EUCLID Mission Baseline Design
|
|
|
- Sherman Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EUCLID Mission Baseline Design Oswald Wallner 1, Klaus Ergenzinger 1, Rainer Wilhelm 1, Ludovic Vaillon 2 Astrium Satellites Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2 31 rue des Cosmonautes, 3142 Toulouse Cedex 4, France Abstract EUCLID is a mission to accurately measure the accelerated expansion of the universe. It has been selected for implementation with a launch planned for 22. EUCLID will map the large-scale structure of the Universe over 15. deg 2 of the extragalactic sky and it will measure galaxies out to redshifts of z=2 EUCLID consists of a 1.2 m telescope and two scientific instruments for ellipticity and redshift measurements in the visible and near infrared wavelength regime. We present a design for the EUCLID space segment, targeting optimum performance in terms of image quality and stability and maximum robustness with respect to performance, resources and instrument interfaces. Index Terms EUCLID, Dark Energy, ESA I. INTRODUCTION EUCLID is a mission to study the geometry and the nature of the dark universe, with a launch planned for 22 [1]. It is a survey mission which shall show how the expansion of the Universe and how the matter distribution within the Universe evolved over the last 1 billion years. EUCLID is the second medium-class mission of the ESA Cosmic Vision programme.. After finalisation of the Definition Phase (Phase A/B1) mid of 212, the mission is currently entering the Implementation Phase (Phase B2/C/D/E1). The current understanding of cosmology is that the Universe has evolved from a highly homogeneous state after the Big Bang to a highly inhomogeneous structure of galaxies, clusters, and superclusters at our epoch, see Fig. 1. This, however, necessitates the introduction of two more or less unknown quantities which dominate the energy density of the Universe. Dark matter, constituting 2% of the total energy density, is exerting gravitational attraction but does not emit or absorb light. Dark energy, constituting 76% of the total energy density, is causing the expansion of the Universe to be currently accelerating. EUCLID is a mission featuring two independent cosmological probes for understanding the nature of dark energy and dark matter by tracking their observational signatures on the geometry of the Universe and on the history of structure formation. Weak Gravitational Lensing (WL) from a highresolution imaging survey of ellipticity of distant galaxies. By correlating a large number of galaxy ellipticities, small systematic distortions can be measured which result from light bending by matter distributed along the line of sight. Baryonic Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) refer to a clustering of baryonic matter at certain length scales due to acoustic waves which propagated in the early universe. A typical (co-moving) length scale of 15 Mpc is derived from Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) observations, and is locked up in the cosmic structures. It serves as a standard ruler, which can be used to trace the accelerated expansion of the universe as a function of cosmic time, by observing the distribution of galaxies as a function of redshift. In addition, EUCLID provides data for additional independent cosmological probes and legacy science. II. MISSION OVERVIEW EUCLID will perform a systematic survey of galaxies over a large fraction of the observable universe, i.e. over a time scale where Dark Energy became dominant (corresponding to a redshift range of <z<2) and over an extragalactic sky area of 15. deg 2 (with the goal of 2. deg 2 ). The EUCLID Mission consists of a Korsch telescope with a free aperture of 1 m 2 and a field of view of deg 2, off-axis by.45 deg, and two scientific instruments which are provided by the EUCLID Consortium [3]: Fig. 1 Expansion history of the Universe. Image adapted from [2].
2 A visible imager (VIS) for shape measurements of galaxies up to mag AB =24.5 in the wavelength regime from nm. The VIS instruments requires from the telescope a point spread function (PSF) with a full width of half maximum (FWHM) of <.142 arcsec and an ellipticity of <13% at any point within the field of view (FoV), specified at 8 nm wavelength. A near-infrared spectrograph and photometer (NISP) for photometric redshift measurements of galaxies up to mag AB =24.5 in the three wavelength bands Y ( nm), J ( nm) and Hp ( nm) to obtain the NIR part of the photometric redshift determination, and for spectroscopic redshift measurements of galaxies up to mag AB =19.5 with a spectral resolution of 25 in the wavelength band of 1 2 nm enabling a redshift resolution of z /(1+z).1%. The NISP instrument requires from the telescope PSF maximum radii of 5% and 8% encircled energy (r EE ) of.245 arcsec and.511 arcsec, respectively, specified at 1486 nm wavelength. Lagrange Point of the Sun-Earth system [4], see Fig. 3. A total nominal scientific operational lifetime of 6 years is planned. z / 1 6 km Fig x / 1 6 km y / 1 6 km EUCLID mission reference orbit. The period until the last transfer correction manoeuvre is indicated by blue color. Fig. 2 Extragalactic sky survey geometry in ecliptic coordinates (left) and step & stare sky survey principle (right). III. SYSTEM OVERVIEW For the EUCLID spacecraft a design has been derived during Phase A/B1 which allows for satisfying all the scientific requirements of the mission. The spacecraft features a payload module (PLM), consisting of the telescope and the scientific instruments VIS and NISP, a sunshield for ensuring a stable thermal environment, and a service module (SVM) providing all the service functionalities to the scientific mission (attitude and orbit control, data handling, communication, etc.), see Fig. 4. EUCLID will observe the extragalactic sky at galactic latitudes b 3 deg, see Fig. 2 (left). The wide survey will cover a total sky area of 15. deg 2 and will embed the deep survey with a total sky area of 4 deg 2. The sky is sampled in step & stare mode, see Fig. 2 (right). Each field is observed in four dither frames to avoid any gaps between the detectors (offset of 1 arcsec and 5 arcsec in latitude and longitude, respectively). Nominally the sky is scanned along Meridians to the ecliptic, allowing for one strip per day. This is achieved (in ecliptic longitude) by the natural rotation of the operational orbit around the Sun and (in latitude) by a spacecraft rotation around the Sun-spacecraft axis, where the sunshield is oriented perpendicular to it (solar aspect angle SAA=9 deg). For the sake of increased temporal efficiency (in particular around the Equinoxes and at the ecliptic poles) and of mission flexibility some limited deviation are allowed (SAA= deg). EUCLID will be launched from Kourou (French Guiana) by a Soyuz ST 2-1B launch vehicle in 22. A direct transfer is targeted to a large-amplitude free-insertion orbit at the Second Fig. 4 EUCLID system overview.
