Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters. I. A Cosmological Primer
|
|
|
- Marjorie Marilynn Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters I. A Cosmological Primer
2 Timetable Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 4pm 4pm 4pm 4pm no lecture 4pm Can we have lectures from ? Timetable shows problems class, but will hold drop-in session in my office would you prefer a set 2-hour block, or an open door? Lecture videos on blackboard
3 About Me Dr Ben Maughan Degree: Cardiff Ph.D: Birmingham Chandra Fellow: Harvard-Smithsonian Centre for Astrophysics Research: X-ray properties of galaxy clusters Cosmology Room
4 Course Overview Observations of galaxy clusters (primarily in X-rays) for cosmological tests Cosmological primer incomplete overview of parts of cosmology important for cluster studies Galaxy clusters and their observation mass determinations Cluster baryon fraction tests constraints on matter density and standard bucket Cluster mass function growth of structure and volume tests
5 Assessment 2,000 3,000 word article on Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters 2,000 plenty! include figures/equations/references as appropriate references should give enough info for reader to locate source aim at level M student level of knowledge write in popular science style readable & engaging see e.g. Physics World articles don't need to cover whole content of lectures decide what to include to make interesting and informative article reader should appreciate how galaxy clusters can be used to obtain cosmological constraints
6 Assessment deadline on 18 Nov 2011 submit via blackboard style and clarity (40%) writing style, grammar, presentation & scope of material, level of material, structure and flow scientific content (60%) quality and quantity of technical content, analytical & critical ability, quality of conclusions, use of literature (beyond references in lectures), understanding of material
7 Cosmological models Distances Volumes Dark Energy Growth of Structure Cosmological Primer
8 Cosmological Models In simplest models of expanding Universe, only the gravitational force of matter influences dynamics of expansion. Three possible scenarios: open not enough matter to halt expansion closed more than enough matter to halt and recollapse flat boundary case The mass-energy density required for flat Universe is referred to as the critical density ρ c with cosmological constant, continual accelerated expansion possible in closed Universe
9 Cosmological Models In general relativity, these cases are thought of in terms of curvature of spacetime, open negative curvature closed positive curvature flat zero curvature (Euclidean geometry) See level 7 GR course for details We will only consider flat cosmologies!
10 Density Contributions It is convenient to write the density of matter in the Universe as a ratio to the critical density: Radiation also contributes energy density to Universe, which we can also write as Ω R dominated in early Universe but is negligible now as drops off faster with z than matter both decrease as 1/V but radiation also redshifted
11 Density Contributions In GR, Einstein proposed a cosmological constant (Λ) term in equations to allow static Universe solutions Inflation theory and observations (e.g. CMB) all suggest flat Universe, while other observations suggest Ω M < 1 new interest in Λ to provide extra energy density Λ acts as constant (in space and time) energy density, and we can write N.B. Λ is constant, but Ω Λ changes with time
12 Density Contributions We can write to total contribution of the density terms: and flatness requires Ω tot = 1 We will assume flat Universe throughout, and neglect Ω R
13 Distances There are several different ways of measuring distances in cosmology differ due to expansion of Universe Proper distance d to an object is distance measured if we froze Universe and stretched tape measure to object In expanding Universe, d increases with time Useful to define comoving distance χ which includes expansion objects moving apart due only to expansion have constant χ
14 Distances Proper distance and comoving distance related by where a(t) is the scale factor describes scale of Universe as function of time
15 Distances Hubble's Law Proper distance and comoving distance related by where a(t) is the scale factor describes scale of Universe as function of time Differentiate this expression wrt time to get Hubble's law: where
16 Distances Hubble's Law is the Hubble parameter H(t) or H(z) expansion rate per unit size Often written as where E(z) is a function describing the evolution of H. For a flat Universe with a cosmological constant
17 Distances - Redshift Consider photon emitted at t e and received at t 0 Universe expanded by factor a 0 is a(t 0 ) N.B. some texts normalise a so a 0 =1 Wavelength of photon stretched by same factor:
18 Distance Redshift Relations Derive expression for distance to object with redshift z depends on cosmological model observational data that provide d and z used to constrain cosmological models Consider photon emitted at t e and received at t 0 In time dt, photon travels proper distance cdt, or comoving distance The total comoving distance to the source is then
19 Distance Redshift Relations can be rewritten as where From the relation between a and z we can write which we substitute in above and rearrange to give
20 Distance Redshift Relations recall so can write comoving distance as: and the proper distance to z at the present time is just
21 Distance Redshift Relations recall so can write comoving distance as: and the proper distance to z at the present time is just If know cosmological parameters in E(z) calculate distance to object with measured z If know distance and redshift of an objects calculate cosmological parameters in E(z)
22 Luminosity Distance Proper distance not measurable, but distances can be determined if physical size or luminosity of object known For an object of known luminosity L, in flat non-expanding Universe, flux received is where d is distance to source equal to proper or comoving distance in non expanding Universe
23 Luminosity Distance In expanding Universe, flux spread over sphere radius d 0 proper distance to source at present time measured flux is reduced: energy of each photon decreased by factor (1+z) due to redshift time between emission of photons is increased by (1+z) due to recession velocity Both effects together reduce flux by factor (1+z) 2
24 Luminosity Distance Motivating us to define luminosity distance d L such that Thus
25 Angular Diameter Distance If physical diameter D of object is known, then in flat, nonexpanding Universe Here d is proper or comoving distance In expanding Universe, the D/θ tells us proper distance when photons were emitted in time light from z took to reach us, Universe is factor larger, so D/θ underestimates d 0 by factor (1+z)
26 Angular Diameter Distance Define angular diameter distance as and thus
