Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date
|
|
|
- Chad Hamilton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on December 21, September 23, and June What happens to the length of the shadow on September 23 from sunrise to sunset? A) It increases only B) It decreases only C) It decreases, then increases D) It increases, then decreases 2. Which diagram best shows the location of Polaris relative to the observer? 3. In which direction will sunrise occur on June 21? A) south of due east B) north of due west C) south of due west D) north of due east 4. How many hours occurred between sunrise and solar noon on September 23? A) 8 B) 12 C) 6 D) 24
2 5. Which graph best shows the altitude of the Sun, as measured by the observer located at 42 N, at various times on December 21? Base your answers to questions 6 and 7 on the diagram below, which shows numbered positions of the Sun at four different times along the Sun s apparent daily path, as seen by an observer in New Jersey. Numbers 1 through represent apparent positions of the Sun. 8. The diagram below shows the latitude and longitude lines on Earth. Points A and B are locations on Earth's surface. 6. The observer had the longest shadow when the Sun was at position A) 4 B) 1 C) 3 D) 2 7. During which day of the year is the Sun most likely to follow the apparent path shown? A) October 1 B) July 1 C) March 1 D) December 1 If it is 4 a.m. at location A, what time is it at location B? A) 6 a.m. B) 8 a.m. C) 2 a.m. D) 10 a.m. 9. When the distance between the foci of an ellipse is increased, the eccentricity of the ellipse will A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same
3 10. The reaction below represents an energy-producing process. The reaction represents how energy is produced A) during nuclear decay B) in the Sun by fusion C) when water condenses in Earth s atmosphere D) from the movement of crustal plates 11. The diagram below represents the shape of the Milky Way Galaxy. 16. The diagrams below represent Earth s ocean tides at four different positions of the Moon. Which diagram shows the Moon position that will produce the highest high tides and the lowest iow tides? (The diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) The Milky Way Galaxy is best described as A) spiral B) circular C) irregular D) elliptical 12. Compared to Jovian planets, terrestrial planets have a A) larger size. B) lower density. C) more rapid rotation. D) more rocky composition. 13. On March 21, at which location in New York State would sunrise occur first? A) Massena B) Buffalo C) Riverhead D) Syracuse 14. Cosmic background radiation provides direct evidence for the origin of A) Earth s ozone layer B) the universe C) Earth s earliest atmosphere D) our solar system 15. The most abundant element on the sun is A) carbon B) helium C) oxygen D) hydrogen B) C) D) 17. Billions of stars in the same region of the universe are called A) constellations B) asteroid belts C) solar systems D) galaxies
4 18. Which diagram best represents the size of the Moon, compared to Earth, when drawn to scale? 19. Which observation is a direct result of changes in distance between Earth and the Sun? A) A Foucault pendulum shows predictable changes in its direction of swing. B) The apparent diameter of the Sun shows predictable changes in size. C) Summer occurs in the Northern Hemisphere at the same time that winter occurs in the Southern Hemisphere. D) The length of daylight at the poles changes from 0 to 24 hours during the year. 20. Which statement best describes the position of the Sun at sunrise and sunset as seen by an observer in New York State on June 21? A) The Sun rises south of due east and sets north of due west. B) The Sun rises south of due east and sets south of due west. C) The Sun rises north of due east and sets south of due west. D) The Sun rises north of due east and sets north of due west. 21. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A) larger, hotter, and less luminous B) smaller, hotter, and less luminous C) smaller, cooler, and more luminous D) larger, cooler, and more luminous
5 22. The symbols below are used to represent different regions of space. Which diagram shows the correct relationship between these four regions? [If one symbol is within another symbol, that means it is part of, or included in, that symbol.] Base your answers to questions 23 through 25 on the diagram below, which represents an exaggerated view of Earth revolving around the Sun. Letters A, B, C, and D represent Earth's location in its orbit on the first day of each of the four seasons. 26. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents Earth revolving around the Sun. Letters A, B, C, and D represent Earth's location in its orbit on the first day of the four seasons. NP represents the North Pole. 23. Which observation provides the best evidence that Earth revolves around the Sun? A) The change from high ocean tide to low ocean tide is a repeating pattern. B) Earth's planetary winds are deflected by the Coriolis effect. C) Different star constellations are seen from Earth at different times of the year. D) Stars seen from Earth appear to circle Polaris. 24. Earth s rate of revolution around the Sun is approximately A) 1 per day B) 360 per day C) 15 per hour D) 23.5 per hour 25. Which location in Earth s orbit represents the first day of fall (autumn) for an observer in Pennsylvania? A) A B) B C) C D) D If the tilt of Earth's axis were decreased from 23.5 to 15, New York State's winters would become A) cooler, and summers would become warmer B) cooler, and summers would become cooler C) warmer, and summers would become warmer D) warmer, and summers would become cooler 27. Which change would occur if the Earth's rate of rotation were to increase? A) The year would be longer. B) The day would be shorter. C) The year would be shorter. D) The day would be longer. 28. The passage of the Moon into Earth's shadow causes a A) lunar eclipse B) full Moon C) solar eclipse D) new Moon
6 Regents Review Packet #2 29. Base your answer to the following question on on the data table below, which shows information about the four largest asteroids found in our solar system. The asteroids shown in the data table are located between the orbits of A) Jupiter and Saturn C) Earth and Mars B) Venus and Earth D) Mars and Jupiter Base your answers to questions 30 through 33 on the world map below. The shaded portion of the map indicates areas of night, and the unshaded portion indicates areas of daylight on a certain day of the year. Dashed latitude lines represent the Arctic Circle (66.5 N) and the Antarctic Circle (66.5 S). Point A is a location on Earth s surface. 30. Approximately what time of day is it at point A? A) sunset B) midnight C) sunrise D) noon 31. On this day, the duration of daylight from the equator to the Arctic Circle A) decreases, only C) increases, then decreases B) increases, only D) decreases, then increases
