Doppler Shift. a. In which situation will the observer receive light that is shifted to shorter wavelengths?
|
|
|
- Sylvia Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 73 Because of the Doppler Effect, light emitted by an object can appear to change wavelength due to its motion toward or away from an observer. When the observer and the source of light are moving toward each other the light is shifted to shorter wavelengths (blueshifted). When the observer and the source of light are moving away from each other the light is shifted to longer wavelengths (redshifted). Part I. Motion of Source a) Star is not moving b) c) d) 1) Consider the situations shown (a d). a. In which situation will the observer receive light that is shifted to shorter wavelengths? b. Will this light be blueshifted or redshifted? c. What direction is the star moving relative to the observer? 2) Consider the situations shown (a d). a. In which situation will the observer receive light that is shifted to longer wavelengths? b. Will this light be blueshifted or redshifted? c. What direction is the star moving relative to the observer?
2 74 Doppler Shift 3) In which of the situations shown (a d) will the observer receive light that is not shifted at all? Explain your 4) Imagine our solar system is moving in the Milky Way toward a group of three stars. Star A is a blue star that is slightly closer to us than the other three. Star B is a red star that is farthest away from us. Star C is a yellow star that is halfway between Stars A and B. a. Which of these three stars, if any, will give off light that appears to be blueshifted? Explain your b. Which of these three stars, if any, will give off light that appears to be redshifted? Explain your c. Which of these three stars, if any, will give off light that appears to have no shift? Explain your 5) You overhear two students discussing the topic of Doppler shifts. Student 1: Since Betelgeuse is a red star, it must be going away from us, and since Rigel is a blue star it must be coming towards us. Student 2: I disagree, the color of the star does not tell you if it is moving. You have to look at the shift in wavelength of the lines in the star s absorption spectrum to determine whether it s moving towards or away from you. Do you agree with Student 1, Student 2, neither or both? Why or why not? Part II. Shift in Absorption Spectra When we study an astronomical object like a star or galaxy, we examine the spectrum of light it gives off. Since the lines of a spectrum occur at specific wavelengths we can determine that an object is moving when we see that the lines have been shifted to either longer or shorter wavelengths. For the absorption line spectra shown on the next page, short wavelength light (the blue end of the spectrum) is shown on the left-hand side and long wavelength light (the red end of the spectrum) is shown on the right-hand side.
3 75 For the three absorption line spectra shown below (A, B and C), one of the spectra corresponds to a star that is not moving relative to you, one of the spectra is from a star that is moving towards you and one of the spectra is from a star that is moving away from you. Blue Red A B C 6) Which of the three spectra above, corresponds with the star moving toward you? Explain your 7) Which of the three spectra, corresponds with the star moving away from you? Explain your Part III. Size of Shift and Speed If two sources of light are moving relative to an observer, the light from the star that is moving faster will appear to undergo a greater Doppler Shift. D Blue Red Consider the four spectra at right. The spectrum labeled F is an absorption line spectrum from a star that is at rest. Again, note that short wavelength (blue) light is shown on the left-hand side of each spectrum and long wavelength (red) light is shown on the right-hand side of each spectrum. E F G 8) Which of the four spectra would be from the star that is moving the fastest? Would this star be moving toward or away form the observer? 9) Which of the four spectra would be from the star that is moving the slowest? Describe the motion of this star.
