2. Lens population. 3. Lens model. 4. Cosmology. z=0.5. z=0
|
|
|
- Baldwin Adams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chuck Keeton Hubble Fellow, University of Chicago ffl Lens statistics probe the volume of the universe to z ο 1 3. ffl Current constraints on Λ. ffl Systematics! ffl Prospects for equation of state (w, _w).
2 z= Lens population 3. Lens model 4. Cosmology z=0 Optical depth : fi = Z dv Z dm dn dm A lens(m)
3 ffl Lens selection effects are important: Seeing ο typical lens size Extinction in lens galaxy Lens galaxy luminosity if L(gal) > L(QSO) Radio sources: ffl Flux distribution known. ffl Redshift distribution not well known. ffl Lens selection functions unimportant. Sample # Lenses # Sources Optical Radio 18 ß 12,000
4 2.1. Phenomenology Models ffl (All) observed lenses are produced by normal galaxies. (Not by group or cluster halos.) ffl Use observed Galaxy Luminosity Function (GLF). ffl Use local GLF and assume constant comoving number density. (Okay for ellipticals?) ffl Luminosity ψ! mass with Faber Jackson: L L Λ = 0 ff A ff Λ with ff Λ ' 220 km/s; fl ' 4 ffl Optical depth (flat cosmology): fi(z s ) = 8 ψ! 2 15 ß3 R 3 H ff 4 Λ ffiλ 41+ff + 4 c fl 3 5 D(zs ) 3 ffl Cosmology dependence: volume
5 ffl Sheth Tormen ffl Jenkins et al. These automatically include cosmology dependence and evolution. Problem: ffl Theoretical mass functions don't match observed luminosity functions. (c.f. semi-analytic models of galaxy formation) ffl Baryons! ffl It's the region around the baryons that matters for lensing. Cosmology dependence: volume, ΩM, growth factor
6 1 ρ / r(s + r) 2 Galaxies: Singular Isothermal Sphere (SIS) ρ / r 2 (inside 5 10 kpc) Cross section A / ff 4. The difference can be attributed to cooling: ffl M > M cool gas has not cooled, system remains NFW. ffl M < M cool gas has cooled and condensed into a galaxy, adiabatic compression has modified dark matter halo, result is SIS. ffl M cool ο M fi scale for which the gas can cool in a Hubble time. (See Kochanek & White 2001 ApJ 559:531.)
7 Li & Ostriker (astro-ph/ ) also Keeton (1998 thesis); Porciani & Madau (2000 ApJ 532:679)
8 ffl Galaxy luminosity function (for phenomenology models) ffl Phenomenology vs. theory mass function ffl Evolution Data: ffl Radio: source redshifts ffl Optical: Poisson statistics, selection effects
9 Autofib SSRS2 CfA EEP Durham/UKST 0.01 Stromlo/APM LCRS Absolute B-Band Magnitude Cross et al. (2001 MNRAS 324:825)
10 Phenomenology Models Study Sample GLF Ω Λ (if flat) Kochanek (1996) Opt+Rad K96 < 0.66 Falco et al. (1998) Opt/Rad K96 < 0.73 / 0.62 / 0.74 (samp Helbig et al. Rad K96 < 0.65 Waga & Miceli (1999) Opt K96 < 0.55 / 0.76 / 0.91 (extin Cooray et al. (1999) HDF HDF < Cooray (1999) Rad ESP < 0.79 EEP ' 0.5 Chiba & Yoshii (1999) Opt+Rad APM ' 0.7 CfA ' 0.8 uncertainties in the luminosity function of galaxies by type The as much to the uncertainties in the cosmological limits contribute from lens statistitics as the Poisson errors arising from the derived size of the samples." small Kochanek et al. (astro-ph/ )
11 Note: increasing Ω Λ increases N lens.
12
13 Li & Ostriker (astro-ph/ ): CLASS survey SCDM 37 LCDM 16 OCDM 12 Observed 18 Higher Ω M =) more galaxies =) more lenses
14 Phenomenology: SCDM predicts fewer lenses than LCDM Theory: SCDM predicts more lenses than LCDM Phenomenology: + (All) normal lenses are produced by normal galaxies. Uncertainties in luminosity function and its evolution. Theory: + Automatically includes cosmology and evolution effects. But does it really describe galaxy populations?
15 ffl Claim little evolution to z ο 1 in early-type galaxies ) Assume constant comoving number density ) N lens / N gal / volume CNOC2 redshift survey (H. Lin et al.): ffl Observe sample 0:12 < z < 0:55, derive evolving Schechter function ffl See small, non-zero evolution in early-types ffl Evolution rate depends on cosmology Degeneracy between evolution and cosmology.
16 N lens (LCDM) N lens (SCDM) = 8 < : 3:1 traditional models 1:1 CNOC2 models If you use models normalized by deep number counts, do you lose most sensitivity to cosmology? Need to measure evolving dn=dff (e.g., DEEP).
17 Keeton & Zabludoff (in prep.) ffl Expect environments to affect the number of lenses by ο<10 20% ffl Working to identify lens environments, study their properties
18 0.3 p x =[ m 3-1]ρ x Ωm m Waga & Miceli (1999 PRD 59:103507); Cooray (1999 A&A 342:353) ffl Upper limits on Ω X ffl Lower limits on w ffl (Increasing w reduces N lens, allows higher Ω X.)
19 ffl project ο2000 lenses in LCDM ffl Redshifts known and binned: z max = 5, ff z = z = 0:3 ffl Flat universe, Ω M = 0:3 ± 0:1 (marginalized)
20 (dw/dz) z maz =5, dz=0.1 z max =5, dz=0.3 z max =3, dz=0.3 (dw/dz) w(z)= z w(z)= w(z)= w w 0
21 Sarbu, Rusin & Ma (2001 ApJL 561:L147) ffl Normal: normal galaxies ffl Wide-sep: groups/clusters more sensitive to growth factor
22 Sarbu, Rusin & Ma (2001 ApJL 561:L147)
23 ffl SDSS and 2dF seem to resolve many of the previous problems with the local GLF. ffl SDSS has dn=dff for ellipticals. ffl Compute robust optical depth (for normal lenses): fi = (const) Z dv 0 D D os 1 A 2 Z dff dn dff ff4 ffl Use with existing lens samples. ffl (Evolution?) 2. Wide-Separation Lenses ffl Define a statistical sample. (Expect a few per 10,000 QSOs.) ffl Know source population, selection functions. ffl Different dependence on cosmology =) complementary test.
