Observings of The Sun
|
|
|
- Bonnie Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 29:50 Astronomy Lab #9 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Name Partner(s) Date Grade Category Max Points Points Received On Time 5 Printed Copy 5 Lab Work 90 Total 100 Observings of The Sun 1. Introduction The Sun is our prototype of a MAIN SEQUENCE star, and it is has provided us with much of what we know about stars in general. In addition, the Sun is the dominant object in the sky, and many of its characteristics are among the most interesting phenomena in astronomy. Examples are SUNSPOTS, PROMINENCES (huge arcs of material suspended above the surface of the Sun by magnetic fields) and SOLAR FLARES. Prominences can be seen in absorption on the disk of the Sun as long, dark lines called FILAMENTS. This laboratory is well equipped for observations of the Sun, and it will provide students with a chance to make real time observations of the Sun in an observatory setting. The Sun is an interesting object to study in a telescope, because it changes from month to month and day to day. Sometimes it even changes from one minute to the next. Observations this year will be made at the time of SOLAR MINIMUM, when surface features like sunspots are rare. Try and check out the Sun again in 5 years, when it has swung around to the maximum state. A general rule is to never directly look at the Sun through a telescope. Even looking directly at the Sun with the naked eye can damage the eye. Sunlight intensified through a telescope can cause permanent damage to the eye. The telescopes used in this project are perfectly safe, due to carefully engineered filters employed to reduce solar light to safe levels. If you are interested in solar observations of your own, either 1
2 use a telescope to project the Sunʼs image on a screen, or buy a special solar telescope. Make sure to get a good one, such as that used in this exercise. There are two types of observation which will be made in this weekʼs project. Observations will be made at the eyepiece of a specialized telescope for solar observations called a PERSONALIZED SOLAR TELESCOPE made by the Coronado Filters Company. More will be said about this telescope in Section 2. These observations will be made during the regular lab period, although students are certainly welcome and encouraged to return for subsequent observations. Additional observations will be made with solar data from research observatories available online on the internet. Real-time, or near-real-time images of the Sun are available from the NATIONAL SOLAR OBSERVATORY at Sunspot, New Mexico ( and the SOHO spacecraft approximately a million kilometers out in space in the direction of the Sun ( 2. Daly Observatory Images During the next week, download an image of the Sun in hydrogen alpha from the National Solar Observatory or an ultraviolet image of the Sun from the SOHO spacecraft. Examine these images and compare them with those you made on the rooftop. You can also examine white light images from the NSO or Big Bear, or the SOHO spacecraft. Accurately sketch any important features and give each an appropriate label. Make sure to record the date and time of your observations, as you will need this information for the final section of this lab. You will be required to do this 4 times over the next week. If you use Images from different sources, make sure you have properly rotated each image so your sources match orientations. 2
3 3. Measuring Solar Rotation If you pick a feature on the solar surface, such as a sunspot or filament, and watch it over a period of several days, you will see it move across the solar disk from east to west. By measuring the rate of change of the feature with respect to time, you can determine the angular speed of rotation of the Sun, and thus its period. 3
4 The steps involved in measuring the angular speed of the Sun are as follows. 1. For each day, note the location of a solar feature that was visible for a majority of your observations. This feature should follow a constant line of LATITUDE on your images. 2. Record LONGITUDE (θ) of the feature in Table 2 found below. Use negative numbers for θ if the feature is to the left (east) of the center and positive values of θ if it is to the right (west). For many of your measurements you will need to estimate the position between grid spaces. Do the best you can. 3. Make a graph in which you plot theta as a function of time in days from the start of your observation. Each observation will be separated by 1.00 days if you make your observations at the same time each day. If you make observations at different times (i.e. at 2PM one day and 9 AM) the next, correct your data appropriately. 4. To account for the earth s motion between your observations, add 1 degree per day to your longitude measurements before you plot them. This needs to be done to effectively measure the sidereal rotation period of the Sun. 5. When you have plotted all of your data points, draw the line through them. The slope of this line will be the angular rotation speed of the Sun, and will have units of degrees/day. This final value for the rotational speed of the Sun can be denoted by the variable W, and has units of degrees/day. Do all of your calculations in the space provided. 6. Finally, the rotational period T of the Sun is given by If there are several features on the surface of the Sun, see if you get the same value for W and T for features at different solar latitudes. TABLE 2 - SOLAR FEATURE POSITIONS DATE AND TIME OF DAY THETA(DEGREES) CORRECTED THETA 4
5 FIGURE 3 - SOLAR FEATURE PLOT 5
6 TABLE 3 - SOLAR ROTATION CALCULATION SLOPE T (PERIOD) 6
PHYS133 Lab 6 Sunspots and Solar Rotation
 PHYS133 Lab 6 Sunspots and Solar Rotation Goals: Select a series of images with sunspots suitable for measurement. View an animation of the images showing the motion of the spots as the Sun rotates. Devise
PHYS133 Lab 6 Sunspots and Solar Rotation Goals: Select a series of images with sunspots suitable for measurement. View an animation of the images showing the motion of the spots as the Sun rotates. Devise
The Sun. Never look directly at the Sun, especially NOT through an unfiltered telescope!!
