAST GBM, along with other observatories such as Swift, will provide trigger information for gammaray bursts (GRBs). Both MAXI and GLAST LAT have some chance of seeing bursts directly, and both will be able to conduct afterglow studies. X-ray afterglows (e.g. Burrows et al 2005) are seen regularly from GRBs, potentially observable by MAXI for hours. Delayed highenergy gamma-ray emission was also seen for a small number of GRBs by EGRET on CGRO (e.g. Hurley et al 1994; Gonzales et al 2003), with components seen up to 90 minutes after the initial flash. The X-ray afterglows were not discovered until late in the CGRO mission, so that none of the EGRET-detected bursts had simultaneous X-ray measurements. MAXI and other X-ray telescopes will provide the first opportunity to determine the relationship, if any, between X-ray afterglows and delayed high-energy gamma-ray emission High-mass X-ray Binaries Some high-mass X-ray binaries (HMXBs) have powerful winds that can accelerate particles and produce nonthermal emission, including both X-rays and gamma rays. An example is shown in Figure 4. LSI has a 26 day period that produces a time-varying signal, although current studies are inconclusive about the nature of the emission. The summary of data and one possible model from Gupta and Böttcher (2006) illustrates the potential for coordinated study with MAXI and GLAST LAT. The X-ray range is likely synchrotron emission, while the gamma rays may be observing a transition between synchrotron and Compton radiation. Having simultaneous monitoring of this source and others like it will be important in resolving the processes important in this binary system Pulsars Rotation-powered pulsars (as opposed to those powered by accretion) are particle accelerators. They can have nonthermal emission that provides insight into the strong gravitational, magnetic, and electric fields in the magnetospheres of these rotating neutron stars. The good timing capabilities of MAXI and GLAST LAT offer two particular possibilities for working together: Discovery of new X-ray and gamma-ray pulsars can be done by searching for short periodicities in sources. Most rotation-powered pulsars have been discovered in the radio band, but some have been found that are radio-quiet. Although MAXI and GLAST LAT have similar sensitivities in terms of energy, MAXI detects far more photons and therefore can potentially find pulse periods that could then be searched for in the LAT data. It is possible,
5 Fig. 4. LSI SED, adapted from Gupta and Böttcher (2006). The approximate one-week sensitivities of MAXI and GLAST LAT are shown by their names. too, that some pulsars could be discovered in the LAT data that MAXI might then search for; and For any pulsar seen in both energy bands, a comparison of light curves and energy spectra helps identify where and how the particle acceleration and interaction processes are taking place in the pulsar magnetospheres. An example is shown in Figure 5 (Thompson et al 1999). The X-ray and gamma-ray light curves differ in both shape and phase, suggesting different emission processes and locations Pulsar Wind Nebulae Although pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe) are not by themselves compact objects, they are powered by pulsars and can exhibit time variability. The summary in Figure 6, from Nakamori et al (2008), shows why having simultaneous MAXI and GLAST LAT data will be valuable for PWNe studies. The X-rays seem well described as synchrotron radiation, implying high-energy electrons, but the gamma-ray origin is far less clear. Finding correlated time variability would be a strong argument in favor of a leptonic (inverse Compton) origin for the gamma rays rather than a hadronic (π -decay) origin The Unknown - Source Identification and Study Although the X-ray sky has been surveyed fairly thoroughly, the gamma-ray sky is far less understood. Over half the sources in the third EGRET catalog (Hartman et al 1999) remain unidentified. One of the major challenges for GLAST will be resolving the nature of these and other newly-discovered gamma-ray sources. Even with arcmin positions, spatial association is often inadequate to make a firm identification of a new source. Correlated variability, by contrast, is a high-confidence means of identification. The all-sky monitoring capabilities of MAXI and GLAST are extremely complementary for this type of identification. 5. Summary With the launch of MAXI to the International Space Station next year and the continued operation of GLAST, astrophysics will have for the first time sensitive all-sky monitors in both both X-ray and gamma-ray bands. For nonthermal processes that are visible to both observatories, the opportunities for cooperation are extensive. Acknowledgements I extend thanks to B. Lott and the LAT team for the calculation of the one-week LAT sensitivity. References Atwood, W. B. et al ApJ, submitted Burrows, D. N. et al Science, 309, 1833 Gonzales, M. M. et al Nature, 424, 74 Gupta, S. and Böttcher, M ApJ, 650, L123 Hartman, R. C. et al ApJS, 123, 79 Hartman, R. C. et al ApJ, 553, 683 Hurley, K. et al 1994 Nature, 372, 652 Meegan, C. A et al ApJ, submitted Michelson, P Proc. SPIE, 4851, 1144 Nakamori, T. et al ApJ, 677, 297 Thompson, D. J. et al ApJ, 516, 297
6 Fig. 5. X-ray and gamma-ray light curves (two cycles shown) of PSR B (Thompson et al. 1999). Fig. 6. MSH SED, adapted from Nakamori et al (2008). The approximate one-week sensitivities of MAXI and GLAST LAT are shown by their names.
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy
 Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Gamma-ray Astronomy Missions, and their Use of a Global Telescope Network
 Gamma-ray Astronomy Missions, and their Use of a Global Telescope Network The Big Picture Whole sky glows Extreme environments Probes of the Universe CGRO/EGRET All Sky Map Early Gamma-ray Astronomy Gamma-ray
Gamma-ray Astronomy Missions, and their Use of a Global Telescope Network The Big Picture Whole sky glows Extreme environments Probes of the Universe CGRO/EGRET All Sky Map Early Gamma-ray Astronomy Gamma-ray
Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT. Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn. NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12.
 Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12 The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Fermi = Large Area Telescope
Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12 The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Fermi = Large Area Telescope
Gamma Ray Physics in the Fermi era. F.Longo University of Trieste and INFN
 Gamma Ray Physics in the Fermi era F.Longo University of Trieste and INFN Vulcano, May 22, 2018 F.Longo et al. -- 1 Gamma-ray astrophysics above 100 MeV AGILE Fermi 2 Picture of the day, Feb. 28, 2011,
Gamma Ray Physics in the Fermi era F.Longo University of Trieste and INFN Vulcano, May 22, 2018 F.Longo et al. -- 1 Gamma-ray astrophysics above 100 MeV AGILE Fermi 2 Picture of the day, Feb. 28, 2011,
Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments
 Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments David J. Thompson NASA Goddard Space Flight Center GLAST Large Area Telescope Collaboration djt@egret.gsfc.nasa.gov D. Thompson 363 rd Heraeus
Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments David J. Thompson NASA Goddard Space Flight Center GLAST Large Area Telescope Collaboration djt@egret.gsfc.nasa.gov D. Thompson 363 rd Heraeus
GLAST Mission: Status and Science Opportunities
 Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope GLAST Mission: Status and Science Opportunities Bill Atwood SCIPP / UCSC atwood@scipp.ucsc.edu Outline GLAST: An International Science Mission Large Area Telescope
Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope GLAST Mission: Status and Science Opportunities Bill Atwood SCIPP / UCSC atwood@scipp.ucsc.edu Outline GLAST: An International Science Mission Large Area Telescope
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
 The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Hiromitsu Takahashi ( 高橋弘充 ) Hiroshima University ( 広島大学 ) hirotaka@hep01.hepl.hiroshima-u.ac.jp for the LAT Collaboration 2008 June 11th Contents Gamma-ray observation
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Hiromitsu Takahashi ( 高橋弘充 ) Hiroshima University ( 広島大学 ) hirotaka@hep01.hepl.hiroshima-u.ac.jp for the LAT Collaboration 2008 June 11th Contents Gamma-ray observation
Fermi Large Area Telescope:
 Fermi Large Area Telescope: Early Results on Pulsars Kent Wood Naval Research Lab kent.wood@nrl.navy.mil for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Tokyo Institute of Technology 7 March 2009 K. Wood (NRL) 1/30 Fermi
Fermi Large Area Telescope: Early Results on Pulsars Kent Wood Naval Research Lab kent.wood@nrl.navy.mil for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Tokyo Institute of Technology 7 March 2009 K. Wood (NRL) 1/30 Fermi
GLAST. Exploring the Extreme Universe. Kennedy Space Center. The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope
 GLAST Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Exploring the Extreme Universe Kennedy Space Center Dave Thompson GLAST Deputy Project Scientist David.J.Thompson@nasa.gov
GLAST Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Exploring the Extreme Universe Kennedy Space Center Dave Thompson GLAST Deputy Project Scientist David.J.Thompson@nasa.gov
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
 Abstract The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Tova Yoast-Hull May 2011 The primary instrument on the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope is the Large Area Telescope (LAT) which detects gamma-rays in the energy
Abstract The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Tova Yoast-Hull May 2011 The primary instrument on the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope is the Large Area Telescope (LAT) which detects gamma-rays in the energy
The Gamma ray sky seen by. Telescope. F.Longo INFN Trieste, CIFS Torino. on behalf of the Fermi LAT collaboration
 The Gamma ray sky seen by the Fermi Large Area Telescope. F.Longo INFN Trieste, CIFS Torino on behalf of the Fermi LAT collaboration 7 th AGILE Workshop Frascati, 29 settembre 2009 Outline Introduction
The Gamma ray sky seen by the Fermi Large Area Telescope. F.Longo INFN Trieste, CIFS Torino on behalf of the Fermi LAT collaboration 7 th AGILE Workshop Frascati, 29 settembre 2009 Outline Introduction
The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi
 INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte 22 February 2012 The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi Elena Pian INAF, Trieste Astronomical Observatory & Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa UNIFIED
INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte 22 February 2012 The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi Elena Pian INAF, Trieste Astronomical Observatory & Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa UNIFIED
First Year Fermi Gamma ray Space Telescope Observations of Centaurus A
 First Year Fermi Gamma ray Space Telescope Observations of Centaurus A C.C. Teddy Cheung (NASA GSFC) Yasushi Fukazawa (Hiroshima Univ) on behalf of the Fermi LAT collaboration The Many Faces of Centaurus
First Year Fermi Gamma ray Space Telescope Observations of Centaurus A C.C. Teddy Cheung (NASA GSFC) Yasushi Fukazawa (Hiroshima Univ) on behalf of the Fermi LAT collaboration The Many Faces of Centaurus
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission
 The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
MeV Quasar Observations with the. COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory
 MeV Quasar Observations with the COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory 1. Introduction Extragalactic gamma-ray astronomy barely existed prior to the launch of the COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) but there
MeV Quasar Observations with the COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory 1. Introduction Extragalactic gamma-ray astronomy barely existed prior to the launch of the COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) but there
Can we constrain GRB shock parameters using the Gamma Ray Large Area Space Telescope? Eduardo do Couto e Silva SLAC/KIPAC SABER Workshop Mar 15, 2006
 Can we constrain GRB shock parameters using the Gamma Ray Large Area Space Telescope? Eduardo do Couto e Silva SLAC/KIPAC SABER Workshop Mar 15, 2006 The Main Questions Is there any connection between
Can we constrain GRB shock parameters using the Gamma Ray Large Area Space Telescope? Eduardo do Couto e Silva SLAC/KIPAC SABER Workshop Mar 15, 2006 The Main Questions Is there any connection between
Active Galactic Nuclei in the MeV-GeV band (first results from Fermi)
 Active Galactic Nuclei in the MeV-GeV band (first results from Fermi) Gino Tosti University & INFN Perugia On behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) EGRET showed that AGN
Active Galactic Nuclei in the MeV-GeV band (first results from Fermi) Gino Tosti University & INFN Perugia On behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) EGRET showed that AGN
The Fermi Gamma-Ray Sky
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 19, 19 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della Supplementi The Fermi Gamma-Ray Sky P. A. Caraveo INAF, Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica, Via Bassini 15, I-20133 Milano, Italy
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 19, 19 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della Supplementi The Fermi Gamma-Ray Sky P. A. Caraveo INAF, Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica, Via Bassini 15, I-20133 Milano, Italy
Highlights of GeV gamma-ray astronomy
 Astrophys. Space Sci. Trans., 6, 59 64, 2010 doi:10.5194/astra-6-59-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Astrophysics and Space Sciences Transactions Highlights of GeV gamma-ray astronomy D.
