Investigations in Earth and Space Science Semester Review: Unit 1 and Unit 2
|
|
|
- Clyde Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IESS Unit 1: Solar Energy & Fluid Circulation Review Directions: Write the answer to each question in the box to the right of the question. Fold your paper along the line and use this as a review sheet! QUESTION/DIAGRAM ANSWER AIR PRESSURE Using the diagram below, arrange the letters on the line from least air pressure greatest air pressure. Least Greatest Air Air Pressure Pressure EXPLANATION: HEAT TRANSFER How is our layer of the atmosphere heated? Use the diagram below and explain including the 3 types of heat transfer. SOLAR ENERGY What absorbs most of the solar energy on Earth? 2. How does this absorbed energy keep Earth warm when the sun isn t shining? 3. How do clouds affect how much the amount of incoming solar energy? 3.
2 QUESTION/DIAGRAM WATER CYCLE A. Label the diagram ANSWER Part A Part B B. Explain how water cycles on Earth including collection sites as well as explaining how the water cycle is powered. MONSOONS Differentiate between a summer and a winter monsoon. Make sure to include the type of weather, as well as which way the winds blow. CORIOLIS EFFECT Explain what the Coriolis Effect is, what causes it, as well as how it impacts winds & ocean currents.
3 QUESTION/DIAGRAM OCEAN CURRENTS 1. ANSWER Compare the temperature & density of deep ocean currents, and surface ocean currents. 2. How do ocean currents affect the climate of an area? GLOBAL DISTRIBUTION OF SOLAR ENERGY Which place on Earth receives a constant amount of solar Energy? 2. What does the air and water do at the equator and why? 3. What does the air and water do at the poles and why? 4. Where do winds and ocean currents move heat energy from? 4.
4 QUESTION/DIAGRAM SEASONS Label all of these events on the diagram: ANSWER What causes the seasons? 1. Northern Hemisphere 2. Southern Hemisphere 1. Northern hemipshere: When does summer begin? When does winter begin: 2. Southern hemipshere: When does summer begin? When does winter begin? 3. North Pole: When does the North Pole get 24 hours of daylight? 24 hours of darkness? 4. South Pole: When does the South Pole get 24 hours of daylight? 24 hours of darkness? PREVAILING WINDS 3. North Pole 4. South Pole How does being located next to a large body of water affect temperatures (and climate) of a location? HIGHS & LOWS How does wind move? Describe a high pressure system? Describe a low pressure system 1. H 2. L
5 Name Date Pd Earth, Moon, Sun TEST REVIEW sheet MOON Phases 1. The moon takes days to complete one rotation around its axis. 2. The moon takes days to complete one revolution around Earth. 3. The moon takes days to complete an entire set of phases. 4. The reason we see the same side of the moon is because 5. The phase of the moon you see depends on how much of the Phase Name 6. Draw the phases of the moon as seen from Earth in the circles 1-8 below. Then identify the name of the phase in the table
6 Eclipses 7. During a lunar eclipse, the is positioned between the and. As a result, the moon will appear in color because the Earth is casting a on it (See page 25 figure 14 in Astronomy Book) 8. Circle ANY letter of each sentence that is true about lunar eclipses. a. People see a total lunar eclipse when the moon is in Earth s penumbra b. A lunar eclipse occurs during a full moon c. During a lunar eclipse, Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the moon d. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when only part of Earth s shadow covers the moon. 9. During a solar eclipse, the is positioned between the and. As a result, the moon will appear in color because we see the shadow of the from Earth. 10. The umbra is the of the moon s shadow and covers 11. The penumbra is the of the moon s shadow and covers. 12. Circle ANY letter of each sentence that is true about solar eclipses. a. People in the umbra see only a partial solar eclipse b. During a partial solar eclipse, part of the sun remains visible c. During a total solar eclipse, the sky grows dark d. People in the penumbra see a total solar eclipse Tides 13. What force pulls the moon and Earth toward each other? 14. Circle ANY letter of each sentence that is true about tides a. The point on Earth farthest from the moon has a high tide b. Every location on Earth has two high tides per month c. A low tide occurs at the point on Earth farthest from the moon d. The point on Earth farthest from the moon has a high tide 15. On the diagram below, draw the position of the moon at a spring tide, and how the tides will appear on Earth. What phases of the moon would someone on Earth see when the moon is in this position?.