 The Sun Introduction We will meet in class for a brief discussion and review of background material. We will then go outside for approximately 1 hour of telescope observing. The telescopes will already
The Sun Introduction We will meet in class for a brief discussion and review of background material. We will then go outside for approximately 1 hour of telescope observing. The telescopes will already
Term Project PHYS Solar Rotation
 Term Project PHYS 1070.03 Solar Rotation Due Date: May 19 th, 2009 (11:30am, in class) Introduction: The objective of this term project is to determine the solar rotation period by using photos of the
Term Project PHYS 1070.03 Solar Rotation Due Date: May 19 th, 2009 (11:30am, in class) Introduction: The objective of this term project is to determine the solar rotation period by using photos of the
Prelab 7: Sunspots and Solar Rotation
 Name: Section: Date: Prelab 7: Sunspots and Solar Rotation The purpose of this lab is to determine the nature and rate of the sun s rotation by observing the movement of sunspots across the field of view
Name: Section: Date: Prelab 7: Sunspots and Solar Rotation The purpose of this lab is to determine the nature and rate of the sun s rotation by observing the movement of sunspots across the field of view
The information you need will be on the internet. Please label your data with the link you used, in case we need to look at the data again.
 Solar Activity in Many Wavelengths In this lab you will be finding the sidereal rotation period of the Sun from observations of sunspots, you will compare the lifetimes of larger and smaller sunspots,
Solar Activity in Many Wavelengths In this lab you will be finding the sidereal rotation period of the Sun from observations of sunspots, you will compare the lifetimes of larger and smaller sunspots,
Student s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere
 Student s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere Name Date Introduction The Sun as you may already know, is not a solid body. It is a massive body of gas constantly
Student s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere Name Date Introduction The Sun as you may already know, is not a solid body. It is a massive body of gas constantly
Using This Flip Chart
 Using This Flip Chart Sunspots are the first indicators that a storm from the Sun is a possibility. However, not all sunspots cause problems for Earth. By following the steps in this flip chart you will
Using This Flip Chart Sunspots are the first indicators that a storm from the Sun is a possibility. However, not all sunspots cause problems for Earth. By following the steps in this flip chart you will
1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths
 1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths 1.3k demonstrate an understanding of the appearance of the Sun at different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including
1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths 1.3k demonstrate an understanding of the appearance of the Sun at different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including
Lecture Tutorial: Measuring the Frequency and Period of Sunspots
 Lecture Tutorial: Measuring the Frequency and Period of Sunspots Description: This data analysis activity requires students to analyze sunspots on NASA s SOHO coronagraph images to make meaning of cyclical
Lecture Tutorial: Measuring the Frequency and Period of Sunspots Description: This data analysis activity requires students to analyze sunspots on NASA s SOHO coronagraph images to make meaning of cyclical
Student s guide CESAR Science Case Rotation period of the Sun and the sunspot activity
 Student s guide CESAR Science Case Rotation period of the Sun and the sunspot activity Name Date Introduction As you may know, the Sun is a luminous globe among many, consisting of hot gas that provides
Student s guide CESAR Science Case Rotation period of the Sun and the sunspot activity Name Date Introduction As you may know, the Sun is a luminous globe among many, consisting of hot gas that provides
Astronomy 101 Lab: Solar Observing
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Solar Observing Pre-Lab Assignment: In this lab, you will determine the rotation rate of the Sun, determine the speed of material ejected from the Sun in a coronal mass ejection,
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Solar Observing Pre-Lab Assignment: In this lab, you will determine the rotation rate of the Sun, determine the speed of material ejected from the Sun in a coronal mass ejection,
HELIOSTAT III - THE SOLAR CHROMOSPHERE
 HELIOSTAT III - THE SOLAR CHROMOSPHERE SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will observe, identify, and sketch features that appear in the solar chromosphere. With luck, you may have the opportunity to watch a solar
HELIOSTAT III - THE SOLAR CHROMOSPHERE SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will observe, identify, and sketch features that appear in the solar chromosphere. With luck, you may have the opportunity to watch a solar
19 The Sun Introduction. Name: Date:
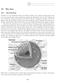 Name: Date: 19 The Sun 19.1 Introduction The Sun is a very important object for all life on Earth. The nuclear reactions that occur in its core produce the energy required by plants and animals for survival.
Name: Date: 19 The Sun 19.1 Introduction The Sun is a very important object for all life on Earth. The nuclear reactions that occur in its core produce the energy required by plants and animals for survival.
