Transiting extra-solar planets: spin-orbit misalignment and rings
|
|
|
- Erika Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transiting extra-solar planets: spin-orbit misalignment and rings λ Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo KASI colloquium September 26, 2006
2 Recent Activities of Observational Cosmology Group, University of Tokyo (1) SDSS galaxy and quasar statistics genus statistics and phase correlation of SDSS galaxies (Hikage et al. 2003, 2004,2005; Hikage, Matsubara, and Suto 2004; Park et al. 2005) 3pt correlation functions of SDSS galaxies Nichol et al. 2004; Nichol et al. 2006) (Kayo, Suto, widest-separation lensed quasar from SDSS (Inada et al. 2003; Oguri et al. 2004; Ota et al. 2006) 2pt correlation functions of SDSS quasars and cosmological constant (Yahata et al. 2005) constraints on the deviation from Newton s law of gravity from SDSS galaxy power spectrum (Shirata, Shiromizu, Yoshida & Suto 2005) SDSS galaxy number counts and SFD dust map (Yahata et al. astroph/ )
3 Recent Activities of Observational Cosmology Group, University of Tokyo (2) Dark halo and galaxy cluster highest-angular resolution SZ maps in submm and mm (Komatsu et al. 1999, 2001; Kitayama et al. 2004) triaxial modeling of dark matter halos (Jing & Suto 2002; Oguri, Lee & Suto 2003; Lee, Jing & Suto 2005) Warm/hot intergalactic medium (WHIM) a proposal of oxygen emission line search with DIOS (Yoshikawa et al. 2003, 2004) feasibility of an absorption line search with XEUS along bright quasars and GRB afterglow (Kawahara et al. 2006) Spectroscopy of transiting extrasolar planets constraints on planetary atmosphere (Winn et al. 2004; Narita et al. 2005) first detection of the spin-orbit misalignment in an extrasolar planetary system using the Rossiter effect (Ohta, Taruya & Suto 2005; Winn et al. 2005)
4 Observation of the Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect the most luminous X-ray cluster: RX J The first submm SZ map with SCUBA, JCMT The highest angular resolution (σ FWHM =13 ) mm SZ map with NOBA, Nobeyama submm SZ map elongation along the line of sight mm SZ map: discovery of substructure cluster peculiar velocity [km/s] Komatsu et al. ApJ 516 (1998) L1 PASJ 53 (2001) 57 Kitayama et al. PASJ 56 (2004) 17
5 SDSS image Subaru 8.2m telescope Widest-separation lensed quasars Subaru image Inada, Oguri et al. (2003) image 1 gravitational bending lensing cluster of light path image 2 (6.2 billion yrs away) SDSS J1004 (9.8 billion yrs Zoomed Subaru image away) image 3 image 4 1 SDSS 2.5m telescope ,000 light yrs apart
6 SDSS J HST photo-release on May 23,
7 Searching for cosmic missing baryons with DIOS (Diffuse Intergalactic Oxygen Surveyor) Yoshikawa et al. PASJ 55 (2003) 879 PASJ 56 (2004) 939 Mock simulations Tokyo Metropolitan Univ.: T. Ohashi JAXA/ISAS: N. Yamasaki K. Mitsuda Nagoya Univ.: Y. Tawara Univ. of Tokyo: K. Yoshikawa Y.Suto
8 Hyper Suprime-Cam and WFMOS on Subaru 3000 thousands of fibers over a 1.5 degree field-of-view on an 8-meter class telescope (Subaru/Gemini) w ~ 5% dw/dz ~ 20% z~1 survey with 2 million galaxies with twice LRG volume 1% accuracy Taken from WFMOS Feasibility Study by NOAO, JHU, AAO, Oxford, Durham, Portsmouth, UA
9 A brief history of the discovery of extrasolar planets 1995 : the first extrasolar planet around the main sequence star 51 Pegasi (Mayor & Queloz) 1999 : transit of a known planet around HD (Charbonneau et al., Henry et al.) 2001 : Na in the atmosphere of HD209458b 2003: first discovery of a planet by transit method alone (1.2 day orbital period: OGLE) 2005: spin-orbit misalignment via the Rossiter effect 200 extrasolar planets are reported (Sept. 2006)
10 Radial velocity of a star perturbed by a planet Even if planets are not directly observable, their presence can be inferred dynamically velocity modulation of the Sun: 12.5 m/s (Jupiter) 0.1 m/s (Earth) an accuracy of 1m/s achieved from the ground observation the current major method in search for Jupiter-sized planets
11 the first discovery of the transit of a planet: HD detected the light curve change at the phase consistent with the radial velocity (Charbonneau et al. 2000, Henry et al. 2000) HST 4 orbits Sum of HST data Ground-based observation (2000) Brown et al. (2001)
12 Extrasolar planet projects at Univ. of Tokyo Search for the planetary atmosphere with Subaru the most stringent upper limits from ground-based obs. Winn et al. PASJ 56(2004) 655 (astro-ph/ ) Narita et al. PASJ 57(2005) 471 (astro-ph/ ) Constraining the stellar spin and the planetary orbital axes from the Rossiter-McLaughlin effect New analytic formulae (Ohta, Taruya & Suto 2005, ApJ, 622, 1118) First detection (Winn et al ApJ, 631, 1215) Search for reflected light from planets collaboration with Andrew Cameron (St. Andrews Univ.) & Chris Leigh (Liverpool John Moores Univ.)
