Relics of the hierarchical assembly of the Milky Way
|
|
|
- Heather Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 5, 83 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della Supplementi Relics of the hierarchical assembly of the Milky Way M. Bellazzini INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, Bologna, Italy Abstract. I briefly review the more recent observational results about the search of stellar relics of the process of formation of the Milky Way galaxy. The stellar tidal stream of the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy is now traced all over the sky providing direct evidence of the last phases of the hyerarchical assembly of the Galactic Halo. The Monoceros ring, and the likely related Canis Major relic, seem to indicate that also the disky components of our Galaxy may have a hyerachical origin, at least in part. Key words. Galactic structure Dwarf galaxies 1. Introduction The process of hierarchical merging (White & Rees 1978; White & Frenk 1991) is generally accepted as the driving mechanism of the formation of giant galaxies. The study of the local (e.g. Galactic or in the Local Group) relics of such process may provide an unprecedentedly detailed insight of the current cosmological model as well as a formidable testbed for theories of galaxy formation. The first clear observational evidence of the very existence of such relics dates back just a decade, e.g. the discovery of the Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxy (Sgr-dSph) Ibata et al. (1994, 1997). The morphology of Sgr suggests that the dwarf galaxy is currently disrupting under the strain of the Galactic tidal field. The discovery of Sgr opened a new epoch in the study of the formation and evolution of our own Galaxy and triggered the interest of several scientists. New analysis began to appear at Send offprint requests to: M. Bellazzini Correspondence to: michele.bellazzini@bo.astro.it an increasing rate since year 2000, when the results of large surveys (2MASS, SDSS) revolutionized the approach to the field and changed our view of the Milky Way. The best way to have a direct idea of this change of perspective is to look at Fig. 1 of Newberg et al. (2002). The slice of Galaxy probed out to R GC 50 kpc by F stars from the SDSS shows that the Halo is far from being homogeneous, but, in fact, is rich of clumps and filaments that are the fingerprints of the recent accretion events that contributed to its construction. The (successful) search for relic substructures has extended to M 31 (Ibata et al. 2001b; McConnachie et al. 2003; Merret et al. 2003), to nearby dwarfs (Coleman et al. 2004; Kleyna et al. 2003), and to galaxies outside the Local Group (Forbes et al. 2003; Peng et al. 2002; Pohlen et al. 2003), but it has to be recalled that the variety of detected structures shouldn t necessarily be ascribed to the same origin. Here I try to give a brief account of the most recent results concerning the substructures of the Milky Way.
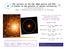
2 84 M. Bellazzini: The assembly of the Milky Way Fig. 1. Galactic coordinates distribution of the M giants from 2MASS, selected according to Majewski et al. (2003). The thicker points are the Sgr Stream members selected in the Y-Z plane (Galactocentric Cartesian coordinates). The position of some globular clusters possibly related with the Stream are also reported. The two blobs around b 40 and l 290 are the Magellanic Clouds. The stars affected by large extinction, near the Galactic plane, have been removed from the sample. 2. The Sagittarius galaxy and its Stream The lucky occurrence that Sgr is dominated by an intermediate-age ( 5 6 gyr) metalrich ([M/H] 0.5) population (Layden & Sarajedini 2000; Monaco et al. 2002) is the key characteristic that make it possible to trace the Sgr Stream all over the sky (see Fig. 1). The brightest Red Giant Branch (RGB) stars of Sgr are of spectral type M, i.e. much redder than the typical Halo stars. The M-giants can be easily selected from their color in the All Sky catalogue of 2MASS. At galactic latitudes larger than l 20, e.g. where the contribution by
3 M. Bellazzini: The assembly of the Milky Way 85 Fig. 2. Galactocentric X-Z distribution of 2Mass M-giants. The Stream stars, selected as in Fig. 1, clearly traces two lobes of the rosette orbit of Sgr. The model orbit by Ibata et al. (2001a) is also reported for comparison. disc M stars is negligible, the Sgr Stream appear clearly as the major substructure of the outer halo, tracing the polar rosette orbit of the parent galaxy (Majewski et al. 2003), as clearly shown in Fig. 2. It is now observationally established that the disruption of Sgr is providing a sizeable contribution to the assembly of the Halo in terms of stars of various ages (from carbon stars to RR Lyrae, from A-F Main sequence stars to Blue Horizontal Branch stars, see Ibata et al. 2001a; Ibata et al. 2002; Ivezic et al. 2000; Newberg et al. 2002; Yanny et al. 2003; Martínez-Delgado et al. 2001; Mateo, Olszewski & Morrison 1998, and references therein), and of globular clusters (Bellazzini, Ferraro & Ibata 2003a; Bellazzini et al. 2003b; Bellazzini, Ibata & Ferraro 2003c; Martínez- Delgado et al. 2002), and, presumably, Cold Dark Matter. While the search for the traces of previous passages of Sgr is going on (Newberg et
