Variable Stars Advanced Lab
|
|
|
- Elvin Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Variable Stars Advanced Lab Introduction In this lab, you will be observing several variable stars to determine the period and classification of the star. A variable star is considered any star which goes through periodic or semi-periodic variations in luminosity. Several examples of the types of variable stars are listed in Table 1: Type Prototype MV Spectral Class Pulsation Period Range Characteristic Period Classical δ Cephei -0.5 to -6 F6 to K2 1d to 50d 5d to 10d Cepheids Population II W. Virginis 0 to -3 F2 to G6 2d to 45d 12d to 28d Cepheids RR Lyrae Stars RR Lyra 0.5 to 1 A2 to F6 1.5h to 24h 0.5d Long Period σ Ceti 1 to -2 M1 to M6 130d to 500d 270d Variables (Mira) RV Tauri Stars RV Tauri -3 G K 20d to 150d 75d â Canis Majoris β Canis Majoris -3 B1, B2 4h to 65h 5h Stars Semiregular σ Herculis -1 to -3 K, M, L, T 100d to 200d 100d Red Variables Dwarf Cepheids δ Scuti 4 to 2 A to F 1h to 3h 2h ZZ Ceti Stars ZZ Ceti 30s to 1500s Table 1: Some Classes of Pulsating Stars (Zeilik, Gregory & Smith, 1992) In this lab you will make the measurements of several variable stars, over several nights. The main instrument you will be using for this experiment will be the Braeside Observatory. The Braeside telescope is a 16 inch telescope located in Flagstaff, AZ. A CCD, or Charged Coupled Device, situated at the end of the telescope converts the light which enters the telescope into the digital image. The CCD camera used on the Braeside telescope is called a SITe CCD. Each pixel making up the CCD chip is a light sensitive device which measures the amount of light falling on it. The plate scale for the camera is arcsecond/pixel which gives a field of view of 6 arcmin square. The CCD camera has several filters. Each filter selects out a region of light known as a passband. The filters are used to measure the color of astronomical objects. If an object emits more light in the blue than in green (known as visual light) then the object will appear brighter in the B filter than in the V filter. The filter wheel has 8 slots open for filters which are described in Table 2. Filter # Filter Name Wavelength Description (nm) 1 Open (no filter) 2 U 365±66 Near Ultraviolet Light 3 B 445±94 Blue Light 4 V 551±88 Visual Light 5 R 658±138 Red Light 6 I 806±149 Near Infrared 7 Pinhole 8 Neutral Density Table 2: Filters of the CCD camera and descriptions
2 Making Measurements To make measurements you will need to acquire each night: Calibration Files Standard star images Images of the Variable Star Calibration Files Calibration files will be necessary each night data is acquired. The images are used to remove obscuring dust on the optics, light sensitivity variations and additional random noise from the CCD camera. Improperly calibrating the images can cause results with larger error. Explained below are three kinds of calibration images which will be used. The bias frame is an exposure of zero exposure time. The bias frame will measure the amount of noise in each image. The electronics of the CCD camera will cause each pixel to register some amount of charge. The charge can then be misinterpreted as signal if not accounted for with the bias frame. The dark frame is an image of the same exposure time as the object, but receives no light. At a given exposure time a CCD chip will accumulate a certain amount of signal that is not related to an image. That is, if you repeat the same exposure under the same circumstances (temperature & time) the signal can be repeated. This means that if we take a dark frame and then take an image at the same temperature and for the same time as the dark frame the unwanted signal that is accumulated and recorded during the exposure on the dark frame will be on the image as well. So, if we subtract the dark frame from the image we can remove all the unwanted signal. Flat fields are images of evenly illuminated surfaces such as the twilight sky. Ideally, we would like to use flat field images taken that evening, however in case of poor weather conditions at sunset, you might use flat field images from a previous session. The images are useful in measuring the amount of dust or dirt in the optical system. A speck of dust on the mirror will be out of focus and appear on the image as faint a doughnut shaped region. Flat field images also take into account vignetting and other light varying problems. To remove these imperfections we divide the final astronomical image by the normalized flat field. Standard Stars Standard stars are stars which have well known magnitudes in several colors. Standard star measurements will allow you to calibrate the observations of the variable star to the magnitude system. Use a standard star which is not too far from the variable star (<5 ), at about the same airmass, and probably brighter than the variable star. And make sure the star is up! Alternate observations of the standard star with the variable star, making sure you have at least three sets of standard star measurements at a variety of airmasses and several images per filter in each set. Obtain measurements of the standard star in each filter used for the variable star. Standard stars are listed in section H of the The Astronomical Almanac, provided in the control room. Use standard stars that are calibrated for the Johnson UBVRI filter system. Variable Stars You will observe several variable stars in the V filter. Listed in Table 3 are possible target stars, their positions in J2000 coordinates, mean apparent visual magnitude (V), availability at 11:00 p.m. MST, and reference to a paper which studies the star. The papers referenced and many others may be found by looking at the ADS website at You may pick another star, but you will need to do a literature search for background information.
3 Name RA Dec V Availability SW And Jul-Dec HU Tau Sep-Mar DY Ori Oct-Mar W Gem Nov-Mar ζ Gem Nov-Mar RR Gem Nov-Mar W UMa Feb-Jun GW Vir Feb-Jul W Vir Feb-Jul RS Boo Mar-Jul AH Her Apr-Sep BL Her Apr-Sep EP Lyr Apr-Oct RU Peg Jul-Dec δ Cep May-Nov RV Lac Jun-Oct Table 3: Table of target stars Data Acquisition To control Braeside from ASU, you will use the program XBOBS (X-based Braeside OBserving System). The program was specifically written to operate the telescope, dome and camera. You can view the telescope via the internet at To observe from ASU and control the observatory, do the following Log into the Braeside computer located in PSH-563-A2. Login name: observer, password: braeside Open an xterm by typing xterm & at a Konsole prompt. At the observer prompt, type in idl. At the idl prompt, type in xbobs In the region marked Telescope Control go to the Dome/Tel section, hit the pulldown button marked Select and hit the Auto Open selection. This will initialize the telescope and set it up for observing. You may watch and listen to the telescope as it sets up by turning the room lights and audio on in the region marked Dome Control. When the telescope is ready for you to use, the top row of red and green lights should be all green, and any warning boxes should have disappeared. Remember to turn the room lights off before taking data. In the region marked Target Acquisition and Pointing turn the Pointing Updates on. The boxes below the switch will fill in with numbers indicating the location of the telescope and where it is pointed. In the Dome Control panel, link the dome by selecting the Link option near the Dome buttons. If this is not done then the dome will not track with the telescope. Find the location of a bright star with in one hour east or west of the meridian at the time of observing. There is a catalog of bright stars built into the program. In the same section of the widget, find the region marked Catalogs and press the button marked Local. In a few seconds a window will appear. Scroll down to find the name of the star near the meridian. Highlight the star. Hit select. The information should appear the in boxes for the Destination. Then hit exit. Move the telescope to the destination by pressing the button marked Go There. You will be able to hear the telescope move into place. Once at the location, enter the observers names in the Observer box and press the Set button all located in the Observing Interface section. Then take a short exposure (~0.5s) of the region. Enter the exposure time in the box marked Exptime, and take the exposure by pressing the button marked Expose. The image will appear in the window. You want the star as close to the center of the frame as possible. If the star is not in the frame, take a longer exposure (~15s). If the star is bright enough (>4th magnitude) then spikes of star light should enter the frame. Move the camera in small increments by going to the Manual Positioning and pressing the N, S, E, or W buttons, and adjusting the increment in the center. You can move the telescope between arcseconds.