27 Angular Diameter Distance Define angular diameter distance as and thus
28 Summary of Distances Proper distance d distance measured with a tape measure at fixed time Comoving distance distance that scales with expansion Luminosity distance d L distance you derive from measuring flux of known L Angular diameter distance d A distance you derive from measuring angle of known D
29 XKCD Break
30 Comoving Volume Element If number density of objects known from theory, can count objects in redshift range and determine volume volume depends on expansion history like distances constrain cosmology from volume
31 Comoving Volume Element If number density of objects known from theory, can count objects in redshift range and determine volume volume depends on expansion history like distances constrain cosmology from volume Consider a proper volume element of Universe with proper area da and proper depth dr where dω is solid angle, and d A is angular diameter distance to element
32 Comoving Volume Element write as comoving volume element dv χ by recalling to give which can be integrated over redshift range and solid angle to give comoving volume
33 Comoving Volume Element Thus if comoving number density of objects known: observe number in some z range and solid angle derive volume constrain cosmological parameters via E(z)
34 Dark Energy Combination of evidence for flat Universe and Ω M <1 support need for cosmological constant Λ Λ appears in Einstein's equations as source of gravitational repulsion to balance gravitational attraction of matter. Most generally, this unknown source of repulsive gravity is referred to as dark energy Λ is simplest form (energy density constant in space and time) other models are possible
35 Dark Energy Dark energy can be thought of as fluid with equation of state where w is equation of state parameter of dark energy For cosmological constant models, w=-1 fluid with negative pressure c.f. tension in spring in GR -ve pressure has repulsive gravitational effect not same as pressure inflating balloon (this due to difference in pressure between regions)
36 Dark Energy Dark energy can be thought of as fluid with equation of state where w is equation of state parameter of dark energy For cosmological constant models, w=-1 fluid with negative pressure c.f. tension in spring in GR -ve pressure has repulsive gravitational effect not same as pressure inflating balloon (this due to difference in pressure between regions) expansion of Universe decreases density but does work on fluid (opposite to e.g. ideal gas) keeps energy density constant with time slows expansion but -ve more than compensates
37 Dark Energy Other values of w correspond to different dark energy models different behaviour with time more general expression for E(z) for w -1 Still more general models exist in which w varies with z By using observations to constrain the expansion history of the Universe through E(z), values of Ω Λ and w can be determined to distinguish dark energy models
38 Growth of Structure In addition to geometrical tests (distances and volumes), can constrain cosmology by growth of structure Tiny density perturbations in early Universe grow to form observed large scale structure growth sensitive to cosmology Model density variation in terms of density contrast δ where is density in a region and is mean matter density N.B. δ depends on size of region considered
39 Growth of Structure Regions with δ>0 are overdense and tend to collapse Regions with δ<0 are underdense and tend to grow less dense In non-expanding Universe, overdense regions collapse exponentially In expanding Universe, collapse must compete with expansion regions denser than a critical value will collapse analogous to Universe as a whole
40 Growth of Structure Growth of structure thus sensitive to initial density distribution expansion history of Universe i.e. E(z) Galaxy clusters sensitive to amplitude of δ distribution measured via sd of δ values measured in spheres of radius 8 Mpc δ
41 Growth of Structure Larger values of correspond to less uniform initial density distribution more structure in Universe Clusters grow from high δ tail of distribution so number of clusters very sensitive to δ
42 Summary Density contributions of mass and dark energy expressed in terms of Several distance measures in expanding Universe observable distances d A, d L related to z via E(z) derive E(z) and constrain Ω M, Ω Λ by measuring d Volume also sensitive to E(z) constraints from known number densities Dark Energy thought of as fluid with can constrain w by measuring E(z) Growth of structure depends on cosmological parameters through competition between collapse and expansion (E(z)) clusters sensitive to - variance of initial density distribution
43 Bibliography S. M. Carroll, W. H. Press, and E. L. Turner, 1992, Annual Reviews of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 30, : "The cosmological constant" D. W. Hogg, 1999, astro-ph/ : "Distance measures in cosmology" T. M. Davis, and C. H. Lineweaver, 2004, Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia, 21, : "Expanding Confusion: Common Misconceptions of Cosmological Horizons and the Superluminal Expansion of the Universe" A. Albrecht, G. Bernstein, R. Cahn, W. L. Freedman, J. Hewitt, W. Hu, J. Huth, M. Kamionkowski, E. W. Kolb, L. Knox, J. C. Mather, S. Staggs, and N. B. Suntzeff, 2006, astro-ph/ : "Report of the Dark Energy Task Force" Extragalactic astronomy and cosmology: an introduction By Peter Schneider, 2006, Springer
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology
 Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology Lecture 4; January 15 2014 Previously The dominant force on the scale of the Universe is gravity Gravity is accurately described by the theory of general
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology Lecture 4; January 15 2014 Previously The dominant force on the scale of the Universe is gravity Gravity is accurately described by the theory of general
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology
 Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology Week 2 Spring 2018 Previously: Empirical foundations of the Big Bang theory. II: Hubble s Law ==> Expanding Universe CMB Radiation ==> Universe was hot
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology Week 2 Spring 2018 Previously: Empirical foundations of the Big Bang theory. II: Hubble s Law ==> Expanding Universe CMB Radiation ==> Universe was hot
AST4320: LECTURE 10 M. DIJKSTRA
 AST4320: LECTURE 10 M. DIJKSTRA 1. The Mass Power Spectrum P (k) 1.1. Introduction: the Power Spectrum & Transfer Function. The power spectrum P (k) emerged in several of our previous lectures: It fully
AST4320: LECTURE 10 M. DIJKSTRA 1. The Mass Power Spectrum P (k) 1.1. Introduction: the Power Spectrum & Transfer Function. The power spectrum P (k) emerged in several of our previous lectures: It fully
