Kepler photometric accuracy with degraded attitude control
|
|
|
- Rafe Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kepler photometric accuracy with degraded attitude control Hans Kjeldsen, Torben Arentoft and Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard KASOC, Stellar Astrophysics Centre, Aarhus University, Denmark - 25 July The present document describes the expected photometric accuracy which may be obtained from analysis of Kepler data in the case of degraded attitude accuracy. All simulations are based on the Photometry simulator developed by Ridder, Arentoft and Kjeldsen (2006, MNRAS, 365, ). The degraded attitude of Kepler Based on information from Martin Still and Steve Howell (NASA Ames) we have specified three scenarios for a degraded attitude. Those are analysed below. The simulations of jitter and drift of Kepler are based on the description in section 3.7 in the Kepler Instrument Handbook (KSCI-19033, 15 July 2009, NASA Ames Research Center): The philosophy behind the simulated degraded attitude is first to create a simulation of the 3-axis stabilized pointing which follows the requirements shown in Figure 18 in the Kepler Instrument Handbook (see Figure 1 below). Figure 1. From Kepler Instrument Handbook (figure 18, pg. 40). The figure indicate the 3σ RMS single-axis attitude error (combined jitter and drift). Reaction wheel jitter above 20 Hz is not included and will mainly affect the PSF. The high frequency attitude noise is a result of spacecraft motion that can t be removed by use of the guiding sensors and can therefore not be corrected by use of the reaction wheels. At low frequencies the main noise is drift and this is corrected almost entirely by the reaction wheels. In the simulations we therefore keep the DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 1
2 high frequency noise component unchanged but increase the low frequency to simulate the degraded performance of the Kepler attitude. The three attitude scenarios are: 1. Over long time scales the attitude in pitch (X-coordinate) and yaw (Y-coordinate) is drifting around with a scatter of 0.5 arcsec. 2. Same as scenario 1 but with 1.0 arcsec scatter. 3. With a period of minutes the attitude in yaw (Y-coordinate) is oscillating with a peak-to-peak amplitude of 3-4 arcsec. On top of this oscillation we add an additional jitter component similar to scenario 1 but with an amplitude of 0.2 arcsec. Based on the attitude scenarios we constructed three ACS time series (in pitch and yaw. We ignore for the moment the roll component) with a time resolution of 1 sec. All data sets are 30 day long and contain the attitude offset in units of arcsec. Based on those time series data we construct images of a single star corresponding to integrations of 60 sec and 30 min. The attitude in the three scenarios are shown in the figures below. Figure 2 show the first two days of each simulation (at the top of the figure we show the simulated attitude that is consistent with the requirements shown in figure 1). Figure 2. Attitude simulation for the three scenarios and the original Kepler attitude (with three functioning reaction wheels). Black is X- coordinate and red is the Y- coordinate. The Z- coordinate (roll) is not included in the present simulation. From top to bottom we show the simulated original attitude followed by scenario 1 to 3. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 2
3 Figure 3. The 3σ attitude-rms (one axis) for scenario 1. The figure can be compared to figure 1 (the original attitude specification). Scenario 1 and 2 is basically a guided random walk (the drift component is times higher than in the original mode of operation) while scenario 3 contains a periodic signal which will be seen in the photometric data. Figure 4. The power density spectrum for a single axis attitude corresponding to the original Kepler specifications (see Figure 1). In the degraded simulations we mainly increase the low frequency component corresponding to excess signal from attitude guiding. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 3
4 The CCD sensitivity An important part of the simulation is the CCD sensitivity variation. There are three major components that are used to describe the relevant sensitivity variability. References are made to the Kepler Instrument handbook: (KSCI , 15 July 2009): 1. Global pixel-to-pixel (inter-pixel) variations. In the present simulation we use about 5% sensitivity variability peak-to-peak of a 30x30 pixel area. According to the Kepler Instrument Handbook table 9 one can expect a 1% standard deviation in the Photoresponse non-uniformity for the Kepler chips which is in agreement with a 5% peak-to-peak sensitivity variation. We assume that 80% of the global pixel-to-pixel variation can be removed via flat fielding (as discussed in the section 4.14 in the Kepler Instrument Handbook). 2. Intra-pixel random variations. In the present simulation we use 25% peak-to-peak variability within a pixel (on a scale corresponding to 1% of the pixel area). 3. Sensitivity drop due to pixel-channel (intra-pixel drop due to the gate structure of the CCD chip). In the present simulation we use 10% drop along 10% of the pixel in both the X- and Y- direction. The corresponding sensitivity variability is shown in figure 5 below. Figure 5. The lower left corner show the combined detector sensitivity variation in the present simulation including global variations as well as intra-pixel and pixel-channel sensitivity drop. The upper left corner show the global sensitivity variations at the same scale as used in the lower left corner. The upper right corner shows the global pixel-to-pixel variability using a finer scale. The lower right show the sensitivity variability without the pixel-channel sensitivity drop. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 4
5 Simulating the photometric performance Using the simulated attitude as well as the simulated sensitivity variability we finally use a stellar PSF (simulating the Kepler PSF) and create images which are then analysed. In figure 6 we show an example of a 30x30 pixel image and in figure 8 we show the extracted photometric variability the series in scenario 1. The photometric analysis is done using three different apertures (defined in the software) and we also measure the position of the PSF on the CCD which can then be compared to the attitude input. Figure 6. A single simulated CCD-frame showing a single star in the chip. Figure 7 (below). Figure 15 from the Kepler Instrument handbook (KSCI-19033) showing the PSF (or PRF) for a point source in the focal plane (detected by use of Kepler). Figure 8. Extracted raw photometric variations using the attitude variations as described in scenario 1. No photon noise is included in this time series and no intrinsic stellar variability is included. This should be compared to figure 9 (showing the photometric variability due to attitude variability in the original mode of operation). DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 5
6 Figure 9. Simulated photometric variability due to pointing variations corresponding the RMS attitude errors in the original mode of operation for Kepler. Figure 10. Extracted raw photometry using the simulated attitude for scenario 2. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 6
7 Figure 11. Extracted raw photometry using the simulated attitude for scenario 3 As part of the data analysis of the simulated data we also determine the position of the star on the CCD. We may therefore compare the input attitude to the measured position. In figure 12 below we show an example of the measured stellar position for the simulation of scenario 1.. Figure 12. The measured position of the stellar profile. The X-coordinate is shown at the top and the Y-coordinate at the bottom. The black curve show the input attitude. On top of this curve we show the measured position. The measured positions are also shown below the input attitude for comparison. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 7
