Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
|
|
|
- Hilda Maud Miller
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy The beautiful visible spectrum of the star Procyon is shown here from red to blue, interrupted by hundreds of dark lines caused by the absorption of light in the hot star s cooler atmosphere. The whole spectrum is normally 6 meters (20 feet) across, but to display it on a single page the full spectrum is cut into dozens of horizontal segments and stacked vertically. (NOAO/AURA)
2 Units of Chapter Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation The Hydrogen Atom The Photoelectric Effect 4.3 The Formation of Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral-Line Analysis
3 4.1 Spectral Lines Spectroscope: Splits light into component colors Figure 4.1 Spectroscope Diagram of a simple spectroscope. A thin slit in the barrier at the left allows a narrow beam of light to pass. The light continues through a prism and is split into its component colors. A lens then focuses the light into a sharp image that is either projected onto a screen, as shown here, or analyzed as it strikes a detector.
4 4.1 Spectral Lines Emission lines: Single frequencies emitted by particular atoms Figure 4.2 Continuous and Emission Spectra When passed through a slit and split up by a prism, light from a source of continuous radiation (a) gives rise to the familiar rainbow of colors. By contrast, the light from excited hydrogen gas (b) consists of a series of distinct bright spectral lines called emission lines. (The focusing lenses have been omitted for clarity see Section 5.1.)
5 4.1 Spectral Lines Emission spectrum can be used to identify elements Figure 4.3 Elemental Emission The emission spectra of some well-known elements. In accordance with the convention adopted throughout this text, frequency increases to the right. Note that wavelengths shorter than approximately 400 nm, shown here in shades of purple, are actually in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum and are not visible to the human eye. (Wabash Instrument Corp.)
6 4.1 Spectral Lines Absorption spectrum: If a continuous spectrum passes through a cool gas, atoms of the gas will absorb the same frequencies they emit Figure 4-5. Absorption Spectrum (a) When cool gas is placed between a source of continuous radiation (such as a hot lightbulb) and a detector/screen, the resulting color spectrum is crossed by a series of dark absorption lines. These lines are formed when the intervening cool gas absorbs certain wavelengths (colors) from the original beam of light. The absorption lines appear at precisely the same wavelengths as the emission lines that would be produced if the gas were heated to high temperatures. (See Figure 4.2.) (b) An everyday analogy for any of these line spectra is a supermarket bar code that uniquely determines the cost of some product.
7 4.1 Spectral Lines An absorption spectrum can also be used to identify elements. These are the emission and absorption spectra of sodium: Figure 4-6. Sodium Spectrum (a) The characteristic emission lines of sodium. The two bright lines in the center appear in the yellow part of the spectrum. (b) The absorption spectrum of sodium. The two dark lines appear at exactly the same wavelengths as the bright lines in the sodium emission spectrum.
8 4.1 Spectral Lines Kirchhoff s laws: Luminous solid, liquid, or dense gas produces continuous spectrum Low-density hot gas produces emission spectrum Continuous spectrum incident on cool, thin gas produces absorption spectrum
9 4.1 Spectral Lines Kirchhoff s laws illustrated
10 Figure 4-7. Kirchhoff s Laws A source of continuous radiation, here represented by a lightbulb, is used to illustrate Kirchhoff s laws of spectroscopy. (a) The unimpeded beam shows the familiar continuous spectrum of colors. (b) When the source is viewed through a cloud of hydrogen gas, a series of dark hydrogen absorption lines appears in the continuous spectrum. These lines are formed when the gas absorbs some of the bulb s radiation and reemits it in random directions. Because most of the reemitted radiation does not go through the slit, the effect is to remove the absorbed radiation from the light that reaches the screen at the left. (c) When the gas is viewed from the side, a fainter hydrogen emission spectrum is seen, consisting of reemitted radiation. The absorption lines in (b) and the emission lines in (c) have the same wavelengths.
11 4.2 Atoms and Radiation Existence of spectral lines required new model of atom, so that only certain amounts of energy could be emitted or absorbed Bohr model had certain allowed orbits for electron Figure 4-8: Classical Atom An early-20th-century conception of the hydrogen atom the Bohr model pictured its electron orbiting the central proton in a well- defined orbit, rather like a planet orbiting the Sun. Two electron orbitals of different energies are shown: (a) the ground state and (b) an excited state.