4 76 Doppler Shift 10) An important line in the absorption spectrum of stars occurs at a wavelength of 656 nm for stars at rest. Imagine that you observe five stars (H-L) from Earth and discover that this important absorption line is measured at the wavelength shown in the table below for each of the five stars. Star H I J K L Wavelength of Absorption Line 649 nm 660 nm 656 nm 658 nm 647 nm a. Which of the stars are giving off light that appears blueshifted? Explain your b. Which of the stars are giving off light that appears redshifted? Explain your c. Which of the stars are giving off light that appears shifted by the greatest amount? Is this light shifted to longer or shorter wavelengths? Explain your d. Which star is moving the fastest? Is it moving toward or away from the observer? Explain your 11) The figure at right shows a space probe and five planets. The motion of the space probe is indicated by the arrow. The space probe is continuously broadcasting a radio signal in all directions. a. Which planets will receive a radio signal that is redshifted? Explain your b. Which planets will receive a radio signal that is shifted to shorter wavelengths? Explain your C E! B A D not to scale
5 77 c. Will all the planets receive radio signals from the space probe that are Doppler shifted? Explain your d. How will the Doppler shift in the radio signals detected at planets A and B compare? Explain your e. How will the Doppler shift in the radio signals detected at planets E and B compare? Explain your
Photographs of a Star Cluster. Spectra of a Star Cluster. What can we learn directly by analyzing the spectrum of a star? 4/1/09
 Photographs of a Star Cluster Spectra of a Star Cluster What can we learn directly by analyzing the spectrum of a star? A star s chemical composition dips in the spectral curve of lines in the absorption
Photographs of a Star Cluster Spectra of a Star Cluster What can we learn directly by analyzing the spectrum of a star? A star s chemical composition dips in the spectral curve of lines in the absorption
Spectra of a Star Cluster. Photographs of a Star Cluster. What can we learn directly by analyzing the spectrum of a star? 4/1/09
 Photographs of a Star Cluster Spectra of a Star Cluster What can we learn directly by analyzing the spectrum of a star? A star s chemical composition dips in the spectral curve of lines in the absorption
Photographs of a Star Cluster Spectra of a Star Cluster What can we learn directly by analyzing the spectrum of a star? A star s chemical composition dips in the spectral curve of lines in the absorption
Modern Astronomy Review #1
 Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
The Physics of Light, part 2. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 7: The Physics of Light, part 2 Astronomy 111 Spectra Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are. Every type of atom, ion, and molecule has a unique spectrum Ion: an atom with electrons
Lecture 7: The Physics of Light, part 2 Astronomy 111 Spectra Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are. Every type of atom, ion, and molecule has a unique spectrum Ion: an atom with electrons
Today. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Stellar Spectra & Composition. Doppler Effect & Motion. Extrasolar Planets
 Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Reading for Meaning and the Electromagnetic Spectrum!
 Earth Science Zimmerman Name: Period: Reading for Meaning and the Electromagnetic Spectrum! HOOK: An astronomer discovers a new galaxy. How can the Doppler Effect be applied to determine if that galaxy
Earth Science Zimmerman Name: Period: Reading for Meaning and the Electromagnetic Spectrum! HOOK: An astronomer discovers a new galaxy. How can the Doppler Effect be applied to determine if that galaxy
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Learning Objectives! What is Electromagnetic Radiation?! What are spectra? How could we measure a spectrum?! How do wavelengths correspond to colors for optical light? Does
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Learning Objectives! What is Electromagnetic Radiation?! What are spectra? How could we measure a spectrum?! How do wavelengths correspond to colors for optical light? Does
The Universe. 3. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents the bright-line spectrum for an element.
 A) B) The Universe 1. According to the Big Bang theory, which graph hest represents the relationship between time and the size of the universe from the beginning of the universe to the present? C) D) 2.
A) B) The Universe 1. According to the Big Bang theory, which graph hest represents the relationship between time and the size of the universe from the beginning of the universe to the present? C) D) 2.
Temperature and Radiation. What can we learn from light? Temperature, Heat, or Thermal Energy? Kelvin Temperature Scale
 What can we learn from light? Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the spectrum! Temperature and Radiation Why do different objects give off different forms of
What can we learn from light? Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the spectrum! Temperature and Radiation Why do different objects give off different forms of
Light carries energy. Lecture 5 Understand Light. Is light. Light as a Particle. ANSWER: Both.
 Light carries energy Lecture 5 Understand Light Reading: Chapter 6 You feel energy carried by light when light hits your skin. Energy Conservation: Radiation energy will be given to molecules making your
Light carries energy Lecture 5 Understand Light Reading: Chapter 6 You feel energy carried by light when light hits your skin. Energy Conservation: Radiation energy will be given to molecules making your
Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos
 Chapter 5 Lecture Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience
Chapter 5 Lecture Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience
Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. White light is made up of many different colors. Interactions of Light with Matter
 Chapter 5 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact?
Chapter 5 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact?
