The Sun. Never look directly at the Sun, especially NOT through an unfiltered telescope!!
|
|
|
- Marybeth Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Sun Introduction We will meet in class for a brief discussion and review of background material. We will then go outside for approximately 1 hour of telescope observing. The telescopes will already be set up you will look a projection of the Sun onto paper, and you will observe the Sun with a solar filter and an H-alpha filter. Never look directly at the Sun, especially NOT through an unfiltered telescope!! Back in the lab, you will view movies of the Sun taken by the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) spacecraft. You will use them to estimate the rotation period of the Sun, and to find the velocity of matter leaving the Sun through a coronal mass ejection. Background Information To a casual Earthbound observer, the Sun looks very different from a star: it appears as a bright disk in the daytime sky, while the stars twinkle as pinpoints of light in the night sky. As stars go, however, the Sun is rather mediocre. It is classed as a yellow dwarf star, because because its visible radiation is most intense in the yellow-green portion of the spectrum. The Sun lies about 32,000 light years from the center of our galaxy and takes 225 million years to complete one orbit of the galactic center. In this lab, we will focus on the external features of the Sun that we can see from Earth and from space telescopes we have set up to observe the Sun. The internal properties of the Sun are inferred from the observations we make of the outer layers. The visible surface of the sun is the photosphere ( Features of the photosphere include limb darkening, sunspots, granules, and faculae ( If we could see sunspots in isolation, they would appear bright red. Compared to the bright surface around them, they appear as black spots. 1 of 12
2 1. Label examples of sunspot umbra and penumbra, faculae, and limb darkening in the following image, which is a visible-light image of the sun: Above the photosphere is the chromosphere ( where features like filaments and prominences can be seen ( 2. We can observe the chromosphere by using a Hydrogen-alpha filter, which blocks all wavelengths of light except for one particular wavelength of red light that is emitted by very hot hydrogen in the chromosphere. A sample Hydrogen-alpha image is shown below. Label examples of filaments, prominences, and plage. 2 of 12
3 3. Is the hydrogen-alpha wavelength of light present in a visible-light image of the sun? 4. Why wouldn t we be able to see the features of the chromosphere in a simple visible light image of the sun? Finally, the outer layer of the sun is the corona ( and has features like active regions ( and loops ( To see the corona, we can either look at x-ray images of the sun, since the corona emits strongly in x-rays, or we can block out the the face of the sun with a disk that obscures the image, so that the outer corona becomes visible. The disk is called an occulting disk and it creates an effect similar to a solar eclipse. Outdoor Observing of the Sun There will be three stations set up outside to view the sun. You will record the visible features of the sun in on the following pages. The three stations are: A. The Projection of the Sun B. Telescope with solar filter C. The H-alpha Image of the Sun You will need to bring: A ruler Your lab printout A writing utensil Never look directly at the Sun! Before you return to the lab, make sure you complete questions 1, 2, and 3 and 4 for the projection, question 10 and 11 for the filtered white light telescope, and questions 12 and 13 for the H-alpha image. 3 of 12
4 A. The Projection of the Sun The solar image can be projected onto a piece of paper using a simple lens system. Instead of focusing the Sun s light to a point (which can set the paper on fire), we use a combination of lenses and mirrors to create a magnified image and spread the light out over a larger area. 1. Measure the size of the projected image s diameter in cm with a ruler. Compare with other student measurements and include an estimate of the uncertainty in your measurement: 2. Measure the size of the largest sunspot in the projected image. Compare with other student measurements and include an estimate of the uncertainty in your measurement: 3. Carefully draw an image of the Sun in visible light. Including any features you see (sunspots, faculae, granulation, limb darkening). Date: Time: Scale of image: 4 of 12
5 4. Give a brief written description of the features in your drawing. 5. The diameter of the Sun is km. Divide the actual diameter of the Sun in km by your measurement of the diameter in the projected image. How many km are there in 1 cm of the projected image? 6. Calculate the diameter of the sunspot on the Sun in km. 7. Calculate the scale of the image you drew on the previous page. How many km are there in 1 cm of your drawing? Write the scale below your drawing. 8. The diameter of the Earth is 13,000 km. What size would the Earth be in your drawing? 9. How many Earths can you fit into the largest Sun spot? Draw an Earth into your picture for scale. 5 of 12
6 B. The visible light filter A strong filter is used to evenly dim the light coming from the sun before it enters the telescope. The filter appears to be a reflective film, since it blocks such a large fraction of light. The telescope then magnifies the solar image for viewing by eye. 10. Carefully draw an image of the Sun in visible light. Including any features you see (sunspots, faculae, granulation, limb darkening). Draw the sunspot groups including the umbra and penumbra (label the umbra, penumbra). Date: Time: 11. Give a brief written description of the features in your drawing: 6 of 12
7 C. The H-alpha filter A H-alpha (Hα) filter can also be used to block all wavelengths except nm. It lets through the light that is emitted by hot hydrogen gas in the chromosphere of the sun. 12. Sketch the filtered image of the Sun including any features you see (sunspots, filaments, prominences). You may be able to see the same sunspot groups as the projection, but they will be dimmer. Date: Time: Scale of image: Estimate the height of the prominences compared the Sun s diameter (a fraction of the Sun s diameter). Measure your drawing for an accurate estimate. 7 of 12
8 15. The diameter of the Sun is km. Calculate the scale of the image you drew above. How many km are there in 1 cm of your drawing? Write the scale below your drawing. 16. What is the estimated size of a prominence in km? 17. The diameter of the Earth is 13,000 km. How many Earths high is a prominence? 8 of 12
