arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 May 1997
|
|
|
- Sharleen Williamson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE DISCOVERY OF 8.9 SECOND PULSATIONS FROM THE VARIABLE X RAY SOURCE 2E IN THE SMALL MAGELLANIC CLOUD G.L. Israel 1,2,3, L. Stella 3,2, L. Angelini 4,5, N. E. White 4, P. Giommi 6 and S. Covino 7 arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 May 1997 Received 03 Feb. 1997; accepted 13 May 1997 Accepted for publication on Ap.J. Letters 1 International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA ISAS), V. Beirut 2 4, I 34014, Trieste, Italy, gianluca@vega.sissa.it 2 Affiliated to the International Center for Relativistic Astrophysics 3 Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, V. dell Osservatorio 2, I Monteporzio Catone (Roma), Italy, stella@coma.mporzio.astro.it 4 Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics, Code 662, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA, white@adhoc.gsfc.nasa.gov, angelini@lheavx.gsfc.nasa.gov 5 University Space Research Association 6 SAX Science Data Center, ASI, Viale Regina Margherita 202, I Roma, Italy, giommi@sax.sdc.asi.it 7 Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera, Via E. Bianchi 46, I Merate (Lecco), Italy, covino@merate.mi.astro.it
2 2 ABSTRACT During a systematic search for periodic signals in a sample of ROSAT PSPC light curves, we discovered 8.9 s X ray pulsations in 2E , a variable X ray source in the Small Magellanic Cloud. The source was detected several times between 1979 and 1993 at luminosity levels ranging from erg s 1 up to erg s 1 with both the Einstein IPC and ROSAT PSPC. The X ray energy spectrum is consistent with a power law spectrum which steepens as the source luminosity decreases. We revealed a pronounced Hα activity from at least two B stars in the X ray error circles. These results strongly suggest that the X ray pulsar 2E is in a Be type massive binary. Subject headings: binaries: general pulsars: individual (2E ) stars: emission line, Be stars: rotation X ray: stars
3 3 1. Introduction Accreting X ray pulsars are mainly found in massive binaries containing an OB donor star and X ray transient activity is fairly common among those systems which host a Be star. The number of X ray pulsars of this class that are found in the Magellanic Clouds (MCs) is small, but recent ROSAT observations have substantially increased the sample (Hughes 1994; Dennerl et al. 1995; McGrath et al. 1994). Compared to those in our galaxy, massive X ray binaries in the MCs are usually characterised by a lower galactic interstellar attenuation in their direction and a better determined, though larger, distance. For three X ray pulsars in the MCs (SMC X 1, A and RX J ) the presence of a soft X ray component, in addition to the characteristic hard power law with exponential cutoff spectrum, has been firmly established (Marshall, White & Becker 1983; Mavromatakis & Haberl 1993; Hughes 1994; Corbet et al. 1995; Campana 1996). Based on several ROSAT PSPC observations, we report here the discovery of 8.9 s X ray pulsations from 1WGA J , a variable X ray source in the SMC, which was tentatively identified (Bruhweiler et al. 1987) with the B star AV111. The X ray spectrum showed a marked softening when the flux was a factor of 20 below its peak value. We report also the detection of Hα activity from AV111 and another B star within the X ray error circles. Based on its position the latter star provides a more likely optical counterpart than AV ROSAT PSPC observations The Position Sensitive Proportional Counter (PSPC, kev) in the focal plane of the X ray telescope on board ROSAT observed the SMC field centered on RA = m 28 s.7 and DEC = (equinox 2000) on 1993 May 9 12 (seq , s exposure; Table 1). The brightest source detected within the field was 1WGA J at a position of RA = m 53 s.3, DEC = (uncertainty radius of 30 ). The ROSAT event list and spectrum of 1WGA J were extracted from a circle of 1.0 radius (corresponding to an encircled energy, EE, of about 90% ) around the X ray position. Out of the 1750 photons contained in the circle we estimated that 100 photons derived from the local background around the source. The May 1993 light curve of 1WGA J was first analysed as part of a systematic study aimed at revealing periodicities in X ray light curves of a sample of X ray sources selected from the White, Giommi & Angelini catalog (1994; Israel 1996). The photon arrival times were corrected to the barycenter of the solar system and a 0.58 s binned light curve accumulated. The corresponding power spectrum calculated over the entire observation duration ( 3.5 d) is shown in Fig. 1a, together with the preliminary peak detection threshold described by Israel & Stella (1996). Significant peaks were clearly detected around Hz and Hz. While the former peaks are due to the wobble of the pointing direction ( 402 s period),
4 4 the multi peaked structure around a frequency of Hz is unique to 1WGA J (Fig. 1b); the highest of these peaks has a significance of 6.5σ over the entire sample of ROSAT light curves analysed. The power spectrum of the window function is shown in Fig. 1c with the same frequency scale as Fig. 1b; the peaks around the central frequency of Hz are the sidelobes due to the satellite orbital occultations. In the absence of a unique phase fitting solution, we determined the best period in each of four consecutive time intervals by using a Rayleigh periodogram (cf. Leahy et al. 1983). The average of these periods gave ± s (90% uncertainties are used throughout this letter) 8. An upper limit to the period derivative of Ṗ < s s 1 (3σ confidence level) was derived. The modulation was fairly sinusoidal, with a pulse fraction (semiamplitude of modulation devided by the mean source count rate) of 25% in the kev band (Fig. 1a). The arrival time of the pulse minima (that we adopted as phase 0) was determined to be JD ± The PSPC energy spectrum was fitted with a simple power law model (Fig. 2a and Table 2). The best fit was obtained for a photon index of Γ = 1.1 ± 0.2 and a column density of N H = (8± 3 2) cm 2 (the galactic hydrogen column in the direction of the SMC is cm 2 ). The kev unabsorbed X ray flux was F x erg cm 2 s 1, corresponding to a luminosity of L x erg s 1 for a distance of 65 kpc. The position of 1WGA J was included in several ROSAT PSPC fields observed between 1991 and 1993 (seq , , n00 and n00). The first observation was carried out on 1991 Oct 8 9 (1700 s exposure). The only detected source compatible with the position of 1WGA J is 1WGA J (RA = , DEC = , uncertainty radius of 50 ; Table1). The 1991 Oct 8 9 ROSAT event list and spectrum of 1WGA J included about 370 photons accumulated from a circle of 1.7 radius (EE of 90%) after background correction. The source count rate was estimated to be (6.9 ± 1.5) 10 3 counts s 1 after correction for PSF and vignetting. The photon arrival times were corrected to the barycenter of the solar system and a search for coherent periodicities was than performed in a narrow range of trial periods ( s) centered around the May 1993 period. No significant peaks were found above the 3σ detection threshold. The corresponding upper limit on the pulsed fraction was 60%. A simple power law model produced an acceptable fit to the spectrum from the 1991 Oct 8 9 pointing (Fig. 2a and Table 2). The best fit parameters were determined to be N H = (7± 9 3 ) 1020 cm 2 and Γ = 2.9 ± 0.8. The corresponding kev unabsorbed flux was about F x ergs cm 2 s 1, converting to a luminosity of L x erg s 1. In the remaining four ROSAT PSPC observations the source was not detected and only upper limits on the count rates were determined (see Table1 for details). In the ROSAT All Sky Survey (RASS) the region around the source was observed on 1990 Oct (667 s exposure). The source was not detected (2σ upper 8 This value and error revise the preliminary ones reported by Israel et al. (1995).
