The Progenitors of Type Ia Supernovae
|
|
|
- Shanon Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Progenitors of Type Ia Supernovae Philipp Podsiadlowski, Richard Booth, Mark Sullivan (Oxford), Shazrene Mohamed (Bonn), Paolo Mazzali (MPA/Padova), Zhanwen Han (Kunming), Stephen Justham (Beijing), Sung-Chul Yoon (Bonn), Stephan Rosswog (Bremen), Brian Schmidt, Wolfgang Kerzendorf (Stromlo), Pierre Lesaffre (ENS), Francisco Förster (Santiago) + PTF Team Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) have been used as standardizable cosmological distance candles first evidence for an accelerating Universe (Nobel Prize 2011) but: large diversity of SN Ia types (super-chandra SNe?) link between progenitors and explosion models still very uncertain I. Supernova Types and Cosmology II. Constraining Supernova Progenitors III. Recent Developments: PTF 11kly, PTF 11kx
2 EXPLOSION MECHANISMS two main, completely different mechanisms Core-Collapse Supernovae ν ν ν ν ν ν NS νν Iron Core ν ν ν ν ν ν ν Collapse ν ν ν Kifonidis triggered after the exhaustion of nuclear fuel in the core of a massive star, if the iron core mass > Chandrasekhar mass energy source is gravitational energy from the collapsing core ( 10% of neutron star rest mass ergs) most of the energy comes out in neutrinos (SN 1987A!) unsolved problem: how is some of the neutrino energy deposited ( 1%, ergs) in the envelope to eject the envelope and produce the supernova? leaves compact remnant (neutron star/black hole)
3 Thermonuclear Explosions occurs in accreting carbon/oxygen white dwarf when it approaches the Chandrasekhar mass carbon ignited under degenerate conditions: nuclear burning raises T, but not P thermonuclear runaway incineration and complete destruction of the star energy source is nuclear energy (10 51 ergs) no compact remnant expected standardizable candle (Hubble constant, acceleration of Universe?) C, O > Fe, Si Roepke but: progenitor evolution not understood single-degenerate channel: accretion from non-degenerate companion double-degenerate channel: merger of two CO white dwarfs
4 Supernova Classification SUPERNOVA CLASSIFICATION observational: Type I: no hydrogen lines in spectrum Type II: hydrogen lines in spectrum theoretical: thermonuclear explosion of degenerate core core collapse neutron star/black hole relation no longer 1 to 1 confusion Type Ia (Si lines): thermonuclear explosion of white dwarf Type Ib/Ic (no Si; He or no He): core collapse of He star Type II-P: classical core collapse of a massive star with hydrogen envelope Type II-L: supernova with linear lightcurve (thermonuclear explosion of intermediatemass star? probably not!) complications: SN Ib SN Ia SN II SN Ic special supernovae like SN 1987A Type IIb: supernovae that change type, SN 1993J (Type II Type Ib) some supernova types (e.g., IIn) occur for both explosion types ( phenomenon, not type; also see SNe Ic) new types: thermonuclear explosion of He star (Type Iab?)
5 TYPE IA SUPERNOVAE Type Ia supernovae have been used as standard distance candles to measure the curvature of the Universe accelerating Universe? Type Ia supernovae are no good standard candles! (peak luminosities vary by a factor up to 10) but they may be standardizable candles, i.e. there appears to be a unique relation between peak luminosity and the width of the lightcurve which can be used to derive good distances significant recent progress on understanding the explosion physics and the relation between lightcurve shape and peak luminosity caveat: the progenitors of Type Ia supernovae are not known
6 Metallicity as a second parameter of SN Ia lightcurves (Timmes et al. 2003) The Second SN Ia Parameter: ( Fe + Ni)/ Ni (Mazzali and Podsiadlowski 2006) the lightcurve is powered by the radioactive decay of 56 Ni to 56 Co (t 1/2 = 6.1d) L peak M 56Ni the lightcurve width is determined by the diffusion time depends on the opacity, in particular the total number of iron-group elements (i.e. 56 Ni, 58 Ni, 54 Fe) t width M iron group 54 Fe, 58 Ni are non-radioactive contribute to opacity but not supernova luminosity necessary second parameter the relative amount of non-radioactive and radioactive Ni depends on neutron excess and hence on the initial metallicity (Timmes et al. 2003) variation of 1/3 to 3Z gives variation of 0.2 mag
7 Thermonuclear Explosions (W7; Nomoto 1984) Burning Layer (= kinetic energy) NSE (= opacity) IME unburned? stable radioactive (= light) C+O (deflagration) O (detonation)
8 Podsiadlowski, Mazzali, Lesaffre, Wolf, Förster (2006) metallicity must be a second parameter that at some level needs to be taken into account cosmic metallicity evolution can mimic accelerating Universe but: metallicity evolution effects on their own appear not large enough to explain the supernova observations without dark energy (also independent evidence from WMAP, galaxy clustering) it will be difficult to measure the equation of state of dark energy with SNe Ia alone without correcting for metallicity effects Linder (2003) Measuring the Equation of State The effect of metallicity evolution (based on PMLWF 2006)
9 SN Ia Host Galaxies SNe Ia occur in young and old stellar populations (Branch 1994) range of time delays between progenitor formation and supernova (typical: 1 Gyr; some, at least several Gyr; comparable integrated numbers) SNe Ia in old populations tend to be faint; luminous SNe Ia occur in young populations ( age important parameter) the faintest SNe Ia (SN 91bg class) avoid galaxies with star formation and spiral galaxies (age + high metallicity?) the radial distribution in ellipticals follows the old star distribution (Förster & Schawinski 2008) not expected if formed in a recent galaxy merger consistent with double-degenerate model and two-population single-degenerate model (supersoft + red-giant channel)
