Cancellation of the Fifth (SM-4) Hubble Servicing Mission
|
|
|
- Lynne Candice Blankenship
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cancellation of the Fifth (SM-4) Hubble Servicing Mission Executive Summary The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was originally launched aboard the Space Shuttle in 1990, with an as designed mission lifetime of 15 years. Since then the telescope has been serviced or upgraded four times, each requiring a very complex, dedicated Space Shuttle mission and unique HST servicing support equipment. Even before its repair mission in 1993, the HST had generated significant scientific discoveries. The science return from HST has already vastly exceeded the original expectations. NASA plans continued operation of the HST until it can no longer support scientific investigations anticipated to occur in the time frame. The telescope s life may, in fact, be extended if NASA is successful in employing operational techniques to preserve battery and gyroscope functions. Meanwhile, NASA is aggressively investigating innovative ways to extend the science lifetime of the HST for as long as possible, including robotic servicing to provide extension of power storage. Current plans are to safely deorbit the HST by a robotic spacecraft by approximately Although the HST deployment mission and four subsequent servicing missions were successfully conducted, the Columbia tragedy underscored the inherent risk in each and every Space Shuttle mission and reinforced the need for increased ability to deal with all potential contingencies, particularly catastrophic damage to the Orbiter s thermal protection system (TPS). Without the benefit of docking at the ISS many new tools, processes, and techniques would be required for inspection and possible repair of the TPS. More significant would be the requirement to dedicate two Space Shuttles to the mission to ensure astronaut safety. In the event of a significant problem with no safe haven for the astronauts to wait as in ISS missions, a second Shuttle would have to be launched and employ untried and uncertified techniques to perform a rescue. Hence, a Shuttle based HST servicing mission presents known additional risks, and offers few options to respond to serious problems in orbit. Recognizing the increased risks involved in all Shuttle flights following the tragic loss of the Columbia and crew NASA elected to reduce its planned Shuttle manifest to only missions to the International Space Station (ISS). The decision was also made, on the basis of risk, to not pursue a final servicing mission to the HST, but instead to investigate other options to extend the life of the Hubble. Columbia Accident Investigation Board Findings and Impact on Future Missions The Columbia Accident Investigation Board presented NASA with 29 recommendations, 15 of which were required to be completed before the Space Shuttle could return to flight. Highlights of these flight-critical recommendations included elimination of damaging insulation shedding from the external tank -- the cause of the Columbia tragedy -- ascent imaging, on-orbit inspection, and thermal protection system tile and Orbiter leading edge repair. NASA will satisfy all of these recommendations before it launches STS-114, the next Shuttle mission. The Board stressed that the Space 1
2 Shuttle is still a developmental vehicle and that risk and risk mitigation must be treated accordingly. NASA s original vision was to fly the Shuttle to mid-decade or 2020 for a total of more flights. NASA fully accepts the Board s recommendation and balancing mission criticality against possible loss of crew and vehicle, consciously decided to retire the Space Shuttle after the completion of the International Space Station (ISS), recognizing that the best risk mitigation strategy is to fly less. In addition, NASA realizes that a safe haven in space capability is required. This safe haven capability goes beyond compliance with the Columbia Accident Investigation Board recommendations and is designed to increase crew safety during the remaining Space Shuttle missions. Should damage occur to the Shuttle thermal protection system that can not be repaired and that would preclude safe reentry, the crew will be able to shelter at the ISS until another vehicle can be readied for rescue. Agency policy will require each Space Shuttle mission to have backup rescue capability. Safe haven is the ultimate recognition that, while NASA will make the Space Shuttle as safe as possible, the Columbia tragedy has taught us that there are still significant risks inherent in Space Shuttle launch, orbit operation, and reentry. Unique Requirements and Increased Risk in the Hubble Servicing Mission Whereas tools, techniques, and procedures would be similar on each ISS mission; e.g., inspection, thermal protection system repair, safe haven readiness, and rescue scenario, an HST servicing mission would have unique requirements, both on-orbit and in ground processing. Options for dealing with an on-orbit emergency are reduced and decisions for reacting to any emergency would have to be made quickly. These two considerations, and the attendant schedule pressure on the flight crews and support teams, add considerable additional risk. Lack of Significant Safe Haven The areas of additional risk relate to the ability to provide safe haven while inspection, repair and potential rescue are undertaken, and to the procedures for inspection and repair themselves. It has been projected that a typical Space Shuttle flight crew of seven astronauts could stay aboard the ISS for up to ninety days, if warranted, due to an emergency situation on the Space Shuttle. This safe haven capability allows the flight crew and ground teams to consider all options, determine the best course of action, take the time required to understand the cause of the failure and affect repairs, or send the appropriate rescue vehicle with the right equipment to bring the crew home. Clearly, rushing this process would introduce considerable new risk and in the worse case result in the loss of another vehicle. In the case of a Hubble servicing mission, the amount of stay time on orbit is significantly shorter due the limited stores of cryogenic oxygen on the Orbiter. Therefore, other measures would be required. Specifically, a second Space Shuttle on an adjacent launch pad would have to be specially prepared, uniquely configured to launch expeditiously if required to perform a rescue mission. This scenario raises several concerns, addressed in the paragraphs below. 2
3 Unprecedented Double Workload for Ground Launch and Processing Teams Two vehicles would be processed for essentially the same launch date. Any processing delays to one vehicle would require a delay in the second vehicle. The launch countdown for the second launch would begin before the actual launch of the first vehicle. This short time period for assessment is a serious concern -- it would require a highly complex process to be carried out in parallel, and it would not permit thorough assessment by the launch team, the flight control team, and the flight crew. No Changes to Cargo or Vehicle Feasible Because of the very short timeframe between the launch of the first vehicle and the requirement for a rescue flight, no significant changes could reasonably be made to the second vehicle or the cargo. This means that it would not be feasible to change the cargo on the second Space Shuttle, to affect a repair to the first Shuttle, add additional rescue hardware, or make vehicle modifications to avoid whatever situation caused the need for a rescue attempt in the first place. Not having sufficient time to make the appropriate changes to the rescue vehicle or the cargo could add significant risk to the rescue flight crew, or to crew transfer. The whole process would be under acute schedule pressure and undoubtedly many safety and operations waivers would be required. Rescue Mission Space Shuttles routinely dock with the ISS; Soyuz evacuation procedures are well trained. These represent the normal operations mode today supported by extensive training, analysis and documentation. A rescue from the ISS, with multiple hatches, airlocks, and at least one other vehicle available (Soyuz), is much less complex and risky than that required by a stranded Space Shuttle being rescued by a second Space Shuttle. In response to a question by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board, NASA analyzed a hypothetical rescue mission between two Space Shuttles and found that the effort would have required many unproven techniques, such as emergency free-space crew transfer in space suits while performing Space Shuttle to Space Shuttle station-keeping while traveling 17,500 mile per hour above the earth. These major safety risks are not incurred during rescue from the ISS. Tile Survey (expanded inspection requirements) and Thermal Protection System Repair The current inspection method for acreage tile, gear door seals, and the elevon cove is to photograph these areas from the ISS during rendezvous. To support an HST servicing mission, NASA would have to develop a new method for inspecting these critical areas using an Orbiter boom. Unvalidated autonomous boom operations represent an unknown risk. NASA s current planned TPS repair method for an ISSbased repair uses the ISS robotic arm to stabilize an EVA crew person over the worksite. These assets are not available for an HST servicing mission, so NASA would have to develop a single-use alternate method for stabilizing the crewmember. This method would have to provide greater stability than the current ISS option under development to protect both the crewmember and the other TPS areas from additional damage. Such a concept represents a challenging undertaking, which could take 3