Observing the Sun Physics 107 Lab
 Name: Date: Observing the Sun Physics 107 Lab In this activity, you will use a solar telescope called a Sunspotter to observe the motion of the Sun. From watching its progress across the screen, you will
Name: Date: Observing the Sun Physics 107 Lab In this activity, you will use a solar telescope called a Sunspotter to observe the motion of the Sun. From watching its progress across the screen, you will
Tracking Sunspots. Overview: Objectives: Lesson Preparation: Procedure: Details. Materials. Standards
 Tracking Sunspots Overview: Students will examine sunspots and track them at different latitudes on the Sun. This activity is adapted from the Tracking Sunspots activity on NASA s Solar and Heliocentric
Tracking Sunspots Overview: Students will examine sunspots and track them at different latitudes on the Sun. This activity is adapted from the Tracking Sunspots activity on NASA s Solar and Heliocentric
Motion of the Sky Prelab
 Motion of the Sky Prelab 1. What is the definition of a Sidereal Day? How does this differ from a Solar Day? What are the lengths of the two in hours and minutes? Include a diagram to illustrate the difference.
Motion of the Sky Prelab 1. What is the definition of a Sidereal Day? How does this differ from a Solar Day? What are the lengths of the two in hours and minutes? Include a diagram to illustrate the difference.
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3. Sun
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 1.25 Hours What s important in this lesson: Sun demonstrate an understanding of the structure, and nature of our solar system investigate the
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 1.25 Hours What s important in this lesson: Sun demonstrate an understanding of the structure, and nature of our solar system investigate the
OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION
 Name(s) Section Day/Time OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION Fill in either Part 1 or Part 2. Part I. SOLO OBSERVER I will do the observing project by myself. I will not copy someone else's paper or show
Name(s) Section Day/Time OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION Fill in either Part 1 or Part 2. Part I. SOLO OBSERVER I will do the observing project by myself. I will not copy someone else's paper or show
Sun s differential rotation. Student s Guide Advanced Level CESAR s Science Case
 Student s Guide Advanced Level Introduction Unlike the Earth, the Sun is not a rigid body. As it s a non rigid body, different parts of the Sun may rotate at different speeds, and they actually do so.
Student s Guide Advanced Level Introduction Unlike the Earth, the Sun is not a rigid body. As it s a non rigid body, different parts of the Sun may rotate at different speeds, and they actually do so.
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
Outline. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Earth Sun comparison. Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned.
 Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned. Next homework due Oct 24 th. I will not be here on Wednesday, but Paul Ricker will present the lecture! My Tuesday
Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned. Next homework due Oct 24 th. I will not be here on Wednesday, but Paul Ricker will present the lecture! My Tuesday
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 786 Level 870L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.16.17 Word Count 786 Level 870L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.16.17 Word Count 786 Level 870L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
Sun s rotation period. Student s Guide Intermediate Level CESAR s Science Case
 Student s Guide Intermediate Level Introduction Like the Earth, the Sun moves. Sun s main movement is a rotation over its axis. In this science case we will look at Sun images and try to determine how
Student s Guide Intermediate Level Introduction Like the Earth, the Sun moves. Sun s main movement is a rotation over its axis. In this science case we will look at Sun images and try to determine how
The Project. National Schools Observatory
 Sunspots The Project This project is devised to give students a good understanding of the structure and magnetic field of the Sun and how this effects solar activity. Students will work with sunspot data
Sunspots The Project This project is devised to give students a good understanding of the structure and magnetic field of the Sun and how this effects solar activity. Students will work with sunspot data
Understanding Positional Astronomy Part 2 Celestial Co-ordinates Difficulty: Intermediate
 Exercise: Understanding Positional Astronomy Part 2 Celestial Co-ordinates Difficulty: Intermediate Objectives In Part 1 you learned about Celestial Sphere and how the stars appear to move across the night
Exercise: Understanding Positional Astronomy Part 2 Celestial Co-ordinates Difficulty: Intermediate Objectives In Part 1 you learned about Celestial Sphere and how the stars appear to move across the night
Solar Observing Curriculum Guide
 Solar Observing Curriculum Guide Developed by: Erek Alper Adapted from: Astronomy 1 Solar Observing Lab http://www.dartmouth.edu/~gk12 Overview The Sun, the source of all life on Earth, is a dynamic, changing
Solar Observing Curriculum Guide Developed by: Erek Alper Adapted from: Astronomy 1 Solar Observing Lab http://www.dartmouth.edu/~gk12 Overview The Sun, the source of all life on Earth, is a dynamic, changing
Sun s rotation period. Teacher s Guide - Intermediate Level CESAR s Science Case
 Teacher s Guide - Intermediate Level Introduction This is the teacher s guide for. Note that this guide does not contain full instructions to successfully develop the science case, those can be found at
Teacher s Guide - Intermediate Level Introduction This is the teacher s guide for. Note that this guide does not contain full instructions to successfully develop the science case, those can be found at
BU IL D A SU NSPO T VIEW ER
