Wednesday, September 7, 2011 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch due. Review sheet posted. Reading posted under announcements on web page, Section
|
|
|
- Shana Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wednesday, September 7, 2011 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch due. Review sheet posted. Reading posted under announcements on web page, Section 5.1, Sections , other background. Exam will draw on material presented in lecture. Use reading for back up, reinforcement. Review Session: Thursday, 5 6 ECJ Astronomy in the news? Jeff Bezos of Amazon.com is building a rocket, Blue Origin, and space port in West Texas near Van Horn and McDonald Observatory. A trial rocket crashed on August 24. Pic of the day: newly discovered star in Milky Way with very few heavy elements, but small mass, contradicting prevailing thinking.
2 Nomenclature of Supernovae in other galaxies: A-Z, aa-az, ba-bz, etc. SN 1987A - 1st of 1987 (also most important, but that is not what the A means). Currently discover roughly one per day. This year s latest officially named, SN 2011fm, discovered September 3 How many so far in 2011? New techniques will discover thousands per year, new nomenclature, SN 2011fe in M101 = SN PTFkly, or just by position: SN 2011fm = PSN J Before announced, internal names. We are currently using characters from South Park.
3 Discussion Point: How would you tell that an explosion was from a massive star or from a white dwarf star?
4 Goal: To understand the observed nature of supernovae and determine whether they came from white dwarfs or massive stars that undergo core collapse.
5 Goal: Certain elements show up in supernova: Oxygen, Magnesium, Silicon, Sulfur, Calcium, Iron. Why those elements?
6 H -> He (2 protons, 2 neutrons - Chapter 1, figure 1.6) 2 Helium -> unstable, no such element 3 Helium -> Carbon (6 protons, 6 neutrons) 4 Helium -> Oxygen (8 protons, 8 neutrons) 5 Helium -> Neon (10 protons, 10 neutrons) 6 Helium -> Magnesium (12 protons, 12 neutrons) 7 Helium -> Silicon (14 protons, 14 neutrons) Common elements forged in stars, and in their explosions, are built on building blocks of helium nuclei
7 Physics: In massive stars (more than about times the Sun) the core is composed of Helium or heavier elements, Carbon, Oxygen, Magnesium, Silicon, Calcium, finally Iron. The core continues to be hot even as it gets dense, always supported by thermal pressure continues to evolve, finally explodes The intermediate-mass elements are produced in the star before the explosion and then expelled into space. In exploding white dwarfs (arising in stars with mass less than about 8 times the Sun), the core is composed of Carbon and Oxygen, and the explosion creates the intermediate-mass elements, Magnesium, Silicon, Calcium, and also Iron. (between about 8 and about 12 solar masses, different story, maybe collapsing white dwarfs)
8 1st category discovered Categories of Supernovae Type Ia - no detectable Hydrogen in the spectrum, rather intermediate mass elements such as oxygen, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, calcium. Iron appears later as the light fades. These occur in all galaxy types: In spiral galaxies they tend to avoid the spiral arms, they have had time to drift away from the birth site the star that explodes is old In irregular galaxies In elliptical galaxies where star formation is thought to have ceased long ago the star that explodes is old the progenitor that explodes must be long-lived, not very massive, suggesting a white dwarf. Sun is long-lived, but won t explode
9 Type Ia - no hydrogen, intermediate mass elements early, iron later Light Curve - brightness vs. time consistent with an exploding C/O white dwarf expect total disruption, no neutron star L u m i n o s i t y weeks T i m e Type Ia occur in elliptical galaxies, tend to avoid spiral arms in spiral galaxies - old when explode, all evidence points to an exploding white dwarf.