4 Once the star is in the frame, you can center it by pressing the Recenter Image button in the Target Acquisition and Pointing section, then click on the center of the star, and then hit Go There. You will want to reset the coordinates by pressing the Reset Curr to Dest button. If the star looks like a doughnut, then you will need to focus the telescope. Go to Focus in the Observing Interface panel and adjust the focus by short amounts, press Set and take short exposures in between changing the focus. Once the star looks in focus, check the seeing estimate of the field stars by pressing Seeing Estimate in the image display panel and clicking on the center of a star. Typical seeing with Braeside is about arcsec, excellent seeing is 2.5 arcseconds and poor seeing is >~6 arcsec. While you adjust the focus, the seeing will decrease until you are at the best focus possible. Continue to get estimates of the seeing while you are observing. You can record the focus and seeing estimate on the observers log sheet in the comments column (Table 4). Once this is all set, you may go to your target. Enter the coordinates of the target and object name in the RA, Dec, and Object Name boxes in the Destination section each time you go the star, or you may add them to the local catalog. To add a star, open the local catalog, press the Add button, enter the information and then press the Add button in the new window. Move the telescope to the target as described above. Center the telescope on the target, set the filter you will be using and obtain an exposure. Get an image where the counts inside the target are between 50,000-60,000 counts in the raw image. You can check the number of counts by hitting the Track button in the image window panel. The mouse position (x and y) and counts (flux) will be displayed while you are moving the mouse over the image. Click the right mouse button to automatically move the mouse to brightest local pixel. You must click the left mouse button to deactivate tracking before proceeding. If the counts for the target are too low, for example 10,000 in 5 seconds, you can use the fact CCDs respond linearly, that is, if you want 60,000 counts, then extend your exposure time by a factor of 6. As the counts exceed 60,000, the response of the CCD changes from linear to logarithmic. Avoid using data with counts greater than 60,000. Images where the counts reach 65,536 are considered saturated and are usually notable by vertical bleeding of the stars. Finding a good exposure time may take several trials. You want images with as many counts as possible to be able to apply Poisson statistics for error analysis. Once you have the image set up the way you would like it, go to the Camera Control panel and turn on the Auto Increment option. When this is set to Off then the filename displayed in the Filename to be written box inside the Observing Interface panel will never change and you will write over the same image. Once the Auto Increment is set to On, then each exposure will save an image. When you have finished using the telescope for the night, close the telescope by selecting the Auto Close option in the Dome/Tel button in the Telescope Control panel. Use lights and camera to confirm the closure and parking of the telescope. Data Reduction The data should be analyzed using a language which you are comfortable with, such as C, Fortran, or IDL. Each file made at the telescope is written as a.fits files, and so you will need a language capable of reading the file in. The first section of each file is a header containing the observation information (filter, exposure time, RA and Dec, airmass, etc) written in ASCII format. To begin the reduction, subtract the bias image (B) from the data image (I(raw)). Then subtract the product of the dark image (D, which is normalized to one second) and the exposure time (t) of the image. Then divide the normalized flat image (F). I ( ) ( raw) B ( D t) I clean = F Measure the light from the object by summing up the pixels within a circular region around the star. Since the light from a star spreads out like a 2-dimensional gaussian, make sure you have used an area large enough to include fainter pixels. The total number of counts for a star is an instrumental flux which can be converted to a magnitude using the following equation: = 2.5 log m 10 where f is the instrumental flux per second, and m is the instrumental magnitude. ( f )
5 The error in the flux will be assumed to follow Poisson statistics, that is: σ f = f which can be used to obtain the error in the magnitude as: σ m = σ f To convert the measurements from instrumental magnitudes to an actual magnitude and correct for observing at different airmasses, you will need to make a plot of the standard star magnitude vs. airmass. Airmass is the is the secant of the angle between the star and the zenith. This value is stored in the header of each file. There is a linear relationship between magnitude and airmass. Each magnitude reported in literature is given at an airmass of 1, that is if the star was at the zenith. The slope will determine the relationship between magnitude and airmass. The offset between the instrumental magnitude and the accepted magnitude is the y-intercept. Apply the slope and y-intercept to the variable star to obtain magnitudes at 1 airmass. Make a plot of the variable star data of magnitude vs. time. Phase the data to the period to better show the periodicity of the star.
6 Start Time: End Time: Weather Conditions: Image Number Extension Number Filter Object Exposure Time Comments V ζ Gem 30s Focus = -330, Temp=25 F Table 4: Observers log sheet
Kuiper Belt Objects Advanced Lab
 Kuiper Belt Objects Advanced Lab Introduction To date, there are over 763 known Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs), including Pluto and Charon, however, because they are so distant, faint, and relatively new to
Kuiper Belt Objects Advanced Lab Introduction To date, there are over 763 known Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs), including Pluto and Charon, however, because they are so distant, faint, and relatively new to
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
 Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual Due Oct. 21, 2011 1 Pre-Lab 1.1 Photometry and the Magnitude Scale The brightness of stars is represented by its value on the magnitude scale. The ancient Greek astronomer
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual Due Oct. 21, 2011 1 Pre-Lab 1.1 Photometry and the Magnitude Scale The brightness of stars is represented by its value on the magnitude scale. The ancient Greek astronomer
You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3
 You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3 Calibration and data reduction Useful references, besides Lessons 1 and 2: The AST 142 Projects manual: http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~dmw/ast142/projects/project.pdf
You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3 Calibration and data reduction Useful references, besides Lessons 1 and 2: The AST 142 Projects manual: http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~dmw/ast142/projects/project.pdf
IN REPORT: Plate Scale and FOV of CCD for Each Telescope using Albireo Stars
 USE ASTROIMAGEJ NOT AIP4WIN To download ALL the public data from Canvas, go to Files, then click the 3 dots next to the Public Data Folder and click Download. It will download all the files at once. 6.1
USE ASTROIMAGEJ NOT AIP4WIN To download ALL the public data from Canvas, go to Files, then click the 3 dots next to the Public Data Folder and click Download. It will download all the files at once. 6.1
Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy
 Name:... Astronomy 101: Observational Astronomy Fall 2006 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy 1 Observations 1.1 Objectives and Observation Schedule During this lab each group will target a few bright stars of
Name:... Astronomy 101: Observational Astronomy Fall 2006 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy 1 Observations 1.1 Objectives and Observation Schedule During this lab each group will target a few bright stars of
CLEA/VIREO PHOTOMETRY OF THE PLEIADES
 CLEA/VIREO PHOTOMETRY OF THE PLEIADES Starting up the program The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a small (diameter=0.4 meters) research telescope.