8 The noise in the power spectrum Based on the simulations we can then calculate the noise level in the power spectrum. This noise should be compared with the stellar signal. A more detailed analysis of this will also follow in a later version of the present document. In figure 13 and 14 we show the power density spectrum (PDS) in units of ppm 2 /µhz. Those figures are based on the simulated data for scenario 1. It is clear that power density is orders of magnitudes higher than the noise level for the brightest Kepler stars. As discussed in a the next section we could however remove some of the photometric noise by modelling the sensitivity as a function of the intra-pixel and inter-pixel position. Figure 13. Power density spectrum for attitude scenario 1. The power density follow a 1/f 1.5 spectrum with high noise a low frequency. The power level should be compared to the stellar signal and stellar background noise for e.g. solar-like stars which is shown in figure 15. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 8
9 Figure 14. Same as figure 13. In this plot the power density is shown in linear units. Figure 15. A number of power density spectra for bright Kepler stars (from Chaplin et al.). The intrinsic noise level is in most cases below the noise shown in figure 14. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 9
10 Figure 16. The power density spectrum for the attitude induced photometric noise during the nominal mission and for scenario 1, 2 and 3. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 10
11 Using the data to model the intra- and inter-pixel sensitivity The photometric variability seen in figure 8,9,10 and 11 is caused by intra- and inter-pixel sensitivity variations across the detector. Using the measured position of the star on the chip we may be able to use the data to construct a model for the intra- and inter-pixel variability. In order to do this we need to consider both the intrinsic stellar variability (due to transits, stellar rotation, oscillations and granulation) and the variability due to the detector sensitivity variability. We describe the photometric signal as the sum of three components: ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ( )) The basic idea is then to build a model the CCD sensitivity and correct the data for this component leaving the intrinsic noise and the stellar variability. The model we use is based on calculating a local weighted mean value at a given measured position (x(t),y(t)). We want to avoid that the model is sensitive to data outliers and to intrinsic variability and this is ensured by constructing an iterative calculation of the mean value: We first calculate the mean value as the weighted mean, where the weight for the data in order to calculate the mean value at position (x 0,y 0 ) at time t 0 is defined as: ( ) ( ) [ ( ) ] [ ( ) ] [ ( ) ] The values for Δt, Δx and Δy specifies the resolution of the model. The three parameters are: Δt: The minimum allowed separation in time between a given data point and t 0 Δx: The maximum distance to x 0 in the measured stellar position (x-coordinate) on the detector Δy: The maximum distance to x 0 in the measured stellar position (y-coordinate) on the detector We now calculate the mean value using all the data in the time series data(t) and the weight W(t,x,y): ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) The next step is to calculate the mean deviation from the mean value: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) In order to avoid the influence of outliers in data(t) we finally optimize the weights by use of the mean and the mean deviation: ( ( )) ( ) [ ( ) ] [ ( ) ] [ ( ) ] [ ( ( ) ( ) ( ) ) ] The C Δ -coefficient specifies the range of data clipping (sigma-clipping). DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 11
12 We finally calculate the model for the CCD-sensitivity at position (x 0,y 0 ) at time t 0 : ( ) ( ( )) ( ) ( ( )) In the next version of the present document we will run a series of simulations where we include additional noise source (photon noise and stellar intrinsic noise ) as well as signals (transits and oscillations) to fully understand the impact of the sensitivity correction. The first analysis indicates that we can correct the raw photometry and reach a noise level very similar to the instrumental noise in the nominal mission (fully 3-axis stabilized). Below we show in figure 17, 18 and 19 the results of using two different set of parameters for modelling the detector sensitivity. In model A we use Δt = 0.1 d, Δx = 0.05 pix, Δy = 0.05 pix and C Δ = 1.0 and in model B we use Δt = 0.1 d, Δx = 0.02 pix, Δy = 0.02 pix and C Δ = 1.0. More analysis is needed in order to fully understand the properties of modelling and correcting for the photometric variations due to detector sensitivity variations. It is however clear that model B provide a much better correction than model A. Both models however are able to lower the noise significantly. Figure 17. The simulated time series photometry for Scenario 1. At the top we show the raw photometry and below we show the corrected photometry using model A and model B. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 12
13 Figure 18. The simulated time series photometry for Scenario 1. At the top we show the raw photometry and below we show the corrected photometry using model A and model B. The plot show a zoom of one day out of the simulated 30 day time series. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 13
14 Figure 19. The power density spectrum (PDS) of the simulated time series photometry for Scenario 1. At the top we show the PDS of the raw photometry and below we show the PDS for the corrected photometry using model A and model B. Based on Figure 19 we conclude that Kepler will be able to deliver photometry of similar quality as we have obtained during the nominal mission if the degraded attitude is similar to the one described in scenario 1. DASC/KASOC/0043(2) 14
Requirements for the Star Tracker Parallel Science Programme
 Requirements for the Star Tracker Parallel Science Programme Rømer System Definition Phase 2000/2001 Document no.: MONS/IFA/PL/RS/0003(1) Date: 22.04.2001 Prepared by: Hans Kjeldsen and Tim Bedding Checked
Requirements for the Star Tracker Parallel Science Programme Rømer System Definition Phase 2000/2001 Document no.: MONS/IFA/PL/RS/0003(1) Date: 22.04.2001 Prepared by: Hans Kjeldsen and Tim Bedding Checked
Asteroseismology with the Kepler mission
 Comm. in Asteroseismology Vol. 150, 2007 Asteroseismology with the Kepler mission J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, 1,2 T. Arentoft, 1,2 T. M. Brown, 3 R. L. Gilliland, 4 H. Kjeldsen, 1,2 W. J. Borucki, 5 D. Koch
Comm. in Asteroseismology Vol. 150, 2007 Asteroseismology with the Kepler mission J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, 1,2 T. Arentoft, 1,2 T. M. Brown, 3 R. L. Gilliland, 4 H. Kjeldsen, 1,2 W. J. Borucki, 5 D. Koch
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Mar 2000
 The MONS Star Trackers 1 Timothy R. Bedding School of Physics, University of Sydney 2006, Australia arxiv:astro-ph/0003249v1 17 Mar 2000 Hans Kjeldsen Teoretisk Astrofysik Center, Danmarks Grundforskningsfond,
The MONS Star Trackers 1 Timothy R. Bedding School of Physics, University of Sydney 2006, Australia arxiv:astro-ph/0003249v1 17 Mar 2000 Hans Kjeldsen Teoretisk Astrofysik Center, Danmarks Grundforskningsfond,
The MOST data pipeline: Lessons for Kepler? Jaymie M. Matthews University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada
 The MOST data pipeline: Lessons for Kepler? Jaymie M. Matthews University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada Observing modes Fabry Imaging Targets: 0 < V < 6 Pupil image: ~1500 pixels fixed to < 0.01
The MOST data pipeline: Lessons for Kepler? Jaymie M. Matthews University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada Observing modes Fabry Imaging Targets: 0 < V < 6 Pupil image: ~1500 pixels fixed to < 0.01
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
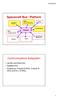 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Expected precision on planet radii with
 Expected precision on planet radii with Adrien Deline 1, Didier Queloz 1,2 1 University of Geneva 2 University of Cambridge 24 th 26 th July 2017 CHEOPS Science Workshop 5 Schloss Seggau, Austria Field
Expected precision on planet radii with Adrien Deline 1, Didier Queloz 1,2 1 University of Geneva 2 University of Cambridge 24 th 26 th July 2017 CHEOPS Science Workshop 5 Schloss Seggau, Austria Field
A CubeSat Mission for Exoplanet Transit Detection and Astroseismology
 A CubeSat Mission for Exoplanet Transit Detection and Astroseismology Jeremy Bailey (UNSW, Physics) Steve Tsitas (UNSW, ACSER) Daniel Bayliss (RSAA, ANU) Tim Bedding (Univ. Sydney) ESO Very Large Telescope