4 86 M. Bellazzini: The assembly of the Milky Way al. 2003), various groups are collecting huge amounts of radial velocities of Stream stars. The kynematics of a coherent structure sampling the Galactic Halo from R GC 16 kpc to R GC 50 kpc may hidden a treasure of information about the shape, the mass and the degree of lumpiness of the CDM halo that hosts the Milky Way. Significant constraints on the shape of the Galactic potential, that appears quite spheric, have been already obtained by Ibata et al. (2001a) and by Majewski et al. (2004). The fact that the stars of the Sgr Stream are currently raining on the solar neightbourhood (Majewski et al. 2004) may also imply phase-space lumpiness in the local distribution of Dark Matter, possibly with relevant consequences on the experiments for the detection of its constituent particles (neutralinos, see Helmi et al. 2002; Freese et al. 2004, and references therein). 3. The Monoceros Ring and the Canis Major relic An even more interesting case is provided by the recently discovered Monoceros Ring structure (hereafter the Ring, for brevity, Newberg et al. 2002; Yanny et al. 2003; Ibata et al. 2003; Majewski et al. 2003; Rocha-Pinto et al. 2003), near the Galactic plane. The more recent observational results (Crane 2003; Martin et al. 2004) suggests that the Ring is the stream remnant of an in-plane accretion that may be contributing to the build-up of the thick disk (see also Helmi et al. 2003; Abadi et al. 2003). In particular Martin et al. (2004), while tracing the whole extent of the Ring using M- giants from the 2MASS database discovered a large overdensity of Ring-like M-giants in the Canis Major constellation. The elliptical shape, the overall structure of this overdensity and its coincidence with a noticeable grouping of globular (and open) clusters led Martin et al. (2004) to the conclusion that it is the relic of the dwarf galaxy whose disruption generated the Ring. The discovered relic is approximately centered at galactic coordinates (l,b) (240 o, 7 o ), it has a FWHM extension in the sky of 12 in the latitude direction and it is located at 7 kpc from the Sun (i.e., (m M) ), as obtained from the photometric parallax to M-giants introduced by Majewski et al. (2003). The mass, luminosity and characteristic dimensions of Canis Major appear quite similar to those of the Sgr dsph. The similarity with Sgr extends to other relevant characteristics: the two objects seem to host a similar grouping of globular clusters, and the upper RGB of both galaxies is dominated by stars of similar colour (M-giants), which are present in similar numbers in both galaxies. The kinematic coherence of the Ring and its association with several clusters has been also confirmed by Rocha-Pinto et al. (2003); Frinchaboy et al. (2004); Forbes, Strader & Brodie (2004). Rocha-Pinto et al. (2004) report on a new overdensity of M giants covering the constellations of Andromeda and Triangulum. The kynematics of the member stars leave open the possibility that this structure is also associated with the Ring. 4. Other structures The examples reported above concern large scale structures that can be identified and followed all over the Galaxy. The solar neighbourhood offers the opportunity to search a very small spot of Galaxy with the full 6-D information, i.e. position and 3-D velocity. The local relics of an ancient disruption event were found by Helmi et al. (1999) as an anomalous phase-space clump of metal poor stars. The conclusions of their analysis is that...about ten per cent of the metal-poor stars in the halo of the Milky Way, outside the radius of the Sun s orbit, come from a single coherent structure that was disrupted during or soon after the Galaxy s formation. This object had a highly inclined orbit about the Milky Way at a maximum distance of 16kpc, and it probably resembled the Fornax and Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxies. A similar case has been recently reported by Navarro et al. (2004), that showed that also a familiar star as Arcturus may have an extragalctic origin. Gilmore et al. (2002) found an unexpected kynematical signal in a radial velocity survey
5 M. Bellazzini: The assembly of the Milky Way 87 performed with the 2dF spectrograph and interpreted it as the signature of a past accretion event. Mizutani et al. (2003) have suggested that Gilmore et al. s anomalous stars may be related to the disruption of the parent galaxy of ω Centauri, an interesting object by itself in the perspective of the present review (see Ferraro et al. 2002; Tsuchiya et al. 2003; Bekki & Freeman 2003, and references therein). 5. Final Considerations The present review cannot be considered neither exhaustive nor complete and I apologize in advance with the authors that cannot find their work reported here. Moreover I largely neglected theoretical studies, focusing only on the observational side. For a more complete approach to the topic see the volume by Martínez-Delgado & Prada (2004) that is expected to present a global picture as of September On the other hand new results appear nearly every day on the astro-ph and the matter cannot be succesfully cristallized in a long living review at the present time. Acknowledgements. I am very grateful to the SOC and LOC of the SAIt 2004 meeting. I am obviously indebted to all the people that works (or worked) with me at these fascinating projects: F.R. Ferraro, R. Ibata, N. Martin, G. Lewis, M.Irwin, L. Monaco, E. Pancino, W. Dehnen, F. Fusi Pecci. The financial support of MIUR is acknowledged. References Abadi M.G., et al., 2003, ApJ, 597, 21 Bekki K., Freeman K.C., 2003, MNRAS, 346, L11 Bellazzini M., Ferraro F.R., Ibata R., 2002, AJ, 124, 915 Bellazzini M., Ferraro F.R., Ibata R., 2003a, AJ, 125, 188 Bellazzini M., et al., 2003b, A&A, 405, 577 Bellazzini M., Ibata R., Ferraro F.R., 2003c, in Satellites and Tidal Tails, D. Martinez- Delgado and F. Prada Eds., S. Francisco, ASP, ASP Conf. Series, in press (astroph/ ) Coleman M., et al., 2004, AJ, 127, 832 Crane J.D., et al., 2003, ApJ, 594, L119 Ferraro F.R., et al., 2002, ApJ, 573, L89 Forbes D.A., et al., 2003, Science, 301, 1217 Forbes D.A., Strader J., Brodie J.P., 2004, AJ, in press (astro-ph/403136) Freese K., et al., 2004, Physical Review Letters, 92, Frinchaboy P.M., et al., 2004, ApJ, 602, L21 Gilmore G., et al., 2002, ApJ, 574, L39 Helmi A., et al., 1999, Nature, 407, 53 Helmi A., et al., 2002, Physical Review D, 66, Helmi A., et al., 2003, ApJ, 592, L25 Kleyna J., et al., 2003, ApJ, 588, L21 Ibata, R.A., Irwin, M.J., Gilmore, G., 1994, Nature, 370, 194 Ibata, R.A., et al., 1997, AJ, 113, 634 Ibata R., et al., 2001a, ApJ, 551, 294 Ibata R., et al., 2001b, Nature, 412, 49 Ibata R., Lewis G., Irwin M., Cambrésy L., 2002, MNRAS, 332, 921 Ibata R., et al., 2003, MNRAS, 340, L21 Ivezic, Z., et al., 2000, AJ, 120, 963 Layden A.C., Sarajedini A., 2000, AJ, 119, 1760 Majewski S., et al., 2003, ApJ, 599, 1082 Majewski S., et al., 2003, AJ, in press, astroph/ Martínez-Delgado, D., et al., 2001, ApJ, 549, L199 Martínez-Delgado, D., et al., 2002, ApJ, 537, L19 Martinez-Delgado D., Prada F., 2004, Satellites and Tidal Tails, ASP Conf. Series, in press Martin N., et al., 2004, MNRAS, 348, 12 (Pap- I) Mateo, M., Olszewski, E.W. & Morrison, H.L., 1998, ApJ, 508, L55 McConnachie A.W., et al., 2003, MNRAS, 343, 1335 Merret H.R., et al., 2003, MNRAS, 346, L62 Mizutani A., et al., 2003, ApJ, 589, L89 Monaco, L., et al., 2002, ApJ, 578, L47 Navarro J., et al., 2004, ApJ, 601, L34 Newberg H., et al., 2002, ApJ, 569, 245 Newberg H., et al., 2003, ApJ, 596, L191 Peng E.W., et al., 2002, AJ, 124, 3144 Pohlen M., et al., 2003, in Satellites and Tidal Tails D. Martinez-delgado and F. Prada Eds.,