4 months or years to develop in order to meet safety and mission assurance standards/requirements. Return to Flight and ISS U.S. Core Complete Timeline In the process of addressing the Columbia Accident Investigation Board recommendations and implementing additional improvements to achieve the safest flight possible, NASA has uncovered a number of problems that had previously gone undetected. The removal and replacement of unsafe hardware has deferred Space Shuttle launch milestones. NASA projects the first opportunity for a Space Shuttle launch to the ISS to be in March Eight flights are scheduled to meet our international commitments, the assembly of the U.S. core segments of the ISS. Given the ISS assembly schedule, the earliest NASA could launch a servicing mission to the HST, based on requirements for daylight launch to fully assess ascent conditions by imagery and thermal constraints when docked to ISS, would be Spring Based on the evaluation of the engineering data on the HST, the lifetime of the Observatory on orbit is ultimately limited by battery life, which may extend in to the timeframe. Scientific operations are limited by gyroscope lifetime that is more difficult to predict. If all of the NASA effort is concentrated on a Shuttle servicing mission, every step in the process must be successful with no allowance for schedule slips. Before launch all of the recommendations of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board must be met. The launch conditions must be perfect, and all tailored HST mission unique components must be in place with very tight schedule constraints. If any of the many elements do not develop as planned, the telescope may cease operations before a successful mission could be mounted. Hubble Space Telescope s Scientific Legacy Not since Galileo turned his telescope towards the heavens in 1610 has any event so changed our understanding of the universe as the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope. From its orbit above Earth s atmosphere, the HST is free from the atmospheric turbulence that all ground-based telescopes must contend. Thus, HST has been able to return images of astounding clarity and sensitivity. HST imaging and spectroscopy have resulted in remarkable scientific achievement, including the determination of the changing rate of expansion of the universe and detailed studies of forming galaxies, black holes, galaxy hosts of gamma-ray bursts and quasars, active galactic nuclei, protostars, planetary atmospheres, and the interstellar and intergalactic medium. Scientific results have significantly surpassed original expectations. By 2005, the HST will have fulfilled every one of its scientific objectives and top-level technical requirements. Moreover, the Hubble will continue to collect observations for several more years. Even after the HST is no longer in service, the rich archive of HST data (already more than 100,000 observations of 20,000 unique targets) will continue to provide new discoveries for the years to come, with full support by NASA for both archive operations and research grants. 4
5 Future Plans for Hubble Space Telescope and Astronomy Astronomy is a critical part of the NASA s exploration initiative. NASA is aggressively investigating innovative ways to extend the science lifetime of the HST for as long as possible, including a possible robotic servicing option. We are receiving several responses to our recently released Request For Information (RFI) on HST End of Mission Alternatives soliciting concepts for robotically-provided battery power extension. Indeed, this option appears to have greater likelihood of success than the possibility of accomplishing all the recommendations of the Board in time for a successful Hubble servicing mission. HST is not NASA s only portal to the stars. It is one of many telescopes used by astronomers to study the universe using various apertures and wavelength bands. Hubble, primarily used for observations of visible light, is one of the four orbital Great Observatories designed for use across the spectrum. The other three include the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory ( ), the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, and the infrared Spitzer Space Telescope. In the years since Hubble was launched with its 2.4-meter aperture, many new ground-based telescopes have been built with larger apertures that enable observations with increasingly higher angular resolution, though subject to the blurring effects of Earth s atmosphere. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) program has been strengthened to assure a 2011 launch date. Once on orbit, this advanced technology infrared telescope will provide insight into the a region of the spectrum where we will be able, like never before, to view the formation of the earliest galaxies. The JWST will build on the successful science of the Hubble via the most advanced instrumentation and a larger 6.5 meter aperture. The following table lists larger optical telescopes now or soon to be available along with Hubble and also several examples of large telescopes available or in development for observations at other wavelengths. Examples of Large Telescope Facilities Available or In Development Radio/MM Infrared Optical +IR Ultraviolet X-Ray Gamma Ray (aperture, meters) VLA Spitzer SALT (11.0) HST Chandra GLAST GBT SOFIA Keck I, II (10.0) GALEX XTE SWIFT ALMA JWST Hobby-Eberly (9.2) XMM-Newton Arecibo HST LBT (8.4 x 2) Astro-E2 FCRAO Subaru (8.3) SWIFT VLBA VLT (8.2 x 3) CSO Gemini (N & S) (8.1) HST (2.4) The HST program has provided a significant amount of funding support for U.S. astronomers; in fact, it is currently providing approximately 20% of all direct grant support. After HST observations have ceased, NASA plans to continue to support ongoing grants and to offer new grant support for HST archival research until a similar grant program is in place for the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope program. 5
6 This will ensure stability to the research community and full use of the rich HST data archive throughout this period of transition. Conclusion The cancellation of HST-SM4 was a difficult decision. HST is producing world-class science. However, NASA cannot justify the additional risk that such a unique mission would entail, based on what must be done to assure greatest protection to the crew. It is increasingly apparent that our choice is to either fully comply with the Columbia Accident Investigation Board report or conduct the servicing mission, but not both. We must be responsible on all future flights and be fully compliant. NASA will continue to aggressively pursue options to extend the science lifetime of the Hubble by means other than Shuttle servicing. NASA will continue to be a major supporter of astronomy in the future as the Agency continues to explore the universe. 6
Hubble Space Telescope: NASA s Plans for a Servicing Mission
 Order Code RS21767 Updated May 23, 2008 Hubble Space Telescope: NASA s Plans for a Servicing Mission Summary Daniel Morgan Analyst in Science and Technology Policy Resources, Science, and Industry Division
Order Code RS21767 Updated May 23, 2008 Hubble Space Telescope: NASA s Plans for a Servicing Mission Summary Daniel Morgan Analyst in Science and Technology Policy Resources, Science, and Industry Division
Challenging Decisions from a Career in Aerospace. AIAA Huntsville Section Michael D. Griffin 8 August 2017
 Challenging Decisions from a Career in Aerospace AIAA Huntsville Section Michael D. Griffin 8 August 2017 Delta 183/Delta Star DoD/SDIO mission to capture phenomenology of rocket plumes on Soviet launch
Challenging Decisions from a Career in Aerospace AIAA Huntsville Section Michael D. Griffin 8 August 2017 Delta 183/Delta Star DoD/SDIO mission to capture phenomenology of rocket plumes on Soviet launch
Human Spaceflight Value Study Was the Shuttle a Good Deal?
