Lecture Tutorial: Using Astronomy Picture of the Day to learn about the life cycle of stars
|
|
|
- Mavis Daniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture Tutorial: Using Astronomy Picture of the Day to learn about the life cycle of stars For this exercise, you will need an ipad or computer and access to the internet. We will be using the website Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD, for short) to learn more about the life cycle of stars. 1. Use your internet browser to go to APOD features a new astronomical image each day, accompanied by a caption, and you can search for and view all past APOD images. See the Search link at the bottom left of the page. 2. First, let s look at the earliest stages of a star s life. Use the search feature to search for the term stellar nursery. Choose one of the images that results from this search. What does the image show? Are the objects in the image located in the Milky Way galaxy, or outside? If outside, what galaxy are they located in? (Note that usually the caption will say if it s located in another galaxy.) What colors are the objects? What do the colors mean? Do you see any unusual structures? What causes them? Write down something interesting you learned about stellar nurseries from this image and caption to share with the class. 3. Now let s look at a main sequence star. Search for the term sun. Choose one of the close-up images of the sun (not a picture of a sunset viewed from the Earth) 1
2 Does the image look the same as the sun usually looks to you? Why or why not? What telescope/instrument/spacecraft obtained this image? How does that affect the way this image looks? What colors does the sun have in this image? What do the colors mean? Do you see any unusual structures? What causes them? Write down something interesting you learned about the sun from this image and caption to share with the class. 4. Many stars come in pairs or multiples! Let s look at a system that has both main sequence stars and more evolved red giant stars. Search for Albireo. Choose the image called Albireo: A bright and beautiful double. How many stars do you see? What is the meaning of the term binary system? 2
3 According to the caption, how many stars are actually in this system? Why can t we see them all in this photo? The fainter star is on the main sequence, like the sun, meaning it is fusing hydrogen to create energy. Does this star look like the Sun? If not, how is it different? The brighter star is a red giant star. Does this star look like the Sun? If not, how is it different? Why is this image not as detailed as the images of the sun from the last part of this activity? If we could see Albireo from very nearby, in what way(s) would it look different from the Sun? 5. Let s look at another evolved star. Search for Aldebaran, also a red giant star. You ll see lots of images of the night sky. Choose one or a few of these, and see if you can locate Aldebaran in the images, by using the descriptions in the caption. What color is Aldebaran? Which star in the Albireo system is it closer to in color the brighter or the fainter? 3
4 6. Now let s look at the latest stages of a low mass star s life. Search for the term planetary nebula. Choose one of the images to answer these questions. What does the planetary nebula look like? Draw a diagram of the planetary nebula and label the features you see. What causes the structures you see in the planetary nebula? What type of star is at the center of the planetary nebula? What colors do you see in the planetary nebula? What do they mean? Write down something interesting you learned about planetary nebulae from this image and caption to share with the class. 7. Now let s look at the latest stages of a high mass star s life. Search for the term supernova remnant. Scan through the images, and look at several of them. What kinds of structures do you see? Do they all look the same? Choose two supernova remnants that look different and write down their names here. Describe 4
5 their similarities and differences. Do the captions give you any hints as to why these two systems might be different? If not, why do you think the structures might be different? What telescopes were used to obtain these images? Write down something interesting you learned about supernova remnants from this image and caption to share with the class. 8. Now let s look at the latest stages of the most massive stars. Search for the term black hole. Choose an image that interests you. Is this image an actual photo, or is it a computer simulation? What does this image have to do with black holes? Write down something interesting you learned about black holes from this image and caption to share with the class. 5
6 9. Using the images you saw, and what you learned from this activity, draw and label a diagram showing the life cycle of a star. 6
Life Cycle of a Star - Activities
 Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
27.1: Characteristics of Stars
 27.1: Characteristics of Stars STAR NOTES: Part 1 What is a Star? A body of gases that gives off energy in the form of light and heat. 27.1: Characteristics of Stars Are all stars the same? No 1. Stars
27.1: Characteristics of Stars STAR NOTES: Part 1 What is a Star? A body of gases that gives off energy in the form of light and heat. 27.1: Characteristics of Stars Are all stars the same? No 1. Stars