A CubeSat Mission for Exoplanet Transit Detection and Astroseismology Jeremy Bailey (UNSW, Physics) Steve Tsitas (UNSW, ACSER) Daniel Bayliss (RSAA, ANU) Tim Bedding (Univ. Sydney) ESO Very Large Telescope
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Oct 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Oct 2016](/thumbs/90/104116717.jpg) On the detectability of solar-like oscillations with the NASA TESS mission arxiv:.00v [astro-ph.sr] 20 Oct 20 Tiago L. Campante,2, School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston,
On the detectability of solar-like oscillations with the NASA TESS mission arxiv:.00v [astro-ph.sr] 20 Oct 20 Tiago L. Campante,2, School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston,
Stellar Observations Network Group
 Stellar Observations Network Group Frank Grundahl, Jørgen Christensen Dalsgaard, Uffe Gråe Jørgensen, Hans Kjeldsen, Søren Frandsen, Per Kjærgaard Rasmussen + participation from IAC (Pere Pallé, Orlagh
Stellar Observations Network Group Frank Grundahl, Jørgen Christensen Dalsgaard, Uffe Gråe Jørgensen, Hans Kjeldsen, Søren Frandsen, Per Kjærgaard Rasmussen + participation from IAC (Pere Pallé, Orlagh
Helioseismology: GONG/BiSON/SoHO
 Helioseismology: GONG/BiSON/SoHO Asteroseismology: Solar-like oscillations in other stars Study stars of different Masses, Ages and Chemical Composition Stellar Structure and Evolution Solar-like oscillations
Helioseismology: GONG/BiSON/SoHO Asteroseismology: Solar-like oscillations in other stars Study stars of different Masses, Ages and Chemical Composition Stellar Structure and Evolution Solar-like oscillations
XMM-Newton Optical-UV Monitor: introduction and calibration status OM instrument and calibration
 XMM-Newton Optical-UV Monitor: introduction and calibration status OM instrument and calibration Antonio Talavera XMM-Newton Science Operation Centre, ESAC, ESA OM: Instrument Description 30 cm Ritchey-Chretien
XMM-Newton Optical-UV Monitor: introduction and calibration status OM instrument and calibration Antonio Talavera XMM-Newton Science Operation Centre, ESAC, ESA OM: Instrument Description 30 cm Ritchey-Chretien
Breathing, Position Drift, and PSF Variations on the UVIS Detector
 SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report WFC3 1-1 Breathing, Position Drift, and PSF Variations on the UVIS Detector L. Dressel July 13, 1 ABSTRACT This study
SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report WFC3 1-1 Breathing, Position Drift, and PSF Variations on the UVIS Detector L. Dressel July 13, 1 ABSTRACT This study
Spacecraft Motions. Carl Grillmair. Time Series Data Reduction with IRAC 1 June 2014 CJG - 1
 Spacecraft Motions Carl Grillmair Time Series Data Reduction with IRAC 1 June 2014 CJG - 1 Photometric Stability 3.6 µm 4.5 µm Would like to achieve a level of pointing stability that enables sub-30 ppm
Spacecraft Motions Carl Grillmair Time Series Data Reduction with IRAC 1 June 2014 CJG - 1 Photometric Stability 3.6 µm 4.5 µm Would like to achieve a level of pointing stability that enables sub-30 ppm
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 4 Dec 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 4 Dec 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 4 Dec 2014](/thumbs/84/89105815.jpg) Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 0 OF THE K2 MISSION Andrew Vanderburg 1,2 Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., Cambridge,
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 0 OF THE K2 MISSION Andrew Vanderburg 1,2 Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., Cambridge,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1201939/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Kepler-Detected Gravity-Mode Period Spacings in a Red Giant Star P. G. Beck,* T. R. Bedding, B. Mosser, D. Stello,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1201939/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Kepler-Detected Gravity-Mode Period Spacings in a Red Giant Star P. G. Beck,* T. R. Bedding, B. Mosser, D. Stello,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Jul 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Jul 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Jul 2008](/thumbs/88/114997315.jpg) Transiting Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 253, 2008 c 2008 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Measurements of Stellar Properties through Asteroseismology: A Tool for
Transiting Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 253, 2008 c 2008 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Measurements of Stellar Properties through Asteroseismology: A Tool for
Diffusion and helioseismology
 Diffusion and helioseismology Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard Institut for Fysik og Astronomi, Aarhus Universitet & Danish AsteroSeismology Centre (DASC) Eddington (1926): The internal constitution of the
Diffusion and helioseismology Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard Institut for Fysik og Astronomi, Aarhus Universitet & Danish AsteroSeismology Centre (DASC) Eddington (1926): The internal constitution of the
The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results
 The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results Thomas N. Gautier, Kepler Project Scientist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology 3 July 2012 SAO STScI 2012
The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results Thomas N. Gautier, Kepler Project Scientist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology 3 July 2012 SAO STScI 2012
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Thermal Payload Power Communication Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Thermal Payload Power Communication Structure and Mechanisms
SONG overview. Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard Department of Physics and Astronomy Aarhus University
 SONG overview Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard Department of Physics and Astronomy Aarhus University The SONG concept Network of 8 telescopes with a global distribution Long, nearly continuous observations
SONG overview Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard Department of Physics and Astronomy Aarhus University The SONG concept Network of 8 telescopes with a global distribution Long, nearly continuous observations
REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 1 OF THE K2 MISSION
 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 1 OF THE K2 MISSION Andrew Vanderburg 1,2 Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 6 Garden St., Cambridge,
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 1 OF THE K2 MISSION Andrew Vanderburg 1,2 Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 6 Garden St., Cambridge,
The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism
 The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism A. Pasquali, N. Pirzkal, J.R. Walsh March 5, 2003 ABSTRACT We present the G800L grism spectra of the Wolf-Rayet stars WR45 and WR96 acquired with
The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism A. Pasquali, N. Pirzkal, J.R. Walsh March 5, 2003 ABSTRACT We present the G800L grism spectra of the Wolf-Rayet stars WR45 and WR96 acquired with
Rømer Science Mission Plan
 Institute of Physics and Astronomy, University of Aarhus Rømer Science Mission Plan Danish Small Satellite Programme Document No.(issue): MONS/IFA/MAN/PLN/0001(1) Date: 2001-05-29 Prepared by: Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard,
Institute of Physics and Astronomy, University of Aarhus Rømer Science Mission Plan Danish Small Satellite Programme Document No.(issue): MONS/IFA/MAN/PLN/0001(1) Date: 2001-05-29 Prepared by: Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard,
Photometric Techniques II Data analysis, errors, completeness
 Photometric Techniques II Data analysis, errors, completeness Sergio Ortolani Dipartimento di Astronomia Universita di Padova, Italy. The fitting technique assumes the linearity of the intensity values
Photometric Techniques II Data analysis, errors, completeness Sergio Ortolani Dipartimento di Astronomia Universita di Padova, Italy. The fitting technique assumes the linearity of the intensity values
Astrophysics Advisory Committee
 Astrophysics Advisory Committee K2 End of Mission Science Planning Charlie Sobeck July 20, 2017 K2 Mission Genesis K2 is a follow-on to the original Kepler mission, driven by the loss of two reaction wheels.