7 16. On the diagram below, draw the possible position(s) of the moon at a neap tide, and how the tides will appear on Earth. What phases of the moon would someone on Earth see when the moon is in these positions? and the. PHYSICAL LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION Kepler s Laws st law states that nd law states that rd law states that Newton s Laws 1. Law of Gravity states that and depends on two variables and 2. Law of Inertia states that 3. Basically the reason why the planets orbit the sun is because of the planet s own and the between the Sun and planet. MODELS OF THE EARTH, MOON, AND SUN Geocentric model 4. In the geocentric model, the is at the center of the revolving planets and stars. 5. Draw a diagram of the model below. Heliocentric model
8 6. In the heliocentric model, the is at the center of the revolving planets and stars. 7. Draw a diagram of the model below. LAYERS OF THE SUN 8. The Sun is made mostly of gas. 9. Explain how nuclear fusion occurs in the Sun s interior core 10. The layer next to the core is the, where photons have difficulty travelling to the exterior. 11. What occurs in the convection zone? 12. The outermost layer of the Sun is the. 13. Why does the Sun appear grainy in appearance? 14. Label the layers and features of the Sun on the diagram below. 15. The Sun s atmosphere is made up of 3 layers. Describe each layer below. a. The Photosphere- b. The Chromosphere- c. Corona-
9 SOLAR PROCESSES Sunspots 16. Sunspots are dark blemishes on the Sun s surface that are created by 17. The is the period in which the number of sunspots it at its greatest. The is the period in which the number of sunspots it at its lowest. 18. Low sunspot activity creates temperatures on Earth. 19. How long is a solar cycle? years Solar flares & prominences 20. Define a solar flare 21. Define a solar prominence Solar winds 22. Describe solar winds 23. Name four ways in which solar winds impact us on Eartha. b. c. d. 24. How do solar winds create auroras? Magnetosphere 25. What is the magnetosphere? 26. How does the magnetosphere help Earth? Life Cycle of a star 27. Explain the stages in the life cycle of a star and the processes that take place between each cycle.
10 Comets Galaxies Asteroids
PHASES, ECLIPSES, AND TIDES
 PHASES, ECLIPSES, AND TIDES MOTIONS OF THE MOON The changing relative positions of the moon, Earth, and sun cause the phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides. The moon rotates once on its axis in the same
PHASES, ECLIPSES, AND TIDES MOTIONS OF THE MOON The changing relative positions of the moon, Earth, and sun cause the phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides. The moon rotates once on its axis in the same
Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy, Universe
 Dr. V s Study Guide : Astronomy Unit 1) Place the following in order of increasing size: The Galaxy, the Solar System, a Star, the Universe,a Moon and a Planet. Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy,
Dr. V s Study Guide : Astronomy Unit 1) Place the following in order of increasing size: The Galaxy, the Solar System, a Star, the Universe,a Moon and a Planet. Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy,
Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide
 Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When are tides highest? a. during the moon s first quarter phase
Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When are tides highest? a. during the moon s first quarter phase
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture.
 Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
EARTH MOON SUN REVIEW
 1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
Student Review Investigations in Earth and Space Science Semester A 2015 Examination
 Investigations in Earth and Space Science Semester A Examination Test Description Length: 2 hours Items: 56 SR (85%), 2 BCRs (15%) Unit Approximate Number of Selected Response Items IESS Skills and Processes
Investigations in Earth and Space Science Semester A Examination Test Description Length: 2 hours Items: 56 SR (85%), 2 BCRs (15%) Unit Approximate Number of Selected Response Items IESS Skills and Processes
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
ES - Astronomy Part 2 Post-Test
 ES - Astronomy Part 2 Post-Test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compared to the human eye, telescopes can collect light over longer periods of time. 2. The inner planets
ES - Astronomy Part 2 Post-Test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compared to the human eye, telescopes can collect light over longer periods of time. 2. The inner planets
FCAT Review Space Science
 FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
Effective August 2007 All indicators in Standard / 14
 8-4.1 Summarize the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Taxonomy level: 2.4-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Previous/Future
8-4.1 Summarize the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Taxonomy level: 2.4-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Previous/Future
Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test
 is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
refractors satellite electromagnetic radiation
 Chapter 19 Exploring Space space probe reflectors mirror refractors satellite electromagnetic radiation light lens thrust 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the. 2. Two types of telescopes
Chapter 19 Exploring Space space probe reflectors mirror refractors satellite electromagnetic radiation light lens thrust 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the. 2. Two types of telescopes
Intro to Astronomy. Looking at Our Space Neighborhood
 Intro to Astronomy Looking at Our Space Neighborhood Astronomy: The Original Science Ancient cultures used the movement of stars, planets and the moon to mark time Astronomy: the study of the universe
Intro to Astronomy Looking at Our Space Neighborhood Astronomy: The Original Science Ancient cultures used the movement of stars, planets and the moon to mark time Astronomy: the study of the universe
Earth in Space. The Sun-Earth-Moon System
 in Space The --Moon System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if
in Space The --Moon System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if
SPI Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe.
 SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
Science Period. Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7
 Name: Date: Science Period Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7 Directions: Write the letter of the BEST answer on the appropriate space on the answer sheet. 2 points each 1.The model in which SUN is
Name: Date: Science Period Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7 Directions: Write the letter of the BEST answer on the appropriate space on the answer sheet. 2 points each 1.The model in which SUN is
What is in outer space?
 What is in outer space? Celestial Objects are any natural objects that move through space. Star:_a huge sphere of gas in space _Nuclear fusion within stars give off enormous amounts of energy such as light
What is in outer space? Celestial Objects are any natural objects that move through space. Star:_a huge sphere of gas in space _Nuclear fusion within stars give off enormous amounts of energy such as light
Earth s Motion. Lesson Outline LESSON 1. A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than
 Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Solar System Glossary. The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting
 Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Mid Term Prep-The Moon
 1. A high tide occurred at 6:00 a.m. at a beach on Long Island. The next high tide at this same beach would occur at approximately A) 12:15 p.m. on the same day B) 6:30 p.m. on the same day C) 12:45 p.m.
1. A high tide occurred at 6:00 a.m. at a beach on Long Island. The next high tide at this same beach would occur at approximately A) 12:15 p.m. on the same day B) 6:30 p.m. on the same day C) 12:45 p.m.
7.4 Universal Gravitation
 Circular Motion Velocity is a vector quantity, which means that it involves both speed (magnitude) and direction. Therefore an object traveling at a constant speed can still accelerate if the direction
Circular Motion Velocity is a vector quantity, which means that it involves both speed (magnitude) and direction. Therefore an object traveling at a constant speed can still accelerate if the direction
3. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole.
 1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
Chapter 3 The Solar System
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 The Solar System Section 1 Observing the Solar System (pp. 72-77) Key Concepts What are the geocentric and heliocentric systems? How did Copernicus, Galileo, and Kepler contribute
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 The Solar System Section 1 Observing the Solar System (pp. 72-77) Key Concepts What are the geocentric and heliocentric systems? How did Copernicus, Galileo, and Kepler contribute
10-20 billion years old
 Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up. Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images What natural phenomena do the motions of Earth and the Moon
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images What natural phenomena do the motions of Earth and the Moon
Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
1/3/12. Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System. Ancient Measurements. Earth s Size and Shape. Ancient Measurements. Ancient Measurements
 // Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
// Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System
 CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
Chapter 19 Exploring Space. I. Fill in the blank
 Chapter 19 Exploring Space 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. 2. Two types of telescopes that collect visible light are refractors and reflectors. 3. An uncrewed
Chapter 19 Exploring Space 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. 2. Two types of telescopes that collect visible light are refractors and reflectors. 3. An uncrewed
Chapter 23. Our Solar System
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Our sun is the star in our solar system, which lies within a galaxy (Milky Way) within the universe. A star is a large glowing ball of gas that
 Our sun is the star in our solar system, which lies within a galaxy (Milky Way) within the universe. A star is a large glowing ball of gas that generates energy through nuclear fusion in its core. The
Our sun is the star in our solar system, which lies within a galaxy (Milky Way) within the universe. A star is a large glowing ball of gas that generates energy through nuclear fusion in its core. The
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Physical Science. Chapter 22 The Earth in Space. Earth s Rotation
 Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science. Chapter 22 The Earth in Space
 Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3. Sun