12 4.2 Atoms and Radiation Emission energies correspond to energy differences between allowed levels Modern model has electron cloud rather than orbit
13 More Precisely 4-1: The Hydrogen Atom Energy levels of the hydrogen atom, showing two series of emission lines: The energies of the electrons in each orbit are given by: 1 = ev. 2 n E n The emission lines correspond to the energy differences
14 Discovery 4-1: The Photoelectric Effect The photoelectric effect: When light shines on metal, electrons can be emitted Frequency must be higher than minimum, characteristic of material Increased frequency more energetic electrons Increased intensity more electrons, same energy
15 Discovery 4-1: The Photoelectric Effect Photoelectric effect can only be understood if light behaves like particles
16 4.2 Atoms and Radiation Light particles each have energy E: E = hf Here, h is Planck s constant: h = joule seconds (J s)
17 4.3 The Formation of Spectral Lines Absorption can boost an electron to the second (or higher) excited state Two ways to decay: 1. Directly to ground state 2. Cascade one orbital at a time
18 4.3 The Formation of Spectral Lines (a) Direct decay (b) Cascade
19 Figure Atomic Excitation (a) Absorption of an ultraviolet photon (left) by a hydrogen atom causes the momentary excitation of the atom into its first excited state (center). After about 10 8 s, the atom returns to its ground state (right), in the process emitting a photon having exactly the same energy as the original photon. (b) Absorption of a higher-energy ultraviolet (UV) photon may boost the atom into a higher excited state, from which there are several possible paths back to the ground state. (Remember, the sharp lines used for the orbitals here and in similar figures that follow are intended merely as a schematic representation of the electron energy levels and are not meant to be taken literally. In actuality, electron orbitals are clouds, as shown in Figure 4.9.) At the top, the electron falls immediately back to the ground state, emitting a photon identical to the one it absorbed. At the bottom, the electron initially falls into the first excited state, producing visible radiation of wavelength nm the characteristic (Hα) red glow of excited hydrogen. Subsequently, the atom emits another photon (having the same energy as in part (a) as it falls back to the ground state). The object shown in the inset, designated N81, is an emission nebula an interstellar cloud made mostly of hydrogen gas excited by absorbing radiation emitted by some extremely hot stars (the white areas near the center). (Inset: NASA)
20 4.3 The Formation of Spectral Lines Absorption spectrum: Created when atoms absorb photons of right energy for excitation Multielectron atoms: Much more complicated spectra, many more possible states Ionization changes energy levels Figure Helium and Carbon (a) A helium atom in its ground state. Two electrons occupy the lowestenergy orbital around a nucleus containing two protons and two neutrons. (b) A carbon atom in its ground state. Six electrons orbit a six-proton, six-neutron nucleus, two of the electrons in an inner orbital, the other four at a greater distance from the center.
21 4.3 The Formation of Spectral Lines Emission lines can be used to identify atoms Figure Emission Nebula The visible spectrum of the hot gases in a nearby gas cloud known as the Omega Nebula (M17). (The word nebula means gas cloud one of many sites in our Galaxy where new stars are forming today.) Shining by the light of several very hot stars, the gas in the nebula produces a complex spectrum of bright and dark lines (bottom). That same spectrum can also be displayed, as shown here, as a white graph of intensity versus frequency, spanning the spectrum from red to blue. (Adapted from ESO)
22 Molecules can vibrate and rotate, besides having energy levels Electron transitions produce visible and ultraviolet lines Vibrational transitions produce infrared lines 4.4 Molecules Rotational transitions produce radio-wave lines
23 Figure Molecular Emission Molecules can change in three ways while emitting or absorbing electromagnetic radiation. The colors and wavelengths of the emitted photons represent the relative energies involved. Sketched here is the molecule carbon monoxide (CO) undergoing (a) a change in which an electron in the outermost orbital of the oxygen atom drops to a lower energy state (emitting a photon of shortest wavelength, in the visible or ultraviolet range), (b) a change in vibrational state (of intermediate wavelength, in the infrared), and (c) a change in rotational state (of longest wavelength, in the radio range).
24 4.4 Molecules Molecular spectra are much more complex than atomic spectra, even for hydrogen (a) Molecular hydrogen (b) Atomic hydrogen Figure Hydrogen Spectra (a) The emission spectrum of molecular hydrogen. Notice how it differs from the spectrum of the simpler atomic hydrogen (b). (Bausch & Lomb, Inc.)
25 4.5 Spectral-Line Analysis Information that can be gleaned from spectral lines: Chemical composition Temperature Radial velocity
26 Figure Doppler Shift Because of the Doppler effect, the entire spectrum of a moving object is shifted to higher or lower frequencies. The spectrum at the center is the unshifted emission spectrum of pure hydrogen, corresponding to the object at rest. The top spectrum shows the slight redshift of the hydrogen lines from an object moving at a speed of 300 km/s away from the observer. Once we recognize the spectrum as that of hydrogen, we can identify specific lines and measure their shifts. The amount of the shift (0.1 percent here) tells us the object s recession velocity 0.001c. The spectrum at the bottom shows the blueshift of the same set of lines from an object approaching us at 600 km/s. The shift is twice as large (0.2 percent), because the speed has doubled, and in the opposite sense because the direction has reversed.
27 4.5 Spectral-Line Analysis Line broadening can be due to a variety of causes Figure Line Profile By tracing the changing brightness across a typical emission line (a) and expanding the scale, we obtain a graph of the line s intensity versus its frequency (b).
28 4.5 Spectral-Line Analysis
29 4.5 Spectral-Line Analysis The Doppler shift may cause thermal broadening of spectral lines Figure Thermal Broadening Atoms moving randomly (a) produce broadened spectral lines (b) as their individual redshifted and blueshifted emission lines merge in our detector. The hotter the gas, the greater is the degree of thermal broadening.
30 4.5 Spectral-Line Analysis Rotation will also cause broadening of spectral lines through the Doppler effect Figure Rotational Broadening The rotation of a star can cause spectral line broadening. Because most stars are unresolved that is, they are so distant that we cannot distinguish one part of the star from another light rays from all parts of the star merge to produce broadened lines. The more rapid the rotation, the greater is the broadening.