3 IV. PAYLOAD DESIGN The EUCLID payload module consists of a common bench, a telescope and the two scientific instruments VIS and NISP. While the optical bench and the telescope will be procured industrially, the nationally funded instruments will be developed by the EUCLID Consortium [3]. The conceptual block diagram of the EUCLID payload module is given in Fig. 5. It shows the interfaces and the share of responsibility between the industrial consortium and the instrument consortium. The optical design of the PLM has been developed by ESA and is characterised as follows: The telescope is a three-mirror Korsch configuration with a.45 deg off-axis field and an aperture stop at the primary mirror. The entrance pupil diameter is 1.2 m, the optically corrected and not vignetted FoV is deg 2, and the focal length is 24.5 m. At the telescope's exit pupil the dichroic is located. The reflected output of the dichroic is imaged on the VIS focal plane. It has a FoV of deg 2. The transmitted output is fed to the NISP instrument. It has a FoV of deg 2. The major drivers for the EUCLID PLM design are: Fig. 5 EUCLID payload module conceptual block diagram. The colors indicate the corresponding responsibilities (instrument images adapted from [1]). High optical quality and opto-mechanical stability to guarantee the specified image quality and image quality stability requirements. These are specified in terms of ellipticity and FWHM of the system PSF for VIS channel and in terms of encircled energy radius for the NISP channel. Robust interfaces between the telescope and the instruments, in particular in terms of passive cooling capability, which is challenging for the VIS FPA proximity electronics and for the NISP detectors operating at a temperature below 1 K. A cold environment (<15K) is required by the two instruments to minimize radiation effects on the VIS FPA and thermal background and detector dark current for NISP. Low mass for compatibility with launch on Soyuz. The industrial part of the payload module consists of the three-mirror telescope, folding mirrors, the dichroic mirror, a common optical bench, the harness (including the instrument harness), and the instrument radiators. The industrial part also includes as part of the AOCS a fine guidance sensor (FGS) located in the VIS image plane. The VIS instrument consists of a shutter, a focal plane assembly (FPA) with 66 CCD's (e2v, CCD 273,.1 arcsec/pixel plate scale), a calibration unit, and warm electronic units (WE) located within the SVM (control and data processing unit, power and mechanism control unit). The NISP instrument consists of a filter wheel and GRISM wheel assembly (FWA/GWA), refractive optics, a focal plane assembly with 44 Hawaii 2RG (Teledyne,.3 arcsec/pixel plate scale), and warm electronic units (WE) located within the SVM (detector control unit, data processing unit, instrument control unit). For the EUCLID payload module a design has been derived during Phase A/B1. The main features are: The payload structural and material concept is determined by the manufacturability and achievable quality of the primary mirror, by the capability of equalising thermal distortions, the total mass and the heritage. Building on the experience from Gaia [5] featuring similar (and actually more challenging) requirements, Astrium decided to make the entire PLM (bench, mirrors, structure) of Silicon Carbide (SiC). This allows an athermal design with very low thermoelastic sensitivity thanks to the homogeneous telescope deformation and the low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). The capability of SiC for extreme light-weighting ensures minimum payload mass. The payload thermal concept is determined by the compatibility to the instruments (requiring a temperature of 15 K), the achievable thermal stability, and the compatibility to available technologies. Astrium decided for passive cool-down below 15 K for telescope and instruments cavity (much colder than 24 K, the maximum temperature compatible with the allowed thermal background for NISP). This avoids
4 dedicated thermal compartments for the instruments and minimises the radiator size. Passive thermal control allows for highest thermal stability and minimum heating power. The resulting settling times after change of the solar aspect angle are compatible with the operational scenario and mission timeline. The PLM is protected by a thermal baffle which decouples from the sunshield thermal variations and which blocks straylight emerging from bright stars within the FoV. The thermal decoupling between the PLM and the SVM is maximised by using iso-static interfaces with low thermal conductivity. The instruments VIS and NISP are connected isostatically to the PLM bench. For the fine guidance sensor (FGS) a dedicated support structure has been designed which allows accommodation within the VIS focal plane but which decouples the FGS completely from the VIS instruments. The payload module design elaborated by Astrium within Phase A/B1 is shown in Fig. 6. It allows optimum thermoelastic stability and minimum mass. The design is fully compatible with the mission requirements. The total PLM mass is estimated to 63 kg, including warm electronics located within the SVM. Fig. 6 EUCLID payload module design. V. SPACECRAFT DESIGN Besides the payload module, the EUCLID spacecraft consists of the service module and the sunshield. The major drivers for the spacecraft design are: High spacecraft pointing stability to guarantee the specified image quality and image quality stability requirements. Besides the optical design and the payload properties, the residual pointing error is the major contributor to the image quality budgets (ellipticity and FWHM). Highly stabile thermal environment for the PLM, also in case of significant changes in SAA between two fields. High volume of science telemetry to be stored and downloaded by a dedicated high-gain antenna (HGA) operating in K-band ( GHz). Mass saving design options to ensure the overall Soyuz launch capability of 216 kg [4] and the required system mass margin of 2%. For the EUCLID spacecraft a design has been derived during Phase A/B1. The main features are: The structural concept has been evolved specifically to meet the requirements of the EUCLID mission but regarding the requirement on high technology readiness also to take direct benefit of previous mission with comparable requirements. The service module (SVM) is of hexagonal shape with a central cylinder for supporting the launch loads from the PLM to the launch vehicle adapter (for mass saving reasons the dedicated GAIA adapter will be used). The SVM structure is made of Aluminium honeycomb with CFRP facts. The sunshield is of panel-type with high-performance MLI insulation behind it. It is combined with the solar generator. The size is driven by the size of the payload and the size of the solar array (8.9 m 2 ). Its canted shape and the support struts are driven by the stiffness requirements. The attitude and orbit control system (AOCS) is responsible for the required spacecraft attitude during all mission phases. The stringent pointing requirements (a few milli-arcsec over the field duration of 565 s, driven by the image quality requirements) ask for a high performance AOCS, including a fine guidance sensor (FGS) located in the VIS focal plane and a cold gas micro-propulsion system for the science mode field dither and field step manoeuvres. The cold gas system allows for best pointing performance, at the cost of mass and limitations w.r.t. mission extension. Due to the low thrust level of 1 mn maximum, the manoeuvre times are rather long but still compatible with the specified timeline per field. The chemical propulsion system is a monopropellant hydrazine system operating in blow-down mode. It is required for transfer dispersion correction, mid-course correction and orbit maintenance at the operational orbit with a total V of 61 m/s (including margin). Fuel sloshing is minimized by use of a membrane tank. For telemetry, tracking and control an X-band communication system with two hemispherical lowgain antennas is considered. The science data (75 GBit/day) is down-linked via a steerable K-band highgain antenna. For the daily available downlink-time of 4 hours a data rate of about 75 Mbit/s is required.
5 The spacecraft design elaborated by Astrium is shown Fig. 7. The total spacecraft dry mass of about 184 kg including proper subsystem margins and 2% system margin is compatible with the Soyuz launch capacity. robustness in terms of heritage, technology readiness and growth potential, and by its flexibility w.r.t. mission operations, interfaces (in particular to the instruments) and procurement approach. The EUCLID mission is feasible. The risks are at a manageable level and a launch in 22 appears realistic. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The work described was performed under ESA/ESTEC Contract No , EUCLID Definition Phase Study. The authors are grateful to L. Duvet, Ph. Gondoin, R. Laureijs, and G. Saavedra (ESA/ESTEC) for valuable contributions and discussions. Fig. 7 EUCLID spacecraft design. VI. CONCLUSIONS AND OUTLOOK The spacecraft design elaborated by Astrium within Phase A/B1 of the EUCLID mission is characterized by its compliance to the mission requirements and interfaces, by its REFERENCES [1] EUCLID Red Book, European Space Agency, ESA/SRE(211)12, July 211 [2] WMAP, web page available online at map.gsfc.nasa.gov, 31 August 212 [3] EUCLID Consortium, web page available online at 31 August 212 [4] EUCLID Consolidated Report on Mission Analysis, M. Landgraf, F. Renk, MAS Working Paper No. 533, Issue 1.3, 26 January 211 [5] GAIA, web page available online at sci.esa.int/gaia, 31 August 212