CLEA/VIREO PHOTOMETRY OF THE PLEIADES Starting up the program The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a small (diameter=0.4 meters) research telescope.
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project
 AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium
Hubble's Law and the Age of the Universe
 Hubble's Law and the Age of the Universe Procedure: Name: 1. Login into the network using your user ID and your password. 2. Double click on the Astronomy shortcuts folder on the desktop. 3. Double click
Hubble's Law and the Age of the Universe Procedure: Name: 1. Login into the network using your user ID and your password. 2. Double click on the Astronomy shortcuts folder on the desktop. 3. Double click
PHYS133 Lab 7 The HR Diagram
 PHYS133 Lab 7 Goals: Measure brightness of various stars in the Pleiades star cluster in two different wavelength bands. Create an HR diagram based on the data taken. Use the distance modulus to determine
PHYS133 Lab 7 Goals: Measure brightness of various stars in the Pleiades star cluster in two different wavelength bands. Create an HR diagram based on the data taken. Use the distance modulus to determine
Open Cluster Photometry: Part II
 Project 4 Open Cluster Photometry: Part II Observational Astronomy ASTR 310 Fall 2005 1 Introduction The objective of this and the previous project is to learn how to produce color-magnitude diagrams of
Project 4 Open Cluster Photometry: Part II Observational Astronomy ASTR 310 Fall 2005 1 Introduction The objective of this and the previous project is to learn how to produce color-magnitude diagrams of
DOAS measurements of Atmospheric Species
 Practical Environmental Measurement Techniques: DOAS measurements of Atmospheric Species Last change of document: April 14, 2014 Supervisor: Dr. Andreas Richter, room U2090, tel 62103, and Dr. Folkard
Practical Environmental Measurement Techniques: DOAS measurements of Atmospheric Species Last change of document: April 14, 2014 Supervisor: Dr. Andreas Richter, room U2090, tel 62103, and Dr. Folkard
Lecture 8. October 25, 2017 Lab 5
 Lecture 8 October 25, 2017 Lab 5 News Lab 2 & 3 Handed back next week (I hope). Lab 4 Due today Lab 5 (Transiting Exoplanets) Handed out and observing will start Friday. Due November 8 (or later) Stellar
Lecture 8 October 25, 2017 Lab 5 News Lab 2 & 3 Handed back next week (I hope). Lab 4 Due today Lab 5 (Transiting Exoplanets) Handed out and observing will start Friday. Due November 8 (or later) Stellar
Data Reduction - Optical / NIR Imaging. Chian-Chou Chen Ph319
 Data Reduction - Optical / NIR Imaging Chian-Chou Chen (T.C.) @ Ph319 Images at different wavelengths... Images at different wavelengths... However, the raw data are always not as pretty Why? The total
Data Reduction - Optical / NIR Imaging Chian-Chou Chen (T.C.) @ Ph319 Images at different wavelengths... Images at different wavelengths... However, the raw data are always not as pretty Why? The total
Lab 1: Introduction to the sky and making telescopic observations with the CCD camera. AST 152M Lab Instructor: Greg Doppmann Due: Feb 11, 2000
 Lab 1: Introduction to the sky and making telescopic observations with the CCD camera. AST 152M Lab Instructor: Greg Doppmann Due: Feb 11, 2000 Objective: The goal of this lab is to give students their
Lab 1: Introduction to the sky and making telescopic observations with the CCD camera. AST 152M Lab Instructor: Greg Doppmann Due: Feb 11, 2000 Objective: The goal of this lab is to give students their
Photometry of Messier 34
 Photometry of Messier 34 J. Kielkopf November 12, 2012 1 Messier 34 The open cluster Messier 34 (M34) is in the solar neighborhood, lying roughly in the plane of the Milky Way galaxy in the direction of
Photometry of Messier 34 J. Kielkopf November 12, 2012 1 Messier 34 The open cluster Messier 34 (M34) is in the solar neighborhood, lying roughly in the plane of the Milky Way galaxy in the direction of
Open Cluster Research Project
 Open Cluster Research Project I. Introduction The observational data indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers
Open Cluster Research Project I. Introduction The observational data indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY. Observational Astronomy (2011) 1
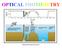 OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
a computer running the CLEA activity The Large Scale Structure of the Universe. a computer running a spreadsheet program
 TAP 704-5: Red shift The CLEA software enables you to simulate controlling a telescope so that it points at a selected galaxy, and then using a spectrometer to record the light received over a range of
TAP 704-5: Red shift The CLEA software enables you to simulate controlling a telescope so that it points at a selected galaxy, and then using a spectrometer to record the light received over a range of
Starlight in the university lab: Astrolab
 Starlight in the university lab: Astrolab Project report (Phase 1) (2- year project, started in 2013, to be completed in 2014) 1. Short summary of the completed project that we can place on the website
Starlight in the university lab: Astrolab Project report (Phase 1) (2- year project, started in 2013, to be completed in 2014) 1. Short summary of the completed project that we can place on the website
ACE Control System. 1.0-m Pomona College Telescope Table Mountain Observatory ACE User Manual April 2005 Revision All rights reserved.