31 Summary of Chapter 4 Spectroscope splits light beam into component frequencies Continuous spectrum is emitted by solid, liquid, and dense gas Hot gas has characteristic emission spectrum Continuous spectrum incident on cool, thin gas gives characteristic absorption spectrum
32 Summary of Chapter 4 (cont.) Spectra can be explained using atomic models, with electrons occupying specific orbitals Emission and absorption lines result from transitions between orbitals Molecules can also emit and absorb radiation when making transitions between vibrational or rotational states
Chapter 4. Spectroscopy. Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah
 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos
 Chapter 5 Lecture Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience
Chapter 5 Lecture Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience
HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
 Astronomy 10 HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate
Astronomy 10 HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. 5.1 Light in Everyday Life. How do we experience light?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. White light is made up of many different colors. Interactions of Light with Matter
 Chapter 5 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact?
Chapter 5 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. How do we experience light? Colors of Light. How do light and matter interact?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Light and Atoms. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies !ATH REVIEW: #AST CLASS: "OMEWORK #1
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!ATH REVIEW: Tonight, 5-6pm, in RAMY N1B23 "OMEWORK #1 -Due THU, Sept. 10, by 5pm, on Mastering Astronomy CLASS RECORDED STARTED - INFO WILL BE POSTED on CULEARN
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!ATH REVIEW: Tonight, 5-6pm, in RAMY N1B23 "OMEWORK #1 -Due THU, Sept. 10, by 5pm, on Mastering Astronomy CLASS RECORDED STARTED - INFO WILL BE POSTED on CULEARN
What is LIGHT? Reading Question
 Reading Question What is LIGHT? A. Light is a wave, like sound only much faster. B. Light is like little particles. Each one is a photon. C. Light is the absence of dark. D. A kind of energy we model with
Reading Question What is LIGHT? A. Light is a wave, like sound only much faster. B. Light is like little particles. Each one is a photon. C. Light is the absence of dark. D. A kind of energy we model with
3/26/2018. Atoms Light and Spectra. Topics For Today s Class. Reminder. Topics For Today s Class. The Atom. Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 7 Atoms Light and Spectra Reminder Homework for Chapter 5, 6 and 7 is posted
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 7 Atoms Light and Spectra Reminder Homework for Chapter 5, 6 and 7 is posted
Today. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Stellar Spectra & Composition. Doppler Effect & Motion. Extrasolar Planets
 Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. What is light? Properties of Waves. Waves. The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos What is light? Light is a form of radiant energy Light can act either like a wave or like a particle (photon) Spectrum of the Sun 1 2 Waves
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos What is light? Light is a form of radiant energy Light can act either like a wave or like a particle (photon) Spectrum of the Sun 1 2 Waves
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16]
![AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16]](/thumbs/78/77847540.jpg) AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] REVIEW Light as Information Bearer We can separate light into its different wavelengths (spectrum).
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] REVIEW Light as Information Bearer We can separate light into its different wavelengths (spectrum).
Chapter 6. Atoms and Starlight
 Chapter 6 Atoms and Starlight What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and Frequency wavelength frequency = speed of light = constant Particles of Light Particles of light are called
Chapter 6 Atoms and Starlight What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and Frequency wavelength frequency = speed of light = constant Particles of Light Particles of light are called
Physics Homework Set I Su2015
 1) The particles which enter into chemical reactions are the atom's: 1) _ A) protons. B) positrons. C) mesons. D) electrons. E) neutrons. 2) Which of the following type of electromagnetic radiation has
1) The particles which enter into chemical reactions are the atom's: 1) _ A) protons. B) positrons. C) mesons. D) electrons. E) neutrons. 2) Which of the following type of electromagnetic radiation has
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 5.1 Our Sun in Ultraviolet Light. This photograph of the Sun was taken at several different wavelengths of ultraviolet, which
ASTRONOMY Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 5.1 Our Sun in Ultraviolet Light. This photograph of the Sun was taken at several different wavelengths of ultraviolet, which
AST 102 chapter 5. Radiation and Spectra. Radiation and Spectra. Radiation and Spectra. What is light? What is radiation?
 5 Radiation and Spectra 1 Radiation and Spectra What is light? According to Webster: a.something that makes vision possible b.the sensation aroused by stimulation of the visual receptors c.electromagnetic
5 Radiation and Spectra 1 Radiation and Spectra What is light? According to Webster: a.something that makes vision possible b.the sensation aroused by stimulation of the visual receptors c.electromagnetic
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
The Amazing Power of Starlight
 The Amazing Power of Starlight Chapter 6 Just by analyzing the light received from a star, astronomers can retrieve information about a star s Starlight and Atoms 1. Total energy output 2. Surface temperature
The Amazing Power of Starlight Chapter 6 Just by analyzing the light received from a star, astronomers can retrieve information about a star s Starlight and Atoms 1. Total energy output 2. Surface temperature
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4)
 Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
ASTRO Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum ABSTRACT Astronomers rely on light to convey almost all of the information we have on distant astronomical objects. In addition to measuring
ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum ABSTRACT Astronomers rely on light to convey almost all of the information we have on distant astronomical objects. In addition to measuring
Today. Spectra. Thermal Radiation. Wien s Law. Stefan-Boltzmann Law. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Spectra & Composition
 Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
10/31/2018. Chapter 7. Atoms Light and Spectra. Thursday Lab Announcement. Topics For Today s Class Black Body Radiation Laws
 Phys1411 Introductory Astronomy Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 7 Atoms Light and Spectra Thursday Lab Announcement Jonah will start the Lab at 6:00 PM. Two pieces of Glass and HST Lunar Phases Topics
Phys1411 Introductory Astronomy Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 7 Atoms Light and Spectra Thursday Lab Announcement Jonah will start the Lab at 6:00 PM. Two pieces of Glass and HST Lunar Phases Topics
Chapter 5 Light and Matter
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
What are the three basic types of spectra?