9 The changing Sun We will use movies made from multiple observations to see how the sun behaves over a longer period of time than our single observing period. Rotation of the sun The rotation period of an object is the time it takes to spin on its axis once. For example, the rotation period of the Earth is one (sidereal) day. In order to observe the rotation period of any rotating sphere, we can measure how many degrees of longitude a surface feature moves in a given time interval. We then solve for the period by taking the ratio of one full rotation (360 degrees) to the observed angular motion, and multiplying by the time interval. For example, if we observe that a given feature moves 30 degrees of longitude in 2 hours, then the rotation period P is: P = 2 hours 360 /30 = 24 hours. This method can be applied to the rotation of the Sun by observing active regions as they are carried across the disk by the Sun s rotation. Open the movie called MDI-Sunspot-Crossings-2001-large.mpg on the desktop and play the movie through a couple of times. The movie was made by combining images taken by the MDI camera. Notice at the top left there is a clock which shows the day and time each frame of the movie was taken. You should be able to see sunspots move across the Sun s photosphere. 1. The Sun s north pole, pointing towards Polaris, is towards the top of the movie image. Which way does the Sun rotate, as viewed from above its North pole? Clockwise Counterclockwise 2. We will now pick one sunspot near the Sun s equator and use it to measure the Sun s rotation period. Play the movie until you see a clearly identifiable sunspot near the equator of the Sun. 3. Pause the movie so that the sunspot is in the center of the Solar image (you may need to move the movie backwards and forwards to do this). Make a sketch of the Sun at this time in the chart on the following page. Label the sunspot that you have chosen. Make sure you label the date and time of your image. (1) 9 of 12
10 Date/time: Appearance of sunspots: 4. Press play and watch the sunspot move across the surface of the sun. Pause the movie at the point where the sunspot just disappears from view. What is the date and time when this happens? 5. How long (in days) did your sunspot take to move from the center of the Sun to just out of view? Include partial days (1 hour = 1/24 of a day). 6. How many degrees of longitude did the sunspot move through in this time? 7. Use equation (1) to compute the rotation period of the Sun (in days). 10 of 12
11 Coronal Mass Ejections A coronal mass ejection (CME) is an ejection of material from the solar corona, usually observed with a white-light coronagraph, such as SOHO s LASCO instrument. The ejected material is a plasma consisting primarily of electrons and protons (in addition to small quantities of heavier elements such as helium, oxygen, and iron). It is magnetized by the coronal magnetic field. When the ejection reaches the Earth as an ICME (Interplanetary CME), it can disrupt the Earth s magnetosphere. The resulting geomagnetic storm leads to particularly bright and widespread aurora (the Northern Lights, an emission spectrum from energized gas in the upper atmosphere). CME events, along with solar flares, can also disrupt radio transmissions, cause power outages (blackouts), and cause damage to satellites and electrical transmission lines. Open the movie called C2_triple_best.mov and watch it a couple of times. This movie is made from pictures of the Sun s corona taken by SOHO s LASCO Instrument. The C2 coronagraphs caught the action as three, separate coronal mass ejections (CMEs) blasted out in succession from the Sun (Dec. 12, 2010). These were each distinct and unconnected events. The first CME event (directly on the right) occurred when a magnetic filament erupted near the equator; the second one erupted near the Sun's north pole, and the last CME erupted on the far side of the Sun. 8. Notice the date and time display in the bottom left of the image. The white circle in the center of the image represents the size of the Sun. Using a ruler, measure the size of the white disk on your screen (in mm) and record your answer below. 9. The diameter of the Sun is km. Divide the actual diameter of the Sun in km by your measurement in mm to obtain the scale of the movie. How many km are there in 1 mm? 10. Pause the movie at 2010/12/12 04:00 and watch the next few frames of the movie. You can see a large coronal mass ejection consisting of the Sun s plasma eject from the right part of the Sun and move outward to the right. 11 of 12
12 Focus on the plasma in the middle of the loop. At what time does the loop mass of plasma becomes visible from behind the LASCO occulting disk? At what time does this plasma leave the region visible in the movie? visible: leaves: 11. How long (in seconds) did it take for the plasma to travel from the edge of the occulting disk to the edge of the image? 12. Measure the distance from the edge of the occulting disk where the plasma appeared to the edge of the image where it disappeared in mm and record your answer below. Then use your scale from Question 3 to convert this to km. 13. How fast did the plasma travel in km/s? Divide the distance it traveled in km by the time in took in seconds. 8. Using the formula below to convert this to miles per hour (mph): (Speed in km/s) (3600 s/hour) / (1.6 km/mile) = speed in mph. 9. How does this speed compare to a typical highway speed? 12 of 12
The Sun as Our Star. Properties of the Sun. Solar Composition. Last class we talked about how the Sun compares to other stars in the sky
 The Sun as Our Star Last class we talked about how the Sun compares to other stars in the sky Today's lecture will concentrate on the different layers of the Sun's interior and its atmosphere We will also
The Sun as Our Star Last class we talked about how the Sun compares to other stars in the sky Today's lecture will concentrate on the different layers of the Sun's interior and its atmosphere We will also
The Sun sends the Earth:
 The Sun sends the Earth: Solar Radiation - peak wavelength.visible light - Travels at the speed of light..takes 8 minutes to reach Earth Solar Wind, Solar flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections of Plasma (ionized
The Sun sends the Earth: Solar Radiation - peak wavelength.visible light - Travels at the speed of light..takes 8 minutes to reach Earth Solar Wind, Solar flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections of Plasma (ionized
HELIOSTAT III - THE SOLAR CHROMOSPHERE
 HELIOSTAT III - THE SOLAR CHROMOSPHERE SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will observe, identify, and sketch features that appear in the solar chromosphere. With luck, you may have the opportunity to watch a solar
HELIOSTAT III - THE SOLAR CHROMOSPHERE SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will observe, identify, and sketch features that appear in the solar chromosphere. With luck, you may have the opportunity to watch a solar
The Project. National Schools Observatory
 Sunspots The Project This project is devised to give students a good understanding of the structure and magnetic field of the Sun and how this effects solar activity. Students will work with sunspot data
Sunspots The Project This project is devised to give students a good understanding of the structure and magnetic field of the Sun and how this effects solar activity. Students will work with sunspot data
Outline. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Earth Sun comparison. Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned.
 Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned. Next homework due Oct 24 th. I will not be here on Wednesday, but Paul Ricker will present the lecture! My Tuesday
Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned. Next homework due Oct 24 th. I will not be here on Wednesday, but Paul Ricker will present the lecture! My Tuesday
1 A= one Angstrom = 1 10 cm
 Our Star : The Sun )Chapter 10) The sun is hot fireball of gas. We observe its outer surface called the photosphere: We determine the temperature of the photosphere by measuring its spectrum: The peak
Our Star : The Sun )Chapter 10) The sun is hot fireball of gas. We observe its outer surface called the photosphere: We determine the temperature of the photosphere by measuring its spectrum: The peak
Chapter 8 The Sun Our Star
 Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 8 The Sun
Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 8 The Sun
The Structure of the Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 How stars work In order to have a stable star, the energy it emits must be the same as it can produce. There must be an equilibrium. The main source of energy of a star it is nuclear fusion, especially
How stars work In order to have a stable star, the energy it emits must be the same as it can produce. There must be an equilibrium. The main source of energy of a star it is nuclear fusion, especially
Using This Flip Chart
 Using This Flip Chart Sunspots are the first indicators that a storm from the Sun is a possibility. However, not all sunspots cause problems for Earth. By following the steps in this flip chart you will
Using This Flip Chart Sunspots are the first indicators that a storm from the Sun is a possibility. However, not all sunspots cause problems for Earth. By following the steps in this flip chart you will
1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths
 1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths 1.3k demonstrate an understanding of the appearance of the Sun at different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including
1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths 1.3k demonstrate an understanding of the appearance of the Sun at different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 15 THE SUN: A GARDEN-VARIETY STAR PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 15 THE SUN: A GARDEN-VARIETY STAR PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 15.1 Our Star. The Sun our local star is quite average in many ways. However, that does not stop it from being a fascinating
ASTRONOMY Chapter 15 THE SUN: A GARDEN-VARIETY STAR PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 15.1 Our Star. The Sun our local star is quite average in many ways. However, that does not stop it from being a fascinating
The General Properties of the Sun
 Notes: The General Properties of the Sun The sun is an average star with average brightness. It only looks bright because it s so close. It contains 99% of the mass of the solar system. It is made of entirely
Notes: The General Properties of the Sun The sun is an average star with average brightness. It only looks bright because it s so close. It contains 99% of the mass of the solar system. It is made of entirely
The Sun Our Extraordinary Ordinary Star
 The Sun Our Extraordinary Ordinary Star 1 Guiding Questions 1. What is the source of the Sun s energy? 2. What is the internal structure of the Sun? 3. How can astronomers measure the properties of the
The Sun Our Extraordinary Ordinary Star 1 Guiding Questions 1. What is the source of the Sun s energy? 2. What is the internal structure of the Sun? 3. How can astronomers measure the properties of the
An Overview of the Details
 The Sun Our Extraordinary Ordinary Star 1 Guiding Questions 1. What is the source of the Sun s energy? 2. What is the internal structure of the Sun? 3. How can astronomers measure the properties of the
The Sun Our Extraordinary Ordinary Star 1 Guiding Questions 1. What is the source of the Sun s energy? 2. What is the internal structure of the Sun? 3. How can astronomers measure the properties of the
An Overview of the Details
 Guiding Questions The Sun Our Extraordinary Ordinary Star 1. What is the source of the Sun s energy? 2. What is the internal structure of the Sun? 3. How can astronomers measure the properties of the Sun
Guiding Questions The Sun Our Extraordinary Ordinary Star 1. What is the source of the Sun s energy? 2. What is the internal structure of the Sun? 3. How can astronomers measure the properties of the Sun
Helios in Greek and Sol in Roman
 Helios in Greek and Sol in Roman Drove his chariot across the sky to provide daylight Returned each night in a huge golden cup on the river Oceanus His son Phaeton drove the chariot one day but lost control
Helios in Greek and Sol in Roman Drove his chariot across the sky to provide daylight Returned each night in a huge golden cup on the river Oceanus His son Phaeton drove the chariot one day but lost control
Guidepost. Chapter 08 The Sun 10/12/2015. General Properties. The Photosphere. Granulation. Energy Transport in the Photosphere.
 Guidepost The Sun is the source of light an warmth in our solar system, so it is a natural object to human curiosity. It is also the star most easily visible from Earth, and therefore the most studied.
Guidepost The Sun is the source of light an warmth in our solar system, so it is a natural object to human curiosity. It is also the star most easily visible from Earth, and therefore the most studied.
The Sun. 1a. The Photosphere. A. The Solar Atmosphere. 1b. Limb Darkening. A. Solar Atmosphere. B. Phenomena (Sunspots) C.
 The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2006Sep18 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind 3 1a. The
The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2006Sep18 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind 3 1a. The
Chapter 9 The Sun. Nuclear fusion: Combining of light nuclei into heavier ones Example: In the Sun is conversion of H into He
 Our sole source of light and heat in the solar system A common star: a glowing ball of plasma held together by its own gravity and powered by nuclear fusion at its center. Nuclear fusion: Combining of
Our sole source of light and heat in the solar system A common star: a glowing ball of plasma held together by its own gravity and powered by nuclear fusion at its center. Nuclear fusion: Combining of
Chapter 23. Light, Astronomical Observations, and the Sun
 Chapter 23 Light, Astronomical Observations, and the Sun The study of light Electromagnetic radiation Visible light is only one small part of an array of energy Electromagnetic radiation includes Gamma
Chapter 23 Light, Astronomical Observations, and the Sun The study of light Electromagnetic radiation Visible light is only one small part of an array of energy Electromagnetic radiation includes Gamma
Astronomy 154 Lab 4: The Sun. NASA Image comparing the Earth with the Sun. Image from:
 Astronomy 154 Lab 3: The Sun NASA Image comparing the Earth with the Sun. Image from: http://www.universetoday.com/16338/the-sun/ The Sun at the center of our Solar System is a massive ball of Hydrogen,
Astronomy 154 Lab 3: The Sun NASA Image comparing the Earth with the Sun. Image from: http://www.universetoday.com/16338/the-sun/ The Sun at the center of our Solar System is a massive ball of Hydrogen,
The Sun s Dynamic Atmosphere
 Lecture 16 The Sun s Dynamic Atmosphere Jiong Qiu, MSU Physics Department Guiding Questions 1. What is the temperature and density structure of the Sun s atmosphere? Does the atmosphere cool off farther
Lecture 16 The Sun s Dynamic Atmosphere Jiong Qiu, MSU Physics Department Guiding Questions 1. What is the temperature and density structure of the Sun s atmosphere? Does the atmosphere cool off farther
Lecture 17 The Sun October 31, 2018
 Lecture 17 The Sun October 31, 2018 1 2 Exam 2 Information Bring a #2 pencil! Bring a calculator. No cell phones or tablets allowed! Contents: Free response problems (2 questions, 10 points) True/False
Lecture 17 The Sun October 31, 2018 1 2 Exam 2 Information Bring a #2 pencil! Bring a calculator. No cell phones or tablets allowed! Contents: Free response problems (2 questions, 10 points) True/False
Spring 2001: The Sun. Equipment:! This write-up, calculator, lab notebook! Data you downloaded from the SOHO website
 Our Sun is a middle-aged, medium sized star, big enough to hold a million Earths. The ancient Greeks thought that the Sun was a perfect sphere of fire. Today we know that the Sun is a variable star that
Our Sun is a middle-aged, medium sized star, big enough to hold a million Earths. The ancient Greeks thought that the Sun was a perfect sphere of fire. Today we know that the Sun is a variable star that
Learning Objectives. wavelengths of light do we use to see each of them? mass ejections? Which are the most violent?