10 SN 1006, almost definitely Type Ia Tycho, SN 1572 definitely Type Ia - recent discovery, spectrum from peak light reflected from surrounding dust, arriving only now. Kepler, 1604, probably Type Ia (no sign of neutron star, same ejected composition as SN 1006, Tycho), but some ambiguities. If recurrent nova U Sco with a white dwarf of more than 1.3 solar masses becomes a supernova, it will probably be a Type Ia
11 Type Ia no Hydrogen or Helium intermediate mass elements (oxygen, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, calcium) early on, iron later avoid spiral arms, occur in elliptical galaxies peaked light curve no neutron star all consistent with thermonuclear explosion in white dwarf that has waited for a long time (hundreds of millons to billions of years) to explode, total disruption
12 Type II Supernovae - other type discovered early in the study of supernovae, show Hydrogen in the spectrum early, Oxygen, Magnesium, Calcium, later Most occur in spiral galaxies, in the spiral arms, they have no time to drift from the birth site sometimes in irregular galaxies never in elliptical galaxies (no young stars) Stars with more mass have more fuel, but they burn it at a prodigous rate, live a shorter time! The progenitor stars are young, short-lived (millions to tens of millions of years) massive stars SN 1999em We expect such stars to evolve to form iron cores and collapse to a neutron star or black hole (physics to come)
13 Light curves of Type II supernovae are consistent with explosion in a Red Giant Betelgeuse is a massive red giant, 15 solar masses: we expect it to become a Type II supernova. Maybe tonight! Rigel probably burning He to C/O, explode later. SN 386, 1181 records are sparse, might have been Type II Crab was a peculiar Type II (high helium abundance, slow explosion) Cas A was probably something else with a very thin layer of Hydrogen (next topic), SN1987A was a peculiar Type II. Not obvious that any of the historical supernovae were a normal Type II, although Type II are common in other galaxies L u m months T i m e
14 One minute exam Why do the elements carbon, oxygen, magnesium, and silicon frequently appear in the matter ejected from supernovae? They are built up from the element iron They are built up from the element hydrogen They are built up from the element helium They are built up from the element calcium
15 One minute exam A supernova explodes in an elliptical galaxy. Near peak light what element do you expect to see in the spectrum? Hydrogen Helium Silicon Iron
16 End of Material for Test 1
Astronomy in the news? Patriots goal-line interception
 Monday, February 2, 2015 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due. Review sheet posted Today. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, RLM 6.104 Reading: Chapter 6 Supernovae, Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 Chapter 1 Introduction,
Monday, February 2, 2015 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due. Review sheet posted Today. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, RLM 6.104 Reading: Chapter 6 Supernovae, Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 Chapter 1 Introduction,
Monday, January 30, 2012 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch due. Review sheet posted. Reading posted under announcements on web page, Chapter 6 -
 Monday, January 30, 2012 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch due. Review sheet posted. Reading posted under announcements on web page, Chapter 6 - Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 (also sections 1.2.4, 2.1-2.5, and
Monday, January 30, 2012 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch due. Review sheet posted. Reading posted under announcements on web page, Chapter 6 - Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 (also sections 1.2.4, 2.1-2.5, and
News? NASA Administrator Griffin visits China Pic of the day - Face on Mars
 9/25/06 Exam grades, answer key will be posted tomorrow, exams returned Wednesday Absence/Failing notices for first exam - formality First Sky Watch extra credit reports due today. News? NASA Administrator
9/25/06 Exam grades, answer key will be posted tomorrow, exams returned Wednesday Absence/Failing notices for first exam - formality First Sky Watch extra credit reports due today. News? NASA Administrator
Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM
 Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM RLM 15.216B (Backup RLM 15.202A) Reading: Chapter 6
Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM RLM 15.216B (Backup RLM 15.202A) Reading: Chapter 6
Lecture 26. High Mass Post Main Sequence Stages
 Lecture 26 Fate of Massive Stars Heavy Element Fusion Core Collapse Supernova Neutrinoes Gaseous Remnants Neutron Stars Mar 27, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 26 1 High Mass Post Main Sequence Stages For M(main
Lecture 26 Fate of Massive Stars Heavy Element Fusion Core Collapse Supernova Neutrinoes Gaseous Remnants Neutron Stars Mar 27, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 26 1 High Mass Post Main Sequence Stages For M(main
Supernova Explosions. Novae
 Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Stellar Evolution Notes
 Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Comparing a Supergiant to the Sun
 The Lifetime of Stars Once a star has reached the main sequence stage of it life, it derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen to helium Stars remain on the main sequence for a long time and most
The Lifetime of Stars Once a star has reached the main sequence stage of it life, it derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen to helium Stars remain on the main sequence for a long time and most
Betelgeuse. The Life of Stars. Stars can be grouped into 4 major categories based on size: supergiants giants main sequence stars dwarfs.