Plato, Euclid and the New Hard X-Ray mission
 Schiaparelli and his Legacy Meeting on Future planetary, scientific and robotic space missions Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria, Torino, 21/10/2010 Template reference : 100181670S-EN Plato, Euclid and
Schiaparelli and his Legacy Meeting on Future planetary, scientific and robotic space missions Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria, Torino, 21/10/2010 Template reference : 100181670S-EN Plato, Euclid and
Observing the dark Universe with Euclid
 Euclid Imaging Instrument Observing the dark Universe with Euclid 18 november 2009 Jerome Amiaux CEA Saclay EIC System Manager On Behalf of the Euclid Imaging Consortium The presented document is Proprietary
Euclid Imaging Instrument Observing the dark Universe with Euclid 18 november 2009 Jerome Amiaux CEA Saclay EIC System Manager On Behalf of the Euclid Imaging Consortium The presented document is Proprietary
Euclid Mission Overview
 Mission Overview René Laureijs G. Racca, L. Stagnaro, J.C. Salvignol, J. Hoar (ESA) Y. Mellier and the EC Synergistic Science with and the SKA Oxford 16 September Outline Setting the scene Science Objectives
Mission Overview René Laureijs G. Racca, L. Stagnaro, J.C. Salvignol, J. Hoar (ESA) Y. Mellier and the EC Synergistic Science with and the SKA Oxford 16 September Outline Setting the scene Science Objectives
Model-based instrument review for the Euclid mission for NISP- and VIS CDR
 Model-based instrument review for the Euclid mission for NISP- and VIS CDR Harold Metselaar 1, Jose Lorenzo Alvarez 1, Michael Kretzenbacher 1 1 ESA / ESTEC, Keplerlaan 1, 2201 AZ Noordwijk; ABSTRACT Euclid
Model-based instrument review for the Euclid mission for NISP- and VIS CDR Harold Metselaar 1, Jose Lorenzo Alvarez 1, Michael Kretzenbacher 1 1 ESA / ESTEC, Keplerlaan 1, 2201 AZ Noordwijk; ABSTRACT Euclid
GAIA: THE SATELLITE AND PAYLOAD. Oscar Pace European Space Agency, ESA-ESTEC, Keplerlaan 1, 2200AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands
 23 GAIA: THE SATELLITE AND PAYLOAD Oscar Pace European Space Agency, ESA-ESTEC, Keplerlaan 1, 2200AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands ABSTRACT This paper summarises the main features of the Gaia technical baseline
23 GAIA: THE SATELLITE AND PAYLOAD Oscar Pace European Space Agency, ESA-ESTEC, Keplerlaan 1, 2200AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands ABSTRACT This paper summarises the main features of the Gaia technical baseline
Gaia ESA's billion star telescope
 Gaia ESA's billion star telescope Gaia is an unmanned space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA) designed for astrometry. The mission aims to compile a 3D space catalogue of approximately 1 billion
Gaia ESA's billion star telescope Gaia is an unmanned space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA) designed for astrometry. The mission aims to compile a 3D space catalogue of approximately 1 billion
Gaia Status & Early Releases Plan
 Gaia Status & Early Releases Plan F. Mignard Univ. Nice Sophia-Antipolis & Observatory of the Côte de Azur Gaia launch: 20 November 2013 The big news @ 08:57:30 UTC 2 Gaia: a many-sided mission Driven
Gaia Status & Early Releases Plan F. Mignard Univ. Nice Sophia-Antipolis & Observatory of the Côte de Azur Gaia launch: 20 November 2013 The big news @ 08:57:30 UTC 2 Gaia: a many-sided mission Driven
Picometre metrology. The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars
 Picometre metrology in space The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars in our Galaxy. Part of ESA s Cosmic Vision program, the Gaia spacecraft is being
Picometre metrology in space The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars in our Galaxy. Part of ESA s Cosmic Vision program, the Gaia spacecraft is being
EUCLID SKY SCANNING TOOL
 EUCLID SKY SCANNING TOOL 5TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ASTRODYNAMICS TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES ESA/ESTEC, NOORDWIJK, THE NETHERLANDS 29 MAY 1 JUNE 2012 Francesco Cacciatore (1), Mariano Sánchez (2), Alberto
EUCLID SKY SCANNING TOOL 5TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ASTRODYNAMICS TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES ESA/ESTEC, NOORDWIJK, THE NETHERLANDS 29 MAY 1 JUNE 2012 Francesco Cacciatore (1), Mariano Sánchez (2), Alberto
CASE/ARIEL & FINESSE Briefing
 CASE/ARIEL & FINESSE Briefing Presentation to NRC Committee for Exoplanet Science Strategy including material from the ARIEL consortium Mark Swain - JPL 19 April 2019 2018 California Institute of Technology.
CASE/ARIEL & FINESSE Briefing Presentation to NRC Committee for Exoplanet Science Strategy including material from the ARIEL consortium Mark Swain - JPL 19 April 2019 2018 California Institute of Technology.
Cosmology with the ESA Euclid Mission
 Cosmology with the ESA Euclid Mission Andrea Cimatti Università di Bologna Dipartimento di Astronomia On behalf of the Euclid Italy Team ESA Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 M-class Mission Candidate Selected in
Cosmology with the ESA Euclid Mission Andrea Cimatti Università di Bologna Dipartimento di Astronomia On behalf of the Euclid Italy Team ESA Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 M-class Mission Candidate Selected in
Presentation by Indian Delegation. to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS. February 2012 Vienna
 Presentation by Indian Delegation to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS February 2012 Vienna ASTROSAT Astrosat is India s first dedicated multiwavelength astronomy satellite with a capability to observe target sources
Presentation by Indian Delegation to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS February 2012 Vienna ASTROSAT Astrosat is India s first dedicated multiwavelength astronomy satellite with a capability to observe target sources
DUNE. Dark UNiverse Explorer. Institut de Ciències de l Espai ICE/CSIC
 DUNE Dark UNiverse Explorer Institut de Ciències de l Espai ICE/CSIC Institut de Física d Altes Energies IFAE Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas, MedioAmbientales y Tecnológicas CIEMAT Francisco avier
DUNE Dark UNiverse Explorer Institut de Ciències de l Espai ICE/CSIC Institut de Física d Altes Energies IFAE Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas, MedioAmbientales y Tecnológicas CIEMAT Francisco avier
Sun Shield. Solar Paddle
 The Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Report SP No.14, December 2000 Current Status of ASTRO-F By Hiroshi Murakami Λ (November 1, 2000) Abstract: The ASTRO-F is the second infrared astronomy
The Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Report SP No.14, December 2000 Current Status of ASTRO-F By Hiroshi Murakami Λ (November 1, 2000) Abstract: The ASTRO-F is the second infrared astronomy
The Quantum Sensor Challenge Designing a System for a Space Mission. Astrid Heske European Space Agency The Netherlands
 The Quantum Sensor Challenge Designing a System for a Space Mission Astrid Heske European Space Agency The Netherlands Rencontres de Moriond - Gravitation, La Thuile, 2017 Quantum Sensors in Lab Experiments
The Quantum Sensor Challenge Designing a System for a Space Mission Astrid Heske European Space Agency The Netherlands Rencontres de Moriond - Gravitation, La Thuile, 2017 Quantum Sensors in Lab Experiments
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
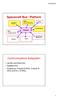 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE
 SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE The Rationale for Infrared Astronomy reveal cool states of matter explore the hidden Universe provide access to many spectral features probe the early life of the cosmos WANT TO
SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE The Rationale for Infrared Astronomy reveal cool states of matter explore the hidden Universe provide access to many spectral features probe the early life of the cosmos WANT TO
ESA STUDY OF A WIDE FIELD IMAGER FOR SUPERNOVAE SURVEYS AND DARK ENERGY CHARACTERIZATION
 ESA STUDY OF A WIDE FIELD IMAGER FOR SUPERNOVAE SURVEYS AND DARK ENERGY CHARACTERIZATION P. Gondoin (1), V. Kirschner (1), A. Santovincenzo (1), A Lyngvi (1), A. Short (1), U. Telljohann (1), G. Chirulli
ESA STUDY OF A WIDE FIELD IMAGER FOR SUPERNOVAE SURVEYS AND DARK ENERGY CHARACTERIZATION P. Gondoin (1), V. Kirschner (1), A. Santovincenzo (1), A Lyngvi (1), A. Short (1), U. Telljohann (1), G. Chirulli
TROPOMI. Sentinel 5 Precursor instrument for air quality and climate observations. R. Voors Dutch Space. ICSO, 11 October 2012
 TROPOMI Sentinel 5 Precursor instrument for air quality and climate observations R. Voors Dutch Space ICSO, 11 October 2012 Sentinel 5 precursor and the TROPOMI payload Climate and Air quality Precursor
TROPOMI Sentinel 5 Precursor instrument for air quality and climate observations R. Voors Dutch Space ICSO, 11 October 2012 Sentinel 5 precursor and the TROPOMI payload Climate and Air quality Precursor
Study Participants: T.E. Sarris, E.R. Talaat, A. Papayannis, P. Dietrich, M. Daly, X. Chu, J. Penson, A. Vouldis, V. Antakis, G.
