The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Project. Steven M. Kahn SLAC Summer Institute August 4, 2005
|
|
|
- Everett Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Project Steven M. Kahn SLAC Summer Institute August 4, 2005
2 What is the LSST? * The LSST will be a large, wide-field ground-based telescope designed to provide time-lapse digital imaging of faint astronomical objects across the entire visible sky every few nights. * LSST will enable a wide variety of complementary scientific investigations, utilizing a common database. These range from searches for small bodies in the solar system to precision astrometry of the outer regions of the galaxy to systematic monitoring for transient phenomena in the optical sky. * Of particular interest for cosmology, LSST will provide strong constraints on models of dark matter and dark energy through weak lensing.
3 The LSST Consortium
4 The Essence of LSST is Deep, Wide, Fast! * Dark matter/dark energy via weak lensing * Dark matter/dark energy via supernovae * Dark energy via baryon acoustic oscillations * Galactic Structure encompassing local group * Dense astrometry over 20,000 sq.deg: rare moving objects * Gamma Ray Bursts and transients to high redshift * Gravitational micro-lensing * Strong galaxy & cluster lensing: physics of dark matter * Multi-image lensed SN time delays: separate test of cosmology * Variable stars/galaxies: black hole accretion * QSO time delays vs z: independent test of dark energy * Optical bursters to 25 mag: the unknown * 5-band 27 mag photometric survey: unprecedented volume * Solar System Probes: Earth-crossing asteroids, Comets, TNOs
5 Relative Survey Power
6 LSST and Dark Energy * LSST will measure 250,000 resolved high-redshift galaxies per square degree! The full survey will cover 18,000 square degrees. * Each galaxy will be moved on the sky and slightly distorted due to lensing by intervening dark matter. Using photometric redshifts, we can determine the shear as a function of z. * Measurements of weak lensing shear over a sufficient volume can determine DE parameters through constraints on the expansion history of the universe and the growth of structure with cosmic time.
7 Results from completed surveys Since the first detections reported in spring 2000, many cosmic shear measurements have been published. Results in 2001 In general there is good agreement between surveys!
8 Dealing with systematics The shear is a spin-2 field and consequently we can measure two independent ellipticity correlation functions. The lensing signal is caused by a gravitational potential and therefore should be curl-free. We can project the correlation functions into one that measures the divergence and one that measures the curl: E-B mode decomposition. E-mode (curl-free) B-mode (curl)
9
10
11
12 Color-redshift
13 LSST and Dark Energy * The LSST Weak Lensing Survey will constrain DE via a variety of related, but different techniques: Shear Tomography: The measurement of the large-angle shear power spectrum and higher moment correlations. With photo-z s, these can be measured as a function of cosmic time. Combining the shear power spectrum with the CMB fluctuation spectrum places constraints on w and w a. Cluster Counts Versus Redshift: The measurement of the number density of clusters as a function of mass and redshift - dn/dmdz. * These techniques have different dependences and different systematics. Probing the Concordance Cosmological Model in multiple ways is probably the best means we have of discovering new underlying physics.
14 Cosmological Constraints from Weak Lensing Shear Underlying physics is extremely simple General Relativity: FRW Universe plus the deflection formula. Any uncertainty in predictions arises from (in)ability to predict the mass distribution of the Universe Method 1: Operate on large scales in (nearly) linear regime. Predictions are as good as for CMB. Only "messy astrophysics" is to know redshift distribution of sources, which is measurable using photo-z s. Method 2: Operate in non-linear, non-gaussian regime. Applies to shear correlations at small angle. Predictions require N-body calculations, but to ~1% level are dark-matter dominated and hence purely gravitational and calculable with foreseeable resources. Hybrids: Combine CMB and weak lens shear vs redshift data. Cross correlations on all scales.
15 LSST Measurements of Cosmic Shear From Takada et al. (2005)
16 Constraints on DE Parameters From Takada et al. (2005)
17 Cluster Counting dn dωdz (w) = dv dωdz M limit (z) C(M,z) dn dm (M,z w)dm * The mass function is steep and exponentially sensitive to errors in M limit (z) and uncertainty in M(observables,z). * Measure mass function, determine M limit (z) from LSST cluster survey, devise a test that is insensitive to the limiting mass.
18 3D Mass Tomography From Wittman et al
19 X-ray follow-up Mass X-ray Courtesy Tony Tyson and the DLS Project Team
20 Cluster Counting Via WL Tomograhpy * dn/dmdz constrains DE models via the dependences on the co-moving volume element, dv/dωdz, and on the exponential growth of structure, δ(z). * Since WL measures DM mass directly, it does not suffer by the various forms of baryon bias and uncertainties in gas dynamical processes. * With a sky coverage of 18,000 square degrees, LSST will find 200,000 clusters. A sample this size will yield a measurement of w to 2-3%. From Haiman et al. (2005)
21 LSST Dark Energy Constraints from Cluster Analysis p/ρ = w 0 + w a (1-a) a = (1+z) -1
22 LSST SNe: Std Observations * SNe from standard survey observations ~250,000 Type Ia SNe found per year Redshift range 0.1 < z < 0.8 All followed with ~5 day cadence in one band (r), with 3 additional bands providing important color information for reddening, etc. Use host photo-z s of both the parent galaxies and the SNe themselves
23 Equation of State Dependence m m = m - m(w= 0.8) w = 1.0 w = 0.9 z w = 0.6 w = 0.4 Difference in apparent SN brightness vs. z Ω Λ =0.73*, flat cosmology
24 LSST SN Ia Redshift Distribution From Garnavich et al. (2005)
25 * Baryon acoustic oscillations in the early universe leave a signature in the matter power spectrum. * This has been detected at low redshift with SDSS. * At higher redshift, more peaks are discernible. Baryon Acoustic Oscillations * BAO s constrain DE via an angular diameter redshift relation. * LSST is competitive with true redshift surveys because of the huge number of galaxies surveyed.
26 LSST Optical Design
27 Optics Configuration * LSST Adopted Baseline Optical Design * M1 and M3 Surfaces Are Continuous at Edge
28 Crisp Images Over Entire Field L. Seppala, LLNL
29 Spin Casting of large optics at the U of A
30 The LBT 8.4m mirror cell with active optics
31 LSST Telescope Mount and Dome Concept
32 LSST Camera
33 Camera Challenges * Detector requirements: 10 µm pixel size Pixel full-well > 90,000 e Low noise (< 5 e rms), fast (< 2 sec) readout ( < 30 C) High QE nm All of above exist, but not simultaneously in one detector * Focal plane position precision of order 3 µm * Package large number of detectors, with integrated readout electronics, with high fill factor and serviceable design * Large diameter filter coatings * Constrained volume (camera in beam) Makes shutter, filter exchange mechanisms challenging * Constrained power dissipation to ambient To limit thermal gradients in optical beam Requires conductive cooling with low vibration
34 Science goals drive sensor requirements * High QE out to 1000nm thick silicon (> 75 µm) * PSF << 0.7 high internal field in the sensor high resistivity substrate (> 5 kohm cm) high applied voltages (> 50 V) * Fast f/1.2 focal ratio sensor flatness < 5µm package with piston, tip, tilt adjustable to ~1µm * Wide FOV 3200 cm 2 focal plane > 200-CCD mosaic (~16 cm 2 each) industrialized production process required * High throughput > 90% fill factor 4-side buttable package, sub-mm gaps * Fast readout highly-segmented sensors (~6400 output ports) > 150 I/O connections per package
35 Advances in State-of-the-Art needed for LSST Detector * The focal plane array will have about an order of magnitude larger number of pixels ( ~3 gigapixels) than the largest arrays realized so far. * The effective pixel readout speed will have to be about two orders of magnitude higher than in previous telescopes in order to achieve a readout time for the telescope of ~1-2 seconds. * The CCDs will have to have an active region ~100 µm thick to provide sufficiently high quantum efficiency at ~1000 nm, and they will have to be fully depleted (with no field free region) so that the signal charge is collected with minimum diffusion as needed to achieve a narrow point spread function. * Packaging ensuring sensor flatness and alignment in focal plane to <5µm (not achieved with presently delivered devices by industry). * Extensive use of ASICs to make the readout of a large number of output ports practical, and to reduce the number of output links and penetrations of the dewar.