 Learning from Light Our goals for learning What are the three basic types of spectra? How does light tell us what things are made of? How does light tell us the temperatures of planets and stars? How do
Learning from Light Our goals for learning What are the three basic types of spectra? How does light tell us what things are made of? How does light tell us the temperatures of planets and stars? How do
Review: Properties of a wave
 Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5. What is light? What is a wave? Radiation carries information
 Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu February 11, 2016 Read: Chap 5 02/11/16 slide 1 Exam #1: Thu 18 Feb
A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu February 11, 2016 Read: Chap 5 02/11/16 slide 1 Exam #1: Thu 18 Feb
From Last Time Pearson Education, Inc.
 From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
Types of Spectra. How do spectrum lines form? 3/30/09. Electron cloud. Atom. Nucleus
 The electron should be thought of as a distribution or cloud of probability around the nucleus that on average behave like a point particle on a fixed circular path Types of Spectra How do spectrum lines
The electron should be thought of as a distribution or cloud of probability around the nucleus that on average behave like a point particle on a fixed circular path Types of Spectra How do spectrum lines
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds
 - - Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
- - Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
Review: Light and Spectra. Absorption and Emission Lines
 1 Review: Light and Spectra Light is a wave It undergoes diffraction and other wave phenomena. But light also is made of particles Energy is carried by photons 1 Wavelength energy of each photon Computer
1 Review: Light and Spectra Light is a wave It undergoes diffraction and other wave phenomena. But light also is made of particles Energy is carried by photons 1 Wavelength energy of each photon Computer
Telescopes have Three Powers
 Telescopes have Three Powers 1. Light Gathering Power: The ability to collect light 2. Resolving Power: The ability to see fine details 3. Magnifying Power: The ability to make objects look bigger Pizzas!!!
Telescopes have Three Powers 1. Light Gathering Power: The ability to collect light 2. Resolving Power: The ability to see fine details 3. Magnifying Power: The ability to make objects look bigger Pizzas!!!
Lecture5PracticeQuiz.txt
 TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 6 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. The difference between radiation and sound is that a. radiation exhibits the Doppler effect, whereas sound does not. b. radiation travels much
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 6 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. The difference between radiation and sound is that a. radiation exhibits the Doppler effect, whereas sound does not. b. radiation travels much
Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger 5.1 Basic Properties of Light and Matter Our goals for learning: What is light? What is matter? How do light and matter interact? What is light? Light is an electromagnetic
Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger 5.1 Basic Properties of Light and Matter Our goals for learning: What is light? What is matter? How do light and matter interact? What is light? Light is an electromagnetic
aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously
 Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
How does your eye form an Refraction
 Astronomical Instruments Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image? Refraction Refraction is the bending of light
Astronomical Instruments Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image? Refraction Refraction is the bending of light
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds. Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules
 Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules 1 Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules 1 Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
Light & Atoms. Electromagnetic [EM] Waves. Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation.
![Light & Atoms. Electromagnetic [EM] Waves. Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation. Light & Atoms. Electromagnetic [EM] Waves. Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation.](/thumbs/88/117441686.jpg) Light & Atoms Electromagnetic [EM] Waves Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation. These have both and electric part and a magnetic part
Light & Atoms Electromagnetic [EM] Waves Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation. These have both and electric part and a magnetic part
Next Homework Due Oct. 9. Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10)
 Today Summary of Chapter 3: Light All of Chapter 4: Spectra & Atoms Optional: Ast. Toolbox 4-2 Optional: Stephan-Boltzmann Law Next Homework Due Oct. 9 Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10) Resolving Power:
Today Summary of Chapter 3: Light All of Chapter 4: Spectra & Atoms Optional: Ast. Toolbox 4-2 Optional: Stephan-Boltzmann Law Next Homework Due Oct. 9 Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10) Resolving Power:
Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY
 Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY The emission and absorption of light energy of particular wavelengths by atoms and molecules is a common phenomenon. The emissions/absorptions are characteristic for each
Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY The emission and absorption of light energy of particular wavelengths by atoms and molecules is a common phenomenon. The emissions/absorptions are characteristic for each
Light and Atoms
 Light and Atoms ASTR 170 2010 S1 Daniel Zucker E7A 317 zucker@science.mq.edu.au ASTR170 Introductory Astronomy: II. Light and Atoms 1 Overview We ve looked at telescopes, spectrographs and spectra now
Light and Atoms ASTR 170 2010 S1 Daniel Zucker E7A 317 zucker@science.mq.edu.au ASTR170 Introductory Astronomy: II. Light and Atoms 1 Overview We ve looked at telescopes, spectrographs and spectra now
LIGHT. Question. Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light.
 LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff. The Bohr Atom. The Bohr Atom Model of Hydrogen atom. Bohr Atom. Bohr Atom
 Periodic Table of Elements Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff Absorption and Emission from Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Universe is mostly (97%) Hydrogen and Helium (H and He) The ONLY
Periodic Table of Elements Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff Absorption and Emission from Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Universe is mostly (97%) Hydrogen and Helium (H and He) The ONLY
9/16/08 Tuesday. Chapter 3. Properties of Light. Light the Astronomer s Tool. and sometimes it can be described as a particle!
 9/16/08 Tuesday Announce: Observations? Milky Way Center movie Moon s Surface Gravity movie Questions on Gravity from Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Newton Movie Chapter 3 Light and Atoms Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
9/16/08 Tuesday Announce: Observations? Milky Way Center movie Moon s Surface Gravity movie Questions on Gravity from Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Newton Movie Chapter 3 Light and Atoms Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
9/19/ Basic Properties of Light and Matter. Chapter 5: Light: The Cosmic Messenger. What is light? Lecture Outline
 Lecture Outline 5.1 Basic Properties of Light and Matter Chapter 5: Light: The Cosmic Messenger Our goals for learning: What is light? What is matter? How do light and matter interact? What is light? Light
Lecture Outline 5.1 Basic Properties of Light and Matter Chapter 5: Light: The Cosmic Messenger Our goals for learning: What is light? What is matter? How do light and matter interact? What is light? Light
Spectroscopy. The wave description of radiation allowed 19thcentury. The Inner Workings of Atoms
 4 Spectroscopy is a powerful observational technique enabling scientists to infer the nature of matter by the way it emits or absorbs radiation. Not only can spectroscopy reveal the chemical composition
4 Spectroscopy is a powerful observational technique enabling scientists to infer the nature of matter by the way it emits or absorbs radiation. Not only can spectroscopy reveal the chemical composition
X Rays must be viewed from space used for detecting exotic objects such as neutron stars and black holes also observing the Sun.
 6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it. 3. Electrons in the outer electron shells have greater potential energy.
 30 Light Emission Answers and Solutions for Chapter 30 Reading Check Questions 1. At these high frequencies, ultraviolet light is emitted. 2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it.
30 Light Emission Answers and Solutions for Chapter 30 Reading Check Questions 1. At these high frequencies, ultraviolet light is emitted. 2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it.
hf = E 1 - E 2 hc = E 1 - E 2 λ FXA 2008 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA
 1 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA Explain how spectral lines are evidence for the existence of discrete energy levels in isolated atoms (i.e. in a gas discharge lamp). Describe the
1 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA Explain how spectral lines are evidence for the existence of discrete energy levels in isolated atoms (i.e. in a gas discharge lamp). Describe the
a. A static electric field exists around a stationary charge such as an electron.
 II. Astronomy Light: A. Analysis of light is by far the primary method with which astronomers obtain information about the Universe. 1. Astronomy is an observational science; classical experiments generally
II. Astronomy Light: A. Analysis of light is by far the primary method with which astronomers obtain information about the Universe. 1. Astronomy is an observational science; classical experiments generally
Next quiz: Monday, October 24
 No homework for Wednesday Read Chapter 8! Next quiz: Monday, October 24 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Types of Spectra: Pictorial Some light sources are comprised of all colors (white light). Other light
No homework for Wednesday Read Chapter 8! Next quiz: Monday, October 24 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Types of Spectra: Pictorial Some light sources are comprised of all colors (white light). Other light
Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 1
 Atoms and Starlight Why do the stars shine? planets shine by reflected sunlight but what generates the Sun s light? What does starlight tell us about the stars? their temperature their chemical composition
Atoms and Starlight Why do the stars shine? planets shine by reflected sunlight but what generates the Sun s light? What does starlight tell us about the stars? their temperature their chemical composition
The Nature of Light. Chapter Five
 The Nature of Light Chapter Five Guiding Questions 1. How fast does light travel? How can this speed be measured? 2. Why do we think light is a wave? What kind of wave is it? 3. How is the light from an
The Nature of Light Chapter Five Guiding Questions 1. How fast does light travel? How can this speed be measured? 2. Why do we think light is a wave? What kind of wave is it? 3. How is the light from an
Wave Description. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves. Physics Department 2/13/2019. Phys1411 Goderya 1. PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies
 PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies for Today s Class 1. How do we explain the motion of energy? 2. What is a wave and what are its properties 3. What is an electromagnetic spectrum? 4. What is a black body and
PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies for Today s Class 1. How do we explain the motion of energy? 2. What is a wave and what are its properties 3. What is an electromagnetic spectrum? 4. What is a black body and
c = l Light: The Cosmic Messenger 1/23/18
 Reading for today s and Thur class: ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 3 Tues 23 Jan 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
Reading for today s and Thur class: ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 3 Tues 23 Jan 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
APAS Laboratory { PAGE } Spectroscopy SPECTROSCOPY
 SPECTROSCOPY SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will eplore different types of emission spectra, calibrate a spectrometer using the spectrum of a known element, and use your calibration to identify an unknown element.
