Astronomy Merit Badge Merit badge requirements as revised 2011 this lesson plan by Glenn Holliday revised January 2013 During daytime teaching session
|
|
|
- Jonathan Fowler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Astronomy Merit Badge Merit badge requirements as revised 2011 this lesson plan by Glenn Holliday revised January 2013 During daytime teaching session 1. Do the following: a. Describe the proper clothing and other precautions for safely making observations at night and in cold weather. Winter observing: You need more protection from cold then when camping. Observing has no sunlight and is inactive. Plan for 20 degrees colder than the actual temperature. b. Tell how to safely observe the Sun, objects near the Sun, and the Moon. Indirect observing with a pinhole camera. If available, show an unacceptable solar filter, an acceptable solar filter, and a solar telescope. c. Explain first aid for injuries or illnesses, such as heat and cold reactions, dehydration, bites and stings, and damage to your eyes that could occur during observation. First aid for eye damage: Protect your eyes. After they are damaged, there is no first aid other than seeking immediate medical help from an eye doctor.. Symptoms: pain, blurred vision, flash blindness. Either the sun or a laser can cause the same kind of burn to the cornea or retina. It is very similar to a sunburn. Recovery varies. See the links to additional resources for a medical article on the subject. (2 do during nighttime session: light pollution) 3. With the aid of diagrams (or real telescopes if available), do each of the following: a. Explain why binoculars and telescopes are important astronomical tools. Demonstrate or explain how these tools are used. b. Describe the similarities and differences of several types of astronomical telescopes. OTAs: Refractor, reflector, Schmidt-Cassegrain Mounts: Altitude-azimuth, equatorial, Dobsonion Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p1
2 c. Explain the purposes of at least three instruments used with astronomical telescopes. Finder, 1x sight, planisphere, charts, camera, spectroscope, reticle, alignment tools, red light d. Describe the proper care and storage of telescopes and binoculars both at home and in the field. (4 do during nighttime session: Identify stars and constellations) 5. Do the following: a. List the names of the five most visible planets. Explain which ones can appear in phases similar to lunar phases and which ones cannot, and explain why. b. Using the Internet (with your parent's permission), books, and other resources, find out when each of the five most visible planets that you identified in requirement 5a will be observable in the evening sky during the next 12 months, then compile this information in the form of a chart or table. Made easier no longer have to update the chart monthly Students need to do the research and create the chart on their own. c. Describe the motion of the planets across the sky. (5 d. do during nighttime session: Observe a planet) 6. Do the following: (6.a. do during nighttime session: Observe Moon.) (6.b. do during nighttime session: Moon phases.) c. List the factors that keep the Moon in orbit around Earth. d. With the aid of diagrams, explain the relative positions of the Sun, Earth, and the Moon at the times of lunar and solar eclipses, and at the times of new, first-quarter, full, and last-quarter phases of the Moon. Students need to draw the diagrams on their own. 7. Do the following: a. Describe the composition of the Sun, its relationship to other stars, and some effects of its radiation on Earth's weather and communications. Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p2
3 b. Define sunspots and describe some of the effects they may have on solar radiation. (7.c. do during nighttime session: Identify colored stars.) 8. With your counselor's approval and guidance, do ONE of the following: Students will need to complete the project on their own. a. Visit a planetarium or astronomical observatory. Submit a written report, a scrapbook, or a video presentation afterward to your counselor that includes the following information: (1) Activities occurring there (2) Exhibits and displays you saw (3) Telescopes and instruments being used (4) Celestial objects you observed. List of planetariums near Rappahannock Astronomy Club Albert Einstein Planetarium National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution Washington, D.C Davis Planetarium Maryland Science Center Baltimore, Maryland Hopkins Planetarium Science Museum of Western Virginia Roanoke, Virginia John C. Wells Planetarium James Madison University Harrisonburg, Virginia free shows on Saturdays Science Museum of Virginia Planetarium Richmond, Virginia List of observatories near the Rappahannock Astronomy Club Fan Mountain Observatory University of Virginia 14 miles south of Charlottesville, off of US-29 Each April and October, a public night is held. Tickets, which are free, are required. Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p3
4 Green Bank Telescope Green Bank, West Virginia The Science Center is open some days Keeble Observatory Randolph Macon College Ashland, Virginia The Keeble Observatory will be closed for public viewing until September, when the College returns for Fall Semester. Leander McCormick Observatory University of Virginia Mount Jefferson Charlottesville, Virginia McCormick Observatory is open to the public on the first and third Friday night of each month (except holidays). United States Naval Observatory Washington, D. C. The observatory has received an overwhelming number of applications for tour reservations. Due to the backlog it is not accepting any new tour requests until further notice. University of Maryland Observatory College Park, Maryland Open house on selected nights b. Plan and participate in a three-hour observation session that includes using binoculars or a telescope. List the celestial objects you want to observe, and find each on a star chart or in a guidebook. Prepare an observing log or notebook. Show your plan, charts, and log or notebook to your counselor before making your observations. Review your log or notebook with your counselor afterward. Importance of planning: What s visible this time of year Limits of observing site on horizon obstructions, light pollution Effect of moonlight Equipment suitable to types of objects you wish to observe Observe objects in order of their setting c. Plan and host a star party for your Scout troop or other group such as your class at school. Use binoculars or a telescope to show and explain celestial objects to the group. Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p4