13 Subaru observation with HDS Spectro-photometric search for scattered light from HD209458b S02B-16 on October 24 and 26, 2002 Yasushi Suto, Norio Narita (Univ. of Tokyo) Toru Yamada, Wako Aoki (National Ast. Obs. Japan) Bun-ei Sato (Kobe Univ.) Edwin L. Turner (Princeton Univ.) Josh Winn (Harvard Univ.)
14 Orbital phase and radial velocity of HD209458b at our observing runs Subaru/HDS previous velocity curve (Wittenmyer et al. 2003) Winn et al. PASJ 56(2004) 655, astro-ph/ Narita et al. PASJ 57(2005)471, astro-ph/
15 radial velocity measurement with I 2 -cell Absorption lines of I 2 as accurate standard rulers Accuracy ~3m/s achieved I 2 -cell HD HDS on Subaru HD I 2 cell Winn et al. (2004)
16 Transit transmission spectroscopy time planetary orbital phase template telluric Narita et al. (2005)
17 Telluric spectrum Search for Hα absorption due to the atmosphere of HD209458b In Transit Hα Na I (D2) A Na I (D1) A Hα A Hβ A Hγ A Template steller spectrum Fractional residual Hα time Winn et al. (2004)
18 most stringent upper limits from ground-based optical observations Comparison with previous results for 0.3 angstrom bandwidth (Bundy and Marcy 2000) time Narita et al. (2005)
19 Spectroscopic transit signature: the Rossiter-McLaughlin effect Approaching part Shadow of the planet planet star Receding part Wavelength shift of line center Time-dependent asymmetry in the stellar Doppler broadened line profile an apparent anomaly of the stellar radial velocity originally discussed in eclipsing binary systems Rossiter (1924) McLaughlin (1924)
20 Velocity anomaly due to the Rossiter effect planetary orbit stellar spin Hoshinavi 2005 Feb. spin-orbit parallel spin-orbit anti-parallel stellar velocity anomaly stellar velocity anomaly (receding) (approaching) (receding) in transit (approaching) time time
21 Previous result of the Rossiter-McLaughlin effect for an extrasolar transit planetary system HD Origin of angular momentum out of transit in transit HD radial velocity data Stellar rotation and planetary orbit Queloz et al. (2000) A&A 359, L13 ELODIE on 193cm telescope
22 Measurement of Spin-Orbit alignment in an Extrasolar Planetary System Joshua N. Winn (MIT), R.W. Noyes, M.J. Holman, D.B. Charbonneau, Y. Ohta, A. Taruya, Y. Suto, N. Narita, E.L. Turner, J.A. Johnson, G.W. Marcy, R.P. Butler, & S.S. Vogt ApJ 631(2005)1215 (astro-ph/ )
23 Precision analysis of the Rossiter- McLaughlin effect for HD perturbation formula by Ohta et al. (2005) HD re-examined with the latest data radial velocity data (Keck) optical photometry (HST) infrared photometry (Spitzer) o o λ = 4.4 ± 1.4 the first detection of the misalignment between the stellar spin and the planetary orbital axes by (-4.4±1.4)deg more than an order-of-magnitude improvement of the previous error-bar (maybe useless but impressive result!) c.f., 6 degree misalignment for the Solar system λ
24 HD parameter fit χ vobs - v model fobs - fmodel = + σ 2 2nd,obs t n= 1 v n= 1 f t σ t + σ 2nd,model 2 12 free parameters data points d.o.f = =489 best-fit : χ 2 /d.o.f=528/489=1.08 for M * =1.06M sun Winn et al. astro-ph/ ApJ 631(2005)1215
25 radial velocity (Keck) residuals first detection of non-zero λ! velocity anomaly residuals residuals misalignment angle [deg] (projected) stellar spin velocity [km/s] λ = 4 o.4 ± o 1.4 transit photometry (HST) 3σ detection! Winn et al. astro-ph/ ApJ 631(2005)1215
26 another example: HD HD Bouchy et al. (2005) K-dwarf (V=7.7)+1.15M J planet 2.2 day orbital period 2.5% photometric transit signal Winn et al. ApJL, submitted (astro-ph/ ) λ=-1.4 ±1.1 consistent with zero
27 Discovery of the Uranus rings 5min exposure (Nov. 2002) Serendipitous discovery Uranus s s transit against a background star (Elliot et al. 1977) Neptune s s ring was discovered also by transit technique in 1986 Transit proved to be useful in detecting rings of the Solar planets!