36 LSST requires sensors in a new thickness range 100 epi thickness limit Limit of selfsupporting bulk wafers Operating Voltage commercial back-thinned CCDs: standard deep depletion LSST required range LBNL technology µm Thickness
37 Multi-port 4K x 4K = 16M CCD strawman 32 segments/ports Detail of output port Full CCD showing segmentation. Note pads on left and right edges only Detail of one edge Strawman has 208 bonding pads total J. Geary, LSST Strawman CCD Design, Dec. 2004
38 CCD Module Assembly Aluminum nitride carrier/pwb Invar frame
39 CCD Assembly AlN Raft structure K K FPA structure To ŅbackendÓelectronics
40 Modeling Deflections, gravity Normal modes Thermal x-y motions FPA Structure
41 Current baseline WFS Layout 3.5 FOV 64 cm X X X X X X 20 Curvature Sensors X X X X X X Shack Hartman Sensor X X X X X X X X X X X X Raft
42 Camera Electronics Architecture * Electronics is distributed over three thermal zones A front end zone, located closely behind the focal plane (analog). A back end zone, located further away, but inside the dewar (ADC, timing and control). External services located outside the inner dewar.
43 Camera Readout Architecture
44 Raft Structure
45 Camera Mechanical Layout 1.6m L1 L2 Shutter L3 Filter Detector array
46 Shutter Design One sheet design Simplest design, fewest moving parts, fits the limited space most easily Sheet Materials titanium or beryllium copper (good tradeoffs between modulus and yield strength)
47 Filter exchange mechanism 4-bar linkage allows filter to move past shutter and fit inside the outer camera Dewar
48 Filter exchange mechanism
49 LSST Data Rates * 3.2 billion pixels read out in less than 2 sec, every 12 sec * 1 pixel = 2 Bytes (raw) * Over 3 GBytes/sec peak raw data from camera * Real-time processing and transient detection: < 10 sec * Dynamic range: 4 Bytes / pixel * > 0.6 GB/sec average in pipeline * 5000 floating point operations per pixel * 2 TFlop/s average, 9 TFlop/s peak * ~ 18 Tbytes/night
50 Computation and Communications Load LSST Archive Center 22 PB/yr (uncomp.) :High- Speed Storage 1.0 Gbps 36.0 Gbps VO Server : Data Access Server 60 TFlop : Pipeline Server Gbps <= 1.0 Gbps <= 1.0 Gbps Tier 2-6 End User 10.0 Gbps 10.0 Gbps Tier 1 End User 10.0 Gbps LSST Data Center VO Server : Data Access Server 1.0 Gbps 22 PB/yr (uncomp.) :High-Speed Storage TFlop : Pipeline Server 25 Gbps 150 TB (uncomp.) :High- Speed Storage Mountain/Base Facilities < 0.1 Gbps 4 Gbps avg, <24.0 Gbps peak Data Management Subsystem Interface : Data Acquisition 4 Gbps < 0.1 Gbps LSST Camera Subsystem : Instrument Subsystem LSST OCS : Observatory Control System
51 Nominal Flow Diagram Sky Science Goals Optics Telescope Controller Scheduler Detectors Camera Controller Image QA Photometrically & Astrometrically Calibrated Template Register and Convolve Image Subtraction Image Archive Flatten Crosstalk, Linearity, etc. Diagnostics (CTE, noise) Source Detection Astrometry WCS update Camera QA CTE, noise... Calibration Library Astrometric Catalog Table Image QA Known Variable Table Difference Object Detection New Detections Table Classifier Astrometrically Calibrated Flatfielded Image Photometry Pipeline Source insertion for detection efficiency determination Photometric Standards Fake object table N Known? Co-added Image Archive Calculate Phot. Calib. CoeffÕs Analysis Packages 1-N Phot. Calibration Table QA Alert Table Detections Table Source insertion for detection efficiency determination Fake Object Table Alert Protocol Aggregation Utility Match and Orbits Table
52 LSST Final Three Sites San Pedro Martir Cerro Pachon Las Campanas
53 LSST Simulators Sheared HDF raytraced + perturbation + atmosphere + wind + pixel LSST Operations, including real weather data: coverage + depth
54 Observation Simulator
55 End-to to-end Simulations Piece of complete Monte Carlo Simulation of the UDF through Atmosphere and optics photons in 20 cpu hours End to End Simulator: Accepts Sky images and SEDs Uses refractive raytrace through screens of Kolmogorov atmospheric turbulence Raytraces complete LSST optics+pert. Simulates detector conversion/diffusion
56 Optics/Detector Simulations Complete Optics/Detector Raytrace Perturbation amplitude vs. Zernike number Optics may contribute Some to the ellipticity of the PSF, but it is highly correlated since the three mirrors are close to the pupil plane Spot diagrams of optics only simulation separated by 0.5 degrees
57 Atmospheric Simulations PSF ellipticity due to averaging over a finite number of turbulent cells. Decorrelates due to high altitude layers but will have enough stars to interpolate at LSST depth and correlation scale Kolmogorov Phase Screen Number of cells ~ (D w t) <e> ~ (D w t) 0.5 ~ D 0.5 / (A w t) 0.5 Correlation angle ~ D / h -> Decorrelation ~ 1/D 0.5 for same depth
58 Project Baseline Schedule Plans CY 05 CY 06 CY 07 CY 08 CY 09 CY 10 CY 11 CY 12 CY 13 NSF D & D Phase Submit MREFC MREFC Construction Phase MREFC Award Comm&Science First Light Telescope Camera Mirror Fabrication/ Cell Assembly Site Preparation Mount/Dome System Integration Camera Design Camera fabrication & integration Sensor Dev l and protoype Sensor Fabrication Data Mngt Software Preliminary Design Software Final Design SoftwareValidation Software Integration
59 Summary * The LSST will enable many diverse investigations in astronomy through a single common database. * Of particular interest for cosmology, it will provide a rich sample of high-z lensed galaxies that will yield multiple probes of the concordance cosmological model. * The LSST camera presents many interesting experimental challenges. While a basic strawman design exists, a significant R&D effort is required in several key areas. * Additional effort is needed to address the demanding requirements on the data management system imposed by the very high data rate, high data volume, and real-time alert functions. * Ultimately, however, we expect the LSST to have very high impact on the field.