6 88 M. Bellazzini: The assembly of the Milky Way S. Francisco, ASP, ASP Conf. Series, in press (astro-ph/ ) Rocha-Pinto H., et al., 2003, ApJ, 594, L115 Rocha-Pinto H., et al., 2004, AJ, submitted, astro-ph/ Tsuchiya T., et al., 2003, ApJ, 589, L29 White S., Rees M., 1978, MNRAS, 183, 341 White S., Frenk C., 1991, ApJ, 379, 52 Yanny B., et al., 2003, ApJ 588, 824
MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
 MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 5071 West Saanich Road Victoria, British Columbia V8X 4M6, Canada vandenbergh@dao.nrc.ca Received: 1996 July 1 ; accepted:
MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 5071 West Saanich Road Victoria, British Columbia V8X 4M6, Canada vandenbergh@dao.nrc.ca Received: 1996 July 1 ; accepted:
The Accretion History of the Milky Way
 The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 26 May 2004
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Gd202 March 20, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) arxiv:astro-ph/0405526v1 26 May 2004 Probing the Canis Major stellar over-density as due to the Galactic
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Gd202 March 20, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) arxiv:astro-ph/0405526v1 26 May 2004 Probing the Canis Major stellar over-density as due to the Galactic
Galactic Globular Clusters: the stellar laboratory
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 3, 80 c SAIt 2003 Memorie della Supplementi Galactic Globular Clusters: the stellar laboratory Francesco R. Ferraro Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Bologna, via Ranzani
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 3, 80 c SAIt 2003 Memorie della Supplementi Galactic Globular Clusters: the stellar laboratory Francesco R. Ferraro Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Bologna, via Ranzani
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 20 Oct 2004
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 27 September 2005 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Why the Canis Major overdensity is not due to the Warp: analysis of its radial profile and velocities
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 27 September 2005 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Why the Canis Major overdensity is not due to the Warp: analysis of its radial profile and velocities
New insights into the Sagittarius stream
 New insights into the Sagittarius stream EWASS, Turku July 8th, 213 Martin C. Smith Shanghai Astronomical Observatory http://hubble.shao.ac.cn/~msmith/ Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal(ish) Since its discovery
New insights into the Sagittarius stream EWASS, Turku July 8th, 213 Martin C. Smith Shanghai Astronomical Observatory http://hubble.shao.ac.cn/~msmith/ Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal(ish) Since its discovery
A dwarf galaxy remnant in Canis Major: the fossil of an in-plane accretion on to the Milky Way
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 348, 12 23 (2004) A dwarf galaxy remnant in Canis Major: the fossil of an in-plane accretion on to the Milky Way N. F. Martin, 1 R. A. Ibata, 1 M. Bellazzini, 2 M. J. Irwin, 3
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 348, 12 23 (2004) A dwarf galaxy remnant in Canis Major: the fossil of an in-plane accretion on to the Milky Way N. F. Martin, 1 R. A. Ibata, 1 M. Bellazzini, 2 M. J. Irwin, 3
Looking into a nucleus with unprecedented detail (structure & kinematics): the case of the Sgr dsph. Results from:
 The nucleus of the Sgr dsph galaxy and M54: A window on the process of galaxy nucleation by Michele Bellazzini INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna Looking into a nucleus with unprecedented detail
The nucleus of the Sgr dsph galaxy and M54: A window on the process of galaxy nucleation by Michele Bellazzini INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna Looking into a nucleus with unprecedented detail
THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE
 THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela), Bob Zinn (Yale U., USA), Sonia Duffau (U. de Chile), Yara Jaffé, Jesús Hernández, Yolimar Subero (CIDA, Venezuela), G. Carraro
THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela), Bob Zinn (Yale U., USA), Sonia Duffau (U. de Chile), Yara Jaffé, Jesús Hernández, Yolimar Subero (CIDA, Venezuela), G. Carraro
Globular clusters and the formation of the outer Galactic halo
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 354, 713 719 (2004) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08228.x Globular clusters and the formation of the outer Galactic halo Sidney van den Bergh 1 and A. D. Mackey 2 1 Dominion Astrophysical
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 354, 713 719 (2004) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08228.x Globular clusters and the formation of the outer Galactic halo Sidney van den Bergh 1 and A. D. Mackey 2 1 Dominion Astrophysical
Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars
 EPJ Web of Conferences 19, 02002 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20121902002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars B. Sesar
EPJ Web of Conferences 19, 02002 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20121902002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars B. Sesar
The Geometry of Sagittarius Stream from PS1 3π RR Lyrae
 The Geometry of Sagittarius Stream from PS1 3π RR Lyrae Nina Hernitschek, Caltech collaborators: Hans-Walter Rix, Branimir Sesar, Judith Cohen Swinburne-Caltech Workshop: Galaxies and their Halos, Sept.
