Quest for Galaxy-Wide Quasar Feedback
|
|
|
- Griffin Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quest for Galaxy-Wide Quasar Feedback Guilin Liu 刘桂琳 University of Science and Technology of China
2 Main collaborators Nadia L. Zakamska Jenny E. Greene Nicole P. H. Nesvadba Xin Liu ( 刘昕 ) Johns Hopkins Univ. Princeton Univ. Université Paris-Sud 11 Univ. of Illinois The USTC company: 王挺贵, 周宏岩, 孔旭 Graduate students at USTC: Michael A. Strauss Princeton Univ. - 何志成, 高玉龙, 赵沁园
3 Outline - Why we need quasar feedback - Luminous z~0.5 quasars are outflowing ubiquitously - Case studies of low-z quasars - BAL quasars: IFU mapping - BAL quasars: absorption troughs - Red quasars at z~0.5 and z>2 - Summary
4 Thirst for Quasar Feedback: Ultimate questions: how do galaxies co-evolve with black holes? Large-scale outflow blows gas away Quasar Mrk 509 (Liu et al. 2015) Black hole BH grows by accreting gas gas collapses to form stars Quasars = active supermassive black holes M16 KPNO 2.1m)
5 Thirst for Quasar Feedback: Galaxy luminosity function Bright end needs mass-dependent quasar feedback to quench star formation! Croton et al (taken from G. Kauffmann's talk)
6 Thirst for Quasar Feedback: Galaxy luminosity function Bright end needs mass-dependent quasar feedback to quench star formation! + SNe Croton et al (taken from G. Kauffmann's talk)
7 Thirst for Quasar Feedback: Galaxy luminosity function Bright end needs mass-dependent quasar feedback to quench star formation! + SNe + SNe + AGN Croton et al (taken from G. Kauffmann's talk)
8 Thirst for Quasar Feedback: Galaxy luminosity function Bright end needs mass-dependent quasar feedback to quench star formation! + SNe + SNe + AGN + SNe + AGN + Reionization Croton et al (taken from G. Kauffmann's talk)
9 Fact Thirst for Quasar Feedback: BH mass-buldge correlation BH masses in nearby galaxies strongly correlate with many galaxy properties L Buldge / M sph / σ c / r e... Implication BH evolution has profound effects on galaxy formation M BH Puzzles Physical mechanism? masses / sptial scales vastly different need galaxy-wide feedback σ (km s -1 ) Gultekin et al. 2009
10 Thirst for Quasar Feedback: To reproduce BH-galaxy correlation... ~0.5-5% of quasar energy Thermal heating? 5%, Hopkins et al Momentum-driven? ~1%, Zubovas & King 2012, J. Ostriker and his group Radiatively-driven? Proga et al. 2000, but scales? Radio jets? strong: radio galaxies / RL quasars weak (?): NGC 3079 Hopkins et al. 2006
11 unobscured (Type 1) Radio-loud objects Jets can destroy host galaxies Jet-driven winds induces bow-shock and cocoon, deposit mechanic energy into ISM/IGM - both in observations and simulations Urry & Padovani 1995 Cyg 5GHz, Perley Gaibler 2011
12 Radio-loud objects Jets can do serious damage to galaxy Turbulent outflows detected at z~2 Emission regions follow the jet Physical scales are tens of kpc Velocity ~ 1000 km/s, dispersion ~ 1000 km/s Kinetic energy ~10 60 ergs Velocity Velocity dispersion Nesvadba et al. 2006, 2008
13 Radio-loud objects Jets can even do serious damage to galaxy clusters! Cluster MS z = 0.22 Size = 550 kpc (radio) Power = ergs McNamara+ 2007
14 Standard wisdom Stockton & MacKenty found ~30% RL quasars have "extended emission line regions" (~50 kpc) RQ quasars don't have them photoionized by nucleus galaxy-scale winds driven by radiation? But only ~10% quasars are radio-loud... Stockton & MacKenty 1987
15
16
17 Our Gemini IFU Observations Strategy 11 SDSS RQ (+3 RL) quasars obscured (type 2) most luminous at z~0.5 L bol ~ erg/s 12 SDSS RQ quasars: unobscured (type 1) z, L [OIII] matched to type 2s Integral field spectroscopy FoV: 5" 7" seeing 0.4"-0.6" spectral resolution FWHM~130 km/s IFU data cube Credit: Durham University FoV
18 Our Gemini IFU Observations Strategy 11 SDSS RQ (+3 RL) quasars obscured (type 2) most luminous at z~0.5 L bol ~ erg/s 12 SDSS RQ quasars: unobscured (type 1) z, L [OIII] matched to type 2s Integral field Gemini FoV: 5" 7" seeing 0.4"-0.6" spectral resolution FWHM~130 km/s IFU data cube
19 [O III]5007Å intensity maps Radio-Quiet Quasars extended ionized nebulae seen in EVERY case Smooth and round!! kpc across All objects are spatially resolved Radio-Loud Quasars Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2013a
20 Ellipticity RQ vs. RL Quasar Nebulae: Morphology RQ quasars are smoother and rounder, inconsistent with illuminated merger debris ε=0.25 Liu, Zakamska, Greene, et al, 2013a, MNRAS
21 Kinematics: Non-Parametric Measurements for Each Spatial Pixel V med W 80 V med W 80
22 Well-organized velocity field, high velocity dispersion, blueshifted asymmetry, heavy wings: RQ type 2 quasars "smoking gun" evidence for gaseous outflows Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2013b
23 W 80 ~1000 km/s in the center, slightly decline W (~3% per kpc) High gas dispersion on >10 kpc scales Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2013b
24 RQ quasar outflows: Why not observed before? Sensitivity? narrow-band imaging shallower than long-slit spectroscopy and IFU Dependence on luminosity? Villar-Martin, Humphrey et al. found <20% at lower luminosities 0.8 dex increase in [O III], detection fraction changes from <20% to >50% Fooled by long-slit data? limited spatial information Humphrey+ 2010
25 Luminous RQ type 2 (obscured) quasars ubiquitously drive outflows galaxy-wide, quasi-spherical, energetic outflows Are type 1 & 2 (unobscured & obscured) quasars in a different evolutionary stage? Blow-out phase? e.g. Sanders, 1988
26 Type 1 quasars sample Direct comparison with type 2 quasars same redshift z~0.5 matched L [OIII] same telescope, instrument and setting similar seeing 0.4"-0.6" Need to remove Fe II -- template: Boroson [O III]4959Å is recovered after Fe II removal Liu, Zakamska, Greene 2014
27 Type 1 & 2 quasar nebulae are surprisingly similar! Galaxy-wide kpc 27±4 kpc Smooth & round K-S tests give high chance Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2014
28 Type 1 & 2 quasars are surprisingly similar! Gas dispersion W 80 ~1000 km/s Well-organized velocity fields Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2014
29 Interpretation & Energetics Low Δv and no correlation => quasi-spherical Velocity dispersion ~ constant in a quasi-spherical model => link W 80 to outflow velocity directly Quasi-spherical outflows with physical v~800 km/s Hβ => gas mass ~ M sun or higher Kinetic energy ~ erg (no extinction correction) Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2013b
30 Interpretation & Energetics Energy flow kinetic luminosity erg/s Mass flow ~10 3 M /yr L bol estimated from WISE 12μm and extrapolation from Richards Energy is too high to originate from star formation (suggested by Spitzer observations, Zakamska+ 2008) Magic number: L kin ~ 2% L bol Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2013b
31 Our Poster Child : SDSS J A pair of super-bubbles X in IFU maps Post-starburst galaxy, W 80 ~2000 km/s Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2013b Gemini long-slit spectroscopy (Xin Liu+, unpublished)
32 Our Poster Child : SDSS J A pair of super-bubbles X in IFU maps Post-starburst galaxy, W 80 ~2000 km/s Liu, Zakamska, Greene+ 2013b Gemini long-slit spectroscopy (Xin Liu+, unpublished) American Astronomical Society direct evidence for AGN-driven outflows proved for the first time that feedback from AGN is occurring on 10 kpc scales.