5 5 limit of cts s 1 ; cf. Kahabka & Pietsch 1996). 3. Einstein IPC observations The SMC was extensively surveyed with the Einstein Observatory. The position of 1WGA J was included in three Imaging Proportional Counter (IPC, kev) sequences (593, 6755 and 7988). These pointings were analysed in detail (Seward & Mitchell 1981; Bruhweiler et al. 1987; Wang & Wu 1992). Two Einstein sources with compatible positions were detected within the ROSAT error circle of 1WGA J : 2E (seq. 6755, source # 27 of Wang & Wu 1992) and 2E (seq. 7988, source # 3 in Bruhweiler et al. 1987). In the following we will use only the designation 2E The count rate of 2E increased by a factor of 5 from 1980 Apr 15 (seq. 6755) to Apr 20 (seq. 7988, Table 2; Wang & Wu 1992). Correspondingly the hardness ratio underwent a significant increase. The source was not detected in sequence 593 (upper limit of cts s 1 ; Wang & Wu 1992). We reanalysed the Einstein IPC sequences 6755 and 7988 to search for the 8.9 s periodicity. The IPC event lists were extracted from a circle of 1.6 radius (corresponding to an EE of 90%) around 2E and contained, respectively, 300 and 100 source photons. The arrival times of the kev photons were corrected only for the earth motion; the search for coherent periodicities was then performed over the s period range. No significant periodic signal was detected (upper limit of 75% and > 100% for sequence 6755 and 7988, respectively). We fitted the IPC spectra with a power law model, keeping N H fixed at cm 2 (the best value obtained with the ROSAT PSPC in May 1993). The derived photon index is in both cases consistent with Γ 1 (large uncertainties are due to poor statistics; Table 2). The inferred kev unabsorbed luminosities were L x and ergs s 1 for sequence 6755 and 7988, respectively. 4. Optical Observations The Einstein error circles of 2E include the optical position of AV111 (< 40 offset), a variable B1 giant in the SMC, that was tentatively identified as the optical counterpart (Bruhweiler et al. 1987; Wang & Wu 1992). In order to reveal the Hα active stars in the Einstein and ROSAT error circles ( 40 and 30 radius, respectively), we obtained three 4 4 images centered on AV111 with the ESO La Silla Dutch 91cm telescope on 1996 Aug The exposure time was 90, 120 and 900s for the V, B and Hα frames, respectively. Comparing, for each object in the X ray error circle, fluxes in the B, V and H α bands, we found several H α bright stars. In particular, the two most prominent were AV111 itself and a previously unclassified star (hereafter Star1) at an optical position R.A. = , DEC = (uncertainty < 10 ; see also Kahabka & Pietsch 1996). While consistent with the Einstein IPC error circles ( 40 radius), the
6 6 position of AV111 was determined to lie 10 outside the ROSAT PSPC error circle ( 30 radius; Fig. 3). On the contrary the position of Star1 is well within the PSPC error circle. The magnitude (V 13.4) and the color (B V 0.28) were also compatible with those of a B giant at the distance of the SMC. A medium resolution spectrum of AV111 was also taken on August 13, 1996 (600 s exposure) with the ESO La Silla 1.5 m Spectroscopic Telescope. The spectral range and resolution were Å and 1Å (at 6500Å). A pronounced Hα emission feature was apparent in the spectrum with an equivalent width of 5.4 ± 0.5Å We determined a line centroid to be at 6566Å corresponding to a radial velocity of 150kms 1 (the SMC line of sight velocity is 168kms 1 s). Two distinct components with comparable intensities could be easily distinguished close to the line centroid. These were peaked at 6564 and 6569 Å respectively, corresponding to a velocity difference of km s Discussion The 8.9 s pulsations from 2E together with the probable identification of an Hα emitting counterpart strongly suggest that the X ray source is an accreting magnetic neutron star likely in a Be star X ray binary. The X ray source was detected over a range of kev luminosities from to ergs s 1 ; on other occasions the source remained undetected, with upper limits that in two cases were just below the minimum detected luminosity. These large variations are suggestive of a transient behaviour. The relatively low peak X ray luminosity detected from 2E indicates that the source was observed either during the decay (or the rise) of a large outburst or during a lower luminosity (possibly recurrent) outburst. Increased Hα emission from AV111 or the other candidate (Star1) could provide a useful indicator of resumed X ray activity from 2E (this might be also useful to confirm the association of either candidates to the X ray source). Based on the orbital period / spin period correlation found by Corbet (1984) for Be star X ray pulsars, the orbit of 2E should be in the 30 d period range. Despite the limited energy range, the power law spectral slope of 2E measured by ROSAT when the source luminosity was ergs s 1 (Γ 1) is similar to that of most accreting X ray pulsars. A substantially softer spectrum (Γ 3) was measured when the source luminosity was ergs s 1. A clear spectral evolution was observed in the outburst decay of a sample of transient X ray pulsars, such as V (Makishima et al. 1990) and EXO (Reynolds, Parmar & White 1993). However in these cases the lowest detected luminosities were substantially higher ( ergs s 1 ) than in the case of 2E ; this suggests that their neutron stars were further away from the regime of centrifugal inhibition of accretion which occurs close to the end of a transient X ray pulsar outburst (Stella, White & Rosner 1986). By requiring that the centrifugal barrier is open for an accretion luminosity of ergs s 1 we derive an upper limit of B < G to the magnetic field of the neutron star in 2E For a
7 7 spin period of 8.9 s the luminosity gap across the centrifugal barrier should be a factor of 700 (Corbet 1996), indicating that when the source was a factor of 20 fainter the centrifugal barrier could not be completely closed and accretion onto the neutron star still took place. The case of 2E , together with that of the other X ray pulsars discussed above, suggests that the production of very soft X ray spectra results (for some yet unknown reason) from the accreting neutron star approaching the regime of centrifugal inhibition of accretion. We are grateful to A. Pizzella and L. Reduzzi for obtaining the optical spectra of AV111. This work was partially supported through ASI grants.
8 8 REFERENCES Bruhweiler, F.C. et al. 1987, ApJ, 317, 152 Campana, S. 1996, A&A, in press Corbet, R.H.D. 1984, A&A, 141, 91 Corbet, R.H.D. 1996, ApJ, 457, L31 Corbet, R.H.D., Smale, A.P., Charles, P.A. & Southwell, K. A. 1995, BAAS, 186, #48.07 Dennerl, K., Maberl, F. & Pietsch, W. 1995, IAU Circ.6184 Hughes, J.P. 1994, ApJ, 427, L25 Israel, G.L. et al. 1995, IAU Circ Israel, G.L. 1996, PhD Thesis, SISSA ISAS, Trieste, Italy Israel, G.L. & Stella, L. 1996, ApJ, 468, 369 Leahy, D. A., et al. 1983, ApJ, 266, 160 Kahabka, P. & Pietsch, W. 1996, A&A, 312, 919 Makishima, K. et al. 1990, PASJ, 42, 295 Marshall, F.E., White, N.E. & Becker, R.H. 1983, ApJ, 266, 814 Mavromatakis, F. & Haberl, F. 1993, A&A, 274, 304 McGrath, T.K. et al. 1994, BAAS, 185, # Raynold, A., Parmar, A.N. & White, N.E. 1993, ApJ, 414, 302 Seward, F.D. & Mitchell, M. 1991, ApJ, 243, 736 Skinner, G.K. et al. 1982, Nature, 297, 568 Stella, L., White, N.E. & Rosner, R. 1986, ApJ, 308, 669 Wang, Q. & Wu, X. 1992, ApJS, 78, 391 White, N. E., Giommi P. & Angelini L. 1994, IAU Circ.6100 This manuscript was prepared with the AAS L A TEX macros v4.0.
9 9 Fig. 1. Power spectrum of the kev ROSAT PSPC light curve of 1WGA J (panel a). The preliminary 3σ detection threshold is also shown. Peaks around multiples of Hz and Hz are spourious (see text for details). The peaks around Hz revealed the presence of a 8.9 s periodic signal in 1WGA J The latter peaks are shown in greater detail (panel b) together with the power spectrum of the window function (panel c) Folded light curves at the best period of s are shown as an insert in panel a for two different energy ranges. Fig. 2. ROSAT PSPC spectrum of 1WGA J during the 1993 May 9 12 and 1991 Oct 8 9 observations (upper panel). The best fit power law models are shown, together with the corresponding residuals. The lower panel gives the 1, 2 and 3σ confidence contours in the N H Γ plane for the 1993 May 9 12 (solid lines) and 1991 Oct 8 9 spectra (dash dotted lines). The crosses indicate the best fit values. The vertical line represents the estimated galactic hydrogen column. Fig. 3. ROSAT PSPC image of the SMC region around 2E / 1WGA J The ROSAT and Einstein best positions are given (crossed circles), together with their error circles ( 30 and 40, respectively). The filled circles indicate the optical positions of AV111 and the previously unclassified B star (Star1).