24 Define the sample (normal or wide-sep lenses) ffl Galaxy luminosity function? Better data: SDSS, 2dF, etc. ffl Evolution? Use the data: CNOC2, DEEP, etc. Data: ffl Larger optical samples? SDSS(?), SNAP, etc. ffl Radio source redshifts? Hard work Proposal: normal vs. wide-separation lenses as a consistency check.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 23 Jan 2005
 Impact of Gravitational Lensing on Cosmology Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 225, 2004 Mellier, Y. & Meylan,G. eds. c 2004 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Quasar Lensing Statistics
Impact of Gravitational Lensing on Cosmology Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 225, 2004 Mellier, Y. & Meylan,G. eds. c 2004 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Quasar Lensing Statistics
How many arcmin-separation lenses are expected in the 2dF QSO survey?
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 339, L23 L27 (2003) How many arcmin-separation lenses are expected in the 2dF QSO survey? Masamune Oguri Department of Physics, School of Science, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 339, L23 L27 (2003) How many arcmin-separation lenses are expected in the 2dF QSO survey? Masamune Oguri Department of Physics, School of Science, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033,
Strong lensing constraints on the velocity dispersion and density profile of elliptical galaxies
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 44, 9 4 () Strong lensing constraints on the velocity dispersion and density profile of elliptical galaxies Adam N. Davis, Dragan Huterer and Lawrence M. Krauss, Department of
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 44, 9 4 () Strong lensing constraints on the velocity dispersion and density profile of elliptical galaxies Adam N. Davis, Dragan Huterer and Lawrence M. Krauss, Department of
Gravitational lensing constraint on the cosmic equation of state
 Gravitational lensing constraint on the cosmic equation of state arxiv:astro-ph/0105551v1 31 May 2001 Deepak Jain, Abha Dev, N. Panchapakesan S. Mahajan and V. B. Bhatia Department of Physics and Astrophysics
Gravitational lensing constraint on the cosmic equation of state arxiv:astro-ph/0105551v1 31 May 2001 Deepak Jain, Abha Dev, N. Panchapakesan S. Mahajan and V. B. Bhatia Department of Physics and Astrophysics
Cosmology and Strongly Lensed QSOs
 Cosmology and Strongly Lensed QSOs Andy Friedman Astronomy 200, Harvard University, Spring 2004 http://cfa-www.harvard.edu/~kstanek/astro200/spring2004.html Ho Outline ΩΛ Determining Ho from Time Delays
Cosmology and Strongly Lensed QSOs Andy Friedman Astronomy 200, Harvard University, Spring 2004 http://cfa-www.harvard.edu/~kstanek/astro200/spring2004.html Ho Outline ΩΛ Determining Ho from Time Delays
Understanding the Properties of Dark Energy in the Universe p.1/37
 Understanding the Properties of Dark Energy in the Universe Dragan Huterer Case Western Reserve University Understanding the Properties of Dark Energy in the Universe p.1/37 The Cosmic Food Pyramid?? Radiation
Understanding the Properties of Dark Energy in the Universe Dragan Huterer Case Western Reserve University Understanding the Properties of Dark Energy in the Universe p.1/37 The Cosmic Food Pyramid?? Radiation
Strong gravitational lensing: Why no central black holes? Da-Ming Chen
 A&A 397, 415 420 (2003) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20021552 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics Strong gravitational lensing: Why no central black holes? Da-Ming Chen National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese
A&A 397, 415 420 (2003) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20021552 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics Strong gravitational lensing: Why no central black holes? Da-Ming Chen National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese
Some issues in cluster cosmology
 Some issues in cluster cosmology Tim McKay University of Michigan Department of Physics 1/30/2002 CFCP Dark Energy Workshop 1 An outline Cluster counting in theory Cluster counting in practice General
Some issues in cluster cosmology Tim McKay University of Michigan Department of Physics 1/30/2002 CFCP Dark Energy Workshop 1 An outline Cluster counting in theory Cluster counting in practice General
Precision Cosmology with X-ray and SZE Galaxy Cluster Surveys?
 Precision Cosmology with X-ray and SZE Galaxy Cluster Surveys? Joe Mohr University of Illinois Outline SZE and X-ray Observations of Clusters Cluster survey yields and cosmology Precision cosmology and
Precision Cosmology with X-ray and SZE Galaxy Cluster Surveys? Joe Mohr University of Illinois Outline SZE and X-ray Observations of Clusters Cluster survey yields and cosmology Precision cosmology and
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Aug 2001
 WEAK AND STRONG LENSING STATISTICS 1 Norbert Straumann Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Zürich, Switzerland arxiv:astro-ph/0108255v1 15 Aug 2001 Abstract After a brief introduction to gravitational
WEAK AND STRONG LENSING STATISTICS 1 Norbert Straumann Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Zürich, Switzerland arxiv:astro-ph/0108255v1 15 Aug 2001 Abstract After a brief introduction to gravitational
Clusters: Observations
 Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters. V. The Cluster Mass Function
 Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters V. The Cluster Mass Function Baryon Fraction Summary Assuming clusters large enough to be representative, mass composition should match Universe observe fb and constrain
Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters V. The Cluster Mass Function Baryon Fraction Summary Assuming clusters large enough to be representative, mass composition should match Universe observe fb and constrain
Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS. Frank van den Bosch.
 Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS In collaboration with: Marcello Cacciato (Leiden), Surhud More (IPMU), Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang
Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS In collaboration with: Marcello Cacciato (Leiden), Surhud More (IPMU), Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang
Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background
 Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background Masato Shirasaki (Univ. of Tokyo) with Shunsaku Horiuchi (UCI), Naoki Yoshida (Univ. of Tokyo, IPMU) Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Background
Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background Masato Shirasaki (Univ. of Tokyo) with Shunsaku Horiuchi (UCI), Naoki Yoshida (Univ. of Tokyo, IPMU) Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Background
1. INTRODUCTION. Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society
 Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society http://dx.doi.org/10.5303/jkas.2015.48.1.83 48: 83 92, 2015 February pissn: 1225-4614 eissn: 2288-890X c 2015. The Korean Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.
Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society http://dx.doi.org/10.5303/jkas.2015.48.1.83 48: 83 92, 2015 February pissn: 1225-4614 eissn: 2288-890X c 2015. The Korean Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.
Probing Dark Matter Halos with Satellite Kinematics & Weak Lensing
 Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
The SNAP Strong Lens Survey
 SLAC-PUB-10922 December 2004 The SNAP Strong Lens Survey Phil Marshall, Roger Blandford and Masao Sako Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, P.O. Box 20450, MS29, Stanford, CA 94309,
SLAC-PUB-10922 December 2004 The SNAP Strong Lens Survey Phil Marshall, Roger Blandford and Masao Sako Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, P.O. Box 20450, MS29, Stanford, CA 94309,
An Introduction to the Dark Energy Survey
 An Introduction to the Dark Energy Survey A study of the dark energy using four independent and complementary techniques Blanco 4m on Cerro Tololo Galaxy cluster surveys Weak lensing Galaxy angular power
An Introduction to the Dark Energy Survey A study of the dark energy using four independent and complementary techniques Blanco 4m on Cerro Tololo Galaxy cluster surveys Weak lensing Galaxy angular power
N-body Simulations. Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY
 N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 11 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 11 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 11 Sep 2013](/thumbs/88/116992309.jpg) To be submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 COSMOLOGICAL DEPENDENCE OF THE MEASUREMENTS OF LUMINOSITY FUNCTION, PROJECTED CLUSTERING AND GALAXY-GALAXY
To be submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 COSMOLOGICAL DEPENDENCE OF THE MEASUREMENTS OF LUMINOSITY FUNCTION, PROJECTED CLUSTERING AND GALAXY-GALAXY
Properties of Wide-separation Lensed Quasars by Clusters of Galaxies in the SDSS
 SLAC-PUB-12330 January 2007 Properties of Wide-separation Lensed Quasars by Clusters of Galaxies in the SDSS G.L. Li 1,2, S. Mao 3, Y.P. Jing 1,2, W.P. Lin 1,2, M. Oguri 4 1 Shanghai Astronomical Observatory;
SLAC-PUB-12330 January 2007 Properties of Wide-separation Lensed Quasars by Clusters of Galaxies in the SDSS G.L. Li 1,2, S. Mao 3, Y.P. Jing 1,2, W.P. Lin 1,2, M. Oguri 4 1 Shanghai Astronomical Observatory;
Clusters: Observations
 Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
The Flatness of Mass-to-Light Ratio on Large Scales
 The Flatness of Mass-to-Light Ratio on Large Scales Li-Zhi Fang 1,andWenXu 2 ABSTRACT It has been suggested that the mass-to-light (M/L) ratio of gravitationally clustering objects is scale-independent
The Flatness of Mass-to-Light Ratio on Large Scales Li-Zhi Fang 1,andWenXu 2 ABSTRACT It has been suggested that the mass-to-light (M/L) ratio of gravitationally clustering objects is scale-independent
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 12 Jul 1999
 The Flatness of Mass-to-Light Ratio on Large Scales Li-Zhi Fang 1, and Wen Xu 2 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/9907141v1 12 Jul 1999 It has been suggested that the mass-to-light (M/L) ratio of gravitationally
The Flatness of Mass-to-Light Ratio on Large Scales Li-Zhi Fang 1, and Wen Xu 2 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/9907141v1 12 Jul 1999 It has been suggested that the mass-to-light (M/L) ratio of gravitationally
Dark Energy in Light of the CMB. (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu. February 2006, NRAO, VA
 Dark Energy in Light of the CMB (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu February 2006, NRAO, VA If its not dark, it doesn't matter! Cosmic matter-energy budget: Dark Energy Dark Matter Dark Baryons Visible
Dark Energy in Light of the CMB (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu February 2006, NRAO, VA If its not dark, it doesn't matter! Cosmic matter-energy budget: Dark Energy Dark Matter Dark Baryons Visible
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 28 Jun 2004
 Light Propagation in Inhomogeneous Universes. IV. Strong Lensing and Environmental Effects. Premana Premadi 1 and Hugo Martel 2,3 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0405603v2 28 Jun 2004 We study the gravitational
Light Propagation in Inhomogeneous Universes. IV. Strong Lensing and Environmental Effects. Premana Premadi 1 and Hugo Martel 2,3 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0405603v2 28 Jun 2004 We study the gravitational
Precise measurement of the radial BAO scale in galaxy redshift surveys
 Precise measurement of the radial BAO scale in galaxy redshift surveys David Alonso (Universidad Autónoma de Madrid - IFT) Based on the work arxiv:1210.6446 In collaboration with: E. Sánchez, F. J. Sánchez,
Precise measurement of the radial BAO scale in galaxy redshift surveys David Alonso (Universidad Autónoma de Madrid - IFT) Based on the work arxiv:1210.6446 In collaboration with: E. Sánchez, F. J. Sánchez,
Cosmology. Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure
 Cosmology Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure Cosmology from Large Scale Structure Sky Surveys Supernovae Ia CMB
Cosmology Introduction Geometry and expansion history (Cosmic Background Radiation) Growth Secondary anisotropies Large Scale Structure Cosmology from Large Scale Structure Sky Surveys Supernovae Ia CMB
Recent BAO observations and plans for the future. David Parkinson University of Sussex, UK
 Recent BAO observations and plans for the future David Parkinson University of Sussex, UK Baryon Acoustic Oscillations SDSS GALAXIES CMB Comparing BAO with the CMB CREDIT: WMAP & SDSS websites FLAT GEOMETRY
Recent BAO observations and plans for the future David Parkinson University of Sussex, UK Baryon Acoustic Oscillations SDSS GALAXIES CMB Comparing BAO with the CMB CREDIT: WMAP & SDSS websites FLAT GEOMETRY
Gravitational Lensing. A Brief History, Theory, and Applications
 Gravitational Lensing A Brief History, Theory, and Applications A Brief History Einstein (1915): light deflection by point mass M due to bending of space-time = 2x Newtonian light tangentially grazing
Gravitational Lensing A Brief History, Theory, and Applications A Brief History Einstein (1915): light deflection by point mass M due to bending of space-time = 2x Newtonian light tangentially grazing
NeoClassical Probes. of the Dark Energy. Wayne Hu COSMO04 Toronto, September 2004
 NeoClassical Probes in of the Dark Energy Wayne Hu COSMO04 Toronto, September 2004 Structural Fidelity Dark matter simulations approaching the accuracy of CMB calculations WMAP Kravtsov et al (2003) Equation
NeoClassical Probes in of the Dark Energy Wayne Hu COSMO04 Toronto, September 2004 Structural Fidelity Dark matter simulations approaching the accuracy of CMB calculations WMAP Kravtsov et al (2003) Equation
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample
 Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample BOMEE LEE 1. Brief Introduction about BAO In our previous class we learned what is the Baryon Acoustic Oscillations(BAO).