5 d. Help an astronomy club in your community hold a star party that is open to the public. e. Personally take a series of photographs or digital images of the movement of the Moon, a planet, an asteroid or meteoroid, or a comet. In your visual display, label each image and include the date and time it was taken. Show all positions on a star chart or map. Show your display at school or at a troop meeting. Explain the changes you observed. 9. Find out about three different career opportunities in astronomy. Pick one and find out the education, training, and experience required for this profession. Discuss this with your counselor, and explain why this profession might interest you. Science astronomer, astrophysicist Education teacher, ranger, museum, creator of planetarium shows Support equipment operation, image processing, computer programming Hardware optics, design, construction of instruments During nighttime observing session (1. do during daytime session: Safety and first aid) 2. Explain what light pollution is and how it and air pollution affect astronomy. (3 do during daytime session: Telescopes and binoculars) 4. Do the following: a. Identify in the sky at least 10 constellations, at least four of which are in the zodiac. If the class observing session does not cover these, students will need to show them in another observing session. Spring: Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, Bootes, Hercules, Corvus, Lyra zodiacal: Gemini, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpius Summer: Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, Bootes, Hercules, Corvus, Lyra, Cygnus, Aquila, Summer Triangle asterism (Vega, Deneb, Altair) zodiacal: Virgo (setting), Libra, Scorpius, Sagittarius, Capricornus, Aquarius Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p5
6 Fall: Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, Bootes, Hercules, Lyra, Cygnus, Aquila, Cassiopeia, Cepheus, Pegasus, Andromeda, Perseus, Cetus zodiacal: Sagittarius (setting), Capricornus, Aquarius, Pisces, Aries, Taurus (after midnight) Winter: Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, Cygnus, Cassiopeia, Cepheus, Orion, Canis Major, Winter Triangle asterism: (Betelgeuse, Sirius, Procyon) zodiacal: Pisces, Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Leo (late) b. Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude 1 or brighter. A century ago an astronomer would have thought this requirement a mistake: there are no stars brighter than magnitude 1. Then we redefined that metric. Spring Dubhe, Merak, Mizar, Alcor, (all Ursa Major), Regulus (Leo), Arcturus, (Bootes), Altair (Aquila), Spica (Virgo), Vega (Lyra), Antares (Scorpius), Capella (Auriga), Castor, Pollux (Gemini), Deneb (Cygnus), Summer Triangle: Vega (Lyra), Deneb (Cygnus), Altair (Aquila) Summer: Fall: Dubhe, Merak, Mizar, Alcor, (all Ursa Major), Arcturus, (Bootes), Altair (Aquila), Spica (Virgo, setting), Vega (Lyra), Antares (Scorpius), Deneb (Cygnus), Summer Triangle: Vega (Lyra), Deneb (Cygnus), Altair (Aquila) Dubhe, Merak, Mizar, Alcor, (all Ursa Major), Arcturus, (Bootes), Altair (Aquila), Vega (Lyra), Deneb (Cygnus), Mirfak (alpha Persi) Winter: Sirius (Canis Major), Betelgeuse (Orion), Rigel (Orion), Procyon (Canis Minor), Capella (Auriga), Aldebaran (Taurus) Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p6
7 1 st magnitude stars visible in northern hemisphere Because modern instruments can measure star brightness in fractions of a magnitude, and measured magnitude depends of how much of the spectrum of a star is measured, different lists choose different points to divide the 1 st magnitude starts from the 2 nd magnitude stars. This list includes the visible energy of stars from magnitude -1.5 to Stars of magnitude 1.4 are classified as 2 nd magnitude stars. It does not include stars that are not easily viewed from the latitude of Virginia. Name Constellation Best Season Color Size Aldebaran Taurus Winter Red Giant Altair Aquila Summer White Dwarf Antares Scorpius Summer Red Supergiant Arcturus Bootes Spring Orange Giant Betelgeuse Orion Winter Red Supergiant Capella Auriga Winter Yellow Giant Deneb Cygnus Fall White Supergiant Fomalhaut Picis Austrinus Fall White Dwarf Pollux Gemini Winter Yellow Giant Procyon Canis Minor Winter White Giant Regulus Leo Spring Blue Dwarf Rigel Orion Winter Blue Supergiant Sirius Canis Major Winter White Dwarf Spica Virgo Spring Blue Dwarf Vega Lyra Summer White Dwarf c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper's orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the North Star and the horizon. Record the date and time each sketch was made. If class observing is not long enough for both viewings, students will need to make the observation and sketches on their own. d. Explain what we see when we look at the Milky Way. Students need to answer this on their workbooks. (5. a.. do during daytime session: List the names of the five most visible planets.) Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p7
8 (5. b. do at home: Find out when each of the five most visible planets that you identified in requirement 5a will be observable) (5. c. do during daytime session: Describe the motion of the planets across the sky.) 5. d. Observe a planet and describe what you saw. 6. a. Sketch the face of the moon and indicate at least five seas and five craters. Label these landmarks. Students need to draw the diagrams on their own. 6. b. Sketch the phase and the daily position of the Moon at the same hour and place, for four days in a row. Include landmarks on the horizon such as hills, trees, and buildings. Explain the changes you observe. Made easier no longer a week of watching it. Students need to observe and sketch on 4 days on their own. (6. c. do during daytime session: List the factors that keep the Moon in orbit around Earth.) (6. d. do during daytime session: Explain the relative positions of the Sun, Earth, and the Moon at the times of eclipses, and at the times phases of the Moon. (7. a. do during daytime session: Describe the composition of the Sun...) (7. b. do during daytime session: Define sunspots...) 7. c. Identify at least one red star, one blue star, and one yellow star (other than the Sun). Explain the meaning of these colors. Blue Regulus (Leo), Vega (Lyra) Red: Antares (Scorpius), Arcturus (Bootes), Betelgeuse (Orion) Yellow:Albireo (Cygnus), Pollux (Gemini), Capella (Auriga), Castor (Gemini) Explain why there are no green stars Spring: Blue: Regulus (Leo) Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p8