8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, galaxies and use models such as HR diagrams for classification
 8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, galaxies and use models such as HR diagrams for classification 8.8B recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a
8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, galaxies and use models such as HR diagrams for classification 8.8B recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a
Wednesday, January 25, 2017
 Wednesday, January 25, 2017 Powerpoint of lectures posted as pdf after every class, on Canvas and at http://www.as.utexas.edu/astronomy/education/spring17/wheeler/ 309n.html?a=lec Wednesday Star Parties
Wednesday, January 25, 2017 Powerpoint of lectures posted as pdf after every class, on Canvas and at http://www.as.utexas.edu/astronomy/education/spring17/wheeler/ 309n.html?a=lec Wednesday Star Parties
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems
 Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct for each
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct for each
The Milky Way Galaxy: galac1c geography
 The Milky Way Galaxy: galac1c geography From Ki8 Peak, looking south toward the constella1on Sagi8arius, summer 1me: the Milky Way! Next, Look at the en1re sky as shown by sofware Stellarium The solar
The Milky Way Galaxy: galac1c geography From Ki8 Peak, looking south toward the constella1on Sagi8arius, summer 1me: the Milky Way! Next, Look at the en1re sky as shown by sofware Stellarium The solar
Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description.
 Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description. 1. The main force responsible for the formation of the universe is: a. Gravity b. Frictional force c. Magnetic force
Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description. 1. The main force responsible for the formation of the universe is: a. Gravity b. Frictional force c. Magnetic force
V. Astronomy Section
 EAS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines V. Astronomy Section 1. Introduction, Astronomical Distances, Solar System Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of Earth s position in the solar
EAS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines V. Astronomy Section 1. Introduction, Astronomical Distances, Solar System Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of Earth s position in the solar
Classifying Stars. Scientists classify stars by: 1. Temperature 2. Brightness
 STARS Classifying Stars Scientists classify stars by: 1. Temperature 2. Brightness Star Temperature 1. The color of a star tells us about its temperature. Blue stars are the hottest, 7500 C- 40,000 C.
STARS Classifying Stars Scientists classify stars by: 1. Temperature 2. Brightness Star Temperature 1. The color of a star tells us about its temperature. Blue stars are the hottest, 7500 C- 40,000 C.
Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam
 Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
The principle of geometrical parallax
 The principle of geometrical parallax One of the hardest things to do in astronomy is to determine how far away things are. Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it s an intrinsically
The principle of geometrical parallax One of the hardest things to do in astronomy is to determine how far away things are. Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it s an intrinsically
Homework on Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, April 8 30 points Prof. Rieke & TA Melissa Halford
 Homework on Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, April 8 30 points Prof. Rieke & TA Melissa Halford You are going to work with some famous astronomical data in this homework.
Homework on Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, April 8 30 points Prof. Rieke & TA Melissa Halford You are going to work with some famous astronomical data in this homework.
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October points Profs. Rieke
 Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October 31 30 points Profs. Rieke You are going to work with some famous astronomical data in this homework. The image data
Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October 31 30 points Profs. Rieke You are going to work with some famous astronomical data in this homework. The image data
Quick Clicker Survey: What do like best about the class so far?
 ASTR 1020: Stars & Galaxies October 14, 2013 Reading: Chapter 18, Section 18.3. Mastering Astronomy Homework on The Lives of Stars is due Oct. 18. Volunteers needed for Astronomy in the News! Next Class
ASTR 1020: Stars & Galaxies October 14, 2013 Reading: Chapter 18, Section 18.3. Mastering Astronomy Homework on The Lives of Stars is due Oct. 18. Volunteers needed for Astronomy in the News! Next Class
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Evolution
 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Evolution Names: The H-R Diagram and Stellar Properties Activity 1. In which corner of the diagram (upper right, upper left, lower right, or lower left) would
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Evolution Names: The H-R Diagram and Stellar Properties Activity 1. In which corner of the diagram (upper right, upper left, lower right, or lower left) would
CONTENT EXPECTATIONS
 THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
The Universe. is space and everything in it.