7 32. Which diagram shows the position of Earth relative to the Sun s rays on this day? 33. Approximately how many hours of daylight would occur at position A on this day? A) 12 B) 15 C) 6 D) Which photograph of star trails was taken by an observer facing directly north in New Jersey? A) B) C) D) 35. The time required for the Moon to show a complete cycle of phases when viewed from Earth is approximately A) 1 week B) 1 day C) 1 month D) 1 year 36. Which planet s orbit around the Sun is most nearly circular? A) Neptune B) Pluto C) Mercury D) Venus 37. Compared to the distances between the planets of our solar system, the distances between stars are usually A) much less B) much greater C) about the same 38. Which star color indicates the hottest star surface temperature? A) white B) yellow C) red D) blue 39. Which planet has the least distance between the two foci of its elliptical orbit? A) Jupiter B) Mars C) Venus D) Earth 40. What is the inferred age of our solar system, in millions of years? A) 4600 B) 544 C) 10,000 D) 1300
8 41. The table below shows gravitational data for a planet traveling in an elliptical orbit around a star. The table shows the relative gravitational force between the star and this planet at eight positions in the orbit (letters A through H). Higher numbers indicate stronger gravitational attraction. Which diagram best represents the positions of the planet in its orbit that would produce the gravitational forces shown in the data table? 42. The diagram below shows the noontime shadows cast by a student and a tree. 43. The diagram below shows Earth s orbit around the Sun and different positions of the Moon as it travels around Earth. Letters A through D represent four different positions of the Moon. If the time is solar noon and the student is located in New York State, in what direction is the student facing? A) north B) south C) west D) east An eclipse of the Moon is most likely to occur when the Moon is at position A) A B) B C) C D) D
9 44. The diagram below shows a satellite in four different positions as it revolves around a planet. Which graph best represents the changes in this satellite s orbital velocity as it revolves around the planet? 45. Which graph best represents the change in gravitational attraction between the Sun and a comet as the distance between them increases? 46. The Sun revolves around the center of A) the Milky Way Galaxy B) Earth C) Polaris D) Aldebaran 47. Why are impact structures more obvious on the Moon than on Earth? A) The Moon has little or no atmosphere. B) The rocks on the Moon are weaker than those on Earth. C) The Moon's gravity is stronger than Earth's gravity. D) The Moon rotates at a slower rate than Earth does.
10 48. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows a portion of the solar system. Mercury and Venus are the only planets that show phases when viewed from Earth because both Mercury and Venus A) revolve around the Sun inside Earth's orbit B) are eclipsed by Earth's shadow C) rotate more slowly than Earth does D) pass behind the Sun in their orbit 49. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. 50. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. The best inference that can be made based on the diagrams is that this planet is A) tilted on its axis B) changing seasons C) revolving D) rotating 51. The diagram below represents two planets in our solar system drawn to scale, Jupiter and planet A. What type of model does the diagram best demonstrate? A) a heliocentric model, in which celestial objects orbit the Sun B) a geocentric model, in which celestial objects orbit the Sun C) a geocentric model, in which celestial objects orbit Earth D) a heliocentric model, in which celestial objects orbit Earth Planet A most likely represents A) Venus B) Earth C) Uranus D) Saturn
11 Base your answers to questions 52 through 55 on the diagram below, which shows positions of the Moon in its orbit and phases of the Moon as viewed from New York State. 52. During which Moon phase might a solar eclipse be viewed on Earth? A) last quarter B) first quarter C) new Moon D) full Moon 53. Approximately how many days occur between the Moon s first-quarter phase and the Moon s last-quarter phase? A) 15 d B) 7 d C) d D) 29.5 d 54. Which statement best explains why the same side of the Moon is viewed from Earth as the Moon goes through its phases? A) The Moon s period of rotation equals the Moon s period of revolution around Earth. B) The Moon s period of rotation equals Earth s period of revolution around the Sun. C) The Moon s period of rotation equals Earth s period of rotation. D) The Moon does not rotate as it revolves around Earth. 55. During which Moon phase might a lunar eclipse be viewed on Earth? A) last quarter B) first quarter C) new Moon D) full Moon 56. A light year is A) the distance traveled by light in one year B) the time it takes light to go once around the Earth's orbit C) the distance the Earth moves in one year D) the time it takes light to travel one year 57. Compared to Jovian planets, terrestrial planets have A) larger equatorial diameters B) shorter periods of rotation C) larger masses D) shorter periods of revolution
12 58. A student in New York State looked toward the eastern horizon to observe sunrise at three different times during the year. The student drew the following diagram that shows the positions of sunrise, A, B, and C, during this one-year period. Which list correctly pairs the location of sunrise to the time of the year? A) A March 21 B June 21 C December 21 B) A June 21 B December 21 C March 21 C) A December 21 B March 21 C June 21 D) A June 21 B March 21 C December Base your answer to the following question on the diagram of the solar system below. According to Kepler's Harmonic Law of Planetary Motion, the farther a planet is located from the Sun, the A) shorter its period of revolution B) longer its period of rotation C) shorter its period of rotation D) longer its period of revolution 60. An astronomical unit (A.U.) is A) equal to a light year B) a term for defining the luminosity of a star C) the average distance of any given planet to the sun D) the average distance from the Earth to the sun 61. In the Northern Hemisphere, planetary winds deflect to the A) left, due to the Coriolis effect B) right, due to the Doppler effect C) left, due to the Doppler effect D) right, due to the Coriolis effect
13 Base your answers to questions 62 through 64 on the diagram below, which shows Earth and the Moon in relation to the Sun. Positions A, B, C, and D show the Moon at specific locations in its orbit. Point X is a location on Earth's surface. 62. A solar eclipse might occur when the Moon is at location A) A B) B C) C D) D 63. What is the time of day at point X? A) 6 p.m. B) midnight C) noon D) 6 a.m. 64. On what date does the line separating day and night pass through Earth's North Pole, as shown in this diagram? A) December 21 B) January 21 C) March 21 D) June Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth s axis relative to the Sun s rays on December 15?