9 (8. project) Red: Arcturus (Bootes) Yellow: Capella (Auriga) Summer: Fall: Blue: Vega (Lyra) Red: Antares (Scorpius), Arcturus (Bootes) Yellow: Albireo (Cygnus) Blue: Vega (Lyra) Red: Arcturus (Bootes) Yellow: Albireo (Cygnus), Capella (Auriga), Castor (Gemini), Pollux (Gemini) Winter Blue: Rigel (Orion), the brighter Pleiades, Bellatrix (gamma Ori) Red: Betelgeuse (Orion), Aldebaran (Taurus) Yellow: Capella (Auriga), Castor (Gemini), Pollux (Gemini) Different authorities give different colors for some stars. For example, Arcturus is claimed to be both red and yellow. It appears to the eye as a red star, but it is not very red. In the Secchi classification, Arcturus is in Class II, which are yellow stars. In the Spectral Class classification, Arcturus is in Class K, which are orangish stars slightly cooler than the Class G yellow stars. (9. do during daytime session: Find out about three different career opportunities in astronomy) Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p9
10 Schedule to Present Astronomy Merit Badge Requirement # Subject Activity Materials # hours Daytime class session 5.c Motion of planets Walk through MB pamphlet a Why telescopes/binoculars Show equipment Telescope, binoculars a Clothing / safety for observing Discuss MB pamphlet 0.2 MB pamphlet, filter, solar 1.b Safety observing Sun Discuss telescope c First aid Discuss MB pamphlet b Types of telescopes Discuss Photos of equipment a Planet phases Walk through Diagram of phases c 3 instruments used with telescopes Show Finder, planisphere, charts d Care of telescopes Show Telescope, binoculars c Explain Moon's orbit Walk through MB pamphlet a Describe Sun Discuss MB pamphlet b Describe sunspots Discuss MB pamphlet Careers Discuss List of careers d Explain eclipses and phases Walk through MB pamphlet 0.3 Nighttime observing session 2 Light pollution / air pollution Show MB pamphlet c Dipper first observation Show Diagram of rotation, story of Dippers, paper and pencil a 10 constellations Show List of current sky b 8 bright stars Show List of current sky d What is Milky Way Show MB pamphlet c Identify colored stars Show List of stars c continued Dipper second observation Show same as for first observation d Observe a planet Show Sky chart a Sketch the Moon Show Moon map, paper and pencil 0.3 Homework 5.b Chart / planets visible Describe how to look up The Sky, Web almanac, paper and pencil b Sketch Moon phase for 4 days Discuss Sky chart, pencil and paper a Visit planetarium Describe how to find one List of planetariums and observatories 4 8.b 3 hour observing Show Observing plan 3 8.c Troop star party Discuss how to do one 3 8.d Club star party Refer to RAC RAC schedule 3 Links to astrophotography 8.e Astrophotos Give references tutorials 10 Class Hours Needed 4.2 Nighttime Observing Hours Needed 2.8 Homework Hours Needed 11.7 Total Hours Needed 18.7 Astronomy Merit Badge Lesson Plan by Glenn Holliday p10
Astronomy Merit Badge
 Astronomy erit Badge (2013 requirements) 1. Do the following: a. xplain to your counselor the most likely hazards you may encounter while participating in astronomy activities, and what you should do to
Astronomy erit Badge (2013 requirements) 1. Do the following: a. xplain to your counselor the most likely hazards you may encounter while participating in astronomy activities, and what you should do to
Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY
 Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY Welcome to the Schenectady Museum & Suits-Bueche Planetarium! During this workshop, you will explore the museum, see a show in the planetarium, and try out some other
Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY Welcome to the Schenectady Museum & Suits-Bueche Planetarium! During this workshop, you will explore the museum, see a show in the planetarium, and try out some other
Astronomy Merit Badge Workbook
 Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge counselor.
Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge counselor.
ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORK SHEET BYU MERIT BADGE POWWOW
 ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORK SHEET BYU MERIT BADGE POWWOW Revision July 2013 Scout s Name Instructor s Name Scout s Address City State Instructions 1) The Scout is to review the merit badge book before the
ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORK SHEET BYU MERIT BADGE POWWOW Revision July 2013 Scout s Name Instructor s Name Scout s Address City State Instructions 1) The Scout is to review the merit badge book before the
BOY SCOUT ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORKSHOP
 Feb2018 BOY SCOUT ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORKSHOP The session is from 8:00am-12:30pm. All pre-requisite questions must be done on your own or with your troop BEFORE 8am on workshop day. Name Troop Leader
Feb2018 BOY SCOUT ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORKSHOP The session is from 8:00am-12:30pm. All pre-requisite questions must be done on your own or with your troop BEFORE 8am on workshop day. Name Troop Leader
Astronomy Merit Badge Workbook
 Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. The work space provided for each requirement should be used by the Scout to make notes for discussing
Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. The work space provided for each requirement should be used by the Scout to make notes for discussing
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements
 ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
Astronomy Merit Badge Workbook
 Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. The work space provided for each requirement should be used by the Scout to make notes for discussing
Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. The work space provided for each requirement should be used by the Scout to make notes for discussing
AMATEUR OBSERVERS' SOCIETY INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY OBSERVING PROGRAM
 AMATEUR OBSERVERS' SOCIETY INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY OBSERVING PROGRAM Introduction When you go out at night to observe the sky, whether with the help of a telescope, a pair of binoculars, or simply using