 Our Beacon: The Sun Learning Objectives! What are the outer layers of the Sun, in order? What wavelengths of light do we use to see each of them?! Why does limb darkening tell us the inner Sun is hotter?!
Our Beacon: The Sun Learning Objectives! What are the outer layers of the Sun, in order? What wavelengths of light do we use to see each of them?! Why does limb darkening tell us the inner Sun is hotter?!
Astronomy 101 Lab: Solar Observing
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Solar Observing Pre-Lab Assignment: In this lab, you will determine the rotation rate of the Sun, determine the speed of material ejected from the Sun in a coronal mass ejection,
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Solar Observing Pre-Lab Assignment: In this lab, you will determine the rotation rate of the Sun, determine the speed of material ejected from the Sun in a coronal mass ejection,
19 The Sun Introduction. Name: Date:
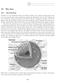 Name: Date: 19 The Sun 19.1 Introduction The Sun is a very important object for all life on Earth. The nuclear reactions that occur in its core produce the energy required by plants and animals for survival.
Name: Date: 19 The Sun 19.1 Introduction The Sun is a very important object for all life on Earth. The nuclear reactions that occur in its core produce the energy required by plants and animals for survival.
Our Star: The Sun. Layers that make up the Sun. Understand the Solar cycle. Understand the process by which energy is generated by the Sun.
 Goals: Our Star: The Sun Layers that make up the Sun. Understand the Solar cycle. Understand the process by which energy is generated by the Sun. Components of the Sun Solar Interior: Core: where energy
Goals: Our Star: The Sun Layers that make up the Sun. Understand the Solar cycle. Understand the process by which energy is generated by the Sun. Components of the Sun Solar Interior: Core: where energy
Astronomy 150: Killer Skies. Lecture 18, March 1
 Assignments: Astronomy 150: Killer Skies HW6 due next Friday at start of class HW5 and Computer Lab 1 due Night Observing continues next week Lecture 18, March 1 Computer Lab 1 due next Friday Guest Lecturer:
Assignments: Astronomy 150: Killer Skies HW6 due next Friday at start of class HW5 and Computer Lab 1 due Night Observing continues next week Lecture 18, March 1 Computer Lab 1 due next Friday Guest Lecturer:
The Sun. 1a. The Photosphere. A. The Solar Atmosphere. 1b. Limb Darkening. A. Solar Atmosphere. B. Phenomena (Sunspots) C.
 The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2014Feb08 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind & earthly
The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2014Feb08 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind & earthly
The information you need will be on the internet. Please label your data with the link you used, in case we need to look at the data again.
 Solar Activity in Many Wavelengths In this lab you will be finding the sidereal rotation period of the Sun from observations of sunspots, you will compare the lifetimes of larger and smaller sunspots,
Solar Activity in Many Wavelengths In this lab you will be finding the sidereal rotation period of the Sun from observations of sunspots, you will compare the lifetimes of larger and smaller sunspots,
The Magnetic Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3. Sun
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 1.25 Hours What s important in this lesson: Sun demonstrate an understanding of the structure, and nature of our solar system investigate the
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 1.25 Hours What s important in this lesson: Sun demonstrate an understanding of the structure, and nature of our solar system investigate the
Observings of The Sun
 29:50 Astronomy Lab #9 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Name Partner(s) Date Grade Category Max Points Points Received On Time 5 Printed Copy 5 Lab Work 90 Total 100 Observings of The Sun 1. Introduction
29:50 Astronomy Lab #9 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Name Partner(s) Date Grade Category Max Points Points Received On Time 5 Printed Copy 5 Lab Work 90 Total 100 Observings of The Sun 1. Introduction
Radiation Zone. AST 100 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. 5. What s inside the Sun? From the Center Outwards. Meanderings of outbound photons
 AST 100 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies 5. What s inside the Sun? From the Center Outwards Core: Hydrogen ANNOUNCEMENTS Midterm I on Tue, Sept. 29 it will cover class material up to today (included)
AST 100 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies 5. What s inside the Sun? From the Center Outwards Core: Hydrogen ANNOUNCEMENTS Midterm I on Tue, Sept. 29 it will cover class material up to today (included)
The Sun ASTR /17/2014
 The Sun ASTR 101 11/17/2014 1 Radius: 700,000 km (110 R ) Mass: 2.0 10 30 kg (330,000 M ) Density: 1400 kg/m 3 Rotation: Differential, about 25 days at equator, 30 days at poles. Surface temperature: 5800
The Sun ASTR 101 11/17/2014 1 Radius: 700,000 km (110 R ) Mass: 2.0 10 30 kg (330,000 M ) Density: 1400 kg/m 3 Rotation: Differential, about 25 days at equator, 30 days at poles. Surface temperature: 5800
1-4-1A. Sun Structure
 Sun Structure A cross section of the Sun reveals its various layers. The Core is the hottest part of the internal sun and is the location of nuclear fusion. The heat and energy produced in the core is
Sun Structure A cross section of the Sun reveals its various layers. The Core is the hottest part of the internal sun and is the location of nuclear fusion. The heat and energy produced in the core is
The Interior Structure of the Sun
 The Interior Structure of the Sun Data for one of many model calculations of the Sun center Temperature 1.57 10 7 K Pressure 2.34 10 16 N m -2 Density 1.53 10 5 kg m -3 Hydrogen 0.3397 Helium 0.6405 The
The Interior Structure of the Sun Data for one of many model calculations of the Sun center Temperature 1.57 10 7 K Pressure 2.34 10 16 N m -2 Density 1.53 10 5 kg m -3 Hydrogen 0.3397 Helium 0.6405 The
Astronomy 210. Outline. Nuclear Reactions in the Sun. Neutrinos. Solar Observing due April 15 th HW 8 due on Friday.