Astrophysics Advisory Committee K2 End of Mission Science Planning Charlie Sobeck July 20, 2017 K2 Mission Genesis K2 is a follow-on to the original Kepler mission, driven by the loss of two reaction wheels.
Fundamental limits to the precision in astrometry and photometry using array detectors through the Cramér-Rao minimum variance bound
 Fundamental limits to the precision in astrometry and photometry using array detectors through the Cramér-Rao minimum variance bound Jorge Silva, Marcos Orchard DIE Rene Mendez DAS U. de Chile Espinosa
Fundamental limits to the precision in astrometry and photometry using array detectors through the Cramér-Rao minimum variance bound Jorge Silva, Marcos Orchard DIE Rene Mendez DAS U. de Chile Espinosa
TESS and Galactic Science
 TESS and Galactic Science! Keivan Stassun!! WFIRST Meeting! 18 November 2014! 1! Preliminary TESS Mission Schedule! Activity! Date! Status! Systems Requirement Review! 12-13 Feb 2014! Completed! Preliminary
TESS and Galactic Science! Keivan Stassun!! WFIRST Meeting! 18 November 2014! 1! Preliminary TESS Mission Schedule! Activity! Date! Status! Systems Requirement Review! 12-13 Feb 2014! Completed! Preliminary
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing
 Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing
 Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO?
 Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Astrometry (STEP) M. Shao
 Technical Issues for Narrow Angle Astrometry (STEP) M. Shao Outline Ground based narrow angle astrometry Current state of the art (0.5~1 mas (in 30 min) What are the limiting error sources Photon noise
Technical Issues for Narrow Angle Astrometry (STEP) M. Shao Outline Ground based narrow angle astrometry Current state of the art (0.5~1 mas (in 30 min) What are the limiting error sources Photon noise
ExoplanetSat: A Nanosatellite Space Telescope for Detecting Transiting Exoplanets
 1 2 ExoplanetSat: A Nanosatellite Space Telescope for Detecting Transiting Exoplanets Matthew W. Smith 1 (m_smith@mit.edu), Sara Seager 1, Christopher M. Pong 1, Sungyung Lim 2, Matthew W. Knutson 1, Timothy
1 2 ExoplanetSat: A Nanosatellite Space Telescope for Detecting Transiting Exoplanets Matthew W. Smith 1 (m_smith@mit.edu), Sara Seager 1, Christopher M. Pong 1, Sungyung Lim 2, Matthew W. Knutson 1, Timothy
KEPLER TELESCOPE AND SOLAR-LIKE PULSATORS
 KEPLER TELESCOPE AND SOLAR-LIKE PULSATORS J. Molenda Żakowicz 1, T. Arentoft 2,3, H. Kjeldsen 2,3, and A. Bonanno 4 1 Instytut Astronomiczny Uniwersytetu Wrocławskiego, Kopernika 11, 51-622 Wrocław, Poland
KEPLER TELESCOPE AND SOLAR-LIKE PULSATORS J. Molenda Żakowicz 1, T. Arentoft 2,3, H. Kjeldsen 2,3, and A. Bonanno 4 1 Instytut Astronomiczny Uniwersytetu Wrocławskiego, Kopernika 11, 51-622 Wrocław, Poland
Observer Anomaly(?): Recent Jitter and PSF Variations
 Instrument Science Report TEL 2005-01 Observer Anomaly(?): Recent Jitter and PSF Variations R. L. Gilliland gillil@stsci.edu February 2005 Abstract An anomaly in the HST Pointing Control System (PCS) has
Instrument Science Report TEL 2005-01 Observer Anomaly(?): Recent Jitter and PSF Variations R. L. Gilliland gillil@stsci.edu February 2005 Abstract An anomaly in the HST Pointing Control System (PCS) has
Probing Stellar Structure with Pressure & Gravity modes the Sun and Red Giants. Yvonne Elsworth. Science on the Sphere 14/15 July 2014
 Probing Stellar Structure with Pressure & Gravity modes the Sun and Red Giants Yvonne Elsworth Science on the Sphere 14/15 July 2014 Evolving stars are building blocks of the galaxy and their cores are
Probing Stellar Structure with Pressure & Gravity modes the Sun and Red Giants Yvonne Elsworth Science on the Sphere 14/15 July 2014 Evolving stars are building blocks of the galaxy and their cores are
Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes
 Instrument Science Report STIS 97-14 Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope Science Institute Nicholas Collins, Hughes STX/LASP/GSFC Anne Gonnella,
Instrument Science Report STIS 97-14 Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope Science Institute Nicholas Collins, Hughes STX/LASP/GSFC Anne Gonnella,
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets
 Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Products for the Q1-Q16 Catalog Using SOC 9.1 KSCI-19103 November 19, 2014 NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 Prepared
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Products for the Q1-Q16 Catalog Using SOC 9.1 KSCI-19103 November 19, 2014 NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 Prepared
VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (1992) 13, 293 305 VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT P. N. Bhat & K. P. Singh Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bombay 400 005 T. P. Prabhu Indian Institute
J. Astrophys. Astr. (1992) 13, 293 305 VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT P. N. Bhat & K. P. Singh Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bombay 400 005 T. P. Prabhu Indian Institute
BUT DOES IT QUACK LIKE A DUCK? STARS IN CLUSTERS. Andrea Miglio, Karsten Brogaard, Rasmus Handberg
 LOOKS LIKE A DUCK, MOVES LIKE A DUCK, BUT DOES IT QUACK LIKE A DUCK? ASTEROSEISMOLOGY OF RED-GIANT STARS IN CLUSTERS Andrea Miglio, Karsten Brogaard, Rasmus Hberg School of Physics Astronomy, University
LOOKS LIKE A DUCK, MOVES LIKE A DUCK, BUT DOES IT QUACK LIKE A DUCK? ASTEROSEISMOLOGY OF RED-GIANT STARS IN CLUSTERS Andrea Miglio, Karsten Brogaard, Rasmus Hberg School of Physics Astronomy, University
Focus-diverse, empirical PSF models for the ACS/WFC
 Instrument Science Report ACS/WFC 2018-08 Focus-diverse, empirical PSF models for the ACS/WFC Andrea Bellini, Jay Anderson, & Norman A. Grogin November 20, 2018 Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700
Instrument Science Report ACS/WFC 2018-08 Focus-diverse, empirical PSF models for the ACS/WFC Andrea Bellini, Jay Anderson, & Norman A. Grogin November 20, 2018 Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700
Copyright 2006 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers.