 The Life of A Star The Life of Stars Stars can be grouped into 4 major categories based on size: supergiants giants main sequence stars dwarfs dwarf star Rigel Sun Betelgeuse The Life of Stars Stars can
The Life of A Star The Life of Stars Stars can be grouped into 4 major categories based on size: supergiants giants main sequence stars dwarfs dwarf star Rigel Sun Betelgeuse The Life of Stars Stars can
April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9,
 April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9, Sections 9.5.2, 9.6.1, 9.6.2. 9.7, 9.8; Chapter 10,
April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9, Sections 9.5.2, 9.6.1, 9.6.2. 9.7, 9.8; Chapter 10,
Astronomy in the news? Government shut down. No astronomy picture of the day
 Wednesday, October 2, 2013 Exam 2 Friday. Review sheet posted. Review session Tomorrow, 5 6 PM, WRW 102 Reading: Sections 6.1 (Type Ib/c), 6.4, 6.5 (but not detail on polarization), 6.6, Betelgeuse, Section
Wednesday, October 2, 2013 Exam 2 Friday. Review sheet posted. Review session Tomorrow, 5 6 PM, WRW 102 Reading: Sections 6.1 (Type Ib/c), 6.4, 6.5 (but not detail on polarization), 6.6, Betelgeuse, Section
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline. HW#7 due Friday by 5 pm! (available Tuesday)
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements HW#7 due Friday by 5 pm! (available Tuesday) Midterm Grades (points) posted today in ICON Exam #2 next week (Wednesday) Review sheet and study guide posted
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements HW#7 due Friday by 5 pm! (available Tuesday) Midterm Grades (points) posted today in ICON Exam #2 next week (Wednesday) Review sheet and study guide posted
Friday, September 23, 2011
 Friday, September 23, 2011 Astronomy in the news? Fall Equinox Friday, September 23 at 4:05 a.m. Story on Tatooine planet in double star system in Thursday s Texan. Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite,
Friday, September 23, 2011 Astronomy in the news? Fall Equinox Friday, September 23 at 4:05 a.m. Story on Tatooine planet in double star system in Thursday s Texan. Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite,
Wednesday, January 25, 2017
 Wednesday, January 25, 2017 Powerpoint of lectures posted as pdf after every class, on Canvas and at http://www.as.utexas.edu/astronomy/education/spring17/wheeler/ 309n.html?a=lec Wednesday Star Parties
Wednesday, January 25, 2017 Powerpoint of lectures posted as pdf after every class, on Canvas and at http://www.as.utexas.edu/astronomy/education/spring17/wheeler/ 309n.html?a=lec Wednesday Star Parties
Goal - to understand what makes supernovae shine (Section 6.7).
 Wednesday, March 11, 2015 (Class Friday) Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A) Background in Chapters 3, 4, 5. Background:
Wednesday, March 11, 2015 (Class Friday) Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A) Background in Chapters 3, 4, 5. Background:
Today. Stars. Evolution of High Mass Stars. Nucleosynthesis. Supernovae - the explosive deaths of massive stars
 Today Stars Evolution of High Mass Stars Nucleosynthesis Supernovae - the explosive deaths of massive stars 1 Another good job on exam! Class average was 71% Given the difficulty of the exam, this was
Today Stars Evolution of High Mass Stars Nucleosynthesis Supernovae - the explosive deaths of massive stars 1 Another good job on exam! Class average was 71% Given the difficulty of the exam, this was
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes
 Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg. Diameter: about km = 100 x the Earth diameter. Density: about kg/m3
 Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg Diameter: about 1 400 00 km = 100 x the Earth diameter Produces a strong gravitational forces: about 28 times greater than the gravitational force produces by the Earth Temperature:
Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg Diameter: about 1 400 00 km = 100 x the Earth diameter Produces a strong gravitational forces: about 28 times greater than the gravitational force produces by the Earth Temperature:
Outline - March 18, H-R Diagram Review. Protostar to Main Sequence Star. Midterm Exam #2 Tuesday, March 23
 Midterm Exam #2 Tuesday, March 23 Outline - March 18, 2010 Closed book Will cover Lecture 8 (Special Relativity) through Lecture 14 (Star Formation) only If a topic is in the book, but was not covered
Midterm Exam #2 Tuesday, March 23 Outline - March 18, 2010 Closed book Will cover Lecture 8 (Special Relativity) through Lecture 14 (Star Formation) only If a topic is in the book, but was not covered
Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti
 Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
Classifying Stars. Scientists classify stars by: 1. Temperature 2. Brightness
 STARS Classifying Stars Scientists classify stars by: 1. Temperature 2. Brightness Star Temperature 1. The color of a star tells us about its temperature. Blue stars are the hottest, 7500 C- 40,000 C.