AMATEUR OBSERVERS' SOCIETY INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY OBSERVING PROGRAM Introduction When you go out at night to observe the sky, whether with the help of a telescope, a pair of binoculars, or simply using
Boy Scout Penguins and Pajamas Sleepover
 Boy Scout Penguins and Pajamas Sleepover February 27th & March 12th, 2016 Welcome to the Morrison Planetarium at the California Academy of Sciences! The Morrison Planetarium opened its doors on Nov 6,
Boy Scout Penguins and Pajamas Sleepover February 27th & March 12th, 2016 Welcome to the Morrison Planetarium at the California Academy of Sciences! The Morrison Planetarium opened its doors on Nov 6,
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky
 INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky Your Name: What is the difference between observing and looking? As John Rummel said to the Madison Astronomical Society, January 11, 2002: Looking implies a passive
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky Your Name: What is the difference between observing and looking? As John Rummel said to the Madison Astronomical Society, January 11, 2002: Looking implies a passive
Exploring the Night Sky
 Lincoln Hills Astronomy Group Exploring the Night Sky October 14, 2009 1 Lincoln Hills Astronomy Group Exploring the Night Sky Objectives Learn how to locate and identify objects in the night sky using
Lincoln Hills Astronomy Group Exploring the Night Sky October 14, 2009 1 Lincoln Hills Astronomy Group Exploring the Night Sky Objectives Learn how to locate and identify objects in the night sky using
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky
 INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky Your Name: What is the difference between observing and looking? As John Rummel said to the Madison Astronomical Society, January 11, 2002: Looking implies a passive
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky Your Name: What is the difference between observing and looking? As John Rummel said to the Madison Astronomical Society, January 11, 2002: Looking implies a passive
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Summer Night Sky
 INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Summer Night Sky What is the difference between observing and looking? As John Rummel said to the Madison Astronomical Society, January 11, 2002: Looking implies a passive exercise
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Summer Night Sky What is the difference between observing and looking? As John Rummel said to the Madison Astronomical Society, January 11, 2002: Looking implies a passive exercise
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Spring Night Sky
 INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Spring Night Sky Your Name: Today s world of clicking and surfing around on the web has probably reduced our ability to patiently, deliberately, and intensely observe. Looking
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Spring Night Sky Your Name: Today s world of clicking and surfing around on the web has probably reduced our ability to patiently, deliberately, and intensely observe. Looking
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky
 INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky Your Name: What is the difference between observing and looking? As John Rummel said to the Madison Astronomical Society, January 11, 2002: Looking implies a passive
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Autumn Night Sky Your Name: What is the difference between observing and looking? As John Rummel said to the Madison Astronomical Society, January 11, 2002: Looking implies a passive
Friday April 21, :30 MDT (7:30 pm) All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited. Ursa Major. Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita
 TAAS Fabulous Fifty Friday April 21, 2017 19:30 MDT (7:30 pm) Ursa Major Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited Evening Events 7:30 pm Meet inside
TAAS Fabulous Fifty Friday April 21, 2017 19:30 MDT (7:30 pm) Ursa Major Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited Evening Events 7:30 pm Meet inside
Sky Quest This event has 12 stations. Print in color, use as many sets as you need for the number of teams you have.
 Sky Quest 2012 This event has 12 stations. Print in color, use as many sets as you need for the number of teams you have. Student response sheet and answer key are at the end. Station 1- Planet Questions
Sky Quest 2012 This event has 12 stations. Print in color, use as many sets as you need for the number of teams you have. Student response sheet and answer key are at the end. Station 1- Planet Questions
Grid lines are drawn at every 15 degrees of declination, and every hour (= 15 degrees at the equator) of right ascension.
 These sky maps were made using the freeware UNIX program "starchart", from Alan Paeth and Craig Counterman, with some postprocessing by Stuart Levy. You re free to use them however you wish. There are
These sky maps were made using the freeware UNIX program "starchart", from Alan Paeth and Craig Counterman, with some postprocessing by Stuart Levy. You re free to use them however you wish. There are
MOREHEAD SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS PLANETARIUM AND SCIENCE CENTER
 SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS 4c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours
SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS 4c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours
Astrochart Links: Pennsic 43: coming July 25
 Astrochart Links: Pennsic 43: coming July 25 Here are the views of the sky each night of Pennsic XLIII, July & August 2014. Stars begin to come out half an hour after sunset, around 9 o'clock to half past,
Astrochart Links: Pennsic 43: coming July 25 Here are the views of the sky each night of Pennsic XLIII, July & August 2014. Stars begin to come out half an hour after sunset, around 9 o'clock to half past,
THE STARS. Information and contacts: -
 THE STARS G. Iafrate (a), M. Ramella (a) and V. Bologna (b) (a) INAF - Astronomical Observatory of Trieste (b) Istituto Comprensivo S. Giovanni Sc. Sec. di primo grado M. Codermatz" - Trieste Information
THE STARS G. Iafrate (a), M. Ramella (a) and V. Bologna (b) (a) INAF - Astronomical Observatory of Trieste (b) Istituto Comprensivo S. Giovanni Sc. Sec. di primo grado M. Codermatz" - Trieste Information
TAAS Fabulous Fifty. Friday July 14, MDT (8:00 pm) All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited.