 The Universe is space and everything in it. Galaxies A galaxy is a supercluster of stars, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. There are three main types of galaxies: Irregular Elliptical Spiral
The Universe is space and everything in it. Galaxies A galaxy is a supercluster of stars, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. There are three main types of galaxies: Irregular Elliptical Spiral
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 April 11, 2003
 Name: Seat Number: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 April 11, 2003 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. If you need additional
Name: Seat Number: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 April 11, 2003 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. If you need additional
Astronomy 201: Cosmology, Fall Professor Edward Olszewski and Charles Kilpatrick
 Astronomy 201: Cosmology, Fall 2013 Professor Edward Olszewski and Charles Kilpatrick Lab 3, Cluster Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams and the Age of Stars Due October 22, Worth 32 points You may work in groups
Astronomy 201: Cosmology, Fall 2013 Professor Edward Olszewski and Charles Kilpatrick Lab 3, Cluster Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams and the Age of Stars Due October 22, Worth 32 points You may work in groups
2. Very generally, describe how the Milky Way Galaxy formed. (Words or labeled picture)
 Potter Name: Date: Hour: Score: /11 Learning Check 2.1 LT 2.1 Galaxy Formation: I am able to describe the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy and our solar system and model earth s position in each. 1. Label
Potter Name: Date: Hour: Score: /11 Learning Check 2.1 LT 2.1 Galaxy Formation: I am able to describe the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy and our solar system and model earth s position in each. 1. Label
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY BACKGROUND READING FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY BACKGROUND READING FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is a huge collection of stars, dust and gas. It s called a spiral galaxy because if you could
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY BACKGROUND READING FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is a huge collection of stars, dust and gas. It s called a spiral galaxy because if you could
Stellar Evolution Lab
 Stellar Evolution Lab Spying into the lives of the stars Developed by: Betsy Mills, UCLA NSF GK-12 Fellow Title of Lesson: Stellar Evolution Lab! Grade Level: 8th Subject(s): Astronomy: Stars, the Sun,
Stellar Evolution Lab Spying into the lives of the stars Developed by: Betsy Mills, UCLA NSF GK-12 Fellow Title of Lesson: Stellar Evolution Lab! Grade Level: 8th Subject(s): Astronomy: Stars, the Sun,
Name Class Date. Chapter 27. Stars and Galaxies. Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided.
 Stars and Galaxies Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. 1. In the majority of stars, the most common element is a. oxygen. b. helium. c. hydrogen. d.
Stars and Galaxies Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. 1. In the majority of stars, the most common element is a. oxygen. b. helium. c. hydrogen. d.
TEK 8 Test Review. 15. Galaxies are best described as -
 TEK 8 Test Review 1. List the three subatomic particles and give each of their masses. 2. Describe and draw an illustration (Bohr Model) of the most common element in the Universe. 3. Describe and draw
TEK 8 Test Review 1. List the three subatomic particles and give each of their masses. 2. Describe and draw an illustration (Bohr Model) of the most common element in the Universe. 3. Describe and draw
I m made up of gas and dust. Particularly thick clumps of gas and dust will collapse under gravity to form the next stage of stellar evolution.
 I m made up of gas and dust. Particularly thick clumps of gas and dust will collapse under gravity to form the next stage of stellar evolution. I m the star that astronomers know the most about. My energy
I m made up of gas and dust. Particularly thick clumps of gas and dust will collapse under gravity to form the next stage of stellar evolution. I m the star that astronomers know the most about. My energy
Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti
 Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
Instructions. Students will underline the portions of the PowerPoint that are underlined.
 STARS Instructions Students will underline the portions of the PowerPoint that are underlined. Nuclear Furnace 1. A star is like a gigantic nuclear furnace. 2. The nuclear reactions inside convert hydrogen
STARS Instructions Students will underline the portions of the PowerPoint that are underlined. Nuclear Furnace 1. A star is like a gigantic nuclear furnace. 2. The nuclear reactions inside convert hydrogen
PENN STATE ASTRONOMY LABORATORY #10
 PENN STATE ASTRONOMY LABORATORY #10 THE LIVES OF THE STARS I. Objective In the labs you have done so far, you have examined the physical properties and classifications of stars. All of these properties
PENN STATE ASTRONOMY LABORATORY #10 THE LIVES OF THE STARS I. Objective In the labs you have done so far, you have examined the physical properties and classifications of stars. All of these properties
telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us?