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample BOMEE LEE 1. Brief Introduction about BAO In our previous class we learned what is the Baryon Acoustic Oscillations(BAO).
Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies
 Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies Focus: High Resolution Cosmological Zoom Simulation of Massive Galaxies ApJ.L.,658,710 (2007) ApJ.,697, 38 (2009) ApJ.L.,699,L178 (2009) ApJ.,725,2312 (2010) ApJ.,744,63(2012)
Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies Focus: High Resolution Cosmological Zoom Simulation of Massive Galaxies ApJ.L.,658,710 (2007) ApJ.,697, 38 (2009) ApJ.L.,699,L178 (2009) ApJ.,725,2312 (2010) ApJ.,744,63(2012)
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 11 May 2001
 Submitted to ApJ Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 19/02/01 COLD DARK MATTER AND STRONG GRAVITATIONAL LENSING: CONCORD OR CONFLICT? Charles R. Keeton Steward Observatory, University of
Submitted to ApJ Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 19/02/01 COLD DARK MATTER AND STRONG GRAVITATIONAL LENSING: CONCORD OR CONFLICT? Charles R. Keeton Steward Observatory, University of
THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS
 GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
Large-scale structure as a probe of dark energy. David Parkinson University of Sussex, UK
 Large-scale structure as a probe of dark energy David Parkinson University of Sussex, UK Question Who was the greatest actor to portray James Bond in the 007 movies? a) Sean Connery b) George Lasenby c)
Large-scale structure as a probe of dark energy David Parkinson University of Sussex, UK Question Who was the greatest actor to portray James Bond in the 007 movies? a) Sean Connery b) George Lasenby c)
does not discriminate between a wide range of models (e.g [Barkana et al.,
 lensed images [Patnaik, Porcas & Browne, 1995; Ros et al., 2000]) and extra modelling constraints [Trotter et al., 2000]. However, in some cases even extensive VLBI information does not discriminate between
lensed images [Patnaik, Porcas & Browne, 1995; Ros et al., 2000]) and extra modelling constraints [Trotter et al., 2000]. However, in some cases even extensive VLBI information does not discriminate between
The Need for Dark Matter in MOND on Galactic Scales
 The Need for Dark Matter in MOND on Galactic Scales Muhammad Furqaan Yusaf Kings College London, Strand Campus, Department of Physics. muhammad.yusaf@kcl.ac.uk September 28, 2007 As presented by I. Ferreras,
The Need for Dark Matter in MOND on Galactic Scales Muhammad Furqaan Yusaf Kings College London, Strand Campus, Department of Physics. muhammad.yusaf@kcl.ac.uk September 28, 2007 As presented by I. Ferreras,
The redshift distribution of gravitational lenses revisited: constraints on galaxy mass evolution
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 343, 639 652 (2003) The redshift distribution of gravitational lenses revisited: constraints on galaxy mass evolution Eran O. Ofek, 1,2 Hans-Walter Rix 2 and Dan Maoz 1 1 School
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 343, 639 652 (2003) The redshift distribution of gravitational lenses revisited: constraints on galaxy mass evolution Eran O. Ofek, 1,2 Hans-Walter Rix 2 and Dan Maoz 1 1 School
Weighing the Giants:
 Weighing the Giants: Accurate Weak Lensing Mass Measurements for Cosmological Cluster Surveys Anja von der Linden Tycho Brahe Fellow DARK Copenhagen + KIPAC, Stanford IACHEC, May 14, 2014 1 Hello! Copenhagen
Weighing the Giants: Accurate Weak Lensing Mass Measurements for Cosmological Cluster Surveys Anja von der Linden Tycho Brahe Fellow DARK Copenhagen + KIPAC, Stanford IACHEC, May 14, 2014 1 Hello! Copenhagen
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: The Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Frank van den Bosch Yale University, Fall 2018 The Halo Model & Occupation Statistics In this lecture we discuss
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: The Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Frank van den Bosch Yale University, Fall 2018 The Halo Model & Occupation Statistics In this lecture we discuss
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More (MPIA) Kunming,
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More (MPIA) Kunming,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 12 May 2003
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 18 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) The redshift distribution of gravitational lenses revisited: Constraints on galaxy mass evolution Eran O.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 18 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) The redshift distribution of gravitational lenses revisited: Constraints on galaxy mass evolution Eran O.
Dark Matter. Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses ~ 0.3 Ω M Ω b.