33 Blue scattered light + host GALFIT Data model Their host galaxies as seen by HST
34 Connecting with the tradition: direct test of BAL analysis Blue-shifted broad absortpion line: traditional outflow indicator R=?? outflow location indirectly derived from ionization models (multiple assumptions) ~10 years of debate ~kpc: engulf the whole host galaxy ~tens of pc: energy insufficient
35 Low-z case study 1: IRAS F04250 Rotation =170 km/s z~0.1 Opening angle ~70 v outflow ~600 km/s v rot ~170 km/s MW: v rot =220, v esc =550 IFU s results: R=2.9 kpc, dm/dt~1.3 M /yr, de k /dt~ erg/s Edmonds+ 2011: R 3 kpc, dm/dt~1.2 M /yr, de k /dt~ erg/s Liu, Arav, Rupke, 2015, ApJS
36 Low-z case study 2: Mrk 509 ~5.4 kpc Liu, Arav, Rupke, 2015, ApJS
37 Original-tail Tail Original Low-z case study 2: Mrk peaked [O III] => remove tail Quasi-spherical outflow v outflow ~300 km/s Hβ traces star formation IFU results: R = 1 kpc, dm/dt~5.2 M /yr, de k /dt~ erg/s Arav+ 2001: R>0.2 kpc, dm/dt~3.3 M /yr, de k /dt~ erg/s Liu, Arav, Rupke, 2015, ApJS
38 BAL: Small-scale outflows The Physical Picture - Spatial location of quasar outflows remains a challenging and contradictory issue, existing methods are complementary - Spiky Lyɑ 1216 emission line, nearly black N V 1240 absorption trough, deemed as broad emission line regions not fully obscured and Lyɑ emission leaks out, can estimate spatial scale from Lyɑ FWHM Three SDSS quasars with these features - 3 prominent quasars from SDSS (z~3), outflow size 3-26 pc New method, new view angle. He ZC, Liu GL, Wang TG+ 2017
39 SDSS/BOSS VLT BAL: Large-scale outflows - Absorption line analysis: most robust way is using troughs from excited states SDSS/BOSS quasar spectra (z>2.6, r<18.5) + 13 quasar spectra from VLT - Identify SIV 1063/SIV* 1073, from ~same physical regions as C IV - At least 50% quasar outflows at R>100 pc, 12% at R>1 kpc!!! Paper under review
40 Marching towards cosmic noon Cosmic SFR & quasar activity peak at z=2-3, the epoch when galaxy properties were largely regulated Our collaboration recently discovered ~300 extremely red quasars at 2-3 in BOSS 1. Extremely high IR/optical ratio 2. Type 2? (high equivalent width of emission lines) 3. Type 1? (UV blue, emission lines >2000 km/s) 4. N V/Lyα ~ 3:1, not ~1:40! Madau & Dickinson, 2014 SDSS J , z=2.366, Ross+ 2015, Hamann+ 2017
41 Marching towards cosmic noon Driving dusty, galaxywide, energetic winds? Blow-out phase? 1. Dust causes high IR/optical ratio 2. Patchy obscuration allows UV photons to escape 3. C IV + N V emission & absorption within differentially moving winds produce extraordinary line shapes 4. Blue-shifted N V absorption suppresses Lyα VLT/Xshooter IR spectra: [O III]+Hβ complex, Zakamska+ 2017
42 Puzzles remain there z~0.5 red quasars Spectacular super-bubbles! -- Step stone towards high z -- Criticism: PSF domination? Beam smearing? Look at the answer! Liu, Zakamska, Greene, Glikman, in prep.
43 Puzzles remain there z~0.5 red quasars Spectacular super-bubbles! -- Step stone towards high z -- Criticism: PSF domination? Beam smearing? Look at the answer! Origin of gas? HST COS has detected 150-kpc HI halo gas commonly surrounding all galaxies, red or blue Liu, Zakamska, Greene, Glikman, in prep. Bimodal metallicity distribution: metal-rich gas from outflows + metal-poor gas from cold accretion streams (Lehner+ 2013) Dekel+ 2009
44 Summary Galaxy-wide quasar feedback will save theorists, but jets are rare -- radio-quiet quasars? Our pioneering work shows that luminous RQ quasars ubiquitously drive >10-kpc scale outflows that are galaxy-wide and energetic Long-sought direct evidence for accretion energy reaching gas far away First direct test of absorption line analysis consistent within 2-3! Type 1 & 2 quasars at z~0.5 both at advanced evolutionary stages. Red quasars more likely caught in the blow-out phase. Super-bubbles seen in z~0.5 red quasars. High-z extremely red quasars at cosmic noon are the signpost of quasar feedback?