The Geometry of Sagittarius Stream from PS1 3π RR Lyrae Nina Hernitschek, Caltech collaborators: Hans-Walter Rix, Branimir Sesar, Judith Cohen Swinburne-Caltech Workshop: Galaxies and their Halos, Sept.
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009](/thumbs/90/104342312.jpg) Discovery of a New, Polar-Orbiting Debris Stream in the Milky Way Stellar Halo Heidi Jo Newberg 1, Brian Yanny 2, & Benjamin A. Willett 1 arxiv:0906.3291v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009 ABSTRACT We show that
Discovery of a New, Polar-Orbiting Debris Stream in the Milky Way Stellar Halo Heidi Jo Newberg 1, Brian Yanny 2, & Benjamin A. Willett 1 arxiv:0906.3291v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009 ABSTRACT We show that
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 5 Nov 2001
 The Dynamics, Structure & History of Galaxies ASP Conference Series, Vol. nnn, 2002 G. S. Da Costa & E. M. Sadler, eds Star Streams in the Milky Way Halo arxiv:astro-ph/0111097v1 5 Nov 2001 Heather Morrison
The Dynamics, Structure & History of Galaxies ASP Conference Series, Vol. nnn, 2002 G. S. Da Costa & E. M. Sadler, eds Star Streams in the Milky Way Halo arxiv:astro-ph/0111097v1 5 Nov 2001 Heather Morrison
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology
 The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The Milky Way Formation Timescale
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 13 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della The Milky Way Formation Timescale A. Aparicio 1,2, A. Rosenberg 2, G. Piotto 3, I. Saviane 4 and A. Recio-Blanco 3 1 Departamento de Astrofisica, Universidad
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 13 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della The Milky Way Formation Timescale A. Aparicio 1,2, A. Rosenberg 2, G. Piotto 3, I. Saviane 4 and A. Recio-Blanco 3 1 Departamento de Astrofisica, Universidad
A disk origin for inner stellar halo structures around the Milky Way
 A disk origin for inner stellar halo structures around the Milky Way Adrian Price-Whelan (Princeton University)! adrn " adrianprw Kathryn Johnston, Allyson Sheffield, Chervin Laporte, Maria Bergemann,
A disk origin for inner stellar halo structures around the Milky Way Adrian Price-Whelan (Princeton University)! adrn " adrianprw Kathryn Johnston, Allyson Sheffield, Chervin Laporte, Maria Bergemann,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 1 Jul 2005
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 19 September 2005 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) A radial velocity survey of low Galactic latitude structures: I. Kinematics of the Canis Major dwarf galaxy
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 19 September 2005 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) A radial velocity survey of low Galactic latitude structures: I. Kinematics of the Canis Major dwarf galaxy
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 21 May 2004
 Exploring Halo Substructure with Giant Stars: A diffuse star cloud or tidal debris around the Milky Way in Triangulum-Andromeda arxiv:astro-ph/0405437 v1 21 May 2004 Helio J. Rocha-Pinto, Steven R. Majewski,
Exploring Halo Substructure with Giant Stars: A diffuse star cloud or tidal debris around the Milky Way in Triangulum-Andromeda arxiv:astro-ph/0405437 v1 21 May 2004 Helio J. Rocha-Pinto, Steven R. Majewski,
Stellar Streams and Their Importance to Galaxy Formation and Evolution
 Department of Physics, Engineering Physics and Astronomy, Queen s University Stellar Streams and Their Importance to Galaxy Formation and Evolution Nicholas Fantin December 9th, 2014 ABSTRACT The Sloan
Department of Physics, Engineering Physics and Astronomy, Queen s University Stellar Streams and Their Importance to Galaxy Formation and Evolution Nicholas Fantin December 9th, 2014 ABSTRACT The Sloan
The distance to the Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxy from the red giant branch tip
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 353, 874 878 (2004) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08122.x The distance to the Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxy from the red giant branch tip L. Monaco, 1,2,3 M. Bellazzini,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 353, 874 878 (2004) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08122.x The distance to the Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxy from the red giant branch tip L. Monaco, 1,2,3 M. Bellazzini,
The HERMES project. Reconstructing Galaxy Formation. Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU. The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012
 The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
Evidence for coupling between the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy and the Milky Way warp
 Evidence for coupling between the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy and the Milky Way warp Jeremy Bailin Steward Observatory, University of Arizona 933 North Cherry Ave, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA ABSTRACT Using recent
Evidence for coupling between the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy and the Milky Way warp Jeremy Bailin Steward Observatory, University of Arizona 933 North Cherry Ave, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA ABSTRACT Using recent
Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN)
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Thomas M. Brown (tbrown@stsci.edu) and Marc Postman (postman@stsci.edu) Space Telescope Science Institute Daniela Calzetti (calzetti@astro.umass.edu)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Thomas M. Brown (tbrown@stsci.edu) and Marc Postman (postman@stsci.edu) Space Telescope Science Institute Daniela Calzetti (calzetti@astro.umass.edu)
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 4 Dec 2002
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 0, 0 c SAIt 2002 ÊÊ ÄÝÖ ËØ Ö Ò Ø À ÐÓ ÌÖ Ö Ó ËØÖ Ñ Ó Ö Ó ÖÙÔØ Ð Ü arxiv:astro-ph/0212116v1 4 Dec 2002 A. Katherina Vivas 1,2 and Robert Zinn 2, 1 Centro de Investigaciones de Astronomía
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 0, 0 c SAIt 2002 ÊÊ ÄÝÖ ËØ Ö Ò Ø À ÐÓ ÌÖ Ö Ó ËØÖ Ñ Ó Ö Ó ÖÙÔØ Ð Ü arxiv:astro-ph/0212116v1 4 Dec 2002 A. Katherina Vivas 1,2 and Robert Zinn 2, 1 Centro de Investigaciones de Astronomía
Signatures of star streams in the phase space distribution of nearby halo stars ABSTRACT
 A&A 474, 857 861 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20077463 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Signatures of star streams in the phase space distribution of nearby halo stars C. Dettbarn 1, B. Fuchs 1,C.Flynn
A&A 474, 857 861 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20077463 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Signatures of star streams in the phase space distribution of nearby halo stars C. Dettbarn 1, B. Fuchs 1,C.Flynn
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 31 May 2006