SPECTROSCOPY SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will eplore different types of emission spectra, calibrate a spectrometer using the spectrum of a known element, and use your calibration to identify an unknown element.
Recall: The Importance of Light
 Key Concepts: Lecture 19: Light Light: wave-like behavior Light: particle-like behavior Light: Interaction with matter - Kirchoff s Laws The Wave Nature of Electro-Magnetic Radiation Visible light is just
Key Concepts: Lecture 19: Light Light: wave-like behavior Light: particle-like behavior Light: Interaction with matter - Kirchoff s Laws The Wave Nature of Electro-Magnetic Radiation Visible light is just
Chapter 8. Spectroscopy. 8.1 Purpose. 8.2 Introduction
 Chapter 8 Spectroscopy 8.1 Purpose In the experiment atomic spectra will be investigated. The spectra of three know materials will be observed. The composition of an unknown material will be determined.
Chapter 8 Spectroscopy 8.1 Purpose In the experiment atomic spectra will be investigated. The spectra of three know materials will be observed. The composition of an unknown material will be determined.
Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 2. Figure 3 UNIT 4 - ELECTRONS & ELECTRON ARRANGEMENT
 Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1 UNIT 4 - ELECTRONS & ELECTRON ARRANGEMENT Figure 2 Figure 3 The energy is released as electromagnetic radiation.
Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1 UNIT 4 - ELECTRONS & ELECTRON ARRANGEMENT Figure 2 Figure 3 The energy is released as electromagnetic radiation.
Next Homework Due March 6. Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10)
 Today Summary of Chapter 3: Light All of Chapter 4: Spectra & Atoms Optional: Ast. Toolbox 4-2 Optional: Stephan-Boltzmann Law Next Homework Due March 6 Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10) Extra Credit Astro-talks:
Today Summary of Chapter 3: Light All of Chapter 4: Spectra & Atoms Optional: Ast. Toolbox 4-2 Optional: Stephan-Boltzmann Law Next Homework Due March 6 Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10) Extra Credit Astro-talks:
Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions o-o-o- 3.4 Spectra
 Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions 1991-2010 -o-o-o- 3.4 Spectra 1992 Q37 The diagram below shows the energy levels for the hydrogen atom. (a) Between which two energy levels would an electron transition
Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions 1991-2010 -o-o-o- 3.4 Spectra 1992 Q37 The diagram below shows the energy levels for the hydrogen atom. (a) Between which two energy levels would an electron transition
Light Emission. Today s Topics. Excitation/De-Excitation 10/26/2008. Excitation Emission Spectra Incandescence
 Light Emission Excitation Emission Spectra Incandescence Absorption Spectra Today s Topics Excitation/De-Excitation Electron raised to higher energy level Electron emits photon when it drops back down
Light Emission Excitation Emission Spectra Incandescence Absorption Spectra Today s Topics Excitation/De-Excitation Electron raised to higher energy level Electron emits photon when it drops back down
Discussion Review Test #2. Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6)
 Discussion Review Test #2 Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Galileo used his observations of the changing phases of Venus to demonstrate that a. the sun moves around the Earth b. the universe
Discussion Review Test #2 Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Galileo used his observations of the changing phases of Venus to demonstrate that a. the sun moves around the Earth b. the universe
= λ. Light: The Cosmic Messenger. Continuing Topics for Today 1/24/17. Your account on Mastering Astronomy. ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies
 REMINDER Your account on Mastering Astronomy ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 3 Tues 24 Jan 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
REMINDER Your account on Mastering Astronomy ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 3 Tues 24 Jan 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I
 Astrophysics Study of Light Study of Atoms Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I 1 Atomic Physics elements: substances which cannot be broken down into simpler substances atom : smallest unit of an element
Astrophysics Study of Light Study of Atoms Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I 1 Atomic Physics elements: substances which cannot be broken down into simpler substances atom : smallest unit of an element
Light Emission.
 Light Emission www.physics.sfasu.edu/friedfeld/ch29lec.ppt Radio waves are produced by electrons moving up and down an antenna. Visible light is produced by electrons changing energy states in an atom.
Light Emission www.physics.sfasu.edu/friedfeld/ch29lec.ppt Radio waves are produced by electrons moving up and down an antenna. Visible light is produced by electrons changing energy states in an atom.
How does your eye form an Refraction
 Astronomical Instruments and : Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image? Refraction Refraction is the of light Eye uses refraction
Astronomical Instruments and : Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image? Refraction Refraction is the of light Eye uses refraction
SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB. 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them.
 NAME: SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB 1) What is a spectrum? 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them. a. b. c. 3) Use Wien s law to calculate the surface temperature of the star Alnilam
NAME: SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB 1) What is a spectrum? 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them. a. b. c. 3) Use Wien s law to calculate the surface temperature of the star Alnilam
Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium
 Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium Guidepost You have begun your study of the sun and other stars, but now it is time to study the thin gas and dust that drifts through space between the stars. This chapter
Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium Guidepost You have begun your study of the sun and other stars, but now it is time to study the thin gas and dust that drifts through space between the stars. This chapter
Next quiz: Monday, October 24 Chp. 6 (nothing on telescopes) Chp. 7 a few problems from previous material cough, cough, gravity, cough, cough...