10 10 Table 1: ROSAT PSPC observations of 2E Start Time Stop Time Seq. Exp. Count Rate (#) (s) (10 3 cts s 1 ) 91 Oct 8 03:10 91 Oct 9 02: ± Oct 10 03:06 91 Oct 10 04: < 30 (a) 92 Apr 10 15:30 92 Apr 25 16: < 5 (b) 92 Apr 17 17:01 92 Apr 27 16: < 10 (c) 93 May 9 07:17 93 May 12 20: ± 3 93 Nov 5 23:21 93 Nov 9 02: < 20 (d) 93 Nov 30 05:39 93 Nov 30 07: < 60 (e) (a) The wobble direction was such that the source was almost always obscured by a rib. (b) As a result of the wobble the source was obscured by a rib for 50% of the time. (c) The wobble direction was such that the source moved parallel to the rib 1 away from it and therefore was unobscured. (d) As a result of the wobble the source was obscured for 25% of the time. (e) The wobble was such that the source spent 90% of the time under a rib or out of the field of view.
11 11 Table 2: ROSAT PSPC and Einstein IPC Spectral Results for 2E ROSAT PSPC Einstein IPC Parameter Seq. (#) a N H (10 20 cm 2 ) 8 ± ± (fixed) 8 (fixed) Γ 1.1 ± ± ± ± F x (10 12 erg s 1 cm 2 ) Count rate (10 3 cts 1 ) 114 ± ± ± ± 1 L x (10 35 erg s 1, d=65 kpc) Reduced chisquare a Oct 1991 data only. Note. X ray fluxes and luminosities are unabsorbed and refer to the kev and kev band for the ROSAT PSPC and Einstein IPC, respectively. Quoted uncertainties are 68% confidence for one parameter of interest.
12
13
14
The discovery of 12-min X-ray pulsations from 1WGA J
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 298, 502 506 (1998) The discovery of 12-min X-ray pulsations from 1WGA J1958.2+3232 G. L. Israel, 1 * L. Angelini, 2;3 * S. Campana, 4 * P. Giommi, 5 * L. Stella 1 * and N. E.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 298, 502 506 (1998) The discovery of 12-min X-ray pulsations from 1WGA J1958.2+3232 G. L. Israel, 1 * L. Angelini, 2;3 * S. Campana, 4 * P. Giommi, 5 * L. Stella 1 * and N. E.
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS The discovery of 96 s pulsations from the variable X-ray source 1SAX J in the Large Magellanic Cloud
 Astron. Astrophys. 337, 772 778 (1998) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS The discovery of 96 s pulsations from the variable X-ray source 1SAX J0544.1-710 in the Large Magellanic Cloud G. Cusumano 1, G.L. Israel
Astron. Astrophys. 337, 772 778 (1998) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS The discovery of 96 s pulsations from the variable X-ray source 1SAX J0544.1-710 in the Large Magellanic Cloud G. Cusumano 1, G.L. Israel
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Nov 1998
 ASCA Discovery of an X-ray Pulsar in the Error Box of SGR1900+14 K. Hurley, P. Li University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720-7450 arxiv:astro-ph/9811388v1 24 Nov
ASCA Discovery of an X-ray Pulsar in the Error Box of SGR1900+14 K. Hurley, P. Li University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720-7450 arxiv:astro-ph/9811388v1 24 Nov
PoS(extremesky2009)103
 The study of the nature of sources AX J1749.1 2733 and AX J1749.2 2725 D. I. Karasev Space Research Institute, Profsoyuznaya str. 84/32, Moscow 117997, Russia E-mail: dkarasev@iki.rssi.ru Space Research
The study of the nature of sources AX J1749.1 2733 and AX J1749.2 2725 D. I. Karasev Space Research Institute, Profsoyuznaya str. 84/32, Moscow 117997, Russia E-mail: dkarasev@iki.rssi.ru Space Research
1. INTRODUCTION. Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 04/03/99
 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 04/03/99 THE DISCOVERY OF QUIESCENT X-RAY EMISSION FROM SAX J1808.4 3658, THE TRANSIENT 2.5 MS PULSAR L. Stella 1,5, S. Campana 2,5, S. Mereghetti 3,
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 04/03/99 THE DISCOVERY OF QUIESCENT X-RAY EMISSION FROM SAX J1808.4 3658, THE TRANSIENT 2.5 MS PULSAR L. Stella 1,5, S. Campana 2,5, S. Mereghetti 3,
discovers a radio-quiet gamma-ray millisecond Journal Group
 Einstein@Home discovers a radio-quiet gamma-ray millisecond pulsar @CHEA Journal Group Contribution of the paper Contribution of the paper Millisecond Pulsars (MSPs) Ver y rapid rotating neutron star
Einstein@Home discovers a radio-quiet gamma-ray millisecond pulsar @CHEA Journal Group Contribution of the paper Contribution of the paper Millisecond Pulsars (MSPs) Ver y rapid rotating neutron star
Discovery of a New Gamma-Ray Binary: 1FGL J
 Discovery of a New Gamma-Ray Binary: 1FGL J1018.6-5856 Robin Corbet (UMBC/NASA GSFC) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration, & M.J. Coe, P.G. Edwards, M.D. Filipovic, J.L. Payne, J. Stevens, M.A.P. Torres
Discovery of a New Gamma-Ray Binary: 1FGL J1018.6-5856 Robin Corbet (UMBC/NASA GSFC) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration, & M.J. Coe, P.G. Edwards, M.D. Filipovic, J.L. Payne, J. Stevens, M.A.P. Torres
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Nov 2003
 Periodic Optical Outbursts from the Be/Neutron Star Binary AX J0049.4 7323 1 A.P. Cowley & P.C. Schmidtke arxiv:astro-ph/0311393v1 17 Nov 2003 Department of Physics & Astronomy, Arizona State University,
Periodic Optical Outbursts from the Be/Neutron Star Binary AX J0049.4 7323 1 A.P. Cowley & P.C. Schmidtke arxiv:astro-ph/0311393v1 17 Nov 2003 Department of Physics & Astronomy, Arizona State University,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 22 Nov 2000
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** OAO1657 415 : A Missing Link in High Mass X-ray Binaries? arxiv:astro-ph/0011401v1 22 Nov 2000 D.H. Maxwell, A.J. Norton
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** OAO1657 415 : A Missing Link in High Mass X-ray Binaries? arxiv:astro-ph/0011401v1 22 Nov 2000 D.H. Maxwell, A.J. Norton
PoS(INTEGRAL 2012)090
 XMM-Newton observations of five INTEGRAL sources located towards the Scutum Arm UC Berkeley - Space Sciences Laboratory E-mail: bodaghee@ssl.berkeley.edu John A. Tomsick UC Berkeley - Space Sciences Laboratory
XMM-Newton observations of five INTEGRAL sources located towards the Scutum Arm UC Berkeley - Space Sciences Laboratory E-mail: bodaghee@ssl.berkeley.edu John A. Tomsick UC Berkeley - Space Sciences Laboratory
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS BeppoSAX monitoring of the anomalous X-ray pulsar 4U
 Astron. Astrophys. 346, 929 935 (1999) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS BeppoSAX monitoring of the anomalous X-ray pulsar 4U 0142+61 G.L. Israel 1,, T. Oosterbroek 2, L. Angelini 3,, S. Campana 4,, S. Mereghetti
Astron. Astrophys. 346, 929 935 (1999) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS BeppoSAX monitoring of the anomalous X-ray pulsar 4U 0142+61 G.L. Israel 1,, T. Oosterbroek 2, L. Angelini 3,, S. Campana 4,, S. Mereghetti
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 30 Jan 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 30 Jan 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 30 Jan 2008](/thumbs/83/87508805.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa xmm c ESO 2018 May 26, 2018 XMM-Newton observations of the Small Magellanic Cloud: X-ray outburst of the 6.85 s pulsar XTE J0103-728 F. Haberl and W. Pietsch
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa xmm c ESO 2018 May 26, 2018 XMM-Newton observations of the Small Magellanic Cloud: X-ray outburst of the 6.85 s pulsar XTE J0103-728 F. Haberl and W. Pietsch
Pulse phase resolved spectroscopy: Probe of the dip phenomenon in the pulse profiles of GX 304-1
 Chapter 4 Pulse phase resolved spectroscopy: Probe of the dip phenomenon in the pulse profiles of GX 34-1 4.1 Introduction GX 34-1 (4U 158-61) is a transient high-mass X-ray binary pulsar discovered using
Chapter 4 Pulse phase resolved spectroscopy: Probe of the dip phenomenon in the pulse profiles of GX 34-1 4.1 Introduction GX 34-1 (4U 158-61) is a transient high-mass X-ray binary pulsar discovered using
FIGURE 1. The total kev logn-logs determined from several ROSAT surveys as indicated in the plot. Adapted from Hasinger et al.