 TAAS Fabulous Fifty Scorpius Friday July 14, 2017 2000 MDT (8:00 pm) All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita Evening Events 8:00 pm Meet inside the
TAAS Fabulous Fifty Scorpius Friday July 14, 2017 2000 MDT (8:00 pm) All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita Evening Events 8:00 pm Meet inside the
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Spring Night Sky
 INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Spring Night Sky Your Name: Today s world of clicking and surfing around on the web has probably reduced our ability to patiently, deliberately, and intensely observe. Looking
INDEPENDENT PROJECT: The Spring Night Sky Your Name: Today s world of clicking and surfing around on the web has probably reduced our ability to patiently, deliberately, and intensely observe. Looking
The light from the stars we see at night travel great distances to reach Earth. Other than the sun, Proxima Centauriis the next closest
 The light from the stars we see at night travel great distances to reach Earth. Other than the sun, Proxima Centauriis the next closest star. The light that we see from it takes over 4 yearsto reach our
The light from the stars we see at night travel great distances to reach Earth. Other than the sun, Proxima Centauriis the next closest star. The light that we see from it takes over 4 yearsto reach our
Science Papercraft Natural Science Series Rotating Star Chart (section 1) 1. Align front pieces 1 and 2 2. Fold over the tabs and glue in place
 Science Papercraft Natural Science Series Rotating Star Chart (section 1) front piece 1 Canon Science Papercraft Mini-book Natural Science Series Rotating Star Chart You can use this handy rotating star
Science Papercraft Natural Science Series Rotating Star Chart (section 1) front piece 1 Canon Science Papercraft Mini-book Natural Science Series Rotating Star Chart You can use this handy rotating star
WHAT ARE THE CONSTELLATIONS
 CONSTELLATIONS WHAT ARE THE CONSTELLATIONS In popular usage, the term constellation is used to denote a recognizable grouping of stars. Astronomers have redefined the constellations as 88 regions of the
CONSTELLATIONS WHAT ARE THE CONSTELLATIONS In popular usage, the term constellation is used to denote a recognizable grouping of stars. Astronomers have redefined the constellations as 88 regions of the
Seasons & Constellations
 Name Bell Date ACTIVITY: Seasons & Constellations Seasons & Constellations * During autumn, we see the constellation Orion in the dark early morning sky. In winter, we see Orion in the night sky. In summer,
Name Bell Date ACTIVITY: Seasons & Constellations Seasons & Constellations * During autumn, we see the constellation Orion in the dark early morning sky. In winter, we see Orion in the night sky. In summer,
OBSERVING THE NIGHT SKY I
 29:50 Astronomy Lab Evening Sections Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Fall 2010 Name Date Grade /10 OBSERVING THE NIGHT SKY I INTRODUCTION In this session we will observe the night sky. The idea is to
29:50 Astronomy Lab Evening Sections Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Fall 2010 Name Date Grade /10 OBSERVING THE NIGHT SKY I INTRODUCTION In this session we will observe the night sky. The idea is to
drinking straw, protractor, string, and rock. observer on Earth. Sun across the sky on March 21 as seen by an
 1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
HR Diagram Lab. Area 1 Area 4. Area 5. Area 2. Area 6 Area 3
 Name / 65 pts HR Diagram Lab Introduction Some of the greatest advances concerning the nature of stars have come about by comparing their properties using graphs. In the early 1900 s, while studying the
Name / 65 pts HR Diagram Lab Introduction Some of the greatest advances concerning the nature of stars have come about by comparing their properties using graphs. In the early 1900 s, while studying the
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Big Dipper
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Big Dipper
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Cassiopeia Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information.
Cassiopeia Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information.
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Unit 2. Cycles of the Sky
 Unit 2 Cycles of the Sky The Celestial Sphere Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
Unit 2 Cycles of the Sky The Celestial Sphere Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
Using the Star Wheel Laboratory 2
 Objective: Using the Star Wheel Laboratory 2 This laboratory introduces the Star Wheel; which is a common tool used in backyard observing. This tool helps approximate the location of constellations and
Objective: Using the Star Wheel Laboratory 2 This laboratory introduces the Star Wheel; which is a common tool used in backyard observing. This tool helps approximate the location of constellations and
MEASURING ANGLES. name. Fig 2: Tycho Brahe in Denmark. His observations were later used by Kepler.
 name MEASURING ANGLES Fig 1: Islamic Astronomers of the Middle Ages in an Observatory in Istanbul. Fig 2: Tycho Brahe in Denmark. His observations were later used by Kepler. Have you ever thought how we
name MEASURING ANGLES Fig 1: Islamic Astronomers of the Middle Ages in an Observatory in Istanbul. Fig 2: Tycho Brahe in Denmark. His observations were later used by Kepler. Have you ever thought how we
 Astr201 http://www.astro.uvic.ca/~venn/a201.html Astr201: The Search for Life in the Universe 05/09/13 9:25 PM Fall 2013 A general science course designed to be accessible to students not majoring in science.
Astr201 http://www.astro.uvic.ca/~venn/a201.html Astr201: The Search for Life in the Universe 05/09/13 9:25 PM Fall 2013 A general science course designed to be accessible to students not majoring in science.