STARS Classifying Stars Scientists classify stars by: 1. Temperature 2. Brightness Star Temperature 1. The color of a star tells us about its temperature. Blue stars are the hottest, 7500 C- 40,000 C.
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
Wednesday, February 26, 2014 No office hours today. Have to go wait for a cable guy. If you want to talk about exam 2, please make an appointment.
 Wednesday, February 26, 2014 No office hours today. Have to go wait for a cable guy. If you want to talk about exam 2, please make an appointment. Exam 2, Skywatch 2, Monday, 3/3. Review sheet posted Review
Wednesday, February 26, 2014 No office hours today. Have to go wait for a cable guy. If you want to talk about exam 2, please make an appointment. Exam 2, Skywatch 2, Monday, 3/3. Review sheet posted Review
Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars
 Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars Low-mass stars lead a relatively peaceful life in their old age: although some may gently blow off their outer envelopes to form beautiful planetary
Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars Low-mass stars lead a relatively peaceful life in their old age: although some may gently blow off their outer envelopes to form beautiful planetary
Chapter 21 Stellar Explosions
 Chapter 21 Stellar Explosions Units of Chapter 21 21.1 XXLife after Death for White Dwarfs (not on exam) 21.2 The End of a High-Mass Star 21.3 Supernovae Supernova 1987A The Crab Nebula in Motion 21.4
Chapter 21 Stellar Explosions Units of Chapter 21 21.1 XXLife after Death for White Dwarfs (not on exam) 21.2 The End of a High-Mass Star 21.3 Supernovae Supernova 1987A The Crab Nebula in Motion 21.4
Stars and Galaxies. Content Outline for Teaching
 Section 1 Stars A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are
Section 1 Stars A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are
25.2 Stellar Evolution. By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star.
 25.2 Stellar Evolution By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star. Star Birth The birthplaces of stars are dark, cool interstellar clouds,
25.2 Stellar Evolution By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star. Star Birth The birthplaces of stars are dark, cool interstellar clouds,
Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused
Supernova Explosions. Novae
 Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Astronomy in the news?
 Friday, September 227, 2013 Exam 2 a week from today. Review session Thursday. See Kevin for exams, skywatch. Reading Chapter 6 (continued) Sections 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, 6.7 (background: Sections 1.2, 2.1, 2.4,
Friday, September 227, 2013 Exam 2 a week from today. Review session Thursday. See Kevin for exams, skywatch. Reading Chapter 6 (continued) Sections 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, 6.7 (background: Sections 1.2, 2.1, 2.4,
Protostars on the HR Diagram. Lifetimes of Stars. Lifetimes of Stars: Example. Pressure-Temperature Thermostat. Hydrostatic Equilibrium
 Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
Low mass stars. Sequence Star Giant. Red. Planetary Nebula. White Dwarf. Interstellar Cloud. White Dwarf. Interstellar Cloud. Planetary Nebula.
 Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud
Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud
CONTENT EXPECTATIONS
 THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
The Death of Stars. Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages ) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars
 The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
Lecture 33: The Lives of Stars
 Lecture 33 The Lives of Stars Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture concerns the life cycle of normal stars. Stars shine because they are hot, and need a source of energy to keep shining. Main Sequence
Lecture 33 The Lives of Stars Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture concerns the life cycle of normal stars. Stars shine because they are hot, and need a source of energy to keep shining. Main Sequence
7/9. What happens to a star depends almost completely on the mass of the star. Mass Categories: Low-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses and less
 7/9 What happens to a star depends almost completely on the mass of the star. Mass Categories: Low-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses and less Medium-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses up to between 2 and 3 solar masses.