Astrophys. Space Sci. Trans., 6, 59 64, 2010 doi:10.5194/astra-6-59-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Astrophysics and Space Sciences Transactions Highlights of GeV gamma-ray astronomy D.
When a Standard Candle Flickers: The Dimming of the Crab Nebula. Gary Case
 When a Standard Candle Flickers: The Dimming of the Crab Nebula Gary Case Louisiana State University IACHEC, Frascati, Italy, 11 April 2011 Collaborators GBM Occultation Team: C.A Wilson-Hodge (NASA/MSFC),
When a Standard Candle Flickers: The Dimming of the Crab Nebula Gary Case Louisiana State University IACHEC, Frascati, Italy, 11 April 2011 Collaborators GBM Occultation Team: C.A Wilson-Hodge (NASA/MSFC),
Gamma-ray Astrophysics
 Gamma-ray Astrophysics AGN Pulsar SNR GRB Radio Galaxy The very high energy -ray sky NEPPSR 25 Aug. 2004 Many thanks to Rene Ong at UCLA Guy Blaylock U. of Massachusetts Why gamma rays? Extragalactic Background
Gamma-ray Astrophysics AGN Pulsar SNR GRB Radio Galaxy The very high energy -ray sky NEPPSR 25 Aug. 2004 Many thanks to Rene Ong at UCLA Guy Blaylock U. of Massachusetts Why gamma rays? Extragalactic Background
Relativistic jets from XRBs with LOFAR. Stéphane Corbel (University Paris 7 & CEA Saclay)
 Relativistic jets from XRBs with LOFAR. Stéphane Corbel (University Paris 7 & CEA Saclay) Outline Introduction: X-ray binaries and flavors of relativistic jets LOFAR Contributions Conclusions Introduction:
Relativistic jets from XRBs with LOFAR. Stéphane Corbel (University Paris 7 & CEA Saclay) Outline Introduction: X-ray binaries and flavors of relativistic jets LOFAR Contributions Conclusions Introduction:
Gamma-Ray Astronomy. Astro 129: Chapter 1a
 Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
The Fermi Large Area Telescope View of Gamma-ray Pulsars
 The Fermi Large Area Telescope View of Gamma-ray Pulsars 1 Tyrel J. Johnson, D.A. Smith2, M. Kerr3, & P. R. den Hartog4 on behalf of the Fermi Large Area Telescope Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing and
The Fermi Large Area Telescope View of Gamma-ray Pulsars 1 Tyrel J. Johnson, D.A. Smith2, M. Kerr3, & P. R. den Hartog4 on behalf of the Fermi Large Area Telescope Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing and
Following up Fermi GBM Gamma-Ray Bursts
 Following up Fermi GBM Gamma-Ray Bursts V. Connaughton, and M. S. Briggs University of Alabama, Huntsville A. Goldstein (NASA Postdoctoral Fellow) NASA Marshall Space Flight Center Abstract The Fermi Gamma-Ray
Following up Fermi GBM Gamma-Ray Bursts V. Connaughton, and M. S. Briggs University of Alabama, Huntsville A. Goldstein (NASA Postdoctoral Fellow) NASA Marshall Space Flight Center Abstract The Fermi Gamma-Ray
GLAST and beyond GLAST: TeV Astrophysics
 GLAST and beyond GLAST: TeV Astrophysics Outline: Greg Madejski Assistant Director for Scientific Programs, SLAC / Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Cosmology Recent excitement of GLAST and plans for
GLAST and beyond GLAST: TeV Astrophysics Outline: Greg Madejski Assistant Director for Scientific Programs, SLAC / Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Cosmology Recent excitement of GLAST and plans for
Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results
 Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results 1. GeV instrumentation and the GeV sky with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope 2. First Fermi Catalog of Gamma Ray Sources and the Fermi Pulsar Catalog 3.
Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results 1. GeV instrumentation and the GeV sky with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope 2. First Fermi Catalog of Gamma Ray Sources and the Fermi Pulsar Catalog 3.
GLAST. Welcome and Introductions. GLAST Pre-launch Media Telecon May 27, The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope
 GLAST Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Welcome and Introductions GLAST Pre-launch Media Telecon May 27, 2008 Lynn Cominsky GLAST Press Officer and E/PO Lead
GLAST Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Welcome and Introductions GLAST Pre-launch Media Telecon May 27, 2008 Lynn Cominsky GLAST Press Officer and E/PO Lead
Gamma-ray Observations of Blazars with VERITAS and Fermi
 Gamma-ray Observations of Blazars with VERITAS and Fermi University College Dublin E-mail: annacannon1984@gmail.com VERITAS (the Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System) is an array of
Gamma-ray Observations of Blazars with VERITAS and Fermi University College Dublin E-mail: annacannon1984@gmail.com VERITAS (the Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System) is an array of
SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies
 SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies 1 Symp. 324, 12-16 September, 2016 Classical view Spinning black hole Accretion disk Collimated jets of particles 2 Looking
SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies 1 Symp. 324, 12-16 September, 2016 Classical view Spinning black hole Accretion disk Collimated jets of particles 2 Looking
Time-domain astronomy with the Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor
 Time-domain astronomy with the Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor C. Michelle Hui (NASA/MSFC) on behalf of the Fermi GBM team TeVPA, Aug 11 2017 GBM: FOV >8sr Whole sky every ~90min Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
Time-domain astronomy with the Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor C. Michelle Hui (NASA/MSFC) on behalf of the Fermi GBM team TeVPA, Aug 11 2017 GBM: FOV >8sr Whole sky every ~90min Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
Gamma-ray Astrophysics and High Density e+ e- Plasma - A new application of Free Electron Laser? -
 Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Gamma-ray Astrophysics and High Density e+ e- Plasma - A new application of Free Electron Laser? - Tuneyoshi Kamae SLAC, GLAST Group Gamma-ray observatories in next
Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Gamma-ray Astrophysics and High Density e+ e- Plasma - A new application of Free Electron Laser? - Tuneyoshi Kamae SLAC, GLAST Group Gamma-ray observatories in next
Gamma-ray observations of blazars with the Whipple 10 m telescope
 Gamma-ray observations of blazars with the Whipple 1 m telescope, presented on behalf of the VERITAS collaboration. E-mail: edward.collins.hughes@gmail.com This paper presents a status update of the current
Gamma-ray observations of blazars with the Whipple 1 m telescope, presented on behalf of the VERITAS collaboration. E-mail: edward.collins.hughes@gmail.com This paper presents a status update of the current
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
The Fermi Zoo : GRB prompt spectra. Michael S. Briggs (Univ. Alabama in Huntsville) for the Fermi GBM & LAT Teams
 The Fermi Zoo : GRB prompt spectra Michael S. Briggs (Univ. Alabama in Huntsville) for the Fermi GBM & LAT Teams Multi-Messenger Workshop KIAA 2013 1 Multi-Messenger Workshop KIAA 2013 2 Before Fermi:
The Fermi Zoo : GRB prompt spectra Michael S. Briggs (Univ. Alabama in Huntsville) for the Fermi GBM & LAT Teams Multi-Messenger Workshop KIAA 2013 1 Multi-Messenger Workshop KIAA 2013 2 Before Fermi:
The Gamma Large Area Space Telescope: GLAST
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol.3 (2003), Suppl., 523 530 (http:/www.chjaa.org) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics The Gamma Large Area Space Telescope: GLAST Aldo Morselli 1 INFN Roma2 and
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol.3 (2003), Suppl., 523 530 (http:/www.chjaa.org) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics The Gamma Large Area Space Telescope: GLAST Aldo Morselli 1 INFN Roma2 and
Discovery of a New Gamma-Ray Binary: 1FGL J
 Discovery of a New Gamma-Ray Binary: 1FGL J1018.6-5856 Robin Corbet (UMBC/NASA GSFC) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration, & M.J. Coe, P.G. Edwards, M.D. Filipovic, J.L. Payne, J. Stevens, M.A.P. Torres
Discovery of a New Gamma-Ray Binary: 1FGL J1018.6-5856 Robin Corbet (UMBC/NASA GSFC) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration, & M.J. Coe, P.G. Edwards, M.D. Filipovic, J.L. Payne, J. Stevens, M.A.P. Torres
Space Astronomy Facilities
 ASI and bi/multilateral Space Astronomy Facilities Paolo Giommi Italian Space Agency, ASI 10 February 2010 COPUOS - Vienna 1 AGILE: an Italian Small Mission AGILE: an Italian small scientific mission Devoted
ASI and bi/multilateral Space Astronomy Facilities Paolo Giommi Italian Space Agency, ASI 10 February 2010 COPUOS - Vienna 1 AGILE: an Italian Small Mission AGILE: an Italian small scientific mission Devoted
EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
 EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Luis C. Reyes KICP The Extragalactic Background Light (EBL) What is it? Accumulation of all energy releases in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Luis C. Reyes KICP The Extragalactic Background Light (EBL) What is it? Accumulation of all energy releases in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
AGILE GRBs: detections and upper limits
 AGILE GRBs: detections and upper limits Outline AGILE quick review; The GRB search pipeline; The AGILE GRBs; The GRB090618: any clue for the detectability in the E>30 MeV band? The GRB sample in the GRID
AGILE GRBs: detections and upper limits Outline AGILE quick review; The GRB search pipeline; The AGILE GRBs; The GRB090618: any clue for the detectability in the E>30 MeV band? The GRB sample in the GRID
The Sun and the Solar System in Gamma Rays
 The Sun and the Solar System in Gamma Rays R. Desiante1 on behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration SciNeGHE 2016 1 INFN Torino Outline Introduction The Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope The active Sun as seen
The Sun and the Solar System in Gamma Rays R. Desiante1 on behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration SciNeGHE 2016 1 INFN Torino Outline Introduction The Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope The active Sun as seen
High-Energy Emission from GRBs: First Year Highlights from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
 High-Energy Emission from GRBs: First Year Highlights from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Jonathan Granot University of Hertfordshire (Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award Holder) on behalf
High-Energy Emission from GRBs: First Year Highlights from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Jonathan Granot University of Hertfordshire (Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award Holder) on behalf
Stellar Binary Systems and CTA. Guillaume Dubus Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble
 Stellar Binary Systems and CTA Guillaume Dubus Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble Barcelona Cherenkov Telescope Array Meeting, 24-25 January 2008 X-ray binaries picture by H. Spruit relativistic outflow
Stellar Binary Systems and CTA Guillaume Dubus Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble Barcelona Cherenkov Telescope Array Meeting, 24-25 January 2008 X-ray binaries picture by H. Spruit relativistic outflow
Dark matter searches with GLAST
 Dark matter searches with GLAST Larry Wai SLAC Representing the GLAST LAT Collaboration Dark Matter and New Physics working group GLAST Large Area Telescope (LAT) 20 MeV 300 GeV 1.8 m γ Anti-Coincidence
Dark matter searches with GLAST Larry Wai SLAC Representing the GLAST LAT Collaboration Dark Matter and New Physics working group GLAST Large Area Telescope (LAT) 20 MeV 300 GeV 1.8 m γ Anti-Coincidence
GLAST LAT Multiwavelength Studies Needs and Resources
 GLAST LAT Multiwavelength Studies Needs and Resources Report of the Ad Hoc Multiwavelength Observation Planning Group Roger Blandford, Co-chair Dave Thompson, Co-chair Seth Digel Greg Madejski Roger Romani
GLAST LAT Multiwavelength Studies Needs and Resources Report of the Ad Hoc Multiwavelength Observation Planning Group Roger Blandford, Co-chair Dave Thompson, Co-chair Seth Digel Greg Madejski Roger Romani
GLAST Large Area Telescope:
 Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope GLAST Large Area Telescope: Project Overview Robert P. Johnson Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics Physics Department University of California at Santa Cruz LAT
Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope GLAST Large Area Telescope: Project Overview Robert P. Johnson Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics Physics Department University of California at Santa Cruz LAT
Supporting the GLAST User Community
 Supporting the GLAST User Community David L. Band and GLAST Science Support Center Code 661, NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, MD 20854 The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST) Science Support Center (GSSC)
Supporting the GLAST User Community David L. Band and GLAST Science Support Center Code 661, NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, MD 20854 The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST) Science Support Center (GSSC)
A New Look at the Galactic Diffuse GeV Excess
 A New Look at the Galactic Diffuse GeV Excess Brian Baughman Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics 1 Overview Diffuse gamma-ray emission The Galactic diffuse gamma-ray GeV excess Discussion of the
A New Look at the Galactic Diffuse GeV Excess Brian Baughman Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics 1 Overview Diffuse gamma-ray emission The Galactic diffuse gamma-ray GeV excess Discussion of the
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY. Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006
 PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
A very wide field focusing telescope for Synoptic studies in the soft X-ray band
 A very wide field focusing telescope for Synoptic studies in the soft X-ray band Paul Gorenstein Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Cambridge, MA 02138 Synoptic Telescopes, (Broad Coverage of
