arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jun 2014
|
|
|
- Vivien Clemence Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Asociación Argentina de Astronomía BAAA, Vol., 2 A.C. Rovero, P.B. Tissera, L.J. Pellizza & M. Lares, eds. PRESENTACION INVITADA arxiv:6.6727v1 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jun 2 Stellar Variability in the VVV Survey: An Update M. Catelan 1,2, I. Dékány 2,1, M. Hempel 1,2 & D. Minniti 1,2 (1) Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Facultad de Física, Instituto de Astrofísica, Santiago, Chile (2) Millennium Institute of Astrophysics, Santiago, Chile Abstract. The Vista Variables in the Vía Láctea (VVV) ESO Public Survey consists in a near-infrared time-series survey of the Galactic bulge and inner disk, covering 2 square degrees of the sky, over a total timespan of more than 5 years. In this paper, we provide an updated account of the current status of the survey, especially in the context of stellar variability studies. In this sense, we give a first description of our efforts towards the construction of the VVV Variable Star Catalog (VVV-VSC). Resumen. El Relevamiento Público ESO titulado Variables Vista en la Vía Láctea (VVV) consiste en un relevamiento con resolución temporal del bulbo y disco interno Galácticos en el infrarrojo cercano, cubriendo 2 grados cuadrados del cielo, en un intervalo de tiempo de más de 5 años. En este artículo, entregamos una descripción actualizada del estado actual del relevamiento, especialmente en el ámbito de los estudios de variabilidad estelar. En ese sentido, describimos, por primera vez, nuestros esfuerzos para la construcción del Catálogo de Estrellas Variables del VVV (VVV-VSC). 1. Overview The Vista Variables in the Vía Láctea (VVV) ESO Public Survey (Minniti et al. 2; Catelan et al. 211; Saito et al. 2; Hempel et al. 2) is a time-series, near-infrared (IR) survey of the Galactic bulge and an adjacent portion of the inner disk, covering 2 square degrees of the sky. The survey, which is based on images taken with the VIRCAM camera mounted on the VISTA telescope, located in Cerro Paranal, northern Chile, has provided multi-color photometry in 5 broadband filters (Z, Y, J, H, and K s ), but its main goal is to provide a homogeneous database for variability studies of the observed regions, particularly in the K s band. An extensive overview of recent work on stellar variability that has been carriedoutintheframeworkofthevvvsurveyhasbeenpresentedbycatelan et al. (2). Here we provide a brief update on the status of the survey, particularly in regard to our ongoing work on stellar variability. 1
2 2 Catelan et al. 2. Status of the Survey Figure 1 shows the complete area covered by VVV, with the different tiles (which constitute individually observed fields) indicated as red squares. Each tile covers 1.1 deg 2 in the sky, and the survey encompasses 3 tiles in total. For each VVVtile, Figure1alsoshowsitsIDnumber(upper label) andthenumberof epochs in K s that have been obtained, as of this writing (bottom label). As far as the cadence, Figure 2 shows the delay (i.e., time interval) between two successive epochsin thevvv K s -banddata, color-coded according tothescale on theright of each plot. By the end of the survey, the bulge region will contain between 6 and epochs for each tile, whereas the disk tiles will have 6 epochs each. Figure 3 shows some examples of VVV light curves for bulge RR Lyrae stars. These stars had been previously identified by the OGLE-III survey (Soszyński et al. 211), and so their pulsation periods are accurately known. The VVV light curves of known RR Lyrae with very accurately known periods will enable us to systematically investigate, with unprecedented detail, the nearinfrared light-curve properties of these stars: note, for instance, how the three RR Lyrae stars shown in Figure 3 have different light-curve morphologies, in spite of their very similar periods. Such detailed studies of light-curve morphology will be important for constraining pulsation models (e.g., Bono et al. 2). Using such well-defined K s -band light curves, we will also study possible relationships between near-infrared light-curve parameters and the metallicity (in addition to stellar physical parameters), as has been done many times previously in the optical for different types of variables, most notably Cepheids and RRLyraestars(e.g., Simon & Lee1981;Simon & Teays 1982;Jurcsik & Kovács 1996; Kovács & Walker 21; Morgan et al. 27; Nemec et al. 2). In turn, this might prove very useful for studying the metallicity distributions/gradients of the stellar populations that these stars trace i.e., in the bulge and the thick disk, in the case of RR Lyrae stars (e.g., Layden 1995). In like vein, by combining RR Lyrae light curves from visual databases and VVV light curves, we are in a position to simultaneously derive extinction and distance to each individual star. This can be achieved by applying the RR Lyrae period-luminosity calibrations in the visual and near-infrared bands, such as provided by Catelan et al. (24) in I, J, H, and K. A first such application has recently been described by Dékány et al. (2), where bulge RR Lyrae stars in common between the OGLE and VVV surveys were used, together with the Catelan et al. period-luminosity relations, to infer an RR Lyrae-based distance to the Galactic center, estimated at R = 8,33±,5±, kpc, where the indicated error bars correspond to the estimated statistical and systematic uncertainties, respectively. This is in remarkable agreement with the dynamical value derived by Gillessen et al. (29), who have obtained R = 8,35±,35 kpc by studying the orbits of stars around the Galaxy s central black hole. The very complete VVV light curves for many different types of variable stars will also be useful as templates and indeed, many such reliably classified light curves with complete phase coverage have already been incorporated into the so-called VVV Templates Database (Angeloni et al. 2), 1 whose main 1
3 VVV Survey Area and Tile numbers (upper index) and number of Ks- epochs (lower index) Galactic Latitude [deg] Galactic Longitude [deg] Figura 1. VVV Survey area, superimposed on a gray-scale image that represents the Galactic dust extinction maps by Schlegel et al. (1998). Each of the 3 tiles of the survey is represented by a red rectangle, and is identified by its ID number (upper label within each tile). Each such tile, which covers a 1.5 square degree field, has already been observed at least once in each of the Z, Y, J, H, and K s filters. The actual number of epochs in the K s -band as of this writing (May 16, 2) is shown underneath each tile s ID number The VVV Survey: An Update 3
4 4 Catelan et al Epoch Tile [Bulge] Epoch 2 Delay in Julian Days Tile [Disk] Figura 2. Time delay (in Julian Days) between two consecutive epochs of K s -band observations for the bulge (top) and disk (bottom) tiles, based on all VVV time-series data obtained as of this writing (May 16, 2). The 8 tiles with the largest number of observed epochs (ID numbers: 293, 294, 295, 296, 37, 38, 39, 3; see also Fig. 1) are bulge tiles situated in Baade s Window, with a much reduced dust extinction and for which independent observations areavailableinthe opticalbandsfromthe OGLEsurvey(Udalski et al.1992).
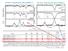
5 The VVV Survey: An Update 5 K s K s K s P= d 234 P=.594 d 7 P= d phase Figura3. ThesepanelsshowtheK s -bandphasediagramsof3bulgeab-type (i.e., fundamental-mode) RR Lyrae stars known from the OGLE-III survey (Soszyński et al. 211; OGLE IDs and periods are shown for each star), illustrating the high quality of the data obtained in the course of the VVV Survey. Note that these three stars have very similar periods, yet quite different lightcurve shapes. The red lines show the Fourier fits with optimized numbers of terms. The figure includes data obtained up to the end of June 2. purpose is to feed the classification algorithms that are currently being devised, in order to perform automated classification of the expected 6 7 variable stars detected in the course of the VVV Survey (Catelan et al. 211, 2). It is worth noting, in this regard, that our team has also recently completed a variable star catalog (Ferreira Lopes et al. 2) using data from the 3.8m United Kingdom Infrared Telescope s (UKIRT) Wide-Field near-ir CAMera(WFCAM; Casali et al. 27) calibration database. This multi-band database has also yielded high-quality lightcurve templates, which have also been incorporated into the VVV Templates Database (Angeloni et al. 2).