10 Pros: Single-Degenerate Models potential counterparts: U Sco, RS Oph, TCrB (WDs close to Chandrasekhar mass), sufficient numbers? Cons: Chandrasekhar white dwarf accreting from a companion star (main-sequence star, helium star, subgiant, giant) Problem: requires fine-tuning of accretion rate accretion rate too low nova explosions inefficient accretion accretion rate too high most mass is lost in a disk wind inefficient accretion expect observable hydrogen in nebular phase, stripped from companion star (Marietta, et al.) not yet observed in normal SN Ia (tight limits! 0.02M ) (Leonard 2007) Recent: surviving companion in Tycho supernova remnant (Ruiz-Lapuente et al.)? Needs to be confirmed. Predicted rapid rotation is not observed (Kerzendorf et al. 2009). SN 2006X (Patat et al. 2007): first discovery of circumstellar material supports giant channel for SNe Ia
11 Direct Detection of Hydrogen in the post-supernova spectrum. Marietta et al. (2000): predict substantial stripping of hydrogen from the companion; MS/SG companion: 0.15M easily detectable in nebular phase problem: in some systems, very tight limits: < 0.01M (Leonard 2007) big problem for the SD model? but: less stripping in more realistic companion models? Pakmor/Röpke: M possible time delay between mass-transfer phase and explosion (di Stefano 2011, Justham 2011) Note: Hydrogen has been observed in large abundance in some notional SNe Ia (e.g. SN 2002ic, PTF2010x) symbiotic link? Marietta et al. (2000)
12 Detection of Circumstellar Wind Material Patat et al. (2007) Patat et al. (2007) CSM material detected in SN 2006X and other since (e.g. Simon, Blondin, Sternberg) time-varying Na lines, flash-ionized and recombining distance to SN: < cm consistent with variable red-giant wind (seen along orbital plane?) similar variability seen in about 10 20% of SNe Ia and in RS Oph after last outburst! (Patat et al. 2011)
13 Kerzendorf et al. (2009) A surviving companion in the Tycho supernova remnant? companion should have been tidally locked and rapidly rotating binary companion should survive supernova explosion detect runaway velocity star Ruiz-Lapuente et al. (2004): candidate Tycho G? rapid rotation is not observed presently no good candidates left (perhaps one)
14 Companion Imprint on SN Ia Remannts (Booth, Podsiadlowski 2012) the interaction of a the supernova ejecta with the companion produces a hole in the ejecta clear imprint on supernova remnant appears not to be observed in Tycho Tycho in Iron-K Line (Warren et al. 2005) Velocity Structure Booth (2011)
15 Companion Interaction Booth (2011)
16 Iron Lines Booth (2011)
17 Double Degenerate Merger merging of two CO white dwarfs with a total mass > Chandrasekhar mass Problem: this more likely leads to the conversion of the CO WD into an ONeMg WD and e-capture core collapse formation of neutron star Pros: merger rate is probably o.k. (few 10 3 yr; SPY) Recent: Yoon, PhP, Rosswog (2007): post-merger evolution depends on neutrino cooling conversion into ONeMg WD may sometimes be avoided thermonuclear explosion may be possible multiple channels? super-chandrasekhar channel? (Howell et al. 2007)
18 . Figure 3. Dynamical evolution of the coalescence of a 0.6 M M CO white dwarf binary. Continued from Fig. 2. C 2007 The Authors. Journal compilation C 2007 RAS, MNRAS 380,
19 Post-Merger Evolution Yoon et al immediate post-merger object: low-entropy massive core surrounded by high-entropy envelope and accretion disk evolution is controlled by thermal evolution of the envelope determines core-accretion rate despite high accretion rate, carbon ignition is avoided because of neutrino losses can lead to thermonuclear explosion iff carbon ignition is avoided during merging process and disk accretion rate after 10 5 yr is less than 10 5 M /yr Note: explosion occurs 10 5 yr after the merger
20 .
21 .
22 Nugent et al PTF 11kly/SN2011fe brightest SN Ia (from the UK) for > 50yr (peak: 10th mag) occurred in M101 (pinwheel galaxy) spectrum: evidence for unburnt carbon and oxygen early light curve: compact star (< a few 0.1R ) exploding CO white dwarf
23 Li et al. (2011) no progenitor detected in HST pre-explosion images times better progenitor constraints than in the past
24 HR diagram rules out luminous red giant donor favours DD or supersoft channel
25 CSM around SN 2006X Patat et al. (2007)
26 CSM around the Recurrent Nova System RS Oph Patat et al. (2011)
27 Binary Mass Loss Simulations Mohamed, Booth & Podsiadlowski (2012) 5-13 log density log density y [AU] 0 z [AU] x [AU] x [AU]
28 Nova RS Oph 2006 Mohamed, Booth & Podsiadlowski (2012)
29 PTF 11kx discovery date: January 16, 2011 z = (SDSS) slightly luminous: (M V 19.3; similar to SN 1999aa) high-resolution spectra (R = 48000) with Keck narrow absorption lines similar to RS Oph, including hydrogen strong interaction with the CSM late lightcurve 3 mag brighter than expected late spectrum similar to SN 2002ic (very H-rich SN Ia?) evidence for disk structure?
30 Dilday et al. (2012)
31 Dilday et al. (2012)
32 Dilday et al. (2012)
33 Dilday et al. (2012)
34 2.5e-16 2e e-16 1e-16 5e Dilday et al. (2012)
35 Conclusions significant progress on understanding the progenitors at least some SNe Ia come from the single degenerate channel PTF 11kx: red-giant donor like RS Oph PTF 11kly: no red-giant donor need for multiple channels? still need to understand short and long time delays most SNe Ia are similar but a significant subset shows large diversity metallicity should be a second parameter for SN lightcurves
36 The Origin of Ultra-Cool Helium White Dwarfs (Justham et al. 2008) ultra-cool white dwarfs (T eff < 4000K) implies very low-mass white dwarfs (cooling timescale! < 0.3M ) can only be formed in binaries some may have pulsar companions, most appear to be single (ultra-cool doubles?) most likely origin: surviving companion after a SN Ia kinematics: pre-sn period d (short end of red-giant island?)