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Winter
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Winter
TRB 6:4 - Act 3 - Dot to Dot: Patterns in the Night Sky
 TRB 6:4 - Act 3 - Dot to Dot: Patterns in the Night Sky Summary Students will observe and record the location of various constellations over time. Materials Activity A black craft paper, shaped in a large
TRB 6:4 - Act 3 - Dot to Dot: Patterns in the Night Sky Summary Students will observe and record the location of various constellations over time. Materials Activity A black craft paper, shaped in a large
IESO 2011 ASTRONOMY PRACTICAL TEST STOP 11
 IESO 2011 ASTRONOMY PRACTICAL TEST STOP 11 NAME:- COUNTRY: On Friday, September 9, 2011, you will perform 3 trials. Each trial is individual, but in some cases you will have to work together with some
IESO 2011 ASTRONOMY PRACTICAL TEST STOP 11 NAME:- COUNTRY: On Friday, September 9, 2011, you will perform 3 trials. Each trial is individual, but in some cases you will have to work together with some
OUTSIDE LAB 1: Observing the Heavens
 OUTSIDE LAB 1: Observing the Heavens OBJECTIVE: To become familiar with some of the more conspicuous constellations and to observe the motions of stars in the night sky. DISCUSSION: Most people are unfamiliar
OUTSIDE LAB 1: Observing the Heavens OBJECTIVE: To become familiar with some of the more conspicuous constellations and to observe the motions of stars in the night sky. DISCUSSION: Most people are unfamiliar
The Moon & Telescopes: Part 2
 Names: Grade The Moon & Telescopes: Part 2 I have four wings, but cannot fly, I never laugh and never cry; On the same spot I m always found, Toiling away with little sound. What am I? Pre-Lab Quiz Record
Names: Grade The Moon & Telescopes: Part 2 I have four wings, but cannot fly, I never laugh and never cry; On the same spot I m always found, Toiling away with little sound. What am I? Pre-Lab Quiz Record
The Night Sky (Part 1)
 The Night Sky (Part 1) Paul Bergeron Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Utah, Salt Lake City April 12, 2018 Today s Plan History of Astronomy Ancient Astronomy Saturday s Trip Stargazing
The Night Sky (Part 1) Paul Bergeron Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Utah, Salt Lake City April 12, 2018 Today s Plan History of Astronomy Ancient Astronomy Saturday s Trip Stargazing
THE LAYOUT OF THE PLANISPHERE
 CONSTELLATIONS The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes the stars to rise and set each evening. In addition, the orbit of the Earth around the Sun places different regions of the sky in our night-time
CONSTELLATIONS The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes the stars to rise and set each evening. In addition, the orbit of the Earth around the Sun places different regions of the sky in our night-time
Name: AST 114 Date: THE DEEP SKY
 Name: AST 114 Date: THE DEEP SKY The purpose of this lab is to familiarize the student with the use of the planisphere, sky atlas, and coordinate systems for the night sky and introduce the student to
Name: AST 114 Date: THE DEEP SKY The purpose of this lab is to familiarize the student with the use of the planisphere, sky atlas, and coordinate systems for the night sky and introduce the student to
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Starfield Cylinder
 A Collection of Curricula for the TARLAB tarfield Cylinder Including: A Look at the tarfield Cylinder by Joyce Kloncz Motion of the tars by Gary D. Kratzer v. 616-2008 by cience First /TARLAB, 86475 Gene
A Collection of Curricula for the TARLAB tarfield Cylinder Including: A Look at the tarfield Cylinder by Joyce Kloncz Motion of the tars by Gary D. Kratzer v. 616-2008 by cience First /TARLAB, 86475 Gene
FYI. 0 You will need to take notes this information will come in handy when going through this unit and on the cok.
 FYI 0 You will need to take notes this information will come in handy when going through this unit and on the cok. One of the best ways to get started as a backyard astronomer is to learn the constellations.
FYI 0 You will need to take notes this information will come in handy when going through this unit and on the cok. One of the best ways to get started as a backyard astronomer is to learn the constellations.
Ricardo Moreno, Rosa M Ros,
 Preparation of one astronomical observation Ricardo Moreno, Rosa M Ros, Beatriz García, Francis Berthomieu International Astronomical Union Colegio Retamar de Madrid, España Universidad Politécnica de
Preparation of one astronomical observation Ricardo Moreno, Rosa M Ros, Beatriz García, Francis Berthomieu International Astronomical Union Colegio Retamar de Madrid, España Universidad Politécnica de
How would you explain the concept of a day, month, and a year to a small child?
 Space.notebook Studying Space Chapter 18 Astronomy study of objects outside the atmosphere of planet Earth, and of the processes by which these objects interact with one another objects are so large and
Space.notebook Studying Space Chapter 18 Astronomy study of objects outside the atmosphere of planet Earth, and of the processes by which these objects interact with one another objects are so large and
Professor Comet Report. March The Bright Comets for 2010!
 Professor Comet Report March 2010 The Bright Comets for 2010! C/2009 K5 (McNaught) This comet is currently bright at a visual magnitude of 9.1 and expected to reach visual Mag 8.8 by 27 March 2010. Then
Professor Comet Report March 2010 The Bright Comets for 2010! C/2009 K5 (McNaught) This comet is currently bright at a visual magnitude of 9.1 and expected to reach visual Mag 8.8 by 27 March 2010. Then
Teacher Idea Kit for. Virginia Skies. A Space Science Program For Grades K-12. Presented by. Funded in part by:
 Teacher Idea Kit for Virginia Skies A Space Science Program For Grades K-12 Presented by Funded in part by: Virginia Skies Suggested for Grades K-12 Objectives After visiting the planetarium for Virginia
Teacher Idea Kit for Virginia Skies A Space Science Program For Grades K-12 Presented by Funded in part by: Virginia Skies Suggested for Grades K-12 Objectives After visiting the planetarium for Virginia
JSR Year: 2008 PX1511 & PX1512. Planetarium Notes
 Planetarium Notes Purpose I hope you ll find these notes and the visit to the Planetarium a help in identifying particular stars and features in the night sky. If you absorb some of the facts you ll be
Planetarium Notes Purpose I hope you ll find these notes and the visit to the Planetarium a help in identifying particular stars and features in the night sky. If you absorb some of the facts you ll be
The Night Sky in October, 2016
 The Night Sky in October, 2016 At the beginning of October, the Sun will rise at 07:12 BST and set at 18:45 BST. By the end of the month it will rise at 07:07 GMT and set at 16:38 GMT. So let s hope for
The Night Sky in October, 2016 At the beginning of October, the Sun will rise at 07:12 BST and set at 18:45 BST. By the end of the month it will rise at 07:07 GMT and set at 16:38 GMT. So let s hope for
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Summer
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Summer
The American Association of Amateur Astronomers
 www.astromax.com A Special Publication of The American Association of Amateur Astronomers Messier Marathon 2005 Maps and Recording Sheets Primary Date: March 12-13, 2005 Alternate Dates: March 5-6 and
www.astromax.com A Special Publication of The American Association of Amateur Astronomers Messier Marathon 2005 Maps and Recording Sheets Primary Date: March 12-13, 2005 Alternate Dates: March 5-6 and
What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year?