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2002) Printed 3 February 2008 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Spatial and Velocity clumping in an SDSS blue horizontal branch star catalogue arxiv:astro-ph/0605740v1 31
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2002) Printed 3 February 2008 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Spatial and Velocity clumping in an SDSS blue horizontal branch star catalogue arxiv:astro-ph/0605740v1 31
Substructure in the Galaxy
 Substructure in the Galaxy Amina Helmi Kapteyn Astronomical Institute Groningen, NL Is this how our Galaxy formed? Jeffrey Gardner Hierarchical paradigm Main characteristic of model: mergers Can we find
Substructure in the Galaxy Amina Helmi Kapteyn Astronomical Institute Groningen, NL Is this how our Galaxy formed? Jeffrey Gardner Hierarchical paradigm Main characteristic of model: mergers Can we find
STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES
 STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES 23. Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen, the Netherlands www.astro.rug.nl/ vdkruit Beijing, September 2011 Outline The local Mass
STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES 23. Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen, the Netherlands www.astro.rug.nl/ vdkruit Beijing, September 2011 Outline The local Mass
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Oct 2003
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Dec 1998
 Spectroscopy of red giants of the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy arxiv:astro-ph/9812267v1 14 Dec 1998 G. Marconi Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma P. Bonifacio Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste L. Pasquini
Spectroscopy of red giants of the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy arxiv:astro-ph/9812267v1 14 Dec 1998 G. Marconi Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma P. Bonifacio Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste L. Pasquini
Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM. Brian Yanny Fermilab. DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug
 Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM Brian Yanny Fermilab DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug 19 2011 M31 (Andromeda) Our Local Group neighbors: Spiral galaxies similar to The Milky Way 150 kpc M33
Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM Brian Yanny Fermilab DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug 19 2011 M31 (Andromeda) Our Local Group neighbors: Spiral galaxies similar to The Milky Way 150 kpc M33
GLOBULAR CLUSTERS IN THE MILKY WAY AND DWARF GALAXIES: A DISTRIBUTION-FREE STATISTICAL COMPARISON
 The Astrophysical Journal, 683:72 77, 2008 August 0 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U. S. A. GLOBULAR CLUSTERS I THE MILKY WAY AD DWARF GALAXIES: A DISTRIBUTIO-FREE
The Astrophysical Journal, 683:72 77, 2008 August 0 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U. S. A. GLOBULAR CLUSTERS I THE MILKY WAY AD DWARF GALAXIES: A DISTRIBUTIO-FREE
Exploring the Structure of the Milky Way with WFIRST
 Exploring the Structure of the Milky Way with WFIRST Heidi Jo Newberg Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Simulation: Stefan Gottlöber/AIP Image Credit: Heidi Newberg Milky Way Structure we want it all: The
Exploring the Structure of the Milky Way with WFIRST Heidi Jo Newberg Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Simulation: Stefan Gottlöber/AIP Image Credit: Heidi Newberg Milky Way Structure we want it all: The
Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history
 Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history Author: Ana Hočevar Advisor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Department of Physics, University of Ljubljana March 18, 2006 Abstract Galaxy formation theory which predicts canibalism
Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history Author: Ana Hočevar Advisor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Department of Physics, University of Ljubljana March 18, 2006 Abstract Galaxy formation theory which predicts canibalism
Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations
 Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations Felice Cusano INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna LBT Team Italy collaborators: Gisella Clementini, Alessia Garofalo, Michele
Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations Felice Cusano INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna LBT Team Italy collaborators: Gisella Clementini, Alessia Garofalo, Michele
Debris streams in the solar neighbourhood as relicts from the formation of the Milky Way
 Debris streams in the solar neighbourhood as relicts from the formation of the Milky Way Amina Helmi, Simon D.M. White, P. Tim de Zeeuw and HongSheng Zhao Leiden Observatory, P.O. Box 9513, 2300 RA Leiden,
Debris streams in the solar neighbourhood as relicts from the formation of the Milky Way Amina Helmi, Simon D.M. White, P. Tim de Zeeuw and HongSheng Zhao Leiden Observatory, P.O. Box 9513, 2300 RA Leiden,
 http://www.eso.org/sci/activities/santiago/personnel/visitors.html Morphological transformation in galaxy clusters > interpreted as the result of galaxy harassment (Moore et al. 1996). Harassment = 1
http://www.eso.org/sci/activities/santiago/personnel/visitors.html Morphological transformation in galaxy clusters > interpreted as the result of galaxy harassment (Moore et al. 1996). Harassment = 1
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo
 Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo L. Aguilar, A. Brown & H. Velázquez Inst. de Astronomía, UNAM (México) & Leiden Observatory (Netherlands) The punch line... When looking for something, sometimes what
Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo L. Aguilar, A. Brown & H. Velázquez Inst. de Astronomía, UNAM (México) & Leiden Observatory (Netherlands) The punch line... When looking for something, sometimes what
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy
 Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Apr 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Apr 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Apr 2009](/thumbs/84/89496149.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 6 (2009) Printed 30 May 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Red Clump stars in the Boötes III stellar system arxiv:0904.3068v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Apr 2009 M. Correnti 1, M. Bellazzini
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 6 (2009) Printed 30 May 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Red Clump stars in the Boötes III stellar system arxiv:0904.3068v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Apr 2009 M. Correnti 1, M. Bellazzini
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 5 Jul 2006
 THE DWARF SATELLITES OF M31 AND THE GALAXY Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National Research Council of Canada, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria,