 X-RAY SURVEYS P. Giommi 1,F.Fiore 1,2,3 and M. Perri 1 1) BeppoSAX Science Data Center, Rome, Italy 2) Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, Monteporzio, Italy 3) Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, 60
X-RAY SURVEYS P. Giommi 1,F.Fiore 1,2,3 and M. Perri 1 1) BeppoSAX Science Data Center, Rome, Italy 2) Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, Monteporzio, Italy 3) Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, 60
4U E. Bozzo. M. Falanga, A. Papitto, L. Stella, R. Perna, D. Lazzati G. Israel, S. Campana, V. Mangano, T. Di Salvo, L.
 X-Ray Eclipse Time Delays in 4U2129+47 E. Bozzo M. Falanga, A. Papitto, L. Stella, R. Perna, D. Lazzati G. Israel, S. Campana, V. Mangano, T. Di Salvo, L. Burderi Università di Roma Tor Vergata, Italy
X-Ray Eclipse Time Delays in 4U2129+47 E. Bozzo M. Falanga, A. Papitto, L. Stella, R. Perna, D. Lazzati G. Israel, S. Campana, V. Mangano, T. Di Salvo, L. Burderi Università di Roma Tor Vergata, Italy
PROPELLER EFFECT IN THE TRANSIENT X-RAY PULSAR SMC X-2
 Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v. 1.0 PROPELLER EFFECT IN THE TRANSIENT X-RAY PULSAR SMC X-2 Alexander A. Lutovinov 1,2, SergeyS.Tsygankov 3,1, RomanA.Krivonos
Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v. 1.0 PROPELLER EFFECT IN THE TRANSIENT X-RAY PULSAR SMC X-2 Alexander A. Lutovinov 1,2, SergeyS.Tsygankov 3,1, RomanA.Krivonos
Searching for black holes in nearby galaxies with Simbol-X
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 79, 208 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Searching for black holes in nearby galaxies with Simbol-X Paul Gorenstein Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St. Cambridge, MA 02138,
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 79, 208 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Searching for black holes in nearby galaxies with Simbol-X Paul Gorenstein Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St. Cambridge, MA 02138,
Timing an Accreting Millisecond Pulsar: Measuring the Accretion Torque in IGR J
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 6 (2006), Suppl. 1, 192 196 (http://www.chjaa.org) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Timing an Accreting Millisecond Pulsar: Measuring the Accretion Torque
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 6 (2006), Suppl. 1, 192 196 (http://www.chjaa.org) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Timing an Accreting Millisecond Pulsar: Measuring the Accretion Torque
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 11 Feb 2004
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. rea February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Timing and spectral changes of the Be X-ray transient EXO0531-6609.2 through high and low state. Nanda
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. rea February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Timing and spectral changes of the Be X-ray transient EXO0531-6609.2 through high and low state. Nanda
Kilo-Hertz QPO and X-ray Bursts in 4U in Low Intensity State
 Kilo-Hertz QPO and X-ray Bursts in 4U 1608-52 in Low Intensity State arxiv:astro-ph/9710069v2 9 Oct 1997 W. Yu, S. N. Zhang, B. A. Harmon, W. S. Paciesas, C. R. Robinson, J. E. Grindlay, P. Bloser, D.
Kilo-Hertz QPO and X-ray Bursts in 4U 1608-52 in Low Intensity State arxiv:astro-ph/9710069v2 9 Oct 1997 W. Yu, S. N. Zhang, B. A. Harmon, W. S. Paciesas, C. R. Robinson, J. E. Grindlay, P. Bloser, D.
A huge explosion in the early Universe
 1 A huge explosion in the early Universe G. Cusumano 1, V. Mangano 1, G. Chincarini 2,3, A. Panaitescu 4, D.N. Burrows 5, V. La Parola 1, T. Sakamoto 6,7, S. Campana 2, T. Mineo 1, G. Tagliaferri 2, L.
1 A huge explosion in the early Universe G. Cusumano 1, V. Mangano 1, G. Chincarini 2,3, A. Panaitescu 4, D.N. Burrows 5, V. La Parola 1, T. Sakamoto 6,7, S. Campana 2, T. Mineo 1, G. Tagliaferri 2, L.
ASCA Observation of the Quiescent X-ray Counterpart to SGR
 Clemson University TigerPrints Publications Physics and Astronomy 1-1-2000 ASCA Observation of the Quiescent X-ray Counterpart to SGR 1627-41 K. Hurley University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences
Clemson University TigerPrints Publications Physics and Astronomy 1-1-2000 ASCA Observation of the Quiescent X-ray Counterpart to SGR 1627-41 K. Hurley University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences
X-ray and infrared properties of Be/X-ray binary pulsars
 Recent Trends in the Study of Compact Objects: Theory and Observation ASI Conference Series, 203, Vol. 8, pp 03 08 Edited by Santabrata Das, Anuj Nandi and Indranil Chattopadhyay X-ray and infrared properties
Recent Trends in the Study of Compact Objects: Theory and Observation ASI Conference Series, 203, Vol. 8, pp 03 08 Edited by Santabrata Das, Anuj Nandi and Indranil Chattopadhyay X-ray and infrared properties
Cooling Limits for the
 Cooling Limits for the Page et al. 2004 Youngest Neutron Stars Cooling from the Youngest NSs SNR Zone NSs younger than ~50 kyr offer strong constraints on rapid cooling - the associated physical processes
Cooling Limits for the Page et al. 2004 Youngest Neutron Stars Cooling from the Youngest NSs SNR Zone NSs younger than ~50 kyr offer strong constraints on rapid cooling - the associated physical processes
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 1 Apr 1999
 A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: (02.01.2; 08.02.1; 08.09.2; 08.23.1; 13.25.5) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS A BeppoSAX observation of the supersoft source 1E
A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: (02.01.2; 08.02.1; 08.09.2; 08.23.1; 13.25.5) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS A BeppoSAX observation of the supersoft source 1E
AX J : a close look at a neutron star interacting with a circumstellar disc
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 350, 756 760 (2004) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07696.x AX J0049.4 7323: a close look at a neutron star interacting with a circumstellar disc M. J. Coe and W. R. T. Edge School
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 350, 756 760 (2004) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07696.x AX J0049.4 7323: a close look at a neutron star interacting with a circumstellar disc M. J. Coe and W. R. T. Edge School
PoS(SWIFT 10)142. The Swift-XRT observations of HBL Source 1ES
 The Swift-XRT observations of HBL Source 1ES 199+ ab, Patrizia Romano b, Stefano Vercellone b, Sergo Kapanadze a, Grigol Kharshiladze c a E. Kharadze Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Ilia State University,
The Swift-XRT observations of HBL Source 1ES 199+ ab, Patrizia Romano b, Stefano Vercellone b, Sergo Kapanadze a, Grigol Kharshiladze c a E. Kharadze Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Ilia State University,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 6 Dec 1999
 RESULTS FROM X-RAY SURVEYS WITH ASCA arxiv:astro-ph/9912084v1 6 Dec 1999 Yoshihiro Ueda Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Kanagawa 229-8510, Japan ABSTRACT We present main results from X-ray
RESULTS FROM X-RAY SURVEYS WITH ASCA arxiv:astro-ph/9912084v1 6 Dec 1999 Yoshihiro Ueda Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Kanagawa 229-8510, Japan ABSTRACT We present main results from X-ray
Compact Stars. Lecture 4
 Compact Stars Lecture 4 X-ray binaries We have talked about the basic structure of accretion disks in X-ray binaries and evolutionary scenarios of low mass and high mass XRBs I will now present the observational
Compact Stars Lecture 4 X-ray binaries We have talked about the basic structure of accretion disks in X-ray binaries and evolutionary scenarios of low mass and high mass XRBs I will now present the observational
Precise Interplanetary Network Localization of a New Soft. Gamma Repeater, SGR
 Precise Interplanetary Network Localization of a New Soft Gamma Repeater, SGR1627-41 K. Hurley University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720-7450 C. Kouveliotou Universities
Precise Interplanetary Network Localization of a New Soft Gamma Repeater, SGR1627-41 K. Hurley University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720-7450 C. Kouveliotou Universities
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 9 Jun 1997
 A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: 06 (08.02.1; 11.13.1; 13.25.5; 08.09.2) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS 1.2.2008 X-Ray Binary Systems in the Small Magellanic Cloud
A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: 06 (08.02.1; 11.13.1; 13.25.5; 08.09.2) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS 1.2.2008 X-Ray Binary Systems in the Small Magellanic Cloud
D. J. MACOMB1 Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics, Code 661, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771; macomb=cossc.gsfc.nasa.