 GLEME: GLOBAL LIDAR EXPLORATION OF THE MESOSPHERE Project Technical Officer: E. Armandillo Study Participants: T.E. Sarris, E.R. Talaat, A. Papayannis, P. Dietrich, M. Daly, X. Chu, J. Penson, A. Vouldis,
GLEME: GLOBAL LIDAR EXPLORATION OF THE MESOSPHERE Project Technical Officer: E. Armandillo Study Participants: T.E. Sarris, E.R. Talaat, A. Papayannis, P. Dietrich, M. Daly, X. Chu, J. Penson, A. Vouldis,
Detection and characterization of exoplanets from space
 Detection and characterization of exoplanets from space Heike Rauer 1,2, 1:Institute for Planetary Research, DLR, Berlin 2:Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics, TU Berlin Exoplanet Space Missions and
Detection and characterization of exoplanets from space Heike Rauer 1,2, 1:Institute for Planetary Research, DLR, Berlin 2:Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics, TU Berlin Exoplanet Space Missions and
TMT and Space-Based Survey Missions
 TMT and Space-Based Survey Missions Daniel Stern Jet Propulsion Laboratory/ California Institute of Technology 2014 California Institute of Technology TMT Science Forum 2014 July 17 Outline Summary of
TMT and Space-Based Survey Missions Daniel Stern Jet Propulsion Laboratory/ California Institute of Technology 2014 California Institute of Technology TMT Science Forum 2014 July 17 Outline Summary of
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 15 Nov 2004
 Mission design for LISA Pathfinder arxiv:gr-qc/0411071v1 15 Nov 2004 M Landgraf, M Hechler, and S Kemble ESA/ESOC, Robert-Bosch-Straße 5, D-64293 Darmstadt, Germany E-mail: Markus.Landgraf@esa.int EADS
Mission design for LISA Pathfinder arxiv:gr-qc/0411071v1 15 Nov 2004 M Landgraf, M Hechler, and S Kemble ESA/ESOC, Robert-Bosch-Straße 5, D-64293 Darmstadt, Germany E-mail: Markus.Landgraf@esa.int EADS
The international scenario Balloons, LiteBIRD, PIXIE, Millimetron
 The international scenario Balloons, LiteBIRD, PIXIE, Millimetron Francesco Piacentini Sapienza Università di Roma, Dipartimento di Fisica on behalf of the Italian CMB community Overview International
The international scenario Balloons, LiteBIRD, PIXIE, Millimetron Francesco Piacentini Sapienza Università di Roma, Dipartimento di Fisica on behalf of the Italian CMB community Overview International
EUCLID Spectroscopy. Andrea Cimatti. & the EUCLID-NIS Team. University of Bologna Department of Astronomy
 EUCLID Spectroscopy Andrea Cimatti University of Bologna Department of Astronomy & the EUCLID-NIS Team Observing the Dark Universe with EUCLID, ESA ESTEC, 17 November 2009 DARK Universe (73% Dark Energy
EUCLID Spectroscopy Andrea Cimatti University of Bologna Department of Astronomy & the EUCLID-NIS Team Observing the Dark Universe with EUCLID, ESA ESTEC, 17 November 2009 DARK Universe (73% Dark Energy
Spitzer Space Telescope
 Spitzer Space Telescope (A.K.A. The Space Infrared Telescope Facility) The Infrared Imaging Chain 1/38 The infrared imaging chain Generally similar to the optical imaging chain... 1) Source (different
Spitzer Space Telescope (A.K.A. The Space Infrared Telescope Facility) The Infrared Imaging Chain 1/38 The infrared imaging chain Generally similar to the optical imaging chain... 1) Source (different
THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe
 THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe Rodrigo Leonardi Planck Science Office ESTEC/ESA OVERVIEW Planck observational objective & science.
THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe Rodrigo Leonardi Planck Science Office ESTEC/ESA OVERVIEW Planck observational objective & science.
Properties of Thermal Radiation
 Observing the Universe: Telescopes Astronomy 2020 Lecture 6 Prof. Tom Megeath Today s Lecture: 1. A little more on blackbodies 2. Light, vision, and basic optics 3. Telescopes Properties of Thermal Radiation
Observing the Universe: Telescopes Astronomy 2020 Lecture 6 Prof. Tom Megeath Today s Lecture: 1. A little more on blackbodies 2. Light, vision, and basic optics 3. Telescopes Properties of Thermal Radiation
4.3 Planck. Scientific goals. Planck payload
 4.3 Planck In late 1992, the NASA COBE team announced the detection of intrinsic temperature fluctuations in the Cosmic Background Radiation Field (CBRF), observed on the sky at angular scales larger than
4.3 Planck In late 1992, the NASA COBE team announced the detection of intrinsic temperature fluctuations in the Cosmic Background Radiation Field (CBRF), observed on the sky at angular scales larger than
Cecilia Fariña - ING Support Astronomer
 Cecilia Fariña - ING Support Astronomer Introduction: WHT William Herschel Telescope 2 Introduction: WHT WHT located in La Palma, Canary Islands, Spain William Herschel Telescope l 2 3 Introduction: WHT
Cecilia Fariña - ING Support Astronomer Introduction: WHT William Herschel Telescope 2 Introduction: WHT WHT located in La Palma, Canary Islands, Spain William Herschel Telescope l 2 3 Introduction: WHT
The next-generation Infrared astronomy mission SPICA Space Infrared Telescope for Cosmology & Astrophysics
 The next-generation Infrared astronomy mission SPICA Space Infrared Telescope for Cosmology & Astrophysics 3.5m cooled telescope mission for mid- and far-infrared astronomy Takao Nakagawa (ISAS/JAXA) for
The next-generation Infrared astronomy mission SPICA Space Infrared Telescope for Cosmology & Astrophysics 3.5m cooled telescope mission for mid- and far-infrared astronomy Takao Nakagawa (ISAS/JAXA) for
cheops Assemble your own planet watcher cheops Paper Model Scale 1:15
 cheops cheops Assemble your own planet watcher Paper Model Scale 1:15 About CHEOPS The CHaracterising ExOPlanet Satellite, or CHEOPS, is a space science mission dedicated to the study of known exoplanets
cheops cheops Assemble your own planet watcher Paper Model Scale 1:15 About CHEOPS The CHaracterising ExOPlanet Satellite, or CHEOPS, is a space science mission dedicated to the study of known exoplanets
Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument
 Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument Oliver Krause (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg) on behalf of Gillian Wright (Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument Oliver Krause (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg) on behalf of Gillian Wright (Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
A DETAILED IMPACT RISK ASSESSMENT OF POSSIBLE PROTECTION ENHANCEMENTS TO TWO LEO SPACECRAFT
 A DETAILED IMPACT RISK ASSESSMENT OF POSSIBLE PROTECTION ENHANCEMENTS TO TWO LEO SPACECRAFT H. Stokes (1), C. Cougnet (2), M. David (3), J. Gelhaus (4), M. Röthlingshöfer (5) (1) PHS Space Ltd, 8 Dixon
A DETAILED IMPACT RISK ASSESSMENT OF POSSIBLE PROTECTION ENHANCEMENTS TO TWO LEO SPACECRAFT H. Stokes (1), C. Cougnet (2), M. David (3), J. Gelhaus (4), M. Röthlingshöfer (5) (1) PHS Space Ltd, 8 Dixon
Goals of the meeting. Catch up with JWST news and developments: ERS and GO call for proposals are coming!!