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 1.25 Hours What s important in this lesson: Sun demonstrate an understanding of the structure, and nature of our solar system investigate the
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 1.25 Hours What s important in this lesson: Sun demonstrate an understanding of the structure, and nature of our solar system investigate the
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide. Assessment Date : Term Rotation Revolution
 Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions
 because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions 1. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in
because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions 1. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in
7 th Grade Science DO NOW. OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 4_Rotation and Revolution Name: Date: Monday, October 24, 2016 Homeroom: DO NOW SWBAT define and identify lines of latitude and longitude. SWBAT
7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 4_Rotation and Revolution Name: Date: Monday, October 24, 2016 Homeroom: DO NOW SWBAT define and identify lines of latitude and longitude. SWBAT
Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date
 Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on
Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on
THE SUN AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 Chapter 26 THE SUN AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM CHAPTER 26 SECTION 26.1: THE SUN S SIZE, HEAT, AND STRUCTURE Objectives: What is the Sun s structure and source of energy? Key Vocabulary: Fusion Photosphere Corona
Chapter 26 THE SUN AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM CHAPTER 26 SECTION 26.1: THE SUN S SIZE, HEAT, AND STRUCTURE Objectives: What is the Sun s structure and source of energy? Key Vocabulary: Fusion Photosphere Corona
2. The distance between the Sun and the next closest star, Proxima Centuari, is MOST accurately measured in
 Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Passwords. ScienceVocabulary
 Passwords ScienceVocabulary F To the Student Mitosis. Apogee. Ion. Sometimes it seems that scientists speak a language all their own. Passwords: Science Vocabulary will help you learn the words you need
Passwords ScienceVocabulary F To the Student Mitosis. Apogee. Ion. Sometimes it seems that scientists speak a language all their own. Passwords: Science Vocabulary will help you learn the words you need
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
Earth/Space/Physics Kristy Halteman.
 Earth/Space/Physics Kristy Halteman http://www.lesia.obspm.fr/~bonnin/fichiers/images/sun-soho011905-1919z.jpg A. Properties 1. 330,000 times more massive than the Earth. http://www.37signals.com/svn/images/sun_v_planets.jpg
Earth/Space/Physics Kristy Halteman http://www.lesia.obspm.fr/~bonnin/fichiers/images/sun-soho011905-1919z.jpg A. Properties 1. 330,000 times more massive than the Earth. http://www.37signals.com/svn/images/sun_v_planets.jpg
Astronomy Regents Review
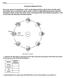 Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Student Sheet 8 Sun-Earth-Moon System Review
 Name: Class: Date: Student Sheet 8 Sun-Earth-Moon System Review Directions To prepare for the written assessment in Lesson 9, answer the following questions in complete sentences. Reading selections you
Name: Class: Date: Student Sheet 8 Sun-Earth-Moon System Review Directions To prepare for the written assessment in Lesson 9, answer the following questions in complete sentences. Reading selections you
Patterns of Change on Earth
 TEKS collect and analyze data to identify sequences and predict patterns of change in shadows, tides, seasons, and the observable appearance of the Moon over time Patterns of Change on Earth Patterns and
TEKS collect and analyze data to identify sequences and predict patterns of change in shadows, tides, seasons, and the observable appearance of the Moon over time Patterns of Change on Earth Patterns and
Earth Moon Motions A B1
 Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Astronomy, PART 2. Vocabulary. A. Universe - Our Milky Way Galaxy is one of of galaxies in an expanding universe.
 Astronomy, PART 2 Vocabulary Aphelion Asteroid Astronomical Unit Comet Constellation Crater Eccentricity Eclipse Equinox Geocentric model Gravitation Heliocentric model Inertia Jovian Perihelion Revolution
Astronomy, PART 2 Vocabulary Aphelion Asteroid Astronomical Unit Comet Constellation Crater Eccentricity Eclipse Equinox Geocentric model Gravitation Heliocentric model Inertia Jovian Perihelion Revolution
Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars.