45 Quasar ionization A transition from ionization to matter-bounded [O III]/Hβ radial profiles Size-luminosity relation Existence of a maximum size
46 [O III]/Hβ He II/Hβ [O III]/Hβ break radius ~7 kpc He II/Hβ rises beyond ~7 kpc Outer regions: pressure falls, clouds expand, become overionized ("fried") Liu, Zakamska, Greene 2013a
47 Size-Luminosity Relation: [O III] isophotal radius at /(1+z) 4 erg/s/cm 2 / " power index = 0.25 ± 0.02 theoretical expectation: 0.5 matter-bounded Liu, Zakamska, Greene 2013a
48 Size-Luminosity Relation: [O III] isophotal radius at /(1+z) 4 erg/s/cm 2 / " power index = 0.23 ± 0.02 theoretical expectation: 0.5 matter-bounded Liu, Zakamska, Greene 2014
49 Size-Luminosity Relation: 8 μm isophotal radius at /(1+z) 4 erg/s/cm 2 / " [O III] nebulae have a maximum radius of ~15 kpc Liu, Zakamska, Greene 2014; (also see Hainline+ 2013)
50 Quasar ionization A transition from ionization to matter-bounded [O III]/Hβ radial profiles -- Persists at a constant ~10, then decline Size-luminosity relation -- Flatter then expected Existence of a maximum size -- no larger than ~30 kpc quasar nebulae exist
Gemini IFU Observations of Feedback from Radio-Quiet Quasars at z~0.5
 Gemini IFU Observations of Feedback from Radio-Quiet Quasars at z~0.5 Black Hole Feedback 2012 Guilin Liu JHU/CAS Nadia L. Zakamska JHU/CAS Jenny E. Greene Princeton Nicole P. H. Nesvadba Insitut d'astrophysique
Gemini IFU Observations of Feedback from Radio-Quiet Quasars at z~0.5 Black Hole Feedback 2012 Guilin Liu JHU/CAS Nadia L. Zakamska JHU/CAS Jenny E. Greene Princeton Nicole P. H. Nesvadba Insitut d'astrophysique
AGN feedback. Nadia Zakamska & Rachael Alexandroff Johns Hopkins University
 AGN feedback Nadia Zakamska & Rachael Alexandroff Johns Hopkins University AGN feedback Mechanism of AGN feedback Ionized gas Extreme ionized gas outflows at high z Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect Quasar winds
AGN feedback Nadia Zakamska & Rachael Alexandroff Johns Hopkins University AGN feedback Mechanism of AGN feedback Ionized gas Extreme ionized gas outflows at high z Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect Quasar winds
Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback
 Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback Christy Tremonti MPIA (Heidelberg) / U. Wisconsin-Madison Aleks Diamond-Stanic (U. Arizona), John Moustakas (NYU) Much observational and theoretical evidence supports
Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback Christy Tremonti MPIA (Heidelberg) / U. Wisconsin-Madison Aleks Diamond-Stanic (U. Arizona), John Moustakas (NYU) Much observational and theoretical evidence supports
AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy
 AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy Feng Yuan Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, CAS Collaborators: Zhaoming Gan (SHAO) Jerry Ostriker (Princeton) Luca Ciotti (Bologna) Greg Novak (Paris) 2014.9.10;
AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy Feng Yuan Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, CAS Collaborators: Zhaoming Gan (SHAO) Jerry Ostriker (Princeton) Luca Ciotti (Bologna) Greg Novak (Paris) 2014.9.10;
Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback
 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback Geoff Bicknell & Alex Wagner Australian National University 1 1 High redshift radio
1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback Geoff Bicknell & Alex Wagner Australian National University 1 1 High redshift radio
Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback
 Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback Clive Tadhunter University of Sheffield ASA, ESA, NRAO Collaborators: C. Ramos Almeida, D. Dicken," R. Morganti,T. Oosterloo, " R. Oonk, M.
Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback Clive Tadhunter University of Sheffield ASA, ESA, NRAO Collaborators: C. Ramos Almeida, D. Dicken," R. Morganti,T. Oosterloo, " R. Oonk, M.
A Unified Model for AGN. Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006
 A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
The Physics, Observational Signatures, and Consequences of AGN-Driven Galactic Winds
 The Physics, Observational Signatures, and Consequences of AGN-Driven Galactic Winds ESA artist's conception Claude-André Faucher-Giguère Northwestern University CIERA With Eliot Quataert, Alex Richings,
The Physics, Observational Signatures, and Consequences of AGN-Driven Galactic Winds ESA artist's conception Claude-André Faucher-Giguère Northwestern University CIERA With Eliot Quataert, Alex Richings,
Impact of relativistic jets on the ISM of their host galaxy
 Impact of relativistic jets on the ISM of their host galaxy Dipanjan Mukherjee Universita di Torino with Geoff Bicknell Alex Wagner Ralph Sutherland AGN feedback and galaxy AGN feedback crucial to match
Impact of relativistic jets on the ISM of their host galaxy Dipanjan Mukherjee Universita di Torino with Geoff Bicknell Alex Wagner Ralph Sutherland AGN feedback and galaxy AGN feedback crucial to match
Massive Outflows from Radio-Loud Quasars. Alan Stockton Hai Fu Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii
 Massive Outflows from Radio-Loud Quasars Alan Stockton Hai Fu Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii 4C 37.43 Continuum 4C 37.43 [O III] 4C 37.43 Continuum 4C 37.43 [O III] Characteristics of EELRs
Massive Outflows from Radio-Loud Quasars Alan Stockton Hai Fu Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii 4C 37.43 Continuum 4C 37.43 [O III] 4C 37.43 Continuum 4C 37.43 [O III] Characteristics of EELRs
Quasar Feedback in Galaxies
 Quasar Feedback in Galaxies Philip Hopkins Lars Hernquist, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, Todd Thompson, Dusan Keres, Chris Hayward, Stijn Wuyts, Kevin Bundy, Desika Narayanan, Ryan Hickox, Rachel Somerville,
Quasar Feedback in Galaxies Philip Hopkins Lars Hernquist, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, Todd Thompson, Dusan Keres, Chris Hayward, Stijn Wuyts, Kevin Bundy, Desika Narayanan, Ryan Hickox, Rachel Somerville,
Introduction to AGN. General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo
 Introduction to AGN General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo 1 AGN What are they? Active galactic nucleus compact object in the gravitational center of a galaxy that shows evidence
Introduction to AGN General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo 1 AGN What are they? Active galactic nucleus compact object in the gravitational center of a galaxy that shows evidence
Observational Evidence of AGN Feedback
 10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
Paul Sell. University of Wisconsin-Madison Advisor: Christy Tremonti
 A SAMPLE OF EXTREME MERGER-DRIVEN STARBURST GALAXIES AS VIEWED BY THE CHANDRA AND HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPES Paul Sell University of Wisconsin-Madison Advisor: Christy Tremonti Collaboration: Aleks Diamond-Stanic,
A SAMPLE OF EXTREME MERGER-DRIVEN STARBURST GALAXIES AS VIEWED BY THE CHANDRA AND HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPES Paul Sell University of Wisconsin-Madison Advisor: Christy Tremonti Collaboration: Aleks Diamond-Stanic,
Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars. Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004
 Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004 High-redshift Quasars and the End of Cosmic Dark Ages Existence of SBHs at the end of Dark Ages BH
Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004 High-redshift Quasars and the End of Cosmic Dark Ages Existence of SBHs at the end of Dark Ages BH
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau
 Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei
 Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
- AGN feedback in action?