 Welcome Goals of the meeting Catch up with JWST news and developments: ERS and GO call for proposals are coming!! What is JWST capable of (focus on H 2 spectroscopy)? What do we need to do (models, lab)
Welcome Goals of the meeting Catch up with JWST news and developments: ERS and GO call for proposals are coming!! What is JWST capable of (focus on H 2 spectroscopy)? What do we need to do (models, lab)
Orbital Orbital Chara Char cte act ristics eristics of the Helios of the Helio sy s s s y te st m Orbit : Low: Sun-synchronous: Quasi-polar: Phased:
 Orbital Characteristics of the Helios system Orbit : Ë Low: suitable for High Resolution imagery. ËSun-synchronous: allows for regular illumination of the observed zones as the satellite always passes
Orbital Characteristics of the Helios system Orbit : Ë Low: suitable for High Resolution imagery. ËSun-synchronous: allows for regular illumination of the observed zones as the satellite always passes
Figure 1. View of ALSAT-2A spacecraft
 ALSAT-2A TRANSFER AND FIRST YEAR OPERATIONS M. Kameche (1), A.H. Gicquel (2), D. Joalland (3) (1) CTS/ASAL, 1 Avenue de la Palestine, BP 13, Arzew 31200 Oran, Algérie, email:mo_kameche@netcourrier.com
ALSAT-2A TRANSFER AND FIRST YEAR OPERATIONS M. Kameche (1), A.H. Gicquel (2), D. Joalland (3) (1) CTS/ASAL, 1 Avenue de la Palestine, BP 13, Arzew 31200 Oran, Algérie, email:mo_kameche@netcourrier.com
The SPICA infrared space observatory project status
 The SPICA infrared space observatory project status Peter Roelfsema SAFARI Principal Investigator SPICA European consortium lead on behalf of the SPICA/J and SAFARI consortia Contents The goal a big cold
The SPICA infrared space observatory project status Peter Roelfsema SAFARI Principal Investigator SPICA European consortium lead on behalf of the SPICA/J and SAFARI consortia Contents The goal a big cold
ASTEROID IMPACT MISSION: AIM3P MISSION AND PAYLOAD OPERATIONS SCENARIO
 estec European Space Research and Technology Centre Keplerlaan 1 2201 AZ Noordwijk The Netherlands T +31 (0)71 565 6565 F +31 (0)71 565 6040 www.esa.int ASTEROID IMPACT MISSION: AIM3P MISSION AND PAYLOAD
estec European Space Research and Technology Centre Keplerlaan 1 2201 AZ Noordwijk The Netherlands T +31 (0)71 565 6565 F +31 (0)71 565 6040 www.esa.int ASTEROID IMPACT MISSION: AIM3P MISSION AND PAYLOAD
Benefits of Infrared. The Spitzer Space Telescope. Instruments/Components of Spitzer. Cryostat. Infrared Telescope
 The Spitzer Space Telescope Benefits of Infrared IR can reveal objects that don't emit visible light IR provides different information than visible light IR is better than visible for viewing cold objects
The Spitzer Space Telescope Benefits of Infrared IR can reveal objects that don't emit visible light IR provides different information than visible light IR is better than visible for viewing cold objects
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
 The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
Status of the JWST Science Instrument Payload
 Status of the JWST Science Instrument Payload Ma9 Greenhouse JWST Project Office NASA Goddard Space Flight Center 12 October 2015 @NASAWebbTelescp #JWST 12 October 2015 PresentaBon to: 49th ESLAB Symposium:
Status of the JWST Science Instrument Payload Ma9 Greenhouse JWST Project Office NASA Goddard Space Flight Center 12 October 2015 @NASAWebbTelescp #JWST 12 October 2015 PresentaBon to: 49th ESLAB Symposium:
DARE Mission and Spacecraft Overview
 DARE Mission and Spacecraft Overview October 6, 2010 Lisa Hardaway, PhD Mike Weiss, Scott Mitchell, Susan Borutzki, John Iacometti, Grant Helling The information contained herein is the private property
DARE Mission and Spacecraft Overview October 6, 2010 Lisa Hardaway, PhD Mike Weiss, Scott Mitchell, Susan Borutzki, John Iacometti, Grant Helling The information contained herein is the private property
MISSION ENGINEERING SPACECRAFT DESIGN
 MISSION ENGINEERING & SPACECRAFT DESIGN Alpbach 2007 - D.J.P. Moura - CNES MISSION ENGINEERING (1) OVERALL MISSION ENGINEERING IS A COMPLEX TASK SINCE AT THE BEGINNING THE PROBLEM IS GENERALLY BADLY EXPRESSED
MISSION ENGINEERING & SPACECRAFT DESIGN Alpbach 2007 - D.J.P. Moura - CNES MISSION ENGINEERING (1) OVERALL MISSION ENGINEERING IS A COMPLEX TASK SINCE AT THE BEGINNING THE PROBLEM IS GENERALLY BADLY EXPRESSED
The James Webb Telescope (NGST) to replace HST
 PROLOGUE The James Webb Telescope (NGST) to replace HST Source: http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/ Key elements: 6.5m primary mirror (18 sections), lightweight, deployable (launch date 2013?) 1 Large sunshield
PROLOGUE The James Webb Telescope (NGST) to replace HST Source: http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/ Key elements: 6.5m primary mirror (18 sections), lightweight, deployable (launch date 2013?) 1 Large sunshield
OTSUKIMI Moon-sighting Satellite Kyushu Institute of Technology. 3 rd Mission Idea Contest UNISEC Global
 OTSUKIMI Moon-sighting Satellite Kyushu Institute of Technology 3 rd Mission Idea Contest UNISEC Global The Idea We want to take image for the moon phases as seen from Earth Why? Introduction 1.6 billion,23.4%
OTSUKIMI Moon-sighting Satellite Kyushu Institute of Technology 3 rd Mission Idea Contest UNISEC Global The Idea We want to take image for the moon phases as seen from Earth Why? Introduction 1.6 billion,23.4%
Announcement of Opportunity for Open Time. SPIRE PACS Parallel Mode Observers' Manual
 Announcement of Opportunity for Open Time SPIRE PACS Parallel Mode Observers' Manual HERSCHEL-HSC-DOC-0883, Version 2.1 4-October-2011 SPIRE PACS Parallel Mode Observers' Manual Published version 2.1,
Announcement of Opportunity for Open Time SPIRE PACS Parallel Mode Observers' Manual HERSCHEL-HSC-DOC-0883, Version 2.1 4-October-2011 SPIRE PACS Parallel Mode Observers' Manual Published version 2.1,
ASTRO-F SURVEY AS INPUT CATALOGUES FOR FIRST. Takao Nakagawa
 67 ASTRO-F SURVEY AS INPUT CATALOGUES FOR FIRST Takao Nakagawa Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), 3-1-1 Yoshinodai, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 229-8510, Japan Abstract ASTRO-F is the second
67 ASTRO-F SURVEY AS INPUT CATALOGUES FOR FIRST Takao Nakagawa Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), 3-1-1 Yoshinodai, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 229-8510, Japan Abstract ASTRO-F is the second
Mechanical and Thermal Design of XMM
 r bulletin 100 december 1999 Mechanical and Thermal Design of XMM K. van Katwijk, T. van der Laan & D. Stramaccioni XMM Project, ESA Directorate for Scientific Programmes, ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands
r bulletin 100 december 1999 Mechanical and Thermal Design of XMM K. van Katwijk, T. van der Laan & D. Stramaccioni XMM Project, ESA Directorate for Scientific Programmes, ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands
Technical Presentation of M3 Candidate Missions
 Technical Presentation of M3 Candidate Missions Frédéric Safa, Future Missions Office (SRE-F) January 2014 EChO Exoplanet Characterization Observatory EChO: Exoplanet Characterization Observatory Science