 Astronomy 210 Outline This Class (Lecture 30): Solar Neutrinos Next Class: Stars: Physical Properties Solar Observing due April 15 th HW 8 due on Friday. The Sun Our closest star The Outer Layers of the
Astronomy 210 Outline This Class (Lecture 30): Solar Neutrinos Next Class: Stars: Physical Properties Solar Observing due April 15 th HW 8 due on Friday. The Sun Our closest star The Outer Layers of the
The point in an orbit around the Sun at which an object is at its greatest distance from the Sun (Opposite of perihelion).
 ASTRONOMY TERMS Albedo Aphelion Apogee A measure of the reflectivity of an object and is expressed as the ratio of the amount of light reflected by an object to that of the amount of light incident upon
ASTRONOMY TERMS Albedo Aphelion Apogee A measure of the reflectivity of an object and is expressed as the ratio of the amount of light reflected by an object to that of the amount of light incident upon
Explain how the sun converts matter into energy in its core. Describe the three layers of the sun s atmosphere.
 Chapter 29 and 30 Explain how the sun converts matter into energy in its core. Describe the three layers of the sun s atmosphere. Explain how sunspots are related to powerful magnetic fields on the sun.
Chapter 29 and 30 Explain how the sun converts matter into energy in its core. Describe the three layers of the sun s atmosphere. Explain how sunspots are related to powerful magnetic fields on the sun.
1. Solar Atmosphere Surface Features and Magnetic Fields
 1. Solar Atmosphere Surface Features and Magnetic Fields Sunspots, Granulation, Filaments and Prominences, Coronal Loops 2. Solar Cycle: Observations The Sun: applying black-body radiation laws Radius
1. Solar Atmosphere Surface Features and Magnetic Fields Sunspots, Granulation, Filaments and Prominences, Coronal Loops 2. Solar Cycle: Observations The Sun: applying black-body radiation laws Radius
8.2 The Sun pg Stars emit electromagnetic radiation, which travels at the speed of light.
 8.2 The Sun pg. 309 Key Concepts: 1. Careful observation of the night sky can offer clues about the motion of celestial objects. 2. Celestial objects in the Solar System have unique properties. 3. Some
8.2 The Sun pg. 309 Key Concepts: 1. Careful observation of the night sky can offer clues about the motion of celestial objects. 2. Celestial objects in the Solar System have unique properties. 3. Some
Summer School Lab Activities
 Summer School Lab Activities Lab #5: Predicting and Modeling the Arrival of the May 12 th 1997 CME In this lab we will use remote observations of the May 12, 1997 solar flare and halo CME made at and near
Summer School Lab Activities Lab #5: Predicting and Modeling the Arrival of the May 12 th 1997 CME In this lab we will use remote observations of the May 12, 1997 solar flare and halo CME made at and near
Sun s Properties. Overview: The Sun. Composition of the Sun. Sun s Properties. The outer layers. Photosphere: Surface. Nearest.
 Overview: The Sun Properties of the Sun Sun s outer layers Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Solar Activity Sunspots & the sunspot cycle Flares, prominences, CMEs, aurora Sun s Interior The Sun as an energy
Overview: The Sun Properties of the Sun Sun s outer layers Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Solar Activity Sunspots & the sunspot cycle Flares, prominences, CMEs, aurora Sun s Interior The Sun as an energy
Our sun is the star in our solar system, which lies within a galaxy (Milky Way) within the universe. A star is a large glowing ball of gas that
 Our sun is the star in our solar system, which lies within a galaxy (Milky Way) within the universe. A star is a large glowing ball of gas that generates energy through nuclear fusion in its core. The
Our sun is the star in our solar system, which lies within a galaxy (Milky Way) within the universe. A star is a large glowing ball of gas that generates energy through nuclear fusion in its core. The
Killer Skies. Homework 5 due Monday Night Observing continuing Last time: White Dwarf Today: Active Sun. Music: Invisible Sun Police
 Killer Skies Homework 5 due Monday Night Observing continuing Last time: White Dwarf Today: Active Sun Music: Invisible Sun Police 1 Night Observing Night Observing probably last week if you do it, need
Killer Skies Homework 5 due Monday Night Observing continuing Last time: White Dwarf Today: Active Sun Music: Invisible Sun Police 1 Night Observing Night Observing probably last week if you do it, need
Correction to Homework
 Today: Chapter 10 Reading Next Week: Homework Due March 12 Midterm Exam: March 19 Correction to Homework #1: Diameter of eye: 2.5 cm #10: See Ch. 11 Office Hours Monday. 11AM -2 PM Help Sessions Available:
Today: Chapter 10 Reading Next Week: Homework Due March 12 Midterm Exam: March 19 Correction to Homework #1: Diameter of eye: 2.5 cm #10: See Ch. 11 Office Hours Monday. 11AM -2 PM Help Sessions Available:
9-1 The Sun s energy is generated by thermonuclear reactions in its core The Sun s luminosity is the amount of energy emitted each second and is
 1 9-1 The Sun s energy is generated by thermonuclear reactions in its core The Sun s luminosity is the amount of energy emitted each second and is produced by the proton-proton chain in which four hydrogen
1 9-1 The Sun s energy is generated by thermonuclear reactions in its core The Sun s luminosity is the amount of energy emitted each second and is produced by the proton-proton chain in which four hydrogen
Stars and Galaxies. The Sun and Other Stars
 CHAPTER 22 Stars and Galaxies LESSON 2 The Sun and Other Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
CHAPTER 22 Stars and Galaxies LESSON 2 The Sun and Other Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
Solar Observation Class Project
 Name: School: Grade or Level: Lesson Plan #: Date: Object Solar Observation Class Project The object of this classroom exercise to involve as individuals or as teams, students in the actual astronomical
Name: School: Grade or Level: Lesson Plan #: Date: Object Solar Observation Class Project The object of this classroom exercise to involve as individuals or as teams, students in the actual astronomical
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline. Exterior Layers of the Sun: HW#5 due Friday by 5 pm!