28 Signatures of planetary rings Spectroscopy (Rossiter) Photometric light curve Ohta, Taruya & Suto, in preparation Ring s s inner and outer radii, gap, planet s radius imprints strong features in the photometric and spectroscopic data Statistical analysis of the residuals with respect to the best-fit ringless model
29 Detectability of a ring Velocity anomaly due to the Rossiter effect residual Photometric signature residual a hypothetical ring around HD R pl <R ring <2R pl deviation from a best-fit single planet δv~1m/s δf/f~0.1% marginally detectable level even with the current technology time Ohta, Taruya & Suto, in preparation
30 How about hot Jupiter and Saturn rings? Ohta, Taruya & Suto, in preparation Hot Jupiter: edge-on rotation due to the tidal locking Saturn:30 deg. inclined, but spin of the Sun is small Worse in either case, but still detectable potentially (S/N=1)
31 A possible roadmap of sciences of extrasolar planet Discovery phase of gas giant planets (1995-) Discovery of planetary atmosphere (2002) Detailed spectroscopic study of planets Discovery of IR emission of planets (2005) Discovery of visible reflection light Discovery of planetary ring Discovery of extrasolar planetary satellite Discovery of terrestrial planets Discovery of Habitable planet Identifying Biomarker Red-edge edge of extrasolar plant? Discovery of Extraterrestrial life
32 Astrobiology? Not yet Discovery of extrasolar planets is a wonderful breakthrough in astronomy (and philosophy, maybe) But mere discovery has no biological information How can we identify the signature of life? Biomarker Suppose our earth is located at 10pc away. Can we identify any signature of life from photometric and spectroscopic data alone? Earth-shine
33 Red edge of (extrasolar)) plants: extrasolar planets a biomarker in extrasolar Significant reflectivity of leaves of terrestrial planets for λ>7000a An interesting (maybe unique) candidate for a biomarker? extrasolar plants as a biomarker in extrasolar planets Reflection spectrum of leaves Chlorophyll A Chlorophyll B Seager, Ford & Turner astro-ph/
34 Expected daily change of the reflected light from the earth Ford, Seager & Turner: Nature 412 (2001) 885 Assume that the earth s reflected light is completely separated from the Sun s flux! TPF (Terrestrial Planet Finder) in (10~20) years from now? Periodic change of 10% level due to different reflectivity of land, ocean, forest, and so on Cloud is the most uncertain factor: weather forecast!
35 Kepler mission (June 2008 launch?) differential photometry survey of transit planets expect to discover > 50 terrestrial planets in 4 years?
36 Future of transiting planet research: follow Hantaro Nagaoka Nagaoka s Saturn model of atom Nagaoka: : Phil. Mag. 7(1904) 445 quantum atomic physics Transit planets Orbital angular momentum(l): radial velocity Spin of star(s): Rossiter effect Spin of planet(s): ring, satellite From planets to atomic physics From atomic physics to planets
37 Extra-solar planet can have a ring? Final sec. of the Nagaoka paper There are various problems which will possibly be capable of being attacked on the hypothesis of a Saturnian system The rough calculation and rather unpolished exposition of various phenomena above sketched may serve is a hint to a more complete solution of atomic structure
The Rossiter effect of transiting extra-solar planets Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo
 The Rossiter effect of transiting extra-solar planets λ λ = 4 o.4 ± 1 o.4 Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo International Workshop on on the 10th Gravitational Microlensing and Related
The Rossiter effect of transiting extra-solar planets λ λ = 4 o.4 ± 1 o.4 Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo International Workshop on on the 10th Gravitational Microlensing and Related
Unveiling the nature of transiting extrasolar planets with the Rossiter effect
 Unveiling the nature of transiting extrasolar planets with the Rossiter effect λ Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, the University of Tokyo MPA cosmology seminar July 3, 2007 Recent Activities of Observational
Unveiling the nature of transiting extrasolar planets with the Rossiter effect λ Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, the University of Tokyo MPA cosmology seminar July 3, 2007 Recent Activities of Observational
Spectroscopic search for atmospheric signature of transiting extrasolar planets
 Spectroscopic search for atmospheric signature of transiting extrasolar planets http://hubblesite.org /newscenter/archive/ 2001/38/ Department of Physics, University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Post-Nishinomiya-Yukawa
Spectroscopic search for atmospheric signature of transiting extrasolar planets http://hubblesite.org /newscenter/archive/ 2001/38/ Department of Physics, University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Post-Nishinomiya-Yukawa
Searching for the atmospheric signature of transiting extrasolar planets. Department of Physics, University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto
 Searching for the atmospheric signature of transiting extrasolar planets Department of Physics, University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Search for extrasolar planets the goal: Are we alone? origin of the earth
Searching for the atmospheric signature of transiting extrasolar planets Department of Physics, University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Search for extrasolar planets the goal: Are we alone? origin of the earth
Extrasolar planets. Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, the University of Tokyo
 Extrasolar planets Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, the University of Tokyo Summer School of of KEK theory group @Hakuba July 30 and 31, 2007 Plan of the talk Ⅰ why extrasolar planets? Ⅱ detection methods
Extrasolar planets Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, the University of Tokyo Summer School of of KEK theory group @Hakuba July 30 and 31, 2007 Plan of the talk Ⅰ why extrasolar planets? Ⅱ detection methods
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets. Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto
 Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
Weighing the universe : baryons, dark matter, and dark energy
 Weighing the universe : baryons, dark matter, and dark energy Department of Physics The University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto The 21 st century COE program of Tohoku University International symposium Exploring
Weighing the universe : baryons, dark matter, and dark energy Department of Physics The University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto The 21 st century COE program of Tohoku University International symposium Exploring