 LESSON 3 What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year? From this vantage point, you can see the moon, sun, stars, and Earth. From Earth s surface, there are patterns to how the sun, moon, and stars appear in
LESSON 3 What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year? From this vantage point, you can see the moon, sun, stars, and Earth. From Earth s surface, there are patterns to how the sun, moon, and stars appear in
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH OCTOBER 2017
 WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH OCTOBER 2017 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart on the last page is included for printing off and use outside The chart above shows the night
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH OCTOBER 2017 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart on the last page is included for printing off and use outside The chart above shows the night
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Little
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Little
STAR PROPERTIES. How Many Stars in Leo? How Many Stars in Orion? How Many Stars in Ursa Major? How Many Stars in Gemini? 4/30/15.
 4/30/15 Contela7ons STAR PROPERTIES How Many Stars in Orion? 25 8 100 >1,000,000 50 21 100 >1,000,000 Scorpius Canis Minor Canis Major Leo How Many Stars in Leo? 25 16 100 >1,000,000 How Many Stars in
4/30/15 Contela7ons STAR PROPERTIES How Many Stars in Orion? 25 8 100 >1,000,000 50 21 100 >1,000,000 Scorpius Canis Minor Canis Major Leo How Many Stars in Leo? 25 16 100 >1,000,000 How Many Stars in
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Big Dipper
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Big Dipper
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Astronomy and Night time Orienteering Private property near War Eagle Mill Cost: $12 per participant
 Astronomy and Night time Orienteering March 18-20, 2016 Private property near War Eagle Mill Cost: $12 per participant (Registration open to all Boy Scout Troops) This Guide is provided to help Youth and
Astronomy and Night time Orienteering March 18-20, 2016 Private property near War Eagle Mill Cost: $12 per participant (Registration open to all Boy Scout Troops) This Guide is provided to help Youth and
Local Coordinates. These are centered upon you, the observer.
 Astronomy 30, Observing #3 Name: Lab Partners: Date: Materials: This lab, with the star chart completed from the pre-lab. Some sheets of paper for sketches. A pencil with eraser. A small flashlight, ideally
Astronomy 30, Observing #3 Name: Lab Partners: Date: Materials: This lab, with the star chart completed from the pre-lab. Some sheets of paper for sketches. A pencil with eraser. A small flashlight, ideally
Introduction to the sky
 Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Little
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Little
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Astronomy Club of Asheville January 2016 Sky Events
 January 2016 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Planet Highlights - page 7 All 5 Naked-Eye Planets in the Dawn Sky - page 10 Moon Phases - page 11 Earth Reaches Perihelion on Jan. 4 - page 12 Quadrantid
January 2016 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Planet Highlights - page 7 All 5 Naked-Eye Planets in the Dawn Sky - page 10 Moon Phases - page 11 Earth Reaches Perihelion on Jan. 4 - page 12 Quadrantid
Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter
 Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter 8 (Neutron Stars), keep for Exam 4. Background: Sections
Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter 8 (Neutron Stars), keep for Exam 4. Background: Sections
Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon.
 Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon https://www.lpi.usra.edu/features/012419/oldest-rock/ Study Points Predict the approximate time of day/night you should look for first quarter
Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon https://www.lpi.usra.edu/features/012419/oldest-rock/ Study Points Predict the approximate time of day/night you should look for first quarter
Today in Space News: Space.com story. More info from NASA. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
 Today in Space News: Space.com story More info from NASA Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS Study Points (marked with *) Describe positions of stars, Moon, Sun on the sky using direction and altitude. Do this
Today in Space News: Space.com story More info from NASA Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS Study Points (marked with *) Describe positions of stars, Moon, Sun on the sky using direction and altitude. Do this
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
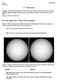 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Date: 5. The bright stars Vega, Deneb, and Altair form A) the summer triangle. B) the winter triangle. C) the Big Dipper. D) Orion, the Hunter.
 Name: Date: 1. If there are about 6000 stars in the entire sky that can be seen by the unaided human eye, about how many stars would be seen at a particular instant on a given dark night from a single
Name: Date: 1. If there are about 6000 stars in the entire sky that can be seen by the unaided human eye, about how many stars would be seen at a particular instant on a given dark night from a single
North Carolina Science Olympiad Elementary Division 2010 Sky Quest. Sky Quest. NCSO Sample Event 2010 Elementary Tournament Grade 3 Goal 3
 NCSO Sample Event 2010 Elementary Tournament Grade 3 Goal 3 STATION 1 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the inner planets? a. Earth b. Neptune c. Venus d. Mercury 2. Which planet is famous for its
NCSO Sample Event 2010 Elementary Tournament Grade 3 Goal 3 STATION 1 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the inner planets? a. Earth b. Neptune c. Venus d. Mercury 2. Which planet is famous for its
Thank you for not chewing gum or anything else. January 31, Daily Objective: Today we will identify typical objects in our night sky.
 Thank you for not chewing gum or anything else Materials: Pencil Notebook/Folder January 31, 2014 Agenda: Bell work Constellations Daily Objective: Today we will identify typical objects in our night sky.