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
 The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope. Steven M. Kahn Presentation to the SLAC Program Review Committee - June 2, 2004
 The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Steven M. Kahn Presentation to the SLAC Program Review Committee - June 2, 2004 What is the LSST? * The LSST will be a large, wide-field ground-based telescope designed
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Steven M. Kahn Presentation to the SLAC Program Review Committee - June 2, 2004 What is the LSST? * The LSST will be a large, wide-field ground-based telescope designed
An end-to-end simulation framework for the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Andrew Connolly University of Washington
 An end-to-end simulation framework for the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Andrew Connolly University of Washington LSST in a nutshell The LSST will be a large, wide-field, ground-based optical/near-ir
An end-to-end simulation framework for the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Andrew Connolly University of Washington LSST in a nutshell The LSST will be a large, wide-field, ground-based optical/near-ir
Astronomy of the Next Decade: From Photons to Petabytes. R. Chris Smith AURA Observatory in Chile CTIO/Gemini/SOAR/LSST
 Astronomy of the Next Decade: From Photons to Petabytes R. Chris Smith AURA Observatory in Chile CTIO/Gemini/SOAR/LSST Classical Astronomy still dominates new facilities Even new large facilities (VLT,
Astronomy of the Next Decade: From Photons to Petabytes R. Chris Smith AURA Observatory in Chile CTIO/Gemini/SOAR/LSST Classical Astronomy still dominates new facilities Even new large facilities (VLT,
New Directions in Observational Cosmology: A New View of our Universe Tony Tyson UC Davis
 New Directions in Observational Cosmology: A New View of our Universe Tony Tyson UC Davis Berkeley May 4, 2007 Technology drives the New Sky! Microelectronics! Software! Large Optics Fabrication Wide+Deep+Fast:
New Directions in Observational Cosmology: A New View of our Universe Tony Tyson UC Davis Berkeley May 4, 2007 Technology drives the New Sky! Microelectronics! Software! Large Optics Fabrication Wide+Deep+Fast:
Scientific Data Flood. Large Science Project. Pipeline
 The Scientific Data Flood Scientific Data Flood Large Science Project Pipeline 1 1 The Dark Energy Survey Study Dark Energy using four complementary* techniques: I. Cluster Counts II. Weak Lensing III.
The Scientific Data Flood Scientific Data Flood Large Science Project Pipeline 1 1 The Dark Energy Survey Study Dark Energy using four complementary* techniques: I. Cluster Counts II. Weak Lensing III.
Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
 Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Željko Ivezić University of Washington Santa Barbara, March 14, 2006 1 Outline 1. LSST baseline design Monolithic 8.4 m aperture, 10 deg 2 FOV, 3.2 Gpix camera 2. LSST science
Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Željko Ivezić University of Washington Santa Barbara, March 14, 2006 1 Outline 1. LSST baseline design Monolithic 8.4 m aperture, 10 deg 2 FOV, 3.2 Gpix camera 2. LSST science
LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST
 LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST Steven M. Kahn Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Stanford University SMK Perspective I believe I bring three potentially
LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST Steven M. Kahn Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Stanford University SMK Perspective I believe I bring three potentially
The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe
 Lecture 15 The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe Intensity weighted second moments Optimal filtering Weak gravitational lensing Shear components Shear detection Inverse problem:
Lecture 15 The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe Intensity weighted second moments Optimal filtering Weak gravitational lensing Shear components Shear detection Inverse problem:
An Introduction to the Dark Energy Survey
 An Introduction to the Dark Energy Survey A study of the dark energy using four independent and complementary techniques Blanco 4m on Cerro Tololo Galaxy cluster surveys Weak lensing Galaxy angular power
An Introduction to the Dark Energy Survey A study of the dark energy using four independent and complementary techniques Blanco 4m on Cerro Tololo Galaxy cluster surveys Weak lensing Galaxy angular power
Cosmic acceleration. Questions: What is causing cosmic acceleration? Vacuum energy (Λ) or something else? Dark Energy (DE) or Modification of GR (MG)?
 Cosmic acceleration 1998 Discovery 2000-2010: confirmation (CMB, LSS, SNe) more precise constraints w = -1 ± 0.2 (with assumptions) Questions: What is causing cosmic acceleration? Vacuum energy (Λ) or
Cosmic acceleration 1998 Discovery 2000-2010: confirmation (CMB, LSS, SNe) more precise constraints w = -1 ± 0.2 (with assumptions) Questions: What is causing cosmic acceleration? Vacuum energy (Λ) or
LSST. Pierre Antilogus LPNHE-IN2P3, Paris. ESO in the 2020s January 19-22, LSST ESO in the 2020 s 1
 LSST Pierre Antilogus LPNHE-IN2P3, Paris ESO in the 2020s January 19-22, 2015 LSST ESO in the 2020 s 1 LSST in a Nutshell The LSST is an integrated survey system designed to conduct a decadelong, deep,
LSST Pierre Antilogus LPNHE-IN2P3, Paris ESO in the 2020s January 19-22, 2015 LSST ESO in the 2020 s 1 LSST in a Nutshell The LSST is an integrated survey system designed to conduct a decadelong, deep,
2-D Images in Astronomy
 2-D Images in Astronomy ZTF camera FOV is 50 square degrees. Largest camera on >1m telescope by area in the world. Or, to make a little clearer, here s Orion. The white box is the ZTF imaging area. The
2-D Images in Astronomy ZTF camera FOV is 50 square degrees. Largest camera on >1m telescope by area in the world. Or, to make a little clearer, here s Orion. The white box is the ZTF imaging area. The
Real Astronomy from Virtual Observatories
 THE US NATIONAL VIRTUAL OBSERVATORY Real Astronomy from Virtual Observatories Robert Hanisch Space Telescope Science Institute US National Virtual Observatory About this presentation What is a Virtual
THE US NATIONAL VIRTUAL OBSERVATORY Real Astronomy from Virtual Observatories Robert Hanisch Space Telescope Science Institute US National Virtual Observatory About this presentation What is a Virtual
Dark Energy. Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey. Survey (DES)
 Dark Energy Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey Survey (DES) What is it? The DES Collaboration will build and use a wide field optical imager (DECam) to perform a wide area,
Dark Energy Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey Survey (DES) What is it? The DES Collaboration will build and use a wide field optical imager (DECam) to perform a wide area,
The Baryon Acoustic Peak (BAP) in the correlation function clustering of the SDSS LRG 47k galaxy sample, and is sensitive to the matter density
 JP AU AS PAU-BRASIL The Baryon Acoustic Peak (BAP) in the correlation function clustering of the SDSS LRG 47k galaxy sample, and is sensitive to the matter density (shown are models with Ω m h 2 = 0.12
JP AU AS PAU-BRASIL The Baryon Acoustic Peak (BAP) in the correlation function clustering of the SDSS LRG 47k galaxy sample, and is sensitive to the matter density (shown are models with Ω m h 2 = 0.12
Weak Gravitational Lensing. Gary Bernstein, University of Pennsylvania KICP Inaugural Symposium December 10, 2005