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Define umbra and penumbra. Then label the umbra and the penumbra on the diagram below. Umbra: Penumbra: Light source
 Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides LA.8.2.2.3, SC.8.E.5.9, SC.8.N.1.1 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts you will learn from the lesson. Discuss
Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides LA.8.2.2.3, SC.8.E.5.9, SC.8.N.1.1 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts you will learn from the lesson. Discuss
Planets Inner vs. outer Composition inner planets are rocky/outer are gas Size inner are smaller/outer are much larger Distance from sun inner are
 Planets Inner vs. outer Composition inner planets are rocky/outer are gas Size inner are smaller/outer are much larger Distance from sun inner are close/outer are farther. Earth is 1 AU from the sun Life
Planets Inner vs. outer Composition inner planets are rocky/outer are gas Size inner are smaller/outer are much larger Distance from sun inner are close/outer are farther. Earth is 1 AU from the sun Life
Which table correctly shows the dates on which the apparent paths of the Sun were observed? A) B) C) D)
 1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
Guided Notes Astronomy. Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses
 Guided Notes Astronomy Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses K. Coder 2015 1. What is the Moon? The Moon: the Earth's only natural satellite. See ESRT page 15 for data on Earth
Guided Notes Astronomy Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses K. Coder 2015 1. What is the Moon? The Moon: the Earth's only natural satellite. See ESRT page 15 for data on Earth
A. the spinning of Earth on its axis B. the path of the Sun around Earth
 stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
Earth Space Systems. Semester 1 Exam. Astronomy Vocabulary
 Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide
 Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes
Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes
Explain the Big Bang Theory and give two pieces of evidence which support it.
 Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: asteroid, celestial object, comet, constellation, Doppler effect, eccentricity, eclipse, ellipse, focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model,
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: asteroid, celestial object, comet, constellation, Doppler effect, eccentricity, eclipse, ellipse, focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model,
C) D) 2. The model below shows the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer in New York State on the first day of one of the four seasons.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM
 Date Period Name THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy In your textbook, read about electromagnetic radiation and telescopes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Date Period Name THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy In your textbook, read about electromagnetic radiation and telescopes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
A) M D) The Moon s distance from Earth varies in a cyclic manner.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
Mid Term Prep-Moon Review 2
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which shows positions of the Moon in its orbit and phases of the Moon as viewed from New York State. 1. Which statement best explains why
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which shows positions of the Moon in its orbit and phases of the Moon as viewed from New York State. 1. Which statement best explains why
Full Moon. Phases of the Moon
 Phases of the Moon The Moon takes 29.5 days to orbit Earth. This is a lunar month. The gravity of the Earth keeps the Moon in orbit. The Moon does not produce light. We see the Moon because it reflects
Phases of the Moon The Moon takes 29.5 days to orbit Earth. This is a lunar month. The gravity of the Earth keeps the Moon in orbit. The Moon does not produce light. We see the Moon because it reflects
STANDARD. S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position.
 STANDARD S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. S6E2 b. Explain the alignment of the earth, moon, and sun during solar and lunar eclipses. c. Relate the
STANDARD S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. S6E2 b. Explain the alignment of the earth, moon, and sun during solar and lunar eclipses. c. Relate the
The Sun-Earth-Moon System
 Name The Sun-Earth-Moon System Section 28.3 The Sun-Earth-Moon System Date Main Idea Details Read the title of Section 3. List three things that might be discussed in this section. 1. 2. 3. Review Vocabulary
Name The Sun-Earth-Moon System Section 28.3 The Sun-Earth-Moon System Date Main Idea Details Read the title of Section 3. List three things that might be discussed in this section. 1. 2. 3. Review Vocabulary
Coriolis Effect - the apparent curved paths of projectiles, winds, and ocean currents
 Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 786 Level 870L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.16.17 Word Count 786 Level 870L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.16.17 Word Count 786 Level 870L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
Which phase of the Moon will be seen from the Earth at position 5? A) B) C) D)
 Name Date 1. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from the Earth? A) the rotation of the Moon on its axis B) the revolution of the Moon around the Earth C) the rotation of the Sun on
Name Date 1. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from the Earth? A) the rotation of the Moon on its axis B) the revolution of the Moon around the Earth C) the rotation of the Sun on
SC.8.E.5.9. Summer and Winter Gizmo
 8 th Grade Science Quarter 1 Recovery Packet SC.8.E.5.9 DAYS/YEARS/SEASONS Go to www.explorelearning.com and search for the Summer and Winter Gizmo. Answer the following questions: Gizmo Warm-up Summer
8 th Grade Science Quarter 1 Recovery Packet SC.8.E.5.9 DAYS/YEARS/SEASONS Go to www.explorelearning.com and search for the Summer and Winter Gizmo. Answer the following questions: Gizmo Warm-up Summer
The Earth & its good friend, the Moon. SNC1D7 - Space
 The Earth & its good friend, the Moon SNC1D7 - Space Key Questions! What causes... day and night? the seasons? the tides? What are eclipses? Let s eat some space oreos! How do we know the Earth is round?