 Human Spaceflight Value Study Was the Shuttle a Good Deal? Andy Prince Billy Carson MSFC Engineering Cost Office/CS50 20 October 2016 Purpose Examine the Space Shuttle Program Relative to its Goals and
Human Spaceflight Value Study Was the Shuttle a Good Deal? Andy Prince Billy Carson MSFC Engineering Cost Office/CS50 20 October 2016 Purpose Examine the Space Shuttle Program Relative to its Goals and
HST AND BEYOND EXPLORATION AND THE SEARCH FOR ORIGINS: A VISION FOR ULTRAVIOLET- OPTICAL-INFRARED SPACE ASTRONOMY
 Chapter Ten HST AND BEYOND EXPLORATION AND THE SEARCH FOR ORIGINS: A VISION FOR ULTRAVIOLET- OPTICAL-INFRARED SPACE ASTRONOMY Bibliographic Information: Dressler, Alan, ed., HST and Beyond Exploration
Chapter Ten HST AND BEYOND EXPLORATION AND THE SEARCH FOR ORIGINS: A VISION FOR ULTRAVIOLET- OPTICAL-INFRARED SPACE ASTRONOMY Bibliographic Information: Dressler, Alan, ed., HST and Beyond Exploration
What do we do with the image?
 Astro 150 Spring 2018: Lecture 7 page 1 Reading: Chapter 6, Sect. 6.4; Chapter 14 + assignment posted on Astro 150 website Homework: questions on special reading - answers due in lecture Thursday Exam
Astro 150 Spring 2018: Lecture 7 page 1 Reading: Chapter 6, Sect. 6.4; Chapter 14 + assignment posted on Astro 150 website Homework: questions on special reading - answers due in lecture Thursday Exam
Space Exploration Earth and Space. Project Mercury Courtesy of NASA Images
 Project Mercury 1959-1963 3 Project Mercury 1959-1963 Project Mercury was America s first manned space program. It had three main goals: to orbit a manned spacecraft around Earth; to see if humans could
Project Mercury 1959-1963 3 Project Mercury 1959-1963 Project Mercury was America s first manned space program. It had three main goals: to orbit a manned spacecraft around Earth; to see if humans could
Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument
 Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument Oliver Krause (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg) on behalf of Gillian Wright (Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument Oliver Krause (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg) on behalf of Gillian Wright (Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
Chapter 26. Objectives. Describe characteristics of the universe in terms of time, distance, and organization
 Objectives Describe characteristics of the universe in terms of time, distance, and organization Identify the visible and nonvisible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum Compare refracting telescopes
Objectives Describe characteristics of the universe in terms of time, distance, and organization Identify the visible and nonvisible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum Compare refracting telescopes
Astro 358/Spring 2006 (48915) Galaxies and the Universe
 Astro 358/Spring 2006 (48915) Galaxies and the Universe Instructor: Professor Shardha Jogee TA: Ben Holder Figures for Lecture 20+21 : Tu Apr 04 + Th Apr 6 Lecture 20 - Collecting area and angular resolution
Astro 358/Spring 2006 (48915) Galaxies and the Universe Instructor: Professor Shardha Jogee TA: Ben Holder Figures for Lecture 20+21 : Tu Apr 04 + Th Apr 6 Lecture 20 - Collecting area and angular resolution
TESTIMONY BEFORE. HOUSE CO1MfITTEE ON SCIENCE AND ASTRONAUTICS SUBCOWITTEE ON SPACE SCIENCES AND APPLICATIONS. Dr. John W.
 October 9, 1973 TESTIMONY BEFORE HOUSE CO1MfITTEE ON SCIENCE AND ASTRONAUTICS SUBCOWITTEE ON SPACE SCIENCES AND APPLICATIONS Dr. John W. Findlay Chairman Space Science Board Suumer Study SCIENTIFIC USES
October 9, 1973 TESTIMONY BEFORE HOUSE CO1MfITTEE ON SCIENCE AND ASTRONAUTICS SUBCOWITTEE ON SPACE SCIENCES AND APPLICATIONS Dr. John W. Findlay Chairman Space Science Board Suumer Study SCIENTIFIC USES
Princeton Astrophysics Community Meeting
 Princeton Astrophysics Community Meeting Michael Moore Program Executive Astrophysics Division Science Mission Directorate September 4, 2012 Timeline 2011 2012 10 January: Identification of hardware availability
Princeton Astrophysics Community Meeting Michael Moore Program Executive Astrophysics Division Science Mission Directorate September 4, 2012 Timeline 2011 2012 10 January: Identification of hardware availability
Telescopes. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. Key Ideas:
 Telescopes A Warm Up Exercise If we measure the wavelengths of emission lines and absorption lines from the same gas, we find that (ignoring any Doppler shifts) a) Some emission lines shift to the red
Telescopes A Warm Up Exercise If we measure the wavelengths of emission lines and absorption lines from the same gas, we find that (ignoring any Doppler shifts) a) Some emission lines shift to the red
TEACHER PAGE CELEBRATING SPACE: A QUICK HISTORY
 Background Putting the Space Age Into Context: The dawn of the space age does not date back that far in human history only 40 years! It is so recent that you can get eye-witness accounts by asking parents,
Background Putting the Space Age Into Context: The dawn of the space age does not date back that far in human history only 40 years! It is so recent that you can get eye-witness accounts by asking parents,
Todays Topics 3/19/2018. Light and Telescope. PHYS 1403 Introduction to Astronomy. CCD Camera Makes Digital Images. Astronomical Detectors
 PHYS 1403 Introduction to Astronomy Light and Telescope Chapter 6 Todays Topics Astronomical Detectors Radio Telescopes Why we need space telescopes? Hubble Space Telescopes Future Space Telescopes Astronomy
PHYS 1403 Introduction to Astronomy Light and Telescope Chapter 6 Todays Topics Astronomical Detectors Radio Telescopes Why we need space telescopes? Hubble Space Telescopes Future Space Telescopes Astronomy
Mars Sample Return Mission
 Mars Sample Return Mission Ryan Supler Saylor.org: SSE101 MSRM Project April 15, 2014 2 Table of Contents The Scoping Elements of the Mars Sample Return Mission page 3 The High-Level Concept of Operations
Mars Sample Return Mission Ryan Supler Saylor.org: SSE101 MSRM Project April 15, 2014 2 Table of Contents The Scoping Elements of the Mars Sample Return Mission page 3 The High-Level Concept of Operations
Universe Now. 2. Astronomical observations
 Universe Now 2. Astronomical observations 2. Introduction to observations Astronomical observations are made in all wavelengths of light. Absorption and emission can reveal different things on different
Universe Now 2. Astronomical observations 2. Introduction to observations Astronomical observations are made in all wavelengths of light. Absorption and emission can reveal different things on different
Directed Reading. Section: Viewing the Universe THE VALUE OF ASTRONOMY. Skills Worksheet. 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Telescopes 3 Feb. Purpose
 Telescopes 3 Feb Key parameters of telescopes Optical telescopes SOAR Telescope, MSU s window on the universe Radio telescopes Telescopes in space SOAR Telescope Cerro Pachon, Chile First Test is Thurs
Telescopes 3 Feb Key parameters of telescopes Optical telescopes SOAR Telescope, MSU s window on the universe Radio telescopes Telescopes in space SOAR Telescope Cerro Pachon, Chile First Test is Thurs
Focus Question: How do astronomers study light?