 Dark Matter Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses Ω M ~ 0.3 2 1 Ω b 0.04 3 Mass Density by Direct Counting Add up the mass of all the galaxies per
Dark Matter Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses Ω M ~ 0.3 2 1 Ω b 0.04 3 Mass Density by Direct Counting Add up the mass of all the galaxies per
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Quasars, Mergers, and the Buildup of Elliptical Galaxies
 Quasars, Mergers, and the Buildup of Elliptical Galaxies Philip Hopkins 10/05/06 Lars Hernquist, Volker Springel, TJ Cox, Brant Robertson, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing Li, Josh Younger Motivation QUASARS
Quasars, Mergers, and the Buildup of Elliptical Galaxies Philip Hopkins 10/05/06 Lars Hernquist, Volker Springel, TJ Cox, Brant Robertson, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing Li, Josh Younger Motivation QUASARS
ALMA and the high redshift Universe. Simon Lilly ETH Zürich
 Simon Lilly ETH Zürich 2012 will be an exciting year 2012 a great year ? Cool material is central to this process Galaxy formation at high z (Hauser and Dwek ARAA 2001) Extragalactic background light:
Simon Lilly ETH Zürich 2012 will be an exciting year 2012 a great year ? Cool material is central to this process Galaxy formation at high z (Hauser and Dwek ARAA 2001) Extragalactic background light:
Observational Cosmology
 (C. Porciani / K. Basu) Lecture 7 Cosmology with galaxy clusters (Mass function, clusters surveys) Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/astro845.html Outline of the two lecture Galaxy clusters
(C. Porciani / K. Basu) Lecture 7 Cosmology with galaxy clusters (Mass function, clusters surveys) Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/astro845.html Outline of the two lecture Galaxy clusters
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Gravitational lensing statistics with extragalactic surveys; 2, Analysis of the Jodrell Bank-VLA Astrometric Survey Helbig, P.; Marlow, D. R.; Quast, R.; Wilkinson, P. N.; Browne,
University of Groningen Gravitational lensing statistics with extragalactic surveys; 2, Analysis of the Jodrell Bank-VLA Astrometric Survey Helbig, P.; Marlow, D. R.; Quast, R.; Wilkinson, P. N.; Browne,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 16 Jan 1997
 Inclination Effects in Spiral Galaxy Gravitational Lensing Ariyeh H. Maller, Ricardo A. Flores and Joel R. Primack ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/9700v 6 Jan 997 Spheroidal components of spiral galaxies have
Inclination Effects in Spiral Galaxy Gravitational Lensing Ariyeh H. Maller, Ricardo A. Flores and Joel R. Primack ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/9700v 6 Jan 997 Spheroidal components of spiral galaxies have
Quasars, Mergers, and the Formation of Elliptical Galaxies
 Quasars, Mergers, and the Formation of Elliptical Galaxies Philip Hopkins 11/02/06 Lars Hernquist, TJ Cox, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson Gordon Richards (JHU), Kevin Bundy (Caltech), Rachel Somerville
Quasars, Mergers, and the Formation of Elliptical Galaxies Philip Hopkins 11/02/06 Lars Hernquist, TJ Cox, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson Gordon Richards (JHU), Kevin Bundy (Caltech), Rachel Somerville
How can Mathematics Reveal Dark Matter?
 How can Mathematics Reveal? Chuck Keeton Rutgers University April 2, 2010 Evidence for dark matter galaxy dynamics clusters of galaxies (dynamics, X-rays) large-scale structure cosmography gravitational
How can Mathematics Reveal? Chuck Keeton Rutgers University April 2, 2010 Evidence for dark matter galaxy dynamics clusters of galaxies (dynamics, X-rays) large-scale structure cosmography gravitational
Clusters and cosmology
 Clusters and cosmology The KICP Inaugural Symposium, Dec 12, 2005 Mike Gladders, Carnegie Observatories Clusters Outline: and cosmology Codex Aggereris Caelestise (The Book of celestial Aggregates a primer)
Clusters and cosmology The KICP Inaugural Symposium, Dec 12, 2005 Mike Gladders, Carnegie Observatories Clusters Outline: and cosmology Codex Aggereris Caelestise (The Book of celestial Aggregates a primer)
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Dec 2007](/thumbs/94/121042676.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2007) Printed 18 November 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Validity of strong lensing statistics for constraints on the galaxy evolution model 1 Akiko Matsumoto and 2
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2007) Printed 18 November 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Validity of strong lensing statistics for constraints on the galaxy evolution model 1 Akiko Matsumoto and 2
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies
 Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
Constraints on dark energy and its models
 Constraints on dark energy and its models Dragan Huterer 1, Eric V. Linder 2 and Jochen Weller 3 1 Department of Physics, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637-1433 2 E. O. Lawrence Berkeley National
Constraints on dark energy and its models Dragan Huterer 1, Eric V. Linder 2 and Jochen Weller 3 1 Department of Physics, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637-1433 2 E. O. Lawrence Berkeley National
Strong gravitational lensing
 Strong gravitational lensing Olaf Wucknitz, JIVE, Dwingeloo, NL Mike Garrett, JIVE, Dwingeloo, NL Neal Jackson, Jodrell Bank, UK Dieter Engels, Hamburger Sternwarte, Germany 1 Introduction The gravitational
Strong gravitational lensing Olaf Wucknitz, JIVE, Dwingeloo, NL Mike Garrett, JIVE, Dwingeloo, NL Neal Jackson, Jodrell Bank, UK Dieter Engels, Hamburger Sternwarte, Germany 1 Introduction The gravitational
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 9 Jul 2001
 To appear in The Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 19/02/01 COLD DARK MATTER AND STRONG GRAVITATIONAL LENSING: CONCORD OR CONFLICT? Charles R. Keeton Steward Observatory,
To appear in The Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 19/02/01 COLD DARK MATTER AND STRONG GRAVITATIONAL LENSING: CONCORD OR CONFLICT? Charles R. Keeton Steward Observatory,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 10 Nov 1999
 Clustering at High Redshift ASP Conference Series, Vol., 1999 A. Mazure and O. Le Fevre, eds. Weak Lensing Observations of High-Redshift Clusters of Galaxies arxiv:astro-ph/9911169v1 10 Nov 1999 D. Clowe
Clustering at High Redshift ASP Conference Series, Vol., 1999 A. Mazure and O. Le Fevre, eds. Weak Lensing Observations of High-Redshift Clusters of Galaxies arxiv:astro-ph/9911169v1 10 Nov 1999 D. Clowe
Complementarity in Dark Energy measurements. Complementarity of optical data in constraining dark energy. Licia Verde. University of Pennsylvania
 Complementarity in Dark Energy measurements Complementarity of optical data in constraining dark energy Licia Verde University of Pennsylvania www.physics.upenn.edu/~lverde The situation: SN 1A (Riess
Complementarity in Dark Energy measurements Complementarity of optical data in constraining dark energy Licia Verde University of Pennsylvania www.physics.upenn.edu/~lverde The situation: SN 1A (Riess
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 27 Nov 1998
 A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: 12 (12.03.3; 12.07.1; 13.18.1; 11.12.2) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS 3.6.2018 Cosmological Parameters from Statistics of Strongly
A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: 12 (12.03.3; 12.07.1; 13.18.1; 11.12.2) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS 3.6.2018 Cosmological Parameters from Statistics of Strongly
halo formation in peaks halo bias if halos are formed without regard to the underlying density, then δn h n h halo bias in simulations
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Bias, the Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Lecture 8 Halo Bias the matter distribution is highly clustered. halos form at the peaks of this distribution 3 2 1 0 halo formation
Physics 463, Spring 07 Bias, the Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Lecture 8 Halo Bias the matter distribution is highly clustered. halos form at the peaks of this distribution 3 2 1 0 halo formation
Subaru Telescope adaptive optics observations of gravitationally lensed quasars
 EAYAM November 17, 2017 Subaru Telescope adaptive optics observations of gravitationally lensed quasars Cristian Eduard Rusu Subaru Fellow Contents Brief description of the adaptive optics imaging campaign
EAYAM November 17, 2017 Subaru Telescope adaptive optics observations of gravitationally lensed quasars Cristian Eduard Rusu Subaru Fellow Contents Brief description of the adaptive optics imaging campaign
What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering. Alison Coil UCSD
 What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering Alison Coil UCSD Talk Outline 1. Brief review of what we know about galaxy clustering from observations 2.