 Innovative image analysis software as a technology driver for advances in space telescope design, Mighell, K. J. 2006, in Space Telescopes and Instrumentation I: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter, edited
Innovative image analysis software as a technology driver for advances in space telescope design, Mighell, K. J. 2006, in Space Telescopes and Instrumentation I: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter, edited
WHAT PHOTOMETRIC PRECISION CAN I ACHIEVE? DAVID BOYD
 WHAT PHOTOMETRIC PRECISION CAN I ACHIEVE? DAVID BOYD If you start using a CCD camera to carry out photometry on variable stars, this is a question that sooner or later you will ask yourself. Prompted by
WHAT PHOTOMETRIC PRECISION CAN I ACHIEVE? DAVID BOYD If you start using a CCD camera to carry out photometry on variable stars, this is a question that sooner or later you will ask yourself. Prompted by
Ivan Valtchanov Herschel Science Centre European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) ESA. ESAC,20-21 Sep 2007 Ivan Valtchanov, Herschel Science Centre
 SPIRE Observing Strategies Ivan Valtchanov Herschel Science Centre European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) ESA Outline SPIRE quick overview Observing with SPIRE Astronomical Observation Templates (AOT)
SPIRE Observing Strategies Ivan Valtchanov Herschel Science Centre European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) ESA Outline SPIRE quick overview Observing with SPIRE Astronomical Observation Templates (AOT)
Space astrometry with the Joint Milliarcsecond Astrometry Pathfinder
 Relativity in Fundamental Astronomy Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 261, 2009 S. A. Klioner, P. K. Seidelman & M. H. Soffel, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309990640 Space
Relativity in Fundamental Astronomy Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 261, 2009 S. A. Klioner, P. K. Seidelman & M. H. Soffel, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309990640 Space
High Signal-to-Noise, Differential NICMOS Spectrophotometry
 Instrument Science Report NICMOS 2003-001 High Signal-to-Noise, Differential NICMOS Spectrophotometry R.L. Gilliland, S. Arribas January 7, 2003 ABSTRACT We report analysis for NICMOS CAL/9642, High S/N
Instrument Science Report NICMOS 2003-001 High Signal-to-Noise, Differential NICMOS Spectrophotometry R.L. Gilliland, S. Arribas January 7, 2003 ABSTRACT We report analysis for NICMOS CAL/9642, High S/N
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014](/thumbs/86/94907870.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 15 (2014) Printed 25 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Precise time-series photometry for the Kepler-2.0 mission arxiv:1412.6304v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014 S. Aigrain
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 15 (2014) Printed 25 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Precise time-series photometry for the Kepler-2.0 mission arxiv:1412.6304v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014 S. Aigrain
Probabilistic modeling and Inference in Astronomy
 Probabilistic modeling and Inference in Astronomy Dan Foreman-Mackey Sagan Fellow, University of Washington github.com/dfm // @exoplaneteer // dfm.io Dan Foreman-Mackey Sagan Fellow, University of Washington
Probabilistic modeling and Inference in Astronomy Dan Foreman-Mackey Sagan Fellow, University of Washington github.com/dfm // @exoplaneteer // dfm.io Dan Foreman-Mackey Sagan Fellow, University of Washington
Fringe Correction for STIS Near-IR Long-Slit Spectra using Contemporaneous Tungsten Flat Fields
 1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. Fringe Correction for STIS Near-IR Long-Slit Spectra using Contemporaneous Tungsten Flat Fields Paul Goudfrooij
1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. Fringe Correction for STIS Near-IR Long-Slit Spectra using Contemporaneous Tungsten Flat Fields Paul Goudfrooij
NGC 1817: the richest population of δ Scuti stars
 Comm. in Asteroseismology Volume 160, August 2009 c Austrian Academy of Sciences NGC 1817: the richest population of δ Scuti stars M.F.Andersen 1, T.Arentoft 1, S.Frandsen 1, L.Glowienka 1, H.R.Jensen
Comm. in Asteroseismology Volume 160, August 2009 c Austrian Academy of Sciences NGC 1817: the richest population of δ Scuti stars M.F.Andersen 1, T.Arentoft 1, S.Frandsen 1, L.Glowienka 1, H.R.Jensen
Solar-like oscillations in intermediate mass stars
 Solar-like oscillations in intermediate mass stars Victoria Antoci SAC (Stellar Astrophysics Centre), Aarhus University, Denmark Why are intermediate mass stars so important? Credit: Kupka & Weiss1999
Solar-like oscillations in intermediate mass stars Victoria Antoci SAC (Stellar Astrophysics Centre), Aarhus University, Denmark Why are intermediate mass stars so important? Credit: Kupka & Weiss1999
Plato, Euclid and the New Hard X-Ray mission
 Schiaparelli and his Legacy Meeting on Future planetary, scientific and robotic space missions Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria, Torino, 21/10/2010 Template reference : 100181670S-EN Plato, Euclid and
Schiaparelli and his Legacy Meeting on Future planetary, scientific and robotic space missions Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria, Torino, 21/10/2010 Template reference : 100181670S-EN Plato, Euclid and
Design Reference Mission. DRM approach
 Design Reference Mission The Design Reference Mission (DRM) is a set of observing programs which together provide a tool to assist with tradeoff decisions in the design of the E-ELT (examples of observing
Design Reference Mission The Design Reference Mission (DRM) is a set of observing programs which together provide a tool to assist with tradeoff decisions in the design of the E-ELT (examples of observing
Calibration Goals and Plans
 CHAPTER 13 Calibration Goals and Plans In This Chapter... Expected Calibration Accuracies / 195 Calibration Plans / 197 This chapter describes the expected accuracies which should be reached in the calibration
CHAPTER 13 Calibration Goals and Plans In This Chapter... Expected Calibration Accuracies / 195 Calibration Plans / 197 This chapter describes the expected accuracies which should be reached in the calibration
Seminar: Measurement of Stellar Parameters with Asteroseismology
 Seminar: Measurement of Stellar Parameters with Asteroseismology Author: Gal Kranjc Kušlan Mentor: dr. Andrej Prša Ljubljana, December 2017 Abstract In this seminar I introduce asteroseismology, which
Seminar: Measurement of Stellar Parameters with Asteroseismology Author: Gal Kranjc Kušlan Mentor: dr. Andrej Prša Ljubljana, December 2017 Abstract In this seminar I introduce asteroseismology, which
Do red giants have short mode lifetimes?