 Telescopes Focus Question: How do astronomers study light? Telescopes Tools for collecting and analyzing electromagnetic radiation (light) in ways beyond what we can do with our eyes alone Properties of
Telescopes Focus Question: How do astronomers study light? Telescopes Tools for collecting and analyzing electromagnetic radiation (light) in ways beyond what we can do with our eyes alone Properties of
4.8 Space Research and Exploration. Getting Into Space
 4.8 Space Research and Exploration Getting Into Space Astronauts are pioneers venturing into uncharted territory. The vehicles used to get them into space are complex and use powerful rockets. Space vehicles
4.8 Space Research and Exploration Getting Into Space Astronauts are pioneers venturing into uncharted territory. The vehicles used to get them into space are complex and use powerful rockets. Space vehicles
HST & Servicing Mission 4
 HST & Servicing Mission 4 This briefing will provide an overview of the present condition of the Hubble observatory and describe the upcoming servicing mission Ambitious mission with three major objectives
HST & Servicing Mission 4 This briefing will provide an overview of the present condition of the Hubble observatory and describe the upcoming servicing mission Ambitious mission with three major objectives
Table of Contents and Executive Summary Final Report, ALTAIR Committee Access to Large Telescopes for Astronomical Instruction and Research (ALTAIR)
 Complete report available from http://www.noao.edu/system/altair 1 TableofContentsandExecutiveSummary FinalReport,ALTAIRCommittee AccesstoLargeTelescopesforAstronomical InstructionandResearch(ALTAIR) ForthecompletereportandmoreinformationabouttheALTAIRcommittee,
Complete report available from http://www.noao.edu/system/altair 1 TableofContentsandExecutiveSummary FinalReport,ALTAIRCommittee AccesstoLargeTelescopesforAstronomical InstructionandResearch(ALTAIR) ForthecompletereportandmoreinformationabouttheALTAIRcommittee,
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds. Chapter 6. Light and Telescopes
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes Guidepost In this chapter, you will consider the techniques astronomers use to study the Universe What is light? How do telescopes work?
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes Guidepost In this chapter, you will consider the techniques astronomers use to study the Universe What is light? How do telescopes work?
TWO SMALL PIECES OF GLASS A Space Science Program for Grades 5-12
 Teacher Idea Kit TWO SMALL PIECES OF GLASS A Space Science Program for Grades 5-12 Presented by Funded in part by: Two Small Pieces of Glass Suggested for Grades 5-12 Objectives After visiting the planetarium
Teacher Idea Kit TWO SMALL PIECES OF GLASS A Space Science Program for Grades 5-12 Presented by Funded in part by: Two Small Pieces of Glass Suggested for Grades 5-12 Objectives After visiting the planetarium
Spitzer Space Telescope Current Status and Future Plans
 Spitzer Space Telescope Current Status and Future Plans Great Observatories Workshop Pasadena, 22-24 May 2006 Current Status Instruments and Observatory are operating well Observing efficiency has continued
Spitzer Space Telescope Current Status and Future Plans Great Observatories Workshop Pasadena, 22-24 May 2006 Current Status Instruments and Observatory are operating well Observing efficiency has continued
Outline HST HST. HST& JWST CARMA and ALMA SOFIA Chandra Blackbodies. Doppler Effect. Homework #5 was due today.
 Outline Homework #5 was due today. Next homework is #6 due next Friday at 11:50 am. There will be another make-up nighttime observing session in November. Stay tuned. I will be teaching Paul s class on
Outline Homework #5 was due today. Next homework is #6 due next Friday at 11:50 am. There will be another make-up nighttime observing session in November. Stay tuned. I will be teaching Paul s class on
Educational Product Teachers Grades K-12 EG MSFC
 Educational Product Teachers Grades K-12 NASA Spacelink Optics: An Educators Guide With Activities In Science and Mathematics is available in electronic format through NASA Spacelink one of the Agency
Educational Product Teachers Grades K-12 NASA Spacelink Optics: An Educators Guide With Activities In Science and Mathematics is available in electronic format through NASA Spacelink one of the Agency
Electromagnetic Spectrum. Name: Period: Electromagnetic Spectrum. 1. What is the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. What is radiation?
 Electromagnetic Spectrum Question Electromagnetic Spectrum Name: Period: Answer 1. What is the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. What is radiation? 3. What is the source of radio waves in space? 4. How do astronomers
Electromagnetic Spectrum Question Electromagnetic Spectrum Name: Period: Answer 1. What is the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. What is radiation? 3. What is the source of radio waves in space? 4. How do astronomers
Dive In What is an advantage of sending unmanned crafts to space?
 Dive In What is an advantage of sending unmanned crafts to space? Manned and Robotic Spacecraft For Each Space Vehicle, complete the worksheet including: 1. If the spacecraft is manned or unmanned. 2.
Dive In What is an advantage of sending unmanned crafts to space? Manned and Robotic Spacecraft For Each Space Vehicle, complete the worksheet including: 1. If the spacecraft is manned or unmanned. 2.
A Large Monolithic-Aperture Optical/UV Serviceable Space Telescope Deployed to L2 by an Ares-V Cargo Launch Vehicle
 A Large Monolithic-Aperture Optical/UV Serviceable Space Telescope Deployed to L2 by an Ares-V Cargo Launch Vehicle Marc Postman (Space Telescope Science Institute) Philip Stahl (MSFC) Daniela Calzetti
A Large Monolithic-Aperture Optical/UV Serviceable Space Telescope Deployed to L2 by an Ares-V Cargo Launch Vehicle Marc Postman (Space Telescope Science Institute) Philip Stahl (MSFC) Daniela Calzetti
Lesson 4 - Telescopes
 Lesson 4 - Telescopes READING ASSIGNMENT Chapter 5.1: Optical Telescopes Chapter 5.3: Images and Detectors Chapter 5.2: Telescope Size Discovery 5-1: The Hubble Space Telescope Chapter 5.4: High-Resolution
Lesson 4 - Telescopes READING ASSIGNMENT Chapter 5.1: Optical Telescopes Chapter 5.3: Images and Detectors Chapter 5.2: Telescope Size Discovery 5-1: The Hubble Space Telescope Chapter 5.4: High-Resolution
Infrastructure for a Permanent LUVOIR Observatory in Space
 Infrastructure for a Permanent LUVOIR Observatory in Space FOUNDATION FOR CONTINUING ASTRONOMY IN SPACE NASA MIRROR TECHNOLOGY DAYS Annapolis, Maryland 10 November 2015 1 REVIRESCO LLC Howard A. MacEwen
Infrastructure for a Permanent LUVOIR Observatory in Space FOUNDATION FOR CONTINUING ASTRONOMY IN SPACE NASA MIRROR TECHNOLOGY DAYS Annapolis, Maryland 10 November 2015 1 REVIRESCO LLC Howard A. MacEwen
@astro_stephi. Telescopes. CAASTRO in the Classroom: National Science Week Stephanie Bernard, University of Melbourne
 @astro_stephi Telescopes CAASTRO in the Classroom: National Science Week 2017 Stephanie Bernard, University of Melbourne About me NASA, ESA NASA, JPL The first telescopes Invented in 1600s in the Netherlands
@astro_stephi Telescopes CAASTRO in the Classroom: National Science Week 2017 Stephanie Bernard, University of Melbourne About me NASA, ESA NASA, JPL The first telescopes Invented in 1600s in the Netherlands
Reading Clicker Q. Spectroscopy analyzing the light. What light gets through? Instruments in the Focal Plane. ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Nicholas Nelson, Zeeshan Parkar Lecture 5 Tues 26 Jan 2010 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Topics for Today What light does and does
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Nicholas Nelson, Zeeshan Parkar Lecture 5 Tues 26 Jan 2010 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Topics for Today What light does and does
Why Use a Telescope?