 Weak Gravitational Lensing Gary Bernstein, University of Pennsylvania KICP Inaugural Symposium December 10, 2005 astrophysics is on the 4th floor... President Amy Gutmann 215 898 7221 Physics Chair Tom
Weak Gravitational Lensing Gary Bernstein, University of Pennsylvania KICP Inaugural Symposium December 10, 2005 astrophysics is on the 4th floor... President Amy Gutmann 215 898 7221 Physics Chair Tom
Some issues in cluster cosmology
 Some issues in cluster cosmology Tim McKay University of Michigan Department of Physics 1/30/2002 CFCP Dark Energy Workshop 1 An outline Cluster counting in theory Cluster counting in practice General
Some issues in cluster cosmology Tim McKay University of Michigan Department of Physics 1/30/2002 CFCP Dark Energy Workshop 1 An outline Cluster counting in theory Cluster counting in practice General
Cosmology with the ESA Euclid Mission
 Cosmology with the ESA Euclid Mission Andrea Cimatti Università di Bologna Dipartimento di Astronomia On behalf of the Euclid Italy Team ESA Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 M-class Mission Candidate Selected in
Cosmology with the ESA Euclid Mission Andrea Cimatti Università di Bologna Dipartimento di Astronomia On behalf of the Euclid Italy Team ESA Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 M-class Mission Candidate Selected in
Weak Lensing (and other) Measurements from Ground and Space Observatories
 Weak Lensing (and other) Measurements from Ground and Space Observatories Gary Bernstein CfCP Workshop 12/16/01 1. Present State of the Art: New Results from the CTIO Weak Lensing Survey. Mike Jarvis GMB,
Weak Lensing (and other) Measurements from Ground and Space Observatories Gary Bernstein CfCP Workshop 12/16/01 1. Present State of the Art: New Results from the CTIO Weak Lensing Survey. Mike Jarvis GMB,
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Cosmology with Wide Field Astronomy
 M. Moniez To cite this version: M. Moniez.. 35th International Conference on High Energy Physics (ICHEP2010), Jul 2010, Paris, France. Proceedings of Science, 441 (4 p.), 2010. HAL Id:
M. Moniez To cite this version: M. Moniez.. 35th International Conference on High Energy Physics (ICHEP2010), Jul 2010, Paris, France. Proceedings of Science, 441 (4 p.), 2010. HAL Id:
Classical Interferometric Arrays. Andreas Quirrenbach Landessternwarte Heidelberg
 Classical Interferometric Arrays Andreas Quirrenbach Landessternwarte Heidelberg The VLT Interferometer Tucson 11/14/2006 Andreas Quirrenbach 2 Optical / Infrared Interferometry Today Access to milliarcsecond-scale
Classical Interferometric Arrays Andreas Quirrenbach Landessternwarte Heidelberg The VLT Interferometer Tucson 11/14/2006 Andreas Quirrenbach 2 Optical / Infrared Interferometry Today Access to milliarcsecond-scale
Dark Energy Research at SLAC
 Dark Energy Research at SLAC Steven M. Kahn, SLAC / KIPAC Sept 14, 2010 DOE Site Visit: Sept 13-14, 2010 1 Constraining the Properties of Dark Energy The discovery of dark energy in the late 90 s has profound
Dark Energy Research at SLAC Steven M. Kahn, SLAC / KIPAC Sept 14, 2010 DOE Site Visit: Sept 13-14, 2010 1 Constraining the Properties of Dark Energy The discovery of dark energy in the late 90 s has profound
Grand Canyon 8-m Telescope 1929
 1 2 Grand Canyon 8-m Telescope 1929 3 A World-wide Sample of Instruments 4 Instrumentation Details Instrument name Observing Modes Start of operations Wavelength Coverage Field of View Instrument cost
1 2 Grand Canyon 8-m Telescope 1929 3 A World-wide Sample of Instruments 4 Instrumentation Details Instrument name Observing Modes Start of operations Wavelength Coverage Field of View Instrument cost
Large Imaging Surveys for Cosmology:
 Large Imaging Surveys for Cosmology: cosmic magnification AND photometric calibration Alexandre Boucaud Thesis work realized at APC under the supervision of James G. BARTLETT and Michel CRÉZÉ Outline Introduction
Large Imaging Surveys for Cosmology: cosmic magnification AND photometric calibration Alexandre Boucaud Thesis work realized at APC under the supervision of James G. BARTLETT and Michel CRÉZÉ Outline Introduction
Plato, Euclid and the New Hard X-Ray mission
 Schiaparelli and his Legacy Meeting on Future planetary, scientific and robotic space missions Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria, Torino, 21/10/2010 Template reference : 100181670S-EN Plato, Euclid and
Schiaparelli and his Legacy Meeting on Future planetary, scientific and robotic space missions Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria, Torino, 21/10/2010 Template reference : 100181670S-EN Plato, Euclid and
Photometric Products. Robert Lupton, Princeton University LSST Pipeline/Calibration Scientist PST/SAC PST/SAC,
 Photometric Products Robert Lupton, Princeton University LSST Pipeline/Calibration Scientist PST/SAC 2018-02-27 PST/SAC, 2018-02-27 LSST2017 Tucson, AZ August 14-18, 2017 1 Outline Photometry Point Sources
Photometric Products Robert Lupton, Princeton University LSST Pipeline/Calibration Scientist PST/SAC 2018-02-27 PST/SAC, 2018-02-27 LSST2017 Tucson, AZ August 14-18, 2017 1 Outline Photometry Point Sources
1 A photometric probe for Pan-STARRS
 The Pan-STARRS Imaging Sky Probe B.R. Granett, K.C. Chambers, E.A. Magnier, K. Fletcher and the Pan-STARRS Project Team University of Hawai i Institute for Astronomy Abstract Photometric performance is
The Pan-STARRS Imaging Sky Probe B.R. Granett, K.C. Chambers, E.A. Magnier, K. Fletcher and the Pan-STARRS Project Team University of Hawai i Institute for Astronomy Abstract Photometric performance is
Image Processing in Astronomy: Current Practice & Challenges Going Forward
 Image Processing in Astronomy: Current Practice & Challenges Going Forward Mario Juric University of Washington With thanks to Andy Connolly, Robert Lupton, Ian Sullivan, David Reiss, and the LSST DM Team
Image Processing in Astronomy: Current Practice & Challenges Going Forward Mario Juric University of Washington With thanks to Andy Connolly, Robert Lupton, Ian Sullivan, David Reiss, and the LSST DM Team
MAORY (Multi conjugate Adaptive Optics RelaY) for E-ELT. Paolo Ciliegi. On behalf of the MAORY Consortium
 MAORY (Multi conjugate Adaptive Optics RelaY) for E-ELT Paolo Ciliegi INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna On behalf of the MAORY Consortium Science ELT Workshop Team Meeting ESO Garching, MPE Garching,
MAORY (Multi conjugate Adaptive Optics RelaY) for E-ELT Paolo Ciliegi INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna On behalf of the MAORY Consortium Science ELT Workshop Team Meeting ESO Garching, MPE Garching,
Synergies between and E-ELT
 Synergies between and E-ELT Aprajita Verma & Isobel Hook 1) E- ELT Summary 2) E- ELT Project Status 3) Parameter space 4) Examples of scientific synergies The World s Biggest Eye on the Sky 39.3m diameter,
Synergies between and E-ELT Aprajita Verma & Isobel Hook 1) E- ELT Summary 2) E- ELT Project Status 3) Parameter space 4) Examples of scientific synergies The World s Biggest Eye on the Sky 39.3m diameter,
Calibration Goals and Plans
 CHAPTER 13 Calibration Goals and Plans In This Chapter... Expected Calibration Accuracies / 195 Calibration Plans / 197 This chapter describes the expected accuracies which should be reached in the calibration
CHAPTER 13 Calibration Goals and Plans In This Chapter... Expected Calibration Accuracies / 195 Calibration Plans / 197 This chapter describes the expected accuracies which should be reached in the calibration
Wide and Fast: A new Era of EMCCD and CMOS?