Thank you for not chewing gum or anything else Materials: Pencil Notebook/Folder January 31, 2014 Agenda: Bell work Constellations Daily Objective: Today we will identify typical objects in our night sky.
Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations
 Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations Last lecture Galaxies are the main building blocks of the universe. Consists of few billions to hundreds of billions of stars, gas clouds (nebulae), star clusters,
Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations Last lecture Galaxies are the main building blocks of the universe. Consists of few billions to hundreds of billions of stars, gas clouds (nebulae), star clusters,
Space Test Review. Unit Test on Thursday April 17
 Space Test Review Unit Test on Thursday April 17 True/False 1. A(n) asteroid is a massive collection of gases in space that emits large amounts of energy. 2. A(n) moon is a large, round celestial object
Space Test Review Unit Test on Thursday April 17 True/False 1. A(n) asteroid is a massive collection of gases in space that emits large amounts of energy. 2. A(n) moon is a large, round celestial object
Index. Cambridge University Press Basics: Getting Started in Recreational Astronomy Paul E. Kinzer. Index.
 (Italics indicate an illustration; bold print indicates an entry in the glossary.) aberration 33, 35, 39, 65, 107, 111 achromatic refractor see telescope afocal see astrophotography air-spaced achromat
(Italics indicate an illustration; bold print indicates an entry in the glossary.) aberration 33, 35, 39, 65, 107, 111 achromatic refractor see telescope afocal see astrophotography air-spaced achromat
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH MAY 2018
 WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH MAY 2018 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart on the last page is included for printing off and use outside The chart above shows the whole night
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH MAY 2018 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart on the last page is included for printing off and use outside The chart above shows the whole night
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
2. The diagram below represents the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer at 65 N on March 21.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH - NOVEMBER 2015
 WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH - NOVEMBER 2015 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart above shows the night sky as it appears on 15 th November at 9 o clock in the evening Greenwich
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH - NOVEMBER 2015 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart above shows the night sky as it appears on 15 th November at 9 o clock in the evening Greenwich
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH - OCTOBER 2015
 WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH - OCTOBER 2015 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart above shows the night sky as it appears on 15 th October at 10 o clock in the evening British
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH - OCTOBER 2015 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart above shows the night sky as it appears on 15 th October at 10 o clock in the evening British
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. The Coathanger
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. The Coathanger
Goal - to understand what makes supernovae shine (Section 6.7).
 Wednesday, March 11, 2015 (Class Friday) Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A) Background in Chapters 3, 4, 5. Background:
Wednesday, March 11, 2015 (Class Friday) Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A) Background in Chapters 3, 4, 5. Background:
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Little
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Little
Astronomy Club of Asheville March 2018 Sky Events
 March 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Close Conjunction of Venus and Mercury page 5 The Crescent Moon Joins Venus and Mercury page 6 A Crescent Moon Pairs with Aldebaran page 7 Planet Highlights
March 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Close Conjunction of Venus and Mercury page 5 The Crescent Moon Joins Venus and Mercury page 6 A Crescent Moon Pairs with Aldebaran page 7 Planet Highlights
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Engagement
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH FEBRUARY 2016
 WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH FEBRUARY 2016 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart above shows the night sky as it appears on 15 th February at 21:00 (9 o clock) in the evening
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH FEBRUARY 2016 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart above shows the night sky as it appears on 15 th February at 21:00 (9 o clock) in the evening
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Big Dipper
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Big Dipper
Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018
 1 Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018 2 What is your year in school? A. New freshman B. Returning freshman C. Sophomore D. Junior E. Senior F. I ve been here, like, forever 3 What is your major?
1 Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018 2 What is your year in school? A. New freshman B. Returning freshman C. Sophomore D. Junior E. Senior F. I ve been here, like, forever 3 What is your major?
365 STARRY NIGHTS BY CHET RAYMO DETAILED CONTENTS
 JANUARY 1 Winter Hexagon Zenith, Winter Hexagon 2 Orion Orion s Belt 3 Celestial Equator 4 Celestial Sphere, Arabic Names 5 Celestial Sphere, Degree Measurements 6 7 Turning of the Stars (24 h = 360 o
JANUARY 1 Winter Hexagon Zenith, Winter Hexagon 2 Orion Orion s Belt 3 Celestial Equator 4 Celestial Sphere, Arabic Names 5 Celestial Sphere, Degree Measurements 6 7 Turning of the Stars (24 h = 360 o
What Objects Are Part of the Solar System?
 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Lesson 1 Quiz Josleen divided some of the planets into two main groups. The table below shows how she grouped them. Paul created a poster showing the solar system.
What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Lesson 1 Quiz Josleen divided some of the planets into two main groups. The table below shows how she grouped them. Paul created a poster showing the solar system.
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Make Edits
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. Make Edits
Modern Astronomy Review #1
 Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Science Period. Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7
 Name: Date: Science Period Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7 Directions: Write the letter of the BEST answer on the appropriate space on the answer sheet. 2 points each 1.The model in which SUN is
Name: Date: Science Period Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7 Directions: Write the letter of the BEST answer on the appropriate space on the answer sheet. 2 points each 1.The model in which SUN is
Exploring the Night Sky: Star Charts and Stellarium
 Names: Grade Exploring the Night Sky: Charts and Stellarium Pre-Lab Quiz Record you team s answer as well as your reasonings and explanations. 1. 2. 3. 4. Part 1: Using a SC001 Constellation Chart Coordinates
Names: Grade Exploring the Night Sky: Charts and Stellarium Pre-Lab Quiz Record you team s answer as well as your reasonings and explanations. 1. 2. 3. 4. Part 1: Using a SC001 Constellation Chart Coordinates