7/9 What happens to a star depends almost completely on the mass of the star. Mass Categories: Low-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses and less Medium-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses up to between 2 and 3 solar masses.
Star Formation A cloud of gas and dust, called a nebula, begins spinning & heating up. Eventually, it gets hot enough for fusion to take place, and a
 Stars Star- large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of energy and shines Sun- our closest star Star Formation A cloud of gas and dust, called a nebula, begins spinning
Stars Star- large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of energy and shines Sun- our closest star Star Formation A cloud of gas and dust, called a nebula, begins spinning
Distant Type Ia supernova Refsdal gravitationally lensed, appears multiple places and times.
 Friday, March 6, 2015 Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A) Background in Chapters 3, 4, 5. Background: Sections 3.1,
Friday, March 6, 2015 Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A) Background in Chapters 3, 4, 5. Background: Sections 3.1,
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
ASTR-101 4/4/2018 Stellar Evolution: Part II Lecture 19
 ASTR-101 4/4/2018 Stellar Evolution: Part II Lecture 19 WHEN S THE NEXT TEST?!?!?!? If anyone is following the syllabus, you know that it says there is a test today. The test will be on April 11 th (a
ASTR-101 4/4/2018 Stellar Evolution: Part II Lecture 19 WHEN S THE NEXT TEST?!?!?!? If anyone is following the syllabus, you know that it says there is a test today. The test will be on April 11 th (a
Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe
 Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe Light Year: Unit of distance used to measure the great vastness of space. Galaxy: Large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Spiral Galaxy: Galaxy in
Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe Light Year: Unit of distance used to measure the great vastness of space. Galaxy: Large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Spiral Galaxy: Galaxy in
Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death
 Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death Stars have lives: born, evolve, die Mass determines stellar evolution: Really Low Mass (0.08 to 0.4 M sun ) Low Mass: (0.4 to 4 M sun ) Long lives High Mass (4
Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death Stars have lives: born, evolve, die Mass determines stellar evolution: Really Low Mass (0.08 to 0.4 M sun ) Low Mass: (0.4 to 4 M sun ) Long lives High Mass (4
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
 LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
17.3 Life as a High-Mass Star
 17.3 Life as a High-Mass Star Our goals for learning: What are the life stages of a high-mass star? How do high-mass stars make the elements necessary for life? How does a high-mass star die? What are
17.3 Life as a High-Mass Star Our goals for learning: What are the life stages of a high-mass star? How do high-mass stars make the elements necessary for life? How does a high-mass star die? What are
Review: HR Diagram. Label A, B, C respectively
 Stellar Evolution Review: HR Diagram Label A, B, C respectively A C B a) A: White dwarfs, B: Giants, C: Main sequence b) A: Main sequence, B: Giants, C: White dwarfs c) A: Main sequence, B: White Dwarfs,
Stellar Evolution Review: HR Diagram Label A, B, C respectively A C B a) A: White dwarfs, B: Giants, C: Main sequence b) A: Main sequence, B: Giants, C: White dwarfs c) A: Main sequence, B: White Dwarfs,
Chapter 12 Review. 2) About 90% of the star's total life is spent on the main sequence. 2)
 Chapter 12 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) As a main-sequence star, the Sun's hydrogen supply should last about 10 billion years from the zero-age
Chapter 12 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) As a main-sequence star, the Sun's hydrogen supply should last about 10 billion years from the zero-age
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 April 11, 2003
 Name: Seat Number: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 April 11, 2003 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. If you need additional
Name: Seat Number: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 April 11, 2003 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. If you need additional
Physics 5K Lecture 5 - Friday May 4, Atoms. Joel Primack Physics Department UCSC. Friday, May 4, 12
 Physics 5K Lecture 5 - Friday May 4, 2012 Atoms Joel Primack Physics Department UCSC Giancoli The Electromagnetic Spectrum Brief History of Atomic Theory 1904 Joseph J. Thomson s "Plum Pudding" model
Physics 5K Lecture 5 - Friday May 4, 2012 Atoms Joel Primack Physics Department UCSC Giancoli The Electromagnetic Spectrum Brief History of Atomic Theory 1904 Joseph J. Thomson s "Plum Pudding" model
Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter
 Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter 8 (Neutron Stars), keep for Exam 4. Background: Sections
Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter 8 (Neutron Stars), keep for Exam 4. Background: Sections
Astronomy 104: Second Exam
 Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
The Universe. is space and everything in it.