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 560:378È383, 2001 October 10 ( 2001. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DISCOVERY OF PULSED X-RAYS FROM THE SMC TRANSIENT RX J0052.1[7319
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 560:378È383, 2001 October 10 ( 2001. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DISCOVERY OF PULSED X-RAYS FROM THE SMC TRANSIENT RX J0052.1[7319
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 24 Dec 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 24 Dec 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 24 Dec 2013](/thumbs/92/108440419.jpg) Research in Astron. & Astrophys. Vol. (x) No., (http://www.raa-journal.org) Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics arxiv:3.6753v [astro-ph.he] 4 Dec 3 Temporal Variations And Spectral Properties of Be/X-ray
Research in Astron. & Astrophys. Vol. (x) No., (http://www.raa-journal.org) Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics arxiv:3.6753v [astro-ph.he] 4 Dec 3 Temporal Variations And Spectral Properties of Be/X-ray
Fermi Large Area Telescope:
 Fermi Large Area Telescope: Early Results on Pulsars Kent Wood Naval Research Lab kent.wood@nrl.navy.mil for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Tokyo Institute of Technology 7 March 2009 K. Wood (NRL) 1/30 Fermi
Fermi Large Area Telescope: Early Results on Pulsars Kent Wood Naval Research Lab kent.wood@nrl.navy.mil for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Tokyo Institute of Technology 7 March 2009 K. Wood (NRL) 1/30 Fermi
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 21 Feb 2002
 Re-submitted to ApJ Letters: February 12, 2002 A Chandra observation of GRO J1744 28: the bursting pulsar in quiescence arxiv:astro-ph/0201293v2 21 Feb 2002 Rudy Wijnands 1,2, Q. Daniel Wang 3 ABSTRACT
Re-submitted to ApJ Letters: February 12, 2002 A Chandra observation of GRO J1744 28: the bursting pulsar in quiescence arxiv:astro-ph/0201293v2 21 Feb 2002 Rudy Wijnands 1,2, Q. Daniel Wang 3 ABSTRACT
Figure 1: Left: Apparent radial velocities of Capella measured with the Chandra/HETGS. The dotted line shows the calculated apparent radial motion of
 Figure 1: Left: Apparent radial velocities of Capella measured with the Chandra/HETGS. The dotted line shows the calculated apparent radial motion of Capella Aa viewed from Earth (including the barycentric,
Figure 1: Left: Apparent radial velocities of Capella measured with the Chandra/HETGS. The dotted line shows the calculated apparent radial motion of Capella Aa viewed from Earth (including the barycentric,
Chandra Observation of Point Sources in the X-Ray Elliptical Galaxy NGC 1407
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 4 (2004), No. 3, 221 230 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Chandra Observation of Point Sources in the X-Ray
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 4 (2004), No. 3, 221 230 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Chandra Observation of Point Sources in the X-Ray
Probing Neutron Star Physics using Thermonuclear X-ray Bursts
 Probing Neutron Star Physics using Thermonuclear X-ray Bursts Sudip Bhattacharyya University of Maryland (CRESST) NASA s Goddard Space Flight Center Outline Neutron Stars: why do we care? Thermonuclear
Probing Neutron Star Physics using Thermonuclear X-ray Bursts Sudip Bhattacharyya University of Maryland (CRESST) NASA s Goddard Space Flight Center Outline Neutron Stars: why do we care? Thermonuclear
Time-domain astronomy with the Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor
 Time-domain astronomy with the Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor C. Michelle Hui (NASA/MSFC) on behalf of the Fermi GBM team TeVPA, Aug 11 2017 GBM: FOV >8sr Whole sky every ~90min Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
Time-domain astronomy with the Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor C. Michelle Hui (NASA/MSFC) on behalf of the Fermi GBM team TeVPA, Aug 11 2017 GBM: FOV >8sr Whole sky every ~90min Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
X-ray Observations of Nearby Galaxies
 X-ray Observations of Nearby Galaxies Wolfgang Pietsch Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik XMM-Newton EPIC view of the starburst galaxy NGC 253 Wolfgang Pietsch Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische
X-ray Observations of Nearby Galaxies Wolfgang Pietsch Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik XMM-Newton EPIC view of the starburst galaxy NGC 253 Wolfgang Pietsch Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische
High-resolution spectroscopy of the low-mass X-ray binary EXO
 A&A 365, L277 L281 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20000053 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics High-resolution spectroscopy of the low-mass X-ray binary EXO 0748 67 J. Cottam 1,S.M.Kahn 1,A.C.Brinkman 2,J.W.denHerder
A&A 365, L277 L281 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20000053 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics High-resolution spectroscopy of the low-mass X-ray binary EXO 0748 67 J. Cottam 1,S.M.Kahn 1,A.C.Brinkman 2,J.W.denHerder
X-ray variability of AGN
 X-ray variability of AGN Magnus Axelsson October 20, 2006 Abstract X-ray variability has proven to be an effective diagnostic both for Galactic black-hole binaries and active galactic nuclei (AGN). This
X-ray variability of AGN Magnus Axelsson October 20, 2006 Abstract X-ray variability has proven to be an effective diagnostic both for Galactic black-hole binaries and active galactic nuclei (AGN). This
Discovery of TeV Gamma-ray Emission Towards Supernova Remnant SNR G Last Updated Tuesday, 30 July :01
 Background-subtracted gamma-ray count map of SNR G78.2+2.1 showing the VERITAS detection (VER2019+407). For details, see Figure 1 below. Reference: E. Aliu et al. (The VERITAS Collaboration), Astrophysical
Background-subtracted gamma-ray count map of SNR G78.2+2.1 showing the VERITAS detection (VER2019+407). For details, see Figure 1 below. Reference: E. Aliu et al. (The VERITAS Collaboration), Astrophysical
astro-ph/ Jun 1996
 The Long-Term X-Ray Lightcurve of RX J0527.8{6954 J. Greiner 1, R. Schwarz 2, G. Hasinger 2, M. Orio 3? 1 Max-Planck-Institut fur Extraterrestrische Physik, 85740 Garching, Germany 2 Astrophysikalisches
The Long-Term X-Ray Lightcurve of RX J0527.8{6954 J. Greiner 1, R. Schwarz 2, G. Hasinger 2, M. Orio 3? 1 Max-Planck-Institut fur Extraterrestrische Physik, 85740 Garching, Germany 2 Astrophysikalisches
RX J and RX J : recent results and status
 RX J0806+15 and RX J1914+24: recent results and status Gavin Ramsay (Armagh Observatory) Overview of talk Remind you what they are! Recent observational work since Nijmegen Meeting. Modelling and theoretical
RX J0806+15 and RX J1914+24: recent results and status Gavin Ramsay (Armagh Observatory) Overview of talk Remind you what they are! Recent observational work since Nijmegen Meeting. Modelling and theoretical
PoS(INTEGRAL 2010)134
 A two-year monitoring campaign of Supergiant Fast X-ray Transients with Swift, a V. La Parola, a G. Cusumano, a S. Vercellone, a P. Esposito, b J.A. Kennea, c D.N. Burrows, c H.A. Krimm, de C. Pagani,
A two-year monitoring campaign of Supergiant Fast X-ray Transients with Swift, a V. La Parola, a G. Cusumano, a S. Vercellone, a P. Esposito, b J.A. Kennea, c D.N. Burrows, c H.A. Krimm, de C. Pagani,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 13 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 13 Jun 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 13 Jun 2017](/thumbs/74/69811844.jpg) EXO 3+37 Restarts in Reverse arxiv:76.3969v [astro-ph.he] 3 Jun 7 European Space Astronomy Centre (ESA/ESAC), Science Operations Department P.O. Box 78, E-869, Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid, Spain E-mail:
EXO 3+37 Restarts in Reverse arxiv:76.3969v [astro-ph.he] 3 Jun 7 European Space Astronomy Centre (ESA/ESAC), Science Operations Department P.O. Box 78, E-869, Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid, Spain E-mail:
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS A BeppoSAX observation of the supersoft source 1E
 Astron. Astrophys. 346, 453 458 (1999) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS A BeppoSAX observation of the supersoft source 1E 0035.4-7230 P. Kahabka 1, A.N. Parmar 2, and H.W. Hartmann 3 1 Astronomical Institute
Astron. Astrophys. 346, 453 458 (1999) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS A BeppoSAX observation of the supersoft source 1E 0035.4-7230 P. Kahabka 1, A.N. Parmar 2, and H.W. Hartmann 3 1 Astronomical Institute
Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs
 Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs The nature of 1WGA J1958.2+3232: a new intermediate polar Journal Item How to cite: Negueruela,
Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs The nature of 1WGA J1958.2+3232: a new intermediate polar Journal Item How to cite: Negueruela,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 22 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 22 Aug 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 22 Aug 2013](/thumbs/71/66040096.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 6 (2010) Printed 23 August 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Finding a 61.0-day orbital period for the HMXB 4U 1036 56 with the Swift-BAT monitoring. arxiv:1305.3610v2 [astro-ph.he]
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 6 (2010) Printed 23 August 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Finding a 61.0-day orbital period for the HMXB 4U 1036 56 with the Swift-BAT monitoring. arxiv:1305.3610v2 [astro-ph.he]
The Orbit and Position of the X-ray Pulsar XTE J an Eclipsing Supergiant System
 The Orbit and Position of the X-ray Pulsar XTE J1855-026 - an Eclipsing Supergiant System Robin H.D. Corbet 1 and Koji Mukai 1 Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics, Code 662, NASA/Goddard Space Flight
The Orbit and Position of the X-ray Pulsar XTE J1855-026 - an Eclipsing Supergiant System Robin H.D. Corbet 1 and Koji Mukai 1 Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics, Code 662, NASA/Goddard Space Flight
ROSAT and follow-up infrared observations of the X-ray burster KS
 Astron. Astrophys. 329, 965 970 (1998) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS ROSAT and follow-up infrared observations of the X-ray burster KS 1731-260 Didier Barret 1,2, Christian Motch,3, and Peter Predehl 4 1
Astron. Astrophys. 329, 965 970 (1998) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS ROSAT and follow-up infrared observations of the X-ray burster KS 1731-260 Didier Barret 1,2, Christian Motch,3, and Peter Predehl 4 1
Fermi GBM Science Highlights.