6 6 Catelan et al b= log N σ (Ks) b = log N σ (Ks) b = log N σ (Ks) Ks Figura 4. This figure shows the number density distribution of the weighted Ks -band average magnitude vs. the weighted standard deviation of the Ks light curves, for 3 tiles at Galactic longitude ℓ = 2o and at different latitudes, namely b = (top), 5,2o (middle), and 9o (bottom). The plots illustrate the large changes in the noise distribution of the light curves as an effect of increasing source crowding towards the Galactic plane. The deviations from the main locus at magnitudes < mag are due to (temporal) saturation. Note that the color scale, mapped on the right, indicates the logarithm of the number of sources in each bin. 3. VVV-VSC: The VVV Variable Star Catalog VVV is a public survey, and so one of our main objectives is to provide a variable star catalog (VSC) that will ultimately be useful to the whole astronomical community. Since we last described our work on stellar variability in the framework of the VVV Survey (Catelan et al. 211, 2), we have made much progress at building a comprehensive, science-ready relational database of variable VVV
7 The VVV Survey: An Update 7 K s K s HJD 2. Figura 5. Examples of transient sources in the VVV data. The upper panel shows the K s -band light curve of VVV-WIT-2 (Dekany et al. 2), which is probably a recurrent nova. The bottom panel shows the VVV K s -band light curve of the candidate young stellar object (YSO) called SSTGLMC G (Robitaille et al. 28), which is located in tile b329 (in the bulge plane), previously known from GLIMPSE. The star has a largeamplitude recurring outburst with an approximate period of about 95 days. point sources. In its current incarnation, the VVV-VSC uses the high-quality aperture photometry provided by the Cambridge Astronomy Survey Unit (CA- SU; see Catelan et al. 2, for more details and extensive references). The pipeline first extracts a master source list from the CASU tile catalogs, and then cross-matches those sources with the individual pawprints that are used to build each tile (six pawprints per tile; Minniti et al. 2). Zero-point errors are then added, a threshold rejection procedure applied, aperture optimization carried out (by means of a minimization of the rms scatter), and descriptive statistics computed. Using a number of variability indices (e.g., Welch & Stetson 1993; Stetson 1996; Ferreira Lopes et al. 2), a list of variable star candidates is then finally obtained. Typically, we have been encountering of order, candidates per VVV tile. Current tests indicate that our procedure is highly successful at recovering variable stars in general, and particularly periodic sources with sufficiently high amplitudes in the near-ir. At present, the procedure does not perform well for variable sources such as the following: very fast transients coming from below detection; high-proper motion objects; extremely faint sources; very blue, faint sources; highly crowded sources; and very bright variables (i.e., K s mag), which are commonly saturated in the VVV images. Figure 4 illustrates the mean scatter of the recovered variable star candidates as a function of the mean K s -band magnitude at three different Galactic latitudes, where the effects of saturation, crowding, and image depth are all apparent. Naturally, not all variables detected in the VVV data are periodic, and many different examples of variable stars that are not strictly periodic are shown, for instance, in Catelan et al. (2) and Saito et al. (2). However, many of the detected variables, such as Cepheids, RR Lyrae, and eclipsing binary stars, are
8 8 Catelan et al. N [%] N [%] PDM GLS frequency [c/d] PDM frequency [c/d] GLS frequency [c/d] Figura 6. (left panel) This plot shows the histograms of the principal frequencies detected by the two methods employed by the VVV variability pipeline, namely PDM (top) and GLS (bottom), after all the contributions from signals in the /T tot vicinity of integer c/d frequencies have been removed where T tot is the total time span covered by the data. The distributions are rather flat, but a small bump due to RR Lyrae stars can be spotted. The peaks at higher frequencies, close to integers and half-integers, are spurious signals, caused mostly by the rotating diffraction spikes around bright stars. The right panel shows the consistency between the frequencies detected by the two methods. Most are in agreement, as indicated by the high concentration of points around the -degree line overplotted on the data. There is, however, an additional sequence, with GLS periods that are half the PDM periods. This sequence is primarily due to eclipsing binary stars where the GLS algorithm recovers half the true orbital period, due to its diminished sensitivity to the presence of alternating peaks, compared to PDM. periodic and thus, once the variable stars are selected following the described procedure, we also carry out a frequency analysis, in order to find periodic and long-term signals, as may be present for each individual star. Figure 5 shows an example of non-periodic transient events detected in our data. To derive the periods, we currently use two different algorithms, namely the generalized Lomb- Scargle periodogram (GLS; Zechmeister & Kürster 29) and phase-dispersion minimization (PDM; Stellingwerf 1978). Figure 6 compares the principal frequencies detected by the GLS and PDM methods. Most of the derived periods are in excellent agreement, as indicated by the large concentration of points around the -degree line that is overplotted in this diagram. However, a secondary sequence is also present, representing favored GLS periods which are half as long as the corresponding PDM periods. Close inspection of the light curves of stars falling along this sequence reveals that it is mostly caused by eclipsing binary stars for which GLS incorrectly favors a period that is half as long as the true orbital period. This is caused by GLS s reduced sensitivity to the presence of alternating peaks in the time series, compared to
9 The VVV Survey: An Update 9 PDM. Note also the presence of a large number of spurious detections at integer and half-integer periods. Most of these variable star candidates are actually not intrinsically variable, but represent instead stars in the vicinity of bright sources, whose spurious, periodic variability signal is actually produced by the rotating diffraction spike pattern that is seen around these very bright stars. By the end of the survey, once the VVV-VSC catalog is completed, we will be in a position to provide a relational database containing variability information for up to several million point sources. Our variability tables will include detailed information on the degree of variability, including for instance mean, median, minimum and maximum magnitudes, standard deviations, rms scatter, skewness, kurtosis, etc.; frequency analysis tables, including information on the power spectra and the periods derived therefrom; and queryable light curves and plots, enabling the display and retrieval of data (both raw and processed) in all 5 bandpasses used in the survey (Sect. 1.). 4. Conclusions The VVV ESO Public Survey provides a treasure trove of scientific data that can be exploited in numerous different scientific contexts. In terms of stellar variability, the project will provide up to several million calibrated K s -band light curves for genuinely variable sources, including pulsating stars, eclipsing systems, rotating variables, cataclysmic stars, microlenses, planetary transits, and even transient events of unknown nature. In this paper, we have provided a brief overview of the current status of the survey, as far as detection, cataloging, and classification of variable point sources is concerned. VVVisapublicsurvey, andsothedatawillquickly bemadeavailable tothe entire astronomical community as we move along, thus opening the door to many additional applications and synergies with other ongoing and future projects that target the same fields as those covered by VVV. In this sense, in this paper we have also described our current efforts at creating the VVV Variable Star Catalog (VVV-VSC) a fully queryable relational database that will allow users to quickly and efficiently retrieve variability and frequency analysis tables for the sources detected, multi-band color information, and last but not least the light curves themselves. Acknowledgements. The VVV Survey is supported by the European Southern Observatory, the Basal Center for Astrophysics and Associated Technologies (PFB-6), and the Chilean Ministry for the Economy, Development, and Tourism s Programa Iniciativa Científica Milenio through grant P7-21-F, awarded to The Milky Way Millennium Nucleus. M.C. gratefully acknowledges the support provided by Fondecyt through grant #111. Referencias Angeloni, R., Contreras Ramos, R., Catelan, M., et al. 2, A&A, in press Bono, G., Castellani, V., & Marconi, M. 2, ApJ, 2, L9 Casali, M., Adamson, A., Alves de Oliveira, C., et al. 27, A&A, 7, 777