Temperature and Radiation. What can we learn from light? Temperature, Heat, or Thermal Energy? Kelvin Temperature Scale
 What can we learn from light? Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the spectrum! Temperature and Radiation Why do different objects give off different forms of
What can we learn from light? Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the spectrum! Temperature and Radiation Why do different objects give off different forms of
DOPPLER EFFECT FOR LIGHT DETECTING MOTION IN THE UNIVERSE HUBBLE S LAW
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DOPPLER EFFECT FOR LIGHT DETECTING MOTION IN THE UNIVERSE HUBBLE S LAW Motion in the Universe Stars and interstellar gas are bound by gravity to form galaxies, and groups of galaxies
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DOPPLER EFFECT FOR LIGHT DETECTING MOTION IN THE UNIVERSE HUBBLE S LAW Motion in the Universe Stars and interstellar gas are bound by gravity to form galaxies, and groups of galaxies
Lecture 8: What we can learn via light
 Lecture 8: What we can learn via light As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. Lecture 8: What we can learn
Lecture 8: What we can learn via light As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. Lecture 8: What we can learn
Miami Dade County Public Schools Educational Transformation Office and the Division of Academics: Department of Science
 Unit 5 Assessment Comprehensive Science III Directions: Read through the questions carefully and select the best answer choice on your bubble sheet. 1. Space exploration has advanced our knowledge of the
Unit 5 Assessment Comprehensive Science III Directions: Read through the questions carefully and select the best answer choice on your bubble sheet. 1. Space exploration has advanced our knowledge of the
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. How do we experience light? Colors of Light. How do light and matter interact?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. 5.1 Light in Everyday Life. How do we experience light?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
TPS. How many Exoplanets have been discovered to date? A B C D
 TPS How many Exoplanets have been discovered to date? A. 1-10 B. 11-100 C. 101-500 D. 501-1000 ExoPlanets Objectives What are Exoplanets How do we find Exoplanets How do Exoplanets compare to our solar
TPS How many Exoplanets have been discovered to date? A. 1-10 B. 11-100 C. 101-500 D. 501-1000 ExoPlanets Objectives What are Exoplanets How do we find Exoplanets How do Exoplanets compare to our solar
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
 Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Midterm Review #3-2018
 1. The reaction below represents an energy-producing process. The reaction represents how energy is produced A) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere B) during nuclear decay C) from the movement of
1. The reaction below represents an energy-producing process. The reaction represents how energy is produced A) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere B) during nuclear decay C) from the movement of
Galaxies and Cosmology
 4/28/17 The Discovery of Galaxies Up to the 1920 s, astronomers were not sure exactly how far away galaxies were, and thus didn t know how big they are! Spiral Nebulae could be assumed to be inside our
4/28/17 The Discovery of Galaxies Up to the 1920 s, astronomers were not sure exactly how far away galaxies were, and thus didn t know how big they are! Spiral Nebulae could be assumed to be inside our
Lecture 7. Outline. ASTR 111 Section 002. Discuss Quiz 5 Light. Light travels through empty space at a speed of 300,000 km/s
 Lecture 7 ASTR 111 Section 002 Outline Discuss Quiz 5 Light Suggested reading: Chapter 5.1-5.2 and 5.6-5.8 of textbook Light travels through empty space at a speed of 300,000 km/s In 1676, Danish astronomer
Lecture 7 ASTR 111 Section 002 Outline Discuss Quiz 5 Light Suggested reading: Chapter 5.1-5.2 and 5.6-5.8 of textbook Light travels through empty space at a speed of 300,000 km/s In 1676, Danish astronomer
1. The symbols below represent the Milky Way galaxy, the solar system, the Sun, and the universe.
 Name Date 1. The symbols below represent the Milky Way galaxy, the solar system, the Sun, and the universe. 4. The diagram below illustrates three stages of a current theory of the formation of the universe.
Name Date 1. The symbols below represent the Milky Way galaxy, the solar system, the Sun, and the universe. 4. The diagram below illustrates three stages of a current theory of the formation of the universe.
o Terms to know o Big Bang Theory o Doppler Effect o Redshift o Universe
 Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Coriolis Effect - the apparent curved paths of projectiles, winds, and ocean currents
 Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Daily Science 04/04/2017
 Daily Science 04/04/2017 Which statement best describes the difference between type A stars and type B stars as shown in the diagram? a. Type A stars burn for a shorter amount of time than type B stars.
Daily Science 04/04/2017 Which statement best describes the difference between type A stars and type B stars as shown in the diagram? a. Type A stars burn for a shorter amount of time than type B stars.
3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was. Timeline of Events 4. This outward expansion
 NOTES BB.notebook The Universe started as a single point of highly concentrated matter 3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was extremely dense Density: the amount of mass contained in a certain
NOTES BB.notebook The Universe started as a single point of highly concentrated matter 3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was extremely dense Density: the amount of mass contained in a certain
Next Homework Due Oct. 9. Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10)
 Today Summary of Chapter 3: Light All of Chapter 4: Spectra & Atoms Optional: Ast. Toolbox 4-2 Optional: Stephan-Boltzmann Law Next Homework Due Oct. 9 Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10) Resolving Power:
Today Summary of Chapter 3: Light All of Chapter 4: Spectra & Atoms Optional: Ast. Toolbox 4-2 Optional: Stephan-Boltzmann Law Next Homework Due Oct. 9 Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10) Resolving Power:
Learning Objectives. distances to objects in our Galaxy and to other galaxies? apparent magnitude key to measuring distances?