THE DWARF SATELLITES OF M31 AND THE GALAXY Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National Research Council of Canada, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 4 Nov 2004
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 7 (2004) Printed 28 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The central density cusp of the Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxy arxiv:astro-ph/0411107v1 4 Nov 2004 L. Monaco
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 7 (2004) Printed 28 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The central density cusp of the Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxy arxiv:astro-ph/0411107v1 4 Nov 2004 L. Monaco
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Gaia-LSST Synergy. A. Vallenari. INAF, Padova
 Gaia-LSST Synergy A. Vallenari INAF, Padova The Galaxy view Unveiling the complex history of the MW assembly and internal evolution is still one of the main interest of astrophysics However the specific
Gaia-LSST Synergy A. Vallenari INAF, Padova The Galaxy view Unveiling the complex history of the MW assembly and internal evolution is still one of the main interest of astrophysics However the specific
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
The power of chemical tagging for studying Galactic evolution
 for studying Galactic evolution RSAA, Australian National University, Cotter Rd, Weston Creek, ACT, 2611, Australia E-mail: ewylie@mso.anu.edu.au Kenneth Freeman RSAA, Australian National University, Cotter
for studying Galactic evolution RSAA, Australian National University, Cotter Rd, Weston Creek, ACT, 2611, Australia E-mail: ewylie@mso.anu.edu.au Kenneth Freeman RSAA, Australian National University, Cotter
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The Milky Way and Local Volume as Rosetta Stones in Galaxy Formation
 0 The Milky Way and Local Volume as Rosetta Stones in Galaxy Formation Kathryn V. Johnston Department of Astronomy, Columbia University contact: 212-854-3884, kvj@astro.columbia.edu James S. Bullock Center
0 The Milky Way and Local Volume as Rosetta Stones in Galaxy Formation Kathryn V. Johnston Department of Astronomy, Columbia University contact: 212-854-3884, kvj@astro.columbia.edu James S. Bullock Center
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 Aug 2002
 Accepted by ApJ Letters First detection of the RGB-bump in the Sagittarius dsph 1,2 arxiv:astro-ph/0208581v1 30 Aug 2002 L. Monaco Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Bologna, via Ranzani,1 40127
Accepted by ApJ Letters First detection of the RGB-bump in the Sagittarius dsph 1,2 arxiv:astro-ph/0208581v1 30 Aug 2002 L. Monaco Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Bologna, via Ranzani,1 40127
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
SMASHing the LMC. Yumi Choi. Montana State University/University of Arizona. Collaborator
 SMASHing the LMC Montana State University/University of Arizona Collaborator David Nidever, Knut Olsen, Gurtina Besla, Robert Blum, Dennis Zaritsky, Roeland van der Marel, Eric Bell, Carme Gallart, Maria-Rosa
SMASHing the LMC Montana State University/University of Arizona Collaborator David Nidever, Knut Olsen, Gurtina Besla, Robert Blum, Dennis Zaritsky, Roeland van der Marel, Eric Bell, Carme Gallart, Maria-Rosa
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Jun 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Jun 2012](/thumbs/93/111784671.jpg) On Rings and Streams in the Galactic Anti-Center Jing Li 1,2, Heidi Jo Newberg 3, Jeffrey L. Carlin 3, Licai Deng 1, Matthew Newby 3, Benjamin A. Willett 3, Yan Xu 1, Zhiquan Luo 2 arxiv:126.3842v1 [astro-ph.ga]
On Rings and Streams in the Galactic Anti-Center Jing Li 1,2, Heidi Jo Newberg 3, Jeffrey L. Carlin 3, Licai Deng 1, Matthew Newby 3, Benjamin A. Willett 3, Yan Xu 1, Zhiquan Luo 2 arxiv:126.3842v1 [astro-ph.ga]
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 31 Jul 1998
 Cosmic Star Formation from the Milky Way and its Satellites arxiv:astro-ph/973v1 31 Jul 199 F.D.A. Hartwick Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, VW 3P Abstract.
Cosmic Star Formation from the Milky Way and its Satellites arxiv:astro-ph/973v1 31 Jul 199 F.D.A. Hartwick Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, VW 3P Abstract.
Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo
 Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo L. Aguilar, A. Brown & H. Velázquez Inst. de Astronomía, UNAM (México) & Leiden Observatory (Netherlands) When looking for something, sometimes what you get, is not
Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo L. Aguilar, A. Brown & H. Velázquez Inst. de Astronomía, UNAM (México) & Leiden Observatory (Netherlands) When looking for something, sometimes what you get, is not
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. For additional information about this
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. For additional information about this
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 Jan 2003
 Galactic Halo Stars in Phase Space :A Hint of Satellite Accretion? Chris B. Brook 1, Daisuke Kawata 1, Brad K. Gibson 1 and Chris Flynn 1,2 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0301596v1 30 Jan 2003 The present day
Galactic Halo Stars in Phase Space :A Hint of Satellite Accretion? Chris B. Brook 1, Daisuke Kawata 1, Brad K. Gibson 1 and Chris Flynn 1,2 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0301596v1 30 Jan 2003 The present day
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf
 The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
Fermilab FERMILAB-Conf-00/339-A January 2001
 Fermilab FERMILAB-Conf-00/339-A January 2001 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** Precision Galactic Structure Stephen Kent Fermilab, P. O. Box 500, Batavia,
Fermilab FERMILAB-Conf-00/339-A January 2001 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** Precision Galactic Structure Stephen Kent Fermilab, P. O. Box 500, Batavia,
The Thick Disk-Halo Interface
 Dynamics of Star Clusters and the Milky Way ASP Conference Series, Vol. 228, 2001 S. Deiters, B. Fuchs, A. Just, R. Spurzem, and R. Wielen eds. The Thick Disk-Halo Interface Gerard Gilmore Institute of
Dynamics of Star Clusters and the Milky Way ASP Conference Series, Vol. 228, 2001 S. Deiters, B. Fuchs, A. Just, R. Spurzem, and R. Wielen eds. The Thick Disk-Halo Interface Gerard Gilmore Institute of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Jan 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Jan 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Jan 2010](/thumbs/94/118159610.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 25 January 2010 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Accreted versus In Situ Milky Way Globular Clusters arxiv:1001.4289v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Jan 2010 Duncan A.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 25 January 2010 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Accreted versus In Situ Milky Way Globular Clusters arxiv:1001.4289v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Jan 2010 Duncan A.