 1 Why Use a Telescope? All astronomical objects are distant so a telescope is needed to Gather light -- telescopes sometimes referred to as light buckets Resolve detail Magnify an image (least important
1 Why Use a Telescope? All astronomical objects are distant so a telescope is needed to Gather light -- telescopes sometimes referred to as light buckets Resolve detail Magnify an image (least important
Tibor Kremic, Glenn Research Center
 Balloon Based Planetary" Science Capability" Tibor Kremic, Glenn Research Center VEXAG Meeting #10 " Nov, 2012 Study Objectives 1) Confirm the science potential of a balloon based telescope deeper exploration
Balloon Based Planetary" Science Capability" Tibor Kremic, Glenn Research Center VEXAG Meeting #10 " Nov, 2012 Study Objectives 1) Confirm the science potential of a balloon based telescope deeper exploration
Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes
 Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes Guidepost In the early chapters of this book, you looked at the sky the way ancient astronomers did, with the unaided eye. In chapter 4, you got a glimpse through Galileo
Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes Guidepost In the early chapters of this book, you looked at the sky the way ancient astronomers did, with the unaided eye. In chapter 4, you got a glimpse through Galileo
Benefits of Infrared. The Spitzer Space Telescope. Instruments/Components of Spitzer. Cryostat. Infrared Telescope
 The Spitzer Space Telescope Benefits of Infrared IR can reveal objects that don't emit visible light IR provides different information than visible light IR is better than visible for viewing cold objects
The Spitzer Space Telescope Benefits of Infrared IR can reveal objects that don't emit visible light IR provides different information than visible light IR is better than visible for viewing cold objects
ASTR 2310: Chapter 6
 ASTR 231: Chapter 6 Astronomical Detection of Light The Telescope as a Camera Refraction and Reflection Telescopes Quality of Images Astronomical Instruments and Detectors Observations and Photon Counting
ASTR 231: Chapter 6 Astronomical Detection of Light The Telescope as a Camera Refraction and Reflection Telescopes Quality of Images Astronomical Instruments and Detectors Observations and Photon Counting
AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Telescopes Mauna Kea Observatories, Big Island, HI Imaging with our Eyes pupil allows light to enter the eye lens focuses light to create an image retina detects
AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Telescopes Mauna Kea Observatories, Big Island, HI Imaging with our Eyes pupil allows light to enter the eye lens focuses light to create an image retina detects
SAFETY GUIDED DESIGN OF CREW RETURN VEHICLE IN CONCEPT DESIGN PHASE USING STAMP/STPA
 SAFETY GUIDED DESIGN OF CREW RETURN VEHICLE IN CONCEPT DESIGN PHASE USING STAMP/STPA Haruka Nakao (1), Masa Katahira (2), Yuko Miyamoto (2), Nancy Leveson (3), (1) Japan Manned Space Systems Corporation,
SAFETY GUIDED DESIGN OF CREW RETURN VEHICLE IN CONCEPT DESIGN PHASE USING STAMP/STPA Haruka Nakao (1), Masa Katahira (2), Yuko Miyamoto (2), Nancy Leveson (3), (1) Japan Manned Space Systems Corporation,
What are the most important properties of a telescope? Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery. What are the two basic designs of telescopes?
 Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery What are the most important properties of a telescope? 1. Light-collecting area: Telescopes with a larger collecting area can gather a greater amount of light
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery What are the most important properties of a telescope? 1. Light-collecting area: Telescopes with a larger collecting area can gather a greater amount of light
Launching Astronomers into the Stratosphere
 Launching Astronomers into the Stratosphere Dan Lester University of Texas DFL 2/19/2010 Next-Generation Suborbital Researchers Conference 1 Considering NGSR, note the path blazed by airborne platforms
Launching Astronomers into the Stratosphere Dan Lester University of Texas DFL 2/19/2010 Next-Generation Suborbital Researchers Conference 1 Considering NGSR, note the path blazed by airborne platforms
Chapter 5. Telescopes. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 5 Telescopes Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Why do we need Telescopes? Large collection area for photons than the eye long integration
Chapter 5 Telescopes Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Why do we need Telescopes? Large collection area for photons than the eye long integration
DOWNLOAD OR READ : SPACE TELESCOPES AND INSTRUMENTS V MARCH 1998 KONA HAWAII ILLUSTRATED EDITION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : SPACE TELESCOPES AND INSTRUMENTS V 25 28 MARCH 1998 KONA HAWAII ILLUSTRATED EDITION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 space telescopes and instruments v 25 28 march 1998 kona hawaii
DOWNLOAD OR READ : SPACE TELESCOPES AND INSTRUMENTS V 25 28 MARCH 1998 KONA HAWAII ILLUSTRATED EDITION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 space telescopes and instruments v 25 28 march 1998 kona hawaii
USA Space Debris Environment and Operational Updates
 USA Space Debris Environment and Operational Updates Presentation to the 46 th Session of the Scientific and Technical Subcommittee Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space United Nations 9-20 February
USA Space Debris Environment and Operational Updates Presentation to the 46 th Session of the Scientific and Technical Subcommittee Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space United Nations 9-20 February
Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy
 Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy The light that comes to Earth from distant objects is the best tool that astronomers can use to learn about the universe. In most cases, there is no other way to study
Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy The light that comes to Earth from distant objects is the best tool that astronomers can use to learn about the universe. In most cases, there is no other way to study
Foreword. Taken from: Hubble 2009: Science Year in Review. Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Foreword Taken from: Hubble 2009: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute. The full contents
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Foreword Taken from: Hubble 2009: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute. The full contents
Light and Telescope 10/24/2018. PHYS 1403 Introduction to Astronomy. Reminder/Announcement. Chapter Outline. Chapter Outline (continued)
 PHYS 1403 Introduction to Astronomy Light and Telescope Chapter 6 Reminder/Announcement 1. Extension for Term Project 1: Now Due on Monday November 12 th 2. You will be required to bring your cross staff
PHYS 1403 Introduction to Astronomy Light and Telescope Chapter 6 Reminder/Announcement 1. Extension for Term Project 1: Now Due on Monday November 12 th 2. You will be required to bring your cross staff
The International Space Station and the Space Shuttle
 Order Code RL33568 The International Space Station and the Space Shuttle Updated April 26, 2007 Carl E. Behrens Specialist in Energy Policy Resources, Science, and Industry Division The International Space
Order Code RL33568 The International Space Station and the Space Shuttle Updated April 26, 2007 Carl E. Behrens Specialist in Energy Policy Resources, Science, and Industry Division The International Space
Light Pollution. Atmospheric Seeing. Seeing Through the Atmosphere. Atmospheric Absorption of Light
 Lec 8: 2 FEB 2012 ASTR 130 - Introductory Astronomy II (Chapter 6) LAST TIME - Optics and Telescopes Basic Functions of a Telescope Reflecting v. Refracting Affects of the Atmosphere TODAY Modern Astronomical
Lec 8: 2 FEB 2012 ASTR 130 - Introductory Astronomy II (Chapter 6) LAST TIME - Optics and Telescopes Basic Functions of a Telescope Reflecting v. Refracting Affects of the Atmosphere TODAY Modern Astronomical
How do they work? Chapter 5
 Telescopes How do they work? Chapter 5 1. History 2. Lenses & Hardware 3. Reflecting Telescopes 4. Refracting Telescopes History Hans Lippershey Middleburg, Holland invented the refractor telescope in
Telescopes How do they work? Chapter 5 1. History 2. Lenses & Hardware 3. Reflecting Telescopes 4. Refracting Telescopes History Hans Lippershey Middleburg, Holland invented the refractor telescope in
Telescopes and the Atmosphere
 Telescopes and the Atmosphere Our goals for learning How does Earth s atmosphere affect ground-based observations? Why do we put telescopes into space? How does Earth s atmosphere affect ground-based observations?