 Next quiz: Monday, October 24 Chp. 6 (nothing on telescopes) Chp. 7 a few problems from previous material cough, cough, gravity, cough, cough... 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Kirchhoff s Laws of Radiation
Next quiz: Monday, October 24 Chp. 6 (nothing on telescopes) Chp. 7 a few problems from previous material cough, cough, gravity, cough, cough... 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Kirchhoff s Laws of Radiation
Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018
 www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
Buy-back points tallied and added: 750 points bought-back. Last Withdrawal date: this friday, Oct 31st.
 Announcements HW #3: Available online now. Due in 1 week, Nov 3rd, 11pm. Buy-back points tallied and added: 750 points bought-back. Last Withdrawal date: this friday, Oct 31st. Evening Observing: next
Announcements HW #3: Available online now. Due in 1 week, Nov 3rd, 11pm. Buy-back points tallied and added: 750 points bought-back. Last Withdrawal date: this friday, Oct 31st. Evening Observing: next
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion #1: A body continues at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a force. Why doesn t the soccer ball move on its own? What causes a soccer ball to roll
Newton s Laws of Motion #1: A body continues at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a force. Why doesn t the soccer ball move on its own? What causes a soccer ball to roll
The Structure of the Atom
 CHAPTER 5 The Structure of the Atom 5.4 Light and Spectroscopy 460 370 BC 1808 1870 1897 1910 1925 Today Democritus Atomism Dalton Modern atomic theory Crookes Cathode rays Thomson Discovery of the electron
CHAPTER 5 The Structure of the Atom 5.4 Light and Spectroscopy 460 370 BC 1808 1870 1897 1910 1925 Today Democritus Atomism Dalton Modern atomic theory Crookes Cathode rays Thomson Discovery of the electron
Name: Partner(s): 1102 or 3311: Desk # Date: Spectroscopy Part I
 Name: Partner(s): 1102 or 3311: Desk # Date: Spectroscopy Part I Purpose Investigate Kirchhoff s Laws for continuous, emission and absorption spectra Analyze the solar spectrum and identify unknown lines
Name: Partner(s): 1102 or 3311: Desk # Date: Spectroscopy Part I Purpose Investigate Kirchhoff s Laws for continuous, emission and absorption spectra Analyze the solar spectrum and identify unknown lines
The Basics of Light. Sunrise from the Space Shuttle, STS-47 mission. The Basics of Light
 The Basics of Light The sun as it appears in X-ray light (left) and extreme ultraviolet light (right). Light as energy Light is remarkable. It is something we take for granted every day, but it's not something
The Basics of Light The sun as it appears in X-ray light (left) and extreme ultraviolet light (right). Light as energy Light is remarkable. It is something we take for granted every day, but it's not something
10/27/2017 [pgs ]
![10/27/2017 [pgs ] 10/27/2017 [pgs ]](/thumbs/82/85139288.jpg) Objectives SWBAT explain the relationship between energy and frequency. SWBAT predict the behavior of and/or calculate quantum and photon energy from frequency. SWBAT explain how the quantization of energy
Objectives SWBAT explain the relationship between energy and frequency. SWBAT predict the behavior of and/or calculate quantum and photon energy from frequency. SWBAT explain how the quantization of energy
Color. 3. Why are the color labels in the table above plural (i.e., Reds rather than Red )?
 NS D3 Electron Energy and Light Name From fireworks to stars, the color of light is useful in finding out what s in matter. The emission of light by hydrogen and other atoms has played a key role in understanding
NS D3 Electron Energy and Light Name From fireworks to stars, the color of light is useful in finding out what s in matter. The emission of light by hydrogen and other atoms has played a key role in understanding
Topics Covered in Chapter. Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation. A Subatomic Interlude II. A Subatomic Interlude. A Subatomic Interlude III
 Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation
 Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation 1 Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation 1 Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
PHYS General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source. c = speed of light = 3 x 10 8 m/s
 PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to analyze the emission of light from a hydrogen source and measure and the wavelengths
PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to analyze the emission of light from a hydrogen source and measure and the wavelengths
Electron Energy and Light
 Why? Electron Energy and Light How does light reveal the behavior of electrons in an atom? From fireworks to stars, the color of light is useful in finding out what s in matter. The emission of light by
Why? Electron Energy and Light How does light reveal the behavior of electrons in an atom? From fireworks to stars, the color of light is useful in finding out what s in matter. The emission of light by
The Nature of Light. We have a dual model
 Light and Atoms Properties of Light We can come to understand the composition of distant bodies by analyzing the light they emit This analysis can tell us about the composition as well as the temperature
Light and Atoms Properties of Light We can come to understand the composition of distant bodies by analyzing the light they emit This analysis can tell us about the composition as well as the temperature
Atoms and Spectroscopy
 Atoms and Spectroscopy Lecture 3 1 ONE SMALL STEP FOR MAN ONE GIANT LEAP FOR MANKIND 2 FROM ATOMS TO STARS AND GALAXIES HOW DO WE KNOW? Observations The Scientific Method Hypothesis Verifications LAW 3
Atoms and Spectroscopy Lecture 3 1 ONE SMALL STEP FOR MAN ONE GIANT LEAP FOR MANKIND 2 FROM ATOMS TO STARS AND GALAXIES HOW DO WE KNOW? Observations The Scientific Method Hypothesis Verifications LAW 3
(in case you missed it yesterday ) Merger of Two Neutron Stars!