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop Educator Version BU IL D A SU NSPO T VIEW ER How
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop Educator Version BU IL D A SU NSPO T VIEW ER How
Transit of Mercury Lab: Motion and Shadows in the Sky. A Lab for Upper Elementary Students. Educator Instructions
 Transit of Mercury Lab: Motion and Shadows in the Sky A Lab for Upper Elementary Students Educator Instructions What follows is a lab experience developed for upper elementary students by Katherine Benson
Transit of Mercury Lab: Motion and Shadows in the Sky A Lab for Upper Elementary Students Educator Instructions What follows is a lab experience developed for upper elementary students by Katherine Benson
MOREHEAD SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS PLANETARIUM AND SCIENCE CENTER
 SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS 4c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours
SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES FOR BOY SCOUTS 4c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours
Goals of this course. Welcome to Stars, Galaxies & the Universe. Grading for Stars, Galaxies & Universe. Other things you need to know: Course Website
 Welcome to Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Grading for Stars, Galaxies & Universe One-hour exams (3 exams, dates on syllabus) 300 Final exam (16 December 2010) 150 Homework (10 of 12 ICON assignments) 100
Welcome to Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Grading for Stars, Galaxies & Universe One-hour exams (3 exams, dates on syllabus) 300 Final exam (16 December 2010) 150 Homework (10 of 12 ICON assignments) 100
ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORK SHEET BYU MERIT BADGE POWWOW
 ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORK SHEET BYU MERIT BADGE POWWOW Revision July 2013 Scout s Name Instructor s Name Scout s Address City State Instructions 1) The Scout is to review the merit badge book before the
ASTRONOMY MERIT BADGE WORK SHEET BYU MERIT BADGE POWWOW Revision July 2013 Scout s Name Instructor s Name Scout s Address City State Instructions 1) The Scout is to review the merit badge book before the
Astronomy Chapter 12 Review
 Astronomy Chapter 12 Review Approximately how massive is the Sun as compared to the Earth? A. 100 times B. 300 times C. 3000 times D. 300,000 times E. One million times Approximately how massive is the
Astronomy Chapter 12 Review Approximately how massive is the Sun as compared to the Earth? A. 100 times B. 300 times C. 3000 times D. 300,000 times E. One million times Approximately how massive is the
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
 Name: Lab Partner: Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Edited by Lucy Kulbago, John Carroll University 11/24/2008
Name: Lab Partner: Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Edited by Lucy Kulbago, John Carroll University 11/24/2008
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
The 2017 Solar Eclipse in Georgia and the Carolinas. Michael A. Covington, Ph.D. Senior Research Scientist Emeritus The University of Georgia
 The 2017 Solar Eclipse in Georgia and the Carolinas Michael A. Covington, Ph.D. Senior Research Scientist Emeritus The University of Georgia You are welcome to use and redistribute this presentation provided
The 2017 Solar Eclipse in Georgia and the Carolinas Michael A. Covington, Ph.D. Senior Research Scientist Emeritus The University of Georgia You are welcome to use and redistribute this presentation provided
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
Spring 2001: The Sun. Equipment:! This write-up, calculator, lab notebook! Data you downloaded from the SOHO website
 Our Sun is a middle-aged, medium sized star, big enough to hold a million Earths. The ancient Greeks thought that the Sun was a perfect sphere of fire. Today we know that the Sun is a variable star that
Our Sun is a middle-aged, medium sized star, big enough to hold a million Earths. The ancient Greeks thought that the Sun was a perfect sphere of fire. Today we know that the Sun is a variable star that
Physics 1401 Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Manual
 Physics 1401 Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Manual Fall 2006 Dr. Keith Mon 5:30-8:30 Wed 2:30-5:30 Thurs 5:30-8:30 Text by R. Thompson, J. Christensen, T. Bykov, and W. Keith, and for the Virtual
Physics 1401 Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Manual Fall 2006 Dr. Keith Mon 5:30-8:30 Wed 2:30-5:30 Thurs 5:30-8:30 Text by R. Thompson, J. Christensen, T. Bykov, and W. Keith, and for the Virtual
An Introduction to Solar Observing:
 An Introduction to Solar Observing: Good Afternoon. Today we are going to review an introduction to observing our nearest star, the Sun. For thousands of years, man has been interested in and inspired
An Introduction to Solar Observing: Good Afternoon. Today we are going to review an introduction to observing our nearest star, the Sun. For thousands of years, man has been interested in and inspired
Contents. Part I Developing Your Skills
 Contents Part I Developing Your Skills 1 Accessing and Developing Your Observing Skills... 3 1.1 Stargazer or Amateur Astronomer?... 3 1.2 Perceptions and Expectations... 7 1.3 Assessing Your Skills and
Contents Part I Developing Your Skills 1 Accessing and Developing Your Observing Skills... 3 1.1 Stargazer or Amateur Astronomer?... 3 1.2 Perceptions and Expectations... 7 1.3 Assessing Your Skills and
OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION
 ASTRONOMY 25 NOON SUN PROJECT P. P. 1 Name(s) Section Day/Time Fill in either Part 1 or Part 2. OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION Part I. SOLO OBSERVER I will do the observing project by myself. I will
ASTRONOMY 25 NOON SUN PROJECT P. P. 1 Name(s) Section Day/Time Fill in either Part 1 or Part 2. OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION Part I. SOLO OBSERVER I will do the observing project by myself. I will
Guidepost. Chapter 08 The Sun 10/12/2015. General Properties. The Photosphere. Granulation. Energy Transport in the Photosphere.