Technical Presentation of M3 Candidate Missions Frédéric Safa, Future Missions Office (SRE-F) January 2014 EChO Exoplanet Characterization Observatory EChO: Exoplanet Characterization Observatory Science
EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS
 1 EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS Nicolas Ludovic LARUE (1), Jean Marie LOME (2), Alice PRADINES (3) (1) Mechanical analysis and test engineer, EADS Astrium - 31 avenue des Cosmonautes,
1 EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS Nicolas Ludovic LARUE (1), Jean Marie LOME (2), Alice PRADINES (3) (1) Mechanical analysis and test engineer, EADS Astrium - 31 avenue des Cosmonautes,
November 3, 2014 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office
 November 3, 014 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office 1 SINCE LAST CAA MEETING... Completed of 3 recommended GAO schedule risk analyses for this year. Mutually agreed to drop 3 rd. Will perform cost-risk study
November 3, 014 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office 1 SINCE LAST CAA MEETING... Completed of 3 recommended GAO schedule risk analyses for this year. Mutually agreed to drop 3 rd. Will perform cost-risk study
FIRST carrier spacecraft
 FIRST carrier spacecraft Height 9 m Width 4.5 m Launch mass 3300 kg Power 1 kw Launch vehicle Ariane 5 Orbit Lissajous around L2 Science data rate 100 kbps Telescope diametre 3.5 m Telescope WFE 10 µm
FIRST carrier spacecraft Height 9 m Width 4.5 m Launch mass 3300 kg Power 1 kw Launch vehicle Ariane 5 Orbit Lissajous around L2 Science data rate 100 kbps Telescope diametre 3.5 m Telescope WFE 10 µm
Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer. Oliver Poyntz-Wright (Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, United Kingdom)
 255 Appendix T Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer Oliver Poyntz-Wright (Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, United Kingdom) 256 Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer
255 Appendix T Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer Oliver Poyntz-Wright (Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, United Kingdom) 256 Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer
Dark Energy. Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey. Survey (DES)
 Dark Energy Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey Survey (DES) What is it? The DES Collaboration will build and use a wide field optical imager (DECam) to perform a wide area,
Dark Energy Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey Survey (DES) What is it? The DES Collaboration will build and use a wide field optical imager (DECam) to perform a wide area,
Herschel Mission Overview and Key Programmes
 Herschel Mission Overview and Key Programmes SPIE Astronomical Instrumentation 2008 Space Telescopes and Instrumentation I: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave Marseille, 23-28 June 2008 Göran L. Pilbratt
Herschel Mission Overview and Key Programmes SPIE Astronomical Instrumentation 2008 Space Telescopes and Instrumentation I: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave Marseille, 23-28 June 2008 Göran L. Pilbratt
Space Cryogenics at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 Space Cryogenics at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Tom Bradshaw Martin Crook Bryan Shaughnessy Cryogenic Cluster Day STFC, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory 22 nd September 2010 Introduction Rutherford
Space Cryogenics at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Tom Bradshaw Martin Crook Bryan Shaughnessy Cryogenic Cluster Day STFC, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory 22 nd September 2010 Introduction Rutherford
MESSIER Unveiling galaxy formation
 MESSIER Unveiling galaxy formation David Valls-Gabaud on behalf of the MESSIER consortium Challenges in UV astronomy ESO - 2013 Oct 09 Two driving science cases for critical tests of the ΛCDM paradigm
MESSIER Unveiling galaxy formation David Valls-Gabaud on behalf of the MESSIER consortium Challenges in UV astronomy ESO - 2013 Oct 09 Two driving science cases for critical tests of the ΛCDM paradigm
WFIRST Science Definition Team and Project Interim Report Presentation to the Astrophysics Sub-Committee
 WFIRST Science Definition Team and Project Interim Report Presentation to the Astrophysics Sub-Committee James Green Paul Schechter Neil Gehrels Kevin Grady SDT Co-Chair SDT Co-Chair Study Scientist Study
WFIRST Science Definition Team and Project Interim Report Presentation to the Astrophysics Sub-Committee James Green Paul Schechter Neil Gehrels Kevin Grady SDT Co-Chair SDT Co-Chair Study Scientist Study
Dark Energy with the Euclid Space Mission. Y. Mellier On behalf of the Euclid Consortium. Euclid Consortium.
 Dark Energy with the Space Mission Y. Mellier On behalf of the http://www.euclid-ec.org Instrument Overall WP Breakdown VG :1 Itzykson, IPhT-CEA Saclay June 18-20, 2012 Objective of the Mission Instrument
Dark Energy with the Space Mission Y. Mellier On behalf of the http://www.euclid-ec.org Instrument Overall WP Breakdown VG :1 Itzykson, IPhT-CEA Saclay June 18-20, 2012 Objective of the Mission Instrument
Proceedings of IAU XXV JD 16 are (finally) available.. Download the ~8Mby.
 Proceedings of IAU XXV JD 16 are (finally) available.. Download the ~8Mby (211 pages) PDF file @ http://ad.usno.navy.mil/jd16.pdf Hardcopies being mailed now to authors: (hicks.brenda@usno brenda@usno.navy.mil)
Proceedings of IAU XXV JD 16 are (finally) available.. Download the ~8Mby (211 pages) PDF file @ http://ad.usno.navy.mil/jd16.pdf Hardcopies being mailed now to authors: (hicks.brenda@usno brenda@usno.navy.mil)
Observational cosmology: the RENOIR team. Master 2 session
 Observational cosmology: the RENOIR team Master 2 session 2014-2015 Observational cosmology: the RENOIR team Outline A brief history of cosmology Introduction to cosmological probes and current projects
Observational cosmology: the RENOIR team Master 2 session 2014-2015 Observational cosmology: the RENOIR team Outline A brief history of cosmology Introduction to cosmological probes and current projects
ATHENA Mission Design and ESA Status. David Lumb ESA Study Scientist MPE Jan 13 th 2012
 ATHENA Mission Design and ESA Status David Lumb ESA Study Scientist MPE Jan 13 th 2012 Topics covered ESA L class mission reformulation Current status & programmatics Athena Mission Design Spacecraft Optics
ATHENA Mission Design and ESA Status David Lumb ESA Study Scientist MPE Jan 13 th 2012 Topics covered ESA L class mission reformulation Current status & programmatics Athena Mission Design Spacecraft Optics
Impact of stellar micro-variability on transit detection from space
 Chapter 5 Impact of stellar micro-variability on transit detection from space 5.1 Introduction This chapter summarises a number of simulations which were performed with the tools developed in the previous
Chapter 5 Impact of stellar micro-variability on transit detection from space 5.1 Introduction This chapter summarises a number of simulations which were performed with the tools developed in the previous