What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering Alison Coil UCSD Talk Outline 1. Brief review of what we know about galaxy clustering from observations 2.
Cosmoogica effects in the high-z universe inear redshift-space distortion coherence between density and veocity fieds finger-of-god noninear veocity f
 Custering statistics on a ight-cone in the cosmoogica redshift space Yasushi Suto Dept. of Phys. and RESCEU, The University of Tokyo, Japan November 7, 999 (The 4th RESCEU Symposium) based on the coaboration
Custering statistics on a ight-cone in the cosmoogica redshift space Yasushi Suto Dept. of Phys. and RESCEU, The University of Tokyo, Japan November 7, 999 (The 4th RESCEU Symposium) based on the coaboration
Testing gravity on cosmological scales with the observed abundance of massive clusters
 Testing gravity on cosmological scales with the observed abundance of massive clusters David Rapetti, KIPAC (Stanford/SLAC) In collaboration with Steve Allen (KIPAC), Adam Mantz (KIPAC), Harald Ebeling
Testing gravity on cosmological scales with the observed abundance of massive clusters David Rapetti, KIPAC (Stanford/SLAC) In collaboration with Steve Allen (KIPAC), Adam Mantz (KIPAC), Harald Ebeling
Dr Carolyn Devereux - Daphne Jackson Fellow Dr Jim Geach Prof. Martin Hardcastle. Centre for Astrophysics Research University of Hertfordshire, UK
 Millennium simulation of the cosmic web MEASUREMENTS OF THE LINEAR BIAS OF RADIO GALAXIES USING CMB LENSING FROM PLANCK Dr Carolyn Devereux - Daphne Jackson Fellow Dr Jim Geach Prof. Martin Hardcastle
Millennium simulation of the cosmic web MEASUREMENTS OF THE LINEAR BIAS OF RADIO GALAXIES USING CMB LENSING FROM PLANCK Dr Carolyn Devereux - Daphne Jackson Fellow Dr Jim Geach Prof. Martin Hardcastle
Cosmology on small scales: Emulating galaxy clustering and galaxy-galaxy lensing into the deeply nonlinear regime
 Cosmology on small scales: Emulating galaxy clustering and galaxy-galaxy lensing into the deeply nonlinear regime Ben Wibking Department of Astronomy Ohio State University with Andres Salcedo, David Weinberg,
Cosmology on small scales: Emulating galaxy clustering and galaxy-galaxy lensing into the deeply nonlinear regime Ben Wibking Department of Astronomy Ohio State University with Andres Salcedo, David Weinberg,
The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004
 The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004 The history of modern cosmology 1917 Static via cosmological constant? (Einstein) 1917 Expansion (Slipher) 1952 Big Bang criticism (Hoyle)
The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004 The history of modern cosmology 1917 Static via cosmological constant? (Einstein) 1917 Expansion (Slipher) 1952 Big Bang criticism (Hoyle)
The Degeneracy of Dark Energy and Curvature
 The Degeneracy of Dark Energy and Curvature Department of Physics and Astronomy, UWC, Cape Town Department of MAM, UCT, Cape Town PhD student: Amadeus Witzemann Collaborators: Philip Bull, HIRAX coll.
The Degeneracy of Dark Energy and Curvature Department of Physics and Astronomy, UWC, Cape Town Department of MAM, UCT, Cape Town PhD student: Amadeus Witzemann Collaborators: Philip Bull, HIRAX coll.