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements HW#5 due Friday by 5 pm! Lab Observing Trip Thursday planning to go Meet outside VAN East end (Linn/Jefferson) Wear warm clothes! 1 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements HW#5 due Friday by 5 pm! Lab Observing Trip Thursday planning to go Meet outside VAN East end (Linn/Jefferson) Wear warm clothes! 1 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe
Solar Activity The Solar Wind
 Solar Activity The Solar Wind The solar wind is a flow of particles away from the Sun. They pass Earth at speeds from 400 to 500 km/s. This wind sometimes gusts up to 1000 km/s. Leaves Sun at highest speeds
Solar Activity The Solar Wind The solar wind is a flow of particles away from the Sun. They pass Earth at speeds from 400 to 500 km/s. This wind sometimes gusts up to 1000 km/s. Leaves Sun at highest speeds
THE SOLAR WIND & SOLAR VARIABILITY
 The Sun-Earth System: CONTENTS AN OVERVIEW The Stars Around Us 1 Our Dependence on the Sun 3 The Sun s Inconstancy 3 Intruders from Afar 5 What Gets By 5 Voyages of Discovery in an Age of Exploration 6
The Sun-Earth System: CONTENTS AN OVERVIEW The Stars Around Us 1 Our Dependence on the Sun 3 The Sun s Inconstancy 3 Intruders from Afar 5 What Gets By 5 Voyages of Discovery in an Age of Exploration 6
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 24 Studying the Sun 24.1 The Study of Light Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 24 Studying the Sun 24.1 The Study of Light Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible
PTYS/ASTR 206. The Sun 3/1/07
 The Announcements Reading Assignment Review and finish reading Chapter 18 Optional reading March 2006 Scientific American: article by Gene Parker titled Shielding Space Travelers http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/solar_variability
The Announcements Reading Assignment Review and finish reading Chapter 18 Optional reading March 2006 Scientific American: article by Gene Parker titled Shielding Space Travelers http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/solar_variability
The Sun Our Star. Properties Interior Atmosphere Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Magnetism Sunspots Solar Cycles Active Sun
 The Sun Our Star Properties Interior Atmosphere Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Magnetism Sunspots Solar Cycles Active Sun General Properties Not a large star, but larger than most Spectral type G2 It
The Sun Our Star Properties Interior Atmosphere Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Magnetism Sunspots Solar Cycles Active Sun General Properties Not a large star, but larger than most Spectral type G2 It
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Observing Highlights. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Lab Observing Trip Next week: Tues (9/28) & Thurs (9/30) let me know ASAP if you have an official conflict (class, work) - website: http://astro.physics.uiowa.edu/~clang/sgu_fall10/observing_trip.html
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Lab Observing Trip Next week: Tues (9/28) & Thurs (9/30) let me know ASAP if you have an official conflict (class, work) - website: http://astro.physics.uiowa.edu/~clang/sgu_fall10/observing_trip.html
What do we see on the face of the Sun? Lecture 3: The solar atmosphere
 What do we see on the face of the Sun? Lecture 3: The solar atmosphere The Sun s atmosphere Solar atmosphere is generally subdivided into multiple layers. From bottom to top: photosphere, chromosphere,
What do we see on the face of the Sun? Lecture 3: The solar atmosphere The Sun s atmosphere Solar atmosphere is generally subdivided into multiple layers. From bottom to top: photosphere, chromosphere,
Chapter 23. Our Solar System
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
CESAR BOOKLET General Understanding of the Sun: Magnetic field, Structure and Sunspot cycle
 CESAR BOOKLET General Understanding of the Sun: Magnetic field, Structure and Sunspot cycle 1 Table of contents Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium... 3 A short introduction
CESAR BOOKLET General Understanding of the Sun: Magnetic field, Structure and Sunspot cycle 1 Table of contents Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium... 3 A short introduction
Stars and Galaxies. Content Outline for Teaching
 Section 1 Stars A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are
Section 1 Stars A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are
The Sun. Basic Properties. Radius: Mass: Luminosity: Effective Temperature:
 The Sun Basic Properties Radius: Mass: 5 R Sun = 6.96 km 9 R M Sun 5 30 = 1.99 kg 3.33 M ρ Sun = 1.41g cm 3 Luminosity: L Sun = 3.86 26 W Effective Temperature: L Sun 2 4 = 4πRSunσTe Te 5770 K The Sun
The Sun Basic Properties Radius: Mass: 5 R Sun = 6.96 km 9 R M Sun 5 30 = 1.99 kg 3.33 M ρ Sun = 1.41g cm 3 Luminosity: L Sun = 3.86 26 W Effective Temperature: L Sun 2 4 = 4πRSunσTe Te 5770 K The Sun
Next quiz: Monday, October 24 Chp. 6 (nothing on telescopes) Chp. 7 a few problems from previous material cough, cough, gravity, cough, cough...
 Next quiz: Monday, October 24 Chp. 6 (nothing on telescopes) Chp. 7 a few problems from previous material cough, cough, gravity, cough, cough... 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Kirchhoff s Laws of Radiation
Next quiz: Monday, October 24 Chp. 6 (nothing on telescopes) Chp. 7 a few problems from previous material cough, cough, gravity, cough, cough... 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Kirchhoff s Laws of Radiation
Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus
 Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus In June 2015, the Sun emitted several M-Class flares over a 2-day period. These flares were concurrent with
Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus In June 2015, the Sun emitted several M-Class flares over a 2-day period. These flares were concurrent with
Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars.