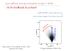 Gas outflows and star formation in type 2 AGNs - AGN feedback in action? Jong-Hak Woo (Seoul National Univ.) & Hyun-Jin Bae, Donghoon Son, Marios Karouzos Muse view of OIII outflows in NGC 7582 (Juneau+16
Gas outflows and star formation in type 2 AGNs - AGN feedback in action? Jong-Hak Woo (Seoul National Univ.) & Hyun-Jin Bae, Donghoon Son, Marios Karouzos Muse view of OIII outflows in NGC 7582 (Juneau+16
AGN winds and outflows
 AGN winds and outflows BAL QSOs (10-40% of all QSOs) Two problems: Fast winds with velocity up to a fraction of c are observed in the central regions of AGNs; they likely originate from the acceleration
AGN winds and outflows BAL QSOs (10-40% of all QSOs) Two problems: Fast winds with velocity up to a fraction of c are observed in the central regions of AGNs; they likely originate from the acceleration
Massive Neutral and Molecular Winds in Nearby Galaxies
 Massive Neutral and Molecular Winds in Nearby Galaxies S. Veilleux (U. Maryland) Powerful wide-angle outflow in Mrk 231 Gemini Press Release February 2011 (Rupke & SV 2011) QUEST: Quasar and ULIRG Evolution
Massive Neutral and Molecular Winds in Nearby Galaxies S. Veilleux (U. Maryland) Powerful wide-angle outflow in Mrk 231 Gemini Press Release February 2011 (Rupke & SV 2011) QUEST: Quasar and ULIRG Evolution
Co-evolution of galaxies and central black holes: Extended emission-line region around quasars
 Co-evolution of galaxies and central black holes: Extended emission-line region around quasars Matsuoka, 2012, ApJ, in press (arxiv:1203.1356) Yoshiki Matsuoka (Nagoya University) INTRODUCTION ELR (or
Co-evolution of galaxies and central black holes: Extended emission-line region around quasars Matsuoka, 2012, ApJ, in press (arxiv:1203.1356) Yoshiki Matsuoka (Nagoya University) INTRODUCTION ELR (or
Observational evidence for AGN feedback throughout the cosmic epochs. Roberto Maiolino
 Observational evidence for AGN feedback throughout the cosmic epochs Roberto Maiolino The need for (nega-ve) feedback Theore-cal expecta-ons: SNe feedback: removes baryons from galaxies and reduce SF efficiency
Observational evidence for AGN feedback throughout the cosmic epochs Roberto Maiolino The need for (nega-ve) feedback Theore-cal expecta-ons: SNe feedback: removes baryons from galaxies and reduce SF efficiency
Junfeng Wang, G. Fabbiano, G. Risaliti, M. Elvis, M. Karovska, A. Zezas (Harvard CfA/SAO), C. G. Mundell (Liverpool John Moores University, UK), G.
 Junfeng Wang, G. Fabbiano, G. Risaliti, M. Elvis, M. Karovska, A. Zezas (Harvard CfA/SAO), C. G. Mundell (Liverpool John Moores University, UK), G. Dumas, E. Schinnerer (MPIA), J. M. Mazzarella, J. H.
Junfeng Wang, G. Fabbiano, G. Risaliti, M. Elvis, M. Karovska, A. Zezas (Harvard CfA/SAO), C. G. Mundell (Liverpool John Moores University, UK), G. Dumas, E. Schinnerer (MPIA), J. M. Mazzarella, J. H.
DLAs Probing Quasar Host Galaxies. Hayley Finley P. Petitjean, P. Noterdaeme, I. Pâris + SDSS III BOSS Collaboration 2013 A&A
 DLAs Probing Quasar Host Galaxies Hayley Finley P. Petitjean, P. Noterdaeme, I. Pâris + SDSS III BOSS Collaboration 2013 A&A 558 111 Outline Feedback mechanisms in QSO host galaxies Strong DLAs at zqso
DLAs Probing Quasar Host Galaxies Hayley Finley P. Petitjean, P. Noterdaeme, I. Pâris + SDSS III BOSS Collaboration 2013 A&A 558 111 Outline Feedback mechanisms in QSO host galaxies Strong DLAs at zqso
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics
 Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Active Galactic Nuclei research with SOAR: present and upcoming capabilities
 Active Galactic Nuclei research with SOAR: present and upcoming capabilities SOAR 2020 WORKSHOP CBPF Rio de Janeiro March 13 15 / 2017 Courtesy: Gabriel Maturana/NOAO/AURA/NSF Alberto Rodríguez Ardila
Active Galactic Nuclei research with SOAR: present and upcoming capabilities SOAR 2020 WORKSHOP CBPF Rio de Janeiro March 13 15 / 2017 Courtesy: Gabriel Maturana/NOAO/AURA/NSF Alberto Rodríguez Ardila
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers
 Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers Yuexing Li et al Presentation by: William Gray Definitions and Jargon QUASAR stands for QUASI-stellAR radio source Extremely bright and active
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers Yuexing Li et al Presentation by: William Gray Definitions and Jargon QUASAR stands for QUASI-stellAR radio source Extremely bright and active
Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55. Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers?
 Elaine M. Sadler Black holes in massive galaxies Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55 Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers? Work done with Russell Cannon, Scott Croom, Helen
Elaine M. Sadler Black holes in massive galaxies Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55 Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers? Work done with Russell Cannon, Scott Croom, Helen
Active Galactic Nuclei
 Active Galactic Nuclei Optical spectra, distance, line width Varieties of AGN and unified scheme Variability and lifetime Black hole mass and growth Geometry: disk, BLR, NLR Reverberation mapping Jets
Active Galactic Nuclei Optical spectra, distance, line width Varieties of AGN and unified scheme Variability and lifetime Black hole mass and growth Geometry: disk, BLR, NLR Reverberation mapping Jets
Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows
![Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows](/thumbs/83/87306418.jpg) Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows Natalie Christopher, University of Oxford Dr Verma and Professor Roche, University of Oxford And the SHINING team, Lead by E. Sturm,
Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows Natalie Christopher, University of Oxford Dr Verma and Professor Roche, University of Oxford And the SHINING team, Lead by E. Sturm,
Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics. Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars
 Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars Emission Mechanisms Synchrotron Radiation Starburst Galaxies Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies BL Lac Galaxies
Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars Emission Mechanisms Synchrotron Radiation Starburst Galaxies Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies BL Lac Galaxies
Active Galaxies & Emission Line Diagnostics
 Active Galaxies & Emission Line Diagnostics Review of Properties Discussed: 1) Powered by accretion unto a supermassive nuclear black hole 2) They are the possible precursors to luminous massive galaxies
Active Galaxies & Emission Line Diagnostics Review of Properties Discussed: 1) Powered by accretion unto a supermassive nuclear black hole 2) They are the possible precursors to luminous massive galaxies
Powerful Neutral-Atomic and Molecular Outflows in Nearby Active Galaxies
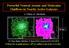 Powerful Neutral-Atomic and Molecular Outflows in Nearby Active Galaxies S. Veilleux (U. Maryland) SX+HX HX / SX 65 kpc 15 (12.9 kpc) Mrk 231 Chandra 0.52 Msec SV, Teng, Rupke, Maiolino, & Sturm (2014;
Powerful Neutral-Atomic and Molecular Outflows in Nearby Active Galaxies S. Veilleux (U. Maryland) SX+HX HX / SX 65 kpc 15 (12.9 kpc) Mrk 231 Chandra 0.52 Msec SV, Teng, Rupke, Maiolino, & Sturm (2014;
Molecular gas & AGN feedback in brightest cluster galaxies
 Molecular gas & AGN feedback in brightest cluster galaxies Helen Russell Brian McNamara Alastair Edge Robert Main Adrian Vantyghem Francoise Combes Andy Fabian Philippe Salomé Outline Introduction Radiative
Molecular gas & AGN feedback in brightest cluster galaxies Helen Russell Brian McNamara Alastair Edge Robert Main Adrian Vantyghem Francoise Combes Andy Fabian Philippe Salomé Outline Introduction Radiative
Massive molecular outflows from ULIRGs - Dynamics and Energetics - E. Sturm for the SHINING and QUEST Team
 Massive molecular outflows from ULIRGs - Dynamics and Energetics - E. Sturm for the SHINING and QUEST Team NGC253 AGN- ULIRGs SB- ULIRGs Sturm+ 2011 Massive molecular outflows detected in ULIRGs v (OH)
Massive molecular outflows from ULIRGs - Dynamics and Energetics - E. Sturm for the SHINING and QUEST Team NGC253 AGN- ULIRGs SB- ULIRGs Sturm+ 2011 Massive molecular outflows detected in ULIRGs v (OH)
Unhidden monsters: Are unobscured quasars the late stages of obscured quasar activity?