 The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
Stars: Stars and their Properties
 Stars: Stars and their Properties Astronomy 110 Class 10 WHEN I heard the learn d astronomer; When the proofs, the figures, were ranged in columns before me; When I was shown the charts and the diagrams,
Stars: Stars and their Properties Astronomy 110 Class 10 WHEN I heard the learn d astronomer; When the proofs, the figures, were ranged in columns before me; When I was shown the charts and the diagrams,
Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies
 Name: Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies You will access your textbook for this lab. Pre-Lab Assignment: As we began to talk about stars beyond the Sun, one of the most important pieces of information
Name: Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies You will access your textbook for this lab. Pre-Lab Assignment: As we began to talk about stars beyond the Sun, one of the most important pieces of information
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Stellar Evolution Notes
 Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Position 1 Position 2 6 after position 1 Distance between positions 1 and 2 is the Bigger = bigger parallax (Ɵ)
 STARS CHAPTER 10.1 the solar neighborhood The distances to the nearest stars can be measured using Parallax => the shift of an object relative to some distant background as the observer s point of view
STARS CHAPTER 10.1 the solar neighborhood The distances to the nearest stars can be measured using Parallax => the shift of an object relative to some distant background as the observer s point of view
Chapter 21: Stars Notes
 Branches of Earth Science Chapter 21: Stars Notes Astronomy: The study of planets, stars, and other objects in space. Lithosphere: the land masses of earth o Litho means rock Hydrosphere: waters of the
Branches of Earth Science Chapter 21: Stars Notes Astronomy: The study of planets, stars, and other objects in space. Lithosphere: the land masses of earth o Litho means rock Hydrosphere: waters of the
Study Guide Chapter 2
 Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
Astronomy 100 Spring 2006 Lecture Questions Twelve Weeks Review
 Astronomy 100 Spring 2006 Lecture Questions Twelve Weeks Review 16-1 Fusion in the Sun The solar corona has temperatures roughly the same as temperatures in the Sun's core, where nuclear fusion takes place.
Astronomy 100 Spring 2006 Lecture Questions Twelve Weeks Review 16-1 Fusion in the Sun The solar corona has temperatures roughly the same as temperatures in the Sun's core, where nuclear fusion takes place.
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates.
 1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Life and Death of High Mass Stars (M > 8 M sun ) REVIEW Last stage: Iron core surrounded by shells of increasingly lighter elements. REVIEW When mass
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Life and Death of High Mass Stars (M > 8 M sun ) REVIEW Last stage: Iron core surrounded by shells of increasingly lighter elements. REVIEW When mass
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A
 29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A There are 20 questions (Note: There will be 32 on the real thing). Read each question and all of the choices before choosing.
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A There are 20 questions (Note: There will be 32 on the real thing). Read each question and all of the choices before choosing.
Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe
 Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe Light Year: Unit of distance used to measure the great vastness of space. Galaxy: Large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Spiral Galaxy: Galaxy in
Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe Light Year: Unit of distance used to measure the great vastness of space. Galaxy: Large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Spiral Galaxy: Galaxy in
The Formation of Stars
 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
Post Activity/ Homework Questions: 1. Before a star forms A. Where do you think the gas and dust originally came from?
 Critical Thinking Questions: (work on these with a partner) 1. During the formation of a Red Giant Star, the core of a star pushes the outer shell back only enough to make the star larger. However, during
Critical Thinking Questions: (work on these with a partner) 1. During the formation of a Red Giant Star, the core of a star pushes the outer shell back only enough to make the star larger. However, during
Stellar Evolution. The lives of low-mass stars. And the lives of massive stars
 Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars The Structure of the Sun Let s review: The Sun is held together by what force? The inward force is balanced by what other force?
Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars The Structure of the Sun Let s review: The Sun is held together by what force? The inward force is balanced by what other force?