 Guidepost The Sun is the source of light an warmth in our solar system, so it is a natural object to human curiosity. It is also the star most easily visible from Earth, and therefore the most studied.
Guidepost The Sun is the source of light an warmth in our solar system, so it is a natural object to human curiosity. It is also the star most easily visible from Earth, and therefore the most studied.
Gnomon (a thin, round stick at least a foot long and capable of being put into the ground or stood up vertically)
 Name: Partner(s): Lab #3 Celestial Navigation Due 7/2 Objectives In this lab you will take measurements of the sun s motion around noon and the north star s position in the sky. You will use this data
Name: Partner(s): Lab #3 Celestial Navigation Due 7/2 Objectives In this lab you will take measurements of the sun s motion around noon and the north star s position in the sky. You will use this data
BU IL D A SU NSPO T VIEW ER
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop Family Version BU IL D A SU NSPO T VIEW ER How can
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop Family Version BU IL D A SU NSPO T VIEW ER How can
The principle of geometrical parallax
 The principle of geometrical parallax One of the hardest things to do in astronomy is to determine how far away things are. Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it s an intrinsically
The principle of geometrical parallax One of the hardest things to do in astronomy is to determine how far away things are. Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it s an intrinsically
Solar Eclipses. A brief overview
 Solar Eclipses A brief overview Solar eclipses: the big picture This drawing shows how the Sun, Moon and Earth line up during a solar eclipse. The shadow area where you could see a total eclipse is only
Solar Eclipses A brief overview Solar eclipses: the big picture This drawing shows how the Sun, Moon and Earth line up during a solar eclipse. The shadow area where you could see a total eclipse is only
THE PERIOD OF ROTATION OF THE SUN
 THE PERIOD OF ROTATION OF THE SUN Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 11: Circ.Version 1.0 Department of Physics Gettysburg College Gettysburg,
THE PERIOD OF ROTATION OF THE SUN Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 11: Circ.Version 1.0 Department of Physics Gettysburg College Gettysburg,
Mercury Transit Viewer s Guide
 Mercury Transit Viewer s Guide the publishers of May 09, 2016 http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/hotshots/2003_05_07 On May 09, 2016, amateur astronomers with small telescopes and solar filters will be able
Mercury Transit Viewer s Guide the publishers of May 09, 2016 http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/hotshots/2003_05_07 On May 09, 2016, amateur astronomers with small telescopes and solar filters will be able
Obtain an optical "bench" setup (there should be three sliding mounts on the calibrated horizontal bar. The setup is shown in the diagram below.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 4: Telescopes and spectroscopy Once the various focal issues are resolved, magnification of a small image is a significant consideration for a telescope. Though a planet
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 4: Telescopes and spectroscopy Once the various focal issues are resolved, magnification of a small image is a significant consideration for a telescope. Though a planet
Astronomy 1 Introductory Astronomy Spring 2014
 Astronomy 1 Introductory Astronomy Spring 2014 Lab 5: Observing the Sky pt. 2 Quick overview Meet at 8 p.m. in Science Center Room 187. We will go up to the roof from there, and make several different
Astronomy 1 Introductory Astronomy Spring 2014 Lab 5: Observing the Sky pt. 2 Quick overview Meet at 8 p.m. in Science Center Room 187. We will go up to the roof from there, and make several different
Chapter 24: Studying the Sun. 24.3: The Sun Textbook pages
 Chapter 24: Studying the Sun 24.3: The Sun Textbook pages 684-690 The sun is one of the 100 billion stars of the Milky Way galaxy. The sun has no characteristics to make it unique to the universe. It is
Chapter 24: Studying the Sun 24.3: The Sun Textbook pages 684-690 The sun is one of the 100 billion stars of the Milky Way galaxy. The sun has no characteristics to make it unique to the universe. It is
Name: Lab Partner: Instructor's Signature: Lab Title: Tracking Sunspots. Equipment:
 Name: Lab Partner: Instructor's Signature: Lab Title: Tracking Sunspots Equipment: Scientific calculator, Macintosh computer, and the National Institutes of Health computer program ImageJ. Purpose: In
Name: Lab Partner: Instructor's Signature: Lab Title: Tracking Sunspots Equipment: Scientific calculator, Macintosh computer, and the National Institutes of Health computer program ImageJ. Purpose: In
ASTRONOMICAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS CELESTIAL SPHERE
 ASTRONOMICAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS CELESTIAL SPHERE To the naked eye, stars appear fixed on the sky with respect to one another. These patterns are often grouped into constellations. Angular measurements
ASTRONOMICAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS CELESTIAL SPHERE To the naked eye, stars appear fixed on the sky with respect to one another. These patterns are often grouped into constellations. Angular measurements
Name: Partner(s): 1101 or 3310: Desk # Date: Eclipses. Purpose
 Name: Partner(s): 1101 or 3310: Desk # Date: Purpose Eclipses Describe the orbit of the Moon Explain the differences between the types of solar eclipses Explain the differences between the types of lunar
Name: Partner(s): 1101 or 3310: Desk # Date: Purpose Eclipses Describe the orbit of the Moon Explain the differences between the types of solar eclipses Explain the differences between the types of lunar
The Dancing Lights Program
 The Sun Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program Margaux Krahe Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun is not actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun
The Sun Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program Margaux Krahe Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun is not actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun
Astronomy 154 Lab 4: The Sun. NASA Image comparing the Earth with the Sun. Image from:
 Astronomy 154 Lab 3: The Sun NASA Image comparing the Earth with the Sun. Image from: http://www.universetoday.com/16338/the-sun/ The Sun at the center of our Solar System is a massive ball of Hydrogen,
Astronomy 154 Lab 3: The Sun NASA Image comparing the Earth with the Sun. Image from: http://www.universetoday.com/16338/the-sun/ The Sun at the center of our Solar System is a massive ball of Hydrogen,
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
Classification of Galaxies
 Name: Partner(s): 1102 or 3311: Desk # Date: Classification of Galaxies Purpose Study and classify galaxies Learn how to measure their distance, mass and radius. Equipment Pictures from online lab manual
Name: Partner(s): 1102 or 3311: Desk # Date: Classification of Galaxies Purpose Study and classify galaxies Learn how to measure their distance, mass and radius. Equipment Pictures from online lab manual
The Earth Orbits the Sun Student Question Sheet (Advanced)
 The Earth Orbits the Sun Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge
The Earth Orbits the Sun Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge
Study Points. What is a mare?
 What is a mare? Study Points What causes craters, especially on the Moon? What is the Moon s terminator? Explain why the Moon exhibits phases. Draw the Sun-Earth-Moon system showing the Moon s orbit (not
What is a mare? Study Points What causes craters, especially on the Moon? What is the Moon s terminator? Explain why the Moon exhibits phases. Draw the Sun-Earth-Moon system showing the Moon s orbit (not
Astron 104 Laboratory #7 Sunspots and the Solar Cycle
 Name: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #7 Sunspots and the Solar Cycle Section 9.4 In this exercise, you will observe how the physical appearance of the Sun changes from day to day over the period of one
Name: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #7 Sunspots and the Solar Cycle Section 9.4 In this exercise, you will observe how the physical appearance of the Sun changes from day to day over the period of one
Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Bayesian analysis
 Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Bayesian analysis Schedule for the next week Office hours: Thu 5:00 6:20pm = Deshpande; Fri 10:20 11:40 = Baker + on call Sections A, C = Baker; Sections
Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Bayesian analysis Schedule for the next week Office hours: Thu 5:00 6:20pm = Deshpande; Fri 10:20 11:40 = Baker + on call Sections A, C = Baker; Sections
Answer Key for Exam C
 Answer Key for Exam C 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam C 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B
 Answer Key for Exam B 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Observing Sessions and Lab Activity Reports
 Coconino Community College Astronomy - PHY180 Observing Sessions and Lab Activity Reports The types of activities in this Astronomy program are divided into two groups: 5 Observing Sessions, and 7 Lab
Coconino Community College Astronomy - PHY180 Observing Sessions and Lab Activity Reports The types of activities in this Astronomy program are divided into two groups: 5 Observing Sessions, and 7 Lab
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
 Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 1.1.1 lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 1.1.1 lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Buy-back points tallied and added: 750 points bought-back. Last Withdrawal date: this friday, Oct 31st.
 Announcements HW #3: Available online now. Due in 1 week, Nov 3rd, 11pm. Buy-back points tallied and added: 750 points bought-back. Last Withdrawal date: this friday, Oct 31st. Evening Observing: next
Announcements HW #3: Available online now. Due in 1 week, Nov 3rd, 11pm. Buy-back points tallied and added: 750 points bought-back. Last Withdrawal date: this friday, Oct 31st. Evening Observing: next
Solar Observation Class Project
 Name: School: Grade or Level: Lesson Plan #: Date: Object Solar Observation Class Project The object of this classroom exercise to involve as individuals or as teams, students in the actual astronomical
Name: School: Grade or Level: Lesson Plan #: Date: Object Solar Observation Class Project The object of this classroom exercise to involve as individuals or as teams, students in the actual astronomical
ASTRO Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky
 ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky ABSTRACT Today we will be calibrating your hand as an angular measuring device, and then heading down to the planetarium to see the night sky in motion.
ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky ABSTRACT Today we will be calibrating your hand as an angular measuring device, and then heading down to the planetarium to see the night sky in motion.
Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4)
 Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
ASTRONOMY 25 SUMMER 2017 PROJECT 2: THE HEIGHT OF THE SUN
 Name(s) Section Time ASTRONOMY 25 SUMMER 2017 PROJECT 2: THE HEIGHT OF THE SUN Rules: 1) Do the project by yourself or with one other person. If you want to work with a partner, get an agreement form from
Name(s) Section Time ASTRONOMY 25 SUMMER 2017 PROJECT 2: THE HEIGHT OF THE SUN Rules: 1) Do the project by yourself or with one other person. If you want to work with a partner, get an agreement form from
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2017 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 30 September 2017 Time limit: 50 min
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2017 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 30 September 2017 Time limit: 50 min
Paper Reference. Tuesday 14 June 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Tuesday 14 June 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Items included with question papers
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Tuesday 14 June 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Items included with question papers
Astronomy Merit Badge Workbook
 Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge counselor.
Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge counselor.
Astronomy 122 Outline
 Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 12): Stars Next Class: The Nature of Stars Homework #5 is posted. Nightlabs have started! Stellar properties Parallax (distance) Colors Spectral Classes Music:
Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 12): Stars Next Class: The Nature of Stars Homework #5 is posted. Nightlabs have started! Stellar properties Parallax (distance) Colors Spectral Classes Music:
Astronomy Studio Exercise Geocentric and Heliocentric World Views Guy Worthey
 Astronomy Studio Exercise Geocentric and Heliocentric World Views Guy Worthey We explore in some detail how the geocentric cosmology worked, and what observations caused the adoption of the heliocentric
Astronomy Studio Exercise Geocentric and Heliocentric World Views Guy Worthey We explore in some detail how the geocentric cosmology worked, and what observations caused the adoption of the heliocentric
Stars Above, Earth Below By Tyler Nordgren Laboratory Exercise for Chapter 10
 Name Lab Partners: Section Date Stars Above, Earth Below By Tyler Nordgren Laboratory Exercise for Chapter 10 Equipment: Balloon Ruler THE EXPANDING UNIVERSE Purpose: To create a simple universe and observe
Name Lab Partners: Section Date Stars Above, Earth Below By Tyler Nordgren Laboratory Exercise for Chapter 10 Equipment: Balloon Ruler THE EXPANDING UNIVERSE Purpose: To create a simple universe and observe
KEELE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES Year 1 ASTROPHYSICS LAB. WEEK 1. Introduction
 KEELE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES Year 1 ASTROPHYSICS LAB WEEK 1. Introduction D. E. McLaughlin January 2011 The purpose of this lab is to introduce you to some astronomical terms
KEELE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES Year 1 ASTROPHYSICS LAB WEEK 1. Introduction D. E. McLaughlin January 2011 The purpose of this lab is to introduce you to some astronomical terms
Observing the Sun for Yourself observe/observe.html
 Hands-on activities for use in the classroom. Observing the Sun for Yourself http://solar-center.stanford.edu/ observe/observe.html Classroom Activities Grade Level 3-5* Courtesy of the Stanford Solar
Hands-on activities for use in the classroom. Observing the Sun for Yourself http://solar-center.stanford.edu/ observe/observe.html Classroom Activities Grade Level 3-5* Courtesy of the Stanford Solar
The Sun. 1a. The Photosphere. A. The Solar Atmosphere. 1b. Limb Darkening. A. Solar Atmosphere. B. Phenomena (Sunspots) C.
 The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2006Sep18 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind 3 1a. The
The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2006Sep18 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind 3 1a. The
Lab Title: Parallax and Astronomical Distances. Equipment: Sextant Meter sticks (or tape measures) Calipers Magnetic compasses.
 Lab Title: Parallax and Astronomical Distances Equipment: Sextant Meter sticks (or tape measures) Calipers Magnetic compasses Introduction: Since we cannot travel to most celestial objects in order to
Lab Title: Parallax and Astronomical Distances Equipment: Sextant Meter sticks (or tape measures) Calipers Magnetic compasses Introduction: Since we cannot travel to most celestial objects in order to
Astronomy Mini-Conference Logistics
 Astronomy Mini-Conference Logistics Who: Y all Also sponsored by the Wyoming NASA Space Grant Consortium (they re providing some funds for food-like items) What: Presentation of Posters You will have some
Astronomy Mini-Conference Logistics Who: Y all Also sponsored by the Wyoming NASA Space Grant Consortium (they re providing some funds for food-like items) What: Presentation of Posters You will have some
Angles Lab. name: Part I - How tall is Founders Hall? Astronomical Ideas, Fall 2012
 Angles Lab Haverford College Astronomical Ideas, Fall 2012 name: Collaborators: With this lab, you will get quantitative experience with the basic relationship between angular size, distance, and physical
Angles Lab Haverford College Astronomical Ideas, Fall 2012 name: Collaborators: With this lab, you will get quantitative experience with the basic relationship between angular size, distance, and physical
USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB
 USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB 1. Explain the main differences between using a star wheel and a star chart to find things in the night sky. 2. Explain the terms Hour Angle, Meridian and
USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB 1. Explain the main differences between using a star wheel and a star chart to find things in the night sky. 2. Explain the terms Hour Angle, Meridian and
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
 Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 0.96lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 0.96lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
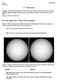 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
The Structure of the Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 How stars work In order to have a stable star, the energy it emits must be the same as it can produce. There must be an equilibrium. The main source of energy of a star it is nuclear fusion, especially
How stars work In order to have a stable star, the energy it emits must be the same as it can produce. There must be an equilibrium. The main source of energy of a star it is nuclear fusion, especially
TELESCOPE OBSERVING. EQUIPMENT: Observatory telescopes, observing forms, and a pencil. Be sure to dress warmly - the observing deck is not heated!