 ACE Control System 1.0-m Pomona College Telescope Table Mountain Observatory ACE User Manual April 2005 Revision 1.1 1999-2005. All rights reserved. Astronomical Consultants & Equipment, Inc. P.O. Box
ACE Control System 1.0-m Pomona College Telescope Table Mountain Observatory ACE User Manual April 2005 Revision 1.1 1999-2005. All rights reserved. Astronomical Consultants & Equipment, Inc. P.O. Box
1 The Preliminary Processing
 AY 257 Modern Observational Techniques...23 1 The Preliminary Processing Frames must be corrected for a bias level and quantum efficiency variations on all scales. For a minority of CCDs and most near-ir
AY 257 Modern Observational Techniques...23 1 The Preliminary Processing Frames must be corrected for a bias level and quantum efficiency variations on all scales. For a minority of CCDs and most near-ir
* All those going out on the roof at night must carry a torch.
 University of Exeter Observatory User Note: Observatory safety Tim Harries, September 2003 Observatory Safety Working at night in proximity to moving equipment is potentially hazardous, and safety is our
University of Exeter Observatory User Note: Observatory safety Tim Harries, September 2003 Observatory Safety Working at night in proximity to moving equipment is potentially hazardous, and safety is our
Lecture 2. September 13, 2018 Coordinates, Telescopes and Observing
 Lecture 2 September 13, 2018 Coordinates, Telescopes and Observing News Lab time assignments are on class webpage. Lab 2 Handed out today and is due September 27. Observing commences starting tomorrow.
Lecture 2 September 13, 2018 Coordinates, Telescopes and Observing News Lab time assignments are on class webpage. Lab 2 Handed out today and is due September 27. Observing commences starting tomorrow.
Lab 7: The H-R Diagram of an Open Cluster
 Lab 7: The H-R Diagram of an Open Cluster Due Date: 2007 Nov 27 (after thanksgiving) 1 Introduction: The HR Diagram In this two week project you will do absolute (not differential) photometry with a CCD
Lab 7: The H-R Diagram of an Open Cluster Due Date: 2007 Nov 27 (after thanksgiving) 1 Introduction: The HR Diagram In this two week project you will do absolute (not differential) photometry with a CCD
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
 Name: Lab Partner: Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Edited by Lucy Kulbago, John Carroll University 11/24/2008
Name: Lab Partner: Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Edited by Lucy Kulbago, John Carroll University 11/24/2008
Operating the Celestron 14 Telescope
 Operating the Celestron 14 Telescope 1. The Telescope and Its Controls The Celestron 14-inch telescope is located in the east bay of the observatory (Fig. 1). It is a Schmidt-Cassegrain type instrument;
Operating the Celestron 14 Telescope 1. The Telescope and Its Controls The Celestron 14-inch telescope is located in the east bay of the observatory (Fig. 1). It is a Schmidt-Cassegrain type instrument;
AAG TPoint Mapper (Version 1.40)
 AAG TPoint Mapper (Version 1.40) AAG_TPointMapper works together with Maxim DL, Pinpoint, TheSky6 and TPoint to automate the process of building a TPoint model for a GOTO telescope connected to TheSky6.
AAG TPoint Mapper (Version 1.40) AAG_TPointMapper works together with Maxim DL, Pinpoint, TheSky6 and TPoint to automate the process of building a TPoint model for a GOTO telescope connected to TheSky6.
Observing Instructions XCOV30 Oct/Nov
 Observing Instructions XCOV30 Oct/Nov 2016 http://darc.physics.udel.edu/wet/xcov30 1. Purpose and Plan: 1) Primary Targets: a) NGC 1501 RA: 04 06 59 DEC: +60 55 14 Epoch: 2000 V=14.36 (central star) NOTE:
Observing Instructions XCOV30 Oct/Nov 2016 http://darc.physics.udel.edu/wet/xcov30 1. Purpose and Plan: 1) Primary Targets: a) NGC 1501 RA: 04 06 59 DEC: +60 55 14 Epoch: 2000 V=14.36 (central star) NOTE:
EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION
 ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
PROJECT GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
 PROJECT 5 GLOBULAR CLUSTERS Objective: The objective of this exercise is the calculation of the core and tidal radius of a globular cluster in the Milky Way. Measure the tidal radius of a globular cluster
PROJECT 5 GLOBULAR CLUSTERS Objective: The objective of this exercise is the calculation of the core and tidal radius of a globular cluster in the Milky Way. Measure the tidal radius of a globular cluster
Influence of moon light on tip-tilt sensing accuracy using STRAP
 Keck Adaptive Optics Note 425 Influence of moon light on tip-tilt sensing accuracy using STRAP Stephan Kellner, David Le Mignant and Marcos van Dam Version 1.0: 2 October 2006 Abstract AO observations
Keck Adaptive Optics Note 425 Influence of moon light on tip-tilt sensing accuracy using STRAP Stephan Kellner, David Le Mignant and Marcos van Dam Version 1.0: 2 October 2006 Abstract AO observations
Physics 344 Lab 4 Observing with a CCD: Photometry of the Galaxies M31 and M32
 Physics 344 Lab 4 Observing with a CCD: Photometry of the Galaxies M31 and M32 Take Data: October 12 17 (weather permitting) Report Due: Thursday, October 25 Text Reference: Chapters 9 & 10 Purpose: This
Physics 344 Lab 4 Observing with a CCD: Photometry of the Galaxies M31 and M32 Take Data: October 12 17 (weather permitting) Report Due: Thursday, October 25 Text Reference: Chapters 9 & 10 Purpose: This
WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS?
 Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 113-120 WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS? Timur Şahin 1*,
Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 113-120 WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS? Timur Şahin 1*,
An Adaptive Autoguider using a Starlight Xpress SX Camera S. B. Foulkes, Westward, Ashperton, Nr. Ledbury, HR8 2RY. Abstract
 An Adaptive Autoguider using a Starlight Xpress SX Camera S. B. Foulkes, Westward, Ashperton, Nr. Ledbury, HR8 2RY. Abstract The acquisition of very faint deep sky objects, be it analog with film or digital
An Adaptive Autoguider using a Starlight Xpress SX Camera S. B. Foulkes, Westward, Ashperton, Nr. Ledbury, HR8 2RY. Abstract The acquisition of very faint deep sky objects, be it analog with film or digital
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
 Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 1.1.1 lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 1.1.1 lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Observing Night 1 DON T FORGET TO KEEP NOTES ON YOUR PROCEDURE AND KEEP AN OBSERVING LOG FOR THE NIGHT!!!!!