 (in case you missed it yesterday ) Merger of Two Neutron Stars! https://cmns.umd.edu/news-events/features/3997 More on this later in the semester Lecture #14: Plan Light (cont d) Atomic physics Formation
(in case you missed it yesterday ) Merger of Two Neutron Stars! https://cmns.umd.edu/news-events/features/3997 More on this later in the semester Lecture #14: Plan Light (cont d) Atomic physics Formation
The Theory of Electromagnetism
 Notes: Light The Theory of Electromagnetism James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Scottish physicist. Found that electricity and magnetism were interrelated. Moving electric charges created magnetism, changing
Notes: Light The Theory of Electromagnetism James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Scottish physicist. Found that electricity and magnetism were interrelated. Moving electric charges created magnetism, changing
Assignments. For Wed. 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial)
 Assignments For Wed. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial) 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12 Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger Which forms of light are lower in energy and frequency than the
Assignments For Wed. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial) 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12 Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger Which forms of light are lower in energy and frequency than the
Lecture: October 6, 2010
 Lecture: October 6, 2010 Announcements: Next Observatory Opportunity: Tonight at 7:30 Problem Set 3 Due next Monday Second Exam October 25 Tides Since gravitational force decreases with (distance) 2, the
Lecture: October 6, 2010 Announcements: Next Observatory Opportunity: Tonight at 7:30 Problem Set 3 Due next Monday Second Exam October 25 Tides Since gravitational force decreases with (distance) 2, the
Possible Extra Credit Option
 Possible Extra Credit Option Attend an advanced seminar on Astrophysics or Astronomy held by the Physics and Astronomy department. There are seminars held every 2:00 pm, Thursday, Room 190, Physics & Astronomy
Possible Extra Credit Option Attend an advanced seminar on Astrophysics or Astronomy held by the Physics and Astronomy department. There are seminars held every 2:00 pm, Thursday, Room 190, Physics & Astronomy
Light carries energy. Lecture 5 Understand Light. Is light. Light as a Particle. ANSWER: Both.
 Light carries energy Lecture 5 Understand Light Reading: Chapter 6 You feel energy carried by light when light hits your skin. Energy Conservation: Radiation energy will be given to molecules making your
Light carries energy Lecture 5 Understand Light Reading: Chapter 6 You feel energy carried by light when light hits your skin. Energy Conservation: Radiation energy will be given to molecules making your
II Light.
 II Light http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 0. Light Light is the main tool we have in astronomy. We detect light from distant objects and can determine the temperature, density, composition,
II Light http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 0. Light Light is the main tool we have in astronomy. We detect light from distant objects and can determine the temperature, density, composition,
Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013
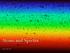 Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013 Announcements Second writing assignment due two weeks from today (again, on a news item of your choice). Be sure to make plans to visit one of the open observing nights
Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013 Announcements Second writing assignment due two weeks from today (again, on a news item of your choice). Be sure to make plans to visit one of the open observing nights
The Physics of Light, part 2. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 7: The Physics of Light, part 2 Astronomy 111 Spectra Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are. Every type of atom, ion, and molecule has a unique spectrum Ion: an atom with electrons
Lecture 7: The Physics of Light, part 2 Astronomy 111 Spectra Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are. Every type of atom, ion, and molecule has a unique spectrum Ion: an atom with electrons
Spectroscopy Lesson Outline
 Spectroscopy Lesson Outline Syllabus References 9.7.3.1 Spectroscopy is a vital tool for astronomers and provides a wealth of information Pre-video Activity: Spectroscopy Worksheet Resources Video: Spectra
Spectroscopy Lesson Outline Syllabus References 9.7.3.1 Spectroscopy is a vital tool for astronomers and provides a wealth of information Pre-video Activity: Spectroscopy Worksheet Resources Video: Spectra
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1. Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017
 Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1 Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017 Reminders Star party tonight! Homework #3 due Monday Exam #1 Monday, September 25 The nature of light Look, but don t
Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1 Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017 Reminders Star party tonight! Homework #3 due Monday Exam #1 Monday, September 25 The nature of light Look, but don t
Homework Due Feb Is the spectrum below a. an absorption line one b. a continuum c. an emission line one d. Doppler shifted e.
 NatSci102 Professors G. and M. Rieke Homework Due Feb. 8 Homework on spectroscopy, colors, and light. Lecture notes for Jan 29 and Feb 1 will be very helpful. This homework will be due on Feb 8 but working
NatSci102 Professors G. and M. Rieke Homework Due Feb. 8 Homework on spectroscopy, colors, and light. Lecture notes for Jan 29 and Feb 1 will be very helpful. This homework will be due on Feb 8 but working
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