BepiColombo. Project and MPO Status. Comprehensive Explora1on of Planet Mercury
 BepiColombo Project and MPO Status Comprehensive Explora1on of Planet Mercury Joe Zender BepiColombo Deputy PS, ESA/ESTEC BepiColombo Previously: Ø Proba2 Science Coordinator, until 12/2013 Ø ProbaV, Project
BepiColombo Project and MPO Status Comprehensive Explora1on of Planet Mercury Joe Zender BepiColombo Deputy PS, ESA/ESTEC BepiColombo Previously: Ø Proba2 Science Coordinator, until 12/2013 Ø ProbaV, Project
Large Area Imaging Survey of Near-Infrared Sky with Korean Compact Space Telescopes
 Large Area Imaging Survey of Near-Infrared Sky with Korean Compact Space Telescopes Science & Technology Satellite Series (KARI) (2000 ~ 2013. 02) 1 st Satellite: FIMS (Far-ultraviolet IMaging Spectrograph)
Large Area Imaging Survey of Near-Infrared Sky with Korean Compact Space Telescopes Science & Technology Satellite Series (KARI) (2000 ~ 2013. 02) 1 st Satellite: FIMS (Far-ultraviolet IMaging Spectrograph)
Centre for Electronic Imaging
 Centre for Electronic Imaging Calibration plans for the Soft X-ray Imager s CCDs on SMILE Open University: George Randall, Matthew Soman, David Hall, Andrew Holland, Ross Burgon, Jonathan Keelan, Thomas
Centre for Electronic Imaging Calibration plans for the Soft X-ray Imager s CCDs on SMILE Open University: George Randall, Matthew Soman, David Hall, Andrew Holland, Ross Burgon, Jonathan Keelan, Thomas
Dark Energy & GEST: the Galactic Exoplanet Survey Telescope
 Dark Energy & GEST: the Galactic Exoplanet Survey Telescope Cosmology with a Exoplanet Search Mission a MIDEX Proposal currently under review $180M NASA OSS Cost cap Related option STEP (Survey for Terrestrial
Dark Energy & GEST: the Galactic Exoplanet Survey Telescope Cosmology with a Exoplanet Search Mission a MIDEX Proposal currently under review $180M NASA OSS Cost cap Related option STEP (Survey for Terrestrial
Euclid Mission: building of a Reference Survey
 Euclid Mission: building of a Reference Survey J. Amiaux a, R. Scaramella b, Y. Mellier c, B. Altieri d, C. Burigana e, A. Da Silva f, P. Gomez d, J. Hoar d, R. Laureijs g, E. Maiorano e, D. Magalhães
Euclid Mission: building of a Reference Survey J. Amiaux a, R. Scaramella b, Y. Mellier c, B. Altieri d, C. Burigana e, A. Da Silva f, P. Gomez d, J. Hoar d, R. Laureijs g, E. Maiorano e, D. Magalhães
Planck 2014 The Microwave Sky in Temperature and Polarisation Ferrara, 1 5 December The Planck mission
 Planck 2014 The Microwave Sky in Temperature and Polarisation Ferrara, 1 5 December 2014 The Planck mission Marco Bersanelli Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano Planck-LFI Deputy PI
Planck 2014 The Microwave Sky in Temperature and Polarisation Ferrara, 1 5 December 2014 The Planck mission Marco Bersanelli Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano Planck-LFI Deputy PI
Overview of the Jovian Exploration Technology Reference Studies
 Overview of the Jovian Exploration Technology Reference Studies The Challenge of Jovian System Exploration Peter Falkner & Alessandro Atzei Solar System Exploration Studies Section ESA/ESTEC Peter.Falkner@esa.int,
Overview of the Jovian Exploration Technology Reference Studies The Challenge of Jovian System Exploration Peter Falkner & Alessandro Atzei Solar System Exploration Studies Section ESA/ESTEC Peter.Falkner@esa.int,
Overview of the Current Baseline of the Solar-C Spacecraft System
 Overview of the Current Baseline of the Solar-C Spacecraft System Keisuke YOSHIHARA (JAXA) 11 November, 2013 Solar-C Science Meeting Hida Earth Wisdom Center, Takayama, Japan Solar-C Spacecraft System
Overview of the Current Baseline of the Solar-C Spacecraft System Keisuke YOSHIHARA (JAXA) 11 November, 2013 Solar-C Science Meeting Hida Earth Wisdom Center, Takayama, Japan Solar-C Spacecraft System
ILWS Italian SpaceAgency (ASI) Contribution
 ILWS Italian SpaceAgency (ASI) Contribution Ester Antonucci Nice April 14-15 2003 ILWS Italian SpaceAgency (ASI) Contribution LWS NASA ESA SPECTRE SolarDynamicsObservatory HERSCHEL Solar Orbiter Bepi Colombo
ILWS Italian SpaceAgency (ASI) Contribution Ester Antonucci Nice April 14-15 2003 ILWS Italian SpaceAgency (ASI) Contribution LWS NASA ESA SPECTRE SolarDynamicsObservatory HERSCHEL Solar Orbiter Bepi Colombo
Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits. G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman
 Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman ITT Aerospace/Communications Division Fort Wayne, Indiana ABSTRACT For a radiometer
Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman ITT Aerospace/Communications Division Fort Wayne, Indiana ABSTRACT For a radiometer
FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E
 FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page 675-683 T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E COSMOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE Is the Universe isotropic or homogeneous? There is no place in the Universe that would be considered
FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page 675-683 T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E COSMOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE Is the Universe isotropic or homogeneous? There is no place in the Universe that would be considered
AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Telescopes Mauna Kea Observatories, Big Island, HI Imaging with our Eyes pupil allows light to enter the eye lens focuses light to create an image retina detects
AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Telescopes Mauna Kea Observatories, Big Island, HI Imaging with our Eyes pupil allows light to enter the eye lens focuses light to create an image retina detects
Space astrometry with the Joint Milliarcsecond Astrometry Pathfinder
 Relativity in Fundamental Astronomy Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 261, 2009 S. A. Klioner, P. K. Seidelman & M. H. Soffel, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309990640 Space
Relativity in Fundamental Astronomy Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 261, 2009 S. A. Klioner, P. K. Seidelman & M. H. Soffel, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309990640 Space
Imaging the Dark Universe with Euclid
 Imaging the Dark Universe with Simon Lilly (ETH Zurich) on behalf of Alexandre Refregier (CEA Saclay) for the Imaging Consortium Conference ESTEC 17/11/09 1 Science Objectives Outstanding questions in
Imaging the Dark Universe with Simon Lilly (ETH Zurich) on behalf of Alexandre Refregier (CEA Saclay) for the Imaging Consortium Conference ESTEC 17/11/09 1 Science Objectives Outstanding questions in
The Gaia Mission. Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany. ISYA 2016, Tehran
 The Gaia Mission Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany ISYA 2016, Tehran What Gaia should ultimately achieve high accuracy positions, parallaxes, proper motions e.g.
The Gaia Mission Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany ISYA 2016, Tehran What Gaia should ultimately achieve high accuracy positions, parallaxes, proper motions e.g.