Determining the GRB (Redshift, Luminosity)-Distribution Using Burst Variability
 8x11double address=department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of Chicago, 5640 South Ellis Avenue address=department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of Chicago, 5640 South Ellis Avenue
8x11double address=department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of Chicago, 5640 South Ellis Avenue address=department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of Chicago, 5640 South Ellis Avenue
Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc. 400 Mpc
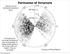 Formation Origin of of Structure Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc 400 Mpc If one galaxy has comoving coordinate, x, then the probability of finding another galaxy in the vicinity
Formation Origin of of Structure Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc 400 Mpc If one galaxy has comoving coordinate, x, then the probability of finding another galaxy in the vicinity
IoP. An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology. Derek Raine. Ted Thomas. Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics
 Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology Derek Raine Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Leicester, UK Ted Thomas Department of Physics and Astronomy
Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology Derek Raine Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Leicester, UK Ted Thomas Department of Physics and Astronomy
Mass and Hot Baryons from Cluster Lensing and SZE Observations
 SZX HUNTSVILLE 2011 Mass and Hot Baryons from Cluster Lensing and SZE Observations Keiichi Umetsu Academia Sinica IAA (ASIAA), Taiwan September 19, 2011 Lensing collaborators: Collaborators T. Broadhurst
SZX HUNTSVILLE 2011 Mass and Hot Baryons from Cluster Lensing and SZE Observations Keiichi Umetsu Academia Sinica IAA (ASIAA), Taiwan September 19, 2011 Lensing collaborators: Collaborators T. Broadhurst
The Power. of the Galaxy Power Spectrum. Eric Linder 13 February 2012 WFIRST Meeting, Pasadena
 The Power of the Galaxy Power Spectrum Eric Linder 13 February 2012 WFIRST Meeting, Pasadena UC Berkeley & Berkeley Lab Institute for the Early Universe, Korea 11 Baryon Acoustic Oscillations In the beginning...
The Power of the Galaxy Power Spectrum Eric Linder 13 February 2012 WFIRST Meeting, Pasadena UC Berkeley & Berkeley Lab Institute for the Early Universe, Korea 11 Baryon Acoustic Oscillations In the beginning...
A.Klypin. Dark Matter Halos
 A.Klypin Dark Matter Halos 1 Major codes: GADET N-body Hydro Cooling/Heating/SF Metal enrichment Radiative transfer Multistepping/Multiple masses Springel, SDM White PKDGRAV - GASOLINE ART ENZO Quinn,
A.Klypin Dark Matter Halos 1 Major codes: GADET N-body Hydro Cooling/Heating/SF Metal enrichment Radiative transfer Multistepping/Multiple masses Springel, SDM White PKDGRAV - GASOLINE ART ENZO Quinn,
The theoretical view of high-z Clusters. Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009
 The theoretical view of high-z Clusters Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009 The Plan: 1) To see what the observations are telling us using models that agree with the cosmology, and with other
The theoretical view of high-z Clusters Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009 The Plan: 1) To see what the observations are telling us using models that agree with the cosmology, and with other
The growth rate index of large scale structure as a probe of the cause of cosmic acceleration
 The growth rate index of large scale structure as a probe of the cause of cosmic acceleration Prof. Mustapha Ishak Collaborators: J. Dossett, Y. Gong, A. Wang Cosmology and Relativity Group Department
The growth rate index of large scale structure as a probe of the cause of cosmic acceleration Prof. Mustapha Ishak Collaborators: J. Dossett, Y. Gong, A. Wang Cosmology and Relativity Group Department
Cosmology with Clusters of Galaxies
 Cosmology with Clusters of Galaxies arxiv:astro-ph/9901076v1 8 Jan 1999 Neta A. Bahcall Princeton University Observatory Princeton, NJ 08544 December 31, 1998 Abstract Rich clusters of galaxies, the largest
Cosmology with Clusters of Galaxies arxiv:astro-ph/9901076v1 8 Jan 1999 Neta A. Bahcall Princeton University Observatory Princeton, NJ 08544 December 31, 1998 Abstract Rich clusters of galaxies, the largest
Structure formation in the concordance cosmology
 Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Mapping the Dark Energy Equation of State
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Mapping the Dark Energy Equation of State Eric V. Linder Berkeley Lab, 1 Cyclotron Road, M/S 50R5008, Berkeley,
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Mapping the Dark Energy Equation of State Eric V. Linder Berkeley Lab, 1 Cyclotron Road, M/S 50R5008, Berkeley,
COSMOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS FROM THE SDSS MAXBCG CLUSTER CATALOG
 Draft version February 21, 2009 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/27/05 SLAC-PUB-13719 July 2009 COSMOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS FROM THE SDSS MAXBCG CLUSTER CATALOG Eduardo Rozo 1, Risa H.
Draft version February 21, 2009 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/27/05 SLAC-PUB-13719 July 2009 COSMOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS FROM THE SDSS MAXBCG CLUSTER CATALOG Eduardo Rozo 1, Risa H.
Strong Gravitational-Lensing by Galaxies: 30 years later...
 Strong Gravitational-Lensing by Galaxies: 30 years later... Léon Koopmans ( Institute (Kapteyn Astronomical Stellar Dynamics Gravitational lensing JENAM - April 22, 2009 Some Applications of Galaxy Lensing
Strong Gravitational-Lensing by Galaxies: 30 years later... Léon Koopmans ( Institute (Kapteyn Astronomical Stellar Dynamics Gravitational lensing JENAM - April 22, 2009 Some Applications of Galaxy Lensing
Gravitational lensing statistics with extragalactic surveys
 Astron. Astrophys. 350, 1 8 (1999) Gravitational lensing statistics with extragalactic surveys ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS III. Joint constraints on and Ω 0 from lensing statistics and the m-z relation
Astron. Astrophys. 350, 1 8 (1999) Gravitational lensing statistics with extragalactic surveys ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS III. Joint constraints on and Ω 0 from lensing statistics and the m-z relation
Cooking with Strong Lenses and Other Ingredients
 Cooking with Strong Lenses and Other Ingredients Adam S. Bolton Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Utah AASTCS 1: Probes of Dark Matter on Galaxy Scales Monterey, CA, USA 2013-July-17
Cooking with Strong Lenses and Other Ingredients Adam S. Bolton Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Utah AASTCS 1: Probes of Dark Matter on Galaxy Scales Monterey, CA, USA 2013-July-17
Astrometric Microlensing by Local Dark Matter Subhalos
 Astrometric Microlensing by Local Dark Matter Subhalos Adrienne Erickcek CITA & Perimeter Institute with Nicholas Law University of Toronto Dunlap Institute arxiv: 17.4228 ApJ in press Dark Matter Halos
Astrometric Microlensing by Local Dark Matter Subhalos Adrienne Erickcek CITA & Perimeter Institute with Nicholas Law University of Toronto Dunlap Institute arxiv: 17.4228 ApJ in press Dark Matter Halos
the galaxy-halo connection from abundance matching: simplicity and complications
 the galaxy-halo connection from abundance matching: simplicity and complications R isa Wechsler with Peter Behroozi, Michael Busha, Rachel Reddick (KIPAC/Stanford) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) subhalo
the galaxy-halo connection from abundance matching: simplicity and complications R isa Wechsler with Peter Behroozi, Michael Busha, Rachel Reddick (KIPAC/Stanford) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) subhalo
Shear Power of Weak Lensing. Wayne Hu U. Chicago
 Shear Power of Weak Lensing 10 3 N-body Shear 300 Sampling errors l(l+1)c l /2π εε 10 4 10 5 Error estimate Shot Noise θ y (arcmin) 200 100 10 6 100 1000 l 100 200 300 θ x (arcmin) Wayne Hu U. Chicago
Shear Power of Weak Lensing 10 3 N-body Shear 300 Sampling errors l(l+1)c l /2π εε 10 4 10 5 Error estimate Shot Noise θ y (arcmin) 200 100 10 6 100 1000 l 100 200 300 θ x (arcmin) Wayne Hu U. Chicago
Sunyaev-Zeldovich Contributions from Early Supernova Winds
 Sunyaev-Zeldovich Contributions from Early Supernova Winds Sarah Benjamin Mentor: Steven Furlanetto Department of Physics and Astronomy, UCLA September 5, 2011 Abstract The purpose of this research was
Sunyaev-Zeldovich Contributions from Early Supernova Winds Sarah Benjamin Mentor: Steven Furlanetto Department of Physics and Astronomy, UCLA September 5, 2011 Abstract The purpose of this research was
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content
 Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
CONSTRAINTS AND TENSIONS IN MG CFHTLENS AND OTHER DATA SETS PARAMETERS FROM PLANCK, INCLUDING INTRINSIC ALIGNMENTS SYSTEMATICS.