Telescopes and the Atmosphere Our goals for learning How does Earth s atmosphere affect ground-based observations? Why do we put telescopes into space? How does Earth s atmosphere affect ground-based observations?
Measuring Light waves
 Measuring Light waves We normally measure wavelengths (λ) using nanometers (nm) 1 nm = 10-9 m 400-700 nm Increasing wavelengths (λ)! Visible light has wavelengths between 400-700 nm! To detect other types
Measuring Light waves We normally measure wavelengths (λ) using nanometers (nm) 1 nm = 10-9 m 400-700 nm Increasing wavelengths (λ)! Visible light has wavelengths between 400-700 nm! To detect other types
Lecture 16: Announcements
 Lecture 16: Announcements Homework 2 due Mon Feb 28 Exam on Wed Mar 9 : Makes up 20% of total grade. See webpage for a description of the exam format http://www.as.utexas.edu/~sj/a301-sp05.html On Mon
Lecture 16: Announcements Homework 2 due Mon Feb 28 Exam on Wed Mar 9 : Makes up 20% of total grade. See webpage for a description of the exam format http://www.as.utexas.edu/~sj/a301-sp05.html On Mon
WikiLeaks Document Release
 WikiLeaks Document Release February 2, 2009 Congressional Research Service Report RL33568 The International Space Station and the Space Shuttle Carl E. Behrens, Environment and Natural Resources Policy
WikiLeaks Document Release February 2, 2009 Congressional Research Service Report RL33568 The International Space Station and the Space Shuttle Carl E. Behrens, Environment and Natural Resources Policy
Doing astronomy with SDSS from your armchair
 Doing astronomy with SDSS from your armchair Željko Ivezić, University of Washington & University of Zagreb Partners in Learning webinar, Zagreb, 15. XII 2010 Supported by: Microsoft Croatia and the Croatian
Doing astronomy with SDSS from your armchair Željko Ivezić, University of Washington & University of Zagreb Partners in Learning webinar, Zagreb, 15. XII 2010 Supported by: Microsoft Croatia and the Croatian
SOLVING THE INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION (ISS) MOTION CONTROL LONG-TERM PLANNING PROBLEM
 SOLVING THE INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION (ISS) MOTION CONTROL LONG-TERM PLANNING PROBLEM V. N. Zhukov, Dr. E. K. Melnikov, A. I. Smirnov Mission Control Center, Central Research Institute of Machine Building,
SOLVING THE INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION (ISS) MOTION CONTROL LONG-TERM PLANNING PROBLEM V. N. Zhukov, Dr. E. K. Melnikov, A. I. Smirnov Mission Control Center, Central Research Institute of Machine Building,
CASE STUDY. Keeping the James Webb Space Telescope on Track
 CASE STUDY Keeping the James Webb Space Telescope on Track In October 2018, NASA, the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), and the European Space Agency are set to launch the James Webb Space Telescope. Billed
CASE STUDY Keeping the James Webb Space Telescope on Track In October 2018, NASA, the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), and the European Space Agency are set to launch the James Webb Space Telescope. Billed
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
Earth based radio telescopes
 I am telescope. My purpose is to collect as much light as possible from some distant source and deliver it to a detector/observer for detailed study. Different Telescopes opaque opaque Space based telescopes
I am telescope. My purpose is to collect as much light as possible from some distant source and deliver it to a detector/observer for detailed study. Different Telescopes opaque opaque Space based telescopes
Technology and Space Exploration
 Technology and Space Exploration When did people first become interested in learning about Space and the Universe? Records from the earliest civilizations show that people studied and asked questions about
Technology and Space Exploration When did people first become interested in learning about Space and the Universe? Records from the earliest civilizations show that people studied and asked questions about
Credit: ESO/B. Tafreshi (twanight.org) Operating the Very Large Telescope
 Credit: ESO/B. Tafreshi (twanight.org) Operating the Very Large Telescope Introduction: From scientific idea to data legacy Credit: ESO/B. Tafreshi (twanight.org) The Very Large Telescope (VLT) was built
Credit: ESO/B. Tafreshi (twanight.org) Operating the Very Large Telescope Introduction: From scientific idea to data legacy Credit: ESO/B. Tafreshi (twanight.org) The Very Large Telescope (VLT) was built
USING THE ISS TO ASSEMBLE A VERY LARGE TELESCOPE
 USING THE ISS TO ASSEMBLE A VERY LARGE TELESCOPE Holland C. Ford (JHU) and James H. Crocker (Lockheed Martin) Presented by Warren Moos (JHU) 4/15/2003 1 A 30-m Very Large Space Telescope (VLST) : Assumptions
USING THE ISS TO ASSEMBLE A VERY LARGE TELESCOPE Holland C. Ford (JHU) and James H. Crocker (Lockheed Martin) Presented by Warren Moos (JHU) 4/15/2003 1 A 30-m Very Large Space Telescope (VLST) : Assumptions
Dr. Robert Goddard s Liquid Fueled Rocket March 16, 1926
 History of Space Exploration Dr. Robert Goddard s Liquid Fueled Rocket March 16, 1926 Courtesy of NASA Goddard Dr. Robert Goddard is known as the father of modern rocketry because of his use of liquid
History of Space Exploration Dr. Robert Goddard s Liquid Fueled Rocket March 16, 1926 Courtesy of NASA Goddard Dr. Robert Goddard is known as the father of modern rocketry because of his use of liquid
Chapter 5. Telescopes. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 5 Telescopes Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Learning Objectives Upon completing this chapter you should be able to: 1. Classify the
Chapter 5 Telescopes Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Learning Objectives Upon completing this chapter you should be able to: 1. Classify the
1/29/14. Topics for Today. UV, X-rays and Gamma-rays. Atmospheric Absorption of Light. Why bother with other light? ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Gran Telescopio Canarias, La Palma 10.4m Topics for Today What our atmosphere does to light Magic of adaptive optics Radio telescopes: many dishes make a big one (interferometry
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Gran Telescopio Canarias, La Palma 10.4m Topics for Today What our atmosphere does to light Magic of adaptive optics Radio telescopes: many dishes make a big one (interferometry
SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE
 SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE The Rationale for Infrared Astronomy reveal cool states of matter explore the hidden Universe provide access to many spectral features probe the early life of the cosmos WANT TO
SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE The Rationale for Infrared Astronomy reveal cool states of matter explore the hidden Universe provide access to many spectral features probe the early life of the cosmos WANT TO
CL# Copyright 2018 California Institute of Technology Government sponsorship acknowledged1
 Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Building the Future: in Space Servicing & Assembly of Large Aperture Space Telescopes Nick Siegler (NASA Exoplanet Exploration Program, Jet
Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Building the Future: in Space Servicing & Assembly of Large Aperture Space Telescopes Nick Siegler (NASA Exoplanet Exploration Program, Jet
International Facilities
 International Facilities A report to the National Committee for Astronomy for the Australian Astronomy Decadal Plan 2006-2015 By Working Group 3.1 September 2005 Executive Summary Over the past decade
International Facilities A report to the National Committee for Astronomy for the Australian Astronomy Decadal Plan 2006-2015 By Working Group 3.1 September 2005 Executive Summary Over the past decade
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery
 Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors Our goals for learning: How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image?