Chapter 12: The Life Cycle of Stars (contʼd) How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/9/09 Habbal Astro Lecture 25 1
 Chapter 12: The Life Cycle of Stars (contʼd) How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/9/09 Habbal Astro 110-01 Lecture 25 1 12.3 Life as a High-Mass Star Learning Goals What are the life stages of a
Chapter 12: The Life Cycle of Stars (contʼd) How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/9/09 Habbal Astro 110-01 Lecture 25 1 12.3 Life as a High-Mass Star Learning Goals What are the life stages of a
The Deaths of Stars. The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant.
 The Deaths of Stars The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant. Once the giant phase of a mediummass star ends, it exhales its outer
The Deaths of Stars The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant. Once the giant phase of a mediummass star ends, it exhales its outer
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
StarTalk. Sanjay Yengul May "To know ourselves, we must know the stars."
 StarTalk Sanjay Yengul May 2016 "To know ourselves, we must know the stars." Twinkle Twinkle How many stars are there? How big are these stars? Picture of night sky What are they made of? Why do they shine?
StarTalk Sanjay Yengul May 2016 "To know ourselves, we must know the stars." Twinkle Twinkle How many stars are there? How big are these stars? Picture of night sky What are they made of? Why do they shine?
Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4
 Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4 Key Ideas HR Diagrams of Star Clusters Ages from the Main Sequence Turn-off Open Clusters Young clusters of ~1000 stars Blue Main-Sequence
Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4 Key Ideas HR Diagrams of Star Clusters Ages from the Main Sequence Turn-off Open Clusters Young clusters of ~1000 stars Blue Main-Sequence
 How do we know the distance to these stars? The Ping Pong Ball Challenge -Devise a method for determining the height of the ping pong ball above the floor. -You are restricted to the floor. -You can only
How do we know the distance to these stars? The Ping Pong Ball Challenge -Devise a method for determining the height of the ping pong ball above the floor. -You are restricted to the floor. -You can only
PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives
 PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives March 11, 2008 1 Introduction This list of questions are questions that will need to be answered in order for students to be successful in the course. Each
PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives March 11, 2008 1 Introduction This list of questions are questions that will need to be answered in order for students to be successful in the course. Each
Chapter 19 Reading Quiz Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Where are globular clusters located
Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Where are globular clusters located
Supernovae and cosmology
 Supernovae and cosmology On the Death of Stars and Standard Candles Gijs Hijmans Supernovae Types of Supernovae Type I Ia (no hydrogen but strong silicon lines in spectrum) Ib (non ionized helium lines)
Supernovae and cosmology On the Death of Stars and Standard Candles Gijs Hijmans Supernovae Types of Supernovae Type I Ia (no hydrogen but strong silicon lines in spectrum) Ib (non ionized helium lines)
Lecture 10: The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Reading: Sections
 Lecture 10: The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Reading: Sections 19.7-19.8 Key Ideas The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Plot of Luminosity vs. Temperature for stars Features: Main Sequence Giant & Supergiant
Lecture 10: The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Reading: Sections 19.7-19.8 Key Ideas The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Plot of Luminosity vs. Temperature for stars Features: Main Sequence Giant & Supergiant
ASTRONOMY 114 Lecture Okay. We re gonna be continuing our discussion of the Milky Way Galaxy and the
 ASTRONOMY 114 Lecture 45 1 Okay. We re gonna be continuing our discussion of the Milky Way Galaxy and the stars that are in it. We ve already talked about double stars, we ve talked about clusters of stars,
ASTRONOMY 114 Lecture 45 1 Okay. We re gonna be continuing our discussion of the Milky Way Galaxy and the stars that are in it. We ve already talked about double stars, we ve talked about clusters of stars,
*Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. *The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass.
 Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass. 1 solar mass = size of our Sun Any star less than about three solar masses
Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass. 1 solar mass = size of our Sun Any star less than about three solar masses
2.) 3.) Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Characteristic:
 Grade / Name: Date: Period: CATALYST 1.) 2.) 3.) Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Characteristic: 1 OBJECTIVE SWBAT describe the life cycle of a star SWBAT identify the major source of 'power' in stars
Grade / Name: Date: Period: CATALYST 1.) 2.) 3.) Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Characteristic: 1 OBJECTIVE SWBAT describe the life cycle of a star SWBAT identify the major source of 'power' in stars
December 18, What do you know about the life of a star?