 The Distance Ladder Learning Objectives! What is the distance ladder? How do we measure distances to objects in our Galaxy and to other galaxies?! How are the concepts of absolute magnitude and apparent
The Distance Ladder Learning Objectives! What is the distance ladder? How do we measure distances to objects in our Galaxy and to other galaxies?! How are the concepts of absolute magnitude and apparent
X Rays must be viewed from space used for detecting exotic objects such as neutron stars and black holes also observing the Sun.
 6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
AY2 Winter 2017 Midterm Exam Prof. C. Rockosi February 14, Name and Student ID Section Day/Time
 AY2 Winter 2017 Midterm Exam Prof. C. Rockosi February 14, 2017 Name and Student ID Section Day/Time Write your name and student ID number on this printed exam, and fill them in on your Scantron form.
AY2 Winter 2017 Midterm Exam Prof. C. Rockosi February 14, 2017 Name and Student ID Section Day/Time Write your name and student ID number on this printed exam, and fill them in on your Scantron form.
Telescopes have Three Powers
 Telescopes have Three Powers 1. Light Gathering Power: The ability to collect light 2. Resolving Power: The ability to see fine details 3. Magnifying Power: The ability to make objects look bigger Pizzas!!!
Telescopes have Three Powers 1. Light Gathering Power: The ability to collect light 2. Resolving Power: The ability to see fine details 3. Magnifying Power: The ability to make objects look bigger Pizzas!!!
What are the three basic types of spectra?
 Learning from Light Our goals for learning What are the three basic types of spectra? How does light tell us what things are made of? How does light tell us the temperatures of planets and stars? How do
Learning from Light Our goals for learning What are the three basic types of spectra? How does light tell us what things are made of? How does light tell us the temperatures of planets and stars? How do
Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger 5.1 Basic Properties of Light and Matter Our goals for learning: What is light? What is matter? How do light and matter interact? What is light? Light is an electromagnetic
Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger 5.1 Basic Properties of Light and Matter Our goals for learning: What is light? What is matter? How do light and matter interact? What is light? Light is an electromagnetic
Midterm Exam. IT Posting scores Finding out about missed questions Reminder about dropping lowest of 3
 Midterm Exam #&%?@)#$! IT Posting scores Finding out about missed questions Reminder about dropping lowest of 3 Nature of Light 10/3 Apparent versus Actual Brightness 10/6 Electromagnetic Spectrum of Light
Midterm Exam #&%?@)#$! IT Posting scores Finding out about missed questions Reminder about dropping lowest of 3 Nature of Light 10/3 Apparent versus Actual Brightness 10/6 Electromagnetic Spectrum of Light
Light: Transverse WAVE
 Light Longitudinal WAVES Light: Transverse WAVE Light: Particle or wave Photon The Wave Nature of Light 1. Unlike other branches of science, astronomers cannot touch or do field work on their samples.
Light Longitudinal WAVES Light: Transverse WAVE Light: Particle or wave Photon The Wave Nature of Light 1. Unlike other branches of science, astronomers cannot touch or do field work on their samples.
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Final Exam Review Problems Revision 2
 Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Final Exam Review Problems Revision 2 Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Final Exam Review Problems Revision 2 Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct
Chapter 6. Atoms and Starlight
 Chapter 6 Atoms and Starlight What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and Frequency wavelength frequency = speed of light = constant Particles of Light Particles of light are called
Chapter 6 Atoms and Starlight What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and Frequency wavelength frequency = speed of light = constant Particles of Light Particles of light are called
29.2 M E A S U R I N G T H E S T A R S
 29.2 M E A S U R I N G T H E S T A R S MAIN IDEA Stellar classification is based on measurement of light, spectra, temperature, and composition Describe the star life cycle Birth of a Star If enough matter
29.2 M E A S U R I N G T H E S T A R S MAIN IDEA Stellar classification is based on measurement of light, spectra, temperature, and composition Describe the star life cycle Birth of a Star If enough matter
Characteristics of Stars
 Characteristics of Stars This section explains how astronomers measure distances to stars. It also describes how stars are classified. Use Target Reading Skills As you read about stars, stop and write
Characteristics of Stars This section explains how astronomers measure distances to stars. It also describes how stars are classified. Use Target Reading Skills As you read about stars, stop and write
Next Homework Due March 6. Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10)
 Today Summary of Chapter 3: Light All of Chapter 4: Spectra & Atoms Optional: Ast. Toolbox 4-2 Optional: Stephan-Boltzmann Law Next Homework Due March 6 Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10) Extra Credit Astro-talks:
Today Summary of Chapter 3: Light All of Chapter 4: Spectra & Atoms Optional: Ast. Toolbox 4-2 Optional: Stephan-Boltzmann Law Next Homework Due March 6 Coming up: The Sun (Chapter 10) Extra Credit Astro-talks:
Lights. And God said, "Let there be light"; and there was light. And God saw that the light was good; (Bible: Genesis I)
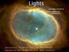 Lights Astronomy is based on observing lights from celestial bodies. And God said, "Let there be light"; and there was light. And God saw that the light was good; (Bible: Genesis I) Cat's Eye planetary
Lights Astronomy is based on observing lights from celestial bodies. And God said, "Let there be light"; and there was light. And God saw that the light was good; (Bible: Genesis I) Cat's Eye planetary
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)
 Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Lecture Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1
 Lecture 13+14 Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1 Important Concepts for Understanding Spectra Electromagnetic Spectrum Continuous Spectrum Absorption Spectrum Emission Spectrum Emission line Wavelength, Frequency
Lecture 13+14 Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1 Important Concepts for Understanding Spectra Electromagnetic Spectrum Continuous Spectrum Absorption Spectrum Emission Spectrum Emission line Wavelength, Frequency
27.1: Characteristics of Stars
 27.1: Characteristics of Stars STAR NOTES: Part 1 What is a Star? A body of gases that gives off energy in the form of light and heat. 27.1: Characteristics of Stars Are all stars the same? No 1. Stars
27.1: Characteristics of Stars STAR NOTES: Part 1 What is a Star? A body of gases that gives off energy in the form of light and heat. 27.1: Characteristics of Stars Are all stars the same? No 1. Stars
Project: Hubble Diagrams
 Project: Hubble Diagrams Distances Exercise 1 In this exercise, you will find the magnitudes of six galaxies in the SDSS database. The table below shows the object IDs and positions (right ascension and
Project: Hubble Diagrams Distances Exercise 1 In this exercise, you will find the magnitudes of six galaxies in the SDSS database. The table below shows the object IDs and positions (right ascension and
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 5.1 Our Sun in Ultraviolet Light. This photograph of the Sun was taken at several different wavelengths of ultraviolet, which
ASTRONOMY Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 5.1 Our Sun in Ultraviolet Light. This photograph of the Sun was taken at several different wavelengths of ultraviolet, which
Mass-Luminosity and Stellar Lifetimes WS
 Name Mass-Luminosity and Stellar Lifetimes WS The graph shows the Mass-Luminosity Relationship for main sequence stars. Use it to answer questions 1-3. 1) A star with a mass of 0.5 solar masses would be
Name Mass-Luminosity and Stellar Lifetimes WS The graph shows the Mass-Luminosity Relationship for main sequence stars. Use it to answer questions 1-3. 1) A star with a mass of 0.5 solar masses would be
c = l Light: The Cosmic Messenger 1/23/18
 Reading for today s and Thur class: ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 3 Tues 23 Jan 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
Reading for today s and Thur class: ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 3 Tues 23 Jan 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
Assignments. For Wed. 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial)
 Assignments For Wed. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial) 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12 Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger Which forms of light are lower in energy and frequency than the
Assignments For Wed. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial) 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12 Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger Which forms of light are lower in energy and frequency than the
Light is a wave. Light is also a particle! 3/23/09
 Wavelength (λ) is the distance between successive peaks of a wave Frequency (ν) is the number of wave peaks that pass by an observer per second λ ν = the speed of a wave ( = c, for light) Light is a wave
Wavelength (λ) is the distance between successive peaks of a wave Frequency (ν) is the number of wave peaks that pass by an observer per second λ ν = the speed of a wave ( = c, for light) Light is a wave
... Explain how an orbiting planet causes a Doppler shift in the spectrum of a star
 Q1.In 1999 a planet was discovered orbiting a star in the constellation of Pegasus. (a) State one reason why it is difficult to make a direct observation of this planet..... (1) The initial discovery of
Q1.In 1999 a planet was discovered orbiting a star in the constellation of Pegasus. (a) State one reason why it is difficult to make a direct observation of this planet..... (1) The initial discovery of
Astronomy 210 Spring 2017: Quiz 5 Question Packet 1. can: 2. An electron moving between energy levels
 Permitted energy levels Astronomy 210 Spring 2017: Quiz 5 Question Packet 1 1. An electron in energy level 1 2 can: (A) only emit a photon. (B) only absorb a photon. (C) either emit, or absorb a photon.
Permitted energy levels Astronomy 210 Spring 2017: Quiz 5 Question Packet 1 1. An electron in energy level 1 2 can: (A) only emit a photon. (B) only absorb a photon. (C) either emit, or absorb a photon.