A very wide field focusing telescope for Synoptic studies in the soft X-ray band Paul Gorenstein Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Cambridge, MA 02138 Synoptic Telescopes, (Broad Coverage of
Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars
 Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars Marie-Hélène Grondin CENBG, Bordeaux (France) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing
Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars Marie-Hélène Grondin CENBG, Bordeaux (France) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing
RXTE Observations of PKS during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst
 RXTE Observations of PKS 2155-304 during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst W. Thomas Vestrand a and P. Sreekumar b a Space Science Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH 03824 arxiv:astro-ph/9901404v1
RXTE Observations of PKS 2155-304 during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst W. Thomas Vestrand a and P. Sreekumar b a Space Science Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH 03824 arxiv:astro-ph/9901404v1
Astrophysics with GLAST: dark matter, black holes and other astronomical exotica
 Astrophysics with GLAST: dark matter, black holes and other astronomical exotica Greg Madejski Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology (KIPAC) Outline:
Astrophysics with GLAST: dark matter, black holes and other astronomical exotica Greg Madejski Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology (KIPAC) Outline:
Two Space High Energy Astrophysics Missions of China: POLAR & HXMT
 Two Space High Energy Astrophysics Missions of China: POLAR & HXMT Shuang-Nan Zhang ( 张双南 ) Institute of High Energy Physics National Astronomical Observatories of China Chinese Academy of Sciences 1/22
Two Space High Energy Astrophysics Missions of China: POLAR & HXMT Shuang-Nan Zhang ( 张双南 ) Institute of High Energy Physics National Astronomical Observatories of China Chinese Academy of Sciences 1/22
from Fermi (Higher Energy Astrophysics)
 Particle Acceleration Results from Fermi (Higher Energy Astrophysics) Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford 3 viii 2011 SLAC SSI 1 Fermi Joint NASA-DOE-Italy- France-Japan- Sweden, Germany mission Launch June
Particle Acceleration Results from Fermi (Higher Energy Astrophysics) Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford 3 viii 2011 SLAC SSI 1 Fermi Joint NASA-DOE-Italy- France-Japan- Sweden, Germany mission Launch June
Cosmic Gamma-ray Bursts Studies with Ioffe Institute Konus Experiments
 Cosmic Gamma-ray Bursts Studies with Ioffe Institute Konus Experiments R. L. Aptekar 1, S. V. Golenetskii, D. D. Frederiks, E. P. Mazets and V. D. Palshin Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute St. Petersburg,
Cosmic Gamma-ray Bursts Studies with Ioffe Institute Konus Experiments R. L. Aptekar 1, S. V. Golenetskii, D. D. Frederiks, E. P. Mazets and V. D. Palshin Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute St. Petersburg,
Introduction. Technical and Production Status L. Klaisner. Instrument Science Operations Center Plans. Project Status, Cost and Schedule L.
 Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Introduction S. Ritz Technical and Production Status L. Klaisner Instrument Science Operations Center Plans R. Cameron Project Status, Cost and Schedule L. Klaisner
Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Introduction S. Ritz Technical and Production Status L. Klaisner Instrument Science Operations Center Plans R. Cameron Project Status, Cost and Schedule L. Klaisner
Status of AGILE (and gravitational wave source search)
 HIGH ENERGY ASTROPHYSICS Status of AGILE (and gravitational wave source search) C. Pittori & M. Tavani Vulcano, May 2016 Vulcano Workshop 2016 1 The AGILE Payload: the most compact instrument for highenergy
HIGH ENERGY ASTROPHYSICS Status of AGILE (and gravitational wave source search) C. Pittori & M. Tavani Vulcano, May 2016 Vulcano Workshop 2016 1 The AGILE Payload: the most compact instrument for highenergy
FERMI. YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars. 25 novembre 2008 Damien Parent. Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope
 FERMI Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars 25 novembre 2008 1 Topics 1. Young pulsars, our best candidates 2 examples : J0205+6449 and
FERMI Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars 25 novembre 2008 1 Topics 1. Young pulsars, our best candidates 2 examples : J0205+6449 and
GLAST - Exploring the high- energy gamma-ray Universe
 GLAST - Exploring the high- energy gamma-ray Universe Julie McEnery NASA/GSFC (many thanks to the members of the LAT DM&NP working group for figures and suggestions for this talk) Julie McEnery 1 Outline
GLAST - Exploring the high- energy gamma-ray Universe Julie McEnery NASA/GSFC (many thanks to the members of the LAT DM&NP working group for figures and suggestions for this talk) Julie McEnery 1 Outline
PoGOLite, PoGO+, SPHiNX High-Energy Polarimetry Missions between Japan and Sweden
 PoGOLite, PoGO+, SPHiNX High-Energy Polarimetry Missions between Japan and Sweden Hiromitsu Takahashi (Hiroshima University) hirotaka@astro.hiroshima-u.ac.jp PoGOLite balloon 10m (2013) PoGO+ balloon 10m
PoGOLite, PoGO+, SPHiNX High-Energy Polarimetry Missions between Japan and Sweden Hiromitsu Takahashi (Hiroshima University) hirotaka@astro.hiroshima-u.ac.jp PoGOLite balloon 10m (2013) PoGO+ balloon 10m
The γ-ray flares from Cygnus X-3 detected by AGILE
 The γ-ray flares from Cygnus X-3 detected by AGILE (INAF-IAPS Roma) on behalf of the AGILE Team AGILE 9th Science Workshop Astrophysics with AGILE: five years of surprise ASDC c/o ESRIN, Frascati, April
The γ-ray flares from Cygnus X-3 detected by AGILE (INAF-IAPS Roma) on behalf of the AGILE Team AGILE 9th Science Workshop Astrophysics with AGILE: five years of surprise ASDC c/o ESRIN, Frascati, April
Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe
 Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe K. Ragan McGill University Soup & Science 11-Jan-2008 Soup & Science Jan. '08 1 How do we know about the Universe? Historically, all
Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe K. Ragan McGill University Soup & Science 11-Jan-2008 Soup & Science Jan. '08 1 How do we know about the Universe? Historically, all
Anders W. Borgland. On behalf of the Fermi/LAT Collaboration. Fermi LAT ISOC/SLAC
 Fermi Status And Prospects borgland@slac.stanford.edu Fermi LAT ISOC/SLAC On behalf of the Fermi/LAT Collaboration 1 A Broad Overview Of The Fermi Mission From GLAST To Fermi The Fermi Mission LAT Instrument
Fermi Status And Prospects borgland@slac.stanford.edu Fermi LAT ISOC/SLAC On behalf of the Fermi/LAT Collaboration 1 A Broad Overview Of The Fermi Mission From GLAST To Fermi The Fermi Mission LAT Instrument
On-Orbit Performance of the GLAST Burst Monitor
 On-Orbit Performance of the GLAST Burst Monitor Curran D. Muhlberger (RA) Charles A. Meegan (PI) Cornell University University of Maryland August 8, 2008 What is GLAST? What is GBM? What is it Good for?