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 406 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Do red giants have short mode lifetimes? D. Stello 1,2,3, H. Kjeldsen 1, T. R. Bedding 2, and D. Buzasi 3 1 Institute for Fysik og Astronomi (IFA), Aarhus
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 406 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Do red giants have short mode lifetimes? D. Stello 1,2,3, H. Kjeldsen 1, T. R. Bedding 2, and D. Buzasi 3 1 Institute for Fysik og Astronomi (IFA), Aarhus
Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect
 Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect Mauro Giavalisco August 10, 2004 ABSTRACT Images acquired with the Wide Field Channel (WFC) of the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) are
Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect Mauro Giavalisco August 10, 2004 ABSTRACT Images acquired with the Wide Field Channel (WFC) of the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) are
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra. Astrophysical observatory of Asiago
 Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
Campaign 9 of K2: News from the K2 team
 Campaign 9 of K2: News from the K2 team A talk by Geert Barentsen & Tom Barclay for the 20th Microlensing workshop in Paris on 14 January 2016. K2 Guest Observer Office (NASA Ames) http://keplerscience.arc.nasa.gov
Campaign 9 of K2: News from the K2 team A talk by Geert Barentsen & Tom Barclay for the 20th Microlensing workshop in Paris on 14 January 2016. K2 Guest Observer Office (NASA Ames) http://keplerscience.arc.nasa.gov
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/332/6026/213/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Ensemble Asteroseismology of Solar-Type Stars with the NASA Kepler Mission W. J. Chaplin,* H. Kjeldsen, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/332/6026/213/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Ensemble Asteroseismology of Solar-Type Stars with the NASA Kepler Mission W. J. Chaplin,* H. Kjeldsen, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard,
The WFIRST Coronagraphic Instrument (CGI)
 The WFIRST Coronagraphic Instrument (CGI) N. Jeremy Kasdin Princeton University CGI Adjutant Scientist WFIRST Pasadena Conference February 29, 2016 The Coronagraph Instrument Optical Bench Triangular Support
The WFIRST Coronagraphic Instrument (CGI) N. Jeremy Kasdin Princeton University CGI Adjutant Scientist WFIRST Pasadena Conference February 29, 2016 The Coronagraph Instrument Optical Bench Triangular Support
GDR1 photometry. CU5/DPCI team
 GDR1 photometry CU5/DPCI team What is, or isn't included GDR1 only provides G mean flux and error Derived mean magnitude, all entries Zero point used is in Vega system Zero point for AB system also available
GDR1 photometry CU5/DPCI team What is, or isn't included GDR1 only provides G mean flux and error Derived mean magnitude, all entries Zero point used is in Vega system Zero point for AB system also available
MEMORANDUM. Focal-Point: Point on the focal plane where the sharpest PSF is located.
 CHANDRA X-ray Center 60 Garden St., Cambridge Massachusetts 02138 USA MEMORANDUM Date: October 16, 2017 From: Ping Zhao To: CXC Subject: Chandra Optical Axis and Aimpoint File: oxap memo 2017.tex Version:
CHANDRA X-ray Center 60 Garden St., Cambridge Massachusetts 02138 USA MEMORANDUM Date: October 16, 2017 From: Ping Zhao To: CXC Subject: Chandra Optical Axis and Aimpoint File: oxap memo 2017.tex Version:
McMath-Pierce Adaptive Optics Overview. Christoph Keller National Solar Observatory, Tucson
 McMath-Pierce Adaptive Optics Overview Christoph Keller National Solar Observatory, Tucson Small-Scale Structures on the Sun 1 arcsec Important astrophysical scales (pressure scale height in photosphere,
McMath-Pierce Adaptive Optics Overview Christoph Keller National Solar Observatory, Tucson Small-Scale Structures on the Sun 1 arcsec Important astrophysical scales (pressure scale height in photosphere,
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method
 Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Wide and Fast: A new Era of EMCCD and CMOS?
 Wide and Fast: A new Era of EMCCD and CMOS? ZTF PTF?????? Gregg Hallinan California Institute of Technology gh@astro.caltech.edu Negligible 1 sec Transient Phase Space: Mansi Kasliwal Conventional CCDs
Wide and Fast: A new Era of EMCCD and CMOS? ZTF PTF?????? Gregg Hallinan California Institute of Technology gh@astro.caltech.edu Negligible 1 sec Transient Phase Space: Mansi Kasliwal Conventional CCDs
Asteroseismology & Exoplanets: A Kepler Success Story
 Asteroseismology & Exoplanets: A Kepler Success Story Daniel Huber SETI Institute / NASA Ames Research Center U Chicago Astronomy Colloquium April 2014 Collaborators Bill Chaplin, Andrea Miglio, Yvonne
Asteroseismology & Exoplanets: A Kepler Success Story Daniel Huber SETI Institute / NASA Ames Research Center U Chicago Astronomy Colloquium April 2014 Collaborators Bill Chaplin, Andrea Miglio, Yvonne
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/96/127816976.jpg) arxiv:87.69v [astro-ph.im] Jul 8 Emese Plachy, László Molnár, Attila Bódi, Marek Skarka, Áron L. Juhász, Ádam Sódor, Péter Klagyivik and Róbert Szabó. Konkoly Observatory, MTA CSFK, Budapest, Hungary.
arxiv:87.69v [astro-ph.im] Jul 8 Emese Plachy, László Molnár, Attila Bódi, Marek Skarka, Áron L. Juhász, Ádam Sódor, Péter Klagyivik and Róbert Szabó. Konkoly Observatory, MTA CSFK, Budapest, Hungary.
MEMORANDUM. Focal-Point: Point on the focal plane where the sharpest PSF is located.
 CHANDRA X-ray Center 60 Garden St., Cambridge Massachusetts 02138 USA MEMORANDUM Date: November 1, 2014 From: Ping Zhao To: CXC Subject: Chandra Optical Axis, Aimpoint and Their Drifts File: oxap memo.tex
CHANDRA X-ray Center 60 Garden St., Cambridge Massachusetts 02138 USA MEMORANDUM Date: November 1, 2014 From: Ping Zhao To: CXC Subject: Chandra Optical Axis, Aimpoint and Their Drifts File: oxap memo.tex
List of submitted target proposals
 List of submitted target proposals Hans Kjeldsen, KASOC, Aarhus University - October 17, 2008 - Below is the complete list of target proposals submitted for the first targets selection round (October 2008).
List of submitted target proposals Hans Kjeldsen, KASOC, Aarhus University - October 17, 2008 - Below is the complete list of target proposals submitted for the first targets selection round (October 2008).
The Joint Milli-Arcsecond Pathfinder Survey: Introduction and Applications
 AIAA SPACE 2009 Conference & Exposition 14-17 September 2009, Pasadena, California AIAA 2009-6458 The Joint Milli-Arcsecond Pathfinder Survey: Introduction and Applications Ralph A. Gaume * and Bryan N.
AIAA SPACE 2009 Conference & Exposition 14-17 September 2009, Pasadena, California AIAA 2009-6458 The Joint Milli-Arcsecond Pathfinder Survey: Introduction and Applications Ralph A. Gaume * and Bryan N.