! Finish Ch. 4.! Start Chapter 10: The Sun.! Homework Due: Oct. 10
 ! Finish Ch. 4! Start Chapter 10: The Sun! Homework Due: Oct. 10 A Spectral Mystery Mystery: Why do so many stars have an absorption spectrum (with certain colors missing)? The atoms that make up these
! Finish Ch. 4! Start Chapter 10: The Sun! Homework Due: Oct. 10 A Spectral Mystery Mystery: Why do so many stars have an absorption spectrum (with certain colors missing)? The atoms that make up these
18 An Eclipsing Extrasolar Planet
 Name: Date: 18 An Eclipsing Extrasolar Planet 18.1 Introduction One of the more recent new fields in astronomy is the search for (and discovery of) planets orbiting around stars other than our Sun, or
Name: Date: 18 An Eclipsing Extrasolar Planet 18.1 Introduction One of the more recent new fields in astronomy is the search for (and discovery of) planets orbiting around stars other than our Sun, or
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name
 ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
Name Date Period. 10. convection zone 11. radiation zone 12. core
 240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
The Cosmic Distance Ladder. Hubble s Law and the Expansion of the Universe!
 The Cosmic Distance Ladder Hubble s Law and the Expansion of the Universe! Last time: looked at Cepheid Variable stars as standard candles. Massive, off-main sequence stars: at a certain stage between
The Cosmic Distance Ladder Hubble s Law and the Expansion of the Universe! Last time: looked at Cepheid Variable stars as standard candles. Massive, off-main sequence stars: at a certain stage between
= λ. Light: The Cosmic Messenger. Continuing Topics for Today 1/24/17. Your account on Mastering Astronomy. ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies
 REMINDER Your account on Mastering Astronomy ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 3 Tues 24 Jan 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
REMINDER Your account on Mastering Astronomy ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 3 Tues 24 Jan 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
The Amazing Power of Starlight
 The Amazing Power of Starlight Chapter 6 Just by analyzing the light received from a star, astronomers can retrieve information about a star s Starlight and Atoms 1. Total energy output 2. Surface temperature
The Amazing Power of Starlight Chapter 6 Just by analyzing the light received from a star, astronomers can retrieve information about a star s Starlight and Atoms 1. Total energy output 2. Surface temperature
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Student Guide From Molecular Cores to Stars
 Team Members: Date: Student Guide From Molecular Cores to Stars Dust Hunt Driving Question: What are the characteristics of dust in our classroom, and how did it get here? Science Objectives: 1. Collect
Team Members: Date: Student Guide From Molecular Cores to Stars Dust Hunt Driving Question: What are the characteristics of dust in our classroom, and how did it get here? Science Objectives: 1. Collect
Spectroscopy in Motion: A Method to Measure Velocity
 Name Partner(s) Date Spectroscopy in Motion: A Method to Measure Velocity Did you ever hear a train whistle or truck on a highway as it approaches you and then passes at a high rate of speed? Go to and
Name Partner(s) Date Spectroscopy in Motion: A Method to Measure Velocity Did you ever hear a train whistle or truck on a highway as it approaches you and then passes at a high rate of speed? Go to and
Measuring Motion, Doppler Effect 22 Oct
 Measuring Motion, Doppler Effect 22 Oct Where are the elements in the baby created? Measuring motion Where were the elements in the baby made? Lighter elements (He, O, C, Ne, Mg, etc) are made by fusion
Measuring Motion, Doppler Effect 22 Oct Where are the elements in the baby created? Measuring motion Where were the elements in the baby made? Lighter elements (He, O, C, Ne, Mg, etc) are made by fusion
Announcement Test 2. is coming up on Mar 19. Start preparing! This test will cover the classes from Feb 27 - Mar points, scantron, 1 hr.
 Announcement Test 2 is coming up on Mar 19. Start preparing! This test will cover the classes from Feb 27 - Mar 14. 50 points, scantron, 1 hr. 1 AST 103 Light, Atoms, and Spectra (continued) Analyzing
Announcement Test 2 is coming up on Mar 19. Start preparing! This test will cover the classes from Feb 27 - Mar 14. 50 points, scantron, 1 hr. 1 AST 103 Light, Atoms, and Spectra (continued) Analyzing
13 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 13 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ EXTRASOLAR PLANETS? DO PLANETS ORBIT AROUND OTHER STARS? WE WOULD
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 13 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ EXTRASOLAR PLANETS? DO PLANETS ORBIT AROUND OTHER STARS? WE WOULD
Sun Building Activity 2 The Signature of the Stars
 Sun Building The Signature of the Stars Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours
Sun Building The Signature of the Stars Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours
Astro 3 Lab Exercise
 Astro 3 Lab Exercise Lab #4: Measuring Redshifts of Galaxies Dates: August 5 6 Lab Report due: 5 pm Friday August 15 Summer 2014 1 Introduction This project involves measuring the redshifts of distant
Astro 3 Lab Exercise Lab #4: Measuring Redshifts of Galaxies Dates: August 5 6 Lab Report due: 5 pm Friday August 15 Summer 2014 1 Introduction This project involves measuring the redshifts of distant
Chapter 4. Spectroscopy. Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah
 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
8-1. Chapter 8 THE DOPPLER EFFECTS OF SOUND AND LIGHT. motion. These are the classical and empirical Doppler effects of sound waves, and the
 8-1 Chapter 8 THE DOPPLER EFFECTS OF SOUND AND LIGHT The classical and empirical Doppler Effects of sound and of light both depend upon: 1) relative motion between the source body (which is emitting the
8-1 Chapter 8 THE DOPPLER EFFECTS OF SOUND AND LIGHT The classical and empirical Doppler Effects of sound and of light both depend upon: 1) relative motion between the source body (which is emitting the
Semester 1 Final Exam Review
 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Concept Check To see the greatest number of stars possible throughout the period of one year, a person should be located at latitude a) 90 degrees. b) 45 degrees. c) 0 degrees.
Semester 1 Final Exam Review Concept Check To see the greatest number of stars possible throughout the period of one year, a person should be located at latitude a) 90 degrees. b) 45 degrees. c) 0 degrees.
OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW S1. This question is about the nature of certain stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and determining
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW S1. This question is about the nature of certain stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and determining
The Theory of Electromagnetism
 Notes: Light The Theory of Electromagnetism James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Scottish physicist. Found that electricity and magnetism were interrelated. Moving electric charges created magnetism, changing
Notes: Light The Theory of Electromagnetism James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Scottish physicist. Found that electricity and magnetism were interrelated. Moving electric charges created magnetism, changing
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems
 Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct for each
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct for each
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam
 Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Test ABCDE. 1. What is the oldest era on the geological timescale? A. Precambrian B. Paleozoic C. Mesozoic D. Cenozoic
 Test - 8.8 ABCDE 1. What is the oldest era on the geological timescale? A. Precambrian B. Paleozoic C. Mesozoic D. Cenozoic 2. A light-year is defined as- F. the distance from Earth to the Sun. G. the
Test - 8.8 ABCDE 1. What is the oldest era on the geological timescale? A. Precambrian B. Paleozoic C. Mesozoic D. Cenozoic 2. A light-year is defined as- F. the distance from Earth to the Sun. G. the
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description.
 Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description. 1. The main force responsible for the formation of the universe is: a. Gravity b. Frictional force c. Magnetic force
Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description. 1. The main force responsible for the formation of the universe is: a. Gravity b. Frictional force c. Magnetic force
Light and Atoms. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies !ATH REVIEW: #AST CLASS: "OMEWORK #1
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!ATH REVIEW: Tonight, 5-6pm, in RAMY N1B23 "OMEWORK #1 -Due THU, Sept. 10, by 5pm, on Mastering Astronomy CLASS RECORDED STARTED - INFO WILL BE POSTED on CULEARN
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!ATH REVIEW: Tonight, 5-6pm, in RAMY N1B23 "OMEWORK #1 -Due THU, Sept. 10, by 5pm, on Mastering Astronomy CLASS RECORDED STARTED - INFO WILL BE POSTED on CULEARN
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4)
 Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
Astronomy Part 1 Regents Questions
 Regents Questions 1. The Sun revolves around the center of A) Polaris B) Aldebaran C) Earth D) the Milky Way Galaxy 4. In which sequence are the items listed from least total mass to greatest total mass?
Regents Questions 1. The Sun revolves around the center of A) Polaris B) Aldebaran C) Earth D) the Milky Way Galaxy 4. In which sequence are the items listed from least total mass to greatest total mass?
OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: # Marks: XX Raw Score: IB Curve: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW S1. This question is about the nature of certain stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: # Marks: XX Raw Score: IB Curve: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW S1. This question is about the nature of certain stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell
Unusual orbits in the Andromeda galaxy Post-16
 Unusual orbits in the Andromeda galaxy Post-16 Topics covered: spectra, Doppler effect, Newton s law of gravitation, galaxy rotation curves, arc lengths, cosmological units, dark matter Teacher s Notes
Unusual orbits in the Andromeda galaxy Post-16 Topics covered: spectra, Doppler effect, Newton s law of gravitation, galaxy rotation curves, arc lengths, cosmological units, dark matter Teacher s Notes
(in case you missed it yesterday ) Merger of Two Neutron Stars!
 (in case you missed it yesterday ) Merger of Two Neutron Stars! https://cmns.umd.edu/news-events/features/3997 More on this later in the semester Lecture #14: Plan Light (cont d) Atomic physics Formation
(in case you missed it yesterday ) Merger of Two Neutron Stars! https://cmns.umd.edu/news-events/features/3997 More on this later in the semester Lecture #14: Plan Light (cont d) Atomic physics Formation
Which letter on the timeline best represents the time when scientists estimate that the Big Bang occurred? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. The red shift of light from most galaxies is evidence that A) most galaxies are moving away from Earth B) a majority of stars in most galaxies are red giants C) the light slows down as it nears Earth
1. The red shift of light from most galaxies is evidence that A) most galaxies are moving away from Earth B) a majority of stars in most galaxies are red giants C) the light slows down as it nears Earth
1. This question is about Hubble s law. The light received from many distant galaxies is red-shifted. (a) State the cause of this red-shift (1)
 ROUND 2 - QUESTIONS 1. This question is about Hubble s law. The light received from many distant galaxies is red-shifted. (a) State the cause of this red-shift (1) expanding universe (b) State Hubble s
ROUND 2 - QUESTIONS 1. This question is about Hubble s law. The light received from many distant galaxies is red-shifted. (a) State the cause of this red-shift (1) expanding universe (b) State Hubble s
The Formation of the Solar System
 Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Astronomy 102 Lab: Hubble Law
 Name: Astronomy 102 Lab: Hubble Law Part of today s lab will involve the use of laptops. If you own one, please bring it to class. Pre-Lab Assignment: In this week's lab, you will study the expansion of
Name: Astronomy 102 Lab: Hubble Law Part of today s lab will involve the use of laptops. If you own one, please bring it to class. Pre-Lab Assignment: In this week's lab, you will study the expansion of
PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives
 PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives April 6, 2008 1 Introduction This list of questions are questions that will need to be answered in order for students to be successful in the course. Each
PH104 Descriptive Astronomy Learning Objectives April 6, 2008 1 Introduction This list of questions are questions that will need to be answered in order for students to be successful in the course. Each
Star Gazing. Part 1. Name: What do you know about stars? Is the Sun a star? Why do we only see some stars at night?
 Star Gazing Name: Part 1 What do you know about stars? Is the Sun a star? Why do we only see some stars at night? Castor Betelgeuse Rigel Pollux Procyon Sirius The picture above shows the stars as seen
Star Gazing Name: Part 1 What do you know about stars? Is the Sun a star? Why do we only see some stars at night? Castor Betelgeuse Rigel Pollux Procyon Sirius The picture above shows the stars as seen
The Doppler Effect is the change in frequency observed when a source of sound waves is moving relative to an observer.
 Doppler Effect The Doppler Effect is the change in frequency observed when a source of sound waves is moving relative to an observer. Examples of the Doppler effect are: Hearing an increase in a car horn
Doppler Effect The Doppler Effect is the change in frequency observed when a source of sound waves is moving relative to an observer. Examples of the Doppler effect are: Hearing an increase in a car horn
13.3 Spectra of Stars
 13.3 Spectra of Stars A star's spectrum depicts the energy it emits at each wavelength and is perhaps the single most important thing we can know about the star. From the spectrum we can find the star's
13.3 Spectra of Stars A star's spectrum depicts the energy it emits at each wavelength and is perhaps the single most important thing we can know about the star. From the spectrum we can find the star's
Stars and Galaxies. The Sun and Other Stars
 CHAPTER 22 Stars and Galaxies LESSON 2 The Sun and Other Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
CHAPTER 22 Stars and Galaxies LESSON 2 The Sun and Other Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
Earth in Space. The Sun-Earth-Moon System
 in Space The --Moon System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if
in Space The --Moon System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if
Killer Skies. HW 10/Moon Report due today Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: Galaxies Collide Today: Hubble s Law
 Killer Skies HW 10/Moon Report due today Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: Galaxies Collide Today: Hubble s Law Music: The Universe is You Sophie Ellis-Bextor 1 Hour Exam 3 Hour Exam 3 Wed, Dec 11th, in class
Killer Skies HW 10/Moon Report due today Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: Galaxies Collide Today: Hubble s Law Music: The Universe is You Sophie Ellis-Bextor 1 Hour Exam 3 Hour Exam 3 Wed, Dec 11th, in class