10 Catelan et al. Catelan, M., Minniti, D., Lucas, P. W., et al. 211, Carnegie Obs. Conf. Ser., 5, 1 Catelan, M., Minniti, D., Lucas, P. W., et al. 2, in 4 Years of Variable Stars: A Celebration of Contributions by Horace A. Smith (ed. K. Kinemuchi, H. A. Smith, N. De Lee, & C. Kuehn), p. 1 Catelan, M., Pritzl, B. J., & Smith, H. A. 24, ApJS, 4, 633 Dékány, I., Minniti, D., Catelan, M., Zoccali, M., Saito, R. K., Hempel, M., & Gonzalez, O. A. 2, ApJ, 776, L19 Dekany, I., Minniti, D., & Saito, R. K. 2, ATel, 5954, 1 Ferreira Lopes, C. E., Dékány, I., Catelan, M., Cross, N. J. G., Angeloni, R., Leão, I. C., & De Medeiros, J. R. 2, A&A, submitted Gillessen, S., Eisenhauer, F., Trippe, S., et al. 29, ApJ, 692, 75 Hempel, M., Minniti, D., Dékány, I, et al. 2, The Messenger, 5, 24 Jurcsik, J., & Kovács, G. 1996, A&A, 3, 111 Kovács, G., & Walker, A. R. 21, A&A, 371, 579 Layden, A. C. 1995, AJ, 1, 23 Minniti, D., Lucas, P. W., Emerson, J. P., et al. 2, NewA,, 3 Morgan, S. M., Wahl, J. N., & Wieckhorst, R. M. 27, MNRAS, 374, 21 Nemec, J. M., Cohen, J. G., Ripepi, V., Derekas, A., Moskalik, P., Sesar, B., Chadid, M., & Bruntt, H. 2, ApJ, 773, 181 Robitaille, T. P., Meade, M. R., Babler, B. L., et al. 28, AJ, 6, 24 Saito, R. K., Hempel, M., Minniti, D., et al. 2, A&A, 7, A7 Saito, R. K., Minniti, D., Angeloni, R., et al. 2, A&A, 554, A3 Schlegel, D. J., Finkbeiner, D. P., & Davis, M. 1998, ApJ,, 5 Simon, N. R., & Lee, A. S. 1981, ApJ, 2, 291 Simon, N. R., & Teays, T. J. 1982, ApJ, 261, 6 Soszyński, I., Dziembowski, W. A., Udalski, A., et al. 211, AcA, 61, 1 Stellingwerf, R. F. 1978, ApJ, 224, 9 Stetson, P. B. 1996, PASP, 8, 8 Udalski, A., Szymanski, M., Kaluzny, J., Kubiak, M., & Mateo, M. 1992, AcA, 42, 2 Welch, D. L., & Stetson, P. B. 1993, AJ, 5, 18 Zechmeister, M., & Kürster, M. 29, A&A, 6, 577
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012](/thumbs/93/112483577.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 62 (2012) pp. 247 268 Photometric Maps Based on the OGLE-III Shallow Survey in the Large Magellanic Cloud arxiv:1210.4702v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012 K. U l a c z y k 1, M. K. S z
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 62 (2012) pp. 247 268 Photometric Maps Based on the OGLE-III Shallow Survey in the Large Magellanic Cloud arxiv:1210.4702v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012 K. U l a c z y k 1, M. K. S z
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2011](/thumbs/92/108211191.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. vvv2 accepted leng ref c ESO 2013 April 29, 2013 The inner Galactic bar traced by the VVV survey O. A. Gonzalez 1, M. Rejkuba 1, D. Minniti 2,3,4, M. Zoccali 2,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. vvv2 accepted leng ref c ESO 2013 April 29, 2013 The inner Galactic bar traced by the VVV survey O. A. Gonzalez 1, M. Rejkuba 1, D. Minniti 2,3,4, M. Zoccali 2,
Results of the OGLE-II and OGLE-III surveys
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 265 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Results of the OGLE-II and OGLE-III surveys I. Soszyński 1,2 1 Warsaw University Observatory, Al. Ujazdowskie 4, 00-478 Warszawa, Poland 2 Universidad
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 265 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Results of the OGLE-II and OGLE-III surveys I. Soszyński 1,2 1 Warsaw University Observatory, Al. Ujazdowskie 4, 00-478 Warszawa, Poland 2 Universidad
Link to the final published version available at the publisher: 2017 The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.
 Citation for the published version: Alonso-García, J., Minniti, D., Catelan, M., Ramos, R. C., Gonzalez, O. A., Hempel, M.,... Zoccali, M. (217). Extinction ratios in the inner Galaxy as revealed by the
Citation for the published version: Alonso-García, J., Minniti, D., Catelan, M., Ramos, R. C., Gonzalez, O. A., Hempel, M.,... Zoccali, M. (217). Extinction ratios in the inner Galaxy as revealed by the
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 4 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 4 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 4 Apr 2018](/thumbs/93/111409999.jpg) Draft version July 26, 218 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX61 A NEAR-INFRARED RR LYRAE CENSUS ALONG THE SOUTHERN GALACTIC PLANE: THE MILKY WAY S STELLAR FOSSIL BROUGHT TO LIGHT István Dékány,
Draft version July 26, 218 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX61 A NEAR-INFRARED RR LYRAE CENSUS ALONG THE SOUTHERN GALACTIC PLANE: THE MILKY WAY S STELLAR FOSSIL BROUGHT TO LIGHT István Dékány,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jan 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jan 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jan 2009](/thumbs/93/113141357.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 58 (28) pp. 329 343 arxiv:91.4632v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jan 29 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. OGLE-III Photometric Maps of the Small Magellanic Cloud A. U d a l s k i
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 58 (28) pp. 329 343 arxiv:91.4632v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jan 29 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. OGLE-III Photometric Maps of the Small Magellanic Cloud A. U d a l s k i
Reddening map of the Large Magellanic Cloud bar region. A. Subramaniam
 A&A 430, 421 426 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041279 c ESO 2005 Astronomy & Astrophysics Reddening map of the Large Magellanic Cloud bar region A. Subramaniam Indian Institute of Astrophysics, II Block,
A&A 430, 421 426 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041279 c ESO 2005 Astronomy & Astrophysics Reddening map of the Large Magellanic Cloud bar region A. Subramaniam Indian Institute of Astrophysics, II Block,
THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA
 143 THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA C. Reylé 1, A.C. Robin 1, M. Schultheis 1, S. Picaud 2 1 Observatoire de Besançon, CNRS UMR 6091, BP 1615, 25010 Besançon cedex, France 2 IAG/USP Departamento de
143 THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA C. Reylé 1, A.C. Robin 1, M. Schultheis 1, S. Picaud 2 1 Observatoire de Besançon, CNRS UMR 6091, BP 1615, 25010 Besançon cedex, France 2 IAG/USP Departamento de
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Mar 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Mar 2015](/thumbs/72/67208885.jpg) The VMC survey Maria-Rosa L. Cioni & the VMC team arxiv:1503.06972v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Mar 2015 The VISTA survey of the Magellanic Clouds system (VMC) is a public survey project of the European Southern
The VMC survey Maria-Rosa L. Cioni & the VMC team arxiv:1503.06972v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Mar 2015 The VISTA survey of the Magellanic Clouds system (VMC) is a public survey project of the European Southern
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Dec 2008](/thumbs/91/105920750.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. olmo ref c ESO 2008 December 22, 2008 Letter to the Editor Double mode RR Lyrae stars in Omega Centauri A. Olech 1 and P. Moskalik 1 arxiv:0812.4173v1 [astro-ph]
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. olmo ref c ESO 2008 December 22, 2008 Letter to the Editor Double mode RR Lyrae stars in Omega Centauri A. Olech 1 and P. Moskalik 1 arxiv:0812.4173v1 [astro-ph]
Colors of c-type RR Lyrae Stars and Interstellar Reddening
 Regional Variable Star Conference: Physics & Astronomy Department, Michigan State University: 40 Years of Variable Stars: A Celebration of Contributions by Horace A. Smith ed. K. Kinemuchi (Sunspot, NM:
Regional Variable Star Conference: Physics & Astronomy Department, Michigan State University: 40 Years of Variable Stars: A Celebration of Contributions by Horace A. Smith ed. K. Kinemuchi (Sunspot, NM:
Updates from the VVV Templates Project
 Pontificia Universidad Católica Departamento de Astronomía y Astrofísica Updates from the VVV Templates Project Rodolfo Angeloni on behalf of the VVV Templates Project Team The VVV Templates Project Team
Pontificia Universidad Católica Departamento de Astronomía y Astrofísica Updates from the VVV Templates Project Rodolfo Angeloni on behalf of the VVV Templates Project Team The VVV Templates Project Team
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 7 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 7 Apr 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 7 Apr 2016](/thumbs/93/112790664.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 66 (2016) pp. 0 0 Analysis of photometric uncertainties in the OGLE-IV Galactic Bulge microlensing survey data 1 arxiv:1604.01966v1 [astro-ph.im] 7 Apr 2016 J. S k o w r o n 1, A.