 Observing Night 1 Objects : Name RA (2000) Dec V B-V V-R R-I MK source HD 5015 00 53 04 +61 07 26 5.34 0.54 0.48 0.30 F9V Ducati 2002 HD 30197 4 46 17 +18 44.1 6.01 1.21 0.620 0.533 K4III J66/T86 HD 7615
Observing Night 1 Objects : Name RA (2000) Dec V B-V V-R R-I MK source HD 5015 00 53 04 +61 07 26 5.34 0.54 0.48 0.30 F9V Ducati 2002 HD 30197 4 46 17 +18 44.1 6.01 1.21 0.620 0.533 K4III J66/T86 HD 7615
LAB: Photometry of the Pleiades Cluster
 LAB: Photometry of the Pleiades Cluster ASTR 203 - Instructors Olszewski & Rigby Due IN CLASS on Oct. 30 You may work with 1 partner. If you do, only turn in 1 assignment with both your names on it! You
LAB: Photometry of the Pleiades Cluster ASTR 203 - Instructors Olszewski & Rigby Due IN CLASS on Oct. 30 You may work with 1 partner. If you do, only turn in 1 assignment with both your names on it! You
Sky Brightness at the Hobby-Eberly Telescope
 Sky Brightness at the Hobby-Eberly Telescope D. Austin Belknap August 15, 2008 Abstract The Hobby-Eberly Telescope (HET) at McDonald Observatory has a 9.2 m effective aperture, and has been in operation
Sky Brightness at the Hobby-Eberly Telescope D. Austin Belknap August 15, 2008 Abstract The Hobby-Eberly Telescope (HET) at McDonald Observatory has a 9.2 m effective aperture, and has been in operation
The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth
 The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth CSC Threads The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth 1 Table of Contents The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth - CSC Introduction How to access CSC data with
The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth CSC Threads The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth 1 Table of Contents The CSC Interface to Sky in Google Earth - CSC Introduction How to access CSC data with
Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases
 Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases Derck P. Smits Dept of Mathematical Sciences, PO Box 392, UNISA, 0003, South Africa E-mail: smitsdp@unisa.ac.za Abstract. A photographic
Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases Derck P. Smits Dept of Mathematical Sciences, PO Box 392, UNISA, 0003, South Africa E-mail: smitsdp@unisa.ac.za Abstract. A photographic
Exploring Data. Keck LRIS spectra. Handbook of CCD Astronomy by Steve Howell Chap. 4, parts of 6
 Exploring Data Keck LRIS spectra Handbook of CCD Astronomy by Steve Howell Chap. 4, parts of 6 FITS: Flexible Image Transport System Digital file format used to store astronomical images, data, and catalogs.
Exploring Data Keck LRIS spectra Handbook of CCD Astronomy by Steve Howell Chap. 4, parts of 6 FITS: Flexible Image Transport System Digital file format used to store astronomical images, data, and catalogs.
CCD Imaging of Planetary Nebulae or H II Regions
 Observational Astronomy ASTR 310 Fall 2010 Project 2 CCD Imaging of Planetary Nebulae or H II Regions 1. Introduction The aim of this project is to gain experience using the CCD camera by obtaining images
Observational Astronomy ASTR 310 Fall 2010 Project 2 CCD Imaging of Planetary Nebulae or H II Regions 1. Introduction The aim of this project is to gain experience using the CCD camera by obtaining images
PHYSICS Observing Guide
 PHYSICS 123-253 Observing Guide v1.4 November 2013 TEAMWORK Working in pairs or groups is quite common in science labs, and this lab is no exception. Teamwork can be quite effective; it's often possible
PHYSICS 123-253 Observing Guide v1.4 November 2013 TEAMWORK Working in pairs or groups is quite common in science labs, and this lab is no exception. Teamwork can be quite effective; it's often possible
Star Cluster Photometry and the H-R Diagram
 Star Cluster Photometry and the H-R Diagram Contents Introduction Star Cluster Photometry... 1 Downloads... 1 Part 1: Measuring Star Magnitudes... 2 Part 2: Plotting the Stars on a Colour-Magnitude (H-R)
Star Cluster Photometry and the H-R Diagram Contents Introduction Star Cluster Photometry... 1 Downloads... 1 Part 1: Measuring Star Magnitudes... 2 Part 2: Plotting the Stars on a Colour-Magnitude (H-R)
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
 Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 0.96lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 0.96lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
3. When you enter the dome the telescope should be in its parked position.
 Chow Telescope Operation (JLW 6-10-16) 1. The green key is located in the large cabinet in the NE area of dome one (16-inch dome). It should be sitting on top of a black pelican case on the third shelf.
Chow Telescope Operation (JLW 6-10-16) 1. The green key is located in the large cabinet in the NE area of dome one (16-inch dome). It should be sitting on top of a black pelican case on the third shelf.
ROSAT Roentgen Satellite. Chandra X-ray Observatory
 ROSAT Roentgen Satellite Joint facility: US, Germany, UK Operated 1990 1999 All-sky survey + pointed observations Chandra X-ray Observatory US Mission Operating 1999 present Pointed observations How do
ROSAT Roentgen Satellite Joint facility: US, Germany, UK Operated 1990 1999 All-sky survey + pointed observations Chandra X-ray Observatory US Mission Operating 1999 present Pointed observations How do
Upgraded Photometric System of The 85-cm Telescope at Xinglong Station
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. 217 Vol. X No. XX, http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Upgraded Photometric System of The 85-cm Telescope at
Research in Astron. Astrophys. 217 Vol. X No. XX, http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Upgraded Photometric System of The 85-cm Telescope at
Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS
 NAME(S)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ASTRONOMY 25 Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD Overview The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes
NAME(S)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ASTRONOMY 25 Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD Overview The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes
RECLASSIFICATION OF ROTSE-I SCUTI STARS WITH MULTIBAND PHOTOMETRY AND FOURIER DECOMPOSITION
 The Astronomical Journal, 128:1847 1856, 2004 October # 2004. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. RECLASSIFICATION OF ROTSE-I SCUTI STARS WITH MULTIBAND PHOTOMETRY
The Astronomical Journal, 128:1847 1856, 2004 October # 2004. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. RECLASSIFICATION OF ROTSE-I SCUTI STARS WITH MULTIBAND PHOTOMETRY
Introduction: Objectives: (a) To understand how to compile a list of objects for imaging with a CCD.