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
 Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
KINEMATICS OF DWARF GALAXIES AND THEIR REMNANTS IN THE MILKY WAY HALO
 KINEMATICS OF DWARF GALAXIES AND THEIR REMNANTS IN THE MILKY WAY HALO Abstract Jeffrey L. Carlin Advisor: Steven R. Majewski Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia Dwarf spheroidal (dsph) galaxies
KINEMATICS OF DWARF GALAXIES AND THEIR REMNANTS IN THE MILKY WAY HALO Abstract Jeffrey L. Carlin Advisor: Steven R. Majewski Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia Dwarf spheroidal (dsph) galaxies
Probing GCs in the GC region with GLAO
 Probing GCs in the GC region with GLAO Masashi Chiba (Tohoku University) AO beginner! Life is good! Subaru/GLAO in Galactic Archaeology Resolved stars provide important information on galaxy formation
Probing GCs in the GC region with GLAO Masashi Chiba (Tohoku University) AO beginner! Life is good! Subaru/GLAO in Galactic Archaeology Resolved stars provide important information on galaxy formation
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11. Tidal Debris
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11 Tidal Debris Goals (1) We ll explore whether we can trace the accretion events that should have formed the Milky Way. (2) We ll discuss the impact of tidal debris on direct detection
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11 Tidal Debris Goals (1) We ll explore whether we can trace the accretion events that should have formed the Milky Way. (2) We ll discuss the impact of tidal debris on direct detection
TNG photometry of the open cluster NGC 6939
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 19 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della TNG photometry of the open cluster NGC 6939 G. Andreuzzi 1, A. Bragaglia 2, M. Tosi 2 and G. Marconi 3 1 INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, via Frascati
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 19 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della TNG photometry of the open cluster NGC 6939 G. Andreuzzi 1, A. Bragaglia 2, M. Tosi 2 and G. Marconi 3 1 INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, via Frascati
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs
 A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
THE STELLAR POPULATION OF NGC 5634: A GLOBULAR CLUSTER IN THE SAGITTARIUS dsph STREAM? 1 Michele Bellazzini and Francesco R.
 The Astronomical Journal, 124:915 923, 2002 August # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. E THE STELLAR POPULATION OF NGC 5634: A GLOBULAR CLUSTER IN THE SAGITTARIUS
The Astronomical Journal, 124:915 923, 2002 August # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. E THE STELLAR POPULATION OF NGC 5634: A GLOBULAR CLUSTER IN THE SAGITTARIUS
Using ground based data as a precursor for Gaia-based proper motions of satellites
 Using ground based data as a precursor for Gaia-based proper motions of satellites 102 Streams T. K. Fritz, N. Kallivayalil, J. Bovy, S.Linden, P. Zivick, R. Beaton, M. Lokken, T. Sohn, D. Angell, M. Boylan-Kolchin,
Using ground based data as a precursor for Gaia-based proper motions of satellites 102 Streams T. K. Fritz, N. Kallivayalil, J. Bovy, S.Linden, P. Zivick, R. Beaton, M. Lokken, T. Sohn, D. Angell, M. Boylan-Kolchin,
Extreme Galaxies: Part I
 M87, giant elliptical in the Virgo Cluster Extreme Galaxies: Part I Looking at the extremes in galaxy properties may tell us much about the systematics of galaxy formation and evolution and can provide
M87, giant elliptical in the Virgo Cluster Extreme Galaxies: Part I Looking at the extremes in galaxy properties may tell us much about the systematics of galaxy formation and evolution and can provide
The M31 Globular Cluster System
 The M31 Globular Cluster System How alike are the GC systems of the Milky Way and M31? Jean Brodie UCO/Lick Observatory UCSC 1 GCs trace the star formation and assembly GC formation occurs early Accompanies
The M31 Globular Cluster System How alike are the GC systems of the Milky Way and M31? Jean Brodie UCO/Lick Observatory UCSC 1 GCs trace the star formation and assembly GC formation occurs early Accompanies
The VPOS: a vast polar structure of satellite galaxies, globular clusters and streams around the MW
 The VPOS: a vast polar structure of satellite galaxies, globular clusters and streams around the MW Marcel S. Pawlowski (mpawlow@astro.uni-bonn.de) Supervisor: Pavel Kroupa (Bonn) Collaborators: Jan Pflamm-Altenburg
The VPOS: a vast polar structure of satellite galaxies, globular clusters and streams around the MW Marcel S. Pawlowski (mpawlow@astro.uni-bonn.de) Supervisor: Pavel Kroupa (Bonn) Collaborators: Jan Pflamm-Altenburg
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2009](/thumbs/89/101193607.jpg) Accepted for Publication in the Astrophysical Journal Exploring the Sagittarius Stream with SEKBO Survey RR Lyrae Stars arxiv:0909.1635v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2009 Sayuri L. Prior, G. S. Da Costa, Stefan
Accepted for Publication in the Astrophysical Journal Exploring the Sagittarius Stream with SEKBO Survey RR Lyrae Stars arxiv:0909.1635v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2009 Sayuri L. Prior, G. S. Da Costa, Stefan
Outer structure of the Galactic warp and flare: explaining the Canis Major over-density
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa4081-05 c ESO 2006 March 14, 2006 Outer structure of the Galactic warp and flare: explaining the Canis Major over-density Y. Momany 1,2, S. Zaggia 3,G.Gilmore
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa4081-05 c ESO 2006 March 14, 2006 Outer structure of the Galactic warp and flare: explaining the Canis Major over-density Y. Momany 1,2, S. Zaggia 3,G.Gilmore
L37 1. INTRODUCTION 2. SAMPLE SELECTION, OBSERVATIONS, AND REDUCTION. The Astrophysical Journal, 508:L37 L41, 1998 November 20
 The Astrophysical Journal, 508:L37 L41, 1998 November 20 1998. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE WFPC2 COLOR-MAGNITUDE DIAGRAMS OF HALO GLOBULAR