On-Orbit Performance of the GLAST Burst Monitor Curran D. Muhlberger (RA) Charles A. Meegan (PI) Cornell University University of Maryland August 8, 2008 What is GLAST? What is GBM? What is it Good for?
Cherenkov Telescope Array ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP
 Cherenkov Telescope Array A SENSITIVE PROBE OF EXTREME UNIVERSE ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP 2015 1 The CTA Observatory SST ( 4m) LST ( 23m) MST ( 12m) South North
Cherenkov Telescope Array A SENSITIVE PROBE OF EXTREME UNIVERSE ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP 2015 1 The CTA Observatory SST ( 4m) LST ( 23m) MST ( 12m) South North
Extreme high-energy variability of Markarian 421
 Extreme high-energy variability of Markarian 421 Mrk 421 an extreme blazar Previous observations outstanding science issues 2001 Observations by VERITAS/Whipple 10 m 2001 Light Curve Energy spectrum is
Extreme high-energy variability of Markarian 421 Mrk 421 an extreme blazar Previous observations outstanding science issues 2001 Observations by VERITAS/Whipple 10 m 2001 Light Curve Energy spectrum is
Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission
 Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission Debbijoy Bhattacharya Manipal Centre for Natural Sciences (MCNS) Manipal University 5 Sept 2014 Observational Gamma-Ray Astronomy Atmospheric Window 00 11 00 11 Figure: Atmospheric
Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission Debbijoy Bhattacharya Manipal Centre for Natural Sciences (MCNS) Manipal University 5 Sept 2014 Observational Gamma-Ray Astronomy Atmospheric Window 00 11 00 11 Figure: Atmospheric
1 Introduction STATUS OF THE GLAST LARGE AREA TELESCOPE. SLAC-PUB December Richard Dubois. Abstract
 SLAC-PUB-10261 December 2003 STATUS OF THE GLAST LARGE AREA TELESCOPE Richard Dubois Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, PO Box 20750, Stanford, CA, USA Abstract The GLAST Large Area
SLAC-PUB-10261 December 2003 STATUS OF THE GLAST LARGE AREA TELESCOPE Richard Dubois Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, PO Box 20750, Stanford, CA, USA Abstract The GLAST Large Area
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope
 A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts
 Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts B.L. Dingus and the Milagro Collaboration Los Alamos National Laboratory University of Maryland, University of California Santa Cruz, University of California
Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts B.L. Dingus and the Milagro Collaboration Los Alamos National Laboratory University of Maryland, University of California Santa Cruz, University of California
Fermi Gamma Ray Space Telescope: Launch+509. Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford (With considerable help from Fermi team members working at Stanford)
 Fermi Gamma Ray Space Telescope: Launch+509 Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford (With considerable help from Fermi team members working at Stanford) 2 2 A Cosmic Reflection on Fermi s First Year Goals To summarize
Fermi Gamma Ray Space Telescope: Launch+509 Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford (With considerable help from Fermi team members working at Stanford) 2 2 A Cosmic Reflection on Fermi s First Year Goals To summarize
TeV Future: APS White Paper
 TeV Future: APS White Paper APS commissioned a white paper on the "Status and Future of very high energy gamma ray astronomy. For preliminary information, see http://cherenkov.physics.iastate.edu/wp Working
TeV Future: APS White Paper APS commissioned a white paper on the "Status and Future of very high energy gamma ray astronomy. For preliminary information, see http://cherenkov.physics.iastate.edu/wp Working
AGILE Highlights. The AGILE Mission. Stefano Vercellone and the AGILE Team at IASF Milano
 The AGILE Mission AGILE Highlights Stefano Vercellone and the AGILE Team at IASF Milano AGILE Highlights Visiting Committee Review - Milano, January 8 th, 2008 1 AGILE in a nutshell Super-AGILE AGILE-GRID
The AGILE Mission AGILE Highlights Stefano Vercellone and the AGILE Team at IASF Milano AGILE Highlights Visiting Committee Review - Milano, January 8 th, 2008 1 AGILE in a nutshell Super-AGILE AGILE-GRID
Tesi di Dottorato in Fisica. Upper Limits on High Energy emissions from GRB
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE FACOLTÀ DI SCIENZE MM.FF.NN Tesi di Dottorato in Fisica PhD Thesis in Physics Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare (FIS04) Upper Limits on High Energy emissions from GRB Candidate:
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TRIESTE FACOLTÀ DI SCIENZE MM.FF.NN Tesi di Dottorato in Fisica PhD Thesis in Physics Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare (FIS04) Upper Limits on High Energy emissions from GRB Candidate:
(Fermi observations of) High-energy emissions from gamma-ray bursts
