Near infrared high resolution spectroscopy of variable stars G. Bono, Univ. Of Rome ToV + D. Magurno, M. Urbaneja + many others
|
|
|
- Melinda Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Near infrared high resolution spectroscopy of variable stars G. Bono, Univ. Of Rome ToV + D. Magurno, M. Urbaneja + many others
2 Near infrared high resolution spectroscopy of variable stars G. Bono, Univ. Of Rome ToV + D. Magurno, M. Urbaneja + many others OUTLINE OF THE LECTURES ONE Why variable stars? Distance indicators Stellar tracers Physics laboratories TWO Validating the machinery Pulsation cycle Telluric subtraction Metallicity gradients THREE WINERED + others NIR diagnostics Near Future: ELT
3 Near infrared high resolution spectroscopy of variable stars G. Bono, Univ. Of Rome ToV + D. Magurno, M. Urbaneja + many others OUTLINE OF THE LECTURE ONE Why variable stars: Cepheids, Miras, RR Lyrae? Distance indicators: cosmology Stellar tracers: Galactic spheroid Physics laboratories: helium abundance
4 Cepheids,Mira & RR Lyrae They can be easily identified Distance better than ~3-5% Age constraints Cepheids young [5-300 Myr] Mira Intermediate [ Gyr] RR Lyrae old [> 10 Gyr] Demanding targets!
5 Pulsation & Evolutionary Properties Cepheids: Intermediate-mass, central He-burning, blue loop, Thin disk Mira: mainly intermediate-mass, double shell burning, AGB ubiquitous
6 Pulsation & Evolutionary Properties BHB EHB RR Lyrae: low-mass, central He burning, Horizontal Branch Halo, Bulge, no Thin disk
7 Why stars pulsate? LOG K [cm2/gr] K & Υ mechanisms Eddington docet! Radial Modes LOG T The main culprit is Cp! FU FO SO
8 Why they do not pulsate? Non-linear non-local time dependent convective models. +. PdV Stellingwerf RR Lyrae pulsation models Based on the treatment of the transport equation by Castor (1968) Based on updates of Stellingwerf s original code followed extensive and detailed investigations of RR Lyrae properties. (Bono & Stellingwerf 1994 ApJS, Bono et al A&AS, ApJ, Bono et al. 2000, 2003 MNRAS, Marconi et al ApJ, Di Criscienzo et al.2004 ApJ, Marconi & Clementini 2005, Marconi & Degl Innocenti 2007, Marconi et al. 2009) Santa Fe Stellar Pulsation Meeting Tuesday, June 2, 2009
9 Basic facts Topology of the instability strip RR Lyrae in M5 K Bono et al. 1995, 1997 J-K Coppola + (2011) Cepheids & RR Lyrae: FU, FO, Mixed mode
10 Miras in the Large Magellanic Cloud FU plus several several overtones Secondary modulation [binarity] Mix between AGB and RGB stars No general consensus on the number of sequences Optical vs NIR Wood diagram
11 Basic facts Intrinsic variability Optical bands Luminosity amplitude: a few tenths to ~1.5 mag Light curve: FOs sinusoidal FUs sawtooth Radial velocity variations: Several tens of km/s Period variations (free fall time): RR Lyrae: 0.25 to less than 1 day Stetson et al. (2014)) Cepheids: a few to > 100 days Mira: from tens of days to years
12 Basic facts Intrinsic variability Surface gravity variations: of the order of 0.5 dex Effective temperature variations: few hundreds to more than 1000 K Micro-turbulence Vel. variations: of the order of a few km Continuous variation in spectral type along the pulsation cycle Proxauf et al. (2017))
13 Cepheids, Miras & RR Lyrae as distance indicators
14 Circumstantial evidence Mbol = const + 5log R + 10log Teff Stefan-Boltzmann P = (R/g) g=surface gravity P = Q ρ von Ritter relation Period-Luminosity-Color Mbol = α + β*log P + γ*log Teff M_X = α + β*log P + γ* CI Warning! The Period brings in the Stellar mass.
15 Cepheid Pulsation & Evolutionary Properties Cepheid do obey to a PLC relations (consequence of a Mass-Luminosity relation) LogL/Lo = α + β Log P + γ Log Te MV = α + β Log P + γ CI The PL neglects the width in temperature of the IS This assumption is valid in the NIR, but not in the optical [σ (V)= mag] Why we use PL instead of PLC relation? Observations: sensitivity to reddening uncertainties Theory: sensitivity to color-temperature relations
16 The largest NIR+MIR data set ever collected for LMC Cepheids Inno + (2013, IRSF survey) Optical-NIR PL relations Absolute calibration HST Galactic Cepheids (9 Benedict + new by Riess ) Empirical/theoretical evidence indicates PL relations are not universal They obey to PLZ relations
17 WMAP + PLANCK Ho = 67.8 ± 0.9 km / (s Mpc) Resolved sources 2.5σ level Re-analysis by Efstathiou (2014) using a new maser distance to NGC σ Tension or not tension?
18 New calibration by Riess + (2016) Using new optical & NIR photometry WFC3@HST for Cepheids in 10 new galaxies hosting Sne Ia (18 calibrators) SN Ia at a redshift z 0.15 Geometrical calibrators Maser galaxy NGC4258 (33% improvement) Larger sample of LMC Cepheids + 8 double eclipsing binary Larger sample of M31 Cepheids + 2 double eclipsing binary HST rigonometric parallaxes from 9 to 15 Ho=73.02 ± 1.79 km / (s Mpc) final uncertainties from 3.3% to 2.4% Worth an independent approach (M. Monelli)..