 The Universe is space and everything in it. Galaxies A galaxy is a supercluster of stars, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. There are three main types of galaxies: Irregular Elliptical Spiral
The Universe is space and everything in it. Galaxies A galaxy is a supercluster of stars, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. There are three main types of galaxies: Irregular Elliptical Spiral
Astronomy 104: Stellar Astronomy
 Astronomy 104: Stellar Astronomy Lecture 18: A High-Mass Star s Life and Death (a.k.a. - Things that go BOOM in the night) Spring Semester 2013 Dr. Matt Craig 1 1 Reading Today: Chapter 12.1 (Life and
Astronomy 104: Stellar Astronomy Lecture 18: A High-Mass Star s Life and Death (a.k.a. - Things that go BOOM in the night) Spring Semester 2013 Dr. Matt Craig 1 1 Reading Today: Chapter 12.1 (Life and
The Life Cycles of Stars. Modified from Information provided by: Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC
 The Life Cycles of Stars Modified from Information provided by: Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star... What do you see? How I Wonder What You Are... Stars have: Different Colors -
The Life Cycles of Stars Modified from Information provided by: Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star... What do you see? How I Wonder What You Are... Stars have: Different Colors -
NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story Thursday, September 25, 2008 Today s NSDL experts: Dr. Susana Deustua, Researcher, Space Telescope
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story Thursday, September 25, 2008 Today s NSDL experts: Dr. Susana Deustua, Researcher, Space Telescope
Astronomy Stars, Galaxies and Cosmology Exam 3. Please PRINT full name
 Astronomy 132 - Stars, Galaxies and Cosmology Exam 3 Please PRINT full name Also, please sign the honor code: I have neither given nor have I received help on this exam The following exam is intended to
Astronomy 132 - Stars, Galaxies and Cosmology Exam 3 Please PRINT full name Also, please sign the honor code: I have neither given nor have I received help on this exam The following exam is intended to
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint
 Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
 LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
Fate of Stars. INITIAL MASS Final State relative to Sun s mass
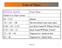 Fate of Stars INITIAL MASS Final State relative to Sun s mass M < 0.01 planet.01 < M
Fate of Stars INITIAL MASS Final State relative to Sun s mass M < 0.01 planet.01 < M
2, 2, 2/ PM, WEL
 Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Exam 2, Skywatch 2, Friday, 2/24. Review sheet posted. Exam review Thursday, 5 6 PM, WEL 2.308. Office Hours today at 5. New guidelines for Sky Watch grading by Leke on Canvas
Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Exam 2, Skywatch 2, Friday, 2/24. Review sheet posted. Exam review Thursday, 5 6 PM, WEL 2.308. Office Hours today at 5. New guidelines for Sky Watch grading by Leke on Canvas
Protostars on the HR Diagram. Lifetimes of Stars. Lifetimes of Stars: Example. Pressure-Temperature Thermostat. Hydrostatic Equilibrium
 Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates.