 Fermi GBM Science Highlights. of the GBM Team. Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor (GBM) on Fermi The Large Area Telescope (LAT) GBM BGO detector. 200 kev -- 40 MeV 126 cm2, 12.7 cm Spectroscopy Bridges gap between
Fermi GBM Science Highlights. of the GBM Team. Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor (GBM) on Fermi The Large Area Telescope (LAT) GBM BGO detector. 200 kev -- 40 MeV 126 cm2, 12.7 cm Spectroscopy Bridges gap between
A BeppoSAX observation of Her X-1 during the first main-on after an anomalous low-state: Evidence for rapid spin-down
 A&A 375, 922 926 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010820 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics A BeppoSAX observation of Her X-1 during the first main-on after an anomalous low-state: Evidence for rapid spin-down
A&A 375, 922 926 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010820 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics A BeppoSAX observation of Her X-1 during the first main-on after an anomalous low-state: Evidence for rapid spin-down
CONTENTS AIM OF THE PROJECT. INTRODUCTION: AGNs, XMM-Newton, ROSAT. TECHNIQUES: IDL, SQL, Catalogues RESULTS SUMMARY DESIRED OUTPUTS QUESTIONS
 CONTENTS AIM OF THE PROJECT INTRODUCTION: AGNs, XMM-Newton, ROSAT TECHNIQUES: IDL, SQL, Catalogues RESULTS SUMMARY DESIRED OUTPUTS QUESTIONS AIM OF THE PROJECT Brightness of AGNs appears to change very
CONTENTS AIM OF THE PROJECT INTRODUCTION: AGNs, XMM-Newton, ROSAT TECHNIQUES: IDL, SQL, Catalogues RESULTS SUMMARY DESIRED OUTPUTS QUESTIONS AIM OF THE PROJECT Brightness of AGNs appears to change very
ROSAT Roentgen Satellite. Chandra X-ray Observatory
 ROSAT Roentgen Satellite Joint facility: US, Germany, UK Operated 1990 1999 All-sky survey + pointed observations Chandra X-ray Observatory US Mission Operating 1999 present Pointed observations How do
ROSAT Roentgen Satellite Joint facility: US, Germany, UK Operated 1990 1999 All-sky survey + pointed observations Chandra X-ray Observatory US Mission Operating 1999 present Pointed observations How do
SOFT X-RAY EMISSION FROM SELECTED ISOLATED PULSARS
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 452 : L115 L119, 1995 October 20 1995. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SOFT X-RAY EMISSION FROM SELECTED ISOLATED PULSARS PATRICK SLANE
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 452 : L115 L119, 1995 October 20 1995. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SOFT X-RAY EMISSION FROM SELECTED ISOLATED PULSARS PATRICK SLANE
V2487 Oph 1998: a puzzling recurrent nova observed with XMM-Newton
 V2487 Oph 1998: a puzzling recurrent nova observed with XMM-Newton Margarita Hernanz Institute of Space Sciences (CSIC-IEEC) - Barcelona (Spain) Gloria Sala (UPC-IEEC), Nataly Ospina (CSIC-IEEC) V2487
V2487 Oph 1998: a puzzling recurrent nova observed with XMM-Newton Margarita Hernanz Institute of Space Sciences (CSIC-IEEC) - Barcelona (Spain) Gloria Sala (UPC-IEEC), Nataly Ospina (CSIC-IEEC) V2487
Position and Variability of 2A
 Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 113:1386 1392, 2001 November 2001. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Position and Variability of 2A
Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 113:1386 1392, 2001 November 2001. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Position and Variability of 2A
Broad band X ray spectra of M31 sources with BeppoSAX
 Astron. Astrophys. 348, 43 62 (1999) Broad band X ray spectra of M31 sources with BeppoSAX ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS G. Trinchieri 1, G.L. Israel 2, L. Chiappetti 3, T. Belloni 1,4, L. Stella 2, F. Primini
Astron. Astrophys. 348, 43 62 (1999) Broad band X ray spectra of M31 sources with BeppoSAX ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS G. Trinchieri 1, G.L. Israel 2, L. Chiappetti 3, T. Belloni 1,4, L. Stella 2, F. Primini
X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma Ray Bursts
 X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma Ray Bursts John Heise 1,2,Jeanin tzand 2,1,R.MarcKippen 3,andPeterM.Woods 4 1 Space Research Organization Netherlands, Utrecht, NL 3484CA Netherlands 2 Astronomical Institute,
X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma Ray Bursts John Heise 1,2,Jeanin tzand 2,1,R.MarcKippen 3,andPeterM.Woods 4 1 Space Research Organization Netherlands, Utrecht, NL 3484CA Netherlands 2 Astronomical Institute,
Pulsars and Timing. Lucas Guillemot, Ismaël Cognard.!! Rencontre CTA, Observatoire de Paris, 28/11/13
 Pulsars and Timing Lucas Guillemot, Ismaël Cognard Rencontre CTA, Observatoire de Paris, 28/11/13 Pulsars radio emission cone γ-ray emission fan beam Pulsars are rapidly rotating highly magnetized neutron
Pulsars and Timing Lucas Guillemot, Ismaël Cognard Rencontre CTA, Observatoire de Paris, 28/11/13 Pulsars radio emission cone γ-ray emission fan beam Pulsars are rapidly rotating highly magnetized neutron
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope
 A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
PoS(extremesky2009)018
 Swift/XRT follow-up observations of unidentified INTEGRAL/IBIS sources E-mail: landi@iasfbo.inaf.it L. Bassani E-mail: bassani@iasfbo.inaf.it A. Malizia E-mail: malizia@iasfbo.inaf.it J. B. Stephen E-mail:
Swift/XRT follow-up observations of unidentified INTEGRAL/IBIS sources E-mail: landi@iasfbo.inaf.it L. Bassani E-mail: bassani@iasfbo.inaf.it A. Malizia E-mail: malizia@iasfbo.inaf.it J. B. Stephen E-mail:
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission
 The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
PoS(extremesky2009)013
 Correlating the WFC and the IBIS hard X-ray surveys IASF-Roma INAF. Via Fosso del Cavaliere, 100 00133 Rome Italy E-mail: fiamma.capitanio@iasf-roma.inaf.it A. J. Bird School of Physics and Astronomy,
Correlating the WFC and the IBIS hard X-ray surveys IASF-Roma INAF. Via Fosso del Cavaliere, 100 00133 Rome Italy E-mail: fiamma.capitanio@iasf-roma.inaf.it A. J. Bird School of Physics and Astronomy,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Oct 2001
 To be published in Astronomy Letters, Vol. 27, No. 12, 2001, pp. 790-793 Translated from Pis ma v Astronomicheskij Zhurnal, Vol. 27, No. 12, 2001, pp. 919-922 Correlation between Break Frequency and Power
To be published in Astronomy Letters, Vol. 27, No. 12, 2001, pp. 790-793 Translated from Pis ma v Astronomicheskij Zhurnal, Vol. 27, No. 12, 2001, pp. 919-922 Correlation between Break Frequency and Power
Extreme optical outbursts from a magnetar-like transient source: SWIFT J
 Extreme optical outbursts from a magnetar-like transient source: SWIFT J1955+26 Gottfried Kanbach 1 Alexander Stefanescu 1,2 Agnieszka Słowikowska 3 Jochen Greiner 1 Sheila McBreen 4 Glòria Sala 5 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Extreme optical outbursts from a magnetar-like transient source: SWIFT J1955+26 Gottfried Kanbach 1 Alexander Stefanescu 1,2 Agnieszka Słowikowska 3 Jochen Greiner 1 Sheila McBreen 4 Glòria Sala 5 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope
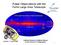 Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope First Light sky survey (4 days of exposure)) Launch: 11 June 2008 Gottfried Kanbach & Matthew Baring for the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 The high-energy
Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope First Light sky survey (4 days of exposure)) Launch: 11 June 2008 Gottfried Kanbach & Matthew Baring for the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 The high-energy
Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results
 Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results 1. GeV instrumentation and the GeV sky with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope 2. First Fermi Catalog of Gamma Ray Sources and the Fermi Pulsar Catalog 3.
Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results 1. GeV instrumentation and the GeV sky with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope 2. First Fermi Catalog of Gamma Ray Sources and the Fermi Pulsar Catalog 3.
Construction and Preliminary Application of the Variability Luminosity Estimator
 Construction and Preliminary Application of the Variability Luminosity Estimator arxiv:astro-ph/0103255v2 19 Mar 2001 Daniel E. Reichart 1,2 and Donald Q. Lamb 3 1 Department of Astronomy, California Institute
Construction and Preliminary Application of the Variability Luminosity Estimator arxiv:astro-ph/0103255v2 19 Mar 2001 Daniel E. Reichart 1,2 and Donald Q. Lamb 3 1 Department of Astronomy, California Institute
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 18 Oct 2002
 Determining the GRB (Redshift, Luminosity)-Distribution Using Burst Variability Timothy Donaghy, Donald Q. Lamb, Daniel E. Reichart and Carlo Graziani arxiv:astro-ph/0210436v2 18 Oct 2002 Department of
Determining the GRB (Redshift, Luminosity)-Distribution Using Burst Variability Timothy Donaghy, Donald Q. Lamb, Daniel E. Reichart and Carlo Graziani arxiv:astro-ph/0210436v2 18 Oct 2002 Department of
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Broad band properties of medium and low L x /L b early type galaxies
 Astron. Astrophys. 364, 53 69 (2000) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Broad band properties of medium and low L x /L b early type galaxies G. Trinchieri 1, S. Pellegrini 2, A. Wolter 1, G. Fabbiano 3, and F.
Astron. Astrophys. 364, 53 69 (2000) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Broad band properties of medium and low L x /L b early type galaxies G. Trinchieri 1, S. Pellegrini 2, A. Wolter 1, G. Fabbiano 3, and F.
Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.
![Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen. Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.](/thumbs/95/126078116.jpg) University of Groningen Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries Wang, Yanan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries Wang, Yanan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Measuring the distances, masses and radii of neutron stars
 Measuring the distances, masses and radii of neutron stars Tolga Güver, Feryal Özel, Antonio Cabrera-Lavers, Patricia Wroblewski, Larry Camarota, Dimitrios Psaltis University of Arizona 1 Distances, Masses,
Measuring the distances, masses and radii of neutron stars Tolga Güver, Feryal Özel, Antonio Cabrera-Lavers, Patricia Wroblewski, Larry Camarota, Dimitrios Psaltis University of Arizona 1 Distances, Masses,
BeppoSAX observation of the X ray binary pulsar Vela X 1
 BeppoSAX observation of the X ray binary pulsar Vela X 1 M. Orlandini 1, D. Dal Fiume 1, L. Nicastro 1, S. Giarrusso 2, A. Segreto 2, S. Piraino 2, G. Cusumano 2, S. Del Sordo 2,M.Guainazzi 3, L. Piro
BeppoSAX observation of the X ray binary pulsar Vela X 1 M. Orlandini 1, D. Dal Fiume 1, L. Nicastro 1, S. Giarrusso 2, A. Segreto 2, S. Piraino 2, G. Cusumano 2, S. Del Sordo 2,M.Guainazzi 3, L. Piro
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 14 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 14 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 14 Feb 2013](/thumbs/84/90977748.jpg) arxiv:1302.3434v1 [astro-ph.he] 14 Feb 2013 European Space Astronomy Centre (ESA/ESAC), Science Operations Department, Villanueva de la Cañada (Madrid), Spain E-mail: peter.kretschmar@esa.int Elisa Nespoli
arxiv:1302.3434v1 [astro-ph.he] 14 Feb 2013 European Space Astronomy Centre (ESA/ESAC), Science Operations Department, Villanueva de la Cañada (Madrid), Spain E-mail: peter.kretschmar@esa.int Elisa Nespoli
PoS(INTEGRAL 2010)131
 Study of the X-ray/gamma source AX J1910.7+0917 and three newly discovered INTEGRAL sources, E. Bozzo a, C. Ferrigno a, C. Ricci a, A. Manousakis a, R. Walter a, L. Stella b a ISDC - Science data center
Study of the X-ray/gamma source AX J1910.7+0917 and three newly discovered INTEGRAL sources, E. Bozzo a, C. Ferrigno a, C. Ricci a, A. Manousakis a, R. Walter a, L. Stella b a ISDC - Science data center
Infrared Spectroscopy of the Black Hole Candidate GRO J
 Infrared Spectroscopy of the Black Hole Candidate GRO J1655-40 1 Francis T. O Donovan March 19th, 2004 1 Based on a paper by F. T. O Donovan & P. J. Callanan (in preparation). Black Holes in the Sky At
Infrared Spectroscopy of the Black Hole Candidate GRO J1655-40 1 Francis T. O Donovan March 19th, 2004 1 Based on a paper by F. T. O Donovan & P. J. Callanan (in preparation). Black Holes in the Sky At
Search for X-ray Transients with MAXI
 Search for X-ray Transients with MAXI Nobuyuki Kawai (Tokyo Tech) M. Serino (RIKEN), H. Negoro (Nihon U.) on behalf of the MAXI Team MAXI Instrumentation and operation Observations for GW 150914 and results
Search for X-ray Transients with MAXI Nobuyuki Kawai (Tokyo Tech) M. Serino (RIKEN), H. Negoro (Nihon U.) on behalf of the MAXI Team MAXI Instrumentation and operation Observations for GW 150914 and results
Identification of seven persistent low-luminosity pulsators. Ramanpreet Kaur University of Amsterdam
 Identification of seven persistent low-luminosity pulsators Ramanpreet Kaur University of Amsterdam Physics of neutron stars -2011 St Petersburg, Russia Low-luminosity pulsators Slowly pulsating (Ps >
Identification of seven persistent low-luminosity pulsators Ramanpreet Kaur University of Amsterdam Physics of neutron stars -2011 St Petersburg, Russia Low-luminosity pulsators Slowly pulsating (Ps >
A Library of the X-ray Universe: Generating the XMM-Newton Source Catalogues
 A Library of the X-ray Universe: Generating the XMM-Newton Source Catalogues Iris Traulsen Axel Schwope, Georg Lamer Leibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP) on behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey Science
A Library of the X-ray Universe: Generating the XMM-Newton Source Catalogues Iris Traulsen Axel Schwope, Georg Lamer Leibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP) on behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey Science
Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays
 The XXVII Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays Wei Wang National Astronomical Observatories, Beijing China Dec 8 13 2013, Dallas TX, USA Contents
The XXVII Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays Wei Wang National Astronomical Observatories, Beijing China Dec 8 13 2013, Dallas TX, USA Contents
9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with BATSE
 9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with CGRO BATSE Large Area Detector (LAD) BATSE 1 of 8 BATSE Colleen A. Wilson (NASA/MSFC), for the BATSE teams at MSFC and Southampton Abstract The hard X-ray
9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with CGRO BATSE Large Area Detector (LAD) BATSE 1 of 8 BATSE Colleen A. Wilson (NASA/MSFC), for the BATSE teams at MSFC and Southampton Abstract The hard X-ray
Outbursts and State Transitions in Black Hole Candidates Observed by MAXI
 Outbursts and State Transitions in Black Hole Candidates Observed by MAXI Hitoshi Negoro and MAXI Team Nihon University, -8 Kanda-Surugadai, Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan -838 E-mail(HN): negoro@phys.cst.nihon-u.ac.jp