 Wide and Fast: A new Era of EMCCD and CMOS? ZTF PTF?????? Gregg Hallinan California Institute of Technology gh@astro.caltech.edu Negligible 1 sec Transient Phase Space: Mansi Kasliwal Conventional CCDs
Wide and Fast: A new Era of EMCCD and CMOS? ZTF PTF?????? Gregg Hallinan California Institute of Technology gh@astro.caltech.edu Negligible 1 sec Transient Phase Space: Mansi Kasliwal Conventional CCDs
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans. Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04
 LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
Collecting Light. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris is fully open and the pupil has a diameter of about 7 mm. pupil
 Telescopes Collecting Light The simplest means of observing the Universe is the eye. The human eye is sensitive to light with a wavelength of about 400 and 700 nanometers. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris
Telescopes Collecting Light The simplest means of observing the Universe is the eye. The human eye is sensitive to light with a wavelength of about 400 and 700 nanometers. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris
Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey
 Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey J. Craig Wheeler Department of Astronomy University of Texas at Austin (adapted from presentation by Josh Frieman) Texas Cosmology
Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey J. Craig Wheeler Department of Astronomy University of Texas at Austin (adapted from presentation by Josh Frieman) Texas Cosmology
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future
 JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
From DES to LSST. Transient Processing Goes from Hours to Seconds. Eric Morganson, NCSA LSST Time Domain Meeting Tucson, AZ May 22, 2017
 From DES to LSST Transient Processing Goes from Hours to Seconds Eric Morganson, NCSA LSST Time Domain Meeting Tucson, AZ May 22, 2017 Hi, I m Eric Dr. Eric Morganson, Research Scientist, Nation Center
From DES to LSST Transient Processing Goes from Hours to Seconds Eric Morganson, NCSA LSST Time Domain Meeting Tucson, AZ May 22, 2017 Hi, I m Eric Dr. Eric Morganson, Research Scientist, Nation Center
LSST Science. Željko Ivezić, LSST Project Scientist University of Washington
 LSST Science Željko Ivezić, LSST Project Scientist University of Washington LSST@Europe, Cambridge, UK, Sep 9-12, 2013 OUTLINE Brief overview of LSST science drivers LSST science-driven design Examples
LSST Science Željko Ivezić, LSST Project Scientist University of Washington LSST@Europe, Cambridge, UK, Sep 9-12, 2013 OUTLINE Brief overview of LSST science drivers LSST science-driven design Examples
Laboratory Emulation of Observations from Space
 Science with a Wide-field Infrared Telescopes in Space, Pasadena, Feb 13, 2012 of Observations from Space Roger Smith -- Caltech Jason Rhodes, Suresh Seshadri -- JPL Previous culture, friendly collaboration
Science with a Wide-field Infrared Telescopes in Space, Pasadena, Feb 13, 2012 of Observations from Space Roger Smith -- Caltech Jason Rhodes, Suresh Seshadri -- JPL Previous culture, friendly collaboration
Data Processing in DES
 Data Processing in DES Brian Yanny Oct 28, 2016 http://data.darkenergysurvey.org/fnalmisc/talk/detrend.p Basic Signal-to-Noise calculation in astronomy: Assuming a perfect atmosphere (fixed PSF of p arcsec
Data Processing in DES Brian Yanny Oct 28, 2016 http://data.darkenergysurvey.org/fnalmisc/talk/detrend.p Basic Signal-to-Noise calculation in astronomy: Assuming a perfect atmosphere (fixed PSF of p arcsec
Cosmology. Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure
 Cosmology Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure Cosmology from Large Scale Structure Sky Surveys Supernovae Ia CMB
Cosmology Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure Cosmology from Large Scale Structure Sky Surveys Supernovae Ia CMB
Telescopes, Observatories, Data Collection
 Telescopes, Observatories, Data Collection Telescopes 1 Astronomy : observational science only input is the light received different telescopes, different wavelengths of light lab experiments with spectroscopy,
Telescopes, Observatories, Data Collection Telescopes 1 Astronomy : observational science only input is the light received different telescopes, different wavelengths of light lab experiments with spectroscopy,
EUCLID Spectroscopy. Andrea Cimatti. & the EUCLID-NIS Team. University of Bologna Department of Astronomy
 EUCLID Spectroscopy Andrea Cimatti University of Bologna Department of Astronomy & the EUCLID-NIS Team Observing the Dark Universe with EUCLID, ESA ESTEC, 17 November 2009 DARK Universe (73% Dark Energy
EUCLID Spectroscopy Andrea Cimatti University of Bologna Department of Astronomy & the EUCLID-NIS Team Observing the Dark Universe with EUCLID, ESA ESTEC, 17 November 2009 DARK Universe (73% Dark Energy
SkyMapper and the Southern Sky Survey
 and the Southern Sky Survey, Brian Schmidt and Mike Bessell Slide 1 What is? 1.35m telescope with a 5.7 sq. degree field of view To reside at Siding Spring Observatory, NSW To conduct the Southern Sky
and the Southern Sky Survey, Brian Schmidt and Mike Bessell Slide 1 What is? 1.35m telescope with a 5.7 sq. degree field of view To reside at Siding Spring Observatory, NSW To conduct the Southern Sky
The Dark Energy Survey Public Data Release 1
 The Dark Energy Survey Public Data Release 1 Matias Carrasco Kind (NCSA/UIUC) and the DR1 Release Team https://des.ncsa.illinois.edu/ Near-Field Cosmology with DES DR1 and Beyond Workshop, June 27-29th,
The Dark Energy Survey Public Data Release 1 Matias Carrasco Kind (NCSA/UIUC) and the DR1 Release Team https://des.ncsa.illinois.edu/ Near-Field Cosmology with DES DR1 and Beyond Workshop, June 27-29th,
PISCO Progress. Antony A. Stark, Christopher Stubbs Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory 20 March 2009
 PISCO Progress Antony A. Stark, Christopher Stubbs Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory 20 March 2009 PISCO Overview South Pole Telescope Survey is underway: 200 square degrees observed so far, 1000 square
PISCO Progress Antony A. Stark, Christopher Stubbs Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory 20 March 2009 PISCO Overview South Pole Telescope Survey is underway: 200 square degrees observed so far, 1000 square
Point spread function reconstruction at W.M. Keck Observatory : progress and beyond
 Point spread function reconstruction at W.M. Keck Observatory : progress and beyond Olivier Beltramo-Martin Aix-Marseille Univ., LAM, A*MIDEX, Extra November 9th, 217 - LAM Olivier Beltramo-Martin (LAM)
Point spread function reconstruction at W.M. Keck Observatory : progress and beyond Olivier Beltramo-Martin Aix-Marseille Univ., LAM, A*MIDEX, Extra November 9th, 217 - LAM Olivier Beltramo-Martin (LAM)
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY. Observational Astronomy (2011) 1
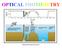 OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
Detection of Artificial Satellites in Images Acquired in Track Rate Mode.