Deciphering colors of a pale blue dot
 Deciphering colors of a pale blue dot Nightfall: We didn t know anything (Alisa Haba) n No night except the total eclipse due to another planet every 2049 years on the Illustration planet Lagash by Alisa
Deciphering colors of a pale blue dot Nightfall: We didn t know anything (Alisa Haba) n No night except the total eclipse due to another planet every 2049 years on the Illustration planet Lagash by Alisa
Colors of a second Earth: towards exoplanetary remote-sensing
 Colors of a second Earth: towards exoplanetary remote-sensing Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, the University of Tokyo & Global Scholar, Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University seminar
Colors of a second Earth: towards exoplanetary remote-sensing Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, the University of Tokyo & Global Scholar, Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University seminar
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Weighing the dark side of the universe
 Weighing the dark side of the universe Department of Physics The University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto June 18, 2004 Particle Physics Group Seminar Tsukuba University Hierarchical structure in the universe
Weighing the dark side of the universe Department of Physics The University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto June 18, 2004 Particle Physics Group Seminar Tsukuba University Hierarchical structure in the universe
Tracing the bright and dark sides of the universe with X-ray observations. Yasushi Suto. Department of Physics University of Tokyo
 Tracing the bright and dark sides of the universe with X-ray observations Yasushi Suto Department of Physics University of Tokyo 1 WMAP summary of cosmic energy budget baryons ordinary matter makes up
Tracing the bright and dark sides of the universe with X-ray observations Yasushi Suto Department of Physics University of Tokyo 1 WMAP summary of cosmic energy budget baryons ordinary matter makes up
Searching for Other Worlds: The Methods
 Searching for Other Worlds: The Methods John Bally 1 1 Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences University of Colorado, Boulder The Search Extra-Solar
Searching for Other Worlds: The Methods John Bally 1 1 Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences University of Colorado, Boulder The Search Extra-Solar
Search for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs. Norio Narita (NAOJ)
 Search for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs Norio Narita (NAOJ) Outline Introduction of Current Status of Exoplanet Studies Motivation for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs Roadmap and
Search for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs Norio Narita (NAOJ) Outline Introduction of Current Status of Exoplanet Studies Motivation for Transiting Planets around Nearby M Dwarfs Roadmap and
Observations of extrasolar planets
 Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Extrasolar Planets. Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects
 Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Planets and Brown Dwarfs
 Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
4 1 Extrasolar Planets
 Extrasolar Planets 4 1 Introduction 4 2 So far: have looked at planets around our Sun Physics question: Is our Solar System normal? = Are there planets around other stars? can then compare solar system
Extrasolar Planets 4 1 Introduction 4 2 So far: have looked at planets around our Sun Physics question: Is our Solar System normal? = Are there planets around other stars? can then compare solar system
Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection
 4 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Young Planetary Systems Workshop
4 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Young Planetary Systems Workshop
Science with Transiting Planets TIARA Winter School on Exoplanets 2008
 Science with Transiting Planets TIARA Winter School on Exoplanets 2008 Eric Agol University of Thanks to Josh Winn for slides 1 Venusian transit 2004 August 6, 2004 from Slovenia (Lajovic et al.) 2 History
Science with Transiting Planets TIARA Winter School on Exoplanets 2008 Eric Agol University of Thanks to Josh Winn for slides 1 Venusian transit 2004 August 6, 2004 from Slovenia (Lajovic et al.) 2 History
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census
 Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems
 Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler. William Cochran McDonald Observatory
 Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler William Cochran McDonald Observatory Who is Bill Cochran? Senior Research Scien;st McDonald Observatory Originally interested in outer planet atmospheres Started
Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler William Cochran McDonald Observatory Who is Bill Cochran? Senior Research Scien;st McDonald Observatory Originally interested in outer planet atmospheres Started
Actuality of Exoplanets Search. François Bouchy OHP - IAP
 Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground
 The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
Observations of Extrasolar Planets
 Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets. Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017
 Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
II. Results from Transiting Planets. 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect
 II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
Application Form for (Subaru Keck) Telescope Time
 (Page 1) Subaru Telescope National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Semester S10B Received 03/12/2010 Application Form for (Subaru Keck) Telescope Time 1. Title of Proposal Search for Outer Massive Bodies
(Page 1) Subaru Telescope National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Semester S10B Received 03/12/2010 Application Form for (Subaru Keck) Telescope Time 1. Title of Proposal Search for Outer Massive Bodies
How Common Are Planets Around Other Stars? Transiting Exoplanets. Kailash C. Sahu Space Tel. Sci. Institute
 How Common Are Planets Around Other Stars? Transiting Exoplanets Kailash C. Sahu Space Tel. Sci. Institute Earth as viewed by Voyager Zodiacal cloud "Pale blue dot" Look again at that dot. That's here.
How Common Are Planets Around Other Stars? Transiting Exoplanets Kailash C. Sahu Space Tel. Sci. Institute Earth as viewed by Voyager Zodiacal cloud "Pale blue dot" Look again at that dot. That's here.