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
The Friedmann Equation R = GM R 2. R(t) R R = GM R GM R. d dt. = d dt 1 2 R 2 = GM R + K. Kinetic + potential energy per unit mass = constant
 The Friedmann Equation R = GM R R R = GM R R R(t) d dt 1 R = d dt GM R M 1 R = GM R + K Kinetic + potential energy per unit mass = constant The Friedmann Equation 1 R = GM R + K M = ρ 4 3 π R3 1 R = 4πGρR
The Friedmann Equation R = GM R R R = GM R R R(t) d dt 1 R = d dt GM R M 1 R = GM R + K Kinetic + potential energy per unit mass = constant The Friedmann Equation 1 R = GM R + K M = ρ 4 3 π R3 1 R = 4πGρR
Introduction to Cosmology
 Introduction to Cosmology João G. Rosa joao.rosa@ua.pt http://gravitation.web.ua.pt/cosmo LECTURE 2 - Newtonian cosmology I As a first approach to the Hot Big Bang model, in this lecture we will consider
Introduction to Cosmology João G. Rosa joao.rosa@ua.pt http://gravitation.web.ua.pt/cosmo LECTURE 2 - Newtonian cosmology I As a first approach to the Hot Big Bang model, in this lecture we will consider
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Cosmology Dark Energy Models ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Cosmology Dark Energy Models ASTR 2120 Sarazin Late Homeworks Last day Wednesday, May 1 My mail box in ASTR 204 Maximum credit 50% unless excused (but, better than nothing) Final Exam Thursday, May 2,
Cosmology Dark Energy Models ASTR 2120 Sarazin Late Homeworks Last day Wednesday, May 1 My mail box in ASTR 204 Maximum credit 50% unless excused (but, better than nothing) Final Exam Thursday, May 2,
NEWTONIAN COSMOLOGY. Figure 2.1: All observers see galaxies expanding with the same Hubble law. v A = H 0 r A (2.1)
 M. Pettini: Introduction to Cosmology Lecture 2 NEWTONIAN COSMOLOGY The equations that describe the time evolution of an expanding universe which is homogeneous and isotropic can be deduced from Newtonian
M. Pettini: Introduction to Cosmology Lecture 2 NEWTONIAN COSMOLOGY The equations that describe the time evolution of an expanding universe which is homogeneous and isotropic can be deduced from Newtonian
3.1 Cosmological Parameters
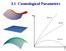 3.1 Cosmological Parameters 1 Cosmological Parameters Cosmological models are typically defined through several handy key parameters: Hubble Constant Defines the Scale of the Universe R 0 H 0 = slope at
3.1 Cosmological Parameters 1 Cosmological Parameters Cosmological models are typically defined through several handy key parameters: Hubble Constant Defines the Scale of the Universe R 0 H 0 = slope at
8. The Expanding Universe, Revisited
 8. The Expanding Universe, Revisited A1143: History of the Universe, Autumn 2012 Now that we have learned something about Einstein s theory of gravity, we are ready to revisit what we have learned about
8. The Expanding Universe, Revisited A1143: History of the Universe, Autumn 2012 Now that we have learned something about Einstein s theory of gravity, we are ready to revisit what we have learned about
Lecture 05. Cosmology. Part I
 Cosmology Part I What is Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe as a whole It asks the biggest questions in nature What is the content of the universe: Today? Long ago? In the far future? How
Cosmology Part I What is Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe as a whole It asks the biggest questions in nature What is the content of the universe: Today? Long ago? In the far future? How
Clusters: Context and Background
 Clusters: Context and Background We re about to embark on a subject rather different from what we ve treated before, so it is useful to step back and think again about what we want to accomplish in this
Clusters: Context and Background We re about to embark on a subject rather different from what we ve treated before, so it is useful to step back and think again about what we want to accomplish in this
Redshift-Distance Relationships
 Redshift-Distance Relationships George Jones April 4, 0. Distances in Cosmology This note considers two conceptually important definitions of cosmological distances, look-back distance and proper distance.
Redshift-Distance Relationships George Jones April 4, 0. Distances in Cosmology This note considers two conceptually important definitions of cosmological distances, look-back distance and proper distance.
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Ay1 Lecture 17. The Expanding Universe Introduction to Cosmology
 Ay1 Lecture 17 The Expanding Universe Introduction to Cosmology 17.1 The Expanding Universe General Relativity (1915) A fundamental change in viewing the physical space and time, and matter/energy Postulates
Ay1 Lecture 17 The Expanding Universe Introduction to Cosmology 17.1 The Expanding Universe General Relativity (1915) A fundamental change in viewing the physical space and time, and matter/energy Postulates
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Friday 8 June 2001 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 41 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Answer any THREE questions. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to read the questions printed on
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Friday 8 June 2001 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 41 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Answer any THREE questions. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to read the questions printed on
Why is the Universe Expanding?
 Why is the Universe Expanding? In general relativity, mass warps space. Warped space makes matter move, which changes the structure of space. Thus the universe should be dynamic! Gravity tries to collapse
Why is the Universe Expanding? In general relativity, mass warps space. Warped space makes matter move, which changes the structure of space. Thus the universe should be dynamic! Gravity tries to collapse
Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017
 Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2017 Structure Formation Until now we have assumed
Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2017 Structure Formation Until now we have assumed
If there is an edge to the universe, we should be able to see our way out of the woods. Olber s Paradox. This is called Olber s Paradox
 Suppose the Universe were not expanding, but was in some kind of steady state. How should galaxy recession velocities correlate with distance? They should a) be directly proportional to distance. b) reverse
Suppose the Universe were not expanding, but was in some kind of steady state. How should galaxy recession velocities correlate with distance? They should a) be directly proportional to distance. b) reverse
Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014
![Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014](/thumbs/75/72758061.jpg) 1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
Introduction. How did the universe evolve to what it is today?
 Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Cosmology. Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick.
 Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters. V. The Cluster Mass Function
 Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters V. The Cluster Mass Function Baryon Fraction Summary Assuming clusters large enough to be representative, mass composition should match Universe observe fb and constrain
Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters V. The Cluster Mass Function Baryon Fraction Summary Assuming clusters large enough to be representative, mass composition should match Universe observe fb and constrain
Astronomy 422. Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Key concepts: The CMB Recombination Radiation and matter eras Next time: Astro 422 Peer Review - Make sure to read all 6 proposals and send in rankings
Astronomy 422 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Key concepts: The CMB Recombination Radiation and matter eras Next time: Astro 422 Peer Review - Make sure to read all 6 proposals and send in rankings
4.3 The accelerating universe and the distant future
 Discovering Astronomy : Galaxies and Cosmology 46 Figure 55: Alternate histories of the universe, depending on the mean density compared to the critical value. The left hand panel shows the idea graphically.
Discovering Astronomy : Galaxies and Cosmology 46 Figure 55: Alternate histories of the universe, depending on the mean density compared to the critical value. The left hand panel shows the idea graphically.
Astronomy, Astrophysics, and Cosmology
 Astronomy, Astrophysics, and Cosmology Luis A. Anchordoqui Department of Physics and Astronomy Lehman College, City University of New York Lesson VI March 15, 2016 arxiv:0706.1988 L. A. Anchordoqui (CUNY)
Astronomy, Astrophysics, and Cosmology Luis A. Anchordoqui Department of Physics and Astronomy Lehman College, City University of New York Lesson VI March 15, 2016 arxiv:0706.1988 L. A. Anchordoqui (CUNY)
Cosmology. Assumptions in cosmology Olber s paradox Cosmology à la Newton Cosmology à la Einstein Cosmological constant Evolution of the Universe
 Cosmology Assumptions in cosmology Olber s paradox Cosmology à la Newton Cosmology à la Einstein Cosmological constant Evolution of the Universe Assumptions in Cosmology Copernican principle: We do not
Cosmology Assumptions in cosmology Olber s paradox Cosmology à la Newton Cosmology à la Einstein Cosmological constant Evolution of the Universe Assumptions in Cosmology Copernican principle: We do not
Dark Universe II. Prof. Lynn Cominsky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University
 Dark Universe II Prof. Lynn Cominsky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University Dark Universe Part II Is the universe "open" or "closed? How does dark energy change our view of the history
Dark Universe II Prof. Lynn Cominsky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University Dark Universe Part II Is the universe "open" or "closed? How does dark energy change our view of the history
Dark Matter and Dark Energy components chapter 7
 Dark Matter and Dark Energy components chapter 7 Lecture 4 See also Dark Matter awareness week December 2010 http://www.sissa.it/ap/dmg/index.html The early universe chapters 5 to 8 Particle Astrophysics,
Dark Matter and Dark Energy components chapter 7 Lecture 4 See also Dark Matter awareness week December 2010 http://www.sissa.it/ap/dmg/index.html The early universe chapters 5 to 8 Particle Astrophysics,
Chapter 29. The Hubble Expansion
 Chapter 29 The Hubble Expansion The observational characteristics of the Universe coupled with theoretical interpretation to be discussed further in subsequent chapters, allow us to formulate a standard
Chapter 29 The Hubble Expansion The observational characteristics of the Universe coupled with theoretical interpretation to be discussed further in subsequent chapters, allow us to formulate a standard
The Cosmological Principle
 Cosmological Models John O Byrne School of Physics University of Sydney Using diagrams and pp slides from Seeds Foundations of Astronomy and the Supernova Cosmology Project http://www-supernova.lbl.gov
Cosmological Models John O Byrne School of Physics University of Sydney Using diagrams and pp slides from Seeds Foundations of Astronomy and the Supernova Cosmology Project http://www-supernova.lbl.gov
A5682: Introduction to Cosmology Course Notes. 11. CMB Anisotropy
 Reading: Chapter 8, sections 8.4 and 8.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
Reading: Chapter 8, sections 8.4 and 8.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments
 The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments Intersection of physics (fundamental laws) and astronomy (contents of the universe)
The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments Intersection of physics (fundamental laws) and astronomy (contents of the universe)
2.1 Basics of the Relativistic Cosmology: Global Geometry and the Dynamics of the Universe Part I
 1 2.1 Basics of the Relativistic Cosmology: Global Geometry and the Dynamics of the Universe Part I 2 Special Relativity (1905) A fundamental change in viewing the physical space and time, now unified
1 2.1 Basics of the Relativistic Cosmology: Global Geometry and the Dynamics of the Universe Part I 2 Special Relativity (1905) A fundamental change in viewing the physical space and time, now unified
Dark Universe II. The shape of the Universe. The fate of the Universe. Old view: Density of the Universe determines its destiny
 Dark Universe II Prof. Lynn Cominsky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University Modifications by H. Geller November 2007 11/27/2007 Prof. Lynn Cominsky 2 Dark Energy and the Shape of the Universe
Dark Universe II Prof. Lynn Cominsky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University Modifications by H. Geller November 2007 11/27/2007 Prof. Lynn Cominsky 2 Dark Energy and the Shape of the Universe
Cosmology: An Introduction. Eung Jin Chun
 Cosmology: An Introduction Eung Jin Chun Cosmology Hot Big Bang + Inflation. Theory of the evolution of the Universe described by General relativity (spacetime) Thermodynamics, Particle/nuclear physics
Cosmology: An Introduction Eung Jin Chun Cosmology Hot Big Bang + Inflation. Theory of the evolution of the Universe described by General relativity (spacetime) Thermodynamics, Particle/nuclear physics
Energy Source for Active Galactic Nuclei
 Quasars Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei Bright radio sources Name comes from Quasi-Stellar Radio Source, as they appeared to be stars! Can have clouds of gas near
Quasars Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei Bright radio sources Name comes from Quasi-Stellar Radio Source, as they appeared to be stars! Can have clouds of gas near
PHY 475/375. Lecture 5. (April 9, 2012)