 Detection of Artificial Satellites in Images Acquired in Track Rate Mode. Martin P. Lévesque Defence R&D Canada- Valcartier, 2459 Boul. Pie-XI North, Québec, QC, G3J 1X5 Canada, martin.levesque@drdc-rddc.gc.ca
Detection of Artificial Satellites in Images Acquired in Track Rate Mode. Martin P. Lévesque Defence R&D Canada- Valcartier, 2459 Boul. Pie-XI North, Québec, QC, G3J 1X5 Canada, martin.levesque@drdc-rddc.gc.ca
TMT and Space-Based Survey Missions
 TMT and Space-Based Survey Missions Daniel Stern Jet Propulsion Laboratory/ California Institute of Technology 2014 California Institute of Technology TMT Science Forum 2014 July 17 Outline Summary of
TMT and Space-Based Survey Missions Daniel Stern Jet Propulsion Laboratory/ California Institute of Technology 2014 California Institute of Technology TMT Science Forum 2014 July 17 Outline Summary of
Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy. Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017
 Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017 Reminders Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm One more lecture after today Monday
Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017 Reminders Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm One more lecture after today Monday
NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ
 FMOS status tt report Science workshop 2011.02.2802 28-03.0202 NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ * Overview * Recent history & current status t * Schedule & future plan
FMOS status tt report Science workshop 2011.02.2802 28-03.0202 NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ * Overview * Recent history & current status t * Schedule & future plan
Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe. Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007
 Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007 Overview How do we measure expansion? Use of supernovae 1a as a good measuring stick Techniques for observing supernovae
Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007 Overview How do we measure expansion? Use of supernovae 1a as a good measuring stick Techniques for observing supernovae
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds. Chapter 6. Light and Telescopes
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes Guidepost In this chapter, you will consider the techniques astronomers use to study the Universe What is light? How do telescopes work?
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes Guidepost In this chapter, you will consider the techniques astronomers use to study the Universe What is light? How do telescopes work?
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method
 Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Cherenkov Telescope Array Status Report. Salvatore Mangano (CIEMAT) On behalf of the CTA consortium
 Cherenkov Telescope Array Status Report Salvatore Mangano (CIEMAT) On behalf of the CTA consortium Outline Very-High-Energy Gamma-Ray Astronomy Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA) Expected Performance of CTA
Cherenkov Telescope Array Status Report Salvatore Mangano (CIEMAT) On behalf of the CTA consortium Outline Very-High-Energy Gamma-Ray Astronomy Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA) Expected Performance of CTA
HETDEX Overview. Hobby Eberly Telescope Dark Energy Experiment. HETDEX is: HETDEX enables a lot of ancillary science. HETDEX Science Workshop Feb 09
 Introduction to WFU, VIRUS, & DEX Gary J. Hill, McDonald Observatory Scope What HETDEX is WFU VIRUS DEX survey parameters 1 HETDEX is: Upgrade of HET to have a new 22 arcmin wide field of view Deployment
Introduction to WFU, VIRUS, & DEX Gary J. Hill, McDonald Observatory Scope What HETDEX is WFU VIRUS DEX survey parameters 1 HETDEX is: Upgrade of HET to have a new 22 arcmin wide field of view Deployment
Astronomy. Optics and Telescopes
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Optics and Telescopes - Refraction, lenses and refracting telescopes - Mirrors and reflecting telescopes - Diffraction limit,
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Optics and Telescopes - Refraction, lenses and refracting telescopes - Mirrors and reflecting telescopes - Diffraction limit,
Hanle Echelle Spectrograph (HESP)
 Hanle Echelle Spectrograph (HESP) Bench mounted High resolution echelle spectrograph fed by Optical Fiber Second generation instrument for HCT The project is a technical collaboration between Indian Institute
Hanle Echelle Spectrograph (HESP) Bench mounted High resolution echelle spectrograph fed by Optical Fiber Second generation instrument for HCT The project is a technical collaboration between Indian Institute
Microlensing Studies in Crowded Fields. Craig Mackay, Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge.
 Microlensing Studies in Crowded Fields Craig Mackay, Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge. Introduction and Outline Will start by summarising the constraints we must work with in order to detect
Microlensing Studies in Crowded Fields Craig Mackay, Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge. Introduction and Outline Will start by summarising the constraints we must work with in order to detect
Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging
 Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging C. F. Claver 3 September 1997 Overview Image motion studies done at WIYN show that a significant improvement to delivered image quality can be obtained from
Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging C. F. Claver 3 September 1997 Overview Image motion studies done at WIYN show that a significant improvement to delivered image quality can be obtained from
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 31 Aug 2005
 Spurious Shear from the Atmosphere in Ground-Based Weak Lensing Observations D. Wittman 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0509003v1 31 Aug 2005 ABSTRACT Weak lensing observations have the potential to be even more powerful
Spurious Shear from the Atmosphere in Ground-Based Weak Lensing Observations D. Wittman 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0509003v1 31 Aug 2005 ABSTRACT Weak lensing observations have the potential to be even more powerful
FMOS. A Wide-field Multi-Object Infra-red Spectrograph for the Subaru Telescope. David Bonfield, Gavin Dalton
 FMOS A Wide-field Multi-Object Infra-red Spectrograph for the Subaru Telescope David Bonfield, Gavin Dalton David Bonfield Oxford University Wide Field NIR Spectroscopy WFCAM, VISTA are about to deliver
FMOS A Wide-field Multi-Object Infra-red Spectrograph for the Subaru Telescope David Bonfield, Gavin Dalton David Bonfield Oxford University Wide Field NIR Spectroscopy WFCAM, VISTA are about to deliver
Stellar Observations Network Group