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors Our goals for learning: How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image?
New Worlds, New Horizons in Astronomy and Astrophysics
 New Worlds, New Horizons in Astronomy and Astrophysics 1 Task and Charge Negotiated by NRC with Agencies; accepted by chair The Committee on Astro2010 will survey the field of space- and groundbased astronomy
New Worlds, New Horizons in Astronomy and Astrophysics 1 Task and Charge Negotiated by NRC with Agencies; accepted by chair The Committee on Astro2010 will survey the field of space- and groundbased astronomy
Space Explorer Glossary
 Space Explorer Glossary A. * Asteroid ~ a rocky object in space that can be a few feet wide to several hundred miles wide. Most asteroids in the Solar System orbit in a belt between Mars and Jupiter. *
Space Explorer Glossary A. * Asteroid ~ a rocky object in space that can be a few feet wide to several hundred miles wide. Most asteroids in the Solar System orbit in a belt between Mars and Jupiter. *
~ λ / D. Diffraction Limit 2/7/17. Topics for Today. Problems in Looking Through Our Atmosphere. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Gran Telescopio Canarias, La Palma 10.4m Topics for Today What our atmosphere does to light Magic of adaptive optics Radio telescopes: many dishes make a big one (interferometry
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Gran Telescopio Canarias, La Palma 10.4m Topics for Today What our atmosphere does to light Magic of adaptive optics Radio telescopes: many dishes make a big one (interferometry
Paul Plucinsky on behalf of Randall Smith on behalf of the ESA JAXA NASA IXO team
 Paul Plucinsky on behalf of Randall Smith on behalf of the ESA JAXA NASA IXO team 1 Basic Facts about IXO Merger of ESA/JAXA XEUS and NASA s Constellation-X missions Part of US Astro2010 Decadal Review
Paul Plucinsky on behalf of Randall Smith on behalf of the ESA JAXA NASA IXO team 1 Basic Facts about IXO Merger of ESA/JAXA XEUS and NASA s Constellation-X missions Part of US Astro2010 Decadal Review
Collecting Light. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris is fully open and the pupil has a diameter of about 7 mm. pupil
 Telescopes Collecting Light The simplest means of observing the Universe is the eye. The human eye is sensitive to light with a wavelength of about 400 and 700 nanometers. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris
Telescopes Collecting Light The simplest means of observing the Universe is the eye. The human eye is sensitive to light with a wavelength of about 400 and 700 nanometers. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris
Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D.
 Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D. UV Rays Science Starter! 10.14-15.13! THE UNIVERSE AND ELECTROMAGNETIC
Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D. UV Rays Science Starter! 10.14-15.13! THE UNIVERSE AND ELECTROMAGNETIC
INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION
 INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION WHAT IS THE ISS? The International Space Station is a special kind of spacecraft in orbit around the Earth. It is a large research facility with people on-board who run science
INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION WHAT IS THE ISS? The International Space Station is a special kind of spacecraft in orbit around the Earth. It is a large research facility with people on-board who run science
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery. Agenda. How does your eye form an image? Refraction. Example: Refraction at Sunset
 Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery Agenda Announce: Read S2 for Thursday Ch. 6 Telescopes 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? Our goals for learning How
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery Agenda Announce: Read S2 for Thursday Ch. 6 Telescopes 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? Our goals for learning How
Properties of the Solar System
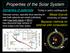 Properties of the Solar System Dynamics of asteroids Telescopic surveys, especially those searching for near-earth asteroids and comets (collectively called near-earth objects or NEOs) have discovered
Properties of the Solar System Dynamics of asteroids Telescopic surveys, especially those searching for near-earth asteroids and comets (collectively called near-earth objects or NEOs) have discovered
Next Generation SOFIA Science Instrument Call for Proposals
 Next Generation SOFIA Science Instrument Call for Proposals Kimberly Ennico-Smith NASA SOFIA Project Scientist Alan Rhodes NASA SOFIA Science Instrument Development Manager NASA Ames Research Center Outline
Next Generation SOFIA Science Instrument Call for Proposals Kimberly Ennico-Smith NASA SOFIA Project Scientist Alan Rhodes NASA SOFIA Science Instrument Development Manager NASA Ames Research Center Outline
The story of NASA. Presented by William Markham
 The story of NASA Presented by William Markham German Rocket Developments WW2 Comet ME 262 V1 flying bomb V2 Rocket Wernher Von Braun Early history An Act to provide for research into the problems of flight
The story of NASA Presented by William Markham German Rocket Developments WW2 Comet ME 262 V1 flying bomb V2 Rocket Wernher Von Braun Early history An Act to provide for research into the problems of flight
The Making of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
 The Making of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field Hubble Science Briefing October 4, 2012 Massimo Stiavelli Space Telescope Science Institute Bold methods and new technology - What happens if you point the most
The Making of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field Hubble Science Briefing October 4, 2012 Massimo Stiavelli Space Telescope Science Institute Bold methods and new technology - What happens if you point the most
Scientific Role of the James Webb Space Telescope in New Worlds, New Horizons
 Scientific Role of the James Webb Space Telescope in New Worlds, New Horizons H. B. Hammel, G. Rieke, and the James Webb Space Telescope Science Working Group 1 September 2010 Abstract: The sixth decadal
Scientific Role of the James Webb Space Telescope in New Worlds, New Horizons H. B. Hammel, G. Rieke, and the James Webb Space Telescope Science Working Group 1 September 2010 Abstract: The sixth decadal
Canadarm Group: Ranger Group Member: Robert Ingino, Arthur Wong, Jeremy Sills
 Canadarm Group: Ranger Group Member: Robert Ingino, Arthur Wong, Jeremy Sills Canadarm History NASA needed a Shuttle Remote Manipulator System (SRMS) in the early 70s A small Canadian firm, DSMA Atcon
Canadarm Group: Ranger Group Member: Robert Ingino, Arthur Wong, Jeremy Sills Canadarm History NASA needed a Shuttle Remote Manipulator System (SRMS) in the early 70s A small Canadian firm, DSMA Atcon
Whether a Soyuz Spacecraft really needs a parachute or is there an alternative?