 Unhidden monsters: Are unobscured quasars the late stages of obscured quasar activity? Carolin Villforth University of Bath! Timothy Hamilton (Schawnee State), M. Pawlik, T. Hewlett, K. Rowlands (St Andrews),
Unhidden monsters: Are unobscured quasars the late stages of obscured quasar activity? Carolin Villforth University of Bath! Timothy Hamilton (Schawnee State), M. Pawlik, T. Hewlett, K. Rowlands (St Andrews),
Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics
 Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics Claire Max Anne Medling Mark Ammons UC Santa Cruz Ric Davies Hauke Engel MPE-Garching Image of NGC 6240: Bush et al.
Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics Claire Max Anne Medling Mark Ammons UC Santa Cruz Ric Davies Hauke Engel MPE-Garching Image of NGC 6240: Bush et al.
Multi-Phase Outflows in ULIRGs
 Multi-Phase Outflows in ULIRGs Sylvain Veilleux (U. Maryland, Joint Space-Science Institute) Powerful wide-angle outflow in Mrk 231, the nearest quasar Gemini Press Release (based on the results of Rupke
Multi-Phase Outflows in ULIRGs Sylvain Veilleux (U. Maryland, Joint Space-Science Institute) Powerful wide-angle outflow in Mrk 231, the nearest quasar Gemini Press Release (based on the results of Rupke
The parsec scale of. ac-ve galac-c nuclei. Mar Mezcua. International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics
 The parsec scale of ESO ac-ve galac-c nuclei International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics COST Ac(on MP0905 - Black Holes in a Violent Universe In collaboration with A. Prieto,
The parsec scale of ESO ac-ve galac-c nuclei International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics COST Ac(on MP0905 - Black Holes in a Violent Universe In collaboration with A. Prieto,
Introduction and Motivation
 1 Introduction and Motivation This last two days at this conference, we ve focused on two large questions regarding the role that AGNs play in galaxy evolution: My research focuses on exploring these questions
1 Introduction and Motivation This last two days at this conference, we ve focused on two large questions regarding the role that AGNs play in galaxy evolution: My research focuses on exploring these questions
Studying Merger Driven BH Growth with Observations of Dual AGN
 Studying Merger Driven BH Growth with Observations of Dual AGN Mike Koss University of Hawaii Richard Mushotzky and Sylvain Veilleux (U Maryland), Dave Sanders and Vivan U (Hawaii), Ezequiel Treister (U
Studying Merger Driven BH Growth with Observations of Dual AGN Mike Koss University of Hawaii Richard Mushotzky and Sylvain Veilleux (U Maryland), Dave Sanders and Vivan U (Hawaii), Ezequiel Treister (U
Massive molecular gas flows and AGN feedback in galaxy clusters
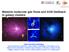 Massive molecular gas flows and AGN feedback in galaxy clusters CO(3-2) Helen Russell (Cambridge) Brian McNamara (Waterloo), Andy Fabian (Cambridge), Paul Nulsen (CfA), Michael McDonald (MIT), Alastair
Massive molecular gas flows and AGN feedback in galaxy clusters CO(3-2) Helen Russell (Cambridge) Brian McNamara (Waterloo), Andy Fabian (Cambridge), Paul Nulsen (CfA), Michael McDonald (MIT), Alastair
The formation of super-stellar clusters
 The formation of super-stellar clusters François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Cynthia Herrera, Edith Falgarone, Pierre Guillard, Nicole Nesvadba, Guillaume Pineau des Forets Outline How
The formation of super-stellar clusters François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Cynthia Herrera, Edith Falgarone, Pierre Guillard, Nicole Nesvadba, Guillaume Pineau des Forets Outline How
A Monster at any other Epoch:
 A Monster at any other Epoch: Are Intermediate Redshift ULIRGs the Progenitors of QSO Host Galaxies? Barry Rothberg Large Binocular Telescope Observatory/George Mason University Co-Is: J. Fischer (NRL),
A Monster at any other Epoch: Are Intermediate Redshift ULIRGs the Progenitors of QSO Host Galaxies? Barry Rothberg Large Binocular Telescope Observatory/George Mason University Co-Is: J. Fischer (NRL),
Feedback from Radiation Pressure during Galaxy Formation
 Feedback from Radiation Pressure during Galaxy Formation Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Norm Murray, Jackson Debuhr, Phil Hopkins... Spitzer s view of Carina Outline Feedback: What is it good for? Absolutely
Feedback from Radiation Pressure during Galaxy Formation Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Norm Murray, Jackson Debuhr, Phil Hopkins... Spitzer s view of Carina Outline Feedback: What is it good for? Absolutely
Francesco Tombesi. University of Rome, Tor Vergata NASA - Goddard Space Flight Center University of Maryland, College Park
 Francesco Tombesi University of Rome, Tor Vergata NASA - Goddard Space Flight Center University of Maryland, College Park (credit JAXA s press release) Warm Absorbers (WAs) (Photo) ionized Mrk 509 v~300-800
Francesco Tombesi University of Rome, Tor Vergata NASA - Goddard Space Flight Center University of Maryland, College Park (credit JAXA s press release) Warm Absorbers (WAs) (Photo) ionized Mrk 509 v~300-800
Vivienne Wild. Timing the starburst AGN connection
 Vivienne Wild Timing the starburst AGN connection There are many theories successful in explaining the observed correlations between black holes and their host galaxies. In turn, these theories play a
Vivienne Wild Timing the starburst AGN connection There are many theories successful in explaining the observed correlations between black holes and their host galaxies. In turn, these theories play a
Active Galactic Alexander David M Nuclei
 d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
AGN Winds, Black Holes, and Galaxies
 AGN Winds, Black Holes, and Galaxies Andrew King Charleston, October 2011 three points 1. brightest AGN should have X-ray or UV outflows with Ṁv L Edd c,v ηc 0.1c 2. outflow shock against host ISM cools
AGN Winds, Black Holes, and Galaxies Andrew King Charleston, October 2011 three points 1. brightest AGN should have X-ray or UV outflows with Ṁv L Edd c,v ηc 0.1c 2. outflow shock against host ISM cools
Feeding the Beast. Chris Impey (University of Arizona)
 Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Warm Molecular Hydrogen at high redshift with JWST
 Warm Molecular Hydrogen at high redshift with JWST Pierre Guillard Institut d Astrophysique de Paris Université Pierre et Marie Curie he Warm H 2 with JWST Outline and take-home messages 1. Observations
Warm Molecular Hydrogen at high redshift with JWST Pierre Guillard Institut d Astrophysique de Paris Université Pierre et Marie Curie he Warm H 2 with JWST Outline and take-home messages 1. Observations
The Powerful Black Hole Wind in the Luminous Quasar PDS 456
 The Powerful Black Hole Wind in the Luminous Quasar PDS 456 James Reeves Astrophysics Group, Keele University & UMBC in collaboration with: E. Nardini (Keele), J. Gofford (Keele/UMBC) - M. Costa, G. Matzeu
The Powerful Black Hole Wind in the Luminous Quasar PDS 456 James Reeves Astrophysics Group, Keele University & UMBC in collaboration with: E. Nardini (Keele), J. Gofford (Keele/UMBC) - M. Costa, G. Matzeu
Circumnuclear Gaseous Kinematics and Excitation of Four Local Radio Galaxies
 Circumnuclear Gaseous Kinematics and Excitation of Four Local Radio Galaxies Guilherme S. Couto T. Storchi-Bergmann, A. Robinson, R.A. Riffel, P. Kharb D. Lena, A. Schnorr-Müller UFSC, Florianópolis, Brazil
Circumnuclear Gaseous Kinematics and Excitation of Four Local Radio Galaxies Guilherme S. Couto T. Storchi-Bergmann, A. Robinson, R.A. Riffel, P. Kharb D. Lena, A. Schnorr-Müller UFSC, Florianópolis, Brazil
Active Galactic Nuclei
 Active Galactic Nuclei How were they discovered? How common are they? How do we know they are giant black holes? What are their distinctive properties? Active Galactic Nuclei for most galaxies the luminosity
Active Galactic Nuclei How were they discovered? How common are they? How do we know they are giant black holes? What are their distinctive properties? Active Galactic Nuclei for most galaxies the luminosity
Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses. E. Pian, R. Falomo, A.
 Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses E. Pian, R. Falomo, A. Treves 1 Outline Extra Background Introduction Sample Selection Data Analysis
Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses E. Pian, R. Falomo, A. Treves 1 Outline Extra Background Introduction Sample Selection Data Analysis
Galactic Scale Winds. Elizabeth Harper-Clark, Mubdi Rahman, Brice Ménard, Eve Lee, Eliot Quataert, Phil Hopkins,Todd Thompson
 Galactic Scale Winds Elizabeth Harper-Clark, Mubdi Rahman, Brice Ménard, Eve Lee, Eliot Quataert, Phil Hopkins,Todd Thompson Phenomenology Weiner, Koo: we see winds in most high z star forming galaxies
Galactic Scale Winds Elizabeth Harper-Clark, Mubdi Rahman, Brice Ménard, Eve Lee, Eliot Quataert, Phil Hopkins,Todd Thompson Phenomenology Weiner, Koo: we see winds in most high z star forming galaxies
Molecular Gas and the Host Galaxies of Infrared-Excess Quasi-Stellar Objects
 Molecular Gas and the Host Galaxies of Infrared-Excess Quasi-Stellar Objects A. S. Evans (Stony Brook) J. A. Surace & D. T. Frayer (Caltech) D. B. Sanders (Hawaii) Luminous Infrared Galaxies Properties
Molecular Gas and the Host Galaxies of Infrared-Excess Quasi-Stellar Objects A. S. Evans (Stony Brook) J. A. Surace & D. T. Frayer (Caltech) D. B. Sanders (Hawaii) Luminous Infrared Galaxies Properties
Optical polarization from AGN
 Optical polarization from AGN Damien Hutsemékers (University of Liège, Belgium) Polarization & AGN II, 11-12 May 2015, Strasbourg, France 1 Outline Polarization properties of radio-quiet AGN including
Optical polarization from AGN Damien Hutsemékers (University of Liège, Belgium) Polarization & AGN II, 11-12 May 2015, Strasbourg, France 1 Outline Polarization properties of radio-quiet AGN including
Redshifted Broad Absorption Troughs in Quasars
 Redshifted Broad Absorption Troughs in Quasars Pat Hall, York University with Niel Brandt and Nur Filiz Ak (PSU), Patrick Petitjean (IAP), and the SDSS-III/BOSS team If due to fallback or rotation, challenge
Redshifted Broad Absorption Troughs in Quasars Pat Hall, York University with Niel Brandt and Nur Filiz Ak (PSU), Patrick Petitjean (IAP), and the SDSS-III/BOSS team If due to fallback or rotation, challenge
Gas and stars in compact (young) radio sources
 Gas and stars in compact (young) radio sources ASTRON, Dwingeloo Kapteyn Inst. Groningen B. Emonts, J. Holt, C. Tadhunter, T. Oosterloo C. Struve Motivations Learn more about the formation and evolution
Gas and stars in compact (young) radio sources ASTRON, Dwingeloo Kapteyn Inst. Groningen B. Emonts, J. Holt, C. Tadhunter, T. Oosterloo C. Struve Motivations Learn more about the formation and evolution
Chapter 17. Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes
 Chapter 17 Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes Guidepost In the last few chapters, you have explored our own and other galaxies, and you are ready to stretch your scientific imagination and study
Chapter 17 Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes Guidepost In the last few chapters, you have explored our own and other galaxies, and you are ready to stretch your scientific imagination and study
Galaxies with Active Nuclei. Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes
 Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Low-Ionization BAL QSOs in Ultraluminous Infrared Systems
 Mass Outflow in Active Galactic Nuclei: New Perspectives ASP Conference Series, Vol. TBD, 2001 D.M. Crenshaw, S.B. Kraemer, and I.M. George Low-Ionization BAL QSOs in Ultraluminous Infrared Systems Gabriela
Mass Outflow in Active Galactic Nuclei: New Perspectives ASP Conference Series, Vol. TBD, 2001 D.M. Crenshaw, S.B. Kraemer, and I.M. George Low-Ionization BAL QSOs in Ultraluminous Infrared Systems Gabriela
PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME
 THE MOST LUMINOUS QUASARS: PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME Enrico Piconcelli Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma - INAF! A. Bongiorno, F. Fiore, M. Bischetti, L. Zappacosta OA-Roma! C.
THE MOST LUMINOUS QUASARS: PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME Enrico Piconcelli Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma - INAF! A. Bongiorno, F. Fiore, M. Bischetti, L. Zappacosta OA-Roma! C.
Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar
 Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar Quasars Quasar = Quasi-stellar (radio) source Optical: faint, blue, star-like objects Radio: point radio sources, faint blue star-like optical
Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar Quasars Quasar = Quasi-stellar (radio) source Optical: faint, blue, star-like objects Radio: point radio sources, faint blue star-like optical
Nuclear X-ray Emission and Mass Outflow From Broad Lined Radio Galaxies (Lorentz Center, Leiden 2009)
 Nuclear X-ray Emission and Mass Outflow From Broad Lined Radio Galaxies (Lorentz Center, Leiden 2009) James Reeves (Keele Univ, UK) Collaborators:- Rita Sambruna (NASA/GSFC), Francesco Tombesi (NASA/GSFC
Nuclear X-ray Emission and Mass Outflow From Broad Lined Radio Galaxies (Lorentz Center, Leiden 2009) James Reeves (Keele Univ, UK) Collaborators:- Rita Sambruna (NASA/GSFC), Francesco Tombesi (NASA/GSFC
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
Multiwavelength observation campaign of Mrk 509: UV spectra of the X-ray Outflow!!!!Gerard Kriss!! STScI!!! (with N. Arav, J. Kaastra & the Mrk 509
 Multiwavelength observation campaign of Mrk 509: UV spectra of the X-ray Outflow!!!!Gerard Kriss!! STScI!!! (with N. Arav, J. Kaastra & the Mrk 509 Team)!! The Influence of AGN Outflows! «They may affect
Multiwavelength observation campaign of Mrk 509: UV spectra of the X-ray Outflow!!!!Gerard Kriss!! STScI!!! (with N. Arav, J. Kaastra & the Mrk 509 Team)!! The Influence of AGN Outflows! «They may affect
A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063
 A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063 K. M. Dasyra (University of Athens) F. Combes (College de France; Observatoire de Paris)
A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063 K. M. Dasyra (University of Athens) F. Combes (College de France; Observatoire de Paris)
Powering Active Galaxies
 Powering Active Galaxies Relativity and Astrophysics ecture 35 Terry Herter Bonus lecture Outline Active Galaxies uminosities & Numbers Descriptions Seyfert Radio Quasars Powering AGN with Black Holes
Powering Active Galaxies Relativity and Astrophysics ecture 35 Terry Herter Bonus lecture Outline Active Galaxies uminosities & Numbers Descriptions Seyfert Radio Quasars Powering AGN with Black Holes
Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs
 Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany
Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany
AC Fabian, M. Cappi, J Sanders. Cosmic Feedback from AGN
 AC Fabian, M. Cappi, J Sanders Cosmic Feedback from AGN AC Fabian, M Cappi, J Sanders, S Heinz, E Churazov, B McNamara, J Croston, D Worrall, F Humphrey, F Tombesi, J Reeves, M Giustini, P O Brien, T Reiprich
AC Fabian, M. Cappi, J Sanders Cosmic Feedback from AGN AC Fabian, M Cappi, J Sanders, S Heinz, E Churazov, B McNamara, J Croston, D Worrall, F Humphrey, F Tombesi, J Reeves, M Giustini, P O Brien, T Reiprich
A zoo of transient sources. (c)2017 van Putten 1
 A zoo of transient sources (c)2017 van Putten 1 First transient @ first light UDFj-39546284, z~10.3 Bouwens, R.J., et al., Nature, 469, 504 Cuchiara, A. et al., 2011, ApJ, 736, 7 z=9.4: GRB 090429B, z~9.4
A zoo of transient sources (c)2017 van Putten 1 First transient @ first light UDFj-39546284, z~10.3 Bouwens, R.J., et al., Nature, 469, 504 Cuchiara, A. et al., 2011, ApJ, 736, 7 z=9.4: GRB 090429B, z~9.4
Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts
 Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts A personal view Gabriele Ponti co-chair of swg 2.3 Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (Garching) Outline 1) Why is feedback required?
Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts A personal view Gabriele Ponti co-chair of swg 2.3 Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (Garching) Outline 1) Why is feedback required?
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Gas Masses and Gas Fractions: Applications of the Kennicutt- Schmidt Law at High Redshift
 Gas Masses and Gas Fractions: Applications of the Kennicutt- Schmidt Law at High Redshift Dawn Erb (CfA) Kennicutt-Schmidt Workshop, UCSD December 19, 2006 Overview Properties of star-forming galaxies
Gas Masses and Gas Fractions: Applications of the Kennicutt- Schmidt Law at High Redshift Dawn Erb (CfA) Kennicutt-Schmidt Workshop, UCSD December 19, 2006 Overview Properties of star-forming galaxies
AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects
 AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects 1 Evidence for Photoionization - continuum and Hβ luminosity
AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects 1 Evidence for Photoionization - continuum and Hβ luminosity
Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy
 Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy Cat Wu Thesis Proposal, Fall 2009 Astronomy Department New Mexico State University Outline Diffuse ionized gas; galaxy halos Origin of halo galactic fountain
Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy Cat Wu Thesis Proposal, Fall 2009 Astronomy Department New Mexico State University Outline Diffuse ionized gas; galaxy halos Origin of halo galactic fountain
Wide Field Camera 3: The SOC Science Program Proposal
 Wide Field Camera 3: The SOC Science Program Proposal Text An extraordinary panchromatic survey efficiency covering a critical decade of frequency space combined Theme I: Star Formation at Half the Hubble
Wide Field Camera 3: The SOC Science Program Proposal Text An extraordinary panchromatic survey efficiency covering a critical decade of frequency space combined Theme I: Star Formation at Half the Hubble
Hunting for Monsters. Selecting and Characterizing Obscured Quasars with WISE Kevin Hainline Hidden Monsters Dartmouth College August 2016
 Hunting for Monsters Selecting and Characterizing Obscured Quasars with WISE Kevin Hainline Hidden Monsters Dartmouth College August 2016 Ryan Hickox Dartmouth College Mike DiPompeo Christopher Carroll
Hunting for Monsters Selecting and Characterizing Obscured Quasars with WISE Kevin Hainline Hidden Monsters Dartmouth College August 2016 Ryan Hickox Dartmouth College Mike DiPompeo Christopher Carroll
Galaxies. Galaxy Diversity. Galaxies, AGN and Quasars. Physics 113 Goderya
 Galaxies, AGN and Quasars Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 16 and 17 Learning Outcomes: Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars. Large variety of shapes
Galaxies, AGN and Quasars Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 16 and 17 Learning Outcomes: Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars. Large variety of shapes
Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN
 Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN Chiara Feruglio Institut de RadioAstronomie Millimétrique, Grenoble Thanks to: G. FABBIANO (CfA), F. FIORE (INAF) INAF - Bologne, 6 Mai 2013 1 Galaxy
Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN Chiara Feruglio Institut de RadioAstronomie Millimétrique, Grenoble Thanks to: G. FABBIANO (CfA), F. FIORE (INAF) INAF - Bologne, 6 Mai 2013 1 Galaxy