 PHY 475/375 Lecture 5 (April 9, 2012) Describing Curvature (contd.) So far, we have studied homogenous and isotropic surfaces in 2-dimensions. The results can be extended easily to three dimensions. As
PHY 475/375 Lecture 5 (April 9, 2012) Describing Curvature (contd.) So far, we have studied homogenous and isotropic surfaces in 2-dimensions. The results can be extended easily to three dimensions. As
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 26. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 26 Cosmology Units of Chapter 26 26.1 The Universe on the Largest Scales 26.2 The Expanding Universe 26.3 The Fate of the
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 26 Cosmology Units of Chapter 26 26.1 The Universe on the Largest Scales 26.2 The Expanding Universe 26.3 The Fate of the
Is inflation really necessary in a closed Universe? Branislav Vlahovic, Maxim Eingorn. Please see also arxiv:
 Is inflation really necessary in a closed Universe? Branislav Vlahovic, Maxim Eingorn North Carolina Central University NASA University Research Centers, Durham NC Please see also arxiv:1303.3203 Chicago
Is inflation really necessary in a closed Universe? Branislav Vlahovic, Maxim Eingorn North Carolina Central University NASA University Research Centers, Durham NC Please see also arxiv:1303.3203 Chicago
The Expanding Universe
 Announcements (this page posted as part of lecture notes on Angel) Homework 7 due late at night Monday April 23 (6:30AM Apr 24) Homework 8 now available on Angel Due late at night Friday April 27 (6:30AM
Announcements (this page posted as part of lecture notes on Angel) Homework 7 due late at night Monday April 23 (6:30AM Apr 24) Homework 8 now available on Angel Due late at night Friday April 27 (6:30AM
Announcements. Homework. Set 8now open. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site.
 Homework. Set 8now. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site. Review for Final. In class on Thursday. Course Evaluation. https://rateyourclass.msu.edu /
Homework. Set 8now. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site. Review for Final. In class on Thursday. Course Evaluation. https://rateyourclass.msu.edu /
Modeling the Universe Chapter 11 Hawley/Holcomb. Adapted from Dr. Dennis Papadopoulos UMCP
 Modeling the Universe Chapter 11 Hawley/Holcomb Adapted from Dr. Dennis Papadopoulos UMCP Spectral Lines - Doppler λ λ em 1+ z = obs z = λ obs λ λ em em Doppler Examples Doppler Examples Expansion Redshifts
Modeling the Universe Chapter 11 Hawley/Holcomb Adapted from Dr. Dennis Papadopoulos UMCP Spectral Lines - Doppler λ λ em 1+ z = obs z = λ obs λ λ em em Doppler Examples Doppler Examples Expansion Redshifts
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09. Astronomy 101
 The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
Physics 463, Spring 07. Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 3 Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum last time: how fluctuations are generated and how the smooth Universe grows
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 3 Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum last time: how fluctuations are generated and how the smooth Universe grows
Theoretical Astrophysics and Cosmology
 Theoretical Astrophysics and Cosmology What is COSMOLOGY? -The study of the Universe as a whole, namely as the collection of its matter/energy components and its constituent phenomena, and of its evolution.
Theoretical Astrophysics and Cosmology What is COSMOLOGY? -The study of the Universe as a whole, namely as the collection of its matter/energy components and its constituent phenomena, and of its evolution.
Lecture 19. Dark Energy
 Dark Energy ΛCDM Recall the lectures on cosmology The universe is flat Total energy density is 1 We know matter and baryon density So far, we called the rest Dark Energy We treated DE in the Friedmann
Dark Energy ΛCDM Recall the lectures on cosmology The universe is flat Total energy density is 1 We know matter and baryon density So far, we called the rest Dark Energy We treated DE in the Friedmann
Power spectrum exercise
 Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Lecture 09. The Cosmic Microwave Background. Part II Features of the Angular Power Spectrum
 The Cosmic Microwave Background Part II Features of the Angular Power Spectrum Angular Power Spectrum Recall the angular power spectrum Peak at l=200 corresponds to 1o structure Exactly the horizon distance
The Cosmic Microwave Background Part II Features of the Angular Power Spectrum Angular Power Spectrum Recall the angular power spectrum Peak at l=200 corresponds to 1o structure Exactly the horizon distance
Astro-2: History of the Universe
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 8; May 7 2013 Previously on astro-2 Wherever we look in the sky there is a background of microwaves, the CMB. The CMB is very close to isotropic better than 0.001%
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 8; May 7 2013 Previously on astro-2 Wherever we look in the sky there is a background of microwaves, the CMB. The CMB is very close to isotropic better than 0.001%
Clusters: Context and Background
 Clusters: Context and Background We reabouttoembarkon asubjectratherdifferentfrom what we vetreatedbefore, soit is useful to step back and think again about what we want to accomplish in this course. We
Clusters: Context and Background We reabouttoembarkon asubjectratherdifferentfrom what we vetreatedbefore, soit is useful to step back and think again about what we want to accomplish in this course. We
Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles
 Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles The basic Cosmological Principles The geometry of the Universe The scale factor R and curvature constant k Comoving coordinates Einstein s initial solutions 3/28/11
Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles The basic Cosmological Principles The geometry of the Universe The scale factor R and curvature constant k Comoving coordinates Einstein s initial solutions 3/28/11
Cosmology. Chapter 18. Cosmology. Observations of the Universe. Observations of the Universe. Motion of Galaxies. Cosmology
 Cosmology Chapter 18 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole How big is the Universe? What shape is it? How old is it? How did it form? What will happen
Cosmology Chapter 18 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole How big is the Universe? What shape is it? How old is it? How did it form? What will happen
PAPER 73 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Wednesday 4 June 2008 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 73 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Wednesday 4 June 2008 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 73 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
Preliminaries. Growth of Structure. Today s measured power spectrum, P(k) Simple 1-D example of today s P(k) Growth in roughness: δρ/ρ. !(r) =!!