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 66 (2016) pp. 0 0 Analysis of photometric uncertainties in the OGLE-IV Galactic Bulge microlensing survey data 1 arxiv:1604.01966v1 [astro-ph.im] 7 Apr 2016 J. S k o w r o n 1, A.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 2 Mar 2000
 1 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Catalog of Microlensing Events in the Galactic Bulge arxiv:astro-ph/0002418v2 2 Mar 2000 A. U d a l s k i 1, K. Ż e b r u ń 1 M. S z y m a ń s k i 1, M.
1 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Catalog of Microlensing Events in the Galactic Bulge arxiv:astro-ph/0002418v2 2 Mar 2000 A. U d a l s k i 1, K. Ż e b r u ń 1 M. S z y m a ń s k i 1, M.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 19 Dec 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 19 Dec 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 19 Dec 2016](/thumbs/91/107604750.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 66 (2016) pp. 0 0 The OGLE Collection of Variable Stars. Eclipsing Binaries in the Magellanic System 1 arxiv:1612.06394v1 [astro-ph.sr] 19 Dec 2016 M. P a w l a k 1, I. S o s z y
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 66 (2016) pp. 0 0 The OGLE Collection of Variable Stars. Eclipsing Binaries in the Magellanic System 1 arxiv:1612.06394v1 [astro-ph.sr] 19 Dec 2016 M. P a w l a k 1, I. S o s z y
The optical gravitational lensing experiment. Variable stars in globular clusters
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS OCTOBER II 1997, PAGE 343 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 125, 343-353 (1997) The optical gravitational lensing experiment. Variable stars in globular clusters
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS OCTOBER II 1997, PAGE 343 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 125, 343-353 (1997) The optical gravitational lensing experiment. Variable stars in globular clusters
OGLE-TR-56. Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha INTRODUCTION
 OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011](/thumbs/89/98822124.jpg) The Edge of the Milky Way Stellar Disk Revealed Using Clump Giant Stars as Distance Indicators arxiv:1105.3151v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011 D. Minniti 1,2,3, R. K. Saito 1, J. Alonso-García 1, P. W. Lucas
The Edge of the Milky Way Stellar Disk Revealed Using Clump Giant Stars as Distance Indicators arxiv:1105.3151v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011 D. Minniti 1,2,3, R. K. Saito 1, J. Alonso-García 1, P. W. Lucas
2 Princeton University Observatory, Princeton, NJ , USA
 ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 49 (1999) pp. 45 57 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Cepheids in the Magellanic Clouds. II. Single-Mode Second Overtone Cepheids in the Small Magellanic Cloud by A. U
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 49 (1999) pp. 45 57 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Cepheids in the Magellanic Clouds. II. Single-Mode Second Overtone Cepheids in the Small Magellanic Cloud by A. U
2016 Bogotá, Colombia
 ADELA PRODUCTS: 2016 Bogotá, Colombia Movies The VVV Survey Extension: RRLyrae, Cepheids and more Dante Minniti The VVV Science Team Dante Minniti VVV Latest Results 1. RR Lyrae in the Bulge-Halo Transition
ADELA PRODUCTS: 2016 Bogotá, Colombia Movies The VVV Survey Extension: RRLyrae, Cepheids and more Dante Minniti The VVV Science Team Dante Minniti VVV Latest Results 1. RR Lyrae in the Bulge-Halo Transition
VISTA HEMISPHERE SURVEY DATA RELEASE 1
 Release date (will be set by ESO) VISTA HEMISPHERE SURVEY DATA RELEASE 1 PROPOSAL ESO No.: 179.A-2010 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Richard McMahon Authors: R. McMahon, M. Banerji, N. Lodieu for the VHS Collaboration
Release date (will be set by ESO) VISTA HEMISPHERE SURVEY DATA RELEASE 1 PROPOSAL ESO No.: 179.A-2010 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Richard McMahon Authors: R. McMahon, M. Banerji, N. Lodieu for the VHS Collaboration
Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars
 Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) The first C-rich Miras found in the bulge All the AGB stars confirmed in the bulge were O-rich. C-rich
Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) The first C-rich Miras found in the bulge All the AGB stars confirmed in the bulge were O-rich. C-rich
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jul 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jul 2018](/thumbs/82/86102568.jpg) Draft version July 13, 2018 Typeset using LATEX default style in AASTeX61 THE VVV SURVEY RR LYRAE POPULATION IN THE GALACTIC CENTRE REGION Rodrigo Contreras Ramos, 1, 2 Dante Minniti, 1, 3, 4 Felipe Gran,
Draft version July 13, 2018 Typeset using LATEX default style in AASTeX61 THE VVV SURVEY RR LYRAE POPULATION IN THE GALACTIC CENTRE REGION Rodrigo Contreras Ramos, 1, 2 Dante Minniti, 1, 3, 4 Felipe Gran,
THE ARAUCARIA PROJECT: AN ACCURATE DISTANCE TO THE LOCAL GROUP GALAXY NGC 6822 FROM NEAR-INFRARED PHOTOMETRY OF CEPHEID VARIABLES 1
 The Astrophysical Journal, 647:1056Y1064, 2006 August 20 # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A THE ARAUCARIA PROJECT: AN ACCURATE DISTANCE TO THE LOCAL GROUP
The Astrophysical Journal, 647:1056Y1064, 2006 August 20 # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A THE ARAUCARIA PROJECT: AN ACCURATE DISTANCE TO THE LOCAL GROUP
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 24, , 2015 A STUDY OF DOUBLE- AND MULTI-MODE RR LYRAE VARIABLES. A. V. Khruslov 1,2
 Baltic Astronomy, vol. 24, 379 386, 2015 A STUDY OF DOUBLE- AND MULTI-MODE RR LYRAE VARIABLES A. V. Khruslov 1,2 1 Institute of Astronomy, Russian Academy of Sciences, Pyatnitskaya str. 48, Moscow 119017,
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 24, 379 386, 2015 A STUDY OF DOUBLE- AND MULTI-MODE RR LYRAE VARIABLES A. V. Khruslov 1,2 1 Institute of Astronomy, Russian Academy of Sciences, Pyatnitskaya str. 48, Moscow 119017,
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
Igor Soszyński. Warsaw University Astronomical Observatory
 Igor Soszyński Warsaw University Astronomical Observatory SATELLITE vs. GROUND-BASED ASTEROSEISMOLOGY SATELLITE: Outstanding precision! High duty cycle (no aliases) HST MOST Kepler CoRoT Gaia IAU GA 2015,
Igor Soszyński Warsaw University Astronomical Observatory SATELLITE vs. GROUND-BASED ASTEROSEISMOLOGY SATELLITE: Outstanding precision! High duty cycle (no aliases) HST MOST Kepler CoRoT Gaia IAU GA 2015,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2018](/thumbs/94/118263605.jpg) AKARI color useful for classifying chemical types of Miras Noriyuki Matsunaga 1 1 Department of Astronomy, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan arxiv:1804.04940v1 [astro-ph.sr]
AKARI color useful for classifying chemical types of Miras Noriyuki Matsunaga 1 1 Department of Astronomy, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan arxiv:1804.04940v1 [astro-ph.sr]
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE VVV SURVEY RR LYRAE POPULATION ACROSS THE SOUTHERN GALACTIC PLANE
 Draft version September 13, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v. 1.0 CHARACTERIZATION OF THE VVV SURVEY RR LYRAE POPULATION ACROSS THE SOUTHERN GALACTIC PLANE Dante Minniti 1,2,3 Istvan
Draft version September 13, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v. 1.0 CHARACTERIZATION OF THE VVV SURVEY RR LYRAE POPULATION ACROSS THE SOUTHERN GALACTIC PLANE Dante Minniti 1,2,3 Istvan
VARIABLE STARS IN LARGE MAGELLANIC CLOUD GLOBULAR CLUSTERS. III. RETICULUM
 C 2013. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/6/160 VARIABLE STARS IN LARGE MAGELLANIC CLOUD GLOBULAR CLUSTERS. III. RETICULUM Charles
C 2013. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/6/160 VARIABLE STARS IN LARGE MAGELLANIC CLOUD GLOBULAR CLUSTERS. III. RETICULUM Charles
PoS(extremesky2009)103
 The study of the nature of sources AX J1749.1 2733 and AX J1749.2 2725 D. I. Karasev Space Research Institute, Profsoyuznaya str. 84/32, Moscow 117997, Russia E-mail: dkarasev@iki.rssi.ru Space Research