37 Symbiotic Binaries as SN Ia Progenitors (Hachisu, Kato, Nomoto) two islands in P orb M 2 diagram where WDs can grow in mass red-giant channel: P orb 100d, M 2 as low as 1M may explain SNe Ia with long time delays Problem: binary population synthesis simulations do not produce many systems in the red-giant island (10 5 yr 1 for optimistic assumptions (Han)) stable RLOF wide systems with P orb > 10 3 d CE evolution close systems with P orb < 10 2 d gap in period distribution for systems with P orb d (e.g. Han, Frankowski) importance of RS Oph suggests problem with binary evolution model
38 Hachisu, Kato, Nomoto
39 What controls the diversity of SNe Ia? dominant post-sn parameter: M Ni56 ignition density (pre-sn) initial WD mass, age (progenitor) other factors: metallicity neutron excess, initial C/O ratio, accretion efficiency the role of rotation? (Yoon & Langer 2005: super-chandra WDs) the progenitor channel (supersoft, red-giant, double degenerate) complex problem to link progenitor evolution/properties to explosion properties
40 The Final Simmering Phase before the final thermonuclear runaway, there is a long phase ( simmering phase) of low-level carbon burning, lasting up to 1000yr this can significantly alter the WD structure significant neutronization (up to X C 0.1 may be burned) density profile convective velocity profile Neutrino cooling time: t Convective turnover time: t c Carbon fusion time: t f t c < t < t f : mild C burning: neutrino cooling gets rids of the energy generated t c < t f < t : C flash: convection sets in, convective core grows rapidly t f < t c < t : C ignition: thermonuclear runaway
41 The Convective Urca Process at high densities, electron captures enter into play neutrino losses due the Urca process electron capture: M+e D+ beta decay: D M+e + (M: mother; D: daughter) most important pair: 23 Na/ 23 Ne with threshold density th = gcm 3 most efficient cooling near Urca shell ( th ) net heating outside Urca shell long history of yet inconclusive investigations
The Evolution of Close Binaries
 The Evolution of Close Binaries Philipp Podsiadlowski (Oxford) The case of RS Ophiuchi as a test of binary stellar evolution as a potential Type Ia supernova (SN Ia) progenitor I. Testing Binary Evolution:
The Evolution of Close Binaries Philipp Podsiadlowski (Oxford) The case of RS Ophiuchi as a test of binary stellar evolution as a potential Type Ia supernova (SN Ia) progenitor I. Testing Binary Evolution:
Evolution and Final Fates of Accreting White Dwarfs. Ken Nomoto (Kavli IPMU / U. Tokyo)
 Evolution and Final Fates of Accreting White Dwarfs Ken Nomoto (Kavli IPMU / U. Tokyo) AD 1572 Korean & Chinese Record Guest Star as bright as Venus (Sonjo Sujong Sillok: Korea) AD 1572 Tycho Brahe s Supernova
Evolution and Final Fates of Accreting White Dwarfs Ken Nomoto (Kavli IPMU / U. Tokyo) AD 1572 Korean & Chinese Record Guest Star as bright as Venus (Sonjo Sujong Sillok: Korea) AD 1572 Tycho Brahe s Supernova
The structure and evolution of stars. Learning Outcomes
 The structure and evolution of stars Lecture14: Type Ia Supernovae The Extravagant Universe By R. Kirshner 1 Learning Outcomes In these final two lectures the student will learn about the following issues:
The structure and evolution of stars Lecture14: Type Ia Supernovae The Extravagant Universe By R. Kirshner 1 Learning Outcomes In these final two lectures the student will learn about the following issues:
The Theory of Supernovae in Massive Binaries
 The Theory of Supernovae in Massive Binaries Philipp Podsiadlowski (Oxford) the majority of massive stars are in interacting binaries the large diversity of observed supernova types and (sub-)types is
The Theory of Supernovae in Massive Binaries Philipp Podsiadlowski (Oxford) the majority of massive stars are in interacting binaries the large diversity of observed supernova types and (sub-)types is
Thermonuclear shell flashes II: on WDs (or: classical novae)
 : on WDs (or: classical novae) Observations Thermonuclear flash model Nova/X-ray burst comparison Effects of super-eddington fluxes To grow or not to grow = to go supernova Ia or not.. 1 Nova Cygni 1975
: on WDs (or: classical novae) Observations Thermonuclear flash model Nova/X-ray burst comparison Effects of super-eddington fluxes To grow or not to grow = to go supernova Ia or not.. 1 Nova Cygni 1975
Boris Gänsicke. Type Ia supernovae and their progenitors
 Boris Gänsicke Type Ia supernovae and their progenitors November 1572, in Cassiopeia: a nova a new star V~-4 Tycho Brahe: De nova et nullius aevi memoria prius visa stella (1602) October 9, 1604, in Ophiuchus
Boris Gänsicke Type Ia supernovae and their progenitors November 1572, in Cassiopeia: a nova a new star V~-4 Tycho Brahe: De nova et nullius aevi memoria prius visa stella (1602) October 9, 1604, in Ophiuchus
SN1987A before(right) and during the explosion. Supernova Explosion. Qingling Ni
 SN1987A before(right) and during the explosion Supernova Explosion Qingling Ni Overview Core-Collapse supernova (including Type II supernova) -Mechanism: collapse+rebound Type Ia supernova -Mechanism:
SN1987A before(right) and during the explosion Supernova Explosion Qingling Ni Overview Core-Collapse supernova (including Type II supernova) -Mechanism: collapse+rebound Type Ia supernova -Mechanism:
Chapter 15. Supernovae Classification of Supernovae
 Chapter 15 Supernovae Supernovae represent the catastrophic death of certain stars. They are among the most violent events in the Universe, typically producing about 10 53 erg, with a large fraction of
Chapter 15 Supernovae Supernovae represent the catastrophic death of certain stars. They are among the most violent events in the Universe, typically producing about 10 53 erg, with a large fraction of
The electrons then interact with the surrounding medium, heat it up, and power the light curve. 56 Ni 56 Co + e (1.72 MeV) half life 6.
 Supernovae The spectra of supernovae fall into many categories (see below), but beginning in about 1985, astronomers recognized that there were physically, only two basic types of supernovae: Type Ia and
Supernovae The spectra of supernovae fall into many categories (see below), but beginning in about 1985, astronomers recognized that there were physically, only two basic types of supernovae: Type Ia and
FORMATION AND EVOLUTION OF COMPACT BINARY SYSTEMS
 FORMATION AND EVOLUTION OF COMPACT BINARY SYSTEMS Main Categories of Compact Systems Formation of Compact Objects Mass and Angular Momentum Loss Evolutionary Links to Classes of Binary Systems Future Work
FORMATION AND EVOLUTION OF COMPACT BINARY SYSTEMS Main Categories of Compact Systems Formation of Compact Objects Mass and Angular Momentum Loss Evolutionary Links to Classes of Binary Systems Future Work
The Death of Stars. Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages ) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars
 The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
Supernovae. Type II, Ib, and Ic supernova are core-collapse supernova. Type Ia supernovae are themonuclear explosions.
 Type Ia Supernovae Supernovae Gravitational collapse powers the explosion. Type Ia supernovae are themonuclear explosions. (Carroll and Ostlie) Type II, Ib, and Ic supernova are core-collapse supernova.
Type Ia Supernovae Supernovae Gravitational collapse powers the explosion. Type Ia supernovae are themonuclear explosions. (Carroll and Ostlie) Type II, Ib, and Ic supernova are core-collapse supernova.