 (Fermi observations of) High-energy emissions from gamma-ray bursts Hiroyasu Tajima on behalf of Fermi LAT and GBM Collaborations Kavli Institute of Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology SLAC National Accelerator
(Fermi observations of) High-energy emissions from gamma-ray bursts Hiroyasu Tajima on behalf of Fermi LAT and GBM Collaborations Kavli Institute of Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology SLAC National Accelerator
Search for X-ray Transients with MAXI
 Search for X-ray Transients with MAXI Nobuyuki Kawai (Tokyo Tech) M. Serino (RIKEN), H. Negoro (Nihon U.) on behalf of the MAXI Team MAXI Instrumentation and operation Observations for GW 150914 and results
Search for X-ray Transients with MAXI Nobuyuki Kawai (Tokyo Tech) M. Serino (RIKEN), H. Negoro (Nihon U.) on behalf of the MAXI Team MAXI Instrumentation and operation Observations for GW 150914 and results
A NEW GENERATION OF GAMMA-RAY TELESCOPE
 A NEW GENERATION OF GAMMA-RAY TELESCOPE Aleksandar GOSTOJIĆ CSNSM, Orsay, France 11 th Russbach School on Nuclear Astrophysics, March 2014. Introduction: Gamma-ray instruments GROUND BASED: ENERGY HIGHER
A NEW GENERATION OF GAMMA-RAY TELESCOPE Aleksandar GOSTOJIĆ CSNSM, Orsay, France 11 th Russbach School on Nuclear Astrophysics, March 2014. Introduction: Gamma-ray instruments GROUND BASED: ENERGY HIGHER
Fermi-LAT Recent Results on Gamma-Ray Bursts
 , on behalf of the Fermi LAT and GBM Collaborations Laboratoire Univers et Particules de Montpellier, Université Montpellier 2, CNRS/IN2P3, Montpellier, France piron@in2p3.fr The Fermi Large Area Telescope
, on behalf of the Fermi LAT and GBM Collaborations Laboratoire Univers et Particules de Montpellier, Université Montpellier 2, CNRS/IN2P3, Montpellier, France piron@in2p3.fr The Fermi Large Area Telescope
GRB Spectra and their Evolution: - prompt GRB spectra in the γ-regime
 GRB Spectra and their Evolution: - prompt GRB spectra in the γ-regime Andreas von Kienlin MPE -Gamma 14. November 2003 1 Outline Time averaged GRB spectra Example spectra Instrumental response Band function
GRB Spectra and their Evolution: - prompt GRB spectra in the γ-regime Andreas von Kienlin MPE -Gamma 14. November 2003 1 Outline Time averaged GRB spectra Example spectra Instrumental response Band function
Gamma-Rays from Radio Galaxies: Fermi-LAT
 Gamma-Rays from Radio Galaxies: Fermi-LAT PAOLA GRANDI INAF/IASF BOLOGNA, ITALY on behalf of the FERMI LAT Collaboration Many thanks to : C. Dermer. G. Ghisellini, L. Maraschi, G. Migliori, E. Torresi,
Gamma-Rays from Radio Galaxies: Fermi-LAT PAOLA GRANDI INAF/IASF BOLOGNA, ITALY on behalf of the FERMI LAT Collaboration Many thanks to : C. Dermer. G. Ghisellini, L. Maraschi, G. Migliori, E. Torresi,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 16 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 16 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 16 Jan 2018](/thumbs/92/110689620.jpg) Unidentified Fermi LAT Transients Near The Galactic Plane Dirk Pandel arxiv:11.v1 [astro-ph.he] 1 Jan 1 Department of Physics, Grand Valley State University, Allendale, MI 91, USA Abstract. The Fermi LAT
Unidentified Fermi LAT Transients Near The Galactic Plane Dirk Pandel arxiv:11.v1 [astro-ph.he] 1 Jan 1 Department of Physics, Grand Valley State University, Allendale, MI 91, USA Abstract. The Fermi LAT
GLAST LAT Overview and Status
 GLAST LAT Overview and Status INPAC Meeting, Berkeley May 5, 2007 Robert Johnson LAT Tracker Subsystem Manager Physics Department and Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics University of California
GLAST LAT Overview and Status INPAC Meeting, Berkeley May 5, 2007 Robert Johnson LAT Tracker Subsystem Manager Physics Department and Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics University of California
Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration
 Measurement of the cosmic ray positron spectrum with the Fermi LAT using the Earth s magnetic field Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration International Cosmic Ray
Measurement of the cosmic ray positron spectrum with the Fermi LAT using the Earth s magnetic field Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration International Cosmic Ray
High Energy Emission. Brenda Dingus, LANL HAWC
 High Energy Emission from GRBs Brenda Dingus, LANL HAWC What are GRBs? Cosmological distance Typical observed z>1 Energy released is up to few times the rest mass of Sun (if isotropic) in a few seconds
High Energy Emission from GRBs Brenda Dingus, LANL HAWC What are GRBs? Cosmological distance Typical observed z>1 Energy released is up to few times the rest mass of Sun (if isotropic) in a few seconds
Multiwavelength Observations of 3C 66A in
 Blazar Variability Workshop II: Entering the GLAST Era ASP Conference Series, Vol. 350, 2006 H. R. Miller, K. Marshall, J. R. Webb, and M. F. Aller Multiwavelength Observations of 3C 66A in 2003 2004 M.
Blazar Variability Workshop II: Entering the GLAST Era ASP Conference Series, Vol. 350, 2006 H. R. Miller, K. Marshall, J. R. Webb, and M. F. Aller Multiwavelength Observations of 3C 66A in 2003 2004 M.