The study of the nature of sources AX J1749.1 2733 and AX J1749.2 2725 D. I. Karasev Space Research Institute, Profsoyuznaya str. 84/32, Moscow 117997, Russia E-mail: dkarasev@iki.rssi.ru Space Research
Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters
 Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters K. Z. Stanek 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., MS20, Cambridge, MA 02138 e-mail: kstanek@cfa.harvard.edu
Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters K. Z. Stanek 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., MS20, Cambridge, MA 02138 e-mail: kstanek@cfa.harvard.edu
MICROLENSING MAPS FOR THE MILKY WAY GALAXY N. W. Evans and V. Belokurov
 The Astrophysical Journal, 57:L119 L123, 2002 March 10 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. MICROLENSING MAPS FOR THE MILKY WAY GALAXY N. W. Evans and V. Belokurov
The Astrophysical Journal, 57:L119 L123, 2002 March 10 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. MICROLENSING MAPS FOR THE MILKY WAY GALAXY N. W. Evans and V. Belokurov
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Jun 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Jun 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Jun 2018](/thumbs/79/80081186.jpg) Draft version June 12, 2018 Typeset using LATEX default style in AASTeX61 AN AUTOMATED TOOL TO DETECT VARIABLE SOURCES IN THE VISTA VARIABLES IN THE VíA LÁCTEA SURVEY. THE VVV VARIABLES (V4 ) CATALOG OF
Draft version June 12, 2018 Typeset using LATEX default style in AASTeX61 AN AUTOMATED TOOL TO DETECT VARIABLE SOURCES IN THE VISTA VARIABLES IN THE VíA LÁCTEA SURVEY. THE VVV VARIABLES (V4 ) CATALOG OF
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 16 Jun 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 16 Jun 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 16 Jun 2011](/thumbs/72/66321273.jpg) Efficient use of simultaneous multi-band observations for variable star analysis Maria Süveges, Paul Bartholdi, Andrew Becker, Željko Ivezić, Mathias Beck and Laurent Eyer arxiv:1106.3164v1 [astro-ph.im]
Efficient use of simultaneous multi-band observations for variable star analysis Maria Süveges, Paul Bartholdi, Andrew Becker, Željko Ivezić, Mathias Beck and Laurent Eyer arxiv:1106.3164v1 [astro-ph.im]
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 12 Jul 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 12 Jul 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 12 Jul 2017](/thumbs/80/80675906.jpg) Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. popii_cep c ESO 7 July 3, 7 Galactic Bulge Population II Cepheids in the VVV Survey: Period-Luminosity Relations and a Distance to the Galactic Center A. Bhardwaj,,
Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. popii_cep c ESO 7 July 3, 7 Galactic Bulge Population II Cepheids in the VVV Survey: Period-Luminosity Relations and a Distance to the Galactic Center A. Bhardwaj,,
Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared
 Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared Preben Grosbøl European Southern Observatory Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany Abstract A sample of 54 spiral galaxies was observed
Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared Preben Grosbøl European Southern Observatory Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany Abstract A sample of 54 spiral galaxies was observed
A Direct Distance to the LMC Cepheid HV12198 from the Infrared Surface Brightness Technique
 A Direct Distance to the LMC Cepheid HV12198 from the Infrared Surface Brightness Technique W. P. Gieren 1,2 Universidad de Concepción, Departamento de Física, Casilla 160-C, Concepción, Chile arxiv:astro-ph/0003213v1
A Direct Distance to the LMC Cepheid HV12198 from the Infrared Surface Brightness Technique W. P. Gieren 1,2 Universidad de Concepción, Departamento de Física, Casilla 160-C, Concepción, Chile arxiv:astro-ph/0003213v1
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Dec 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Dec 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Dec 2010](/thumbs/73/68907833.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Minniti c ESO 2013 October 31, 2013 Discovery of VVV CL001. A Low-Mass Globular Cluster Next to UKS 1 in the Direction of the Galactic Bulge D. Minniti 1, M. Hempel
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Minniti c ESO 2013 October 31, 2013 Discovery of VVV CL001. A Low-Mass Globular Cluster Next to UKS 1 in the Direction of the Galactic Bulge D. Minniti 1, M. Hempel
The OGLE search for microlensing events towards the LMC
 The OGLE search for microlensing events towards the LMC 1,2, Szymon Kozłowski 3, Vasily Belokurov 1, Martin C. Smith 1, Jan Skowron 2 and Andrzej Udalski 2 1 Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge
The OGLE search for microlensing events towards the LMC 1,2, Szymon Kozłowski 3, Vasily Belokurov 1, Martin C. Smith 1, Jan Skowron 2 and Andrzej Udalski 2 1 Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge
RECLASSIFICATION OF ROTSE-I SCUTI STARS WITH MULTIBAND PHOTOMETRY AND FOURIER DECOMPOSITION
 The Astronomical Journal, 128:1847 1856, 2004 October # 2004. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. RECLASSIFICATION OF ROTSE-I SCUTI STARS WITH MULTIBAND PHOTOMETRY
The Astronomical Journal, 128:1847 1856, 2004 October # 2004. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. RECLASSIFICATION OF ROTSE-I SCUTI STARS WITH MULTIBAND PHOTOMETRY
The Cepheid distance to the LMC from the first results of the VISTA Magellanic Cloud (VMC) Survey.
 The Cepheid distance to the LMC from the first results of the VISTA Magellanic Cloud (VMC) Survey. Vincenzo Ripepi Marcella Marconi Maria Ida Moretti Gisella Clementini Maria Rosa Cioni INAF-Osservatorio
The Cepheid distance to the LMC from the first results of the VISTA Magellanic Cloud (VMC) Survey. Vincenzo Ripepi Marcella Marconi Maria Ida Moretti Gisella Clementini Maria Rosa Cioni INAF-Osservatorio
Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center Kailash C. Sahu Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book include more
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center Kailash C. Sahu Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book include more
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Sep 2018](/thumbs/87/95678907.jpg) Draft version October 2, 2018 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 VVV Survey of Blue Horizontal-Branch Stars in the Bulge-Halo Transition Region of the Milky Way Katherine Montenegro, 1, 2
Draft version October 2, 2018 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 VVV Survey of Blue Horizontal-Branch Stars in the Bulge-Halo Transition Region of the Milky Way Katherine Montenegro, 1, 2
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 7 Apr 1999
 1 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Cepheids in the Magellanic Clouds. I. Double-Mode Cepheids in the Small Magellanic Cloud arxiv:astro-ph/9903391v2 7 Apr 1999 A. U d a l s k i 1, I. S o s
1 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Cepheids in the Magellanic Clouds. I. Double-Mode Cepheids in the Small Magellanic Cloud arxiv:astro-ph/9903391v2 7 Apr 1999 A. U d a l s k i 1, I. S o s
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 1 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 1 Jul 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 1 Jul 2012](/thumbs/81/83375876.jpg) BD+36 3317: An Algol Type Eclipsing Binary in Delta Lyrae Cluster arxiv:1207.0194v1 [astro-ph.sr] 1 Jul 2012 O. Özdarcan, E. Sipahi, H. A. Dal Ege University, Science Faculty, Department of Astronomy and
BD+36 3317: An Algol Type Eclipsing Binary in Delta Lyrae Cluster arxiv:1207.0194v1 [astro-ph.sr] 1 Jul 2012 O. Özdarcan, E. Sipahi, H. A. Dal Ege University, Science Faculty, Department of Astronomy and
Accurate dynamical mass determination of a classical Cepheid in an eclipsing binary system
 1 Accurate dynamical mass determination of a classical Cepheid in an eclipsing binary system G. Pietrzyński 1,2, I.B. Thompson 3,W. Gieren 1, D. Graczyk 1, G. Bono 4,5, A. Udalski 2, I. Soszyński 2, D.