 1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4
 Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4 Key Ideas HR Diagrams of Star Clusters Ages from the Main Sequence Turn-off Open Clusters Young clusters of ~1000 stars Blue Main-Sequence
Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4 Key Ideas HR Diagrams of Star Clusters Ages from the Main Sequence Turn-off Open Clusters Young clusters of ~1000 stars Blue Main-Sequence
GALAXIES AND STARS. 2. Which star has a higher luminosity and a lower temperature than the Sun? A Rigel B Barnard s Star C Alpha Centauri D Aldebaran
 GALAXIES AND STARS 1. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A smaller, hotter, and less luminous B smaller, cooler, and more luminous C larger, hotter, and less luminous D larger, cooler, and more
GALAXIES AND STARS 1. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A smaller, hotter, and less luminous B smaller, cooler, and more luminous C larger, hotter, and less luminous D larger, cooler, and more
Evolution of High Mass Stars
 Luminosity (L sun ) Evolution of High Mass Stars High Mass Stars O & B Stars (M > 4 M sun ): Burn Hot Live Fast Die Young Main Sequence Phase: Burn H to He in core Build up a He core, like low-mass stars
Luminosity (L sun ) Evolution of High Mass Stars High Mass Stars O & B Stars (M > 4 M sun ): Burn Hot Live Fast Die Young Main Sequence Phase: Burn H to He in core Build up a He core, like low-mass stars
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
Birth & Death of Stars
 Birth & Death of Stars Objectives How are stars formed How do they die How do we measure this The Interstellar Medium (ISM) Vast clouds of gas & dust lie between stars Diffuse hydrogen clouds: dozens of
Birth & Death of Stars Objectives How are stars formed How do they die How do we measure this The Interstellar Medium (ISM) Vast clouds of gas & dust lie between stars Diffuse hydrogen clouds: dozens of
CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES
 CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES Characteristics of the Sun 1. The Sun is located about 150 million kilometres from the Earth. 2. The Sun is made up of hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. 3. The size of
CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES Characteristics of the Sun 1. The Sun is located about 150 million kilometres from the Earth. 2. The Sun is made up of hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. 3. The size of
Supernovae Through the Ages
 Supernovae Through the Ages We ourselves are stardust. -Carl Sagan Jason Kezwer September 11, 2013 Outline - What are supernovae? Why are they important? - An observational history - How supernovae affect
Supernovae Through the Ages We ourselves are stardust. -Carl Sagan Jason Kezwer September 11, 2013 Outline - What are supernovae? Why are they important? - An observational history - How supernovae affect
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
 Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Life and Death of a Star. Chapters 20 and 21
 Life and Death of a Star Chapters 20 and 21 90 % of a stars life Most stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. A star like the Sun, for example, after spending a few tens of millions of years
Life and Death of a Star Chapters 20 and 21 90 % of a stars life Most stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. A star like the Sun, for example, after spending a few tens of millions of years
In the Beginning. After about three minutes the temperature had cooled even further, so that neutrons were able to combine with 1 H to form 2 H;
 In the Beginning Obviously, before we can have any geochemistry we need some elements to react with one another. The most commonly held scientific view for the origin of the universe is the "Big Bang"
In the Beginning Obviously, before we can have any geochemistry we need some elements to react with one another. The most commonly held scientific view for the origin of the universe is the "Big Bang"
The Formation of Stars
 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars
 Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources
 Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources The Algol Mystery Algol is a double-lined eclipsing binary system with a period of about 3 days (very short). The two stars are: Star A: B8, 3.4M o
Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources The Algol Mystery Algol is a double-lined eclipsing binary system with a period of about 3 days (very short). The two stars are: Star A: B8, 3.4M o
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Life and Death of High Mass Stars (M > 8 M sun ) REVIEW Last stage: Iron core surrounded by shells of increasingly lighter elements. REVIEW When mass
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Life and Death of High Mass Stars (M > 8 M sun ) REVIEW Last stage: Iron core surrounded by shells of increasingly lighter elements. REVIEW When mass
Astronomy 1504 Section 002 Astronomy 1514 Section 10 Midterm 2, Version 1 October 19, 2012
 Astronomy 1504 Section 002 Astronomy 1514 Section 10 Midterm 2, Version 1 October 19, 2012 Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers.
Astronomy 1504 Section 002 Astronomy 1514 Section 10 Midterm 2, Version 1 October 19, 2012 Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers.