From Far East to Far Infra-Red: galaxy clustering and Galactic extinction map
 From Far East to Far Infra-Red: galaxy clustering and Galactic extinction map redshift 2.0 1.6 1.2 4000 3000 0.8 0.4 2000 1000 distance [h -1 Mpc] 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 100 500 400 200 300 [h -1 Mpc] 0.05
From Far East to Far Infra-Red: galaxy clustering and Galactic extinction map redshift 2.0 1.6 1.2 4000 3000 0.8 0.4 2000 1000 distance [h -1 Mpc] 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 100 500 400 200 300 [h -1 Mpc] 0.05
The Rossiter- McLaughlin Effect
 The Rossiter- McLaughlin Effect B. Scott Gaudi The Ohio State University (special thanks to Josh Winn) Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative
The Rossiter- McLaughlin Effect B. Scott Gaudi The Ohio State University (special thanks to Josh Winn) Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative flux Time Relative
The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets!
 The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets! Kepler Spacecraft Can we believe this result? What techniques and data were used to derive this important result? 1 How to
The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets! Kepler Spacecraft Can we believe this result? What techniques and data were used to derive this important result? 1 How to
Class 15 Formation of the Solar System
 Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones
 Lecture Overview Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones Our Galaxy has 200 Billion Stars, Our Sun has 8 planets. It seems like an awful waste if we are alone Exoplanets Karen J. Meech, Svetlana
Lecture Overview Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones Our Galaxy has 200 Billion Stars, Our Sun has 8 planets. It seems like an awful waste if we are alone Exoplanets Karen J. Meech, Svetlana
HD Transits HST/STIS First Transiting Exo-Planet. Exoplanet Discovery Methods. Paper Due Tue, Feb 23. (4) Transits. Transits.
 Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Exploring dark energy in the universe through baryon acoustic oscillation
 Exploring dark energy in the universe through baryon acoustic oscillation WMAP CMB power spectrum SDSS galaxy correlation Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo KEK Annual Theory Meeting
Exploring dark energy in the universe through baryon acoustic oscillation WMAP CMB power spectrum SDSS galaxy correlation Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo KEK Annual Theory Meeting
OGLE-TR-56. Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha INTRODUCTION
 OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
Young Solar-like Systems
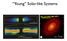 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
What is to expect from the transit method. M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France
 What is to expect from the transit method M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France Transit - method Occurrence: only if the planet orbital plane is close to
What is to expect from the transit method M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France Transit - method Occurrence: only if the planet orbital plane is close to
Exoplanets Atmospheres. Characterization of planetary atmospheres. Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging
 Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS. Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence
 The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence CHEOPS Characterizing Exoplanets Satellite Science Workshop
The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence CHEOPS Characterizing Exoplanets Satellite Science Workshop
Confronting the CDM paradigm with numerical simulations
 Evrard et al. (2002) Miyoshi & Kihara (1975) 1/4 century Ludwig-Maximilians- University August 6, 2003 Munich, Germany Confronting the CDM paradigm with numerical simulations Yasushi Suto Department of
Evrard et al. (2002) Miyoshi & Kihara (1975) 1/4 century Ludwig-Maximilians- University August 6, 2003 Munich, Germany Confronting the CDM paradigm with numerical simulations Yasushi Suto Department of
Locating missing baryons from oxygen emission lines with DIOS
 Locating missing baryons from oxygen emission lines with DIOS (Diffuse Intergalactic Oxygen Surveyor) Yasushi Suto Department of Physics University of Tokyo July 19, 2004 University College London WHIM
Locating missing baryons from oxygen emission lines with DIOS (Diffuse Intergalactic Oxygen Surveyor) Yasushi Suto Department of Physics University of Tokyo July 19, 2004 University College London WHIM
SPICA Science for Transiting Planetary Systems
 SPICA Science for Transiting Planetary Systems Norio Narita Takuya Yamashita National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 2009/06/02 SPICA Science Workshop @ UT 1 Outline For Terrestrial/Jovian Planets 1.
SPICA Science for Transiting Planetary Systems Norio Narita Takuya Yamashita National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 2009/06/02 SPICA Science Workshop @ UT 1 Outline For Terrestrial/Jovian Planets 1.
Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical
 Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical Trigonometry p. 9 The Earth p. 12 The Celestial Sphere p. 14 The
Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical Trigonometry p. 9 The Earth p. 12 The Celestial Sphere p. 14 The
Colors of a second earth: from exoplanets to astrobiology
 Colors of a second earth: from exoplanets to astrobiology Yasushi Suto Department of Physics and Research Center for the Early Universe, the University of Tokyo Introductory astronomy class @ Sejong University,
Colors of a second earth: from exoplanets to astrobiology Yasushi Suto Department of Physics and Research Center for the Early Universe, the University of Tokyo Introductory astronomy class @ Sejong University,
Planets & Life. Planets & Life PHYS 214. Please start all class related s with 214: 214: Dept of Physics (308A)
 Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s lecture Assignment 1 marked will hand
Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s lecture Assignment 1 marked will hand
The evolution of a Solar-like system. Young Solar-like Systems. Searching for Extrasolar Planets: Motivation
 Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab
 ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab Author: Anders Johansen Revision date: $Date: 2015/08/28 14:55:59 $ Planets orbiting stars other than the Sun are called exoplanets. Stellar light reflected off
ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab Author: Anders Johansen Revision date: $Date: 2015/08/28 14:55:59 $ Planets orbiting stars other than the Sun are called exoplanets. Stellar light reflected off
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview. PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009
 Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Finding Other Earths. Jason H. Steffen. Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009
 Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion. Exoplanets Doppler method
 Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion Exoplanets The reflex motion of the star is proportional to M p /M * This introduces an observational bias that favours the detection
Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion Exoplanets The reflex motion of the star is proportional to M p /M * This introduces an observational bias that favours the detection
From quasars to dark energy Adventures with the clustering of luminous red galaxies
 From quasars to dark energy Adventures with the clustering of luminous red galaxies Nikhil Padmanabhan 1 1 Lawrence Berkeley Labs 04-15-2008 / OSU CCAPP seminar N. Padmanabhan (LBL) Cosmology with LRGs
From quasars to dark energy Adventures with the clustering of luminous red galaxies Nikhil Padmanabhan 1 1 Lawrence Berkeley Labs 04-15-2008 / OSU CCAPP seminar N. Padmanabhan (LBL) Cosmology with LRGs
Introducing DENET, HSC, & WFMOS
 RESCEU & JSPS core-tocore program DENET Summer School Dark energy in the universe September 1-4, 2007 Introducing DENET, HSC, & WFMOS Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo 1 International
RESCEU & JSPS core-tocore program DENET Summer School Dark energy in the universe September 1-4, 2007 Introducing DENET, HSC, & WFMOS Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo 1 International
Gravitational microlensing. Exoplanets Microlensing and Transit methods
 Gravitational microlensing Exoplanets Microlensing and s Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo May take place when a star-planet system crosses the visual of a background star, as a result of
Gravitational microlensing Exoplanets Microlensing and s Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo May take place when a star-planet system crosses the visual of a background star, as a result of
2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Thought Question Suppose you found a star with the same mass as the Sun moving back and forth with a period of 16 months. What could you conclude? A. It has a planet orbiting at less than 1 AU. B. It has
Thought Question Suppose you found a star with the same mass as the Sun moving back and forth with a period of 16 months. What could you conclude? A. It has a planet orbiting at less than 1 AU. B. It has
Astronomy Today. Eighth edition. Eric Chaisson Steve McMillan
 Global edition Astronomy Today Eighth edition Eric Chaisson Steve McMillan The Distance Scale ~1 Gpc Velocity L Distance Hubble s law Supernovae ~200 Mpc Time Tully-Fisher ~25 Mpc ~10,000 pc Time Variable
Global edition Astronomy Today Eighth edition Eric Chaisson Steve McMillan The Distance Scale ~1 Gpc Velocity L Distance Hubble s law Supernovae ~200 Mpc Time Tully-Fisher ~25 Mpc ~10,000 pc Time Variable
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
Astronomy. Catherine Turon. for the Astronomy Working Group
 Astronomy Catherine Turon for the Astronomy Working Group Answers to the call for ideas Illustration of the strong expectation of the community from the ESA Science Programme: In astronomy 1983: Horizon
Astronomy Catherine Turon for the Astronomy Working Group Answers to the call for ideas Illustration of the strong expectation of the community from the ESA Science Programme: In astronomy 1983: Horizon
The Main Point(s) Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars. Extrasolar Planets! Reading: Chapter 13. Theory Observations
 Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars Extrasolar Planets! Theory Observations Detection methods Results to date... Implications for "Habitable Zones" Reading: Chapter 13 Astro 102/104 1 The Main Point(s)
Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars Extrasolar Planets! Theory Observations Detection methods Results to date... Implications for "Habitable Zones" Reading: Chapter 13 Astro 102/104 1 The Main Point(s)
Searching for Earth-Like Planets:
 Searching for Earth-Like Planets: NASA s Terrestrial Planet Finder Space Telescope Robert J. Vanderbei January 11, 2004 Amateur Astronomers Association of Princeton Peyton Hall, Princeton University Page
Searching for Earth-Like Planets: NASA s Terrestrial Planet Finder Space Telescope Robert J. Vanderbei January 11, 2004 Amateur Astronomers Association of Princeton Peyton Hall, Princeton University Page
10/16/ Detecting Planets Around Other Stars. Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds
 10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
Key Ideas: The Search for New Planets. Scientific Questions. Are we alone in the Universe? Direct Imaging. Searches for Extrasolar Planets
 The Search for New Planets Key Ideas: Search for planets around other stars. Successful Search Techniques: Astrometric Wobble Doppler Wobble major discovery method Planetary Transits planets we can study
The Search for New Planets Key Ideas: Search for planets around other stars. Successful Search Techniques: Astrometric Wobble Doppler Wobble major discovery method Planetary Transits planets we can study
Planets: Name Distance from Sun Satellites Year Day Mercury 0.4AU yr 60 days Venus yr 243 days* Earth 1 1 yr 1 day Mars 1.