14 Base your answers to questions 66 through 68 on the calendar below, which shows the month of July of a recent year. The dates of major Moon phases, as seen in New York State, are shown. The diagram below represents the phase of the Moon observed from New York State one night during the month of July. 66. On which date was this phase of the Moon visible from New York State? A) July 4 B) July 11 C) July 19 D) July Why does the Moon s gravity have a greater effect on Earth s ocean tides than the Sun s gravity? A) The Moon has a greater mass. B) The Sun s gravity influences more planets. C) The Moon is much closer to Earth. D) The Sun is composed mostly of gases. 68. Eclipses do not occur every month because the Moon s A) rate of rotation is 15 each hour B) orbit is inclined to Earth s orbit C) period of revolution is 27.3 days D) period of rotation and period of revolution are the same 69. Which diagram sequence correctly shows the order of Moon phases, as viewed from Earth, for a period of 1 month? [Note that some phases have been omitted.]
15 70. A camera was placed outside at night and pointed directly at Polaris and several other stars. The lens was kept open and a time-exposure photograph was taken. The diagram below represents that photograph of Polaris and star trails, with an angular protractor to measure apparent motion. How many hours was the lens kept open to create the star trails in this photograph? A) 1 hour B) 6 hours C) 3 hours D) 4 hours 71. The diagram below shows the altitude of the Sun at solar noon on March 21, as seen by an observer at 42 N latitude. 72. Base your answer to the question below on the diagram below. The diagram represents the path of a planet orbiting a star. Points A, B, C, and D indicate four orbital positions of the planet. Compared to the altitude of the Sun observed at solar noon on March 21, the altitude of the Sun observed at solar noon on June 21 will be A) 48 higher in the sky B) 15 higher in the sky C) 42 higher in the sky D) 23.5 higher in the sky When viewed by an observer on the planet, the star has the largest apparent diameter at position A) A B) B C) C D) D 73. The best evidence that the distance between the Moon and the Earth varies is provided by the apparent change in the Moon's A) diameter B) shape C) altitude D) phase
16 74. The diagram below represents the Moon in its orbit, as viewed from above Earth s North Pole. Position 1 represents a specific location of the Moon in its orbit. 76. Which graph best illustrates the average temperatures of the planets in the solar system? A) B) C) Which phase of the Moon will be seen from Earth when the Moon is at position 1? D) 75. Which sequence of Moon phases could be observed from Earth during a 2-week period? 77. The diagram below shows a planet's orbit around the Sun. A) B) C) At which location is the planet's orbital velocity greatest? A) C B) D C) B D) A D)
17 78. The diagram below shows the position of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth during a solar eclipse. The full shadow (umbra) and partial shadow (penumbra) of the Moon and Earth are shown. Which diagram best represents the appearance of the Sun and the Moon to an observer located within the umbra of the Moon s shadow on Earth s surface? 79. The atmosphere of Venus is composed primarily of A) carbon dioxide B) hydrogen and helium C) ammonia D) methane 80. The period of time a planet takes to make one revolution around the Sun is most dependent on the planet's average A) rotation rate B) insolation from the Sun C) distance from the Sun D) mass 81. During a total solar eclipse one might view A) the sun's solar winds B) the sun's corona C) sun spots D) nothing of the sun, since it is totally blocked by the moon 82. The force of gravity between two objects is greatest when A) masses are small and the objects are close together B) masses are small and the objects are far apart C) masses are large and the objects are close together D) masses are large and the objects are far apart
18 Base your answers to questions 83 through 85 on the diagram below. The diagram represents the Earth at a position in orbit around the Sun, the Sun's rays at solar noon, and the direction to Polaris. Letters A through D represent positions on the Earth's surface. 87. Which diagram most correctly shows the portion of Earth that is illuminated by sunlight and the portion that is in shadow on the first day of summer in the Northern Hemisphere? 83. During one complete rotation of the Earth on its axis, which position receives the least number of hours of daylight? A) D B) C C) A D) B 84. Which date is represented by the diagram? A) June 21 B) September 23 C) December 21 D) March Which position is receiving the Sun's rays from directly overhead at solar noon? A) D B) B C) C D) A 86. The diagram below shows the elliptical orbit of a planet revolving around a star. The star and F2 are the foci of this ellipse. What is the approximate eccentricity of this ellipse? A) 1.47 B) 0.47 C) 0.68 D) 0.22 Base your answers to questions 88 and 89 on the diagram below which represents nine positions of the Earth in orbit around the Sun during one complete orbit of the Moon around the Earth. 88. The elliptical shape of the Moon's orbit around the Earth causes A) the Moon's period of rotation to equal its period of revolution B) the 23 tilt of the Earth's axis of rotation C) changes in the gravitational attraction between the Moon and the Earth D) the Earth to have an equatorial bulge 89. The Earth rotates on its axis, causing the Moon to appear to rise each day. Moonrise occurs about 52 minutes later each day because as the Earth completes one rotation, the Moon also A) completes one rotation on its axis B) revolves part way around the Earth C) wobbles on its axis D) is inclined 23
19 Base your answers to questions 90 through 93 on the diagram below, which shows a model of the apparent path and position of the Sun in relation to an observer at four different locations, A, B, C, and D, on Earth s surface on the dates indicated. The zenith (z) and the actual position of the Sun in the model at the time of the observation are shown. [The zenith is the point directly over the observer.] 90. Where on Earth's surface is the observer at location D located? A) at the North Pole B) mid latitude northern hemisphere C) mid latitude southern hemisphere D) at the Equator 91. From sunrise to sunset at location B, the length of the observer s shadow will A) increase, only B) increase, then decrease C) decrease, then increase D) decrease, only 92. According to the Sun s actual position shown in the diagrams, the most intense insolation is being received by the observer at location A) A B) B C) C D) D 93. Where on Earth s surface is the observer at location C located? A) at the North Pole B) at the Equator C) at the South Pole D) in Oswego, New York 94. A tree in New York State casts a shadow as shown in the diagram below. 95. The diagram below represents the elliptical orbit of a moon revolving around a planet. The foci of this orbit are the points labeled F 1 and F 2. What time of day and season are represented by the diagram? A) early morning in summer B) early morning in winter C) late afternoon in summer D) late afternoon in winter What is the approximate eccentricity of this elliptical orbit? A) 0.7 B) 0.5 C) 1.4 D) 0.3