 Growth of Structure Notes based on Teaching Company lectures, and associated undergraduate text with some additional material added. For a more detailed discussion, see the article by Peacock taken from
Growth of Structure Notes based on Teaching Company lectures, and associated undergraduate text with some additional material added. For a more detailed discussion, see the article by Peacock taken from
Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter
 Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter Jesús Zavala Franco e-mail: jzavalaf@uwaterloo.ca UW, Department of Physics and Astronomy, office: PHY 208C, ext. 38400 Perimeter Institute for
Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter Jesús Zavala Franco e-mail: jzavalaf@uwaterloo.ca UW, Department of Physics and Astronomy, office: PHY 208C, ext. 38400 Perimeter Institute for
TESTING GRAVITY WITH COSMOLOGY
 21 IV. TESTING GRAVITY WITH COSMOLOGY We now turn to the different ways with which cosmological observations can constrain modified gravity models. We have already seen that Solar System tests provide
21 IV. TESTING GRAVITY WITH COSMOLOGY We now turn to the different ways with which cosmological observations can constrain modified gravity models. We have already seen that Solar System tests provide
AST Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy. Lecture 1. Introduction/Background
 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Lecture 1 Introduction/Background 1 Relevant information: Pre-Midterm Schedule Week 1 (22/8-26/8) Week 2 (29/8-02/9) Lecture 1,2 Week 3 (05/9-09/9) Lecture
AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Lecture 1 Introduction/Background 1 Relevant information: Pre-Midterm Schedule Week 1 (22/8-26/8) Week 2 (29/8-02/9) Lecture 1,2 Week 3 (05/9-09/9) Lecture
Cosmology Lite. A brief treatment of some basic topics in cosmology. 1) Overall framework: expansion and three differential relations
 Cosmology Lite A brief treatment of some basic topics in cosmology 1) Overall framework: expansion and three differential relations 2) The Friedman equation and its solutions 3) The angular relations:
Cosmology Lite A brief treatment of some basic topics in cosmology 1) Overall framework: expansion and three differential relations 2) The Friedman equation and its solutions 3) The angular relations:
Lecture 8. Observational Cosmology. Parameters of Our Universe. The Concordance Model
 Lecture 8 Observational Cosmology Parameters of Our Universe The Concordance Model Time and Distance vs Redshift d dt x =1+ z = R 0 R dt = dx x H(x) Friedmann : H(x) = x 3 + Ω Λ + (1 Ω 0 ) x 2 look - back
Lecture 8 Observational Cosmology Parameters of Our Universe The Concordance Model Time and Distance vs Redshift d dt x =1+ z = R 0 R dt = dx x H(x) Friedmann : H(x) = x 3 + Ω Λ + (1 Ω 0 ) x 2 look - back
The Early Universe: A Journey into the Past
 Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity Galileo and falling
Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity Galileo and falling
Large Scale Structure After these lectures, you should be able to: Describe the matter power spectrum Explain how and why the peak position depends on
 Observational cosmology: Large scale structure Filipe B. Abdalla Kathleen Lonsdale Building G.22 http://zuserver2.star.ucl.ac.uk/~hiranya/phas3136/phas3136 Large Scale Structure After these lectures, you
Observational cosmology: Large scale structure Filipe B. Abdalla Kathleen Lonsdale Building G.22 http://zuserver2.star.ucl.ac.uk/~hiranya/phas3136/phas3136 Large Scale Structure After these lectures, you
Gravitation: Cosmology
 An Introduction to General Relativity Center for Relativistic Astrophysics School of Physics Georgia Institute of Technology Notes based on textbook: Spacetime and Geometry by S.M. Carroll Spring 2013
An Introduction to General Relativity Center for Relativistic Astrophysics School of Physics Georgia Institute of Technology Notes based on textbook: Spacetime and Geometry by S.M. Carroll Spring 2013
The Cosmic Microwave Background
 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney June 26, 2018 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney November 28, 2016 Cosmic star formation history inf 10 4 3 2 1 0 z Peak of
The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney June 26, 2018 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney November 28, 2016 Cosmic star formation history inf 10 4 3 2 1 0 z Peak of
CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks. Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI. l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu
 CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu Physical Landscape 100 IAB Sask 80 Viper BAM TOCO Sound Waves
CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu Physical Landscape 100 IAB Sask 80 Viper BAM TOCO Sound Waves
The Early Universe: A Journey into the Past
 The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Galileo and falling bodies Galileo Galilei: all bodies fall at the same speed force needed to accelerate a body is
The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Galileo and falling bodies Galileo Galilei: all bodies fall at the same speed force needed to accelerate a body is
El Universo en Expansion. Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004
 El Universo en Expansion Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004 5 billion years (you are here) Space is Homogeneous and Isotropic General Relativity An Expanding Universe
El Universo en Expansion Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004 5 billion years (you are here) Space is Homogeneous and Isotropic General Relativity An Expanding Universe
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Need for an exponential
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Need for an exponential