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
The Sun. the main show in the solar system. 99.8% of the mass % of the energy. Homework due next time - will count best 5 of 6
 The Sun the main show in the solar system 99.8% of the mass 99.9999...% of the energy 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Homework due next time - will count best 5 of 6 The
The Sun the main show in the solar system 99.8% of the mass 99.9999...% of the energy 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Homework due next time - will count best 5 of 6 The
The Sun. The Sun Is Just a Normal Star 11/5/2018. Phys1411 Introductory Astronomy. Topics. Star Party
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Phys1411 Introductory Astronomy Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 8 The Sun Star Party This Friday November 9 weather permitting. See the flyer for updates in case of cancellations
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Phys1411 Introductory Astronomy Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 8 The Sun Star Party This Friday November 9 weather permitting. See the flyer for updates in case of cancellations
The Sun. How are these quantities measured? Properties of the Sun. Chapter 14
 The Sun Chapter 14 The Role of the Sun in the Solar System > 99.9% of the mass Its mass is responsible for the orderly orbits of the planets Its heat is responsible for warming the planets It is the source
The Sun Chapter 14 The Role of the Sun in the Solar System > 99.9% of the mass Its mass is responsible for the orderly orbits of the planets Its heat is responsible for warming the planets It is the source
Student s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere
 Student s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere Name Date Introduction The Sun as you may already know, is not a solid body. It is a massive body of gas constantly
Student s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere Name Date Introduction The Sun as you may already know, is not a solid body. It is a massive body of gas constantly
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Lecture 6: Our star, the Sun
 Lecture 6: Our star, the Sun 1 Age = 4.6 x 10 9 years Mean Radius = 7.0x10 5 km = 1.1x10 2 R = 1R Volume = 1.4x10 18 km 3 = 1.3x10 6 R = 1V Mass = 2x10 30 kg = 3.3x10 5 M = 1M Surface Temperature = 5,778K
Lecture 6: Our star, the Sun 1 Age = 4.6 x 10 9 years Mean Radius = 7.0x10 5 km = 1.1x10 2 R = 1R Volume = 1.4x10 18 km 3 = 1.3x10 6 R = 1V Mass = 2x10 30 kg = 3.3x10 5 M = 1M Surface Temperature = 5,778K
A Closer Look at the Sun
 Our Star A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery? Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun s structure? Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery?
Our Star A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery? Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun s structure? Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery?
Next quiz: Monday, October 24
 No homework for Wednesday Read Chapter 8! Next quiz: Monday, October 24 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Types of Spectra: Pictorial Some light sources are comprised of all colors (white light). Other light
No homework for Wednesday Read Chapter 8! Next quiz: Monday, October 24 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Types of Spectra: Pictorial Some light sources are comprised of all colors (white light). Other light
Term Project PHYS Solar Rotation
 Term Project PHYS 1070.03 Solar Rotation Due Date: May 19 th, 2009 (11:30am, in class) Introduction: The objective of this term project is to determine the solar rotation period by using photos of the
Term Project PHYS 1070.03 Solar Rotation Due Date: May 19 th, 2009 (11:30am, in class) Introduction: The objective of this term project is to determine the solar rotation period by using photos of the
Earth Space Systems. Semester 1 Exam. Astronomy Vocabulary
 Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Solar Magnetic Fields Jun 07 UA/NSO Summer School 1
 Solar Magnetic Fields 1 11 Jun 07 UA/NSO Summer School 1 If the sun didn't have a magnetic field, then it would be as boring a star as most astronomers think it is. -- Robert Leighton 11 Jun 07 UA/NSO
Solar Magnetic Fields 1 11 Jun 07 UA/NSO Summer School 1 If the sun didn't have a magnetic field, then it would be as boring a star as most astronomers think it is. -- Robert Leighton 11 Jun 07 UA/NSO
How the Sun Works. Presented by the
 How the Sun Works Presented by the The Sun warms our planet every day, provides the light by which we see and is absolutely necessary for life on Earth. In this presentation, we will examine the fascinating
How the Sun Works Presented by the The Sun warms our planet every day, provides the light by which we see and is absolutely necessary for life on Earth. In this presentation, we will examine the fascinating
B B E D B E D A C A D D C
 B B A C E E E E C E D E B B A D B E E A E E B C C A B B E D B E D A C A D D C E D Assigned Reading Read Chapters 8.1 and 8.2 Colonel Cady Coleman, Astronaut: Lessons from Space Lead Straight Back to Earth,
B B A C E E E E C E D E B B A D B E E A E E B C C A B B E D B E D A C A D D C E D Assigned Reading Read Chapters 8.1 and 8.2 Colonel Cady Coleman, Astronaut: Lessons from Space Lead Straight Back to Earth,
The Dancing Lights Program
 The Sun Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program Margaux Krahe Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun is not actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun
The Sun Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program Margaux Krahe Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun is not actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun
Potter Name: Date: Hour: Earth Science Unit 2: Astronomy
 Unit 2: Astronomy #1 LT 2.1 Galaxy Formation: I am able to describe the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy and our solar system and model earth s position in each. Yes I can 1. Can you roughly explain how
Unit 2: Astronomy #1 LT 2.1 Galaxy Formation: I am able to describe the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy and our solar system and model earth s position in each. Yes I can 1. Can you roughly explain how
Convection causes granules. Photosphere isn t actually smooth! Granules Up-Close: like boiling water. Corona or of the Sun. Chromosphere: sphere of
 Overview Properties of the Sun Sun s outer layers Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Solar Activity Sunspots & the sunspot cycle Flares, prominences, CMEs, aurora Sun s Interior The Sun as an energy source
Overview Properties of the Sun Sun s outer layers Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Solar Activity Sunspots & the sunspot cycle Flares, prominences, CMEs, aurora Sun s Interior The Sun as an energy source
CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES
 CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES Characteristics of the Sun 1. The Sun is located about 150 million kilometres from the Earth. 2. The Sun is made up of hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. 3. The size of
CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES Characteristics of the Sun 1. The Sun is located about 150 million kilometres from the Earth. 2. The Sun is made up of hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. 3. The size of
The Sun: Our Star. A glowing ball of gas held together by its own gravity and powered by nuclear fusion
 Our Star, the Sun The Sun: Our Star A glowing ball of gas held together by its own gravity and powered by nuclear fusion Radius: 700,000 km (435,000 miles) Diameter: 1.392 million km (865,000 miles) Circumference:
Our Star, the Sun The Sun: Our Star A glowing ball of gas held together by its own gravity and powered by nuclear fusion Radius: 700,000 km (435,000 miles) Diameter: 1.392 million km (865,000 miles) Circumference:
The Quiet Sun The sun is currently being studied by several spacecraft Ulysses, SOHO, STEREO, and ACE.