Outbursts and State Transitions in Black Hole Candidates Observed by MAXI Hitoshi Negoro and MAXI Team Nihon University, -8 Kanda-Surugadai, Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan -838 E-mail(HN): negoro@phys.cst.nihon-u.ac.jp
X-ray Nova XTE J : Discovery of a QPO Near 185 Hz
 X-ray Nova XTE J1550-564: Discovery of a QPO Near 185 Hz Ronald A. Remillard Center for Space Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Room 37-595, Cambridge MA 02139 Jeffrey E. McClintock Harvard-Smithsonian
X-ray Nova XTE J1550-564: Discovery of a QPO Near 185 Hz Ronald A. Remillard Center for Space Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Room 37-595, Cambridge MA 02139 Jeffrey E. McClintock Harvard-Smithsonian
PoS(MQW7)050. Cygnus X-3 s "Little" Friend. Michael McCollough. CXC/SAO
 CXC/SAO E-mail: mmccollough@head.cfa.harvard.edu Cygnus X-3 is a well know microquasar which shows state changes, strong radio emission, hard X-ray/X-ray/radio correlations, and relativistic jets. The
CXC/SAO E-mail: mmccollough@head.cfa.harvard.edu Cygnus X-3 is a well know microquasar which shows state changes, strong radio emission, hard X-ray/X-ray/radio correlations, and relativistic jets. The
Spectral Lines from Rotating Neutron Stars
 Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Letters Spectral Lines from Rotating Neutron Stars Feryal Özel1 and Dimitrios Psaltis Institute for Advanced Study, School of Natural Sciences, Einstein Dr., Princeton,
Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Letters Spectral Lines from Rotating Neutron Stars Feryal Özel1 and Dimitrios Psaltis Institute for Advanced Study, School of Natural Sciences, Einstein Dr., Princeton,
Hard X-ray emission from magnetars
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 79, 97 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Hard X-ray emission from magnetars A case study for Simbol-X Diego Götz CEA Saclay, DSM/Dapnia/Service d Astrophysique, F-91191, Gif sur Yvette, France
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 79, 97 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Hard X-ray emission from magnetars A case study for Simbol-X Diego Götz CEA Saclay, DSM/Dapnia/Service d Astrophysique, F-91191, Gif sur Yvette, France
XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J / RBS 1774
 XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J214303.7+065419 / RBS 1774 Mark Cropper, Silvia Zane Roberto Turolla Luca Zampieri Matteo Chieregato Jeremy Drake Aldo Treves MSSL/UCL Univ Padova
XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J214303.7+065419 / RBS 1774 Mark Cropper, Silvia Zane Roberto Turolla Luca Zampieri Matteo Chieregato Jeremy Drake Aldo Treves MSSL/UCL Univ Padova
The central region of M 31 observed with XMM-Newton
 A&A 365, L195 L201 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20000243 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics The central region of M 31 observed with XMM-Newton I. Group properties and diffuse emission R. Shirey 1,R.Soria
A&A 365, L195 L201 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20000243 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics The central region of M 31 observed with XMM-Newton I. Group properties and diffuse emission R. Shirey 1,R.Soria
X : AN X-RAY BINARY WITH A 4.4 DAY PERIOD
 THE ASTROPHYSCAL JOURNAL, 999:L1-L4, 2000 January 1 c 2000. The American Astrological Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. X 1908+075: AN X-RAY BINARY WITH A 4.4 DAY PERIOD LINQING WEN,RONALD
THE ASTROPHYSCAL JOURNAL, 999:L1-L4, 2000 January 1 c 2000. The American Astrological Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. X 1908+075: AN X-RAY BINARY WITH A 4.4 DAY PERIOD LINQING WEN,RONALD
The fundamental INTEGRAL contributions to advance the millisecond X-ray pulsars research field
 The fundamental INTEGRAL contributions to advance the millisecond X-ray pulsars research field M A U R I Z I O F A L A N G A Collaborators: L. Kuipers, W. Hermsen, J. Poutanen, A. Goldwurm, L. Stella June
The fundamental INTEGRAL contributions to advance the millisecond X-ray pulsars research field M A U R I Z I O F A L A N G A Collaborators: L. Kuipers, W. Hermsen, J. Poutanen, A. Goldwurm, L. Stella June
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Dec 2003
 Electromagnetic Signals from Planetary Collisions Bing Zhang and Steinn Sigurdsson arxiv:astro-ph/0312439 v1 17 Dec 2003 Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, Penn State University, University Park,
Electromagnetic Signals from Planetary Collisions Bing Zhang and Steinn Sigurdsson arxiv:astro-ph/0312439 v1 17 Dec 2003 Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, Penn State University, University Park,
A confirmed stellar-mass ULX with recurrent X-ray occultations from its precessing disk
 A confirmed stellar-mass ULX with recurrent X-ray occultations from its precessing disk C. Motch, R. Soria and M. Pakull Thanks to F. Grisé and J. Greiner P13 in NGC 7793 : a key ULX D = 3.7 Mpc In Sculptor
A confirmed stellar-mass ULX with recurrent X-ray occultations from its precessing disk C. Motch, R. Soria and M. Pakull Thanks to F. Grisé and J. Greiner P13 in NGC 7793 : a key ULX D = 3.7 Mpc In Sculptor
Simulations Applied to the Bright SHARC XCLF: Results and Implications
 The Evolution of Galaxies on Cosmological Timescales ASP Conference Series, Vol. 3 10 8, 1999 J. E. Beckman, and T. J. Mahoney, eds. Simulations Applied to the Bright SHARC XCLF: Results and Implications
The Evolution of Galaxies on Cosmological Timescales ASP Conference Series, Vol. 3 10 8, 1999 J. E. Beckman, and T. J. Mahoney, eds. Simulations Applied to the Bright SHARC XCLF: Results and Implications
A Hard Tail in the Broad Band Spectrum of the Dipper XB
 A Hard Tail in the Broad Band Spectrum of the Dipper XB 1254 690 R. Iaria 1,T.DiSalvo 1, L. Burderi 2,N.R.Robba 1 ABSTRACT We report on the results of spectral analysis of the dipping source XB 1254 690
A Hard Tail in the Broad Band Spectrum of the Dipper XB 1254 690 R. Iaria 1,T.DiSalvo 1, L. Burderi 2,N.R.Robba 1 ABSTRACT We report on the results of spectral analysis of the dipping source XB 1254 690
Orbital evolution and apsidal motion studies: Transient sources. 3.1 Introduction
 53 CHAPTER 3. Orbital evolution and apsidal motion studies: Transient sources 3.1 Introduction In the previous chapter we described our study of persistent X-ray binary pulsars and their orbital evolution.
53 CHAPTER 3. Orbital evolution and apsidal motion studies: Transient sources 3.1 Introduction In the previous chapter we described our study of persistent X-ray binary pulsars and their orbital evolution.
Supernova Remnants and GLAST
 SLAC-PUB-14797 Supernova Remnants and GLAST Patrick Slane Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Abstract. It has long been speculated that supernova remnants represent a major source of cosmic rays
SLAC-PUB-14797 Supernova Remnants and GLAST Patrick Slane Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Abstract. It has long been speculated that supernova remnants represent a major source of cosmic rays