 December 18, 2013 What do you know about the life of a star? Bellwork December 18, 2014 What determines the life cycle and life time of a star? Scale 4 3 2 1 0 I am a 3 and can apply the stages to the
December 18, 2013 What do you know about the life of a star? Bellwork December 18, 2014 What determines the life cycle and life time of a star? Scale 4 3 2 1 0 I am a 3 and can apply the stages to the
How do we measure properties of a star? Today. Some Clicker Questions - #1. Some Clicker Questions - #1
 Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
The distance modulus in the presence of absorption is given by
 Problem 4: An A0 main sequence star is observed at a distance of 100 pc through an interstellar dust cloud. Furthermore, it is observed with a color index B-V = 1.5. What is the apparent visual magnitude
Problem 4: An A0 main sequence star is observed at a distance of 100 pc through an interstellar dust cloud. Furthermore, it is observed with a color index B-V = 1.5. What is the apparent visual magnitude
Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM
 Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM RLM 15.216B (Backup RLM 15.202A) Reading: Chapter 6
Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM RLM 15.216B (Backup RLM 15.202A) Reading: Chapter 6
Parenting Tip of the Month. April. Lower Elementary Teachers
 Parenting Tip of the Month April Lower Elementary Teachers Why Use Higher Order Thinking Skills Everyday? Research tells us that Higher Order Thinking Skills help to build life long interaction and communication
Parenting Tip of the Month April Lower Elementary Teachers Why Use Higher Order Thinking Skills Everyday? Research tells us that Higher Order Thinking Skills help to build life long interaction and communication
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 20. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 20 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 20 Stellar Evolution Units of Chapter 20 20.1 Leaving the Main Sequence 20.2 Evolution of a Sun-Like Star 20.3 The Death
Lecture Outlines Chapter 20 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 20 Stellar Evolution Units of Chapter 20 20.1 Leaving the Main Sequence 20.2 Evolution of a Sun-Like Star 20.3 The Death
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27, Section 1. Composition & Temperature. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of Stars
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet
 Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
Stars and Planets GPS S4E1 A-D: Students will compare and contrast the physical attributes of stars, star patterns, and planets. Ms.
 Stars and Planets GPS S4E1 A-D: Students will compare and contrast the physical attributes of stars, star patterns, and planets. Ms. D AngeloD Physical Attributes of Stars Number Size Color Pattern A star
Stars and Planets GPS S4E1 A-D: Students will compare and contrast the physical attributes of stars, star patterns, and planets. Ms. D AngeloD Physical Attributes of Stars Number Size Color Pattern A star
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
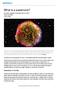 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Star Magnitudes & Distances with Stellarium (Stellarium Exercise #2)
 Name Date Star Magnitudes & Distances with Stellarium (Stellarium Exercise #2) Millions of stars are scattered across the sky. Astronomers want to study these stars as carefully as possible. This means
Name Date Star Magnitudes & Distances with Stellarium (Stellarium Exercise #2) Millions of stars are scattered across the sky. Astronomers want to study these stars as carefully as possible. This means
Galaxies and Star Systems
 Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Astronomy 10 Test #2 Practice Version
 Given (a.k.a. `First ) Name(s): Family (a.k.a. `Last ) name: ON YOUR PARSCORE: `Bubble your name, your student I.D. number, and your multiple-choice answers. I will keep the Parscore forms. ON THIS TEST
Given (a.k.a. `First ) Name(s): Family (a.k.a. `Last ) name: ON YOUR PARSCORE: `Bubble your name, your student I.D. number, and your multiple-choice answers. I will keep the Parscore forms. ON THIS TEST
A1101, Lab 8: Distances and Ages of Star Clusters Lab Worksheet
 Student Name: Lab Partner Name: Lab TA Name: Background A1101, Lab 8: Distances and Ages of Star Clusters Lab Worksheet Here are a few important things to remember about stellar evolution and star clusters
Student Name: Lab Partner Name: Lab TA Name: Background A1101, Lab 8: Distances and Ages of Star Clusters Lab Worksheet Here are a few important things to remember about stellar evolution and star clusters
Introduction to the Universe
 What makes up the Universe? Introduction to the Universe Book page 642-644 Objects in the Universe Astrophysics is the science that tries to make sense of the universe by - describing the Universe (Astronomy)
What makes up the Universe? Introduction to the Universe Book page 642-644 Objects in the Universe Astrophysics is the science that tries to make sense of the universe by - describing the Universe (Astronomy)
Directed Reading A. Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS THE LIFE CYCLE OF SUNLIKE STARS A TOOL FOR STUDYING STARS.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
Hubble s Law: Finding the Age of the Universe
 Lab 16 Name: Hubble s Law: Finding the Age of the Universe 16.1 Introduction In your lecture sessions (or the lab on spectroscopy), you will find out that an object s spectrum can be used to determine
Lab 16 Name: Hubble s Law: Finding the Age of the Universe 16.1 Introduction In your lecture sessions (or the lab on spectroscopy), you will find out that an object s spectrum can be used to determine
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives
 PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives April 6, 2008 1 Introduction This list of questions are questions that will need to be answered in order for students to be successful in the course. Each
PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives April 6, 2008 1 Introduction This list of questions are questions that will need to be answered in order for students to be successful in the course. Each