 The Quiet Sun The sun is currently being studied by several spacecraft Ulysses, SOHO, STEREO, and ACE. Messenger also contains instruments that can do some solar studies. http://www.stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov
The Quiet Sun The sun is currently being studied by several spacecraft Ulysses, SOHO, STEREO, and ACE. Messenger also contains instruments that can do some solar studies. http://www.stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov
Exploring the Solar Wind with Ultraviolet Light
 Timbuktu Academy Seminar, Southern University and A&M College, November 19, 2003 Exploring the Solar Wind with Ultraviolet Light Steven R. Cranmer Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge,
Timbuktu Academy Seminar, Southern University and A&M College, November 19, 2003 Exploring the Solar Wind with Ultraviolet Light Steven R. Cranmer Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge,
On 1 September 1859, a small white light flare erupted on the Solar surface
 The Sun Our Star On 1 September 1859, a small white light flare erupted on the Solar surface 17 hours later Magnetometers recorded a large disturbance Aurorae were seen in the Carribean, Telegraphs went
The Sun Our Star On 1 September 1859, a small white light flare erupted on the Solar surface 17 hours later Magnetometers recorded a large disturbance Aurorae were seen in the Carribean, Telegraphs went
The Sun. The Sun is a star: a shining ball of gas powered by nuclear fusion. Mass of Sun = 2 x g = 330,000 M Earth = 1 M Sun
 The Sun The Sun is a star: a shining ball of gas powered by nuclear fusion. Mass of Sun = 2 x 10 33 g = 330,000 M Earth = 1 M Sun Radius of Sun = 7 x 10 5 km = 109 R Earth = 1 R Sun Luminosity of Sun =
The Sun The Sun is a star: a shining ball of gas powered by nuclear fusion. Mass of Sun = 2 x 10 33 g = 330,000 M Earth = 1 M Sun Radius of Sun = 7 x 10 5 km = 109 R Earth = 1 R Sun Luminosity of Sun =
Chapter 24: Studying the Sun. 24.3: The Sun Textbook pages
 Chapter 24: Studying the Sun 24.3: The Sun Textbook pages 684-690 The sun is one of the 100 billion stars of the Milky Way galaxy. The sun has no characteristics to make it unique to the universe. It is
Chapter 24: Studying the Sun 24.3: The Sun Textbook pages 684-690 The sun is one of the 100 billion stars of the Milky Way galaxy. The sun has no characteristics to make it unique to the universe. It is
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Hydrogen Lines. What can we learn from light? Spectral Classification. Visible Hydrogen Spectrum Lines: Series. Actual Spectrum from SDSS
 What can we learn from light? Hydrogen Lines Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the! Lower E, Lower f, λ Visible! Higher E, Higher f, λ Visible Hydrogen Spectrum
What can we learn from light? Hydrogen Lines Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the! Lower E, Lower f, λ Visible! Higher E, Higher f, λ Visible Hydrogen Spectrum
An Introduction to Space Weather. J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR
 An Introduction to Space Weather J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR What is Space Weather? Space Weather refers to conditions in interplanetary space, produced by the Sun, that can disrupt
An Introduction to Space Weather J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR What is Space Weather? Space Weather refers to conditions in interplanetary space, produced by the Sun, that can disrupt
Solar Observing at SBO
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 43 Solar Observing at SBO Solar Observing at SBO WARNING: The intense solar light from the heliostat can cause instant eye damage! NOT look back up the beam of sunlight! Do The
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 43 Solar Observing at SBO Solar Observing at SBO WARNING: The intense solar light from the heliostat can cause instant eye damage! NOT look back up the beam of sunlight! Do The
Sunspots and Solar Spectrum
 Sunspots and Solar Spectrum Alexandre Costa, Beatriz García, Ricardo Moreno International Astronomical Union Comm 46, Escola Secundária de Loulé, Portugal Universida Tecnológica Nacional, Argentina Colegio
Sunspots and Solar Spectrum Alexandre Costa, Beatriz García, Ricardo Moreno International Astronomical Union Comm 46, Escola Secundária de Loulé, Portugal Universida Tecnológica Nacional, Argentina Colegio
Chapter 14 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Star Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is
Chapter 14 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is
Sunspots and Solar Spectrum
 Sunspots and Solar Spectrum Alexandre Costa, Beatriz García, Ricardo Moreno International Astronomical Union Comm 46, Escola Secundária de Loulé, Portugal Universida Tecnológica Nacional, Argentina Colegio
Sunspots and Solar Spectrum Alexandre Costa, Beatriz García, Ricardo Moreno International Astronomical Union Comm 46, Escola Secundária de Loulé, Portugal Universida Tecnológica Nacional, Argentina Colegio
The sun, yellow dwarf star at the heart of the solar system NASA.gov, adapted by Newsela staff
 Name: Period: Date: Article of the Week Directions: Read the following article carefully and annotate. You need to include at least 1 annotation per paragraph. Be sure to include all of the following in
Name: Period: Date: Article of the Week Directions: Read the following article carefully and annotate. You need to include at least 1 annotation per paragraph. Be sure to include all of the following in
Chapter 10 Our Star. X-ray. visible
 Chapter 10 Our Star X-ray visible Radius: 6.9 10 8 m (109 times Earth) Mass: 2 10 30 kg (300,000 Earths) Luminosity: 3.8 10 26 watts (more than our entire world uses in 1 year!) Why does the Sun shine?
Chapter 10 Our Star X-ray visible Radius: 6.9 10 8 m (109 times Earth) Mass: 2 10 30 kg (300,000 Earths) Luminosity: 3.8 10 26 watts (more than our entire world uses in 1 year!) Why does the Sun shine?
Chapter 14 Our Star A Closer Look at the Sun. Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery?
 Chapter 14 Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery? Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun s structure? Why was the Sun s energy source
Chapter 14 Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery? Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun s structure? Why was the Sun s energy source
Today The Sun. Events
 Today The Sun Events Last class! Homework due now - will count best 5 of 6 Final exam Dec. 20 @ 12:00 noon here Review this Course! www.case.edu/utech/course-evaluations/ The Sun the main show in the solar
Today The Sun Events Last class! Homework due now - will count best 5 of 6 Final exam Dec. 20 @ 12:00 noon here Review this Course! www.case.edu/utech/course-evaluations/ The Sun the main show in the solar