 Texas Tech University Department of Physics Astronomy 2401 Observational Astronomy Lab 2:- Planning Observations Introduction: Observing time at the telescope is generally very limited. Therefore, in order
Texas Tech University Department of Physics Astronomy 2401 Observational Astronomy Lab 2:- Planning Observations Introduction: Observing time at the telescope is generally very limited. Therefore, in order
Midterm Observing Project: RR Lyrae, Rapidly Pulsating Stars
 AY 145: Topics in Astrophysics Spring, 2005 Midterm Observing Project: RR Lyrae, Rapidly Pulsating Stars Observations: March 21-24, 2005 Lab Report Due: Friday April 15, 2005 Purpose: In place of a midterm
AY 145: Topics in Astrophysics Spring, 2005 Midterm Observing Project: RR Lyrae, Rapidly Pulsating Stars Observations: March 21-24, 2005 Lab Report Due: Friday April 15, 2005 Purpose: In place of a midterm
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
 Introduction + Aims Installing the Software Theory of Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams Method: Part 1 - Distance to the Star Cluster Part 2 - Age of the Star Cluster Part 3 - Comparison of Star Clusters Extension
Introduction + Aims Installing the Software Theory of Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams Method: Part 1 - Distance to the Star Cluster Part 2 - Age of the Star Cluster Part 3 - Comparison of Star Clusters Extension
Okay now go back to your pyraf window
 PHYS 391 Astronomical Image Data: Measuring the Distance and Age of a Stellar Cluster Goals This lab is designed to demonstrate basic astronomy data analysis and how extracting stellar population information
PHYS 391 Astronomical Image Data: Measuring the Distance and Age of a Stellar Cluster Goals This lab is designed to demonstrate basic astronomy data analysis and how extracting stellar population information
Life Cycle of Stars. Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ. Authors: Daniel Duggan & Sarah Roberts
 Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ Authors: Daniel Duggan & Sarah Roberts Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ Introduction Photometry is the measurement of the intensity or brightness of an astronomical
Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ Authors: Daniel Duggan & Sarah Roberts Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ Introduction Photometry is the measurement of the intensity or brightness of an astronomical
Physics Lab #2:! Starry Night Introduction!
 Physics 10293 Lab #2: Starry Night Introduction Introduction In this lab, we'll learn how to use the Starry Night software to learn about the sky. Starry Night has a large number of features and options,
Physics 10293 Lab #2: Starry Night Introduction Introduction In this lab, we'll learn how to use the Starry Night software to learn about the sky. Starry Night has a large number of features and options,
CCD Double-Star Measurements at Altimira Observatory in 2007
 Page 27 CCD Double-Star Measurements at Altimira Observatory in 2007 Robert K. Buchheim Altimira Observatory (G76) 18 Altimira Coto de Caza, CA 92679 Email: RBuchheim@earthlink.net Abstract: CCD measurements
Page 27 CCD Double-Star Measurements at Altimira Observatory in 2007 Robert K. Buchheim Altimira Observatory (G76) 18 Altimira Coto de Caza, CA 92679 Email: RBuchheim@earthlink.net Abstract: CCD measurements
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra. Astrophysical observatory of Asiago
 Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Iowa 29:137 Astronomical Laboratory Fall 2011 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy
 Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Iowa 29:137 Astronomical Laboratory Fall 2011 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy 1 Introduction Throughout your astronomy education, you have read about stellar
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Iowa 29:137 Astronomical Laboratory Fall 2011 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy 1 Introduction Throughout your astronomy education, you have read about stellar
STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES
 STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES 2., classification, surface photometry Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen the Netherlands February 2010, classification, surface photometry
STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES 2., classification, surface photometry Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen the Netherlands February 2010, classification, surface photometry
2. 4 m O b s e r v a t o r y T e c h n i c a l N o t e Date: 2008 June 9 version 1.9
 2. 4 m O b s e r v a t o r y T e c h n i c a l N o t e Date: 2008 June 9 version 1.9 Subject: Obscon User's Manual Obscon is the main user interface tool for MROST. It provides the following overall functionality:
2. 4 m O b s e r v a t o r y T e c h n i c a l N o t e Date: 2008 June 9 version 1.9 Subject: Obscon User's Manual Obscon is the main user interface tool for MROST. It provides the following overall functionality:
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
 Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 1 Department of Physics Gettysburg College Gettysburg,
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 1 Department of Physics Gettysburg College Gettysburg,
Question Details UNCAstro101L1 5.IL.001. [ ]
![Question Details UNCAstro101L1 5.IL.001. [ ] Question Details UNCAstro101L1 5.IL.001. [ ]](/thumbs/77/76276408.jpg) Lab 5: Distance Ladder II: Standard Candles (T) (2628698) Due: Fri Nov 7 2014 12:00 PM EST Question 1 Instructions Lab 5: The Cosmic Distance Ladder II: Standard Candles Read the lab before attending lab.
Lab 5: Distance Ladder II: Standard Candles (T) (2628698) Due: Fri Nov 7 2014 12:00 PM EST Question 1 Instructions Lab 5: The Cosmic Distance Ladder II: Standard Candles Read the lab before attending lab.
PHYS133 Lab 6 Sunspots and Solar Rotation
 PHYS133 Lab 6 Sunspots and Solar Rotation Goals: Select a series of images with sunspots suitable for measurement. View an animation of the images showing the motion of the spots as the Sun rotates. Devise
PHYS133 Lab 6 Sunspots and Solar Rotation Goals: Select a series of images with sunspots suitable for measurement. View an animation of the images showing the motion of the spots as the Sun rotates. Devise
MANUAL for GLORIA light curve demonstrator experiment test interface implementation
 GLORIA is funded by the European Union 7th Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n 283783 MANUAL for GLORIA light curve demonstrator experiment test interface implementation Version:
GLORIA is funded by the European Union 7th Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n 283783 MANUAL for GLORIA light curve demonstrator experiment test interface implementation Version:
The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation
 The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 3: Version 1 Department of Physics Gettysburg College Gettysburg,
The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 3: Version 1 Department of Physics Gettysburg College Gettysburg,
Operation of the 1-m Telescope and Echelle Spectrograph Ritter Observatory
 Operation of the 1-m Telescope and Echelle Spectrograph Ritter Observatory Nancy D. Morrison Revised September 13, 2008 This manual is not a substitute for thorough training in the use of the telescope,
Operation of the 1-m Telescope and Echelle Spectrograph Ritter Observatory Nancy D. Morrison Revised September 13, 2008 This manual is not a substitute for thorough training in the use of the telescope,
Photometric Calibration of the CCD Camera of 1-m Telescope at VBO
 J. Astrophys. Astr.(1991) 12, 319 331 Photometric Calibration of the CCD Camera of 1-m Telescope at VBO Y. D. Mayya* Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore 560034 Received 1991 July 7; accepted 1991
J. Astrophys. Astr.(1991) 12, 319 331 Photometric Calibration of the CCD Camera of 1-m Telescope at VBO Y. D. Mayya* Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore 560034 Received 1991 July 7; accepted 1991
Keck Adaptive Optics Note 1069
 Keck Adaptive Optics Note 1069 Tip-Tilt Sensing with Keck I Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics: Sensor Selection and Performance Predictions DRAFT to be updated as more performance data becomes available
Keck Adaptive Optics Note 1069 Tip-Tilt Sensing with Keck I Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics: Sensor Selection and Performance Predictions DRAFT to be updated as more performance data becomes available
Double Star Observations
 Double Star Observations Canopus now includes enhanced features for measurnig double stars. This includes easier setting of the reference position (the primary star) as well as recording the observations
Double Star Observations Canopus now includes enhanced features for measurnig double stars. This includes easier setting of the reference position (the primary star) as well as recording the observations
The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3
 336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
WeatherWatcher ACP. Astronomers Control Panel (V4 or >) Ambient Virtual Weather Station (Pro or Internet editions) ASCOM platform v4.