19 RR Lyrae as distance indicators They obey to NIR PL relations due to variations in BCs The spread at fixed period is intrinsic, it is not caused by photometric error RR Lyrae in ω Cen by Braga
20 RR Lyrae as distance indicators RR Lyrae in ω Cen cover more than 1 dex in iron abundance Braga
21 Beaton + (2016) An independent approach to the extragalactic distance scale: RR Lyrae + tip RGB
22 We are approaching Gaia era Very accurate geometrical distances and proper motions for primary distance indicators [spring 2018] Shallower limits for radial velocities & metallicities Running different large programmes for optical/nir Photometry + Spectroscopy M. Monelli
23 Metallicities for variable stars Are a crucial ingredient to fully exploit Gaia Trig. Parallaxes their impact on the cosmic distance scale and on cosmological parameters This appears a trivial problem, and indeed
24 spectra for ~115 Cepheids R~38,000 Red & blue arm Δλ= A t~ s S/N > From several tens to hundreds of weak FeI lines (EW<120mA) From several to tens of FeII lines Multiple spectra for Calibrating Cepheids (~12) Genovali et al. (2013;2014)
25 ~250 A new spin 50% of known Cepheids ~ % new Homogenous temperature & metallicity scale based on EWs LTE R 35,000 SNR 100 Approaching a complete census of known Cepheids Master Thesis by B. Proxauf
26 but life is never a bed of roses!!! RR Lyrae experience nonlinear phenomena: shock formation & propagation Solid empirical & theoretical evidence: UV emission, line doubling, P Cygni Steeper is the rising branch stronger the nonlinear phenomena Well known dating back to Preston & Paczynski (60s) Observing strategy: short exposures 4-8m telescopes possibly avoiding rising branch Metal abundances for RR Lyrae based on HR optical spectra are only available for ~70 field stars!!!
27 This is not a trivial issue! The cosmic conspiracy concerning the measurement of primordial He abundance (Yp) Whenever He can be measured (absorption lines) it is useless!! Early spectral types already enriched Hot & Extreme HB stars affected by grav. settling, radiative levitation, evolutionary effects
28 STELLAR PARAMETERS TO ESTIMATE Yp R Parameter (Iben 1968) A-parameter, RR Lyrae pulsation equation (Caputo 1983) Δ-parameter, difference in V magnitude Between ZAHB & LMS (Carney 90s) See Sandquist 2000, Zoccali , Salaris , Catelan 2009.but we should do better.
29 He abundance (NIR HeI line at 10830A) for 12 RGs in ω Cen by Dupree et al. (2010) Teff > 4500 K WHY NIR? Detection of HeI lines in 5 out of 12 RGs
30 He abundance (NIR HeI line at 10830A) for 12 RGs in ω Cen by Dupree et al. (2010) WHY NIR? No correlation with [Fe/H] Correlation with [Al/Fe] & [Na/Fe] Small number statistics Solid cromospheric models
31 RR Lyrae are very promising concerning He content Hot &Extreme HB stars affected by gravitational settling & radiative levitation [Behr et al. 2000; Behr 2003] Warm HB stars might not be affected by gravitational settling & radiative levitation, the temperature range is very limited [Villanova et al. 2009] RR Lyrae are not (minimally) affected by gravitational settling & radiative levitation, since a significant fraction of their envelope is convective
32 Measurements of Yp quite rewarding Boxes He recomb. Lines from No se puede mostrar la imagen. metal-poor HII regions Izotov et al ±0.002 Olive et al ±0.002 A serious discrepancy only with neutral Li Charbonnel & Primas 2005) Boesgaard et al (2005) But systematics.. ¼ of the mass in the Universe!!!
33 New paths in RR LYRAE He abundance Preston (2009,2010) He lines show up at specific phases and then disappear They are driven by shocks! I am desperately looking for atmosphere models that can allow us to measure He abundance in RR Lyrae
34 New ideas to overcome the problem Circumstantial empirical evidence Luminosity amplitudes steadily decrease when moving from optical to NIR bands by a factor 3/4 Braga + (2016,2017)
35 New ideas to overcome the problem Circumstantial empirical evidence The slope of the PL relation approaches an almost constant value when moving from optical to NIR WHY?? Neeley + (2016,2017) Optical is dominated by temperature variations NIR is dominated by radius variations Nonlinear phenomena are mitigated in NIR regime
36 Deep into the crowd! 5 Cepheids in the Nuclear Bulge! Selective absorption in K-band is Of the order of Ak~3 This means 30 magnitudes in the optical Gaia & LSST are not going to be killing machines in these environments Matsunaga , nature
37 Beyond The Galactic Centre: classical Cepheids New constraints on stellar populations & Kinematics beyond the Nuclear bulge Matsunaga + (2016)
38 Pseudo bulge or classical bulge RR Lyrae excellent to trace 3D structure of the Galactic bulge Galaxy formation & Evolution The role played by the Bar Zoccali & Valenti 2017 The transition between inner & outer Bulge metallicity gradients [?] abundances & kinematics
39 Conclusions I: (preliminary) Metal abundances (α, Fe) are fundamental ingredients to make sense of Gaia & primary distance indicators Added values in moving from optical to NIR spectroscopy: Less affected by nonlinear phenomena Exploring crucial regions of the Galactic spheroid Yp abundance: cosmic conspiracy still in act!!! Continue. Stay with us the best has to come!!!
Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative.
 Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars
 Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) The first C-rich Miras found in the bulge All the AGB stars confirmed in the bulge were O-rich. C-rich
Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) The first C-rich Miras found in the bulge All the AGB stars confirmed in the bulge were O-rich. C-rich
RR Lyraes and Distances (a neverending story)
 RR Lyraes and Distances (a neverending story) RR Lyraes are the primary Standard Candles for Population II stellar systems and the widely used method to get their visual is tied to a linear relation between
RR Lyraes and Distances (a neverending story) RR Lyraes are the primary Standard Candles for Population II stellar systems and the widely used method to get their visual is tied to a linear relation between
Building the cosmic distance scale: from Hipparcos to Gaia
 The Fundamental Distance Scale: state of the art and the Gaia perspectives 3-6 May 2011 Building the cosmic distance scale: from Hipparcos to Gaia Catherine TURON and Xavier LURI 1 ESA / ESO-H. Heyer Fundamental
The Fundamental Distance Scale: state of the art and the Gaia perspectives 3-6 May 2011 Building the cosmic distance scale: from Hipparcos to Gaia Catherine TURON and Xavier LURI 1 ESA / ESO-H. Heyer Fundamental
Simple Stellar Populations
 Stellar Objects: Simple Stellar Populations 1 Simple Stellar Populations 1 Theoretical isochrones Update date: December 14, 2010 Simple Stellar Population consists of stars born at the same time and having
Stellar Objects: Simple Stellar Populations 1 Simple Stellar Populations 1 Theoretical isochrones Update date: December 14, 2010 Simple Stellar Population consists of stars born at the same time and having
Chapter 8: Simple Stellar Populations
 Chapter 8: Simple Stellar Populations Simple Stellar Population consists of stars born at the same time and having the same initial element composition. Stars of different masses follow different evolutionary
Chapter 8: Simple Stellar Populations Simple Stellar Population consists of stars born at the same time and having the same initial element composition. Stars of different masses follow different evolutionary
The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920)
 The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920) Heber Curtis Our Galaxy is rather small, with Sun near the center. 30,000 LY diameter. Universe composed of many separate galaxies Spiral nebulae = island
The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920) Heber Curtis Our Galaxy is rather small, with Sun near the center. 30,000 LY diameter. Universe composed of many separate galaxies Spiral nebulae = island