The Earth & its good friend, the Moon SNC1D7 - Space Key Questions! What causes... day and night? the seasons? the tides? What are eclipses? Let s eat some space oreos! How do we know the Earth is round?
4 Layers of the Sun. CORE : center, where fusion occurs
 4 Layers of the Sun CORE : center, where fusion occurs RADIATION LAYER: energy transfer by radiation (like energy coming from a light bulb or heat lamp which you can feel across the room) CONVECTION LAYER:
4 Layers of the Sun CORE : center, where fusion occurs RADIATION LAYER: energy transfer by radiation (like energy coming from a light bulb or heat lamp which you can feel across the room) CONVECTION LAYER:
*These items are to be integrated throughout the content. However, you will find new resources for student practice with these concepts here.
 6 th Grade Science Scope and Sequence 1 st Quarter 2017-2018 Sequence of Concepts Rationale for Sequence Prior Knowledge Scientific Method and Engineering Design *These items are to be integrated throughout
6 th Grade Science Scope and Sequence 1 st Quarter 2017-2018 Sequence of Concepts Rationale for Sequence Prior Knowledge Scientific Method and Engineering Design *These items are to be integrated throughout
Moon Occurrences. Eclipses. Tides
 Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
12.1 Earth, Moon and Sun Interactions
 12.1 Earth, Moon and Sun Interactions Humans have been aware of the relationships between the Earth, Sun and Moon for thousands of years, but only recently have we began to better understand the true nature
12.1 Earth, Moon and Sun Interactions Humans have been aware of the relationships between the Earth, Sun and Moon for thousands of years, but only recently have we began to better understand the true nature
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system.
 1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
The rock probably formed 200million years ago. The mineral sample is purple.
 Midterm Study Guide 1) Intro to Earth Science (Chapters 1& 2) a) Fact (observation) vs. Inference (assumption/hypothesis) Recognize whether a statement is a fact or an inference. For example: The rock
Midterm Study Guide 1) Intro to Earth Science (Chapters 1& 2) a) Fact (observation) vs. Inference (assumption/hypothesis) Recognize whether a statement is a fact or an inference. For example: The rock
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES SAMPLE. Earth and Space. Secondary Science 7C. Years 7 9. Written by Valerie Marett. CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544
 AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Earth and Space Secondary Science 7C Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544 Secondary Science Earth and Space Contents The Earth. 2 Movements
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Earth and Space Secondary Science 7C Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544 Secondary Science Earth and Space Contents The Earth. 2 Movements
Name: Exam 1, 9/30/05
 Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon
 Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon Goals: To understand the phases of the moon To understand how the moon affects tides To understand lunar and solar eclipses To learn some of the history associated with
Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon Goals: To understand the phases of the moon To understand how the moon affects tides To understand lunar and solar eclipses To learn some of the history associated with
Moon Occurrences. Eclipses. Tides
 Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
1. The diagram below shows Earth, four different positions of the Moon, and the direction of incoming sunlight.
 G8 Semester I MCAS Pre-Test Please answer on Scantron Card; not on this test form Standard: 9 - Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and tides. Relate them to the relative positions
G8 Semester I MCAS Pre-Test Please answer on Scantron Card; not on this test form Standard: 9 - Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and tides. Relate them to the relative positions
AST101IN Final Exam. 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points)
 Name: Possibly useful formulae: AST101IN Final Exam F g = Gm 1 m 2 /r 2 p 2 =a 3 F=ma E=mc 2 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points) The sun The Earth The universe The Milky
Name: Possibly useful formulae: AST101IN Final Exam F g = Gm 1 m 2 /r 2 p 2 =a 3 F=ma E=mc 2 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points) The sun The Earth The universe The Milky
THE UNIVERSE AND THE EARTH
 ESO1 THE UNIVERSE AND THE EARTH Unit 1 What is the Universe like? Universe theories Ideas about the Universe: Geocentric theory Aristotle (B.C) and Ptolomy (A.D) Heliocentric theory Copernicus in 1542
ESO1 THE UNIVERSE AND THE EARTH Unit 1 What is the Universe like? Universe theories Ideas about the Universe: Geocentric theory Aristotle (B.C) and Ptolomy (A.D) Heliocentric theory Copernicus in 1542
Chapter 16 Astronomy Study Guide. VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW geocentric system meteorite meteoroid
 NAME: Period: asteroid asteroid belt comet ellipse force Galilean moons gas giants Chapter 16 Astronomy Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW geocentric system meteorite gravity meteoroid greenhouse effect
NAME: Period: asteroid asteroid belt comet ellipse force Galilean moons gas giants Chapter 16 Astronomy Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW geocentric system meteorite gravity meteoroid greenhouse effect
Practice Seasons Moon Quiz
 1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
The Sun-Earth-Moon System. Learning Guide. Visit for Online Learning Resources. Copyright NewPath Learning
 The Sun-Earth-Moon System Learning Guide Visit www.newpathlearning.com for Online Learning Resources. Copyright NewPath Learning Table of Contents Lesson 1 - How the Earth Moves... 2 Lesson 2 - Seasons
The Sun-Earth-Moon System Learning Guide Visit www.newpathlearning.com for Online Learning Resources. Copyright NewPath Learning Table of Contents Lesson 1 - How the Earth Moves... 2 Lesson 2 - Seasons
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface.