 CONSTRAINTS AND TENSIONS IN MG PARAMETERS FROM PLANCK, CFHTLENS AND OTHER DATA SETS INCLUDING INTRINSIC ALIGNMENTS SYSTEMATICS 1 Mustapha Ishak The University of Texas at Dallas Jason Dossett INAF Osservatorio
CONSTRAINTS AND TENSIONS IN MG PARAMETERS FROM PLANCK, CFHTLENS AND OTHER DATA SETS INCLUDING INTRINSIC ALIGNMENTS SYSTEMATICS 1 Mustapha Ishak The University of Texas at Dallas Jason Dossett INAF Osservatorio
Weak lensing measurements of Dark Matter Halos around galaxies
 Weak lensing measurements of Dark Matter Halos around galaxies Rachel Mandelbaum Carnegie Mellon University 1 Image credits: NASA, ESA, S. Beckwith (STScI), the HUDF Team 2 Image credit: ESA/Planck 3 The
Weak lensing measurements of Dark Matter Halos around galaxies Rachel Mandelbaum Carnegie Mellon University 1 Image credits: NASA, ESA, S. Beckwith (STScI), the HUDF Team 2 Image credit: ESA/Planck 3 The
Dark Energy. Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey. Survey (DES)
 Dark Energy Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey Survey (DES) What is it? The DES Collaboration will build and use a wide field optical imager (DECam) to perform a wide area,
Dark Energy Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey Survey (DES) What is it? The DES Collaboration will build and use a wide field optical imager (DECam) to perform a wide area,
A look into the Dark Universe
 Zentrum für Astronomie, Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Universität Heidelberg Dark Energy dark energy: assumed to drive accelerated cosmic expansion scalar field having negative pressure? early
Zentrum für Astronomie, Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Universität Heidelberg Dark Energy dark energy: assumed to drive accelerated cosmic expansion scalar field having negative pressure? early
Extragalactic DM Halos and QSO Properties Through Microlensing
 Extragalactic DM Halos and QSO Properties Through Micro Eduardo Guerras (student) - Evencio Mediavilla (supervisor) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias Photon deflection by gravitating mass α = 4GM 2
Extragalactic DM Halos and QSO Properties Through Micro Eduardo Guerras (student) - Evencio Mediavilla (supervisor) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias Photon deflection by gravitating mass α = 4GM 2
THE ROAD TO DARK ENERGY
 Modern Physics Letters A Vol. 23, Nos. 17 20 (2008) 1346 1353 c World Scientific Publishing Company THE ROAD TO DARK ENERGY DRAGAN HUTERER Department of Physics, University of Michigan 450 Church St.,
Modern Physics Letters A Vol. 23, Nos. 17 20 (2008) 1346 1353 c World Scientific Publishing Company THE ROAD TO DARK ENERGY DRAGAN HUTERER Department of Physics, University of Michigan 450 Church St.,
Galaxy formation and evolution. Astro 850
 Galaxy formation and evolution Astro 850 Introduction What are galaxies? Systems containing many galaxies, e.g. 10 11 stars in the Milky Way. But galaxies have different properties. Properties of individual
Galaxy formation and evolution Astro 850 Introduction What are galaxies? Systems containing many galaxies, e.g. 10 11 stars in the Milky Way. But galaxies have different properties. Properties of individual
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 26 Jul 2002
 Non linear predictions from linear theories in models with Dark Energy R. Mainini, A.V. Macciò & S.A. Bonometto arxiv:astro-ph/0207581v1 26 Jul 2002 Physics Department G. Occhialini, Università degli Studi
Non linear predictions from linear theories in models with Dark Energy R. Mainini, A.V. Macciò & S.A. Bonometto arxiv:astro-ph/0207581v1 26 Jul 2002 Physics Department G. Occhialini, Università degli Studi
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 18 Oct 2002
 Determining the GRB (Redshift, Luminosity)-Distribution Using Burst Variability Timothy Donaghy, Donald Q. Lamb, Daniel E. Reichart and Carlo Graziani arxiv:astro-ph/0210436v2 18 Oct 2002 Department of
Determining the GRB (Redshift, Luminosity)-Distribution Using Burst Variability Timothy Donaghy, Donald Q. Lamb, Daniel E. Reichart and Carlo Graziani arxiv:astro-ph/0210436v2 18 Oct 2002 Department of