1 Accurate dynamical mass determination of a classical Cepheid in an eclipsing binary system G. Pietrzyński 1,2, I.B. Thompson 3,W. Gieren 1, D. Graczyk 1, G. Bono 4,5, A. Udalski 2, I. Soszyński 2, D.
RR Lyrae light curve decomposition and the Oosterhoff dichotomy
 RR Lyrae light curve decomposition and the Oosterhoff dichotomy A. Arellano Ferro Instituto de Astronomía Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México collaborators: Sunetra Giridhar, IIA, India Carlos Lázaro;
RR Lyrae light curve decomposition and the Oosterhoff dichotomy A. Arellano Ferro Instituto de Astronomía Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México collaborators: Sunetra Giridhar, IIA, India Carlos Lázaro;
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2016](/thumbs/72/67853981.jpg) Preprint 26 July 2016 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3.0 Variable Stars in the Quintuplet stellar cluster with the VVV Survey arxiv:1607.01795v2 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2016 Claudio Navarro Molina,
Preprint 26 July 2016 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3.0 Variable Stars in the Quintuplet stellar cluster with the VVV Survey arxiv:1607.01795v2 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2016 Claudio Navarro Molina,
Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases
 Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases Derck P. Smits Dept of Mathematical Sciences, PO Box 392, UNISA, 0003, South Africa E-mail: smitsdp@unisa.ac.za Abstract. A photographic
Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases Derck P. Smits Dept of Mathematical Sciences, PO Box 392, UNISA, 0003, South Africa E-mail: smitsdp@unisa.ac.za Abstract. A photographic
The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3
 336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
G.Witzel Physics and Astronomy Department, University of California, Los Angeles, CA , USA
 E-mail: shahzaman@ph1.uni-koeln.de A.Eckart E-mail: eckart@ph1.uni-koeln.de G.Witzel Physics and Astronomy Department, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1547, USA N. Sabha M. Zamaninasab
E-mail: shahzaman@ph1.uni-koeln.de A.Eckart E-mail: eckart@ph1.uni-koeln.de G.Witzel Physics and Astronomy Department, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1547, USA N. Sabha M. Zamaninasab
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
 The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
A Search for New Variable and Proper Motion Stars in the Galactic Disk. Robert A Benjamin 1 University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Whitewater, WI
 A Search for New Variable and Proper Motion Stars in the Galactic Disk Robert A Benjamin 1 University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Whitewater, WI Abstract Mid-infrared observations of sections of the Galactic
A Search for New Variable and Proper Motion Stars in the Galactic Disk Robert A Benjamin 1 University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Whitewater, WI Abstract Mid-infrared observations of sections of the Galactic
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future
 JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION
 Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Reduced data products in the ESO Phase 3 archive (Status: 02 August 2017)
 Reduced data products in the ESO Phase 3 archive (Status: 02 August 2017) The ESO Phase 3 archive provides access to reduced and calibrated data products. All these data are stored in standard formats
Reduced data products in the ESO Phase 3 archive (Status: 02 August 2017) The ESO Phase 3 archive provides access to reduced and calibrated data products. All these data are stored in standard formats
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 8 Jan 2002
 1 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Difference Image Analysis of LMC and SMC Data. The Method K. Ż e b r u ń 1,2, I. S o s z y ń s k i 1,2 and P.R. W o ź n i a k 2,3 arxiv:astro-ph/0110612v2
1 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Difference Image Analysis of LMC and SMC Data. The Method K. Ż e b r u ń 1,2, I. S o s z y ń s k i 1,2 and P.R. W o ź n i a k 2,3 arxiv:astro-ph/0110612v2
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Nov 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Nov 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Nov 2008](/thumbs/77/76265018.jpg) Self-Organizing Maps. An application to the OGLE data and the Gaia Science Alerts Łukasz Wyrzykowski, and Vasily Belokurov arxiv:0811.1808v1 [astro-ph] 12 Nov 2008 Institute of Astronomy, University of
Self-Organizing Maps. An application to the OGLE data and the Gaia Science Alerts Łukasz Wyrzykowski, and Vasily Belokurov arxiv:0811.1808v1 [astro-ph] 12 Nov 2008 Institute of Astronomy, University of
Time-Series Photometric Surveys: Some Musings
 Steve B. Howell NASA Ames Research Center 1 Introduction Time-Series surveys are designed to detect variable, transient, rare, and new astronomical sources. They aim at discovery with a goal to provide
Steve B. Howell NASA Ames Research Center 1 Introduction Time-Series surveys are designed to detect variable, transient, rare, and new astronomical sources. They aim at discovery with a goal to provide
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Aug 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Aug 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Aug 2018](/thumbs/83/88787705.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa1 c ESO 2 August 21, 2 Milky Way demographics with the VVV survey. IV. PSF photometry from almost one billion stars in the Galactic bulge and adjacent southern
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa1 c ESO 2 August 21, 2 Milky Way demographics with the VVV survey. IV. PSF photometry from almost one billion stars in the Galactic bulge and adjacent southern
On the double-mode RR Lyrae variables of the Sculptor dwarf galaxy
 A&A 375, 469 475 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010880 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics On the double-mode RR Lyrae variables of the Sculptor dwarf galaxy G. Kovács Konkoly Observatory, PO Box 67,
A&A 375, 469 475 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010880 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics On the double-mode RR Lyrae variables of the Sculptor dwarf galaxy G. Kovács Konkoly Observatory, PO Box 67,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jan 2019](/thumbs/88/115899635.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (0000) Printed 25 January 2019 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Three candidate globular clusters discovered in the Galactic bulge arxiv:1901.08574v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jan 2019
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (0000) Printed 25 January 2019 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Three candidate globular clusters discovered in the Galactic bulge arxiv:1901.08574v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jan 2019
Addendum: GLIMPSE Validation Report
 August 18, 2004 Addendum: GLIMPSE Validation Report The GLIMPSE Team 1. Motivation In our Validation Report of Jan. 30, 2004, we produced reliability calculations and discussed photometric accuracy estimates
August 18, 2004 Addendum: GLIMPSE Validation Report The GLIMPSE Team 1. Motivation In our Validation Report of Jan. 30, 2004, we produced reliability calculations and discussed photometric accuracy estimates
C. Watson, E. Churchwell, R. Indebetouw, M. Meade, B. Babler, B. Whitney
 Reliability and Completeness for the GLIMPSE Survey C. Watson, E. Churchwell, R. Indebetouw, M. Meade, B. Babler, B. Whitney Abstract This document examines the GLIMPSE observing strategy and criteria
Reliability and Completeness for the GLIMPSE Survey C. Watson, E. Churchwell, R. Indebetouw, M. Meade, B. Babler, B. Whitney Abstract This document examines the GLIMPSE observing strategy and criteria
VISTA SV Orion Survey
 VISTA SV Orion Survey M. Petr-Gotzens, J. M. Alcalá, F. ComerÓn, T. Stanke, S. Ramsay, C. Briceño, M. McCaughrean, M. R. Zapatero Osorio, G. Hussain, H. Zinnecker, P. Teixeira, L. Spezzi, J. Oliviera,
VISTA SV Orion Survey M. Petr-Gotzens, J. M. Alcalá, F. ComerÓn, T. Stanke, S. Ramsay, C. Briceño, M. McCaughrean, M. R. Zapatero Osorio, G. Hussain, H. Zinnecker, P. Teixeira, L. Spezzi, J. Oliviera,