 1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
GRADE 6: Earth and space 1. UNIT 6E.1 12 hours. The movement of the Earth and the Moon. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 6: Earth and space 1 The movement of the Earth and the Moon UNIT 6E.1 12 hours About this unit This unit is the only unit on Earth and space in Grade 6. The unit requires some knowledge of light
GRADE 6: Earth and space 1 The movement of the Earth and the Moon UNIT 6E.1 12 hours About this unit This unit is the only unit on Earth and space in Grade 6. The unit requires some knowledge of light
Answer Questions 1 4
 Name Date Period Introduction: Even though the moon does not appear to turn on its own axis from the Earth s point of view, it is indeed rotating as it revolves around the Earth. In the following activity,
Name Date Period Introduction: Even though the moon does not appear to turn on its own axis from the Earth s point of view, it is indeed rotating as it revolves around the Earth. In the following activity,
Basics of Kepler and Newton. Orbits of the planets, moons,
 Basics of Kepler and Newton Orbits of the planets, moons, Kepler s Laws, as derived by Newton. Kepler s Laws Universal Law of Gravity Three Laws of Motion Deriving Kepler s Laws Recall: The Copernican
Basics of Kepler and Newton Orbits of the planets, moons, Kepler s Laws, as derived by Newton. Kepler s Laws Universal Law of Gravity Three Laws of Motion Deriving Kepler s Laws Recall: The Copernican
Day, Night, Year, and Seasons
 Welcome Astronomers to the Sun, Moon, and Earth! The relationship between the Sun, Moon, and Earth is very important to the existence of life on Earth. Our quest is to find out how their relationships
Welcome Astronomers to the Sun, Moon, and Earth! The relationship between the Sun, Moon, and Earth is very important to the existence of life on Earth. Our quest is to find out how their relationships
CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES
 CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES Characteristics of the Sun 1. The Sun is located about 150 million kilometres from the Earth. 2. The Sun is made up of hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. 3. The size of
CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES Characteristics of the Sun 1. The Sun is located about 150 million kilometres from the Earth. 2. The Sun is made up of hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. 3. The size of
Astronomy 11. No, this course isn t all about Star Wars
 Astronomy 11 No, this course isn t all about Star Wars Earth s Rotation How fast are people on the equator moving? s=d/t =circumference/24 hours =(40,000 km)/24 hours =1670 km/h That s Mach 1.4! What
Astronomy 11 No, this course isn t all about Star Wars Earth s Rotation How fast are people on the equator moving? s=d/t =circumference/24 hours =(40,000 km)/24 hours =1670 km/h That s Mach 1.4! What
LESSON 2 THE EARTH-SUN-MOON SYSTEM. Chapter 8 Astronomy
 LESSON 2 THE EARTH-SUN-MOON SYSTEM Chapter 8 Astronomy OBJECTIVES Investigate how the interaction of Earth, the Moon, and the Sun causes lunar phases. Describe conditions that produce lunar and solar eclipses.
LESSON 2 THE EARTH-SUN-MOON SYSTEM Chapter 8 Astronomy OBJECTIVES Investigate how the interaction of Earth, the Moon, and the Sun causes lunar phases. Describe conditions that produce lunar and solar eclipses.