 WeatherWatcher ACP Software This is a minimum equipment list: Astronomers Control Panel (V4 or >) Ambient Virtual Weather Station (Pro or Internet editions) ASCOM platform v4.1 or higher Hardware Weather
WeatherWatcher ACP Software This is a minimum equipment list: Astronomers Control Panel (V4 or >) Ambient Virtual Weather Station (Pro or Internet editions) ASCOM platform v4.1 or higher Hardware Weather
VARIABLE STARS. What will you learn in this Lab?
 VARIABLE STARS What will you learn in this Lab? This lab will cover three of the main types of variable stars that we observe in our night sky: RR Lyrae stars, Cepheid variable stars and Eclipsing Binary
VARIABLE STARS What will you learn in this Lab? This lab will cover three of the main types of variable stars that we observe in our night sky: RR Lyrae stars, Cepheid variable stars and Eclipsing Binary
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method
 Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Southern African Large Telescope
 Southern African Large Telescope Title: Author(s): HRS pipeline for MR red-arm data with MIDAS Alexei Kniazev Doc. number: HRS0000003 Version: 1.0 Date: August 14, 2016 Keywords: HRS, Pipeline Approved:
Southern African Large Telescope Title: Author(s): HRS pipeline for MR red-arm data with MIDAS Alexei Kniazev Doc. number: HRS0000003 Version: 1.0 Date: August 14, 2016 Keywords: HRS, Pipeline Approved:
BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 305 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 305 310 (1998) BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields I. Photometric sequences
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 305 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 305 310 (1998) BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields I. Photometric sequences
Background The power radiated by a black body of temperature T, is given by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law
 Phys316 Exploration 2: Verifying Stefan-Boltzmann Relationship Background The power radiated by a black body of temperature T, is given by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Where A is the effective radiating area,
Phys316 Exploration 2: Verifying Stefan-Boltzmann Relationship Background The power radiated by a black body of temperature T, is given by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Where A is the effective radiating area,
Lab 4: Differential Photometry of an Extrasolar Planetary Transit
 Lab 4: Differential Photometry of an Extrasolar Planetary Transit Neil Lender 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Sean Lockwood 3 December 3, 2007 Abstract An upward change in brightness of 3.97 ± 0.29 millimags in
Lab 4: Differential Photometry of an Extrasolar Planetary Transit Neil Lender 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Sean Lockwood 3 December 3, 2007 Abstract An upward change in brightness of 3.97 ± 0.29 millimags in
Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters
 Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters Sean Lockwood 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Neil Lender 3 December 2, 2007 Abstract We used the Doppler velocity of 29 stars in the open clusters
Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters Sean Lockwood 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Neil Lender 3 December 2, 2007 Abstract We used the Doppler velocity of 29 stars in the open clusters
Objectives: (a) To understand how to display a spectral image both as an image and graphically.
 Texas Tech University Department of Physics & Astronomy Astronomy 2401 Observational Astronomy Lab 8:- CCD Image Analysis:- Spectroscopy Objectives: There are two principle objectives for this laboratory
Texas Tech University Department of Physics & Astronomy Astronomy 2401 Observational Astronomy Lab 8:- CCD Image Analysis:- Spectroscopy Objectives: There are two principle objectives for this laboratory
NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation
 NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation Ron Probst NEWFIRM Instrument Scientist September 2008 NEWFIRM is a 1-2.4 micron IR camera for the NOAO 4-m telescopes. It has a flexible complement of broad
NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation Ron Probst NEWFIRM Instrument Scientist September 2008 NEWFIRM is a 1-2.4 micron IR camera for the NOAO 4-m telescopes. It has a flexible complement of broad
Study of Physical Characteristics of High Apogee Space Debris
 Study of Physical Characteristics of High Apogee Space Debris Yongna Mao, Jianfeng Wang, Xiaomeng Lu, Liang Ge, Xiaojun Jiang (National Astronomical Observatories, Beijing, 100012, China) Abstract Date
Study of Physical Characteristics of High Apogee Space Debris Yongna Mao, Jianfeng Wang, Xiaomeng Lu, Liang Ge, Xiaojun Jiang (National Astronomical Observatories, Beijing, 100012, China) Abstract Date
Mees Observatory telescope checklist
 Mees Observatory telescope checklist Last revised 30 April 2003 DMW Startup 1. Turn on all circuit breakers in the breaker box by the front door. (Those with tape on them are always on; don t turn them
Mees Observatory telescope checklist Last revised 30 April 2003 DMW Startup 1. Turn on all circuit breakers in the breaker box by the front door. (Those with tape on them are always on; don t turn them
Telescopes. Optical Telescope Design. Reflecting Telescope
 Telescopes The science of astronomy was revolutionized after the invention of the telescope in the early 17th century Telescopes and detectors have been constantly improved over time in order to look at
Telescopes The science of astronomy was revolutionized after the invention of the telescope in the early 17th century Telescopes and detectors have been constantly improved over time in order to look at
Chapter 3 Observational Program: Phase I The first phase of the observing program was begun in 1996 by Prof. Janes, prior to the Lowell Observatory pa
 Chapter 3 Observational Program: Phase I The first phase of the observing program was begun in 1996 by Prof. Janes, prior to the Lowell Observatory partnership that allowed Boston University access to
Chapter 3 Observational Program: Phase I The first phase of the observing program was begun in 1996 by Prof. Janes, prior to the Lowell Observatory partnership that allowed Boston University access to
Polar alignment in 5 steps based on the Sánchez Valente method
 1 Polar alignment in 5 steps based on the Sánchez Valente method Compared to the drift alignment method, this one, allows you to easily achieve a perfect polar alignment in just one step. By "perfect polar