 The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder. AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life
 Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life The Drake Equation: N = N * f pl n hab f L f C f T L/T Stars? Planets? Habitable Origin Complex Intelligence, Lifetime planets?
Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life The Drake Equation: N = N * f pl n hab f L f C f T L/T Stars? Planets? Habitable Origin Complex Intelligence, Lifetime planets?
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets. PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009
 Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture hot Jupiters; transiting planets primary eclipses and atmospheric
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture hot Jupiters; transiting planets primary eclipses and atmospheric
Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Planet is Much Fainter than Star!
 Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets. Exoplanets Introduction. Importance of the study of extrasolar planets
 Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa<ons of Transi<ng Systems
 June. 4, 215 @ NAOJ Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa
June. 4, 215 @ NAOJ Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa
Extrasolar Planets = Exoplanets III.
 Extrasolar Planets = Exoplanets III http://www.astro.keele.ac.uk/~rdj/planets/images/taugruishydra2.jpg Outline Gravitational microlensing Direct detection Exoplanet atmospheres Detecting planets by microlensing:
Extrasolar Planets = Exoplanets III http://www.astro.keele.ac.uk/~rdj/planets/images/taugruishydra2.jpg Outline Gravitational microlensing Direct detection Exoplanet atmospheres Detecting planets by microlensing:
TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack
 Transiting Extrasolar Planets Workshop ASP Conference Series, Vol. 366, 2007 C. Afonso, D. Weldrake and Th. Henning TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack F. T. O Donovan
Transiting Extrasolar Planets Workshop ASP Conference Series, Vol. 366, 2007 C. Afonso, D. Weldrake and Th. Henning TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack F. T. O Donovan
Exoplanet Atmosphere Characterization & Biomarkers
 Giovanna Tinetti ESA/Institut d Astrophysique de Paris γ Exoplanet Atmosphere Characterization & Biomarkers Can we use Remote Sensing Spectroscopy, - Interaction between photon coming from the parent star
Giovanna Tinetti ESA/Institut d Astrophysique de Paris γ Exoplanet Atmosphere Characterization & Biomarkers Can we use Remote Sensing Spectroscopy, - Interaction between photon coming from the parent star
Extrasolar Planets. Today. Dwarf Planets. Extrasolar Planets. Next week. Review Tuesday. Exam Thursday. also, Homework 6 Due
 Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008](/thumbs/88/116854716.jpg) Planet influence on the shape of the hosting star - ellipsoidal variations of tau Bootis W. Dimitrov Astronomical Observatory of Adam Mickiewicz University ul. S loneczna 36, 60-286 Poznań, Poland dimitrov@amu.edu.pl
Planet influence on the shape of the hosting star - ellipsoidal variations of tau Bootis W. Dimitrov Astronomical Observatory of Adam Mickiewicz University ul. S loneczna 36, 60-286 Poznań, Poland dimitrov@amu.edu.pl
Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology
 Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology A. Sozzetti INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino Detection/Characterization Detection (Visible): - Doppler spectroscopy (95%) -
Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology A. Sozzetti INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino Detection/Characterization Detection (Visible): - Doppler spectroscopy (95%) -
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology
 Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space
 The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Kira Bonk ascension.html
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
The Main Point. Planetary Ring Systems
 Lecture #31: Satellites and Rings II Ring Systems Overview of rings: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. What are rings made of? How do they form? Reading: Chapter 11.3. The Main Point All of the giant planets
Lecture #31: Satellites and Rings II Ring Systems Overview of rings: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. What are rings made of? How do they form? Reading: Chapter 11.3. The Main Point All of the giant planets
3.4 Transiting planets
 64 CHAPTER 3. TRANSITS OF PLANETS: MEAN DENSITIES 3.4 Transiting planets A transits of a planet in front of its parent star occurs if the line of sight is very close to the orbital plane. The transit probability
64 CHAPTER 3. TRANSITS OF PLANETS: MEAN DENSITIES 3.4 Transiting planets A transits of a planet in front of its parent star occurs if the line of sight is very close to the orbital plane. The transit probability
ASTR2050: Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics Syllabus for Spring 1999 January 4, 1999
 ASTR2050: Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics Syllabus for Spring 1999 January 4, 1999 This is a working document and will change periodically. It outlines the topics that will be covered during the
ASTR2050: Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics Syllabus for Spring 1999 January 4, 1999 This is a working document and will change periodically. It outlines the topics that will be covered during the
Dark Energy. Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey. Survey (DES)
 Dark Energy Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey Survey (DES) What is it? The DES Collaboration will build and use a wide field optical imager (DECam) to perform a wide area,
Dark Energy Cluster counts, weak lensing & Supernovae Ia all in one survey Survey (DES) What is it? The DES Collaboration will build and use a wide field optical imager (DECam) to perform a wide area,
Searching for planets around other stars. Searching for planets around other stars. Searching for other planetary systems this is a hard problem!