HYPER Industrial Feasibility Study Final Presentation Precision Star Tracker Activity 3, WP 3100
 HYPER Industrial Feasibility Study Final Presentation Precision Star Tracker Activity 3, WP 3100 ESTEC, Noordwijk The Netherlands 6 -th March 2003 Agenda Introduction 1 PST Requirements 2 PST CCD Characteristics
HYPER Industrial Feasibility Study Final Presentation Precision Star Tracker Activity 3, WP 3100 ESTEC, Noordwijk The Netherlands 6 -th March 2003 Agenda Introduction 1 PST Requirements 2 PST CCD Characteristics
LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST
 LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST Steven M. Kahn Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Stanford University SMK Perspective I believe I bring three potentially
LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST Steven M. Kahn Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Stanford University SMK Perspective I believe I bring three potentially
R. Alonso, 11th CoRoT Week, La Laguna, 22 Mars The. CHEOPS Mission
 R. Alonso, 11th CoRoT Week, La Laguna, 22 Mars 2013 The CHEOPS Mission ESA s ESA s first first small small mission mission ESA small missions requirements Science top rated science in any area of space
R. Alonso, 11th CoRoT Week, La Laguna, 22 Mars 2013 The CHEOPS Mission ESA s ESA s first first small small mission mission ESA small missions requirements Science top rated science in any area of space
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Sample Review Test for Examination 3
 October 28, 2003 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Sample Review Test for Examination 3 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. No
October 28, 2003 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Sample Review Test for Examination 3 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. No
Hubble Science Briefing April 7, 2011
 Studying the First Galaxies with the Hubble and the Webb Space Telescopes Hubble Science Briefing April 7, 2011 Massimo Stiavelli Space Telescope Science Institute Modern Cosmology 2 COBE satellite The
Studying the First Galaxies with the Hubble and the Webb Space Telescopes Hubble Science Briefing April 7, 2011 Massimo Stiavelli Space Telescope Science Institute Modern Cosmology 2 COBE satellite The
Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014
![Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014](/thumbs/75/72758061.jpg) 1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
Team X Study Summary for ASMCS Theia. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology. with contributions from the Theia Team
 Team X Study Summary for ASMCS Theia Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology with contributions from the Theia Team P. Douglas Lisman, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory David Spergel,
Team X Study Summary for ASMCS Theia Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology with contributions from the Theia Team P. Douglas Lisman, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory David Spergel,
March 4, 2013 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office
 March 4, 2013 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office 1 SIMPLIFIED SCHEDULE OTE = Optical Telescope Element OTIS = Optical Telescope + ISIM k months of project funded critical path (mission pacing) schedule
March 4, 2013 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office 1 SIMPLIFIED SCHEDULE OTE = Optical Telescope Element OTIS = Optical Telescope + ISIM k months of project funded critical path (mission pacing) schedule
Status of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Observatory
 Status of the James Webb Space Telescope () Observatory ESTEC Mark Clampin Observatory Project Scientist mark.clampin@nasa.gov Goddard Space Flight Center HUBBLE and its Precursors SPITZER 2.4-meter T
Status of the James Webb Space Telescope () Observatory ESTEC Mark Clampin Observatory Project Scientist mark.clampin@nasa.gov Goddard Space Flight Center HUBBLE and its Precursors SPITZER 2.4-meter T
ESA Technical Development Activities An Overview
 ESA Technical Development Activities An Overview Christian Erd EJSM Instrument Workshop 18 20 January 2010 18 20 January 2010 C. Erd 1 Technology Overview A preliminary list was compiled ESA activities
ESA Technical Development Activities An Overview Christian Erd EJSM Instrument Workshop 18 20 January 2010 18 20 January 2010 C. Erd 1 Technology Overview A preliminary list was compiled ESA activities
3D metrology with a laser tracker inside a vacuum chamber for NISP test campaign
 In: SPIE astronomical Telescope and Instrumentation, Austin 2018 3D metrology with a laser tracker inside a vacuum chamber for NISP test campaign Anne Costille *,a, Florent Beaumont b, Eric Prieto a, Michael
In: SPIE astronomical Telescope and Instrumentation, Austin 2018 3D metrology with a laser tracker inside a vacuum chamber for NISP test campaign Anne Costille *,a, Florent Beaumont b, Eric Prieto a, Michael
Exploring the Mysteries of the Cosmos on the MOST Microsatellite Mission
 Exploring the Mysteries of the Cosmos on the MOST Microsatellite Mission Dr. Simon Grocott Dr. Robert E Zee Dr. Jaymie Matthews Dynacon Inc UTIAS SFL UBC 13 August 2003 Outline MOST (Microvariability and
Exploring the Mysteries of the Cosmos on the MOST Microsatellite Mission Dr. Simon Grocott Dr. Robert E Zee Dr. Jaymie Matthews Dynacon Inc UTIAS SFL UBC 13 August 2003 Outline MOST (Microvariability and
HaloSat Overview. Philip Kaaret August 17, 2016
 HaloSat Overview Philip Kaaret (philip-kaaret@uiowa.edu) August 17, 2016 Outline Scientific Motivation Missing Baryon Problem Mission Goal and Science Requirements Impediments Mission Level 1 Requirements
HaloSat Overview Philip Kaaret (philip-kaaret@uiowa.edu) August 17, 2016 Outline Scientific Motivation Missing Baryon Problem Mission Goal and Science Requirements Impediments Mission Level 1 Requirements
Introduction. How did the universe evolve to what it is today?
 Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
JWST Fine Guidance Sensor Calibration
 The 2010 STScI Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2010 Susana Deustua and Cristina Oliveira, eds. JWST Fine Guidance Sensor Calibration P. Chayer, S. Holfeltz, E. Nelan Space Telescope
The 2010 STScI Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2010 Susana Deustua and Cristina Oliveira, eds. JWST Fine Guidance Sensor Calibration P. Chayer, S. Holfeltz, E. Nelan Space Telescope
SIMBOL-X: A FORMATION FLYING MISSION ON HEO FOR EXPLORING THE UNIVERSE
 SIMBOL-X: A FORMATION FLYING MISSION ON HEO FOR EXPLORING THE UNIVERSE P. Gamet, R. Epenoy, C. Salcedo Centre National D Etudes Spatiales (CNES) 18 avenue Edouard Belin, 31401 TOULOUSE Cedex 9, France
SIMBOL-X: A FORMATION FLYING MISSION ON HEO FOR EXPLORING THE UNIVERSE P. Gamet, R. Epenoy, C. Salcedo Centre National D Etudes Spatiales (CNES) 18 avenue Edouard Belin, 31401 TOULOUSE Cedex 9, France
EUROSTAR 3000 INCLINED ORBIT MISSION : LIFETIME OPTIMISATION IN CASE OF INJECTION WITH A LOW INCLINATION
 EUROSTAR 3000 INCLINED ORBIT MISSION : LIFETIME OPTIMISATION IN CASE OF INJECTION WITH A LOW INCLINATION Franck Raballand (1), Julie De Lamarzelle (2), François Bonaventure (3), Anne-Hélène Gicquel (4)
EUROSTAR 3000 INCLINED ORBIT MISSION : LIFETIME OPTIMISATION IN CASE OF INJECTION WITH A LOW INCLINATION Franck Raballand (1), Julie De Lamarzelle (2), François Bonaventure (3), Anne-Hélène Gicquel (4)
Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction. Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009
 Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009 Missions in Operations Rosetta Hubble Integral Newton Mars Express SOHO Ulysses Cluster Venus
Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009 Missions in Operations Rosetta Hubble Integral Newton Mars Express SOHO Ulysses Cluster Venus
SDSS-IV and eboss Science. Hyunmi Song (KIAS)
 SDSS-IV and eboss Science Hyunmi Song (KIAS) 3rd Korea-Japan Workshop on Dark Energy April 4, 2016 at KASI Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2.5m telescopes at Apache Point Observatory (US) and Las Campanas Observatory
SDSS-IV and eboss Science Hyunmi Song (KIAS) 3rd Korea-Japan Workshop on Dark Energy April 4, 2016 at KASI Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2.5m telescopes at Apache Point Observatory (US) and Las Campanas Observatory
STUDY OF THE LARGE-SCALE STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE USING GALAXY CLUSTERS
 STUDY OF THE LARGE-SCALE STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE USING GALAXY CLUSTERS BÙI VĂN TUẤN Advisors: Cyrille Rosset, Michel Crézé, James G. Bartlett ASTROPARTICLE AND COSMOLOGY LABORATORY PARIS DIDEROT UNIVERSITY
STUDY OF THE LARGE-SCALE STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE USING GALAXY CLUSTERS BÙI VĂN TUẤN Advisors: Cyrille Rosset, Michel Crézé, James G. Bartlett ASTROPARTICLE AND COSMOLOGY LABORATORY PARIS DIDEROT UNIVERSITY