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 4, Issue 1, January-2013 1 Whether a Soyuz Spacecraft really needs a parachute or is there an alternative? Pratham M Alag Abstract - This
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 4, Issue 1, January-2013 1 Whether a Soyuz Spacecraft really needs a parachute or is there an alternative? Pratham M Alag Abstract - This
The Space Launch System the most powerful rocket ever built 31 July 2017, by Universe Today
 The Space Launch System the most powerful rocket ever built 31 July 2017, by Universe Today orbit to the moon. Instead of continuing on with the Saturn program, NASA decided to shift gears and build the
The Space Launch System the most powerful rocket ever built 31 July 2017, by Universe Today orbit to the moon. Instead of continuing on with the Saturn program, NASA decided to shift gears and build the
= λ. Topics for Today. Clicker Q: Radio Waves. Radios. Light Pollution. Problems in Looking Through Our Atmosphere
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nick Featherstone Lecture 5 Tues 30 Jan 07 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Topics for Today Twinkle and absorption by our atmosphere
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nick Featherstone Lecture 5 Tues 30 Jan 07 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Topics for Today Twinkle and absorption by our atmosphere
NASA: BACK TO THE MOON
 NASA: BACK TO THE MOON Don Campbell Cornell University "I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him
NASA: BACK TO THE MOON Don Campbell Cornell University "I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him
The Space InfraRed Telescope Facility - SIRTF SIRTF an Overview
 The Space InfraRed Telescope Facility - SIRTF SIRTF an Overview Jay A. Frogel SIRTF Program Scientist, NASA Michael Werner SIRTF Project Scientist, JPL/Caltech January, 2003 Lifting the Cosmic Veil Views
The Space InfraRed Telescope Facility - SIRTF SIRTF an Overview Jay A. Frogel SIRTF Program Scientist, NASA Michael Werner SIRTF Project Scientist, JPL/Caltech January, 2003 Lifting the Cosmic Veil Views
ATHENA in the Context of the Next Decade. R. Kennicutt, IoA Cambridge
 ATHENA in the Context of the Next Decade R. Kennicutt, IoA Cambridge 1 Cosmic Dawn Searching for the first stars, galaxies, and black holes New Worlds Seeking nearby, habitable planets Physics of the Universe
ATHENA in the Context of the Next Decade R. Kennicutt, IoA Cambridge 1 Cosmic Dawn Searching for the first stars, galaxies, and black holes New Worlds Seeking nearby, habitable planets Physics of the Universe
Zoink Questions: Tools of Astronomy
 1. Optical telescopes are designed to do what? Gather and focus visible light to see distant objects more clearly 2. Visible light can be separated into various colors to form a(n). Spectrum 3. The full
1. Optical telescopes are designed to do what? Gather and focus visible light to see distant objects more clearly 2. Visible light can be separated into various colors to form a(n). Spectrum 3. The full
The James Webb Space Telescope
 The Session: ENGINEERING THE SEARCH FOR EARTH-LIKE EXOPLANETS Author: Amy Lo, Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems Abstract NASA s is the premier space telescope of its time. Set to launch in Oct. 2018,
The Session: ENGINEERING THE SEARCH FOR EARTH-LIKE EXOPLANETS Author: Amy Lo, Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems Abstract NASA s is the premier space telescope of its time. Set to launch in Oct. 2018,
Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction. Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009
 Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009 Missions in Operations Rosetta Hubble Integral Newton Mars Express SOHO Ulysses Cluster Venus
Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009 Missions in Operations Rosetta Hubble Integral Newton Mars Express SOHO Ulysses Cluster Venus
Table of Contents and Executive Summary Final Report, ReSTAR Committee Renewing Small Telescopes for Astronomical Research (ReSTAR)
 For the complete report, see http://www.noao.edu/system/restar 1 TableofContentsandExecutiveSummary FinalReport,ReSTARCommittee RenewingSmallTelescopesforAstronomical Research(ReSTAR) ForthecompletereportandmoreinformationabouttheReSTARcommittee,
For the complete report, see http://www.noao.edu/system/restar 1 TableofContentsandExecutiveSummary FinalReport,ReSTARCommittee RenewingSmallTelescopesforAstronomical Research(ReSTAR) ForthecompletereportandmoreinformationabouttheReSTARcommittee,
The Road to Improving your GIS Data. An ebook by Geo-Comm, Inc.
 The Road to Improving your GIS Data An ebook by Geo-Comm, Inc. An individual observes another person that appears to be in need of emergency assistance and makes the decision to place a call to 9-1-1.
The Road to Improving your GIS Data An ebook by Geo-Comm, Inc. An individual observes another person that appears to be in need of emergency assistance and makes the decision to place a call to 9-1-1.
On to Telescopes. Imaging with our Eyes. Telescopes and cameras work much like our eyes. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies !
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies On to Telescopes!AST CLASS Learning from light: temperature (from continuum spectrum) chemical composition (from spectral lines) velocity (from Doppler shift)
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies On to Telescopes!AST CLASS Learning from light: temperature (from continuum spectrum) chemical composition (from spectral lines) velocity (from Doppler shift)
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 5. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 5 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 5 Telescopes Units of Chapter 5 5.1 Optical Telescopes 5.2 Telescope Size 5.3 Images and Detectors 5.4 High-Resolution Astronomy
Lecture Outlines Chapter 5 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 5 Telescopes Units of Chapter 5 5.1 Optical Telescopes 5.2 Telescope Size 5.3 Images and Detectors 5.4 High-Resolution Astronomy
SDT Interim Reports. Paul Hertz. Director, Astrophysics Division Science Mission Directorate. March 26, 2014
 SDT Interim Reports March 26, 2014 Paul Hertz Director, Astrophysics Division Science Mission Directorate Astrophysics Strategy A goal is to be prepared to start a new strategic NASA Astrophysics mission
SDT Interim Reports March 26, 2014 Paul Hertz Director, Astrophysics Division Science Mission Directorate Astrophysics Strategy A goal is to be prepared to start a new strategic NASA Astrophysics mission
ACOUSTIC EMISSION DETECTION OF IMPACT DAMAGE ON SPACE SHUTTLE STRUCTURES
 ACOUSTIC EMISSION DETECTION OF IMPACT DAMAGE ON SPACE SHUTTLE STRUCTURES WILLIAM PROSSER 1, ERIC MADARAS 1, GEORGE STUDOR 2, and MICHAEL GORMAN 3 1) NASA Langley Research Center, MS 231, 3 E. Taylor St.,
ACOUSTIC EMISSION DETECTION OF IMPACT DAMAGE ON SPACE SHUTTLE STRUCTURES WILLIAM PROSSER 1, ERIC MADARAS 1, GEORGE STUDOR 2, and MICHAEL GORMAN 3 1) NASA Langley Research Center, MS 231, 3 E. Taylor St.,