BRITE One Year in Orbit
 BRITE One Year in Orbit O. Koudelka, M.Unterberger, P.Romano Graz University of Technology W.Weiss, R.Kuschnig University of Vienna 1 Contents Scientific Goals Mission Description Commissioning Science
BRITE One Year in Orbit O. Koudelka, M.Unterberger, P.Romano Graz University of Technology W.Weiss, R.Kuschnig University of Vienna 1 Contents Scientific Goals Mission Description Commissioning Science
Asteroseismology of the Open Clusters NGC 6791, NGC 6811, and NGC 6819 from 19 months of Kepler photometry
 GREAT-ESF Workshop The World of Clusters Padova, Italy, 23-26 September 2013 Asteroseismology of the Open Clusters NGC 6791, NGC 6811, and NGC 6819 from 19 months of Kepler photometry Enrico Corsaro Postdoctoral
GREAT-ESF Workshop The World of Clusters Padova, Italy, 23-26 September 2013 Asteroseismology of the Open Clusters NGC 6791, NGC 6811, and NGC 6819 from 19 months of Kepler photometry Enrico Corsaro Postdoctoral
Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission
 Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Member, TESS Follow-up Observing Program Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2018 1 Copyright Dennis
Amateur Astronomer Participation in the TESS Exoplanet Mission Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Member, TESS Follow-up Observing Program Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2018 1 Copyright Dennis
CCD photometry of δ Scuti stars 7 Aql and 8 Aql
 Comm. in Asteroseismology Vol. 153, 2008 CCD photometry of δ Scuti stars 7 Aql and 8 Aql Abstract L. Fox Machado 1, R. Michel 1, M. Álvarez1, L. Parrao 2, A. Castro 1, and J. H. Peña 2 1 Observatorio Astronómico
Comm. in Asteroseismology Vol. 153, 2008 CCD photometry of δ Scuti stars 7 Aql and 8 Aql Abstract L. Fox Machado 1, R. Michel 1, M. Álvarez1, L. Parrao 2, A. Castro 1, and J. H. Peña 2 1 Observatorio Astronómico
Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra
 Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra S. Moehler (SDP) June 15, 2015 Executive Summary I investigated the causes for wavelength offsets seen in telluric lines and sky lines of extracted
Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra S. Moehler (SDP) June 15, 2015 Executive Summary I investigated the causes for wavelength offsets seen in telluric lines and sky lines of extracted
The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe
 Lecture 15 The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe Intensity weighted second moments Optimal filtering Weak gravitational lensing Shear components Shear detection Inverse problem:
Lecture 15 The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe Intensity weighted second moments Optimal filtering Weak gravitational lensing Shear components Shear detection Inverse problem:
ACS after SM4: RELATIVE GAIN VALUES AMONG THE FOUR WFC AMPLIFIERS
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2009-03 ACS after SM4: RELATIVE GAIN VALUES AMONG THE FOUR WFC AMPLIFIERS R. C. Bohlin, A. Maybhate, & J. Mack 2009 October 8 ABSTRACT For the default setting of gain=2, the
Instrument Science Report ACS 2009-03 ACS after SM4: RELATIVE GAIN VALUES AMONG THE FOUR WFC AMPLIFIERS R. C. Bohlin, A. Maybhate, & J. Mack 2009 October 8 ABSTRACT For the default setting of gain=2, the
The Impact of x-cte in the WFC3/UVIS detector on Astrometry
 Instrument Science Report WFC3 2014-02 The Impact of x-cte in the WFC3/UVIS detector on Astrometry Jay Anderson April 4, 2014 ABSTRACT Recent observations of the center of globular cluster Omega Centauri
Instrument Science Report WFC3 2014-02 The Impact of x-cte in the WFC3/UVIS detector on Astrometry Jay Anderson April 4, 2014 ABSTRACT Recent observations of the center of globular cluster Omega Centauri
Convection in Cool Stars, as Seen through Kepler's Eyes
 Convection in Cool Stars, as Seen through Kepler's Eyes Fabienne A. Bastien (Hubble Fellow, Penn State) Keivan G. Stassun (Vanderbilt), Gibor Basri (Berkeley), Jason Wright (Penn State), Joshua Pepper
Convection in Cool Stars, as Seen through Kepler's Eyes Fabienne A. Bastien (Hubble Fellow, Penn State) Keivan G. Stassun (Vanderbilt), Gibor Basri (Berkeley), Jason Wright (Penn State), Joshua Pepper
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Oct 2001
 1 MONS ON THE DANISH RØMER SATELLITE: MEASURING OSCILLATIONS IN NEARBY STARS Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard arxiv:astro-ph/0110444 v1 19 Oct 2001 Teoretisk Astrofysik Center, Danmarks Grundforskningsfond,
1 MONS ON THE DANISH RØMER SATELLITE: MEASURING OSCILLATIONS IN NEARBY STARS Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard arxiv:astro-ph/0110444 v1 19 Oct 2001 Teoretisk Astrofysik Center, Danmarks Grundforskningsfond,
FLAT FIELDS FROM THE MOONLIT EARTH
 Instrument Science Report WFPC2 2008-01 FLAT FIELDS FROM THE MOONLIT EARTH R. C. Bohlin, J. Mack, and J. Biretta 2008 February 4 ABSTRACT The Earth illuminated by light from the full Moon was observed
Instrument Science Report WFPC2 2008-01 FLAT FIELDS FROM THE MOONLIT EARTH R. C. Bohlin, J. Mack, and J. Biretta 2008 February 4 ABSTRACT The Earth illuminated by light from the full Moon was observed
Pan-Planets. A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars. J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team
 Pan-Planets A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team Pan-STARRS 1: 1.8m prototype telescope operated on Haleakala/Hawaii consortium of few
Pan-Planets A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team Pan-STARRS 1: 1.8m prototype telescope operated on Haleakala/Hawaii consortium of few
Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider
 Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider Copenhagen University Observatory Edited November 10, 2005 Figure 1: First light image for the Hanle autoguider, obtained on September 17, 2005. A 5 second exposure
Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider Copenhagen University Observatory Edited November 10, 2005 Figure 1: First light image for the Hanle autoguider, obtained on September 17, 2005. A 5 second exposure
Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging
 Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging C. F. Claver 3 September 1997 Overview Image motion studies done at WIYN show that a significant improvement to delivered image quality can be obtained from
Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging C. F. Claver 3 September 1997 Overview Image motion studies done at WIYN show that a significant improvement to delivered image quality can be obtained from
NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation
 NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation Ron Probst NEWFIRM Instrument Scientist September 2008 NEWFIRM is a 1-2.4 micron IR camera for the NOAO 4-m telescopes. It has a flexible complement of broad
NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation Ron Probst NEWFIRM Instrument Scientist September 2008 NEWFIRM is a 1-2.4 micron IR camera for the NOAO 4-m telescopes. It has a flexible complement of broad