Chapter 23 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
Lecture 34. General relativity
 Lecture 34 The Shape of Space General Relativity Curvature of Space Critical Density Dark Energy Apr 17, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 34 1 General relativity So far, just needed simple Newton's Gravity. Because
Lecture 34 The Shape of Space General Relativity Curvature of Space Critical Density Dark Energy Apr 17, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 34 1 General relativity So far, just needed simple Newton's Gravity. Because
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe
 Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 7 Oct. 30, 2015 Today Relativistic Cosmology Dark Side of the Universe I: Dark Matter Assignments This week: read Hawley and
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 7 Oct. 30, 2015 Today Relativistic Cosmology Dark Side of the Universe I: Dark Matter Assignments This week: read Hawley and
Chapter 17 Cosmology
 Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
Outline. Cosmological parameters II. Deceleration parameter I. A few others. Covers chapter 6 in Ryden
 Outline Covers chapter 6 in Ryden Cosmological parameters I The most important ones in this course: M : Matter R : Radiation or DE : Cosmological constant or dark energy tot (or just ): Sum of the other
Outline Covers chapter 6 in Ryden Cosmological parameters I The most important ones in this course: M : Matter R : Radiation or DE : Cosmological constant or dark energy tot (or just ): Sum of the other
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence
 CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
AU/Mpc km/au s 1 (2) = s 1 (3) n(t 0 ) = ɛ(t 0) mc 2 (7) m(h) = m p = kg (8)
 Cosmology Solutions Useful constants: 1AU = 1.50 10 11 m 1pc = 206, 265AU G = 6.67 10 11 kg 1 m 3 s 2 M sun = 1.99 10 30 kg m proton = 1.67 10 27 kg 1. Cosmic density (a) Calculate the energy density of
Cosmology Solutions Useful constants: 1AU = 1.50 10 11 m 1pc = 206, 265AU G = 6.67 10 11 kg 1 m 3 s 2 M sun = 1.99 10 30 kg m proton = 1.67 10 27 kg 1. Cosmic density (a) Calculate the energy density of
Astro-2: History of the Universe
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 11; May 21 2013 Previously on astro-2 In an expanding universe the relationship between redshift and distance depends on the cosmological parameters (i.e. the geometry
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 11; May 21 2013 Previously on astro-2 In an expanding universe the relationship between redshift and distance depends on the cosmological parameters (i.e. the geometry
Cosmology. An Analogy 11/28/2010. Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe
 Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
Lecture 34: The Big Bang Readings: Sections 28-3 and 28-6
 Lecture 34: The Big Bang Readings: Sections 28-3 and 28-6 Key Ideas: Big Bang Model of the Universe Universe starts in a hot, dense state in the past Universe expands & cools with time Cosmological Redshift
Lecture 34: The Big Bang Readings: Sections 28-3 and 28-6 Key Ideas: Big Bang Model of the Universe Universe starts in a hot, dense state in the past Universe expands & cools with time Cosmological Redshift
Fire and Ice. The Fate of the Universe. Jon Thaler
 Fire and Ice The Fate of the Universe Jon Thaler Saturday Physics Honors Program Oct. 13, 2007 Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice. From what I've tasted of desire I hold with those who
Fire and Ice The Fate of the Universe Jon Thaler Saturday Physics Honors Program Oct. 13, 2007 Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice. From what I've tasted of desire I hold with those who
Chapter 23 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
Licia Verde. Introduction to cosmology. Lecture 4. Inflation
 Licia Verde Introduction to cosmology Lecture 4 Inflation Dividing line We see them like temperature On scales larger than a degree, fluctuations were outside the Hubble horizon at decoupling Potential
Licia Verde Introduction to cosmology Lecture 4 Inflation Dividing line We see them like temperature On scales larger than a degree, fluctuations were outside the Hubble horizon at decoupling Potential
Relativity, Gravitation, and Cosmology
 Relativity, Gravitation, and Cosmology A basic introduction TA-PEI CHENG University of Missouri St. Louis OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Parti RELATIVITY Metric Description of Spacetime 1 Introduction
Relativity, Gravitation, and Cosmology A basic introduction TA-PEI CHENG University of Missouri St. Louis OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Parti RELATIVITY Metric Description of Spacetime 1 Introduction
Ta-Pei Cheng PCNY 9/16/2011
 PCNY 9/16/2011 Ta-Pei Cheng For a more quantitative discussion, see Relativity, Gravitation & Cosmology: A Basic Introduction (Oxford Univ Press) 2 nd ed. (2010) dark matter & dark energy Astronomical
PCNY 9/16/2011 Ta-Pei Cheng For a more quantitative discussion, see Relativity, Gravitation & Cosmology: A Basic Introduction (Oxford Univ Press) 2 nd ed. (2010) dark matter & dark energy Astronomical
Outline. Covers chapter 2 + half of chapter 3 in Ryden
 Outline Covers chapter + half of chapter 3 in Ryden The Cosmological Principle I The cosmological principle The Cosmological Principle II Voids typically 70 Mpc across The Perfect Cosmological Principle
Outline Covers chapter + half of chapter 3 in Ryden The Cosmological Principle I The cosmological principle The Cosmological Principle II Voids typically 70 Mpc across The Perfect Cosmological Principle
Cosmology. Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure
 Cosmology Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure Cosmology from Large Scale Structure Sky Surveys Supernovae Ia CMB
Cosmology Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure Cosmology from Large Scale Structure Sky Surveys Supernovae Ia CMB