20 Base your answers to questions 96 through 98 on the diagram below, which represents the Moon orbiting Earth as viewed from space above the North Pole. The Moon is shown at eight different positions in its orbit. 96. The approximate time required for the Moon to move from position 3 to position 7 is A) 1 hour B) 2 weeks C) 3 months D) 4 days 97. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from Earth? A) revolution of Earth B) rotation of Earth C) rotation of the Sun D) revolution of the Moon 98. As the Moon changes location from position 2 to position 6, the visible portion of the Moon as observed from Earth A) decreases, only B) increases, then decreases C) increases, only D) decreases, then increases 99. In each diagram below, the mass of the star is the same. In which diagram is the force of gravity greatest between the star and the planet shown?
21 100. Which two factors cause the perpendicular rays of the Sun to move between 23.5º N and 23.5º S? A) tilt of Earth's axis and Earth's revolution B) tilt of Earth's axis and Earth's rotation C) eccentricity of Earth's orbit and Earth's revolution D) eccentricity of Earth's orbit and Earth's rotation 101. The diagram below represents the direction of Earth's rotation as it appears from above the North Pole. Point X is a location on Earths surface Two stars of the same color are plotted on an H-R diagram. Star A is more luminous than star B. Which one of the following statements could explain this? A) Star A is hotter than star B. B) Star A is more distant than star B. C) Star A is larger than star B. D) Star A appears brighter in the sky than star B The diagram below represents the development of our universe from the time of the Big Bang until the present. Letter A indicates two celestial objects. The time at point X is closest to A) 12 midnight B) 12 noon C) 9 a.m. D) 9 p.m Which diagram correctly shows how surface winds are deflected (curved) in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres due to Earth's rotation? The present-day celestial objects labeled A are best identified as A) eccentric comets B) terrestrial planets C) spiral galaxies D) asteroid belts 105. The diagram below represents the direction of Earth s rotation as it appears from above the North Pole. Point X is a location on Earth s surface. The time at point X is closest to A) 6 a.m. B) 12 midnight C) 12 noon D) 6 p.m.
22 Regents Review Packet # Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows an inferred sequence in which our solar system formed from a giant interstellar cloud of gas and debris. Stage A shows the collapse of the gas cloud, stage B shows its flattening, and stage C shows the sequence that led to the formation of planets. From stage B to stage C, the young Sun was created A) B) C) D) when gravity caused the center of the cloud to contract by outgassing from Earth s interior when gravity caused heavy dust particles to split apart by outgassing from the spinning interstellar cloud 107. The diagram below shows the positions of the Moon and the Sun at sunset during an evening in New York State. Points A, B, C, and D represent positions along the western horizon. At sunset on the following evening, the Moon will be located at position A) A B) B C) C D) D
23 108. The diagram below shows Earth s orbit around the Sun. Locations A, B, C, and D represent Earth on th first day of each season. Which location represents March 21? A) A B) C C) B D) D 109. Diagram 1 shows the Moon in its orbit at four positions labeled A, B, C, and D. Diagram 2 shows a phase of the Moon as viewed from New York State. At which labeled Moon position would the phase of the Moon shown in diagram 2 be observed from New York State? A) D B) C C) B D) A
24 110. The diagram below represents a planet in orbit around a star. Which statement best describes how the planet's energy is changing as it moves from point A to point B? A) Kinetic energy is increasing and potential energy is decreasing. B) Both kinetic and potential energy are increasing. C) Kinetic energy is decreasing and potential energy is increasing. D) Both kinetic and potential energy are decreasing How do Jupiter s density and period of rotation compare to Earth s? A) Jupiter is less dense and has a longer period of rotation. B) Jupiter is more dense and has a shorter period of rotation. C) Jupiter is more dense and has a longer period of rotation. D) Jupiter is less dense and has a shorter period of rotation Which statement best describes the age of our solar system and the universe? A) The universe is at least twice as old as our solar system. B) Our solar system and the universe are estimated to be 10 billion years old. C) Our solar system is at least twice as old as the universe. D) Our solar system and the universe are estimated to be 5 billion years old Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovian planets have A) slower rates of rotation B) smaller diameters C) greater average densities D) longer periods of revolution 114. In order to describe the apparent daily motion of stars, a person must observe the A) position of one star relative to the horizon over a period of time B) position of one particular star at one particular time C) locations of several stars at the same time D) brightness of several stars over a period of time 115. The constellation Pisces changes position during a night, as shown in the diagram below. Which motion is mainly responsible for this change in position? A) rotation of Earth on its axis B) revolution of Pisces around the Sun C) revolution of Earth around the Sun D) rotation of Pisces on its axis 116. For what reason did the heliocentric model of the universe replace the geocentric model of the universe? A) The geocentric model did not predict the phases of the Moon. B) The heliocentric model provided a simpler explanation of the motions of the planets. C) The geocentric model no longer predicted the positions of the constellations. D) The heliocentric model proved that the Earth rotates Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the daily rising and setting of the Sun B) the apparent deflection of winds C) the changing of the Moon phases D) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky
25 118. Which model best represents the apparent path of the Sun observed at various times during the year at the Equator? A) 121. The diagram below represents our solar system. B) C) D) 119. The diagram below represents the bright-line spectrum for an element. This system is best classified as A) heliocentric, with elliptical orbits B) heliocentric, with circular orbits C) geocentric, with elliptical orbits D) geocentric, with circular orbits 122. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) The spectrum of the same element observed in the light from a distant star is shown below. The shift in the spectral lines indicates that the star is moving A) in a circular orbit around the Sun B) in an elliptical orbit around the Sun C) away from Earth D) toward Earth 120. Which motion causes the apparent rising and setting of the Moon each day, as seen from a location in Kansas? A) the Earth rotating on its axis B) the Earth revolving around the Sun C) the Moon revolving around the Earth D) the Moon rotating on its axis 123. Which diagram shows a planet with the least eccentric orbit? ( Key: = planet * = star )
26 124. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows sunlight entering a room through the same window at three different times on the same winter day. This room is located in a building in Connecticut. On which side of the building is the window located? A) west B) south C) east D) north 125. Base your answer to the following question on the map below, which shows locations A and B on Earth's surface at the same distance from the ocean, at the same elevation above sea level, and at the same latitude. There is a four-hour solar time difference between locations A and B. What is the difference in longitude between locations A and B? A) 45 B) 23.5 C) 15 D) 60
27 126. The diagram below represents the Earth's orbital path around the Sun. The Earth takes the same amount of time to move from A to B as from C to D The diagram below represents a swinging Foucault pendulum. Which values are equal within the system? A) The shaded sections of the diagram are equal in area. B) The gravitational force between the Earth and the Sun at point B is the same as the gravitational force at point D. C) The distance from the Sun to the Earth is the same at point A and at point D. D) The orbital velocity of the Earth at point A equals its orbital velocity at point C The diagram below represents a standard dark-line spectrum for an element. This pendulum will show an apparent change in the direction of its swing due to Earth s A) tilted axis B) revolution C) curved surface D) rotation 129. The diagram below shows the equipment used to demonstrate a Foucault pendulum. The spectral lines of this element are observed in light from a distant galaxy. Which diagram represents these spectral lines? A) B) C) In the demonstration, a student swings the weight hanging in the pail and then spins the stool. The stool represents A) the revolving Earth B) the rotating Earth C) convection currents D) the Coriolis effect D)
28 130. The diagram below shows the Moon in different positions as it revolves around Earth, as observed from above the North Pole (NP). Which image correctly represents the Moon at position 8, as observed from Earth?
3. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole.
 1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice
 A) B) Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's
A) B) Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
2. The diagram below represents the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer at 65 N on March 21.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in space.
 Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: 3653-1 - Page 1 The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in
Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: 3653-1 - Page 1 The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in
Which table correctly shows the dates on which the apparent paths of the Sun were observed? A) B) C) D)
 1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
C) D) 2. The model below shows the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer in New York State on the first day of one of the four seasons.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface.
 1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
Earth Moon Motions A B1
 Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
D. most intense and of longest duration C. D.
 Astronomy Take Home Test Answer on a separate sheet of paper In complete sentences justify your answer Name: 1. The Moon s cycle of phases can be observed from Earth because the Moon 4. The accompanying
Astronomy Take Home Test Answer on a separate sheet of paper In complete sentences justify your answer Name: 1. The Moon s cycle of phases can be observed from Earth because the Moon 4. The accompanying
EARTH MOON SUN REVIEW
 1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
10-20 billion years old
 Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
drinking straw, protractor, string, and rock. observer on Earth. Sun across the sky on March 21 as seen by an
 1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
Which letter on the timeline best represents the time when scientists estimate that the Big Bang occurred? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. The red shift of light from most galaxies is evidence that A) most galaxies are moving away from Earth B) a majority of stars in most galaxies are red giants C) the light slows down as it nears Earth
1. The red shift of light from most galaxies is evidence that A) most galaxies are moving away from Earth B) a majority of stars in most galaxies are red giants C) the light slows down as it nears Earth
Apparent Motion. How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky?
 Apparent Motion How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky? 1 Apparent Motions Geocentric Universe - idea that Earth was at the center of the solar system Stars all rotate around the Earth
Apparent Motion How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky? 1 Apparent Motions Geocentric Universe - idea that Earth was at the center of the solar system Stars all rotate around the Earth
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
GALAXIES AND STARS. 2. Which star has a higher luminosity and a lower temperature than the Sun? A Rigel B Barnard s Star C Alpha Centauri D Aldebaran
 GALAXIES AND STARS 1. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A smaller, hotter, and less luminous B smaller, cooler, and more luminous C larger, hotter, and less luminous D larger, cooler, and more
GALAXIES AND STARS 1. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A smaller, hotter, and less luminous B smaller, cooler, and more luminous C larger, hotter, and less luminous D larger, cooler, and more
THE SOLAR SYSTEM. Base your answers to questions 2 through 6 on the diagram below, which shows a portion of the solar system.
 THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1. The atmosphere of Venus is composed primarily of A hydrogen and helium B carbon dioxide C methane D ammonia Base your answers to questions 2 through 6 on the diagram below, which shows
THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1. The atmosphere of Venus is composed primarily of A hydrogen and helium B carbon dioxide C methane D ammonia Base your answers to questions 2 through 6 on the diagram below, which shows
Topic 10: Earth in Space Workbook Chapters 10 and 11
 Topic 10: Earth in Space Workbook Chapters 10 and 11 We can imagine all the celestial objects seen from Earth the sun, stars, the Milky way, and planets as being positioned on a celestial sphere. Earth
Topic 10: Earth in Space Workbook Chapters 10 and 11 We can imagine all the celestial objects seen from Earth the sun, stars, the Milky way, and planets as being positioned on a celestial sphere. Earth
Class Notes: Astronomy
 Name: Date: Period: Astronomy The Physical Setting: Earth Science Class Notes: Astronomy I. Apparent Motion Geocentric Universe -! Starts all rotate around the Earth on a single sphere at º/hour Planets
Name: Date: Period: Astronomy The Physical Setting: Earth Science Class Notes: Astronomy I. Apparent Motion Geocentric Universe -! Starts all rotate around the Earth on a single sphere at º/hour Planets
Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test
 is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel.
 NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel. EARTH MOTIONS (Video 10.1) 1. Define rotation, how long it takes, which direction it happens, the proof it happens, and the result. 2. Define revolution,
NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel. EARTH MOTIONS (Video 10.1) 1. Define rotation, how long it takes, which direction it happens, the proof it happens, and the result. 2. Define revolution,
A. the spinning of Earth on its axis B. the path of the Sun around Earth
 stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system.
 1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
Practice Questions: Seasons #2
 1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
Galaxies and Stars. 3. Base your answer to the following question on The reaction below represents an energy-producing process.
 Galaxies and Stars 1. To an observer on Earth, the Sun appears brighter than the star Rigel because the Sun is A) hotter than Rigel B) more luminous than Rigel C) closer than Rigel D) larger than Rigel
Galaxies and Stars 1. To an observer on Earth, the Sun appears brighter than the star Rigel because the Sun is A) hotter than Rigel B) more luminous than Rigel C) closer than Rigel D) larger than Rigel
FCAT Review Space Science
 FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
C) wavelength C) eastern horizon B) the angle of insolation is high B) increases, only D) thermosphere D) receive low-angle insolation
 1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
Astronomy Part 1 Regents Questions
 Regents Questions 1. The Sun revolves around the center of A) Polaris B) Aldebaran C) Earth D) the Milky Way Galaxy 4. In which sequence are the items listed from least total mass to greatest total mass?
Regents Questions 1. The Sun revolves around the center of A) Polaris B) Aldebaran C) Earth D) the Milky Way Galaxy 4. In which sequence are the items listed from least total mass to greatest total mass?
Midterm Review #2-2018
 1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
Coriolis Effect - the apparent curved paths of projectiles, winds, and ocean currents
 Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)
 MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
What is in outer space?
 What is in outer space? Celestial Objects are any natural objects that move through space. Star:_a huge sphere of gas in space _Nuclear fusion within stars give off enormous amounts of energy such as light
What is in outer space? Celestial Objects are any natural objects that move through space. Star:_a huge sphere of gas in space _Nuclear fusion within stars give off enormous amounts of energy such as light
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe
 Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Explain the Big Bang Theory and give two pieces of evidence which support it.
 Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: asteroid, celestial object, comet, constellation, Doppler effect, eccentricity, eclipse, ellipse, focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model,
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: asteroid, celestial object, comet, constellation, Doppler effect, eccentricity, eclipse, ellipse, focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model,
Practice Seasons Moon Quiz
 1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -NOTES ASTRONOMY
 EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -NOTES ASTRONOMY UNIT 9- ASTRONOMY 2 THE SOLAR SYSTEM I. The Solar System:. a. Celestial Body:. i. Examples:. b. MAIN COMPONENTS/MEMBERS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM: i. 1. Planets are objects
EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -NOTES ASTRONOMY UNIT 9- ASTRONOMY 2 THE SOLAR SYSTEM I. The Solar System:. a. Celestial Body:. i. Examples:. b. MAIN COMPONENTS/MEMBERS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM: i. 1. Planets are objects
THE UNIVERSE AND THE EARTH
 ESO1 THE UNIVERSE AND THE EARTH Unit 1 What is the Universe like? Universe theories Ideas about the Universe: Geocentric theory Aristotle (B.C) and Ptolomy (A.D) Heliocentric theory Copernicus in 1542
ESO1 THE UNIVERSE AND THE EARTH Unit 1 What is the Universe like? Universe theories Ideas about the Universe: Geocentric theory Aristotle (B.C) and Ptolomy (A.D) Heliocentric theory Copernicus in 1542
Which Earth latitude receives the greatest intensity of insolation when Earth is at the position shown in the diagram? A) 0 B) 23 N C) 55 N D) 90 N
 1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
Solar System Glossary. The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting
 Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
A) M D) The Moon s distance from Earth varies in a cyclic manner.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
EARTHS SHAPE AND POLARIS PRACTICE 2017
 1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
18. Which graph best represents the relationship between the number of sunspots and the amount of magnetic activity in the Sun?
 1. Which star has a surface temperature most similar to the surface temperature of Alpha Centauri? A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 2. Giant stars have greater luminosity than our sun mainly
1. Which star has a surface temperature most similar to the surface temperature of Alpha Centauri? A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 2. Giant stars have greater luminosity than our sun mainly
Topic 1: Earth s Motion Topic 2: The Moon Earth s Satellite Topic 3: Solar System Topic 4: The Planets Topic 5: Stars & Galaxies
 Topic 1: Earth s Motion Topic 2: The Moon Earth s Satellite Topic 3: Solar System Topic 4: The Planets Topic 5: Stars & Galaxies Topic 1: Earth s Motion Essential Question: What causes the cycle of seasons
Topic 1: Earth s Motion Topic 2: The Moon Earth s Satellite Topic 3: Solar System Topic 4: The Planets Topic 5: Stars & Galaxies Topic 1: Earth s Motion Essential Question: What causes the cycle of seasons
Chapter 26 Section 1 pages Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe
 Name: Period: Chapter 26 Section 1 pages 659-666 Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 2. What is the main reason people study the
Name: Period: Chapter 26 Section 1 pages 659-666 Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 2. What is the main reason people study the
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Astronomy A B1. 9.The diagram below shows the spectral lines for an element.