25.2 Stellar Evolution. By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star.
 25.2 Stellar Evolution By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star. Star Birth The birthplaces of stars are dark, cool interstellar clouds,
25.2 Stellar Evolution By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star. Star Birth The birthplaces of stars are dark, cool interstellar clouds,
5. A particular star has an angle of parallax of 0.2 arcsecond. What is the distance to this star? A) 50 pc B) 2 pc C) 5 pc D) 0.
 Name: Date: 1. How far away is the nearest star beyond the Sun, in parsecs? A) between 1 and 2 pc B) about 12 pc C) about 4 pc D) between 1/2 and 1 pc 2. Parallax of a nearby star is used to estimate its
Name: Date: 1. How far away is the nearest star beyond the Sun, in parsecs? A) between 1 and 2 pc B) about 12 pc C) about 4 pc D) between 1/2 and 1 pc 2. Parallax of a nearby star is used to estimate its
The Night Sky. The Universe. The Celestial Sphere. Stars. Chapter 14
 The Night Sky The Universe Chapter 14 Homework: All the multiple choice questions in Applying the Concepts and Group A questions in Parallel Exercises. Celestial observation dates to ancient civilizations
The Night Sky The Universe Chapter 14 Homework: All the multiple choice questions in Applying the Concepts and Group A questions in Parallel Exercises. Celestial observation dates to ancient civilizations
Star Systems and Galaxies
 Star Systems and Galaxies Why Does the Milky Way Look Hazy? 1. Using a pencil, carefully poke at least 20 holes close together in a sheet of white paper. 2. Tape the paper to a chalkboard or dark-colored
Star Systems and Galaxies Why Does the Milky Way Look Hazy? 1. Using a pencil, carefully poke at least 20 holes close together in a sheet of white paper. 2. Tape the paper to a chalkboard or dark-colored
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Review: HR Diagram. Label A, B, C respectively
 Stellar Evolution Review: HR Diagram Label A, B, C respectively A C B a) A: White dwarfs, B: Giants, C: Main sequence b) A: Main sequence, B: Giants, C: White dwarfs c) A: Main sequence, B: White Dwarfs,
Stellar Evolution Review: HR Diagram Label A, B, C respectively A C B a) A: White dwarfs, B: Giants, C: Main sequence b) A: Main sequence, B: Giants, C: White dwarfs c) A: Main sequence, B: White Dwarfs,
The Life Cycle of Stars. : Is the current theory of how our Solar System formed.