Parametrization and Classification of 20 Billion LSST Objects: Lessons from SDSS
 SLAC-PUB-14716 Parametrization and Classification of 20 Billion LSST Objects: Lessons from SDSS Ž. Ivezić, T. Axelrod, A.C. Becker, J. Becla, K. Borne, D.L. Burke, C.F. Claver, K.H. Cook, A. Connolly,
SLAC-PUB-14716 Parametrization and Classification of 20 Billion LSST Objects: Lessons from SDSS Ž. Ivezić, T. Axelrod, A.C. Becker, J. Becla, K. Borne, D.L. Burke, C.F. Claver, K.H. Cook, A. Connolly,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 4 Nov 2008
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 4 Nov 2008 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 4 Nov 2008](/thumbs/95/122570119.jpg) Comm. in Asteroseismology Vol. number, publication date (will be inserted in the production process) On the nature of HD 207331: a new δ Scuti variable arxiv:0810.0476v2 [astro-ph] 4 Nov 2008 L.Fox Machado
Comm. in Asteroseismology Vol. number, publication date (will be inserted in the production process) On the nature of HD 207331: a new δ Scuti variable arxiv:0810.0476v2 [astro-ph] 4 Nov 2008 L.Fox Machado
The Inner Milky Way Structure with VVV. Marina Rejkuba ESO, Germany
 The Inner Milky Way Structure with VVV Marina Rejkuba ESO, Germany Overview Red Clump stars as distance indicators Dependence on age and metallicity Tracing the bar with RC stars in VVV Inner bar flafening
The Inner Milky Way Structure with VVV Marina Rejkuba ESO, Germany Overview Red Clump stars as distance indicators Dependence on age and metallicity Tracing the bar with RC stars in VVV Inner bar flafening
Sampler of Interdisciplinary Measurement Error and Complex Data Problems
 Sampler of Interdisciplinary Measurement Error and Complex Data Problems James Long April 22, 2016 1 / 28 Time Domain Astronomy and Variable Stars An Observation on Heteroskedasticity and Misspecified
Sampler of Interdisciplinary Measurement Error and Complex Data Problems James Long April 22, 2016 1 / 28 Time Domain Astronomy and Variable Stars An Observation on Heteroskedasticity and Misspecified
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space
 The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
VARIABLE STARS IN THE UNUSUAL, METAL-RICH GLOBULAR CLUSTER NGC 6388
 AJ, IN PRESS Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 25/04/01 VARIABLE STARS IN THE UNUSUAL, METAL-RICH GLOBULAR CLUSTER NGC 6388 BARTON J. PRITZL 1,2 AND HORACE A. SMITH Dept. of Physics and
AJ, IN PRESS Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 25/04/01 VARIABLE STARS IN THE UNUSUAL, METAL-RICH GLOBULAR CLUSTER NGC 6388 BARTON J. PRITZL 1,2 AND HORACE A. SMITH Dept. of Physics and
Concepción, Chile ABSTRACT
 1 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Search for Planetary and Low-Luminosity Object Transits in the Galactic Disk. Results of 2001 Campaign Supplement A. Udalski 1, K. Żebruń 1, M. S z y m a
1 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. Search for Planetary and Low-Luminosity Object Transits in the Galactic Disk. Results of 2001 Campaign Supplement A. Udalski 1, K. Żebruń 1, M. S z y m a
Review of results from the EROS microlensing search for massive compact objects
 Author manuscript, published in "IDM008 - identification of dark matter 008, Stockholm : Sweden (008)" Review of results from the EROS microlensing search for massive compact objects Laboratoire de l Accélérateur
Author manuscript, published in "IDM008 - identification of dark matter 008, Stockholm : Sweden (008)" Review of results from the EROS microlensing search for massive compact objects Laboratoire de l Accélérateur
The Correlation Between Supermassive Black Hole Mass and the Structure of Ellipticals and Bulges
 1 The Correlation Between Supermassive Black Hole Mass and the Structure of Ellipticals and Bulges Peter Erwin 1, Alister W. Graham 2, Nicola Caon 1 (1) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, La Laguna,
1 The Correlation Between Supermassive Black Hole Mass and the Structure of Ellipticals and Bulges Peter Erwin 1, Alister W. Graham 2, Nicola Caon 1 (1) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, La Laguna,
Non-radial pulsations in RR Lyrae stars from the OGLE photometry
 Non-radial pulsations in RR Lyrae stars from the OGLE photometry Henryka Netzel CATS, 2015 with Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center Rados law Smolec Pawe l Moskalik Wojciech Dziembowski 1 / 39 RR Lyrae
Non-radial pulsations in RR Lyrae stars from the OGLE photometry Henryka Netzel CATS, 2015 with Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center Rados law Smolec Pawe l Moskalik Wojciech Dziembowski 1 / 39 RR Lyrae
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Dec 2018 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Dec 2018](/thumbs/91/106907670.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 68 (218) pp. 1 1 New Galactic multi-mode Cepheids from the ASAS-SN Survey J. J u r c s i k 1, G. H a j d u 2,3,4, and M. C a t e l a n 2,4 arxiv:1812.1575v2 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Dec 218
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 68 (218) pp. 1 1 New Galactic multi-mode Cepheids from the ASAS-SN Survey J. J u r c s i k 1, G. H a j d u 2,3,4, and M. C a t e l a n 2,4 arxiv:1812.1575v2 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Dec 218
Using globular clusters to test gravity in the weak acceleration regime
 Using globular clusters to test gravity in the weak acceleration regime Riccardo Scarpa 1, Gianni Marconi 2, Roberto Gilmozzi 2, and Giovanni Carraro 3 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain 2 European
Using globular clusters to test gravity in the weak acceleration regime Riccardo Scarpa 1, Gianni Marconi 2, Roberto Gilmozzi 2, and Giovanni Carraro 3 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain 2 European
CCD photometry of variable stars in the globular cluster NGC 288
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 120, 83-88 (1996) NOVEMBER II 1996, PAGE83 CCD photometry of variable stars in the globular cluster NGC 288 J. Kaluzny Warsaw University
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 120, 83-88 (1996) NOVEMBER II 1996, PAGE83 CCD photometry of variable stars in the globular cluster NGC 288 J. Kaluzny Warsaw University
Microlensing towards the Galactic Centre with OGLE
 Microlensing towards the Galactic Centre with OGLE Łukasz Wyrzykowski (pron.: woo-cash vi-zhi-kov-ski) Warsaw University Astronomical Observatory, Poland Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge,
Microlensing towards the Galactic Centre with OGLE Łukasz Wyrzykowski (pron.: woo-cash vi-zhi-kov-ski) Warsaw University Astronomical Observatory, Poland Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Dec 2011
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Dec 2011 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Dec 2011](/thumbs/72/66469435.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 61 (2011) pp. 285 301 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. The OGLE-III Catalog of Variable Stars. XIV. Classical and Type II Cepheids in the Galactic Bulge arxiv:1112.1406v2
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 61 (2011) pp. 285 301 The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. The OGLE-III Catalog of Variable Stars. XIV. Classical and Type II Cepheids in the Galactic Bulge arxiv:1112.1406v2
Impact of the uncertainties of the ISM when studying the IMF at intermediate masses
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 86, 562 c SAIt 2015 Memorie della Impact of the uncertainties of the ISM when studying the IMF at intermediate masses R. Mor 1, A.C. Robin 2, B. Lemasle 3, and F. Figueras 1 1 Dept. d
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 86, 562 c SAIt 2015 Memorie della Impact of the uncertainties of the ISM when studying the IMF at intermediate masses R. Mor 1, A.C. Robin 2, B. Lemasle 3, and F. Figueras 1 1 Dept. d
1 Introduction. 2 Observations. HD , an Eccentric Ellipsoidal System
 Peremennye Zvezdy (Variable Stars) 33, No. 7, 2013 Received 24 August; accepted 30 August. HD 305629, an Eccentric Ellipsoidal System S. A. Otero 1,2, G. Di Scala 3,4 1 Buenos Aires, Argentina 2 American
Peremennye Zvezdy (Variable Stars) 33, No. 7, 2013 Received 24 August; accepted 30 August. HD 305629, an Eccentric Ellipsoidal System S. A. Otero 1,2, G. Di Scala 3,4 1 Buenos Aires, Argentina 2 American