Compton Lecture #4: Massive Stars and. Supernovae. Welcome! On the back table:
 Compton Lecture #4: Massive Stars and Welcome! On the back table: Supernovae Lecture notes for today s s lecture Extra copies of last week s s are on the back table Sign-up sheets please fill one out only
Compton Lecture #4: Massive Stars and Welcome! On the back table: Supernovae Lecture notes for today s s lecture Extra copies of last week s s are on the back table Sign-up sheets please fill one out only
Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources
 Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources The Algol Mystery Algol is a double-lined eclipsing binary system with a period of about 3 days (very short). The two stars are: Star A: B8, 3.4M o
Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources The Algol Mystery Algol is a double-lined eclipsing binary system with a period of about 3 days (very short). The two stars are: Star A: B8, 3.4M o
Brian P. Schmidt Wolfgang Kerzendorf, Anna Frebel, Martin Asplund, Ken Nomoto, Philipp Podsiadlowski
 Brian P. Schmidt Wolfgang Kerzendorf, Anna Frebel, Martin Asplund, Ken Nomoto, Philipp Podsiadlowski The Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Mount Stromlo and Siding Spring Observatories 1 2 SkyMapper
Brian P. Schmidt Wolfgang Kerzendorf, Anna Frebel, Martin Asplund, Ken Nomoto, Philipp Podsiadlowski The Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Mount Stromlo and Siding Spring Observatories 1 2 SkyMapper
Introductory Astrophysics A113. Death of Stars. Relation between the mass of a star and its death White dwarfs and supernovae Enrichment of the ISM
 Goals: Death of Stars Relation between the mass of a star and its death White dwarfs and supernovae Enrichment of the ISM Low Mass Stars (M
Goals: Death of Stars Relation between the mass of a star and its death White dwarfs and supernovae Enrichment of the ISM Low Mass Stars (M
The Algol Mystery. Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources. Algol. Mass Transfer in Binaries
 The Algol Mystery Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Algol is a double-lined eclipsing binary system with a period of about 3 days (very short). The two stars
The Algol Mystery Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Algol is a double-lined eclipsing binary system with a period of about 3 days (very short). The two stars
Guiding Questions. The Deaths of Stars. Pathways of Stellar Evolution GOOD TO KNOW. Low-mass stars go through two distinct red-giant stages
 The Deaths of Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
The Deaths of Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
The Deaths of Stars 1
 The Deaths of Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
The Deaths of Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
Stellar Evolution: The Deaths of Stars. Guiding Questions. Pathways of Stellar Evolution. Chapter Twenty-Two
 Stellar Evolution: The Deaths of Stars Chapter Twenty-Two Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come
Stellar Evolution: The Deaths of Stars Chapter Twenty-Two Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come
SUPERNOVAE: A COSMIC CATASTROPHE. Gloria Dubner IAFE- ARGENTINA
 SUPERNOVAE: A COSMIC CATASTROPHE Gloria Dubner IAFE- ARGENTINA A Supernova is not an object, but an event It is the catastrophic end of a long stellar life. It represents the sudden injection of: about
SUPERNOVAE: A COSMIC CATASTROPHE Gloria Dubner IAFE- ARGENTINA A Supernova is not an object, but an event It is the catastrophic end of a long stellar life. It represents the sudden injection of: about
Guiding Questions. The Deaths of Stars. Pathways of Stellar Evolution GOOD TO KNOW. Low-mass stars go through two distinct red-giant stages
 The Deaths of Stars Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
The Deaths of Stars Guiding Questions 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula,
Type Ia supernovae observable nuclear astrophysics
 Astrophysics and Nuclear Structure Hirschegg, January 27, 2013 Type Ia supernovae observable nuclear astrophysics Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, Germany W. Hillebrandt, S. Woosley, S. Sim, I.
Astrophysics and Nuclear Structure Hirschegg, January 27, 2013 Type Ia supernovae observable nuclear astrophysics Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, Germany W. Hillebrandt, S. Woosley, S. Sim, I.
Chapter 6: Stellar Evolution (part 2): Stellar end-products
 Chapter 6: Stellar Evolution (part 2): Stellar end-products Final evolution stages of high-mass stars Stellar end-products White dwarfs Neutron stars and black holes Supernovae Core-collapsed SNe Pair-Instability
Chapter 6: Stellar Evolution (part 2): Stellar end-products Final evolution stages of high-mass stars Stellar end-products White dwarfs Neutron stars and black holes Supernovae Core-collapsed SNe Pair-Instability
Lecture 13: Binary evolution
 Lecture 13: Binary evolution Senior Astrophysics 2017-04-12 Senior Astrophysics Lecture 13: Binary evolution 2017-04-12 1 / 37 Outline 1 Conservative mass transfer 2 Non-conservative mass transfer 3 Cataclysmic
Lecture 13: Binary evolution Senior Astrophysics 2017-04-12 Senior Astrophysics Lecture 13: Binary evolution 2017-04-12 1 / 37 Outline 1 Conservative mass transfer 2 Non-conservative mass transfer 3 Cataclysmic
STELLAR DEATH, AND OTHER THINGS THAT GO BOOM IN THE NIGHT. Kevin Moore - UCSB
 STELLAR DEATH, AND OTHER THINGS THAT GO BOOM IN THE NIGHT Kevin Moore - UCSB Overview Stellar evolution basics! Fates of stars related to their mass! Mass transfer adds many possibilities Historical supernovae
STELLAR DEATH, AND OTHER THINGS THAT GO BOOM IN THE NIGHT Kevin Moore - UCSB Overview Stellar evolution basics! Fates of stars related to their mass! Mass transfer adds many possibilities Historical supernovae
Supernova events and neutron stars
 Supernova events and neutron stars So far, we have followed stellar evolution up to the formation of a C-rich core. For massive stars ( M initial > 8 M Sun ), the contracting He core proceeds smoothly
Supernova events and neutron stars So far, we have followed stellar evolution up to the formation of a C-rich core. For massive stars ( M initial > 8 M Sun ), the contracting He core proceeds smoothly
Diverse Energy Sources for Stellar Explosions. Lars Bildsten Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics University of California Santa Barbara
 Diverse Energy Sources for Stellar Explosions Lars Bildsten Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics University of California Santa Barbara Traditional Energy Sources Core collapse to NS or BH depositing
Diverse Energy Sources for Stellar Explosions Lars Bildsten Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics University of California Santa Barbara Traditional Energy Sources Core collapse to NS or BH depositing
Searching for the Progenitors of Subluminous Type Ia Supernovae with SN 2013bc
 Hubble Space Telescope Cycle 11 General Observer Proposal Searching for the Progenitors of Subluminous Type Ia Supernovae with SN 2013bc Principal Investigator: Institution: Electronic mail: Maximilian
Hubble Space Telescope Cycle 11 General Observer Proposal Searching for the Progenitors of Subluminous Type Ia Supernovae with SN 2013bc Principal Investigator: Institution: Electronic mail: Maximilian
White dwarf dynamical interactions. Enrique García-Berro. Jornades de Recerca, Departament de Física