 Reading: Chap. 21, Sect.21.4-21.6 Final Exam: Tuesday, December 12; 4:30-6:30PM Homework 10: Due in recitation Dec. 1,4 1 Brief review of last time: Formation of Planetary Systems Observational Clues:
Reading: Chap. 21, Sect.21.4-21.6 Final Exam: Tuesday, December 12; 4:30-6:30PM Homework 10: Due in recitation Dec. 1,4 1 Brief review of last time: Formation of Planetary Systems Observational Clues:
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, KITP Public Lecture
 Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Fundamental Astronomy
 H. Karttunen P. Kroger H. Oja M.Poutanen K.J. Donner (Eds.) Fundamental Astronomy Fifth Edition With 449 Illustrations Including 34 Colour Plates and 75 Exercises with Solutions < J Springer VII 1. Introduction
H. Karttunen P. Kroger H. Oja M.Poutanen K.J. Donner (Eds.) Fundamental Astronomy Fifth Edition With 449 Illustrations Including 34 Colour Plates and 75 Exercises with Solutions < J Springer VII 1. Introduction
GJ 436. Michaël Gillon (Geneva)
 Michaël Gillon (Geneva) Michelson Summer Workshop - July 25, 2007 2004: first hot Neptunes detected by radial velocity Among them: b (Butler et al. 2004, Maness et al. 2007) M * ~ 0.44 M Sun (M2.5V) R
Michaël Gillon (Geneva) Michelson Summer Workshop - July 25, 2007 2004: first hot Neptunes detected by radial velocity Among them: b (Butler et al. 2004, Maness et al. 2007) M * ~ 0.44 M Sun (M2.5V) R
Other planetary systems
 Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 22 Nov 2005
 Tenth anniversary of 51 Peg-b : Status of and prospects for hot Jupiter studies Proceedings of Haute Provence Observatory Colloquium (22-25 august 2005) Edited by L. Arnold, F. Bouchy, & C. Moutou Hot
Tenth anniversary of 51 Peg-b : Status of and prospects for hot Jupiter studies Proceedings of Haute Provence Observatory Colloquium (22-25 august 2005) Edited by L. Arnold, F. Bouchy, & C. Moutou Hot
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems. Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? Brightness Difference
 Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Extrasolar Planets Our goals for learning:! Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars?! How do we detect
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Extrasolar Planets Our goals for learning:! Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars?! How do we detect
Chapter 13 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects
 Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects 1 What about Pluto? Pluto used to be considered a planet Pluto is one of a large number of Trans-Neptunian Objects, not even the largest one! Discovery
Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects 1 What about Pluto? Pluto used to be considered a planet Pluto is one of a large number of Trans-Neptunian Objects, not even the largest one! Discovery
Planets are plentiful
 Extra-Solar Planets Planets are plentiful The first planet orbiting another Sun-like star was discovered in 1995. We now know of 209 (Feb 07). Including several stars with more than one planet - true planetary
Extra-Solar Planets Planets are plentiful The first planet orbiting another Sun-like star was discovered in 1995. We now know of 209 (Feb 07). Including several stars with more than one planet - true planetary
Extrasolar Planets. Dieter Schmitt Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau
 Extrasolar Planets Dieter Schmitt Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau Lecture Introduction to Solar System Physics Uni Göttingen, 8 June 2009 Outline Historical Overview Detection
Extrasolar Planets Dieter Schmitt Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau Lecture Introduction to Solar System Physics Uni Göttingen, 8 June 2009 Outline Historical Overview Detection
Exoplanets Direct imaging. Direct method of exoplanet detection. Direct imaging: observational challenges
 Black body flux (in units 10-26 W m -2 Hz -1 ) of some Solar System bodies as seen from 10 pc. A putative hot Jupiter is also shown. The planets have two peaks in their spectra. The short-wavelength peak
Black body flux (in units 10-26 W m -2 Hz -1 ) of some Solar System bodies as seen from 10 pc. A putative hot Jupiter is also shown. The planets have two peaks in their spectra. The short-wavelength peak
Extrasolar Planets. Properties Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Transneptunian objects. Minor bodies in the outer Solar System. Transneptunian objects
 Transneptunian objects Minor bodies in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Around 1980 it was proposed that the hypothetical disk of small bodies beyond Neptune (called
Transneptunian objects Minor bodies in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Around 1980 it was proposed that the hypothetical disk of small bodies beyond Neptune (called
Exoplanets and their Atmospheres. Josh Destree ATOC /22/2010
 Exoplanets and their Atmospheres Josh Destree ATOC 3500 4/22/2010 Outline What is an exoplanet? Why do we care? Detecting exoplanets Exoplanets compared to planets in the solar system Exoplanet atmospheres
Exoplanets and their Atmospheres Josh Destree ATOC 3500 4/22/2010 Outline What is an exoplanet? Why do we care? Detecting exoplanets Exoplanets compared to planets in the solar system Exoplanet atmospheres
Comparative Planetology: Transiting Exoplanet Science with JWST
 Comparative Planetology: Transiting Exoplanet Science with JWST Mark Clampin, JWST Science Working Group, JWST Transits Working Group, Drake Deming, and Don Lindler MarkClampin JWSTObservatoryProjectScientist
Comparative Planetology: Transiting Exoplanet Science with JWST Mark Clampin, JWST Science Working Group, JWST Transits Working Group, Drake Deming, and Don Lindler MarkClampin JWSTObservatoryProjectScientist