Origin of X-rays in blazars
 Origin of X-rays in blazars Greg Madejski, Stanford / KIPAC With much of the work presented here done by Amy Furniss, Masaaki Hayashida, Krzysztof Nalewajko, Marek Sikora, Jim Chiang, David Paneque, Mislav
Origin of X-rays in blazars Greg Madejski, Stanford / KIPAC With much of the work presented here done by Amy Furniss, Masaaki Hayashida, Krzysztof Nalewajko, Marek Sikora, Jim Chiang, David Paneque, Mislav
PoS(extremesky2009)023
 Université Joseph Fourier - Grenoble 1/CNRS, laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble (LAOG) UMR 5571, BP 53, 38041 Grenoble Cedex 09, France E-mail: adam.hill@obs.ujf-grenoble.fr on behalf of the Fermi-LAT
Université Joseph Fourier - Grenoble 1/CNRS, laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble (LAOG) UMR 5571, BP 53, 38041 Grenoble Cedex 09, France E-mail: adam.hill@obs.ujf-grenoble.fr on behalf of the Fermi-LAT
AGILE and Blazars: the Unexpected, the Unprecedented, and the Uncut
 AGILE and Blazars: the Unexpected, the Unprecedented, and the Uncut Rome, AGILE γ-ray Symposium 2017.12.12 Stefano Vercellone (INAF-OAB) 1 Rationale A review of the whole set of AGILE results on extra-galactic
AGILE and Blazars: the Unexpected, the Unprecedented, and the Uncut Rome, AGILE γ-ray Symposium 2017.12.12 Stefano Vercellone (INAF-OAB) 1 Rationale A review of the whole set of AGILE results on extra-galactic
Aldo Morselli INFN Roma Tor Vergata On behalf of Marco Tavani and the AGILE Team
 the AGILE space mission Aldo Morselli INFN Roma Tor Vergata On behalf of Marco Tavani and the AGILE Team Annapolis Sept. 18 2014 10th INTEGRAL Workshop A Synergistic View of the High Energy Sky Aldo Morselli,
the AGILE space mission Aldo Morselli INFN Roma Tor Vergata On behalf of Marco Tavani and the AGILE Team Annapolis Sept. 18 2014 10th INTEGRAL Workshop A Synergistic View of the High Energy Sky Aldo Morselli,
Physics of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts Explored by CTA and DECIGO/B-DECIGO
 Physics of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts Explored by CTA and DECIGO/B-DECIGO Hiroyasu Tajima Institute for Space Earth Environmental Research Nagoya University 17th DECIGO Workshop Nov 1, 18 Nagoya University
Physics of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts Explored by CTA and DECIGO/B-DECIGO Hiroyasu Tajima Institute for Space Earth Environmental Research Nagoya University 17th DECIGO Workshop Nov 1, 18 Nagoya University
On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere
 On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere for the HAWC collaboration E-mail: miguel@psu.edu Observations of high energy gamma rays are an
On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere for the HAWC collaboration E-mail: miguel@psu.edu Observations of high energy gamma rays are an
T. J. Brandt. CRISM: 27 Jun On behalf of the Fermi- LAT Collabora:on IRAP/Université Paul Saba:er.
 On behalf of the Fermi- LAT Collabora:on IRAP/Université Paul Saba:er brandt@cesr.fr CRISM: 27 Jun 2011 All- par:cle CR Spectrum Cosmic rays are: charged particles from outer space (V. Hess, 1912) { ~90%
On behalf of the Fermi- LAT Collabora:on IRAP/Université Paul Saba:er brandt@cesr.fr CRISM: 27 Jun 2011 All- par:cle CR Spectrum Cosmic rays are: charged particles from outer space (V. Hess, 1912) { ~90%
Galactic Novae Simulations for the Cherenkov Telescope Array
 Galactic Novae Simulations for the Cherenkov Telescope Array REU Final Presentation August 4, 2017 Colin Adams Primary Mentors: Brian Humensky, Deivid Ribeiro Outline Introduction Why and how do we study
Galactic Novae Simulations for the Cherenkov Telescope Array REU Final Presentation August 4, 2017 Colin Adams Primary Mentors: Brian Humensky, Deivid Ribeiro Outline Introduction Why and how do we study
1. GAMMA-RAY BURSTS & 2. FAST RADIO BURSTS
 1. GAMMA-RAY BURSTS & 2. FAST RADIO BURSTS WITH TAM, Pak Hin (Sun Yat-sen University/ICRR) GAMMA-RAY BURST OBSERVATIONS WITH CTA LESSONS LEARNT FROM FERMI/LAT TAM, Pak Hin (Sun Yat-sen University/ICRR,
1. GAMMA-RAY BURSTS & 2. FAST RADIO BURSTS WITH TAM, Pak Hin (Sun Yat-sen University/ICRR) GAMMA-RAY BURST OBSERVATIONS WITH CTA LESSONS LEARNT FROM FERMI/LAT TAM, Pak Hin (Sun Yat-sen University/ICRR,
Status of the MAGIC telescopes
 SNOWPAC 2010 Status of the MAGIC telescopes Pierre Colin for the MAGIC collaboration Max-Planck-Institut für physik (Munich) Status of the MAGIC telescopes MAGIC-1 MAGIC-2 Outline: Recent results of the
SNOWPAC 2010 Status of the MAGIC telescopes Pierre Colin for the MAGIC collaboration Max-Planck-Institut für physik (Munich) Status of the MAGIC telescopes MAGIC-1 MAGIC-2 Outline: Recent results of the
Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics Astroparticle Physics Lecture 5 Gamma Rays & x-rays Sept. 22, 2015 Sun Kee Kim Seoul National University Gamma ray astronomy gamma ray synchrotron radition
Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics Astroparticle Physics Lecture 5 Gamma Rays & x-rays Sept. 22, 2015 Sun Kee Kim Seoul National University Gamma ray astronomy gamma ray synchrotron radition
Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope
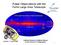 Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope First Light sky survey (4 days of exposure)) Launch: 11 June 2008 Gottfried Kanbach & Matthew Baring for the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 The high-energy
Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope First Light sky survey (4 days of exposure)) Launch: 11 June 2008 Gottfried Kanbach & Matthew Baring for the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 The high-energy
Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants
 1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
Fermi Source Analyses and Identifying VERITAS Candidates
 Fermi Source Analyses and Identifying VERITAS Candidates 1 1 1. University of California, Berkeley 2 Overview Introduction VERITAS Fermi Analysis Likelihood Doppler Factor Estimation Motivations Blazars
Fermi Source Analyses and Identifying VERITAS Candidates 1 1 1. University of California, Berkeley 2 Overview Introduction VERITAS Fermi Analysis Likelihood Doppler Factor Estimation Motivations Blazars