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
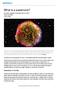 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars
 Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars Senior Astrophysics 2018-03-27 Senior Astrophysics Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars 2018-03-27 1 / 29 Outline 1 Stellar models 2 Convection
Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars Senior Astrophysics 2018-03-27 Senior Astrophysics Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars 2018-03-27 1 / 29 Outline 1 Stellar models 2 Convection
Fate of Stars. relative to Sun s mass
 INITIAL MASS relative to Sun s mass M < 0.01 Fate of Stars Final State planet.01 < M
INITIAL MASS relative to Sun s mass M < 0.01 Fate of Stars Final State planet.01 < M
Chapter 17 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Stuff Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 17 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Stuff Star Stuff 17.1 Lives in the Balance Our goals for learning: How does a star's mass affect nuclear fusion? How does a star's mass affect
Chapter 17 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Stuff Star Stuff 17.1 Lives in the Balance Our goals for learning: How does a star's mass affect nuclear fusion? How does a star's mass affect
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story Thursday, September 25, 2008 6:30 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern time Agenda: 1. Introductions 2. Tech-help
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story Thursday, September 25, 2008 6:30 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern time Agenda: 1. Introductions 2. Tech-help
5) Which stage lasts the longest? a) viii b) I c) iv d) iii e) vi
 1) Which of the following statements about globular clusters is false? a) Globular cluster stars are very metal- poor relative to the Sun. b) Globular cluster stars are more than 12 billion years old.
1) Which of the following statements about globular clusters is false? a) Globular cluster stars are very metal- poor relative to the Sun. b) Globular cluster stars are more than 12 billion years old.
Beyond the Solar System 2006 Oct 17 Page 1 of 5
 I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Life Cycle of a Star - Activities
 Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Star Death ( ) High Mass Star. Red Supergiant. Supernova + Remnant. Neutron Star
 Star Death High Mass Star Red Supergiant A star with mass between 8 M and 20 M will become a red supergiant and will subsequently experience a supernova explosion. The core of this star will have a mass
Star Death High Mass Star Red Supergiant A star with mass between 8 M and 20 M will become a red supergiant and will subsequently experience a supernova explosion. The core of this star will have a mass
Announcements. L! m 3.5 BRIGHT FAINT. Mass Luminosity Relation: Why? Homework#3 will be handed out at the end of this lecture.
 Announcements BRIGHT Homework#3 will be handed out at the end of this lecture. Due October 14 (next Thursday) Review of Mid-term exam will be handed out Tuesday. Mid-term exam will be variants (if not
Announcements BRIGHT Homework#3 will be handed out at the end of this lecture. Due October 14 (next Thursday) Review of Mid-term exam will be handed out Tuesday. Mid-term exam will be variants (if not
Guiding Questions. The Deaths of Stars. Pathways of Stellar Evolution GOOD TO KNOW. Low-mass stars go through two distinct red-giant stages
 The Deaths of Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
The Deaths of Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
The Deaths of Stars 1
 The Deaths of Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
The Deaths of Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
Clicker Questions (chapters 6-18)
 Clicker Questions (chapters 6-18) 1. Officially, how many planets are there in our solar system? a. 8 b. 9 c. dozens 2. The Doppler formula is v = ( λ/λ) 300,000 km/sec for light waves. A particular feature
Clicker Questions (chapters 6-18) 1. Officially, how many planets are there in our solar system? a. 8 b. 9 c. dozens 2. The Doppler formula is v = ( λ/λ) 300,000 km/sec for light waves. A particular feature
The Life Cycles of Stars. Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC
 STARS I. Stellar Evolution The Life Cycles of Stars Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC A. Nebula- cloud of gas and dust B. Protostar- spinning disk C. Main Sequence 1. When the protostar reaches 15 million C,
STARS I. Stellar Evolution The Life Cycles of Stars Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC A. Nebula- cloud of gas and dust B. Protostar- spinning disk C. Main Sequence 1. When the protostar reaches 15 million C,
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09. Astronomy 101
 High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
The light curves for a nova look like the following.
 End of high mass stars Nova Supernova Type I Type II Stellar nucleo-synthesis Stellar Recycling Nova (means new): is a star that suddenly increases greatly in brightness, then slowly fades back to its
End of high mass stars Nova Supernova Type I Type II Stellar nucleo-synthesis Stellar Recycling Nova (means new): is a star that suddenly increases greatly in brightness, then slowly fades back to its