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
That other way to measure H0:
 That other way to measure H0: Rachael L. Beaton Carnegie Observatories Carnegie-Chicago Hubble Program A prospectus on distance measurement with Image: NASA/JPL WFIRST-AFTA Distance Ladder The distance
That other way to measure H0: Rachael L. Beaton Carnegie Observatories Carnegie-Chicago Hubble Program A prospectus on distance measurement with Image: NASA/JPL WFIRST-AFTA Distance Ladder The distance
Myung Gyoon Lee with In Sung Jang
 Myung Gyoon Lee with In Sung Jang Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Cosmological Quests for the Next Decade, Apr 16-18, 2014, KASI, Korea 1 Past: Two number cosmology A
Myung Gyoon Lee with In Sung Jang Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Cosmological Quests for the Next Decade, Apr 16-18, 2014, KASI, Korea 1 Past: Two number cosmology A
Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations
 Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations We now consider the case when individual stars are not resolved. So we need to use photometric and spectroscopic observations of integrated magnitudes, colors
Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations We now consider the case when individual stars are not resolved. So we need to use photometric and spectroscopic observations of integrated magnitudes, colors
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars
 Summary: Nuclear burning in stars Reaction 4 1 H 4 He 3 4 He 12 C 12 C + 4 He 16 O, Ne, Na, Mg Ne O, Mg O Mg, S Si Fe peak Min. Temp. 10 7 o K 2x10 8 8x10 8 1.5x10 9 2x10 9 3x10 9 Evolution through nuclear
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars Reaction 4 1 H 4 He 3 4 He 12 C 12 C + 4 He 16 O, Ne, Na, Mg Ne O, Mg O Mg, S Si Fe peak Min. Temp. 10 7 o K 2x10 8 8x10 8 1.5x10 9 2x10 9 3x10 9 Evolution through nuclear
Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances
 Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances Final Results from the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project to Measure the Hubble Constant Freedman, Madore, Gibson, et al., Astrophysical Journal
Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances Final Results from the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project to Measure the Hubble Constant Freedman, Madore, Gibson, et al., Astrophysical Journal
ASTR STELLAR PULSATION COMPONENT. Peter Wood Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics
 ASTR 3007 - STELLAR PULSATION COMPONENT Peter Wood Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics TOPICS COVERED Main types of variable stars Linear adiabatic pulsation theory => periods of pulsation Linear
ASTR 3007 - STELLAR PULSATION COMPONENT Peter Wood Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics TOPICS COVERED Main types of variable stars Linear adiabatic pulsation theory => periods of pulsation Linear
Myung Gyoon Lee. Seoul National University (SNU), Korea. The 7 th Survey Science Workshop, Jan 15-17, 2018, High-1 Resort, Korea
 Myung Gyoon Lee with In Sung Jang (AIP) Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University (SNU), Korea The 7 th Survey Science Workshop, Jan 15-17, 2018, High-1 Resort, Korea 1 H 0 Today s Expansion
Myung Gyoon Lee with In Sung Jang (AIP) Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University (SNU), Korea The 7 th Survey Science Workshop, Jan 15-17, 2018, High-1 Resort, Korea 1 H 0 Today s Expansion
Mira variables They have very regular light curves, with amplitude V > 2.5 m, and periods Π > 100 days.
 5 Pulsations Most AGB stars are variable stars, due to the fact that they pulsate. The periods are long, from 10 to 1000s of days, and they are therefore called Long Period Variables, or LPVs. These long
5 Pulsations Most AGB stars are variable stars, due to the fact that they pulsate. The periods are long, from 10 to 1000s of days, and they are therefore called Long Period Variables, or LPVs. These long
Cosmology at a Crossroads: Tension With the Hubble Constant
 Cosmology at a Crossroads: Tension With the Hubble Constant Wendy L. Freedman We are at an interesting juncture in cosmology. With new methods and technology, the accuracy in measurement of the Hubble
Cosmology at a Crossroads: Tension With the Hubble Constant Wendy L. Freedman We are at an interesting juncture in cosmology. With new methods and technology, the accuracy in measurement of the Hubble
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 4 Sep 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 4 Sep 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 4 Sep 2009](/thumbs/86/94443895.jpg) RR Lyrae Pulsation Theory Marcella Marconi INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, Vicolo Moiariello 16, 80131 Napoli, Italy arxiv:0909.0900v1 [astro-ph.sr] 4 Sep 2009 Abstract. RR Lyrae stars play
RR Lyrae Pulsation Theory Marcella Marconi INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, Vicolo Moiariello 16, 80131 Napoli, Italy arxiv:0909.0900v1 [astro-ph.sr] 4 Sep 2009 Abstract. RR Lyrae stars play
The Old Stellar Population Studies with Subaru Young-Wook Lee Yonsei Univ., Seoul, Korea
 (Some humble suggestions for) The Old Stellar Population Studies with Subaru Young-Wook Lee Yonsei Univ., Seoul, Korea 1. Globular cluster Dwarf galaxy Connection (Some) Globular clusters show multiple
(Some humble suggestions for) The Old Stellar Population Studies with Subaru Young-Wook Lee Yonsei Univ., Seoul, Korea 1. Globular cluster Dwarf galaxy Connection (Some) Globular clusters show multiple
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Sep 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Sep 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Sep 2007](/thumbs/77/74735149.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 2018 March 19, 2018 RR Lyrae stars in Galactic globular clusters. I. The Period-Amplitude relation. G. Bono 1,2, F. Caputo 1, M. Di Criscienzo 1,3 (Affiliations
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 2018 March 19, 2018 RR Lyrae stars in Galactic globular clusters. I. The Period-Amplitude relation. G. Bono 1,2, F. Caputo 1, M. Di Criscienzo 1,3 (Affiliations
Evolution Beyond the Red Giants
 Evolution Beyond the Red Giants Interior Changes Sub-giant star 1 Post-Helium Burning What happens when there is a new core of non-burning C and O? 1. The core must contract, which increases the pressure
Evolution Beyond the Red Giants Interior Changes Sub-giant star 1 Post-Helium Burning What happens when there is a new core of non-burning C and O? 1. The core must contract, which increases the pressure
THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS. B. Barbuy
 THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS B. Barbuy IAG - Universidade de São Paulo Outline: Interest of studies on Galactic bulge and globulars Data available on metallicity,, kinematics in field
THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS B. Barbuy IAG - Universidade de São Paulo Outline: Interest of studies on Galactic bulge and globulars Data available on metallicity,, kinematics in field
Star clusters laboratories of stellar structure theory. Achim Weiss Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics (Garching, Germany)
 Star clusters laboratories of stellar structure theory Achim Weiss Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics (Garching, Germany) Motivation Stars are complex objects Stellar evolution theory tries to treat
Star clusters laboratories of stellar structure theory Achim Weiss Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics (Garching, Germany) Motivation Stars are complex objects Stellar evolution theory tries to treat
Lecture 1: Introduction. Literature: Onno Pols chapter 1, Prialnik chapter 1
 Lecture 1: Introduction Literature: Onno Pols chapter 1, Prialnik chapter 1!" Goals of the Course! Understand the global characteristics of stars! Relate relevant microphysics to the global stellar characteristics!
Lecture 1: Introduction Literature: Onno Pols chapter 1, Prialnik chapter 1!" Goals of the Course! Understand the global characteristics of stars! Relate relevant microphysics to the global stellar characteristics!
Measuring the Hubble Constant. Fundamental Cosmic Distance Scale Naples, May 3, 2011 Wendy Freedman Carnegie Observatories
 Measuring the Hubble Constant Fundamental Cosmic Distance Scale Naples, May 3, 2011 Wendy Freedman Carnegie Observatories Allan Sandage (1926-2010) UnProgress in Measuring H o HST Factor of 2 Era Era of
Measuring the Hubble Constant Fundamental Cosmic Distance Scale Naples, May 3, 2011 Wendy Freedman Carnegie Observatories Allan Sandage (1926-2010) UnProgress in Measuring H o HST Factor of 2 Era Era of
The physics of stars. A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure.
 Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 15 May 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 15 May 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 15 May 2015](/thumbs/92/108118305.jpg) Draft version April 4, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 ON A NEW THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK FOR RR LYRAE STARS I: THE METALLICITY DEPENDENCE M. Marconi 1, G. Coppola 1, G. Bono
Draft version April 4, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 ON A NEW THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK FOR RR LYRAE STARS I: THE METALLICITY DEPENDENCE M. Marconi 1, G. Coppola 1, G. Bono
Recent Researches concerning Semi-Regular Variables
 Recent Researches concerning Semi-Regular Variables I.S. Glass (SAAO) ASSA Symposium, Durban 2008 Distances in the Universe - the distance ladder a summary Trig parallaxes only direct method Variable stars
Recent Researches concerning Semi-Regular Variables I.S. Glass (SAAO) ASSA Symposium, Durban 2008 Distances in the Universe - the distance ladder a summary Trig parallaxes only direct method Variable stars
Chapter 7: From theory to observations
 Chapter 7: From theory to observations Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle, predict the evolution of the stellar bolometric luminosity, effective
Chapter 7: From theory to observations Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle, predict the evolution of the stellar bolometric luminosity, effective
Lecture 25: The Cosmic Distance Scale Sections 25-1, 26-4 and Box 26-1
 Lecture 25: The Cosmic Distance Scale Sections 25-1, 26-4 and Box 26-1 Key Ideas The Distance Problem Geometric Distances Trigonometric Parallaxes Luminosity Distances Standard Candles Spectroscopic Parallaxes
Lecture 25: The Cosmic Distance Scale Sections 25-1, 26-4 and Box 26-1 Key Ideas The Distance Problem Geometric Distances Trigonometric Parallaxes Luminosity Distances Standard Candles Spectroscopic Parallaxes
Lecture 11: Ages and Metalicities from Observations A Quick Review
 Lecture 11: Ages and Metalicities from Observations A Quick Review Ages from main-sequence turn-off stars Main sequence lifetime: lifetime = fuel / burning rate $ M " MS = 7 #10 9 % & M $ L " MS = 7 #10
Lecture 11: Ages and Metalicities from Observations A Quick Review Ages from main-sequence turn-off stars Main sequence lifetime: lifetime = fuel / burning rate $ M " MS = 7 #10 9 % & M $ L " MS = 7 #10
Stellar Evolution & issues related to the post Turn-Off evolution
 Stellar Evolution & issues related to the post Turn-Off evolution Santi Cassisi INAF - Astronomical Observatory of Teramo, Italy The point of view of Population Synthesis users What do they want? Magnitudes
Stellar Evolution & issues related to the post Turn-Off evolution Santi Cassisi INAF - Astronomical Observatory of Teramo, Italy The point of view of Population Synthesis users What do they want? Magnitudes
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Nov 2005
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 76/4, 1 c SAIt 24 Memorie della Å Ø ÐÐ ØÝ «Ø ÓÒ Ø Ò ÓÒ ÓÙ Ð ¹ÑÓ Ô G. Kovács arxiv:astro-ph/511524v1 17 Nov 25 Konkoly Observatory, Budapest, Hungary e-mail: kovacs@konkoly.hu Abstract.
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 76/4, 1 c SAIt 24 Memorie della Å Ø ÐÐ ØÝ «Ø ÓÒ Ø Ò ÓÒ ÓÙ Ð ¹ÑÓ Ô G. Kovács arxiv:astro-ph/511524v1 17 Nov 25 Konkoly Observatory, Budapest, Hungary e-mail: kovacs@konkoly.hu Abstract.
The Next 2-3 Weeks. Important to read through Chapter 17 (Relativity) before I start lecturing on it.
 The Next 2-3 Weeks [27.1] The Extragalactic Distance Scale. [27.2] The Expansion of the Universe. [29.1] Newtonian Cosmology [29.2] The Cosmic Microwave Background [17] General Relativity & Black Holes
The Next 2-3 Weeks [27.1] The Extragalactic Distance Scale. [27.2] The Expansion of the Universe. [29.1] Newtonian Cosmology [29.2] The Cosmic Microwave Background [17] General Relativity & Black Holes
Stellar Populations in the Local Group
 Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
RR Lyrae light curve decomposition and the Oosterhoff dichotomy
 RR Lyrae light curve decomposition and the Oosterhoff dichotomy A. Arellano Ferro Instituto de Astronomía Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México collaborators: Sunetra Giridhar, IIA, India Carlos Lázaro;
RR Lyrae light curve decomposition and the Oosterhoff dichotomy A. Arellano Ferro Instituto de Astronomía Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México collaborators: Sunetra Giridhar, IIA, India Carlos Lázaro;
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars. Exoplanets Properties of the host stars. Characterization of the exoplanet host stars
 Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Distance measurements
 Distance measurements Pierre Hily-Blant 2018-19 Contents A current issue: The Hubble constant As you know, the Universe is expanding (this expansion is currently accelerating). The Hubble's law says that
Distance measurements Pierre Hily-Blant 2018-19 Contents A current issue: The Hubble constant As you know, the Universe is expanding (this expansion is currently accelerating). The Hubble's law says that
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
Practice Problem!! Assuming a uniform protogalactic (H and He only) cloud with a virial temperature of 10 6 K and a density of 0.
 Practice Problem Assuming a uniform protogalactic (H and He only) cloud with a virial temperature of 10 6 K and a density of 0.05 cm -3 (a) estimate the minimum mass that could collapse, (b) what is the
Practice Problem Assuming a uniform protogalactic (H and He only) cloud with a virial temperature of 10 6 K and a density of 0.05 cm -3 (a) estimate the minimum mass that could collapse, (b) what is the
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 18 Jun 2003
 RR Lyrae stars in Galactic globular clusters. II. A theoretical approach to variables in M3 Marconi, M. 1, Caputo, F. 2, Di Criscienzo, M. 1, and Castellani, M. 2 arxiv:astro-ph/0306356v1 18 Jun 2003 ABSTRACT
RR Lyrae stars in Galactic globular clusters. II. A theoretical approach to variables in M3 Marconi, M. 1, Caputo, F. 2, Di Criscienzo, M. 1, and Castellani, M. 2 arxiv:astro-ph/0306356v1 18 Jun 2003 ABSTRACT
Results of the OGLE-II and OGLE-III surveys
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 265 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Results of the OGLE-II and OGLE-III surveys I. Soszyński 1,2 1 Warsaw University Observatory, Al. Ujazdowskie 4, 00-478 Warszawa, Poland 2 Universidad
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 265 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Results of the OGLE-II and OGLE-III surveys I. Soszyński 1,2 1 Warsaw University Observatory, Al. Ujazdowskie 4, 00-478 Warszawa, Poland 2 Universidad
Oxygen in red giants from near-infrared OH lines: 3D effects and first results from. Puerto de la Cruz, May 14, 2012! Carlos Allende Prieto!
 Oxygen in red giants from near-infrared OH lines: 3D effects and first results from Puerto de la Cruz, May 14, 2012! Carlos Allende Prieto! Overview! 1. APOGEE: status and prospects! 2. A first look at
Oxygen in red giants from near-infrared OH lines: 3D effects and first results from Puerto de la Cruz, May 14, 2012! Carlos Allende Prieto! Overview! 1. APOGEE: status and prospects! 2. A first look at
From theory to observations
 Stellar Objects: From theory to observations 1 From theory to observations Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle, give the prediction of the
Stellar Objects: From theory to observations 1 From theory to observations Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle, give the prediction of the
The Giant Branches. Stellar evolution of RGB and AGB stars. Importance, features, uncertainties
 The Giant Branches Stellar evolution of RGB and AGB stars Importance, features, uncertainties Achim Weiss (Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik, Garching) M5 (Rosenberg et al. 2000) Giant Branches MACHO
The Giant Branches Stellar evolution of RGB and AGB stars Importance, features, uncertainties Achim Weiss (Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik, Garching) M5 (Rosenberg et al. 2000) Giant Branches MACHO
From theory to observations
 Stellar Objects: From theory to observations 1 From theory to observations Update date: December 13, 2010 Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle,
Stellar Objects: From theory to observations 1 From theory to observations Update date: December 13, 2010 Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle,
Modeling of RR Lyrae light curves: the case of M3 ABSTRACT
 A&A 474, 557 563 (27) DOI: 151/4-6361:26584 c ESO 27 Astronomy & Astrophysics Modeling of RR Lyrae light curves: the case of M3 M. Marconi 1 and S. Degl Innocenti 2,3 1 INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di
A&A 474, 557 563 (27) DOI: 151/4-6361:26584 c ESO 27 Astronomy & Astrophysics Modeling of RR Lyrae light curves: the case of M3 M. Marconi 1 and S. Degl Innocenti 2,3 1 INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di
Stellar Population Synthesis: The Role of Adaptive Optics
 Stellar Population Synthesis: The Role of Adaptive Optics Jason Melbourne (Caltech) Nearby (2.5 Mpc) Dwarf Irregular Galaxy KKH 98 HST F475W (Blue), HST F814W (Green), Keck AO K-band (red) Melbourne et
Stellar Population Synthesis: The Role of Adaptive Optics Jason Melbourne (Caltech) Nearby (2.5 Mpc) Dwarf Irregular Galaxy KKH 98 HST F475W (Blue), HST F814W (Green), Keck AO K-band (red) Melbourne et
Chemistry & Dynamics of the Milky Way From Before Hipparcos Until Gaia
 Chemistry & Dynamics of the Milky Way From Before Hipparcos Until Gaia J. Andersen 1,2, B. Nordström 1,2 1 Dark Cosmology Centre, The Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, Denmark 2 Stellar Astrophysics
Chemistry & Dynamics of the Milky Way From Before Hipparcos Until Gaia J. Andersen 1,2, B. Nordström 1,2 1 Dark Cosmology Centre, The Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, Denmark 2 Stellar Astrophysics
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli. Lecture 16
 University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution
 Ay 1 Lecture 9 M7 ESO HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution 9.1 The HR Diagram Stellar Spectral Types Temperature L T Y The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR) Diagram It is a plot of stellar luminosity
Ay 1 Lecture 9 M7 ESO HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution 9.1 The HR Diagram Stellar Spectral Types Temperature L T Y The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR) Diagram It is a plot of stellar luminosity
Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations
 Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations Felice Cusano INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna LBT Team Italy collaborators: Gisella Clementini, Alessia Garofalo, Michele
Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations Felice Cusano INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna LBT Team Italy collaborators: Gisella Clementini, Alessia Garofalo, Michele
Lecture 28: Spiral Galaxies Readings: Section 25-4, 25-5, and 26-3
 Lecture 28: Spiral Galaxies Readings: Section 25-4, 25-5, and 26-3 Key Ideas: Disk & Spheroid Components Old Stars in Spheroid Old & Young Stars in Disk Rotation of the Disk: Differential Rotation Pattern
Lecture 28: Spiral Galaxies Readings: Section 25-4, 25-5, and 26-3 Key Ideas: Disk & Spheroid Components Old Stars in Spheroid Old & Young Stars in Disk Rotation of the Disk: Differential Rotation Pattern
An Extended View of the Pulsating Stars in the Carina Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy
 Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela) & Mario Mateo (University of Michigan, USA) ESO/G. Bono & CTIO An Extended View of the Pulsating Stars in the Carina Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy CMD from Monelli et al (2003)
Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela) & Mario Mateo (University of Michigan, USA) ESO/G. Bono & CTIO An Extended View of the Pulsating Stars in the Carina Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy CMD from Monelli et al (2003)
The Cepheid distance to the LMC from the first results of the VISTA Magellanic Cloud (VMC) Survey.
 The Cepheid distance to the LMC from the first results of the VISTA Magellanic Cloud (VMC) Survey. Vincenzo Ripepi Marcella Marconi Maria Ida Moretti Gisella Clementini Maria Rosa Cioni INAF-Osservatorio
The Cepheid distance to the LMC from the first results of the VISTA Magellanic Cloud (VMC) Survey. Vincenzo Ripepi Marcella Marconi Maria Ida Moretti Gisella Clementini Maria Rosa Cioni INAF-Osservatorio
Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy
 Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy Measuring distances to stars is one of the biggest challenges in Astronomy. If we had some standard candle, some star with a known luminosity, then
Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy Measuring distances to stars is one of the biggest challenges in Astronomy. If we had some standard candle, some star with a known luminosity, then
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 5 Jan 1996
 A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: 01 (08.05.3; 08.08.2; 08.22.3; 11.04.1; 11.13.1) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS 1.2.2008 The distance modulus of the Large Magellanic
A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: 01 (08.05.3; 08.08.2; 08.22.3; 11.04.1; 11.13.1) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS 1.2.2008 The distance modulus of the Large Magellanic
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio.
![Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio. Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio.](/thumbs/94/121056697.jpg) More abs. Dust [1.1] kev V Wavelength Optical Infra-red More abs. Wilms et al. 000, ApJ, 54, 914 No grains Grains from http://www.astro.princeton.edu/~draine/dust/dustmix.html See DraineH 003a, column
More abs. Dust [1.1] kev V Wavelength Optical Infra-red More abs. Wilms et al. 000, ApJ, 54, 914 No grains Grains from http://www.astro.princeton.edu/~draine/dust/dustmix.html See DraineH 003a, column
Lecture 11: Ages and Metalicities from Observations. A Quick Review. Multiple Ages of stars in Omega Cen. Star Formation History.
 Ages from main-sequence turn-off stars Lecture 11: Main sequence lifetime: Ages and Metalicities from Observations R diagram lifetime = fuel / burning rate MV *1 M ' L ' MS = 7 10 9 ) ) M. ( L. ( A Quick
Ages from main-sequence turn-off stars Lecture 11: Main sequence lifetime: Ages and Metalicities from Observations R diagram lifetime = fuel / burning rate MV *1 M ' L ' MS = 7 10 9 ) ) M. ( L. ( A Quick
The Physics of the Interstellar Medium
 The Physics of the Interstellar Medium Ulrike Heiter Contact: 471 5970 ulrike@astro.uu.se www.astro.uu.se Matter between stars Average distance between stars in solar neighbourhood: 1 pc = 3 x 1013 km,
The Physics of the Interstellar Medium Ulrike Heiter Contact: 471 5970 ulrike@astro.uu.se www.astro.uu.se Matter between stars Average distance between stars in solar neighbourhood: 1 pc = 3 x 1013 km,
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future
 JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
Predicted properties of galactic and magellanic classical Cepheids in the SDSS filters
 MNRAS 428, 212 219 (2013) doi:10.1093/mnras/sts023 Predicted properties of galactic and magellanic classical Cepheids in the SDSS filters M. Di Criscienzo, 1 M. Marconi, 1 I. Musella, 1 M. Cignoni 2 and
MNRAS 428, 212 219 (2013) doi:10.1093/mnras/sts023 Predicted properties of galactic and magellanic classical Cepheids in the SDSS filters M. Di Criscienzo, 1 M. Marconi, 1 I. Musella, 1 M. Cignoni 2 and
Lecture 7.1: Pulsating Stars
 Lecture 7.1: Pulsating Stars Literature: KWW chapter 41!" 1 a) Classes of pulsating stars Many stars Intrinsically variable Subset: regular pulsation Type Period (d) RR Lyrae 0.3-0.9 Cepheids 1-50 W Virginis
Lecture 7.1: Pulsating Stars Literature: KWW chapter 41!" 1 a) Classes of pulsating stars Many stars Intrinsically variable Subset: regular pulsation Type Period (d) RR Lyrae 0.3-0.9 Cepheids 1-50 W Virginis
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
Observing Miras as tracers of the inner part of the Milky Way
 Observing Miras as tracers of the inner part of the Milky Way ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) Outline Introduction Miras as tracers of the Milky Way Case study 1 Miras in the bulge
Observing Miras as tracers of the inner part of the Milky Way ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) Outline Introduction Miras as tracers of the Milky Way Case study 1 Miras in the bulge
Lecture Three: Stellar Populations. Stellar Properties: Stellar Populations = Stars in Galaxies. What defines luminous properties of galaxies
 Lecture Three: ~2% of galaxy mass in stellar light Stellar Populations What defines luminous properties of galaxies face-on edge-on https://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog16/ 18 th April 2016 Sparke & Gallagher,
Lecture Three: ~2% of galaxy mass in stellar light Stellar Populations What defines luminous properties of galaxies face-on edge-on https://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog16/ 18 th April 2016 Sparke & Gallagher,
The Chemical/Dynamical Evolution of the Galactic Bulge
 Astro2020 Science White Paper The Chemical/Dynamical Evolution of the Galactic Bulge Thematic Areas: Stars and Stellar Evolution Resolved Stellar Populations and their Environments Galaxy Evolution Principal
Astro2020 Science White Paper The Chemical/Dynamical Evolution of the Galactic Bulge Thematic Areas: Stars and Stellar Evolution Resolved Stellar Populations and their Environments Galaxy Evolution Principal
Chapter 19: The Evolution of Stars
 Chapter 19: The Evolution of Stars Why do stars evolve? (change from one state to another) Energy Generation fusion requires fuel, fuel is depleted [fig 19.2] at higher temperatures, other nuclear process
Chapter 19: The Evolution of Stars Why do stars evolve? (change from one state to another) Energy Generation fusion requires fuel, fuel is depleted [fig 19.2] at higher temperatures, other nuclear process
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy
 AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
Spectroscopy of M81 Globular Clusters. Julie B. Nantais & John P. Huchra MMT Science Symposium 5/19/10
 Spectroscopy of M81 Globular Clusters Julie B. Nantais & John P. Huchra MMT Science Symposium 5/19/10 Galaxy Formation and Globular Clusters Questions: How did galaxies get to be different? Did all galaxies