1 Polar alignment in 5 steps based on the Sánchez Valente method Compared to the drift alignment method, this one, allows you to easily achieve a perfect polar alignment in just one step. By "perfect polar
Analysis of Errors in the Measurement of Double Stars Using Imaging and the Reduc Software
 Page 193 Analysis of Errors in the Measurement of Double Stars Using Imaging and the Reduc Software Tim Napier-Munn and Graeme Jenkinson Astronomical Association of Queensland Abstract: This paper reports
Page 193 Analysis of Errors in the Measurement of Double Stars Using Imaging and the Reduc Software Tim Napier-Munn and Graeme Jenkinson Astronomical Association of Queensland Abstract: This paper reports
CONFIRMATION OF A SUPERNOVA IN THE GALAXY NGC6946
 CONFIRMATION OF A SUPERNOVA IN THE GALAXY NGC6946 G. Iafrate and M. Ramella INAF - Astronomical Observatory of Trieste 1 Introduction Suddenly a star runs out its nuclear fuel. Its life as a normal star
CONFIRMATION OF A SUPERNOVA IN THE GALAXY NGC6946 G. Iafrate and M. Ramella INAF - Astronomical Observatory of Trieste 1 Introduction Suddenly a star runs out its nuclear fuel. Its life as a normal star
Keck Adaptive Optics Note #385. Feasibility of LGS AO observations in the vicinity of Jupiter. Stephan Kellner and Marcos van Dam
 Keck Adaptive Optics Note #385 Feasibility of LGS AO observations in the vicinity of Jupiter Stephan Kellner and Marcos van Dam Version 2: 25 July 2006 1 Introduction It has been proposed by Imke De Pater
Keck Adaptive Optics Note #385 Feasibility of LGS AO observations in the vicinity of Jupiter Stephan Kellner and Marcos van Dam Version 2: 25 July 2006 1 Introduction It has been proposed by Imke De Pater
C2A for Pulsar2 how to control your telescope from C2A
 C2A for Pulsar2 how to control your telescope from C2A C2a is a free and powerful planetarium program available from.http://www.astrosurf.com/c2a/english/ that offers native support for Pulsar2 without
C2A for Pulsar2 how to control your telescope from C2A C2a is a free and powerful planetarium program available from.http://www.astrosurf.com/c2a/english/ that offers native support for Pulsar2 without
SKINAKAS OBSERVATORY Astronomy Projects for University Students COLOUR IN ASTRONOMY
 P R O J E C T 3 COLOUR IN ASTRONOMY Objective: Explain what colour means in an astronomical context and its relationship with the temperature of a star. Learn how to create colour-colour diagrams and how
P R O J E C T 3 COLOUR IN ASTRONOMY Objective: Explain what colour means in an astronomical context and its relationship with the temperature of a star. Learn how to create colour-colour diagrams and how
ARISTARCHOS TELESCOPE 2.3 m
 National Observatory of Athens Institute of Astronomy & Astrophysics Helmos Observatory ARISTARCHOS TELESCOPE 2.3 m OBSERVER S COOKBOOK GETTING STARTED The program ZEISS GUI is selected and run in the
National Observatory of Athens Institute of Astronomy & Astrophysics Helmos Observatory ARISTARCHOS TELESCOPE 2.3 m OBSERVER S COOKBOOK GETTING STARTED The program ZEISS GUI is selected and run in the
2. To measure the emission lines in the hydrogen, helium and possibly other elemental spectra, and compare these to know values.
 4.1. Purpose 1. To record several elemental emission spectra using arc lamps filled with each element using the Ocean Optics USB650 spectrometer. 2. To measure the emission lines in the hydrogen, helium
4.1. Purpose 1. To record several elemental emission spectra using arc lamps filled with each element using the Ocean Optics USB650 spectrometer. 2. To measure the emission lines in the hydrogen, helium
CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM
 Name Partner(s) Section Date CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM You have had the opportunity to look at two different tools to display the night sky, the celestial sphere and the star chart.
Name Partner(s) Section Date CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM You have had the opportunity to look at two different tools to display the night sky, the celestial sphere and the star chart.
Mimir NIR Spectroscopy Data Processing Cookbook V2.0 DPC
 Mimir NIR Spectroscopy Data Processing Cookbook V2.0 DPC - 20111130 1. Fetch and install the software packages needed a. Get the MSP_WCT, MSP_CCS, MSP_SXC packages from the Mimir/Software web site: http://people.bu.edu/clemens/mimir/software.html
Mimir NIR Spectroscopy Data Processing Cookbook V2.0 DPC - 20111130 1. Fetch and install the software packages needed a. Get the MSP_WCT, MSP_CCS, MSP_SXC packages from the Mimir/Software web site: http://people.bu.edu/clemens/mimir/software.html
Relative Photometry with data from the Peter van de Kamp Observatory D. Cohen and E. Jensen (v.1.0 October 19, 2014)
 Relative Photometry with data from the Peter van de Kamp Observatory D. Cohen and E. Jensen (v.1.0 October 19, 2014) Context This document assumes familiarity with Image reduction and analysis at the Peter
Relative Photometry with data from the Peter van de Kamp Observatory D. Cohen and E. Jensen (v.1.0 October 19, 2014) Context This document assumes familiarity with Image reduction and analysis at the Peter
David Hiriart Observatorio Astronómico Nacional en la Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, B.C. Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM
 David Hiriart Observatorio Astronómico Nacional en la Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, B.C. Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM Telescopes 1 OUTLINE Scientific motivation Telescope Instrument Pipe-line data reduction
David Hiriart Observatorio Astronómico Nacional en la Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, B.C. Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM Telescopes 1 OUTLINE Scientific motivation Telescope Instrument Pipe-line data reduction
Detection of Artificial Satellites in Images Acquired in Track Rate Mode.
 Detection of Artificial Satellites in Images Acquired in Track Rate Mode. Martin P. Lévesque Defence R&D Canada- Valcartier, 2459 Boul. Pie-XI North, Québec, QC, G3J 1X5 Canada, martin.levesque@drdc-rddc.gc.ca
Detection of Artificial Satellites in Images Acquired in Track Rate Mode. Martin P. Lévesque Defence R&D Canada- Valcartier, 2459 Boul. Pie-XI North, Québec, QC, G3J 1X5 Canada, martin.levesque@drdc-rddc.gc.ca
Physics Lab #6: Citizen Science - Variable Star Zoo
 Physics 10263 Lab #6: Citizen Science - Variable Star Zoo Introduction This lab is the another Citizen Science lab we will do together this semester as part of the zooniverse.org project family. This time,
Physics 10263 Lab #6: Citizen Science - Variable Star Zoo Introduction This lab is the another Citizen Science lab we will do together this semester as part of the zooniverse.org project family. This time,