The Astrophysical Journal, 508:L37 L41, 1998 November 20 1998. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE WFPC2 COLOR-MAGNITUDE DIAGRAMS OF HALO GLOBULAR
A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 05, 2016 Read: Chap 19 04/05/16 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned by next class meeting
A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 05, 2016 Read: Chap 19 04/05/16 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned by next class meeting
Smoking Gun in the Milky Way Galaxy: Dwarf Galaxies and Open Clusters
 : Dwarf Galaxies and Open Clusters 1 March, 2015 Abstract Although many open clusters (OCs) have been found to date, little has been done with them to investigate problems and questions about the Milky
: Dwarf Galaxies and Open Clusters 1 March, 2015 Abstract Although many open clusters (OCs) have been found to date, little has been done with them to investigate problems and questions about the Milky
THE OVERDENSITY IN VIRGO, SAGITTARIUS DEBRIS, AND THE ASYMMETRIC SPHEROID
 The Astrophysical Journal, 668:221Y235, 2007 October 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE OVERDENSITY IN VIRGO, SAGITTARIUS DEBRIS, AND THE ASYMMETRIC
The Astrophysical Journal, 668:221Y235, 2007 October 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE OVERDENSITY IN VIRGO, SAGITTARIUS DEBRIS, AND THE ASYMMETRIC
Three Major Components
 The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles
 Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Theorem : Proof... Pavel Kroupa. Pavel Kroupa: AIfA, University of Bonn
 Theorem : dsph = TDG = LCDM Proof... Pavel Kroupa 1 Two Zwicky Conjectures of fundamental importance : 1. Zwicky (1937) galaxies are about 500 times heavier in the Coma galaxy cluster than judged from
Theorem : dsph = TDG = LCDM Proof... Pavel Kroupa 1 Two Zwicky Conjectures of fundamental importance : 1. Zwicky (1937) galaxies are about 500 times heavier in the Coma galaxy cluster than judged from
Cosmologia locale: origine e storia della Via Lattea
 Cosmologia locale: origine e storia della Via Lattea Mario G. Lattanzi (OATo) & Michele Bellazzini (OABo) Roma, 14 feb 2013 L Italia in Gaia, INAF Hq Collaborators Anna Curir Alessandro Spagna Francesca
Cosmologia locale: origine e storia della Via Lattea Mario G. Lattanzi (OATo) & Michele Bellazzini (OABo) Roma, 14 feb 2013 L Italia in Gaia, INAF Hq Collaborators Anna Curir Alessandro Spagna Francesca
Astronomy 114. Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 29 20 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 26 Astronomy 114 1/16 Announcements
Astronomy 114 Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 29 20 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 26 Astronomy 114 1/16 Announcements
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Jun 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Jun 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Jun 2007](/thumbs/80/81793328.jpg) The Overdensity in Virgo, Sagittarius Debris, and the Asymmetric Spheroid Heidi Jo Newberg 1, Brian Yanny 2, Nate Cole 1, Timothy C. Beers 3, Paola Re Fiorentin 4, Donald P. Schneider 5, Ron Wilhelm 6
The Overdensity in Virgo, Sagittarius Debris, and the Asymmetric Spheroid Heidi Jo Newberg 1, Brian Yanny 2, Nate Cole 1, Timothy C. Beers 3, Paola Re Fiorentin 4, Donald P. Schneider 5, Ron Wilhelm 6
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters
 Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 15 Apr 2003
 A Capture Scenario for Globular Cluster ω Centauri Toshio Tsuchiya 1, Dana I. Dinescu 2,3, Vladimir I. Korchagin 2,4 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0304262v2 15 Apr 2003 We explore an accretion origin for ω Cen
A Capture Scenario for Globular Cluster ω Centauri Toshio Tsuchiya 1, Dana I. Dinescu 2,3, Vladimir I. Korchagin 2,4 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0304262v2 15 Apr 2003 We explore an accretion origin for ω Cen
Star systems like our Milky Way. Galaxies
 Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
IV. Interacting Galaxies
 IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
1924: Hubble classification scheme 1925: Hubble measures Cepheids (Period-Luminosity) in Andromeda case closed
 Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure
 Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure The Celestial Sphere http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog14 We use equatorial coordinates to determine the positions of stars in the sky. A stars declination (like
Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure The Celestial Sphere http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog14 We use equatorial coordinates to determine the positions of stars in the sky. A stars declination (like
Using Globular Clusters to. Study Elliptical Galaxies. The View Isn t Bad... Omega Centauri. Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office M13
 Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
IMPACT OF A MAJOR MERGER IN THE LOCAL GROUP
 SF2A 2013 L. Cambrésy, F. Martins, E. Nuss and A. Palacios (eds) IMPACT OF A MAJOR MERGER IN THE LOCAL GROUP S. Fouquet 1, F. Hammer 1,, Y. Yang 1, 2, M. Puech 1 and H. Flores 1 Abstract. The Local Group
SF2A 2013 L. Cambrésy, F. Martins, E. Nuss and A. Palacios (eds) IMPACT OF A MAJOR MERGER IN THE LOCAL GROUP S. Fouquet 1, F. Hammer 1,, Y. Yang 1, 2, M. Puech 1 and H. Flores 1 Abstract. The Local Group
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Feb 2003
 23 arxiv:astro-ph/3248v1 24 Feb 23 Field and cluster RR Lyrae stars as stellar tracers S. Petroni Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Pisa, via Buonarroti 2, Pisa, 56127 Italy; email: petroni@df.unipi.it
23 arxiv:astro-ph/3248v1 24 Feb 23 Field and cluster RR Lyrae stars as stellar tracers S. Petroni Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Pisa, via Buonarroti 2, Pisa, 56127 Italy; email: petroni@df.unipi.it