Spectroscopy of M81 Globular Clusters Julie B. Nantais & John P. Huchra MMT Science Symposium 5/19/10 Galaxy Formation and Globular Clusters Questions: How did galaxies get to be different? Did all galaxies
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
 Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Identification of classical Cepheids: We identified three classical Cepheids amongst the 45 short-period variables discovered. Our sample includes classical Cepheids, type II Cepheids, eclipsing binaries
1. Identification of classical Cepheids: We identified three classical Cepheids amongst the 45 short-period variables discovered. Our sample includes classical Cepheids, type II Cepheids, eclipsing binaries
STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES
 STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES 2., classification, surface photometry Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen the Netherlands February 2010, classification, surface photometry
STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES 2., classification, surface photometry Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen the Netherlands February 2010, classification, surface photometry
Supergiant Studies out to Virgo & Fornax
 Supergiant Studies out to Virgo & Fornax Norbert Przybilla R.P. Kudritzki, M.A. Urbaneja (IfA Hawaii), A. Seifahrt (Univ. Chicago), K. Butler (LMU Munich), M.F. Nieva (Bamberg), H.-U. Käufl, A. Kaufer
Supergiant Studies out to Virgo & Fornax Norbert Przybilla R.P. Kudritzki, M.A. Urbaneja (IfA Hawaii), A. Seifahrt (Univ. Chicago), K. Butler (LMU Munich), M.F. Nieva (Bamberg), H.-U. Käufl, A. Kaufer
Determining distance. L 4π f. d = d = R θ. Standard candle. Standard ruler
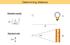 Determining distance Standard candle d = L 4π f 1 2 d L Standard ruler d = R θ θ R Determining distance: Parallax RULER tanπ = R d π R d π R = 1AU = 1.5 10 13 cm Define new distance unit: parsec (parallax-second)
Determining distance Standard candle d = L 4π f 1 2 d L Standard ruler d = R θ θ R Determining distance: Parallax RULER tanπ = R d π R d π R = 1AU = 1.5 10 13 cm Define new distance unit: parsec (parallax-second)
Astronomy C UT Regional, Spring 2018 Contact: Dhruva Karkada,
 Astronomy C UT Regional, Spring 2018 Contact: Dhruva Karkada, dkarkada@gmail.com Competitors: School Name: Team Number: This test contains 5 sections, cumulatively worth 150 points. As always, you ll have
Astronomy C UT Regional, Spring 2018 Contact: Dhruva Karkada, dkarkada@gmail.com Competitors: School Name: Team Number: This test contains 5 sections, cumulatively worth 150 points. As always, you ll have
Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 15 Terry Herter. RR Lyrae Variables Cepheids Variables Period-Luminosity Relation. A Stellar Properties 2
 Stellar Properties Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 15 Terry Herter Outline Spectroscopic Parallax Masses of Stars Periodic Variable Stars RR Lyrae Variables Cepheids Variables Period-Luminosity Relation
Stellar Properties Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 15 Terry Herter Outline Spectroscopic Parallax Masses of Stars Periodic Variable Stars RR Lyrae Variables Cepheids Variables Period-Luminosity Relation
Synthetic properties of bright metal-poor variables. II. BL Hercules stars ABSTRACT
 A&A 471, 893 900 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066541 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Synthetic properties of bright metal-poor variables II. BL Hercules stars M. Di Criscienzo 1,2,F.Caputo 3, M.
A&A 471, 893 900 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066541 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Synthetic properties of bright metal-poor variables II. BL Hercules stars M. Di Criscienzo 1,2,F.Caputo 3, M.
Globular Clusters: hot stellar populations and internal dynamics
 Globular Clusters: hot stellar populations and internal dynamics Giornate dell Osservatorio, Bologna 18-19 February 2016 Emanuele Dalessandro Globular clusters: I. hot stellar populations OABO people involved:
Globular Clusters: hot stellar populations and internal dynamics Giornate dell Osservatorio, Bologna 18-19 February 2016 Emanuele Dalessandro Globular clusters: I. hot stellar populations OABO people involved:
ASTRONOMY II Spring 1995 FINAL EXAM. Monday May 8th 2:00pm
 ASTRONOMY II - 79202 Spring 1995 FINAL EXAM Monday May 8th 2:00pm Name: You have three hours to complete this exam. I suggest you read through the entire exam before you spend too much time on any one
ASTRONOMY II - 79202 Spring 1995 FINAL EXAM Monday May 8th 2:00pm Name: You have three hours to complete this exam. I suggest you read through the entire exam before you spend too much time on any one
2. Stellar evolution a crash course
 2. Stellar evolution a crash course Extragalactic stellar distance indicators need to be bright advanced stages of stellar evolution Red Giant Star (SFB) Tip of Red Giant Branch (TRGB) Horizontal Branch
2. Stellar evolution a crash course Extragalactic stellar distance indicators need to be bright advanced stages of stellar evolution Red Giant Star (SFB) Tip of Red Giant Branch (TRGB) Horizontal Branch
Key words. Stars : evolution Stars: helium burning phase- Variables: low-mass Cepheids. arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 May 2007
![Key words. Stars : evolution Stars: helium burning phase- Variables: low-mass Cepheids. arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 May 2007 Key words. Stars : evolution Stars: helium burning phase- Variables: low-mass Cepheids. arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 May 2007](/thumbs/71/66187176.jpg) 1 Key words. Stars : evolution Stars: helium burning phase- Variables: low-mass Cepheids arxiv:0705.2679v1 [astro-ph] 18 May 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Di Criscienzo etal January 7, 2014
1 Key words. Stars : evolution Stars: helium burning phase- Variables: low-mass Cepheids arxiv:0705.2679v1 [astro-ph] 18 May 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Di Criscienzo etal January 7, 2014
Igor Soszyński. Warsaw University Astronomical Observatory
 Igor Soszyński Warsaw University Astronomical Observatory SATELLITE vs. GROUND-BASED ASTEROSEISMOLOGY SATELLITE: Outstanding precision! High duty cycle (no aliases) HST MOST Kepler CoRoT Gaia IAU GA 2015,