Olbers Paradox. Lecture 14: Cosmology. Resolutions of Olbers paradox. Cosmic redshift
 Lecture 14: Cosmology Olbers paradox Redshift and the expansion of the Universe The Cosmological Principle Ω and the curvature of space The Big Bang model Primordial nucleosynthesis The Cosmic Microwave
Lecture 14: Cosmology Olbers paradox Redshift and the expansion of the Universe The Cosmological Principle Ω and the curvature of space The Big Bang model Primordial nucleosynthesis The Cosmic Microwave
Astroparticle physics the History of the Universe
 Astroparticle physics the History of the Universe Manfred Jeitler and Wolfgang Waltenberger Institute of High Energy Physics, Vienna TU Vienna, CERN, Geneva Wintersemester 2016 / 2017 1 The History of
Astroparticle physics the History of the Universe Manfred Jeitler and Wolfgang Waltenberger Institute of High Energy Physics, Vienna TU Vienna, CERN, Geneva Wintersemester 2016 / 2017 1 The History of
Lecture notes 20: Inflation
 Lecture notes 20: Inflation The observed galaxies, quasars and supernovae, as well as observations of intergalactic absorption lines, tell us about the state of the universe during the period where z
Lecture notes 20: Inflation The observed galaxies, quasars and supernovae, as well as observations of intergalactic absorption lines, tell us about the state of the universe during the period where z
Vasiliki A. Mitsou. IFIC Valencia TAUP International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics
 Vasiliki A. Mitsou IFIC Valencia TAUP 2009 International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome, Italy, 1-5 July 2009 Dark energy models CDM Super-horizon CDM (SHCDM) [Kolb,
Vasiliki A. Mitsou IFIC Valencia TAUP 2009 International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome, Italy, 1-5 July 2009 Dark energy models CDM Super-horizon CDM (SHCDM) [Kolb,
Chapter 18. Cosmology. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 18 Cosmology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole
Chapter 18 Cosmology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole
May bring 1 sheet of paper with notes!! Both sides!! Printed/handwritten/whatever.. I don t really care
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p5_msrdg3hk This Class (Lecture 25): Death by Black Hole: Spaghettification Next Class: Compact Objects in the Solar System Night Obs due today HW9 due Monday Exam 2 next
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p5_msrdg3hk This Class (Lecture 25): Death by Black Hole: Spaghettification Next Class: Compact Objects in the Solar System Night Obs due today HW9 due Monday Exam 2 next
Outline. The Cosmological Principle II. The Perfect Cosmological Principle. The cosmological principle. Covers chapter 2 + half of chapter 3 in Ryden
 Outline Covers chapter 2 + half of chapter 3 in Ryden The Cosmological Principle I The Cosmological Principle II The cosmological principle Voids typically 70 Mpc across The Perfect Cosmological Principle
Outline Covers chapter 2 + half of chapter 3 in Ryden The Cosmological Principle I The Cosmological Principle II The cosmological principle Voids typically 70 Mpc across The Perfect Cosmological Principle
MIT Exploring Black Holes
 THE UNIVERSE and Three Examples Alan Guth, MIT MIT 8.224 Exploring Black Holes EINSTEIN'S CONTRIBUTIONS March, 1916: The Foundation of the General Theory of Relativity Feb, 1917: Cosmological Considerations
THE UNIVERSE and Three Examples Alan Guth, MIT MIT 8.224 Exploring Black Holes EINSTEIN'S CONTRIBUTIONS March, 1916: The Foundation of the General Theory of Relativity Feb, 1917: Cosmological Considerations
with Matter and Radiation By: Michael Solway
 Interactions of Dark Energy with Matter and Radiation By: Michael Solway Advisor: Professor Mike Berger What is Dark Energy? Dark energy is the energy needed to explain the observed accelerated expansion
Interactions of Dark Energy with Matter and Radiation By: Michael Solway Advisor: Professor Mike Berger What is Dark Energy? Dark energy is the energy needed to explain the observed accelerated expansion
Chapter 26: Cosmology
 Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Physical Cosmology 18/5/2017
 Physical Cosmology 18/5/2017 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2017 Summary If we consider perturbations in a pressureless
Physical Cosmology 18/5/2017 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2017 Summary If we consider perturbations in a pressureless
Week 2 Part 2. The Friedmann Models: What are the constituents of the Universe?
 Week Part The Friedmann Models: What are the constituents of the Universe? We now need to look at the expansion of the Universe described by R(τ) and its derivatives, and their relation to curvature. For
Week Part The Friedmann Models: What are the constituents of the Universe? We now need to look at the expansion of the Universe described by R(τ) and its derivatives, and their relation to curvature. For
PHY326/426:Lecture 19
 PHY326/426:Lecture 19 Dark Energy Finish WIMP signals Evidence for Dark Energy Type Ia Supernovae What is Dark Energy The fate of the Universe The Distance-Redshift relation Recall from lecture 2: The
PHY326/426:Lecture 19 Dark Energy Finish WIMP signals Evidence for Dark Energy Type Ia Supernovae What is Dark Energy The fate of the Universe The Distance-Redshift relation Recall from lecture 2: The
Dark Energy Task Force
 Dark Energy Task Force Nicholas Suntzeff Texas A&M 15 September 2006 Texas Cosmology Network Meeting Dark Energy Task Force (DETF) http://www.nsf.gov/mps/ast/detf.jsp Three agencies: Two subcommittees:
Dark Energy Task Force Nicholas Suntzeff Texas A&M 15 September 2006 Texas Cosmology Network Meeting Dark Energy Task Force (DETF) http://www.nsf.gov/mps/ast/detf.jsp Three agencies: Two subcommittees:
