Made-to-Measure (M2M) Dynamical modelling of external galaxies and the Milky Way
|
|
|
- Spencer Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Made-to-Measure (M2M) Dynamical modelling of external galaxies and the Milky Way Shude Mao (NAOC/Manchester) Oct. 31, Collaborators: Richard Long, Yougang Wang, Juntai Shen
2 Motivation Important for inferring mass (dark matter) distribution: shape, radial profiles, central supermassive black holes establishing scaling relations, and finding clues for galaxy formation and evolution much better data becoming available Milky Way: BRAVA, ARGOS, APOGEE, OGLE (proper motions), GAIA External galaxies (IFUs): SAMI, MANGA Require better modeling techniques which will also guide observations
3 How to perform dynamical modelling? Jeans equation Schwarzschild method: Orbit based method Made-to-Measure (M2M): Particle based method Torus Method In the last three methods, orbits play essential roles
4 Orbits in 3D triaxial potentials z y x short-axis (z-) tube orbits (from Barnes)
5 Orbits in 3D triaxial potentials box orbits (from Barnes)
6 Schwarzschild Method ρ L ρϕ orbits box long axis tube Schwarzschild (1979) Orbit individual particles short axis tube End of run, use linear / quadratic programming to determine weights of different orbits Well established (applications: black hole/galaxy masses) [See Yougang Wang s talk tomorrow] +Chaotic orbits
7 Made-to-Measure Method (Syer & Tremaine 1996) Orbit system of particles Inflight weight adjustment to reproduce observations (not at the end) More flexibility than Schwarzschild's method Cross-checks on the Schwarzschild method: degeneracy?
8 Actual Observables Examples Surface brightness Mean line-of-sight (los) velocity Los velocity dispersion Los velocity distribution eg h3 (skewness), h4 (kurtosis) Also los velocities of individual stars, globular clusters Kinematics are luminosity weighted
9 Sky In a given potential N (~10 6 ) particles are orbited Particle weights adjusted as a function of time Regular Irregular Cartesian, polar, logarithmic in radius los e.g. from Voronoi binning of actual data
10 Model Observables v los, j = N i w v N i i los,i wδ i δ ij ij Position = j Number of particles = N Individual particle = i v los, j = N i w i v I los,i j A j δ ij y j Kernel: N = i w i K ji Surface brightness Average velocity, dispersion,
11 Weight Evolution Weight evolution equation (Syer & Tremaine 96): dw i dt % J εw i ' K ji & j Δ j ( *, Δ j = y j Y j, ε > 0 ) Y j When the predicted y j > observed Y j, weight is reduced, and vice versa, until convergence is reached. (Syer & Tremaine 96; Bissantz et al. 04; De Lorenzo 07, 08; Dehnen 09; Long & Mao 10; Morganti & Gerhard 2012)
12 Weight Evolution F ( w) = χ + µ S + 1 ε ds dt K χ 2 = λ χ k k 2 k S = N i & w $ iln % w m i i #! " dw i dt ) K J K = εw i k, ji λ k Δ σ k, j µ S + * k j k, j w i,. -
13 Particle Initial Conditions Spatial coordinates match luminosity distribution Use (approximate) distribution function if available Sample integral space eg energy, angular momentum Velocity coordinates Created using a given set of velocity dispersion functions eg from Jeans equations Random
14 Mock Galaxy Model Plummer sphere ϕ( r) = Υ ( r 2 +1) 1/ 2 Constructed mock data surface brightness, los velocity dispersion, h4, isotropic dispersion Task: use M2M to determine the mass-to-light ratio of the constructed data
15 M2M M/L = 4.97, Input: 5 Long & Mao (2010)
16 Elliptical and Lenticular Galaxies Motivation Compare M2M with Schwarzschild's method Based on Sauron data (Cappellari et al 2006) 24 galaxies, fast / slow rotators, various kinematic features eg Kinematically Decoupled Cores (KDC), Counter Rotating Cores (CRC) All have Sauron results M2M Implementation MGE potential interpolated acceleration tables Voronoi binning kdtree, nearest neighbour search Rotation set sign of v_theta appropriately
17 NGC 4660 SB sigma h3 h4
18 NGC KDC Can reproduce the kinematics well, e.g., Kinetically Decoupled Cores in NGC 4458
19 Mass-to-Light ratio: M2M vs. Schwarzschild Long & Mao (2012)
20 Global anisotropy Slow rotators M2M method more radially anisotropic Model not unique? A larger value indicates more radial orbits
21 External galaxies: summary Good agreement between M2M and Schwarzschild in terms of mass-to-light ratios M2M appears to have slight larger anisotropies Model may not be unique Require data at large radii (Morganti & Gerhard 2012) Comparison between different methods can be useful cross-checks
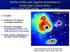
22 COBE Satellite View of the Milky Way Light is asymmetric! MW is a barred SBc galaxy
23 Top-down view of the Galaxy Why do we study the MW bar? Bar parameters are uncertain Provide clues for external barred galaxies: formation, evolution and dynamical processes SUN Credit: Robert Hurt (SSC/JPL/Caltech)
24 M2M modeling of MW Photometric data: Star counts (from OGLE) over large area Kinematic data BRAVA Proper motions from microlensing surveys Adjustment of M2M to the Milky Way Takes into rotating frame kinematics Non-parallel projection los to observers First M2M + MW kinematic model Initial conditions: Shen et al. (2010) numerical model
25 Radial velocity fields of BRAVA Radial velocities of 8500 red giants (Kunder et al. 2012) Velocity accuracy ~ 5 km/s
26 Reproducing BRAVA radial velocity 70 km/s/kpc 0 40 Velocity dispersion Mean velocity: rotation Long, Mao, Wang & Shen (2012)
27 Constraints on the Galactic bar parameters Fit both surface brightness and BRAVA radial velocities Bar pattern speed: 40 km/s/kpc, angle: 30 degrees (consistent with Shen et al & Weiner & Sellwood 1999) Not well constrained, need more data! Long, Mao, Wang & Shen (2012)
28 Summary & future outlook M2M has been applied successfully to both the MW and external galaxies More new data to come APOGEE, ARGOS, GAIA for the Milky Way E.g., SAMI/MANGA for external galaxies Much theoretical work yet to be done Self-gravity, stability, degeneracy? provide hints for how galaxies form and evolve
Modelling the Milky Way bar
 Modelling the Milky Way bar Shude Mao Tsinghua University/NAOC June 25, 2015@IPMU Collaborators: Yougang Wang, Richard Long, Juntai Shen, Liang Cao, Outline! Observed properties of barred galaxies " The
Modelling the Milky Way bar Shude Mao Tsinghua University/NAOC June 25, 2015@IPMU Collaborators: Yougang Wang, Richard Long, Juntai Shen, Liang Cao, Outline! Observed properties of barred galaxies " The
What can M2M do for Milky Way Models?
 What can M2M do for Milky Way Models? Ortwin Gerhard Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de Thanks to F. de Lorenzi, V. Debattista, P. Das, L. Morganti I. Made-to-Measure
What can M2M do for Milky Way Models? Ortwin Gerhard Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de Thanks to F. de Lorenzi, V. Debattista, P. Das, L. Morganti I. Made-to-Measure
Inner dynamics of massive galaxies (ETG) Michele Cappellari
 Inner dynamics of massive galaxies (ETG) Michele Cappellari First rotation curve of an elliptical (Bertola+Capaccioli75) Elliptical galaxy NGC4697 2 hr of observations at 5-m Palomar Angular momentum much
Inner dynamics of massive galaxies (ETG) Michele Cappellari First rotation curve of an elliptical (Bertola+Capaccioli75) Elliptical galaxy NGC4697 2 hr of observations at 5-m Palomar Angular momentum much
Dynamical modelling of galaxies. Eugene Vasiliev
 Dynamical modelling of galaxies Eugene Vasiliev DAGAL summer school, Marseille, 2014 Plan Overview of dynamical modelling problem Theoretical and observational approaches The Schwarzschild orbit superposition
Dynamical modelling of galaxies Eugene Vasiliev DAGAL summer school, Marseille, 2014 Plan Overview of dynamical modelling problem Theoretical and observational approaches The Schwarzschild orbit superposition
NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies NMAGIC - 2 M2M
 NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de I. Made-to-measure dynamical modeling with NMAGIC II Elliptical galaxy halo kinematics with planetary
NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de I. Made-to-measure dynamical modeling with NMAGIC II Elliptical galaxy halo kinematics with planetary
Overview of Dynamical Modeling. Glenn van de Ven
 Overview of Dynamical Modeling Glenn van de Ven glenn@mpia.de 1 Why dynamical modeling? -- mass total mass stellar systems key is to their evolution compare luminous mass: constrain DM and/or IMF DM radial
Overview of Dynamical Modeling Glenn van de Ven glenn@mpia.de 1 Why dynamical modeling? -- mass total mass stellar systems key is to their evolution compare luminous mass: constrain DM and/or IMF DM radial
Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia
 Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Chengqun Yang Contents 1 Stellar Halo
Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Chengqun Yang Contents 1 Stellar Halo
MAMPOSSt modeling of true & mock dwarf spheroidal galaxies
 MAMPOSSt modeling of true & mock dwarf spheroidal galaxies Gary Mamon (IAP), 30 Oct 2014, GAIA Challenge in Heidelberg, MAMPOSSt modeling of true & mock dwarf spheroidals 1 Motivations Mass profiles of
MAMPOSSt modeling of true & mock dwarf spheroidal galaxies Gary Mamon (IAP), 30 Oct 2014, GAIA Challenge in Heidelberg, MAMPOSSt modeling of true & mock dwarf spheroidals 1 Motivations Mass profiles of
Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching
 Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de 1. Preamble Arnaboldi et al 2013 2. Predictions: ETG halos in cosmological simulations 3.
Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de 1. Preamble Arnaboldi et al 2013 2. Predictions: ETG halos in cosmological simulations 3.
AY202a Galaxies & Dynamics Lecture 7: Jeans Law, Virial Theorem Structure of E Galaxies
 AY202a Galaxies & Dynamics Lecture 7: Jeans Law, Virial Theorem Structure of E Galaxies Jean s Law Star/Galaxy Formation is most simply defined as the process of going from hydrostatic equilibrium to gravitational
AY202a Galaxies & Dynamics Lecture 7: Jeans Law, Virial Theorem Structure of E Galaxies Jean s Law Star/Galaxy Formation is most simply defined as the process of going from hydrostatic equilibrium to gravitational
Epicycles the short form.
 Homework Set 3 Due Sept 9 CO 4.15 just part (a). (see CO pg. 908) CO 4.1 CO 4.36 (a),(b) CO 5.14 (assume that Sun currently has its max. u velocity.) CO 5.16 (Keplerian orbit = orbit around a point mass)
Homework Set 3 Due Sept 9 CO 4.15 just part (a). (see CO pg. 908) CO 4.1 CO 4.36 (a),(b) CO 5.14 (assume that Sun currently has its max. u velocity.) CO 5.16 (Keplerian orbit = orbit around a point mass)
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Constraints on secular evolution in unbarred spiral galaxies: understanding bulge and disk formation
 Constraints on secular evolution in unbarred spiral galaxies: understanding bulge and disk formation July 10 th 2012 Marja Kristin Seidel Jesús Falcón - Barroso Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias www.iac.es/project/traces
Constraints on secular evolution in unbarred spiral galaxies: understanding bulge and disk formation July 10 th 2012 Marja Kristin Seidel Jesús Falcón - Barroso Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias www.iac.es/project/traces
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND
 Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles
 Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Astronomy: Division C Science Olympiad, Round 1 Tryout Test
 Astronomy: Division C Science Olympiad, Round 1 Tryout Test Student Name : Student Number : DIRECTIONS 1. Write the answers that you want graded legibly on the answer sheet, along with your name and student
Astronomy: Division C Science Olympiad, Round 1 Tryout Test Student Name : Student Number : DIRECTIONS 1. Write the answers that you want graded legibly on the answer sheet, along with your name and student
Joint mass and anisotropy modeling of the. Fornax Dwarf Spheroidal
 Joint mass and anisotropy modeling of the Fornax Dwarf Spheroidal Fornax Dwarf Spheroidal with Chris GORDON (Oxford) Andrea BIVIANO (Trieste) DSS 1 Motivations Large velocity data sets in Dwarf Spheroidals
Joint mass and anisotropy modeling of the Fornax Dwarf Spheroidal Fornax Dwarf Spheroidal with Chris GORDON (Oxford) Andrea BIVIANO (Trieste) DSS 1 Motivations Large velocity data sets in Dwarf Spheroidals
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter
 Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
A M BLACK HOLE IN NGC 1277 FROM ADAPTIVE OPTICS SPECTROSCOPY. WALSH et al Akiyama Group M1 Genki Suzuki
 A 5 10 9 M BLACK HOLE IN NGC 1277 FROM ADAPTIVE OPTICS SPECTROSCOPY WALSH et al. 2015 Akiyama Group M1 Genki Suzuki Introduction NGC 1277 is thought to harbor one of the most massive black holes in the
A 5 10 9 M BLACK HOLE IN NGC 1277 FROM ADAPTIVE OPTICS SPECTROSCOPY WALSH et al. 2015 Akiyama Group M1 Genki Suzuki Introduction NGC 1277 is thought to harbor one of the most massive black holes in the
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
An Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology. Jun 29, 2005 Chap.2.1~2.3
 An Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology Jun 29, 2005 Chap.2.1~2.3 2.1 Introduction external galaxies normal galaxies - majority active galaxies - 2% high luminosity (non-stellar origin) variability
An Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology Jun 29, 2005 Chap.2.1~2.3 2.1 Introduction external galaxies normal galaxies - majority active galaxies - 2% high luminosity (non-stellar origin) variability
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Gas and Stellar Dynamical Black Hole Mass Measurements:
 Gas and Stellar Dynamical Black Hole Mass Measurements: Revisiting M84 and a Consistency Test with NGC 3998 Jonelle Walsh (UC Irvine/UT Austin) Aaron Barth (UC Irvine) Remco van den Bosch (MPIA) Marc Sarzi
Gas and Stellar Dynamical Black Hole Mass Measurements: Revisiting M84 and a Consistency Test with NGC 3998 Jonelle Walsh (UC Irvine/UT Austin) Aaron Barth (UC Irvine) Remco van den Bosch (MPIA) Marc Sarzi
The Milky Way Nuclear Star Cluster beyond 1 pc
 The Milky Way Nuclear Star Cluster beyond 1 pc Anja Feldmeier, Nadine Neumayer, Anil Seth, Rainer Schödel, P. T. de Zeeuw, Nora Lützgendorf, C. J. Walcher, Shogo Nishiyama, Markus Kissler-Patig Oct. 1,
The Milky Way Nuclear Star Cluster beyond 1 pc Anja Feldmeier, Nadine Neumayer, Anil Seth, Rainer Schödel, P. T. de Zeeuw, Nora Lützgendorf, C. J. Walcher, Shogo Nishiyama, Markus Kissler-Patig Oct. 1,
distribution of mass! The rotation curve of the Galaxy ! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk
 Today in Astronomy 142:! The local standard of rest the Milky Way, continued! Rotation curves and the! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk distribution
Today in Astronomy 142:! The local standard of rest the Milky Way, continued! Rotation curves and the! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk distribution
View of the Galaxy from within. Lecture 12: Galaxies. Comparison to an external disk galaxy. Where do we lie in our Galaxy?
 Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
ASTRON 331 Astrophysics TEST 1 May 5, This is a closed-book test. No notes, books, or calculators allowed.
 ASTRON 331 Astrophysics TEST 1 May 5, 2003 Name: This is a closed-book test. No notes, books, or calculators allowed. Orders of Magnitude (20 points): simply circle the correct answer. 1. The brightest
ASTRON 331 Astrophysics TEST 1 May 5, 2003 Name: This is a closed-book test. No notes, books, or calculators allowed. Orders of Magnitude (20 points): simply circle the correct answer. 1. The brightest
The motions of stars in the Galaxy
 The motions of stars in the Galaxy The stars in the Galaxy define various components, that do not only differ in their spatial distribution but also in their kinematics. The dominant motion of stars (and
The motions of stars in the Galaxy The stars in the Galaxy define various components, that do not only differ in their spatial distribution but also in their kinematics. The dominant motion of stars (and
Microlensing (planet detection): theory and applications
 Microlensing (planet detection): theory and applications Shude Mao Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics University of Manchester (& NAOC) 19/12/2009 @ KIAA Outline What is (Galactic) microlensing? Basic
Microlensing (planet detection): theory and applications Shude Mao Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics University of Manchester (& NAOC) 19/12/2009 @ KIAA Outline What is (Galactic) microlensing? Basic
Collisionless Boltzmann Eq (Vlasov eq)" S+G sec 3.4! Collisionless Boltzmann Eq S&G 3.4!
 Collisionless Boltzmann Eq (Vlasov eq)" S+G sec 3.4 When considering the structure of galaxies cannot follow each individual star (10 11 of them), Consider instead stellar density and velocity distributions.
Collisionless Boltzmann Eq (Vlasov eq)" S+G sec 3.4 When considering the structure of galaxies cannot follow each individual star (10 11 of them), Consider instead stellar density and velocity distributions.
Dynamics of the Milky Way
 Dynamics of the Milky Way Part 1: Part 2: Part 3: Part 4: I. Introduction Formation of Disk Galaxies II. Fundamentals of Stellar Dynamics Stellar Orbits and Jeans Theorem The Galactic Bulge and Bar The
Dynamics of the Milky Way Part 1: Part 2: Part 3: Part 4: I. Introduction Formation of Disk Galaxies II. Fundamentals of Stellar Dynamics Stellar Orbits and Jeans Theorem The Galactic Bulge and Bar The
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf
 The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
Our Galaxy. Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust. Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye
 Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
Outline. Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks
 Outline Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks Why is the night sky dark? (Olber s Paradox 1826) Or what
Outline Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks Why is the night sky dark? (Olber s Paradox 1826) Or what
The Nuclear Cluster of the Milky Way
 The Nuclear Cluster of the Milky Way VLT/NACO Ks-band 87''=3.4 pc box Fritz et al ApJ submitted Chatzopolus et al. in prep. Pfuhl et al. 2011, ApJ, 741, 108 T.K. Fritz 1,2, S. Chatzopoulos 1, O. Pfuhl
The Nuclear Cluster of the Milky Way VLT/NACO Ks-band 87''=3.4 pc box Fritz et al ApJ submitted Chatzopolus et al. in prep. Pfuhl et al. 2011, ApJ, 741, 108 T.K. Fritz 1,2, S. Chatzopoulos 1, O. Pfuhl
The Milky Way - Chapter 23
 The Milky Way - Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy A galaxy: huge collection of stars (10 7-10 13 ) and interstellar matter (gas & dust). Held together by gravity. Much bigger than any star cluster we have
The Milky Way - Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy A galaxy: huge collection of stars (10 7-10 13 ) and interstellar matter (gas & dust). Held together by gravity. Much bigger than any star cluster we have
Black Hole Subsystems in Galactic Globular Clusters: Unravelling BH Populations in GCs using MOCCA Star Cluster Simulations
 Black Hole Subsystems in Galactic Globular Clusters: Unravelling BH Populations in GCs using MOCCA Star Cluster Simulations Artist impression of a stellar mass BH detected in NGC 3201 (Giesers et al. 2018)
Black Hole Subsystems in Galactic Globular Clusters: Unravelling BH Populations in GCs using MOCCA Star Cluster Simulations Artist impression of a stellar mass BH detected in NGC 3201 (Giesers et al. 2018)
A new model for the Milky Way bar
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 47, 149 1440 (01) doi:10.1111/j.1365-966.01.063.x A new model for the Milky Way bar Yougang Wang, 1, Hongsheng Zhao,,3,4 Shude Mao,5 andr.m.rich 6 1 Key Laboratory of Optical
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 47, 149 1440 (01) doi:10.1111/j.1365-966.01.063.x A new model for the Milky Way bar Yougang Wang, 1, Hongsheng Zhao,,3,4 Shude Mao,5 andr.m.rich 6 1 Key Laboratory of Optical
Kinematics of the Solar Neighborhood
 Chapter 15 Kinematics of the Solar Neighborhood Unlike an elliptical galaxy, the Milky Way rotates with a speed much larger than the random velocities of typical stars. Our position inside the disk of
Chapter 15 Kinematics of the Solar Neighborhood Unlike an elliptical galaxy, the Milky Way rotates with a speed much larger than the random velocities of typical stars. Our position inside the disk of
Chapter 30. Galaxies and the Universe. Chapter 30:
 Chapter 30 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter 30: Galaxies and the Universe Chapter 30.1: Stars with varying light output allowed astronomers to map the Milky Way, which has a halo, spiral arm, and a massive
Chapter 30 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter 30: Galaxies and the Universe Chapter 30.1: Stars with varying light output allowed astronomers to map the Milky Way, which has a halo, spiral arm, and a massive
A MUSE view of cd galaxy NGC 3311
 A MUSE view of cd galaxy NGC 3311 C. E. Barbosa 1, M. Arnaboldi 2, L. Coccato 2, O. Gerhard 3, C. Mendes de Oliveira 1, M. Hilker 2, T. Richtler 4 1 Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil 2 European
A MUSE view of cd galaxy NGC 3311 C. E. Barbosa 1, M. Arnaboldi 2, L. Coccato 2, O. Gerhard 3, C. Mendes de Oliveira 1, M. Hilker 2, T. Richtler 4 1 Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil 2 European
CAULDRON: dynamics meets gravitational lensing. Matteo Barnabè
 CAULDRON: dynamics meets gravitational lensing Matteo Barnabè KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University Collaborators: Léon Koopmans (Kapteyn), Oliver Czoske (Vienna), Tommaso Treu (UCSB), Aaron Dutton (MPIA), Matt
CAULDRON: dynamics meets gravitational lensing Matteo Barnabè KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University Collaborators: Léon Koopmans (Kapteyn), Oliver Czoske (Vienna), Tommaso Treu (UCSB), Aaron Dutton (MPIA), Matt
Lecture 30. The Galactic Center
 Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick, and our solar system is located 26,000 ly away from the center of the galaxy.
 The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
The Galaxy. (The Milky Way Galaxy)
 The Galaxy (The Milky Way Galaxy) Which is a picture of the Milky Way? A A is what we see from Earth inside the Milky Way while B is what the Milky Way might look like if we were far away looking back
The Galaxy (The Milky Way Galaxy) Which is a picture of the Milky Way? A A is what we see from Earth inside the Milky Way while B is what the Milky Way might look like if we were far away looking back
Tidal streams as gravitational experiments!
 Tidal streams as gravitational experiments! Benoit Famaey CNRS - Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg MOND paradigm MDAR: McGaugh et al. 2016 Lelli et al. 2016 Famaey & McGaugh 2012 MOND paradigm Prediction:
Tidal streams as gravitational experiments! Benoit Famaey CNRS - Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg MOND paradigm MDAR: McGaugh et al. 2016 Lelli et al. 2016 Famaey & McGaugh 2012 MOND paradigm Prediction:
Ellipticals. Ellipticals. Huge mass range:
 Ellipticals Huge mass range: Dwarf spheroidal (Leo I) Dwarf spheroidals: 1 7-1 8 M Blue compact dwarfs: ~1 9 M Dwarf ellipticals: 1 7-1 9 M Normal (giant) ellipticals: 1 8-1 13 M cd galaxies in cluster
Ellipticals Huge mass range: Dwarf spheroidal (Leo I) Dwarf spheroidals: 1 7-1 8 M Blue compact dwarfs: ~1 9 M Dwarf ellipticals: 1 7-1 9 M Normal (giant) ellipticals: 1 8-1 13 M cd galaxies in cluster
Astro 242. The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu
 Astro 242 The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu Syllabus Text: An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics 2nd Ed., Carroll and Ostlie First class Wed Jan 3. Reading period Mar 8-9
Astro 242 The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu Syllabus Text: An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics 2nd Ed., Carroll and Ostlie First class Wed Jan 3. Reading period Mar 8-9
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8
 The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Using globular clusters to test gravity in the weak acceleration regime
 Using globular clusters to test gravity in the weak acceleration regime Riccardo Scarpa 1, Gianni Marconi 2, Roberto Gilmozzi 2, and Giovanni Carraro 3 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain 2 European
Using globular clusters to test gravity in the weak acceleration regime Riccardo Scarpa 1, Gianni Marconi 2, Roberto Gilmozzi 2, and Giovanni Carraro 3 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain 2 European
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7
 The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11. Tidal Debris
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11 Tidal Debris Goals (1) We ll explore whether we can trace the accretion events that should have formed the Milky Way. (2) We ll discuss the impact of tidal debris on direct detection
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11 Tidal Debris Goals (1) We ll explore whether we can trace the accretion events that should have formed the Milky Way. (2) We ll discuss the impact of tidal debris on direct detection
Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history
 Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history Author: Ana Hočevar Advisor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Department of Physics, University of Ljubljana March 18, 2006 Abstract Galaxy formation theory which predicts canibalism
Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history Author: Ana Hočevar Advisor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Department of Physics, University of Ljubljana March 18, 2006 Abstract Galaxy formation theory which predicts canibalism
Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies
 Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies Vincent Bonnivard bonnivard@lpsc.in2p3.fr TAUP 2015 07/09/15 Collaborators: D. Maurin, C. Combet, M. G. Walker, A.
Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies Vincent Bonnivard bonnivard@lpsc.in2p3.fr TAUP 2015 07/09/15 Collaborators: D. Maurin, C. Combet, M. G. Walker, A.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 9 Oct 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 9 Oct 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 9 Oct 2007](/thumbs/88/115643205.jpg) Constraining the Mass Profiles of Stellar Systems: Schwarzschild Modeling of Discrete Velocity Datasets Julio Chanamé 1, Jan Kleyna 2, & Roeland van der Marel 1 1 Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700
Constraining the Mass Profiles of Stellar Systems: Schwarzschild Modeling of Discrete Velocity Datasets Julio Chanamé 1, Jan Kleyna 2, & Roeland van der Marel 1 1 Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
Active Galactic Nuclei-I. The paradigm
 Active Galactic Nuclei-I The paradigm An accretion disk around a supermassive black hole M. Almudena Prieto, July 2007, Unv. Nacional de Bogota Centers of galaxies Centers of galaxies are the most powerful
Active Galactic Nuclei-I The paradigm An accretion disk around a supermassive black hole M. Almudena Prieto, July 2007, Unv. Nacional de Bogota Centers of galaxies Centers of galaxies are the most powerful
Central supermassive black holes from SINFONI observations
 Central supermassive black holes from SINFONI observations R.P Saglia, MPE with R.Bender, N.Nowak, P. Erwin, J. Thomas Gas and stars in Galaxies A Multi-Wavelength 3D Perspective Garching, 10th June 2008
Central supermassive black holes from SINFONI observations R.P Saglia, MPE with R.Bender, N.Nowak, P. Erwin, J. Thomas Gas and stars in Galaxies A Multi-Wavelength 3D Perspective Garching, 10th June 2008
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes
 In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 16 Dec 2004
 arxiv:astro-ph/0412433v1 16 Dec 2004 The Nuclear Orbital Distribution in Galaxies as Fossil Record of Black Hole Formation from Integral-Field Spectroscopy Michele Cappellari and Richard McDermid Leiden
arxiv:astro-ph/0412433v1 16 Dec 2004 The Nuclear Orbital Distribution in Galaxies as Fossil Record of Black Hole Formation from Integral-Field Spectroscopy Michele Cappellari and Richard McDermid Leiden
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars
 Summary: Nuclear burning in stars Reaction 4 1 H 4 He 3 4 He 12 C 12 C + 4 He 16 O, Ne, Na, Mg Ne O, Mg O Mg, S Si Fe peak Min. Temp. 10 7 o K 2x10 8 8x10 8 1.5x10 9 2x10 9 3x10 9 Evolution through nuclear
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars Reaction 4 1 H 4 He 3 4 He 12 C 12 C + 4 He 16 O, Ne, Na, Mg Ne O, Mg O Mg, S Si Fe peak Min. Temp. 10 7 o K 2x10 8 8x10 8 1.5x10 9 2x10 9 3x10 9 Evolution through nuclear
Veilleux! see MBW ! 23! 24!
 Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Bayesian Mass Estimates of the Milky Way: incorporating incomplete data
 Bayesian Mass Estimates of the Milky Way: incorporating incomplete data Gwendolyn Eadie, PhD Candidate Dr. William Harris (McMaster), Dr. Lawrence Widrow (Queen's) AstroStat Seminar - March 23, 2015 Measuring
Bayesian Mass Estimates of the Milky Way: incorporating incomplete data Gwendolyn Eadie, PhD Candidate Dr. William Harris (McMaster), Dr. Lawrence Widrow (Queen's) AstroStat Seminar - March 23, 2015 Measuring
Spiral and Bar Pattern Time-Dependence in Galaxies
 Spiral and Bar Pattern Time-Dependence in Galaxies M95 Daniel Pfenniger Geneva Observatory, University of Geneva, Switzerland Collaborators: Kanak Saha (Pune), Yu-Ting Wu & Ron Taam (Taipei) NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESO/R.
Spiral and Bar Pattern Time-Dependence in Galaxies M95 Daniel Pfenniger Geneva Observatory, University of Geneva, Switzerland Collaborators: Kanak Saha (Pune), Yu-Ting Wu & Ron Taam (Taipei) NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESO/R.
SLACS Spectroscopy. Observations, Kinematics & Stellar Populations. Oliver Czoske Kapteyn Institute, Groningen, NL
 SLACS Spectroscopy Observations, Kinematics & Stellar Populations Oliver Czoske Kapteyn Institute, Groningen, NL Strong Gravitational Lensing in the Next Decade Cogne, 22 June 2009 Collaborators Léon Koopmans
SLACS Spectroscopy Observations, Kinematics & Stellar Populations Oliver Czoske Kapteyn Institute, Groningen, NL Strong Gravitational Lensing in the Next Decade Cogne, 22 June 2009 Collaborators Léon Koopmans
Galaxies. Nebulae. Virgo Cluster of Galaxies sky.google.com
 Virgo Cluster of Galaxies sky.google.com Galaxies Mid 18th century, Kant and Wright suggested that the Milky Way is a finite system of stars. Turns out this is accurate. Kant went on to suggest that the
Virgo Cluster of Galaxies sky.google.com Galaxies Mid 18th century, Kant and Wright suggested that the Milky Way is a finite system of stars. Turns out this is accurate. Kant went on to suggest that the
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters
 Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Fabrizio Nesti. Ruđer Boškovic Institute, Zagreb Gran Sasso Science Institute, L Aquila. ULB, Bruxelles, March 7 th 2014
 The Dark Fabrizio Nesti Ruđer Boškovic Institute, Zagreb Gran Sasso Science Institute, L Aquila ULB, Bruxelles, March 7 th 2014 P. Salucci, F.N., C.F. Martins, G. Gentile, A&A 2010 F.N., P. Salucci, JCAP
The Dark Fabrizio Nesti Ruđer Boškovic Institute, Zagreb Gran Sasso Science Institute, L Aquila ULB, Bruxelles, March 7 th 2014 P. Salucci, F.N., C.F. Martins, G. Gentile, A&A 2010 F.N., P. Salucci, JCAP
Everything in baryons?
 Everything in baryons? Benoit Famaey (ULB) Rencontres de Blois 2007 General Relativity -> Dark Matter R αβ - 1/2 R g αβ + Λg αβ = (8πG/c 4 ) T αβ very precisely tested on solar system scales (but Pioneer)
Everything in baryons? Benoit Famaey (ULB) Rencontres de Blois 2007 General Relativity -> Dark Matter R αβ - 1/2 R g αβ + Λg αβ = (8πG/c 4 ) T αβ very precisely tested on solar system scales (but Pioneer)
The Milky Way s rotation curve out to 100 kpc and its constraint on the Galactic mass distribution
 I S I The Milky Way s rotation curve out to 100 kpc and its constraint on the Galactic mass distribution Yang Huang (LAMOST Fellow, yanghuang@pku.edu.cn) N G U N I V E R P E K T Y 1 8 9 8 Peking University
I S I The Milky Way s rotation curve out to 100 kpc and its constraint on the Galactic mass distribution Yang Huang (LAMOST Fellow, yanghuang@pku.edu.cn) N G U N I V E R P E K T Y 1 8 9 8 Peking University
On the orbits that generate the X-shape in the Milky Way bulge
 Advance Access publication 2017 May 23 doi:10.1093/mnras/stx1262 On the orbits that generate the X-shape in the Milky Way bulge Caleb G. Abbott, 1,2 Monica Valluri, 1 Juntai Shen 3,4 and Victor P. Debattista
Advance Access publication 2017 May 23 doi:10.1093/mnras/stx1262 On the orbits that generate the X-shape in the Milky Way bulge Caleb G. Abbott, 1,2 Monica Valluri, 1 Juntai Shen 3,4 and Victor P. Debattista
PE#4: It contains some useful diagrams and formula which we ll use today
 Sep 6, 2017 Overview of the MW PE#4: It contains some useful diagrams and formula which we ll use today HW#2 is due next Wed and is now posted. Don t wait for the last minute to start it. Includes a short
Sep 6, 2017 Overview of the MW PE#4: It contains some useful diagrams and formula which we ll use today HW#2 is due next Wed and is now posted. Don t wait for the last minute to start it. Includes a short
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
5 Dark matter and dark energy, the Universe revealed
 5 Dark matter and dark energy, the Universe revealed Our place Courtesy: NASA How much matter? Add up all we can see ~ 1 atom per 10 m -3 Ω = 1? ~ 1 atom m -3 Dark matter MACHOS WIMPS The quintuplet cluster,
5 Dark matter and dark energy, the Universe revealed Our place Courtesy: NASA How much matter? Add up all we can see ~ 1 atom per 10 m -3 Ω = 1? ~ 1 atom m -3 Dark matter MACHOS WIMPS The quintuplet cluster,
24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification
 Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble s Law 24.4 XXActive Galactic Nuclei XXRelativistic Redshifts and Look-Back
Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble s Law 24.4 XXActive Galactic Nuclei XXRelativistic Redshifts and Look-Back
Astronomy 730. Milky Way
 Astronomy 730 Milky Way Outline } The Milky Way } Star counts and stellar populations } Chemical cartography } Galactic center and bar } Galactic rotation } Departures from circular rotation Modeling the
Astronomy 730 Milky Way Outline } The Milky Way } Star counts and stellar populations } Chemical cartography } Galactic center and bar } Galactic rotation } Departures from circular rotation Modeling the
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
 Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 05, 2016 Read: Chap 19 04/05/16 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned by next class meeting
A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 05, 2016 Read: Chap 19 04/05/16 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned by next class meeting
Name: unid: Foundations of Astronomy ASTR/PHYS Final Exam
 Name: unid: Physical Constants * Foundations of Astronomy ASTR/PHYS 2500 Final Exam Gravitational constant G 6.673 x 10-11 m 3 kg - 1 s - 2 Elementary charge e 1.602 x 10-19 C Vacuum permittivity ε 0 8.854
Name: unid: Physical Constants * Foundations of Astronomy ASTR/PHYS 2500 Final Exam Gravitational constant G 6.673 x 10-11 m 3 kg - 1 s - 2 Elementary charge e 1.602 x 10-19 C Vacuum permittivity ε 0 8.854
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System
 Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
For β = 0, we have from our previous equations: d ln ν d ln r + d ln v2 r
 Isotropic models Now simplify the equation, and assume β = 0, or isotropic velocity dispersions - i.e., they are the same in all directions. Below we show how the observed light distribution and observed
Isotropic models Now simplify the equation, and assume β = 0, or isotropic velocity dispersions - i.e., they are the same in all directions. Below we show how the observed light distribution and observed
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Aug 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Aug 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Aug 2016](/thumbs/88/116589810.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 1 17 (214) Printed 11 October 218 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) A discrete chemo-dynamical model of the giant elliptical galaxy NGC 5846: dark matter fraction, internal rotation
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 1 17 (214) Printed 11 October 218 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) A discrete chemo-dynamical model of the giant elliptical galaxy NGC 5846: dark matter fraction, internal rotation
midterm exam thurs june 14 morning? evening? fri june 15 morning? evening? sat june 16 morning? afternoon? sun june 17 morning? afternoon?
 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 11 June 11, 2018 midterm exam thurs june 14 morning? evening? fri june 15 morning? evening? sat june 16 morning? afternoon? sun june 17 morning? afternoon? observing session tomorrow
Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 11 June 11, 2018 midterm exam thurs june 14 morning? evening? fri june 15 morning? evening? sat june 16 morning? afternoon? sun june 17 morning? afternoon? observing session tomorrow
1 [3 p.] First things first. 4 [2p.] Mass to light II. 5 [3p.] Merger remnants
![1 [3 p.] First things first. 4 [2p.] Mass to light II. 5 [3p.] Merger remnants 1 [3 p.] First things first. 4 [2p.] Mass to light II. 5 [3p.] Merger remnants](/thumbs/94/121056601.jpg) Name and student number: [will be needed in the real exam] ASTC22 (GALACTIC AND EXTRAGALACTIC ASTROPHYSICS) PREPARATION SETFOR FINAL EXAM (#7) - PROBLEMS. SOLVED, SOME NOT. SOME FULLY Points in the square
Name and student number: [will be needed in the real exam] ASTC22 (GALACTIC AND EXTRAGALACTIC ASTROPHYSICS) PREPARATION SETFOR FINAL EXAM (#7) - PROBLEMS. SOLVED, SOME NOT. SOME FULLY Points in the square
Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution. Elliptical Galaxies (II)
 Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution Elliptical Galaxies (II) Layout of the Course Feb 5: Review: Galaxies and Cosmology Feb 12: Review: Disk Galaxies and Galaxy Formation Basics Feb 19: Disk Galaxies
Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution Elliptical Galaxies (II) Layout of the Course Feb 5: Review: Galaxies and Cosmology Feb 12: Review: Disk Galaxies and Galaxy Formation Basics Feb 19: Disk Galaxies
PROJECT GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
 PROJECT 5 GLOBULAR CLUSTERS Objective: The objective of this exercise is the calculation of the core and tidal radius of a globular cluster in the Milky Way. Measure the tidal radius of a globular cluster
PROJECT 5 GLOBULAR CLUSTERS Objective: The objective of this exercise is the calculation of the core and tidal radius of a globular cluster in the Milky Way. Measure the tidal radius of a globular cluster
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Accretion Disks. Review: Stellar Remnats. Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath 2/25/10. Review: Creating Stellar Remnants
 Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: Creating Stellar Remnants Binaries may be destroyed in white dwarf supernova Binaries be converted into black holes Review: Stellar
Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: Creating Stellar Remnants Binaries may be destroyed in white dwarf supernova Binaries be converted into black holes Review: Stellar
Spiral Structure. m ( Ω Ω gp ) = n κ. Closed orbits in non-inertial frames can explain the spiral pattern
 Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Fabrizio Nesti. LNGS, July 5 th w/ C.F. Martins, G. Gentile, P. Salucci. Università dell Aquila, Italy. The Dark Matter density. F.
 Global The Dark Matter Fabrizio Nesti Università dell Aquila, Italy LNGS, July 5 th 2012 w/ C.F. Martins, G. Gentile, P. Salucci Global Dark Matter? A number of indirect supporting evidences Modify Gravity
Global The Dark Matter Fabrizio Nesti Università dell Aquila, Italy LNGS, July 5 th 2012 w/ C.F. Martins, G. Gentile, P. Salucci Global Dark Matter? A number of indirect supporting evidences Modify Gravity
Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway. More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy
 Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy "What good are Mercator's North Poles and Equators Tropics, Zones, and Meridian Lines?" So the Bellman would cry, and the
Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy "What good are Mercator's North Poles and Equators Tropics, Zones, and Meridian Lines?" So the Bellman would cry, and the
NEUTRON STARS, GAMMA RAY BURSTS, and BLACK HOLES (chap. 22 in textbook)
 NEUTRON STARS, GAMMA RAY BURSTS, and BLACK HOLES (chap. 22 in textbook) Neutron Stars For carbon detonation SN probably no remnant For core-collapse SN remnant is a neutron-degenerate core neutron star
NEUTRON STARS, GAMMA RAY BURSTS, and BLACK HOLES (chap. 22 in textbook) Neutron Stars For carbon detonation SN probably no remnant For core-collapse SN remnant is a neutron-degenerate core neutron star
Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE
 IAU Symposium 330 Nice, 27. April 2017 Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE Wilma Trick (MPIA, Heidelberg) Hans-Walter Rix (MPIA) Jo Bovy (Uni Toronto) Open Questions
IAU Symposium 330 Nice, 27. April 2017 Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE Wilma Trick (MPIA, Heidelberg) Hans-Walter Rix (MPIA) Jo Bovy (Uni Toronto) Open Questions
The Milky Way. Mass of the Galaxy, Part 2. Mass of the Galaxy, Part 1. Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya
 Foundations Chapter of Astronomy 15 13e Our Milky Way Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Selected Topics in Chapter 15 A view our Milky Way? The Size of our Milky Way The Mass of
Foundations Chapter of Astronomy 15 13e Our Milky Way Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Selected Topics in Chapter 15 A view our Milky Way? The Size of our Milky Way The Mass of
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies. Spherically symmetric objects Vasily Belokurov vasily@ast.cam.ac.uk Institute of Astronomy Lent Term 2016 1 / 21 Outline I 1 2 Globular of galaxies 2 / 21 Why
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies. Spherically symmetric objects Vasily Belokurov vasily@ast.cam.ac.uk Institute of Astronomy Lent Term 2016 1 / 21 Outline I 1 2 Globular of galaxies 2 / 21 Why
Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect
 Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect On the Shoulders of Giants Workshop Case Western Reserve University June 7, 2017 Stephen Alexander Physics Department
Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect On the Shoulders of Giants Workshop Case Western Reserve University June 7, 2017 Stephen Alexander Physics Department
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Cooking with Strong Lenses and Other Ingredients
 Cooking with Strong Lenses and Other Ingredients Adam S. Bolton Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Utah AASTCS 1: Probes of Dark Matter on Galaxy Scales Monterey, CA, USA 2013-July-17
Cooking with Strong Lenses and Other Ingredients Adam S. Bolton Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Utah AASTCS 1: Probes of Dark Matter on Galaxy Scales Monterey, CA, USA 2013-July-17