 Stellar Observations Network Group Frank Grundahl, Jørgen Christensen Dalsgaard, Uffe Gråe Jørgensen, Hans Kjeldsen, Søren Frandsen, Per Kjærgaard Rasmussen + participation from IAC (Pere Pallé, Orlagh
Stellar Observations Network Group Frank Grundahl, Jørgen Christensen Dalsgaard, Uffe Gråe Jørgensen, Hans Kjeldsen, Søren Frandsen, Per Kjærgaard Rasmussen + participation from IAC (Pere Pallé, Orlagh
Modern Image Processing Techniques in Astronomical Sky Surveys
 Modern Image Processing Techniques in Astronomical Sky Surveys Items of the PhD thesis József Varga Astronomy MSc Eötvös Loránd University, Faculty of Science PhD School of Physics, Programme of Particle
Modern Image Processing Techniques in Astronomical Sky Surveys Items of the PhD thesis József Varga Astronomy MSc Eötvös Loránd University, Faculty of Science PhD School of Physics, Programme of Particle
Astrometry (STEP) M. Shao
 Technical Issues for Narrow Angle Astrometry (STEP) M. Shao Outline Ground based narrow angle astrometry Current state of the art (0.5~1 mas (in 30 min) What are the limiting error sources Photon noise
Technical Issues for Narrow Angle Astrometry (STEP) M. Shao Outline Ground based narrow angle astrometry Current state of the art (0.5~1 mas (in 30 min) What are the limiting error sources Photon noise
Baryon acoustic oscillations A standard ruler method to constrain dark energy
 Baryon acoustic oscillations A standard ruler method to constrain dark energy Martin White University of California, Berkeley Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory... with thanks to Nikhil Padmanabhan
Baryon acoustic oscillations A standard ruler method to constrain dark energy Martin White University of California, Berkeley Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory... with thanks to Nikhil Padmanabhan
RLW paper titles:
 RLW paper titles: http://www.wordle.net Astronomical Surveys and Data Archives Richard L. White Space Telescope Science Institute HiPACC Summer School, July 2012 Overview Surveys & catalogs: Fundamental
RLW paper titles: http://www.wordle.net Astronomical Surveys and Data Archives Richard L. White Space Telescope Science Institute HiPACC Summer School, July 2012 Overview Surveys & catalogs: Fundamental
CHARA Collaboration Year-Eight Science Review. VLTI update. F. Delplancke
 VLTI update F. Delplancke Summary Infrastructure Current instruments: MIDI, AMBER, PIONIER Under test & commissioning: PRIMA 2 nd generation instruments Long Range Plan Infrastructure Infrastructure 4
VLTI update F. Delplancke Summary Infrastructure Current instruments: MIDI, AMBER, PIONIER Under test & commissioning: PRIMA 2 nd generation instruments Long Range Plan Infrastructure Infrastructure 4
Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background
 Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background Masato Shirasaki (Univ. of Tokyo) with Shunsaku Horiuchi (UCI), Naoki Yoshida (Univ. of Tokyo, IPMU) Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Background
Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background Masato Shirasaki (Univ. of Tokyo) with Shunsaku Horiuchi (UCI), Naoki Yoshida (Univ. of Tokyo, IPMU) Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Background
The Transneptunian Automated Occultation Survey (TAOS II) Matthew Lehner ASIAA
 The Transneptunian Automated Occultation Survey (TAOS II) Matthew Lehner ASIAA Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Harvard-Smithsonian Center
The Transneptunian Automated Occultation Survey (TAOS II) Matthew Lehner ASIAA Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Harvard-Smithsonian Center
Spitzer Space Telescope
 Spitzer Space Telescope (A.K.A. The Space Infrared Telescope Facility) The Infrared Imaging Chain 1/38 The infrared imaging chain Generally similar to the optical imaging chain... 1) Source (different
Spitzer Space Telescope (A.K.A. The Space Infrared Telescope Facility) The Infrared Imaging Chain 1/38 The infrared imaging chain Generally similar to the optical imaging chain... 1) Source (different
The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY
 The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY PARAMETRIC MODEL 16 spectra in total C(θ) = CMB theoretical spectra plus physically motivated templates for the
The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY PARAMETRIC MODEL 16 spectra in total C(θ) = CMB theoretical spectra plus physically motivated templates for the
SDSS-IV and eboss Science. Hyunmi Song (KIAS)
 SDSS-IV and eboss Science Hyunmi Song (KIAS) 3rd Korea-Japan Workshop on Dark Energy April 4, 2016 at KASI Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2.5m telescopes at Apache Point Observatory (US) and Las Campanas Observatory
SDSS-IV and eboss Science Hyunmi Song (KIAS) 3rd Korea-Japan Workshop on Dark Energy April 4, 2016 at KASI Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2.5m telescopes at Apache Point Observatory (US) and Las Campanas Observatory
SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR
 SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR Release Lynne Jones 2017-12-05 Contents 1 Source Counts 3 2 Instrumental Zeropoints 5 3 Sky Counts 7 4 Instrumental Noise 9 5 Source footprint (n
SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR Release Lynne Jones 2017-12-05 Contents 1 Source Counts 3 2 Instrumental Zeropoints 5 3 Sky Counts 7 4 Instrumental Noise 9 5 Source footprint (n
SDSS Data Management and Photometric Quality Assessment
 SDSS Data Management and Photometric Quality Assessment Željko Ivezić Princeton University / University of Washington (and SDSS Collaboration) Thinkshop Robotic Astronomy, Potsdam, July 12-15, 2004 1 Outline
SDSS Data Management and Photometric Quality Assessment Željko Ivezić Princeton University / University of Washington (and SDSS Collaboration) Thinkshop Robotic Astronomy, Potsdam, July 12-15, 2004 1 Outline
Present and Future Large Optical Transient Surveys. Supernovae Rates and Expectations
 Present and Future Large Optical Transient Surveys Supernovae Rates and Expectations Phil Marshall, Lars Bildsten, Mansi Kasliwal Transients Seminar Weds 12th December 2007 Many surveys designed to find
Present and Future Large Optical Transient Surveys Supernovae Rates and Expectations Phil Marshall, Lars Bildsten, Mansi Kasliwal Transients Seminar Weds 12th December 2007 Many surveys designed to find
Dark Energy: Measuring the Invisible with X-Ray Telescopes
 Black holes, Galactic Dark Center Matter and Galactic Center Dark Energy: Measuring the Invisible with X-Ray Telescopes Christine Jones Before 1930 -- only optical observations of the sky Intro Before
Black holes, Galactic Dark Center Matter and Galactic Center Dark Energy: Measuring the Invisible with X-Ray Telescopes Christine Jones Before 1930 -- only optical observations of the sky Intro Before
What shall we learn about the Milky Way using Gaia and LSST?