Our View of the Milky Way. 23. The Milky Way Galaxy
 23. The Milky Way Galaxy The Sun s location in the Milky Way galaxy Nonvisible Milky Way galaxy observations The Milky Way has spiral arms Dark matter in the Milky Way galaxy Density waves produce spiral
23. The Milky Way Galaxy The Sun s location in the Milky Way galaxy Nonvisible Milky Way galaxy observations The Milky Way has spiral arms Dark matter in the Milky Way galaxy Density waves produce spiral
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Oct 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Oct 2014](/thumbs/96/129296441.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 64 (2014) pp. 1 1 Over 38 000 RR Lyrae Stars in the OGLE Galactic Bulge Fields arxiv:1410.1542v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Oct 2014 I. Soszyński 1, A. Udalski 1, M. K. Szymański 1, P. Pietrukowicz
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 64 (2014) pp. 1 1 Over 38 000 RR Lyrae Stars in the OGLE Galactic Bulge Fields arxiv:1410.1542v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Oct 2014 I. Soszyński 1, A. Udalski 1, M. K. Szymański 1, P. Pietrukowicz
Multi-wavelength study of the Milky Way Galaxy
 29 th ASI Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 3, pp 79 83 Edited by Pushpa Khare & C. H. Ishwara-Chandra Multi-wavelength study of the Milky Way Galaxy Shashikiran Ganesh Physical Research Laboratory,
29 th ASI Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 3, pp 79 83 Edited by Pushpa Khare & C. H. Ishwara-Chandra Multi-wavelength study of the Milky Way Galaxy Shashikiran Ganesh Physical Research Laboratory,
Ground Based Gravitational Microlensing Searches for Extra-Solar Terrestrial Planets Sun Hong Rhie & David Bennett (University of Notre Dame)
 Ground Based Gravitational Microlensing Searches for Extra-Solar Terrestrial Planets Sun Hong Rhie & David Bennett (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: A gravitational microlensing terrestrial planet search
Ground Based Gravitational Microlensing Searches for Extra-Solar Terrestrial Planets Sun Hong Rhie & David Bennett (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: A gravitational microlensing terrestrial planet search
The chemical evolution of the Galactic Bulge seen through micro-lensing events
 The chemical evolution of the Galactic Bulge seen through micro-lensing events Sofia Feltzing Lund Observatory Main collaborators: Martin Asplund (MPA),Thomas Bensby (Lund), Andy Gold (Ohio), Jennifer
The chemical evolution of the Galactic Bulge seen through micro-lensing events Sofia Feltzing Lund Observatory Main collaborators: Martin Asplund (MPA),Thomas Bensby (Lund), Andy Gold (Ohio), Jennifer
Selection of stars to calibrate Gaia
 Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VIII, Proceedings of the XI Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on September 8 12, 2014, in Teruel, Spain. A. J. Cenarro, F. Figueras, C. Hernández-
Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VIII, Proceedings of the XI Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on September 8 12, 2014, in Teruel, Spain. A. J. Cenarro, F. Figueras, C. Hernández-
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 22 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 22 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 22 Oct 2018](/thumbs/89/98792346.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 68 (2018) pp. 0 0 OGLE Collection of Galactic Cepheids arxiv:1810.09489v1 [astro-ph.sr] 22 Oct 2018 A. Udalski 1, I. Soszyński 1, P. Pietrukowicz 1, M. K. Szymański 1, D. M. Skowron
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 68 (2018) pp. 0 0 OGLE Collection of Galactic Cepheids arxiv:1810.09489v1 [astro-ph.sr] 22 Oct 2018 A. Udalski 1, I. Soszyński 1, P. Pietrukowicz 1, M. K. Szymański 1, D. M. Skowron
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Sep 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Sep 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Sep 2016](/thumbs/93/111936231.jpg) MNRAS, 1 (1) Preprint September 1 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3. The Stellar Halo in the Inner Milky Way: Predicted Shape and Kinematics Angeles Pérez-Villegas 1, Matthieu Portail 1 and Ortwin
MNRAS, 1 (1) Preprint September 1 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3. The Stellar Halo in the Inner Milky Way: Predicted Shape and Kinematics Angeles Pérez-Villegas 1, Matthieu Portail 1 and Ortwin
Gravitational microlensing. Exoplanets Microlensing and Transit methods
 Gravitational microlensing Exoplanets Microlensing and s Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo May take place when a star-planet system crosses the visual of a background star, as a result of
Gravitational microlensing Exoplanets Microlensing and s Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo May take place when a star-planet system crosses the visual of a background star, as a result of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Mar 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Mar 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Mar 2017](/thumbs/87/95568421.jpg) Draft version August 27, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v. 1.0 arxiv:1703.02033v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Mar 2017 FSR 1716: A NEW MILKY WAY GLOBULAR CLUSTER CONFIRMED USING VVV RR LYRAE STARS
Draft version August 27, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v. 1.0 arxiv:1703.02033v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Mar 2017 FSR 1716: A NEW MILKY WAY GLOBULAR CLUSTER CONFIRMED USING VVV RR LYRAE STARS
A Calibration Method for Wide Field Multicolor. Photometric System 1
 A Calibration Method for Wide Field Multicolor Photometric System 1 Xu Zhou,Jiansheng Chen, Wen Xu, Mei Zhang... Beijing Astronomical Observatory,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, China Beijing
A Calibration Method for Wide Field Multicolor Photometric System 1 Xu Zhou,Jiansheng Chen, Wen Xu, Mei Zhang... Beijing Astronomical Observatory,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, China Beijing
New variable stars in the globular cluster NGC 288
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS OCTOBER II 1997, PAGE 337 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 125, 337-341 (1997) New variable stars in the globular cluster NGC 288 J. Kaluzny 1,W.Krzemiński 2, and
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS OCTOBER II 1997, PAGE 337 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 125, 337-341 (1997) New variable stars in the globular cluster NGC 288 J. Kaluzny 1,W.Krzemiński 2, and
High quality seeing V, I and Gunn z imaging of Terzan 4: a blue horizontal branch bulge globular cluster
 Astron. Astrophys. 319, 850 854 (1997) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS High quality seeing V, I and Gunn z imaging of Terzan 4: a blue horizontal branch bulge globular cluster S. Ortolani 1, B. Barbuy 2, and
Astron. Astrophys. 319, 850 854 (1997) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS High quality seeing V, I and Gunn z imaging of Terzan 4: a blue horizontal branch bulge globular cluster S. Ortolani 1, B. Barbuy 2, and
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 9 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 9 Jan 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 9 Jan 2015](/thumbs/96/126599964.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Navarrete2014-accepted c ESO 2018 August 11, 2018 An Updated Census of RR Lyrae Stars in the Globular Cluster ω Centauri (NGC 5139) C. Navarrete 1, 2, R. Contreras
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Navarrete2014-accepted c ESO 2018 August 11, 2018 An Updated Census of RR Lyrae Stars in the Globular Cluster ω Centauri (NGC 5139) C. Navarrete 1, 2, R. Contreras
Light curve solutions of eclipsing binaries in SMC
 Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2010) 38, 83 92 Light curve solutions of eclipsing binaries in SMC V. P. Ivanov 1, D. P. Kjurkchieva 1 and M. Srinivasa Rao 2 1 Department of Physics, Shumen University, 9700 Shumen,
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2010) 38, 83 92 Light curve solutions of eclipsing binaries in SMC V. P. Ivanov 1, D. P. Kjurkchieva 1 and M. Srinivasa Rao 2 1 Department of Physics, Shumen University, 9700 Shumen,