 Life Cycle of a Star Video (5 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pm9cqdlqi0a The Life Cycle of Stars Solar Nebula Theory : Is the current theory of how our Solar System formed. This theory states that
Life Cycle of a Star Video (5 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pm9cqdlqi0a The Life Cycle of Stars Solar Nebula Theory : Is the current theory of how our Solar System formed. This theory states that
COLOR MAGNITUDE DIAGRAMS
 COLOR MAGNITUDE DIAGRAMS What will you learn in this Lab? This lab will introduce you to Color-Magnitude, or Hertzsprung-Russell, Diagrams: one of the most useful diagnostic tools developed in 20 th century
COLOR MAGNITUDE DIAGRAMS What will you learn in this Lab? This lab will introduce you to Color-Magnitude, or Hertzsprung-Russell, Diagrams: one of the most useful diagnostic tools developed in 20 th century
MOREHEAD SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS PLANETARIUM AND SCIENCE CENTER
 SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS 4c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours
SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS 4c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
The Birth and Death of Stars
 The Birth and Death of Stars 2013 Simulation Curriculum Teachers may make copies for their classes Part 1: Stellar Cradles With a small telescope the central region of M42 reveals a group of at least four
The Birth and Death of Stars 2013 Simulation Curriculum Teachers may make copies for their classes Part 1: Stellar Cradles With a small telescope the central region of M42 reveals a group of at least four
11/8/18. Tour of Galaxies. Our Schedule
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Ryan Horton, Loren Matilsky Lecture 22 Thur 8 Nov 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Ryan Horton, Loren Matilsky Lecture 22 Thur 8 Nov 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
Background and Theory
 Homework 4. Cluster HR Diagrams and the Age of Stars NAME: Due: Thursday, October 7, 2010 In Class Astro 201: Cosmology Prof. Bechtold In this assignment, we are going to measure the age of stars in star
Homework 4. Cluster HR Diagrams and the Age of Stars NAME: Due: Thursday, October 7, 2010 In Class Astro 201: Cosmology Prof. Bechtold In this assignment, we are going to measure the age of stars in star
GALAXIES AND STARS. 2. Which star has a higher luminosity and a lower temperature than the Sun? A Rigel B Barnard s Star C Alpha Centauri D Aldebaran
 GALAXIES AND STARS 1. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A smaller, hotter, and less luminous B smaller, cooler, and more luminous C larger, hotter, and less luminous D larger, cooler, and more
GALAXIES AND STARS 1. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A smaller, hotter, and less luminous B smaller, cooler, and more luminous C larger, hotter, and less luminous D larger, cooler, and more
A Stars Characteristics
 Cha Stars and Galaxies 5 "W Ttiat's the most powerful event you can imagine? k/%/ A thunderstorm? A rocket launch? An erupting volcano? How about an exploding star? That's one of the amazing events taking
Cha Stars and Galaxies 5 "W Ttiat's the most powerful event you can imagine? k/%/ A thunderstorm? A rocket launch? An erupting volcano? How about an exploding star? That's one of the amazing events taking
4/6/17. SEMI-WARM stuff: dust. Tour of Galaxies. Our Schedule
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 22 Thur 6 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 22 Thur 6 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
Low-mass Stellar Evolution
 Low-mass Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars The Structure of the Sun Let s review: The Sun is held together by? The inward force is balanced by? Thinking about
Low-mass Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars The Structure of the Sun Let s review: The Sun is held together by? The inward force is balanced by? Thinking about
Stars. For Jupiter: M/Msun = 0.001
 Stars Stars are classified by spectral classes O,B,A,F,G,K,M Oh be a fine girl (or guy), kiss me! Key here is the effective temperature of the star (surface temperature) Difference in spectrum is due to
Stars Stars are classified by spectral classes O,B,A,F,G,K,M Oh be a fine girl (or guy), kiss me! Key here is the effective temperature of the star (surface temperature) Difference in spectrum is due to
HR Diagram Student Guide
 Name: HR Diagram Student Guide Pretest Score: Background Information Work through the background sections on Spectral Classification, Luminosity, and the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Then complete the
Name: HR Diagram Student Guide Pretest Score: Background Information Work through the background sections on Spectral Classification, Luminosity, and the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Then complete the
National Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event 19 May 2012 University of Central Florida Orlando, FL
 National Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event 19 May 2012 University of Central Florida Orlando, FL Artist Illustration of Red Giant, White Dwarf and Accretion Disk (Wikimedia) TEAM NUMBER: TEAM
National Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event 19 May 2012 University of Central Florida Orlando, FL Artist Illustration of Red Giant, White Dwarf and Accretion Disk (Wikimedia) TEAM NUMBER: TEAM
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