 White dwarf dynamical interactions Enrique García-Berro Jornades de Recerca, Departament de Física CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics 3. White dwarf mergers 4. White dwarf collisions
White dwarf dynamical interactions Enrique García-Berro Jornades de Recerca, Departament de Física CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics 3. White dwarf mergers 4. White dwarf collisions
The Origin of Type Ia Supernovae
 The Origin of Type Ia Supernovae Gijs Nelemans Radboud University Nijmegen with Rasmus Voss, Mikkel Nielsel, Silvia Toonen, Madelon Bours, Carsten Dominik Outline Introduction: supernovae Relevance Type
The Origin of Type Ia Supernovae Gijs Nelemans Radboud University Nijmegen with Rasmus Voss, Mikkel Nielsel, Silvia Toonen, Madelon Bours, Carsten Dominik Outline Introduction: supernovae Relevance Type
Stellar Explosions (ch. 21)
 Stellar Explosions (ch. 21) First, a review of low-mass stellar evolution by means of an illustration I showed in class. You should be able to talk your way through this diagram and it should take at least
Stellar Explosions (ch. 21) First, a review of low-mass stellar evolution by means of an illustration I showed in class. You should be able to talk your way through this diagram and it should take at least
HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution
 Ay 1 Lecture 9 M7 ESO HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution 9.1 The HR Diagram Stellar Spectral Types Temperature L T Y The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR) Diagram It is a plot of stellar luminosity
Ay 1 Lecture 9 M7 ESO HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution 9.1 The HR Diagram Stellar Spectral Types Temperature L T Y The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR) Diagram It is a plot of stellar luminosity
Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources
 Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ http://www.space.com/32150-farthest-galaxy-smashes-cosmic-distance-record.html The Algol Mystery Algol is a double-lined
Binary Evolution Novae, Supernovae, and X-ray Sources http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ http://www.space.com/32150-farthest-galaxy-smashes-cosmic-distance-record.html The Algol Mystery Algol is a double-lined
Type II Supernovae Overwhelming observational evidence that Type II supernovae are associated with the endpoints of massive stars: Association with
 Type II Supernovae Overwhelming observational evidence that Type II supernovae are associated with the endpoints of massive stars: Association with spiral arms in spiral galaxies Supernova in M75 Type
Type II Supernovae Overwhelming observational evidence that Type II supernovae are associated with the endpoints of massive stars: Association with spiral arms in spiral galaxies Supernova in M75 Type
Nuclear Astrophysics
 Nuclear Astrophysics IV: Novae, x-ray bursts and thermonuclear supernovae Karlheinz Langanke GSI & TU Darmstadt Aarhus, October 6-10, 2008 Karlheinz Langanke ( GSI & TU Darmstadt) Nuclear Astrophysics
Nuclear Astrophysics IV: Novae, x-ray bursts and thermonuclear supernovae Karlheinz Langanke GSI & TU Darmstadt Aarhus, October 6-10, 2008 Karlheinz Langanke ( GSI & TU Darmstadt) Nuclear Astrophysics
What Are Type Ia Supernovae?
 What Are Type Ia Supernovae? Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik Based on collaborations with: W. Hillebrandt (MPA Garching) S.E. Woosley (UC Santa Cruz) M. Reinecke (MPA Garching) B. Leibundgut (ESO Garching)
What Are Type Ia Supernovae? Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik Based on collaborations with: W. Hillebrandt (MPA Garching) S.E. Woosley (UC Santa Cruz) M. Reinecke (MPA Garching) B. Leibundgut (ESO Garching)
Supernova Explosions. Novae
 Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Observable constraints on nucleosynthesis conditions in Type Ia supernovae
 Observable constraints on nucleosynthesis conditions in Type Ia supernovae MPE Eurogenesis Garching, March 26, 2013 Ivo Rolf Seitenzahl Institut für Theoretische Physik und Astrophysik Julius-Maximilians-Universität
Observable constraints on nucleosynthesis conditions in Type Ia supernovae MPE Eurogenesis Garching, March 26, 2013 Ivo Rolf Seitenzahl Institut für Theoretische Physik und Astrophysik Julius-Maximilians-Universität
Comparing a Supergiant to the Sun
 The Lifetime of Stars Once a star has reached the main sequence stage of it life, it derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen to helium Stars remain on the main sequence for a long time and most
The Lifetime of Stars Once a star has reached the main sequence stage of it life, it derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen to helium Stars remain on the main sequence for a long time and most
Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused
Supernovae. M. Della Valle. INAF-Napoli ICRANet-Pescara
 Supernovae M. Della Valle INAF-Napoli ICRANet-Pescara Nice, September 4 2011 Supernova types Explosion trigger mechanisms SN & GRB connection What Supernovae? SUPERNOVA = super - nova very bright new star
Supernovae M. Della Valle INAF-Napoli ICRANet-Pescara Nice, September 4 2011 Supernova types Explosion trigger mechanisms SN & GRB connection What Supernovae? SUPERNOVA = super - nova very bright new star
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics of Exploding Stars
 Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics of Exploding Stars Lars Bildsten Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics Department of Physics University of California, Santa Barbara Dan Kasen (UCSC), Kevin Moore (UCSB),
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics of Exploding Stars Lars Bildsten Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics Department of Physics University of California, Santa Barbara Dan Kasen (UCSC), Kevin Moore (UCSB),
Astronomy 110: SURVEY OF ASTRONOMY. 11. Dead Stars. 1. White Dwarfs and Supernovae. 2. Neutron Stars & Black Holes
 Astronomy 110: SURVEY OF ASTRONOMY 11. Dead Stars 1. White Dwarfs and Supernovae 2. Neutron Stars & Black Holes Low-mass stars fight gravity to a standstill by becoming white dwarfs degenerate spheres
Astronomy 110: SURVEY OF ASTRONOMY 11. Dead Stars 1. White Dwarfs and Supernovae 2. Neutron Stars & Black Holes Low-mass stars fight gravity to a standstill by becoming white dwarfs degenerate spheres
Supernovae. For several weeks a supernova s luminosity rivals that of a large galaxy. SUPERNOVAE. A supernova is the explosive death of a star.
 SUPERNOVAE Supernovae Pols 13 Glatzmaier and Krumholz 17, 18 Prialnik 10 A supernova is the explosive death of a star. Two types are easily distinguishable by their spectrum. Type II has hydrogen (H ).
SUPERNOVAE Supernovae Pols 13 Glatzmaier and Krumholz 17, 18 Prialnik 10 A supernova is the explosive death of a star. Two types are easily distinguishable by their spectrum. Type II has hydrogen (H ).
Supernovae. Pols 13 Glatzmaier and Krumholz 17, 18 Prialnik 10
 Supernovae Pols 13 Glatzmaier and Krumholz 17, 18 Prialnik 10 SUPERNOVAE A supernova is the explosive death of a star. Two types are easily distinguishable by their spectrum. Type II has hydrogen (H ).
Supernovae Pols 13 Glatzmaier and Krumholz 17, 18 Prialnik 10 SUPERNOVAE A supernova is the explosive death of a star. Two types are easily distinguishable by their spectrum. Type II has hydrogen (H ).