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 161 Telescope Observing TELESCOPE OBSERVING SYNOPSIS: You will view and sketch a number of different astronomical objects through the SBO telescopes. The requirements for credit
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 161 Telescope Observing TELESCOPE OBSERVING SYNOPSIS: You will view and sketch a number of different astronomical objects through the SBO telescopes. The requirements for credit
Astronomy Merit Badge
 Astronomy erit Badge (2013 requirements) 1. Do the following: a. xplain to your counselor the most likely hazards you may encounter while participating in astronomy activities, and what you should do to
Astronomy erit Badge (2013 requirements) 1. Do the following: a. xplain to your counselor the most likely hazards you may encounter while participating in astronomy activities, and what you should do to
ESAC VOSPEC SCIENCE TUTORIAL
 SCIENCE ARCHIVES AND VO TEAM ESAC VOSPEC SCIENCE TUTORIAL COMPARING SPECTRA OF THE SUN AND SIMILAR STARS THEORY SECTION Tutorial created by Luis Sánchez, ESAC SOHO Archive scientist, adapted from the Tracking
SCIENCE ARCHIVES AND VO TEAM ESAC VOSPEC SCIENCE TUTORIAL COMPARING SPECTRA OF THE SUN AND SIMILAR STARS THEORY SECTION Tutorial created by Luis Sánchez, ESAC SOHO Archive scientist, adapted from the Tracking
OBSERVING THE NIGHT SKY I
 29:50 Astronomy Lab Evening Sections Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Fall 2010 Name Date Grade /10 OBSERVING THE NIGHT SKY I INTRODUCTION In this session we will observe the night sky. The idea is to
29:50 Astronomy Lab Evening Sections Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Fall 2010 Name Date Grade /10 OBSERVING THE NIGHT SKY I INTRODUCTION In this session we will observe the night sky. The idea is to
Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY
 Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY Welcome to the Schenectady Museum & Suits-Bueche Planetarium! During this workshop, you will explore the museum, see a show in the planetarium, and try out some other
Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY Welcome to the Schenectady Museum & Suits-Bueche Planetarium! During this workshop, you will explore the museum, see a show in the planetarium, and try out some other
Astronomy 150 K. Nordsieck Spring Exam 1 Solutions. 1. ( T F ) In Madison the North Star, Polaris, is situated almost exactly at the zenith.
 Astronomy 150 K. Nordsieck Spring 2000 Exam 1 Solutions True or False (Circle T or F) 1. ( T F ) In Madison the North Star, Polaris, is situated almost exactly at the zenith. False. Polaris is near the
Astronomy 150 K. Nordsieck Spring 2000 Exam 1 Solutions True or False (Circle T or F) 1. ( T F ) In Madison the North Star, Polaris, is situated almost exactly at the zenith. False. Polaris is near the
INTRODUCTION TO THE TELESCOPE
 INTRODUCTION TO THE TELESCOPE What will you learn in this Lab? For a few of the labs this semester, you will be using an 8-inch Celestron telescope to take observations. This lab will introduce you to
INTRODUCTION TO THE TELESCOPE What will you learn in this Lab? For a few of the labs this semester, you will be using an 8-inch Celestron telescope to take observations. This lab will introduce you to
Venus Project Book, the Galileo Project, GEAR
 1 Venus Project Book, the Galileo Project, GEAR Jeffrey La Favre November, 2013 Updated March 31, 2016 You have already learned about Galileo and his telescope. Recall that he built his first telescopes
1 Venus Project Book, the Galileo Project, GEAR Jeffrey La Favre November, 2013 Updated March 31, 2016 You have already learned about Galileo and his telescope. Recall that he built his first telescopes
Chapter 8 The Sun Our Star
 Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 8 The Sun
Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 8 The Sun
Physical Science Astronomy: Phases of the Moon 2. Science and Mathematics Education Research Group
 F FA ACULTY C U L T Y OF O F EDUCATION E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Physical Science Astronomy: Phases of the Moon 2 Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported
F FA ACULTY C U L T Y OF O F EDUCATION E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Physical Science Astronomy: Phases of the Moon 2 Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported
ASTR 101L: Motion of the Sun Take Home Lab
 Name: CWID: Section: Introduction Objectives This lab is designed to help you understand the Sun s apparent motion in the sky over the course of the year. In Section 2 you are asked to answer some questions
Name: CWID: Section: Introduction Objectives This lab is designed to help you understand the Sun s apparent motion in the sky over the course of the year. In Section 2 you are asked to answer some questions
Before you Sit. Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium
 Before you Sit Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium Evening Observing Observing at the Brooks Observatory: Three different weeks
Before you Sit Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium Evening Observing Observing at the Brooks Observatory: Three different weeks