 What shall we learn about the Milky Way using Gaia and LSST? Astr 511: Galactic Astronomy! Winter Quarter 2015! University of Washington, Željko Ivezić!! The era of surveys... Standard: What data do I
What shall we learn about the Milky Way using Gaia and LSST? Astr 511: Galactic Astronomy! Winter Quarter 2015! University of Washington, Željko Ivezić!! The era of surveys... Standard: What data do I
n=0 l (cos θ) (3) C l a lm 2 (4)
 Cosmic Concordance What does the power spectrum of the CMB tell us about the universe? For that matter, what is a power spectrum? In this lecture we will examine the current data and show that we now have
Cosmic Concordance What does the power spectrum of the CMB tell us about the universe? For that matter, what is a power spectrum? In this lecture we will examine the current data and show that we now have
The Silicon-Tungsten Tracker of the DAMPE Mission
 The Silicon-Tungsten Tracker of the DAMPE Mission Philipp Azzarello, DPNC, University of Geneva for the DAMPE-STK collaboration 10th International Hiroshima Symposium on the Development and Application
The Silicon-Tungsten Tracker of the DAMPE Mission Philipp Azzarello, DPNC, University of Geneva for the DAMPE-STK collaboration 10th International Hiroshima Symposium on the Development and Application
Dark Energy in Light of the CMB. (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu. February 2006, NRAO, VA
 Dark Energy in Light of the CMB (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu February 2006, NRAO, VA If its not dark, it doesn't matter! Cosmic matter-energy budget: Dark Energy Dark Matter Dark Baryons Visible
Dark Energy in Light of the CMB (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu February 2006, NRAO, VA If its not dark, it doesn't matter! Cosmic matter-energy budget: Dark Energy Dark Matter Dark Baryons Visible
BARYON ACOUSTIC OSCILLATIONS. Cosmological Parameters and You
 BARYON ACOUSTIC OSCILLATIONS Cosmological Parameters and You OUTLINE OF TOPICS Definitions of Terms Big Picture (Cosmology) What is going on (History) An Acoustic Ruler(CMB) Measurements in Time and Space
BARYON ACOUSTIC OSCILLATIONS Cosmological Parameters and You OUTLINE OF TOPICS Definitions of Terms Big Picture (Cosmology) What is going on (History) An Acoustic Ruler(CMB) Measurements in Time and Space
Cosmology The Road Map
 Cosmology The Road Map Peter Schneider Institut für Astrophysik, Bonn University on behalf of the Astronomy Working Group Cosmology s Themes Fundamental Cosmology Probing inflation Investigating Dark Energy
Cosmology The Road Map Peter Schneider Institut für Astrophysik, Bonn University on behalf of the Astronomy Working Group Cosmology s Themes Fundamental Cosmology Probing inflation Investigating Dark Energy
Optical/IR Observational Astronomy Telescopes I: Optical Principles. David Buckley, SAAO. 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1
 David Buckley, SAAO 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1 1 What Do Telescopes Do? They collect light They form images of distant objects The images are analyzed by instruments The human eye Photographic
David Buckley, SAAO 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1 1 What Do Telescopes Do? They collect light They form images of distant objects The images are analyzed by instruments The human eye Photographic
Keck/Subaru Exchange Program Subaru Users Meeting January 20, 2011
 Keck/Subaru Exchange Program Subaru Users Meeting January 20, 2011 Taft Armandroff, Director W. M. Keck Observatory With science results from: Drew Newman and Richard Ellis, Caltech A. Romanowsky, J. Strader,
Keck/Subaru Exchange Program Subaru Users Meeting January 20, 2011 Taft Armandroff, Director W. M. Keck Observatory With science results from: Drew Newman and Richard Ellis, Caltech A. Romanowsky, J. Strader,
LISA: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves. Tom Prince Caltech/JPL. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna LISA
 : Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
Picometre metrology. The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars
 Picometre metrology in space The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars in our Galaxy. Part of ESA s Cosmic Vision program, the Gaia spacecraft is being
Picometre metrology in space The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars in our Galaxy. Part of ESA s Cosmic Vision program, the Gaia spacecraft is being
EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION
 ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
The Dark Energy Survey
 The Dark Energy Survey A study of the dark energy using four independent and complementary techniques Galaxy cluster surveys Galaxy angular power spectrum Weak lensing SN Ia distances Two linked, multiband
The Dark Energy Survey A study of the dark energy using four independent and complementary techniques Galaxy cluster surveys Galaxy angular power spectrum Weak lensing SN Ia distances Two linked, multiband
Lensing with KIDS. 1. Weak gravitational lensing
 Lensing with KIDS studying dark matter and dark energy with light rays Konrad Kuijken Leiden Observatory Outline: 1. Weak lensing introduction 2. The KIDS survey 3. Galaxy-galaxy lensing (halos) 4. Cosmic
Lensing with KIDS studying dark matter and dark energy with light rays Konrad Kuijken Leiden Observatory Outline: 1. Weak lensing introduction 2. The KIDS survey 3. Galaxy-galaxy lensing (halos) 4. Cosmic
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
The CTA SST-1M cherenkov telescope. for high-energy gamma-ray astronomy. and its SiPM-based camera. Victor Coco (DPNC, Universite de Geneve)
 The SST-1M Cherenkov telescope for high-energy gamma-ray astronomy and its SiPM-based camera (DPNC, Universite de Geneve) on behalf of the SST-1M sub-consortium and the CTA consortium The CTA SST-1M cherenkov
The SST-1M Cherenkov telescope for high-energy gamma-ray astronomy and its SiPM-based camera (DPNC, Universite de Geneve) on behalf of the SST-1M sub-consortium and the CTA consortium The CTA SST-1M cherenkov
The Future of Cosmology
 The Future of Cosmology Ay21, March 10, 2010 Announcements: final exams available beginning 9am on March 12 (Friday), from Swarnima (note that the final will not be distributed electronically). finals
The Future of Cosmology Ay21, March 10, 2010 Announcements: final exams available beginning 9am on March 12 (Friday), from Swarnima (note that the final will not be distributed electronically). finals
Observing the dark Universe with Euclid
 Euclid Imaging Instrument Observing the dark Universe with Euclid 18 november 2009 Jerome Amiaux CEA Saclay EIC System Manager On Behalf of the Euclid Imaging Consortium The presented document is Proprietary
Euclid Imaging Instrument Observing the dark Universe with Euclid 18 november 2009 Jerome Amiaux CEA Saclay EIC System Manager On Behalf of the Euclid Imaging Consortium The presented document is Proprietary
REU Final Presentation: VERITAS Update. Summer 2011 Advisors: John Finley and Glenn Sembroski Purdue University By: Kara Ponder
 REU Final Presentation: VERITAS Update Summer 2011 Advisors: John Finley and Glenn Sembroski Purdue University By: Kara Ponder Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System Ground-based gamma-ray
REU Final Presentation: VERITAS Update Summer 2011 Advisors: John Finley and Glenn Sembroski Purdue University By: Kara Ponder Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System Ground-based gamma-ray
in the Mediterranean
 PIRATE in the Mediterranean Ulrich Kolb 1, Robert Lucas 1, Vadim Burwitz 2 (1) picetl & OU Physics & Astronomy (2) MPE Garching PIRATE The picetlrobotic Astronomical Telescope Explorer Ulrich Kolb, Robert
PIRATE in the Mediterranean Ulrich Kolb 1, Robert Lucas 1, Vadim Burwitz 2 (1) picetl & OU Physics & Astronomy (2) MPE Garching PIRATE The picetlrobotic Astronomical Telescope Explorer Ulrich Kolb, Robert
Virgo Ego Scientific Forum VESF school 2011 Optical Image Analysis Tutorial by Marica Branchesi
 Virgo Ego Scientific Forum VESF school 2011 Optical Image Analysis Tutorial by Marica Branchesi The main goal of present laboratory is to introduce the students to Optical Image Analysis processing for
Virgo Ego Scientific Forum VESF school 2011 Optical Image Analysis Tutorial by Marica Branchesi The main goal of present laboratory is to introduce the students to Optical Image Analysis processing for