 Astronomy A B1 1. In which sequence are the items listed from least total mass to greatest total mass? (1) solar system, Milky Way, universe (2) Milky Way, solar system, universe (3) universe, Milky Way,
Astronomy A B1 1. In which sequence are the items listed from least total mass to greatest total mass? (1) solar system, Milky Way, universe (2) Milky Way, solar system, universe (3) universe, Milky Way,
Astronomy Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
The color of a star provides a measure of its A. size B. mass C. composition D. surface temperature
 Which statement best describes the Big Bang Theory? A. Galaxies within the universe collided about 13.5 billion years ago forming the present objects in the universe. B. Existing objects in the universe
Which statement best describes the Big Bang Theory? A. Galaxies within the universe collided about 13.5 billion years ago forming the present objects in the universe. B. Existing objects in the universe
Earth Science Seasons Test Name Per Date
 Name Per Date Page 1 1. The diagram below represents four positions of the Earth as it revolves around the Sun. 5. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows the apparent
Name Per Date Page 1 1. The diagram below represents four positions of the Earth as it revolves around the Sun. 5. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows the apparent
SPI Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe.
 SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
Chapter 17 Solar System
 Chapter 17 Solar System Rotation Earth spinning on its axis (like a top) "TOP" imaginary rod running through the center of the Earth from North pole to South pole The Earth is tilted on its axis at an
Chapter 17 Solar System Rotation Earth spinning on its axis (like a top) "TOP" imaginary rod running through the center of the Earth from North pole to South pole The Earth is tilted on its axis at an
1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth.
 1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth. Which diagram best represents the change in the motion of a Foucault pendulum that provides evidence of Earth's rotation?
1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth. Which diagram best represents the change in the motion of a Foucault pendulum that provides evidence of Earth's rotation?
ASTRONOMY. S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c,
 ASTRONOMY S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c, UNIVERSE Age 13.7 billion years old The Big Bang Theory Protons and Neutrons formed hydrogen and helium. This created heat that formed the stars. Other elements
ASTRONOMY S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c, UNIVERSE Age 13.7 billion years old The Big Bang Theory Protons and Neutrons formed hydrogen and helium. This created heat that formed the stars. Other elements
Astronomy, PART 2. Vocabulary. A. Universe - Our Milky Way Galaxy is one of of galaxies in an expanding universe.
 Astronomy, PART 2 Vocabulary Aphelion Asteroid Astronomical Unit Comet Constellation Crater Eccentricity Eclipse Equinox Geocentric model Gravitation Heliocentric model Inertia Jovian Perihelion Revolution
Astronomy, PART 2 Vocabulary Aphelion Asteroid Astronomical Unit Comet Constellation Crater Eccentricity Eclipse Equinox Geocentric model Gravitation Heliocentric model Inertia Jovian Perihelion Revolution
UNIT 1: EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM.
 UNIT 1: EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM. 1) A BRIEF HISTORY Theories of the Universe In the second century BC, the astronomer Ptolemy proposed that the Earth was the centre of the Universe, and that the Sun,
UNIT 1: EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM. 1) A BRIEF HISTORY Theories of the Universe In the second century BC, the astronomer Ptolemy proposed that the Earth was the centre of the Universe, and that the Sun,
1. The symbols below represent the Milky Way galaxy, the solar system, the Sun, and the universe.
 Name Date 1. The symbols below represent the Milky Way galaxy, the solar system, the Sun, and the universe. 4. The diagram below illustrates three stages of a current theory of the formation of the universe.
Name Date 1. The symbols below represent the Milky Way galaxy, the solar system, the Sun, and the universe. 4. The diagram below illustrates three stages of a current theory of the formation of the universe.
2. Identify the nuclear process that occurs when lighter elements in a star combine to form heavier elements, producing the star's radiant energy.
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the flowchart below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The flowchart represents possible pathways in the evolution of stars. 1. Circle the relative surface
Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the flowchart below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The flowchart represents possible pathways in the evolution of stars. 1. Circle the relative surface
Effective August 2007 All indicators in Standard / 14
 8-4.1 Summarize the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Taxonomy level: 2.4-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Previous/Future
8-4.1 Summarize the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Taxonomy level: 2.4-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Previous/Future
EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -KEY ASTRONOMY
 EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -KEY ASTRONOMY UNIT 9- ASTRONOMY 2 THE SOLAR SYSTEM I. The Solar System: THE SUN AND ALL CELESTIAL OBJECTS THAT ORBIT THE SUN HELD BY THE SUN S GRAVITY. a. Celestial Body: ANY OBJECT
EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -KEY ASTRONOMY UNIT 9- ASTRONOMY 2 THE SOLAR SYSTEM I. The Solar System: THE SUN AND ALL CELESTIAL OBJECTS THAT ORBIT THE SUN HELD BY THE SUN S GRAVITY. a. Celestial Body: ANY OBJECT
Astronomy Regents Review
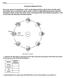 Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n)
 When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
Astronomy. Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe.
 Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY. Test 1: May 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 614
 ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: May 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 614 Examination date: 13 May 2017 Time limit: 50 min Time of Examination:
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: May 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 614 Examination date: 13 May 2017 Time limit: 50 min Time of Examination:
Modern Astronomy Review #1
 Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Brock University. Test 1, October 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of Students: 470 Date of Examination: October 3, 2017
 Brock University Test 1, October 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of Students: 470 Date of Examination: October 3, 2017 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 17:00 17:50
Brock University Test 1, October 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of Students: 470 Date of Examination: October 3, 2017 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 17:00 17:50
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS
 UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
Astronomy 3. Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets
 Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
1/3/12. Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System. Ancient Measurements. Earth s Size and Shape. Ancient Measurements. Ancient Measurements
 // Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
// Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
5. In which diagram is the observer experiencing the greatest intensity of insolation? A) B)
 1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
The Earth in the Universe Geology
 The Earth in the Univers e The Earth in the Universe Geology The origin of the Universe The position of the Earth in the Universe Distances in the Universe Galaxies The Milky Way Stars: The Sun The Solar
The Earth in the Univers e The Earth in the Universe Geology The origin of the Universe The position of the Earth in the Universe Distances in the Universe Galaxies The Milky Way Stars: The Sun The Solar
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide. Assessment Date : Term Rotation Revolution
 Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
a. 1/3 AU b. 3 AU 5. Meteor showers occur
 1 AST104 Sp. 2006: WELCOME TO EXAM 3 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice on the answer form. Read all answer choices before making selection. CHECK YOUR WORK CAREFULLY BEFORE HANDING
1 AST104 Sp. 2006: WELCOME TO EXAM 3 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice on the answer form. Read all answer choices before making selection. CHECK YOUR WORK CAREFULLY BEFORE HANDING
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES SAMPLE. Earth and Space. Secondary Science 7C. Years 7 9. Written by Valerie Marett. CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544
 AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Earth and Space Secondary Science 7C Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544 Secondary Science Earth and Space Contents The Earth. 2 Movements
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Earth and Space Secondary Science 7C Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544 Secondary Science Earth and Space Contents The Earth. 2 Movements
The Curious Tale of Asteroid Hermes
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and diagram below. The diagram shows the orbits of the four inner planets and the asteroid Hermes around the Sun. Point A represents a position
Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and diagram below. The diagram shows the orbits of the four inner planets and the asteroid Hermes around the Sun. Point A represents a position
Midterm Review #3-2018
 1. The reaction below represents an energy-producing process. The reaction represents how energy is produced A) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere B) during nuclear decay C) from the movement of
1. The reaction below represents an energy-producing process. The reaction represents how energy is produced A) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere B) during nuclear decay C) from the movement of
Practice Packet Topic 9: Earth in Space & Beyond
 Practice Packet Topic 9: Earth in Space & Beyond Vocabulary: Lesson 1: Lesson 2: Lesson 3: Lesson 4: Name: Lesson 5: Lesson 6: 1 VOCABULARY For each word, provide a short but specific definition from YOUR
Practice Packet Topic 9: Earth in Space & Beyond Vocabulary: Lesson 1: Lesson 2: Lesson 3: Lesson 4: Name: Lesson 5: Lesson 6: 1 VOCABULARY For each word, provide a short but specific definition from YOUR
a. 0.5 AU b. 5 AU c. 50 AU d.* AU e AU
 1 AST104 Sp04: WELCOME TO EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1. A galaxy
1 AST104 Sp04: WELCOME TO EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1. A galaxy
Earth s Motions. Rotation -!! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours.
 Name: Date: Period: Earth In the Solar System The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES! Rotation -! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours
Name: Date: Period: Earth In the Solar System The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES! Rotation -! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours
Investigations in Earth and Space Science Semester Review: Unit 1 and Unit 2
 IESS Unit 1: Solar Energy & Fluid Circulation Review Directions: Write the answer to each question in the box to the right of the question. Fold your paper along the line and use this as a review sheet!
IESS Unit 1: Solar Energy & Fluid Circulation Review Directions: Write the answer to each question in the box to the right of the question. Fold your paper along the line and use this as a review sheet!
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Physical Science 1 Chapter 16 INTRODUCTION. Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time.
 INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
Which phase of the Moon will be seen from the Earth at position 5? A) B) C) D)
 Name Date 1. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from the Earth? A) the rotation of the Moon on its axis B) the revolution of the Moon around the Earth C) the rotation of the Sun on
Name Date 1. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from the Earth? A) the rotation of the Moon on its axis B) the revolution of the Moon around the Earth C) the rotation of the Sun on
Brock University. Test 1, September 2014 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: September 29, 2014
 Brock University Test 1, September 2014 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: September 29, 2014 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 18:00 18:50 Instructor:
Brock University Test 1, September 2014 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: September 29, 2014 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 18:00 18:50 Instructor:
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science. Solar System Review
 Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
STANDARD. S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position.
 STANDARD S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. S6E2 b. Explain the alignment of the earth, moon, and sun during solar and lunar eclipses. c. Relate the
STANDARD S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. S6E2 b. Explain the alignment of the earth, moon, and sun during solar and lunar eclipses. c. Relate the
1UNIT. The Universe. What do you remember? Key language. Content objectives
 1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
2. The distance between the Sun and the next closest star, Proxima Centuari, is MOST accurately measured in
 Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy
 CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM)
 Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM) The Milky Way the galaxy that contains our solar system Our solar system is a speck in the Milky Way galaxy Pluto is now considered
Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM) The Milky Way the galaxy that contains our solar system Our solar system is a speck in the Milky Way galaxy Pluto is now considered
C) D) 2. The diagram below shows a large pendulum in motion over an 8-hour period.
 1. An observer on Earth measured the apparent diameter of the Sun over a period of 2 years. Which graph best represents the Sun's apparent diameter during the 2 years? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below
1. An observer on Earth measured the apparent diameter of the Sun over a period of 2 years. Which graph best represents the Sun's apparent diameter during the 2 years? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below