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12)
 Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
PHYS Further Stellar Evolution Prof. Maurizio Salaris
 PHYS 383 - Further Stellar Evolution Prof. Maurizio Salaris PROF. 1 Standard Big Bang model and the problem of galaxy formation Stellar evolution can put independent constraints on the cosmological model
PHYS 383 - Further Stellar Evolution Prof. Maurizio Salaris PROF. 1 Standard Big Bang model and the problem of galaxy formation Stellar evolution can put independent constraints on the cosmological model
Mass Transfer in Binaries
 Mass Transfer in Binaries Philipp Podsiadlowski (Oxford) Understanding the physics of mass transfer is essential for understanding binary evolution Simplest assumption: stable, conservative mass transfer
Mass Transfer in Binaries Philipp Podsiadlowski (Oxford) Understanding the physics of mass transfer is essential for understanding binary evolution Simplest assumption: stable, conservative mass transfer
Publications: Prof. Philipp Podsiadlowski
 Publications: Prof. Philipp Podsiadlowski Citations Google Scholar [10/2014]: 9661 (overall), 5852 (since 2009), h-index: 53 (overall), 42 (since 2009) ADS [10/2014]: 8274 (overall), h-index: 49 (overall)
Publications: Prof. Philipp Podsiadlowski Citations Google Scholar [10/2014]: 9661 (overall), 5852 (since 2009), h-index: 53 (overall), 42 (since 2009) ADS [10/2014]: 8274 (overall), h-index: 49 (overall)
Star Death ( ) High Mass Star. Red Supergiant. Supernova + Remnant. Neutron Star
 Star Death High Mass Star Red Supergiant A star with mass between 8 M and 20 M will become a red supergiant and will subsequently experience a supernova explosion. The core of this star will have a mass
Star Death High Mass Star Red Supergiant A star with mass between 8 M and 20 M will become a red supergiant and will subsequently experience a supernova explosion. The core of this star will have a mass
THE 82ND ARTHUR H. COMPTON LECTURE SERIES
 THE 82ND ARTHUR H. COMPTON LECTURE SERIES by Dr. Manos Chatzopoulos Enrico Fermi Postdoctoral Fellow FLASH Center for Computational Science Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics University of Chicago
THE 82ND ARTHUR H. COMPTON LECTURE SERIES by Dr. Manos Chatzopoulos Enrico Fermi Postdoctoral Fellow FLASH Center for Computational Science Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics University of Chicago
20. Stellar Death. Interior of Old Low-Mass AGB Stars
 20. Stellar Death Low-mass stars undergo three red-giant stages Dredge-ups bring material to the surface Low -mass stars die gently as planetary nebulae Low -mass stars end up as white dwarfs High-mass
20. Stellar Death Low-mass stars undergo three red-giant stages Dredge-ups bring material to the surface Low -mass stars die gently as planetary nebulae Low -mass stars end up as white dwarfs High-mass
Evolution of Low-Mass stars M < 4 M sun No C Burning!
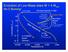 Evolution of Low-Mass stars M < 4 M sun No C Burning! C-O Core Envelope Ejection 0.1Myr Luminosity (L sun ) 10 6 10 4 10 2 1 10-2 10-4 C-O White Dwarf (forever) Asymptotic Giant Branch C-O core contraction,
Evolution of Low-Mass stars M < 4 M sun No C Burning! C-O Core Envelope Ejection 0.1Myr Luminosity (L sun ) 10 6 10 4 10 2 1 10-2 10-4 C-O White Dwarf (forever) Asymptotic Giant Branch C-O core contraction,
Abundance Constraints on Early Chemical Evolution. Jim Truran
 Abundance Constraints on Early Chemical Evolution Jim Truran Astronomy and Astrophysics Enrico Fermi Institute University of Chicago Argonne National Laboratory MLC Workshop Probing Early Structure with
Abundance Constraints on Early Chemical Evolution Jim Truran Astronomy and Astrophysics Enrico Fermi Institute University of Chicago Argonne National Laboratory MLC Workshop Probing Early Structure with
Supernovae. Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization
 Supernovae Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization 1 Supernova Basics Supernova (SN) explosions in our Galaxy and others
Supernovae Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization 1 Supernova Basics Supernova (SN) explosions in our Galaxy and others
The Deaths of Stars. The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant.
 The Deaths of Stars The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant. Once the giant phase of a mediummass star ends, it exhales its outer
The Deaths of Stars The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant. Once the giant phase of a mediummass star ends, it exhales its outer
Stars with Mⵙ go through two Red Giant Stages
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Death of Stars Nuclear reactions in small stars How stars disperse carbon How low mass stars die The nature of white dwarfs
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Death of Stars Nuclear reactions in small stars How stars disperse carbon How low mass stars die The nature of white dwarfs
The 2006 Outburst of RS Oph: What are the questions that need to be discussed --and answered?
 The 2006 Outburst of RS Oph: What are the questions that need to be discussed --and answered? Sumner Starrfield School of Earth and Space Exploration Arizona State University WHY DO WE CARE? RS Oph may
The 2006 Outburst of RS Oph: What are the questions that need to be discussed --and answered? Sumner Starrfield School of Earth and Space Exploration Arizona State University WHY DO WE CARE? RS Oph may
Evolution, Death and Nucleosynthesis of the First Stars
 First Stars IV, Kyoto, Japan, May 24, 2012 Alexander Heger Stan Woosley Ken Chen Pamela Vo Bernhad Müller Thomas Janka Candace Joggerst http://cosmicexplosions.org Evolution, Death and Nucleosynthesis
First Stars IV, Kyoto, Japan, May 24, 2012 Alexander Heger Stan Woosley Ken Chen Pamela Vo Bernhad Müller Thomas Janka Candace Joggerst http://cosmicexplosions.org Evolution, Death and Nucleosynthesis
Supernovae. Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization
 Supernovae Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization 1 Supernova Basics Supernova (SN) explosions in our Galaxy and others
Supernovae Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization 1 Supernova Basics Supernova (SN) explosions in our Galaxy and others
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Wolfgang Hillebrandt. Garching. DEISA PRACE Symposium Barcelona May 10 12, 2010
 Modelling Cosmic Explosions Wolfgang Hillebrandt MPI für Astrophysik Garching DEISA PRACE Symposium Barcelona May 10 12, 2010 Outline of the talk Supernova types and phenomenology (in brief) Models of
Modelling Cosmic Explosions Wolfgang Hillebrandt MPI für Astrophysik Garching DEISA PRACE Symposium Barcelona May 10 12, 2010 Outline of the talk Supernova types and phenomenology (in brief) Models of
Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
R-process in Low Entropy Neutrino Driven Winds
 R-process in Low Entropy Neutrino Driven Winds E. Baron John J. Cowan, Tamara Rogers, 1 and Kris Gutierrez 2 Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Oklahoma, 440 W. Brooks, Rm 131, Norman, OK 73019-0225
R-process in Low Entropy Neutrino Driven Winds E. Baron John J. Cowan, Tamara Rogers, 1 and Kris Gutierrez 2 Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Oklahoma, 440 W. Brooks, Rm 131, Norman, OK 73019-0225
Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death
 Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death Stars have lives: born, evolve, die Mass determines stellar evolution: Really Low Mass (0.08 to 0.4 M sun ) Low Mass: (0.4 to 4 M sun ) Long lives High Mass (4
Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death Stars have lives: born, evolve, die Mass determines stellar evolution: Really Low Mass (0.08 to 0.4 M sun ) Low Mass: (0.4 to 4 M sun ) Long lives High Mass (4
Supernovae. Richard McCray University of Colorado. 1. Supernovae 2. Supernova Remnants 3. Supernova 1987A
 Supernovae Richard McCray University of Colorado 1. Supernovae 2. Supernova Remnants 3. Supernova 1987A Why are supernovae interesting? They are the source of all elements in the universe (except H, He,
Supernovae Richard McCray University of Colorado 1. Supernovae 2. Supernova Remnants 3. Supernova 1987A Why are supernovae interesting? They are the source of all elements in the universe (except H, He,
Stellar Evolution. Eta Carinae
 Stellar Evolution Eta Carinae Evolution of Main Sequence Stars solar mass star: from: Markus Bottcher lecture notes, Ohio University Evolution off the Main Sequence: Expansion into a Red Giant Inner core
Stellar Evolution Eta Carinae Evolution of Main Sequence Stars solar mass star: from: Markus Bottcher lecture notes, Ohio University Evolution off the Main Sequence: Expansion into a Red Giant Inner core
Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4
 Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4 Key Ideas HR Diagrams of Star Clusters Ages from the Main Sequence Turn-off Open Clusters Young clusters of ~1000 stars Blue Main-Sequence
Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4 Key Ideas HR Diagrams of Star Clusters Ages from the Main Sequence Turn-off Open Clusters Young clusters of ~1000 stars Blue Main-Sequence
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015
 Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
CATACLYSMIC VARIABLES. AND THE TYPE Ia PROGENITOR PROBLEM PROGENITOR PROBLEM
 CATACLYSMIC VARIABLES AND THE TYPE Ia PROGENITOR PROBLEM PROGENITOR PROBLEM Lorne Nelson SNOVAE07 Feb. 23, 2007 Cataclysmic Variables CVs are characterized by a low-mass star/bd (donor) losing mass to
CATACLYSMIC VARIABLES AND THE TYPE Ia PROGENITOR PROBLEM PROGENITOR PROBLEM Lorne Nelson SNOVAE07 Feb. 23, 2007 Cataclysmic Variables CVs are characterized by a low-mass star/bd (donor) losing mass to
The Evolution of Low Mass Stars
 The Evolution of Low Mass Stars Key Ideas: Low Mass = M < 4 M sun Stages of Evolution of a Low Mass star: Main Sequence star star star Asymptotic Giant Branch star Planetary Nebula phase White Dwarf star
The Evolution of Low Mass Stars Key Ideas: Low Mass = M < 4 M sun Stages of Evolution of a Low Mass star: Main Sequence star star star Asymptotic Giant Branch star Planetary Nebula phase White Dwarf star
Termination of Stars
 Termination of Stars Some Quantum Concepts Pauli Exclusion Principle: "Effectively limits the amount of certain kinds of stuff that can be crammed into a given space (particles with personal space ). When
Termination of Stars Some Quantum Concepts Pauli Exclusion Principle: "Effectively limits the amount of certain kinds of stuff that can be crammed into a given space (particles with personal space ). When
Impact of Type Ia Supernova Ejecta on Binary Companions
 Impact of Type Ia Supernova Ejecta on Binary Companions Speaker: Kuo-Chuan Pan (ASTR) Charm++ Workshop, April 18, 2011 1 [Dept. of Astronomy] Advisor: Prof. Paul Ricker Collaborator: Prof. Ronald Taam
Impact of Type Ia Supernova Ejecta on Binary Companions Speaker: Kuo-Chuan Pan (ASTR) Charm++ Workshop, April 18, 2011 1 [Dept. of Astronomy] Advisor: Prof. Paul Ricker Collaborator: Prof. Ronald Taam
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Regional Event February 11, 2017 Maryland
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Regional Event February 11, 2017 Maryland TEAM NUMBER: TEAM NAME: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) Please turn in ALL MATERIALS at the end of this event. 2) Do not forget to put your TEAM
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Regional Event February 11, 2017 Maryland TEAM NUMBER: TEAM NAME: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) Please turn in ALL MATERIALS at the end of this event. 2) Do not forget to put your TEAM
Chapter 12 Review. 2) About 90% of the star's total life is spent on the main sequence. 2)
 Chapter 12 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) As a main-sequence star, the Sun's hydrogen supply should last about 10 billion years from the zero-age
Chapter 12 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) As a main-sequence star, the Sun's hydrogen supply should last about 10 billion years from the zero-age
Friday, April 29, 2011
 Lecture 29: The End Stages of Massive Stellar Evolution & Supernova Review: Elemental Abundances in the Solar System Review: Elemental Abundances in the Solar System Synthesized by S and R-processes Review:
Lecture 29: The End Stages of Massive Stellar Evolution & Supernova Review: Elemental Abundances in the Solar System Review: Elemental Abundances in the Solar System Synthesized by S and R-processes Review:
Supernova Explosions. Novae
 Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars
 Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars Senior Astrophysics 2018-03-27 Senior Astrophysics Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars 2018-03-27 1 / 29 Outline 1 Stellar models 2 Convection
Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars Senior Astrophysics 2018-03-27 Senior Astrophysics Lecture 8: Stellar evolution II: Massive stars 2018-03-27 1 / 29 Outline 1 Stellar models 2 Convection
An Overview of Stellar Evolution
 Stellar Objects: An Overview of Stellar Evolution 1 An Overview of Stellar Evolution 1 the Main Sequence Zero-age Main Sequence stars (ZAMS) are those stars who arrived at the MS recently. Practically,
Stellar Objects: An Overview of Stellar Evolution 1 An Overview of Stellar Evolution 1 the Main Sequence Zero-age Main Sequence stars (ZAMS) are those stars who arrived at the MS recently. Practically,
Chapter 12 Stellar Evolution
 Chapter 12 Stellar Evolution Guidepost Stars form from the interstellar medium and reach stability fusing hydrogen in their cores. This chapter is about the long, stable middle age of stars on the main
Chapter 12 Stellar Evolution Guidepost Stars form from the interstellar medium and reach stability fusing hydrogen in their cores. This chapter is about the long, stable middle age of stars on the main
Multidimensional Simulations of Type Ia Supernova Explosions:
 Multidimensional Simulations of Type Ia Supernova Explosions: Confronting Model Predictions with Observations Wolfgang Hillebrandt MPI für Astrophysik Garching Dark Energy Conference, Munich, October 7-11,
Multidimensional Simulations of Type Ia Supernova Explosions: Confronting Model Predictions with Observations Wolfgang Hillebrandt MPI für Astrophysik Garching Dark Energy Conference, Munich, October 7-11,
White dwarf populations. Gijs Nelemans Radboud University Nijmegen
 White dwarf populations Gijs Nelemans Radboud University Nijmegen Outline Introduction: Population synthesis Basic ingredients Observational inputs White dwarf populations Different types and mergers WD
White dwarf populations Gijs Nelemans Radboud University Nijmegen Outline Introduction: Population synthesis Basic ingredients Observational inputs White dwarf populations Different types and mergers WD
Supernovae. Graham Kribs University of Oregon
 Supernovae Graham Kribs University of Oregon ***warning*** I m *not* at all supernova expert; just a few thoughts about how supernova play a critical role in understanding disparate aspects of physics!