The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction
 The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction Outline Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): > Why are they special? > The power source > Sources of Continuum Emission > Emission & absorption lines
The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction Outline Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): > Why are they special? > The power source > Sources of Continuum Emission > Emission & absorption lines
ALMA Synergy with ATHENA
 ALMA Synergy with ATHENA Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris 9 September 2015 ALMA & Athena: common issues Galaxy formation and evolution, clustering Surveys of galaxies at high and intermediate redshifts
ALMA Synergy with ATHENA Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris 9 September 2015 ALMA & Athena: common issues Galaxy formation and evolution, clustering Surveys of galaxies at high and intermediate redshifts
Active Galactic Nuclei OIII
 Active Galactic Nuclei In 1908, Edward Fath (1880-1959) observed NGC 1068 with his spectroscope, which displayed odd (and very strong) emission lines. In 1926 Hubble recorded emission lines of this and
Active Galactic Nuclei In 1908, Edward Fath (1880-1959) observed NGC 1068 with his spectroscope, which displayed odd (and very strong) emission lines. In 1926 Hubble recorded emission lines of this and
A search for gravitationally lensed water masers
 A search for gravitationally lensed water masers Violette Impellizzeri (NRAO) with John McKean (ASTRON) Paola Castangia (INAF) Alan Roy (MPIfR) Christian Henkel (MPIfR) Andreas Brunthaler (MPIfR) Olaf
A search for gravitationally lensed water masers Violette Impellizzeri (NRAO) with John McKean (ASTRON) Paola Castangia (INAF) Alan Roy (MPIfR) Christian Henkel (MPIfR) Andreas Brunthaler (MPIfR) Olaf
Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs
 Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs Roberto J. Assef Núcleo de Astronomía Universidad Diego Portales This Talk Will focus on two topics: 1. The most luminous (obscured) quasars 2. AGN surveys Big
Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs Roberto J. Assef Núcleo de Astronomía Universidad Diego Portales This Talk Will focus on two topics: 1. The most luminous (obscured) quasars 2. AGN surveys Big
The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies
 The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies Philip Hopkins Ø (Nearly?) Every massive galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole Ø Mass accreted in ~couple bright quasar phase(s) (Soltan, Salucci+,
The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies Philip Hopkins Ø (Nearly?) Every massive galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole Ø Mass accreted in ~couple bright quasar phase(s) (Soltan, Salucci+,
Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution. Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory
 Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of
Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of
Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review)
 Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review) Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Delivered by Fangzhou Jiang Dali, China, November 2018 See also Claude-Andre s talk and Joel s talk
Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review) Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Delivered by Fangzhou Jiang Dali, China, November 2018 See also Claude-Andre s talk and Joel s talk
NEW CONSTRAINTS ON THE BLACK HOLE SPIN IN RADIO LOUD QUASARS
 NEW CONSTRAINTS ON THE BLACK HOLE SPIN IN RADIO LOUD QUASARS Andreas Schulze (NAOJ, EACOA Fellow)) Chris Done, Youjun Lu, Fupeng Zhang, Yoshiyuki Inoue East Asian Young Astronomers Meeting, EAYAM 2017
NEW CONSTRAINTS ON THE BLACK HOLE SPIN IN RADIO LOUD QUASARS Andreas Schulze (NAOJ, EACOA Fellow)) Chris Done, Youjun Lu, Fupeng Zhang, Yoshiyuki Inoue East Asian Young Astronomers Meeting, EAYAM 2017
Nuclear Star Formation, The Torus, & Gas Inflow in Seyfert Galaxies
 Nuclear Star Formation, The Torus, & Gas Inflow in Seyfert Galaxies Richard Davies 1, H. Engel 1, M. Schartmann 1, G. Orban de Xivry 1, E. Sani 2, E. Hicks 3, A. Sternberg 4, R. Genzel 1, L. Tacconi 1,
Nuclear Star Formation, The Torus, & Gas Inflow in Seyfert Galaxies Richard Davies 1, H. Engel 1, M. Schartmann 1, G. Orban de Xivry 1, E. Sani 2, E. Hicks 3, A. Sternberg 4, R. Genzel 1, L. Tacconi 1,
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution. Fabio Fontanot (HITS)
 AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests
 Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests My recent research projects study galaxy evolution with emphasis on star formation histories, gas accretion and outflow, and galaxy
Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests My recent research projects study galaxy evolution with emphasis on star formation histories, gas accretion and outflow, and galaxy
Driving hot and cold gas flows with AGN feedback in galaxy clusters Credit: ESO
 Driving hot and cold gas flows with AGN feedback in galaxy clusters Credit: ESO Helen Russell (Cambridge) Brian McNamara (Waterloo), Andy Fabian (Cambridge), Paul Nulsen (CfA), Michael McDonald (MIT),
Driving hot and cold gas flows with AGN feedback in galaxy clusters Credit: ESO Helen Russell (Cambridge) Brian McNamara (Waterloo), Andy Fabian (Cambridge), Paul Nulsen (CfA), Michael McDonald (MIT),
Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically faint ellipticals. Part 3. After Chandra?
 Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
Caitlin Casey, Jacqueline Hodge, Mark Lacy
 Next Generation VLA: Galaxy Assembly through Cosmic Time High-z working group: Caitlin Casey, Jacqueline Hodge, Mark Lacy Katherine Alatalo, Amy Barger, Sanjay Bhatnagar, Chris Carilli, Christopher Hales,
Next Generation VLA: Galaxy Assembly through Cosmic Time High-z working group: Caitlin Casey, Jacqueline Hodge, Mark Lacy Katherine Alatalo, Amy Barger, Sanjay Bhatnagar, Chris Carilli, Christopher Hales,
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Thaisa Storchi Bergmann Instituto de Física, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
 [Fe II] and H 2 Outflows N Far side E Inflows -600-520 -440-360 -280-200 -120-40 2 1 0 1 2 40 120 200 280 360 440 520 600 2 1 0 1 2 Thaisa Storchi Bergmann Instituto de Física, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS,
[Fe II] and H 2 Outflows N Far side E Inflows -600-520 -440-360 -280-200 -120-40 2 1 0 1 2 40 120 200 280 360 440 520 600 2 1 0 1 2 Thaisa Storchi Bergmann Instituto de Física, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS,
Narrow (UV) Absorption Line Outflows from Quasars
 Narrow (UV) Absorption Line Outflows from Quasars Fred Hamann University of Florida Leah Simon (Berea), Paola Rodriguez Hidalgo (PSU), Daniel Nestor (UCLA), Dan Capellupo (UF), Jason Prochaska (UCSD),
Narrow (UV) Absorption Line Outflows from Quasars Fred Hamann University of Florida Leah Simon (Berea), Paola Rodriguez Hidalgo (PSU), Daniel Nestor (UCLA), Dan Capellupo (UF), Jason Prochaska (UCSD),