On-Orbit Performance & Operation of the Attitude & Pointing Control Subsystems on ASTERIA
 SSC18-PI-34 On-Orbit Performance & Operation of the Attitude & Pointing Control Subsystems on ASTERIA Christopher M. Pong Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive,
SSC18-PI-34 On-Orbit Performance & Operation of the Attitude & Pointing Control Subsystems on ASTERIA Christopher M. Pong Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive,
John Barnes. Red Optical Planet Survey (ROPS): A radial velocity search for low mass M dwarf planets
 Red Optical Planet Survey (ROPS): A radial velocity search for low mass M dwarf planets John Barnes Centre for Astrophysics Research University of Hertfordshire UK -H. Jones, D. Pinfield, M. Tuomi (University
Red Optical Planet Survey (ROPS): A radial velocity search for low mass M dwarf planets John Barnes Centre for Astrophysics Research University of Hertfordshire UK -H. Jones, D. Pinfield, M. Tuomi (University
Planet Detection Metrics:
 Planet Detection Metrics: Pipeline Detection Efficiency KSCI-19094-001 Jessie L. Christiansen 31 August 2015 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date 8/31/15 Jessie L. Christiansen,
Planet Detection Metrics: Pipeline Detection Efficiency KSCI-19094-001 Jessie L. Christiansen 31 August 2015 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date 8/31/15 Jessie L. Christiansen,
Detection and characterization of exoplanets from space
 Detection and characterization of exoplanets from space Heike Rauer 1,2, 1:Institute for Planetary Research, DLR, Berlin 2:Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics, TU Berlin Exoplanet Space Missions and
Detection and characterization of exoplanets from space Heike Rauer 1,2, 1:Institute for Planetary Research, DLR, Berlin 2:Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics, TU Berlin Exoplanet Space Missions and
A Stellar Gyroscope for CubeSat Attitude Determination
 A Stellar Gyroscope for CubeSat Attitude Determination Samir A. Rawashdeh and James E. Lumpp, Jr. Space Systems Laboratory University of Kentucky James Barrington-Brown and Massimiliano Pastena SSBV Space
A Stellar Gyroscope for CubeSat Attitude Determination Samir A. Rawashdeh and James E. Lumpp, Jr. Space Systems Laboratory University of Kentucky James Barrington-Brown and Massimiliano Pastena SSBV Space
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets
 Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Products for the Q1-Q17 DR24 Catalog KSCI-19104 NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date: Jeffrey L.
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Products for the Q1-Q17 DR24 Catalog KSCI-19104 NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date: Jeffrey L.
Period and amplitude changes in the δ Scuti star V 1162 Orionis
 Astron. Astrophys. 354, 589 594 (2000) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Period and amplitude changes in the δ Scuti star V 1162 Orionis T. Arentoft and C. Sterken University of Brussels (VUB), Pleinlaan 2, 1050
Astron. Astrophys. 354, 589 594 (2000) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Period and amplitude changes in the δ Scuti star V 1162 Orionis T. Arentoft and C. Sterken University of Brussels (VUB), Pleinlaan 2, 1050
Webster Cash University of Colorado. X-ray Interferometry
 Webster Cash University of Colorado X-ray Interferometry Co-Investigators Steve Kahn - Columbia University Mark Schattenburg - MIT David Windt - Lucent (Bell-Labs) Outline of Presentation Science Potential
Webster Cash University of Colorado X-ray Interferometry Co-Investigators Steve Kahn - Columbia University Mark Schattenburg - MIT David Windt - Lucent (Bell-Labs) Outline of Presentation Science Potential
First Results from BOKS: Searching for extra-solar planets in the Kepler Field
 First Results from BOKS: Searching for extra-solar planets in the Kepler Field John Feldmeier Youngstown State University The BOKS TEAM PIs: John Feldmeier (YSU), Steve Howell (NOAO/WIYN) Co-Is: Mandy
First Results from BOKS: Searching for extra-solar planets in the Kepler Field John Feldmeier Youngstown State University The BOKS TEAM PIs: John Feldmeier (YSU), Steve Howell (NOAO/WIYN) Co-Is: Mandy
Fine Guidance Sensor Data
 Fine Guidance Sensor Data KSCI-19112-001 Jeffrey Van Cleve & Jennifer Campbell 19 Apr 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 of 19 Document Control Ownership This document is part of
Fine Guidance Sensor Data KSCI-19112-001 Jeffrey Van Cleve & Jennifer Campbell 19 Apr 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 of 19 Document Control Ownership This document is part of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 9 Feb 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 9 Feb 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 9 Feb 2017](/thumbs/91/106429822.jpg) Revision 4.4 Friday 9 th November, 2018 08:40 Preprint typeset using LATEX style AASTeX6 v. 1.0 TIME-SERIES ANALYSIS OF BROADBAND PHOTOMETRY OF NEPTUNE FROM K2 arxiv:1702.02943v1 [astro-ph.ep] 9 Feb 2017
Revision 4.4 Friday 9 th November, 2018 08:40 Preprint typeset using LATEX style AASTeX6 v. 1.0 TIME-SERIES ANALYSIS OF BROADBAND PHOTOMETRY OF NEPTUNE FROM K2 arxiv:1702.02943v1 [astro-ph.ep] 9 Feb 2017
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 31 Jul 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 31 Jul 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 31 Jul 2014](/thumbs/80/80626696.jpg) A new method of CCD dark current correction via extracting the dark information from scientific images arxiv:1407.8279v1 [astro-ph.im] 31 Jul 2014 Bin Ma 1, Zhaohui Shang 2,1, Yi Hu 1, Qiang Liu 1, Lifan
A new method of CCD dark current correction via extracting the dark information from scientific images arxiv:1407.8279v1 [astro-ph.im] 31 Jul 2014 Bin Ma 1, Zhaohui Shang 2,1, Yi Hu 1, Qiang Liu 1, Lifan
NICMOS Status and Plans
 1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. NICMOS Status and Plans Rodger I. Thompson Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. NICMOS Status and Plans Rodger I. Thompson Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
Expected asteroseismic performances with the space project PLATO
 Expected asteroseismic performances with the space project PLATO Mariejo Goupil 1 and the WP120 2 Members 1 Observatoire de Paris, LESIA, Observatoire de Paris, PSL Research University, CNRS, Université
Expected asteroseismic performances with the space project PLATO Mariejo Goupil 1 and the WP120 2 Members 1 Observatoire de Paris, LESIA, Observatoire de Paris, PSL Research University, CNRS, Université
A down-to-earth guide to high-resolution solar observations. Kevin Reardon National Solar Observatory
 A down-to-earth guide to high-resolution solar observations Kevin Reardon kreardon@nso.edu National Solar Observatory Seeing Adaptive Optics Image Reconstruction Atmospheric Effects Spectral Lines Calibration
A down-to-earth guide to high-resolution solar observations Kevin Reardon kreardon@nso.edu National Solar Observatory Seeing Adaptive Optics Image Reconstruction Atmospheric Effects Spectral Lines Calibration