Supernovae Graham Kribs University of Oregon ***warning*** I m *not* at all supernova expert; just a few thoughts about how supernova play a critical role in understanding disparate aspects of physics!
Supernovae and cosmology
 Supernovae and cosmology On the Death of Stars and Standard Candles Gijs Hijmans Supernovae Types of Supernovae Type I Ia (no hydrogen but strong silicon lines in spectrum) Ib (non ionized helium lines)
Supernovae and cosmology On the Death of Stars and Standard Candles Gijs Hijmans Supernovae Types of Supernovae Type I Ia (no hydrogen but strong silicon lines in spectrum) Ib (non ionized helium lines)
Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM
 Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM RLM 15.216B (Backup RLM 15.202A) Reading: Chapter 6
Wednesday, February 3, 2016 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch Due (typed, 8.5x11 paper). Review sheet posted. Review session Thursday, 4:30 5:30 PM RLM 15.216B (Backup RLM 15.202A) Reading: Chapter 6
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
 Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational February 11, 2017
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational February 11, 2017 Team Name: Team Number: Directions: ~Answer all questions on the answer sheet provided. ~Please do NOT access the
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational February 11, 2017 Team Name: Team Number: Directions: ~Answer all questions on the answer sheet provided. ~Please do NOT access the
A search for supernova type Ia progenitors in the Magellanic Clouds. Kelly Lepo
 A search for supernova type Ia progenitors in the Magellanic Clouds by Kelly Lepo A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Graduate Department of Astronomy
A search for supernova type Ia progenitors in the Magellanic Clouds by Kelly Lepo A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Graduate Department of Astronomy
Type Ibn Supernovae. Type Ibn Supernovae. Andrea Pastorello (INAF-OAPd) Andrea Pastorello (INAF-OAPd) Stockholm May 28 - June 1, 2018
 Type Ibn Supernovae Type Ibn Supernovae Andrea Pastorello (INAF-OAPd) Stockholm May 28 - June 1, 2018 Andrea Pastorello (INAF-OAPd) Overview Introduction; SN 2006jc Heterogeneity of SN Ibn observables
Type Ibn Supernovae Type Ibn Supernovae Andrea Pastorello (INAF-OAPd) Stockholm May 28 - June 1, 2018 Andrea Pastorello (INAF-OAPd) Overview Introduction; SN 2006jc Heterogeneity of SN Ibn observables
Announcement: Quiz Friday, Oct 31
 Announcement: Quiz Friday, Oct 31 What is the difference between the giant, horizontal, and asymptotic-giant branches? What is the Helium flash? Why can t high-mass stars support themselves in hydrostatic
Announcement: Quiz Friday, Oct 31 What is the difference between the giant, horizontal, and asymptotic-giant branches? What is the Helium flash? Why can t high-mass stars support themselves in hydrostatic
Chapter 17 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Stuff Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 17 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Stuff Star Stuff 17.1 Lives in the Balance Our goals for learning: How does a star's mass affect nuclear fusion? How does a star's mass affect
Chapter 17 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Stuff Star Stuff 17.1 Lives in the Balance Our goals for learning: How does a star's mass affect nuclear fusion? How does a star's mass affect
Models of Type Ia supernova explosions
 Fifty-one erg workshop Raleigh, May 14, 2013 Models of Type Ia supernova explosions Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, Germany I. Seitenzahl, M. Fink, R. Pakmor, S. Sim, M. Kromer, A. Summa, F. CiaraldiSchoolmann,
Fifty-one erg workshop Raleigh, May 14, 2013 Models of Type Ia supernova explosions Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, Germany I. Seitenzahl, M. Fink, R. Pakmor, S. Sim, M. Kromer, A. Summa, F. CiaraldiSchoolmann,
Systematic Effects on the Brightness of Type Ia Supernovae
 Systematic Effects on the Brightness of Type Ia Supernovae Alan Calder D. Willcox, A. Jackson, B. Krueger (Stony Brook) D. Townsley, B. Miles (Alabama), E. Brown (MSU), F. Timmes (ASU) P. Denissenkov,
Systematic Effects on the Brightness of Type Ia Supernovae Alan Calder D. Willcox, A. Jackson, B. Krueger (Stony Brook) D. Townsley, B. Miles (Alabama), E. Brown (MSU), F. Timmes (ASU) P. Denissenkov,
Learning Objectives: Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars. AST 2010: Chapter 13. AST 2010 Descriptive Astronomy
 Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars Define red dwarf, and describe the internal dynamics and later evolution of these low-mass stars. Appreciate the time scale of late-stage stellar evolution
Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars Define red dwarf, and describe the internal dynamics and later evolution of these low-mass stars. Appreciate the time scale of late-stage stellar evolution
Hybrid C-O-Ne White Dwarfs as Progenitors of Diverse SNe Ia
 Hybrid C-O-Ne White Dwarfs as Progenitors of Diverse SNe Ia Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of Victoria, P.O. Box 1700, STN CSC, Victoria, B.C., V8W 2Y2, Canada; The Joint Institute for Nuclear
Hybrid C-O-Ne White Dwarfs as Progenitors of Diverse SNe Ia Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of Victoria, P.O. Box 1700, STN CSC, Victoria, B.C., V8W 2Y2, Canada; The Joint Institute for Nuclear
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9
 Phys 0 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because * a. they are more luminous but have about the
Phys 0 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because * a. they are more luminous but have about the
Five and a half roads to from a millisecond pulsar. Thomas Tauris AIfA, University of Bonn Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn
 Five and a half roads to from a millisecond pulsar Thomas Tauris AIfA, University of Bonn Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn Evolution of Compact Binaries, ESO Chile, March 6-11, 2011 Millisecond
Five and a half roads to from a millisecond pulsar Thomas Tauris AIfA, University of Bonn Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn Evolution of Compact Binaries, ESO Chile, March 6-11, 2011 Millisecond
Introduction to nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars
 Introduction to nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars Amanda Karakas 1 and John Lattanzio 2 1) Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Mt. Stromlo Observatory 2) School of Mathematical Sciences,
Introduction to nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars Amanda Karakas 1 and John Lattanzio 2 1) Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Mt. Stromlo Observatory 2) School of Mathematical Sciences,