Igor Soszyński Warsaw University Astronomical Observatory SATELLITE vs. GROUND-BASED ASTEROSEISMOLOGY SATELLITE: Outstanding precision! High duty cycle (no aliases) HST MOST Kepler CoRoT Gaia IAU GA 2015,
Outline. Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks
 Outline Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks Why is the night sky dark? (Olber s Paradox 1826) Or what
Outline Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks Why is the night sky dark? (Olber s Paradox 1826) Or what
Distance measurements
 Distance measurements Pierre Hily-Blant Université Grenoble Alpes Université Grenoble Alpes // 2018-19 Contents 1 A current issue: The Hubble constant 2 2 Introduction 3 3 Trigonometric parallax 4 4 Photometric
Distance measurements Pierre Hily-Blant Université Grenoble Alpes Université Grenoble Alpes // 2018-19 Contents 1 A current issue: The Hubble constant 2 2 Introduction 3 3 Trigonometric parallax 4 4 Photometric
Braneworld Cosmological Perturbations
 2005 2005 2005 Spectropolarimetric Studies on Circumstellar Structure of Low-Mass Pre-Main-Sequence Stars ELT Statistical Properties of Lyman a Emitters at Redshift 5.7 Neutrino Probes of Galactic and
2005 2005 2005 Spectropolarimetric Studies on Circumstellar Structure of Low-Mass Pre-Main-Sequence Stars ELT Statistical Properties of Lyman a Emitters at Redshift 5.7 Neutrino Probes of Galactic and
DIFFERENT CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BRIGHT BRANCHES OF THE GLOBULAR CLUSTERS M3 AND M13
 The Astronomical Journal, 129:1922 1933, 2005 April # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DIFFERENT CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BRIGHT BRANCHES OF THE GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
The Astronomical Journal, 129:1922 1933, 2005 April # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DIFFERENT CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BRIGHT BRANCHES OF THE GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
Review of stellar evolution and color-magnitude diagrams
 Review of stellar evolution and color-magnitude diagrams The evolution of stars can be used to study the properties of galaxies Very characteristic features pinpoint at the age (chemistry) of the stars
Review of stellar evolution and color-magnitude diagrams The evolution of stars can be used to study the properties of galaxies Very characteristic features pinpoint at the age (chemistry) of the stars
A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 05, 2016 Read: Chap 19 04/05/16 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned by next class meeting
A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 05, 2016 Read: Chap 19 04/05/16 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned by next class meeting
12. Physical Parameters from Stellar Spectra. Fundamental effective temperature calibrations Surface gravity indicators Chemical abundances
 12. Physical Parameters from Stellar Spectra Fundamental effective temperature calibrations Surface gravity indicators Chemical abundances 1 Fundamental Properties of Stars Temperature (T) Radius (R) Chemical
12. Physical Parameters from Stellar Spectra Fundamental effective temperature calibrations Surface gravity indicators Chemical abundances 1 Fundamental Properties of Stars Temperature (T) Radius (R) Chemical
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Following the evolution of the Galactic disc with Open Clusters
 Following the evolution of the Galactic disc with Open Clusters Laura Magrini INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri With Nikos Prantzos and the GES collaboration (in particular Lorenzo Spina, Sofia
Following the evolution of the Galactic disc with Open Clusters Laura Magrini INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri With Nikos Prantzos and the GES collaboration (in particular Lorenzo Spina, Sofia
RR Lyrae in Galex. RASPUTIN Resolved And unresolved Stellar PopUlaTIoNs
 RR Lyrae in Galex Giuliano Giuffrida RASPUTIN Resolved And unresolved Stellar PopUlaTIoNs ASDC-INAF Giuseppe Bono (Univ. Tor Vergata Rome) Vittorio Braga (Univ. Tor Vergata Rome) Massimo Dall Ora (INAF-OACN)
RR Lyrae in Galex Giuliano Giuffrida RASPUTIN Resolved And unresolved Stellar PopUlaTIoNs ASDC-INAF Giuseppe Bono (Univ. Tor Vergata Rome) Vittorio Braga (Univ. Tor Vergata Rome) Massimo Dall Ora (INAF-OACN)
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12)
 Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 6 Jun 2002
 On the distance of Magellanic Clouds: first overtone Cepheids G. Bono 1, M.A.T. Groenewegen 2, M. Marconi 3, F. Caputo 1 1. Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, Via Frascati 33, 00040 Monte Porzio Catone,
On the distance of Magellanic Clouds: first overtone Cepheids G. Bono 1, M.A.T. Groenewegen 2, M. Marconi 3, F. Caputo 1 1. Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, Via Frascati 33, 00040 Monte Porzio Catone,
Globular Cluster Ages and Strömgren CCD Photometry
 Globular Cluster Ages and Strömgren CCD Photometry Frank Grundahl 1 University of Victoria, Department of Physics and Astronomy PO Box 3055, Victoria, BC, V8W 3P6, Canada Abstract. Strömgren uvby CCD photometry
Globular Cluster Ages and Strömgren CCD Photometry Frank Grundahl 1 University of Victoria, Department of Physics and Astronomy PO Box 3055, Victoria, BC, V8W 3P6, Canada Abstract. Strömgren uvby CCD photometry
Studying stars in M31 GCs using NIRI and GNIRS
 Studying stars in M31 GCs using NIRI and GNIRS Ricardo Schiavon Gemini Observatory GSM 2012 San Francisco July 19, 2012 Collaborators Andy Stephens (Gemini) Nelson Caldwell (SAO) Matthew Shetrone (HET)
Studying stars in M31 GCs using NIRI and GNIRS Ricardo Schiavon Gemini Observatory GSM 2012 San Francisco July 19, 2012 Collaborators Andy Stephens (Gemini) Nelson Caldwell (SAO) Matthew Shetrone (HET)
The King's University College Astronomy 201 Mid-Term Exam Solutions
 The King's University College Astronomy 201 Mid-Term Exam Solutions Instructions: The exam consists of two sections. Part A is 20 multiple choice questions - please record answers on the sheet provided.
The King's University College Astronomy 201 Mid-Term Exam Solutions Instructions: The exam consists of two sections. Part A is 20 multiple choice questions - please record answers on the sheet provided.
