sin u 5 opp } cos u 5 adj } hyp opposite csc u 5 hyp } sec u 5 hyp } opp Using Inverse Trigonometric Functions
|
|
|
- Andrew Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13 Big Idea 1 CHAPTER SUMMARY BIG IDEAS Using Trigonometric Fnctions Algebra classzone.com Electronic Fnction Library For Yor Notebook hypotense acent osite sine cosine tangent sin 5 hyp cos 5 hyp tan 5 cosecant secant cotangent csc 5 hyp sec 5 hyp cot 5 Big Idea Using Inverse Trigonometric Fnctions Inverse trigonometric fnctions can be sed to solve trigonometric eqations. If 1 a 1, then the inverse sine of a is an angle, written sin 1 a 5, where sin 5 a and p p. If 1 a 1, then the inverse cosine of a is an angle, written cos 1 a 5, where cos 5 a and 0 π. If a is any real nmber, then the inverse tangent of a is an angle, written tan 1 a 5, where tan 5 a and p < < p sin cos1 Ï tan1 Ï Big Idea 3 Applying the Law of Sines and Law of Cosines Use the table below to help yo remember when to apply each law. If yo know this information... se this law... to find this information. angle-angle-side Law of sines remaining sides* angle-side-angle Law of sines remaining sides* side-side-angle Law of sines remaining side and one angle* side-angle-side Law of cosines remaining side and one angle* side-side-side Law of cosines two angles* * Find the remaining angle by sing the triangle sm theorem. Chapter Smmary 897 npe-1380.indd /16/05 1:34:16 PM
2 13 CHAPTER REVIEW REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY classzone.com Mlti-Langage Glossary Vocablary practice sine, p. 85 cosine, p. 85 tangent, p. 85 cosecant, p. 85 secant, p. 85 cotangent, p. 85 angle of elevation, p. 855 angle of depression, p. 855 initial side of an angle, p. 859 terminal side of an angle, p. 859 standard position of an angle, p. 859 coterminal angles, p. 860 radian, p. 860 sector, p. 861 central angle, p. 861 nit circle, p. 867 qadrantal angle, p. 867 reference angle, p. 868 inverse sine, p. 875 inverse cosine, p. 875 inverse tangent, p. 875 law of sines, p. 88 law of cosines, p. 889 VOCABULARY 1. WRITING Describe an angle in standard position.. Identify the relationship between the angles 58 and What is the name of a circle with center at the origin and radis 1 nit? 4. Copy and complete: If cos 5 a and 0 π, then the? of a eqals. 5. WRITING State the law of sines in words. REVIEW EXAMPLES AND Use the review examples and exercises below to check yor nderstanding of the concepts yo have learned in each lesson of Chapter Use Trigonometry with Right Triangles pp Evalate the six trigonometric fnctions of the angle. From the Pythagorean theorem, the length of the hypotense is Ï Ï sin 5 hyp csc 5 hyp cos 5 hyp sec 5 hyp tan cot EXAMPLES 1 and 3 on pp for Exs In n ABC, a 5 4, b 5 5, and C Evalate the six trigonometric fnctions of angle B. 7. HOT AIR BALLOON Yo are standing 50 meters from a hot air balloon that is preparing to take off. The angle of elevation to the top of the balloon is 88. Find the height of the balloon. 898 Chapter 13 Trigonometric Ratios and Fnctions npe-1380.indd /16/05 1:34:19 PM
3 classzone.com Chapter Review Practice 13. Define General Angles and Use Radian Measre pp Convert 1108 to radians and 7p radians to degrees p radians 7p 1808 radians 5 1 7p radians p radians p radians EXAMPLE 3 on p. 861 for Exs Convert the degree measre to radians or the radian measre to degrees p p Evalate Trigonometric Fnctions of Any Angle pp Evalate sec 08. The reference angle is The secant fnction is negative in Qadrant II, so yo can write: sec 08 5 sec EXAMPLE 4 on p. 869 for Exs. 15 Evalate the fnction withot sing a calclator.. tan csc (4058) 14. sin 13p sec 11p Evalate Inverse Trigonometric Fnctions pp Evalate tan 1 1 in both radians and degrees. When p < < p, or 908 < < 908, the angle whose tangent is 1 is: 5 tan p 4 or 5 tan EXAMPLES 1 and 4 on pp for Exs Evalate sin 1 (0.5) in both radians and degrees. 17. RAMP Yo se a foot ramp to load items into a van. If the floor of the van is 4 feet off the grond, what is the angle of elevation of the ramp? Chapter Review 899 npe-1380.indd /16/05 1:34:1 PM
4 CHAPTER REVIEW Apply the Law of Sines pp Solve n ABC with A 5 88, C 5 748, and b 5. Find angle B: B Use the law of sines to solve for a and c. a sin 88 5 sin 788 c sin sin 788 a 5 sin 88 ø 10.6 c 5 sin 748 ø 1.6 sin 788 sin 788 c For n ABC, B 5 788, a ø 10.6, and c ø 1.6. A b 5 88 c C 748 a B EXAMPLES 1,, 3 and 4 on pp for Exs Solve n ABC. (Hint: Some of the triangles may have no soltion and some may have two soltions.) 18. A 5 438, C 5 838, b B , b 5 5, c C 5 558, a 5 17, c B 5 608, C 5 738, b Apply the Law of Cosines pp Solve n ABC with A 5 668, b 5 16, and c 5 1. Use the law of cosines to find the length a. a 5 b 1 c bc cos A a (16)(1) cos 668 a ø 43.7 a ø 0.6 Now find angle B and angle C. sin B 16 5 sin sin B 5 16 sin 668 ø B 5 sin ø 45.8 C ø ø c For n ABC, B ø 45.8, C ø 68.88, and a ø 0.6. C b A c 5 1 B EXAMPLES 1 and on pp for Exs. 4 Solve n ABC.. a 5 19, b 5 11, c B 5 758, a 5 0, c a 5 30, b 5 35, c Chapter 13 Trigonometric Ratios and Fnctions npe-1380.indd /16/05 1:34:4 PM
5 13 CHAPTER TEST Evalate the six trigonometric fnctions of the angle Convert the degree measre to radians or the radian measre to degrees p p 3 Evalate the fnction withot sing a calclator. 8. tan sec(4808) 10. sin1 5p cos 11p 6 Evalate the expression in both radians and degrees withot sing a calclator.. cos tan 1 Ï sin 1 Ï 15. cos 1 Ï 3 Solve nabc. (Hint: Some of the triangles may have no soltion and some may have two soltions.) 16. A 5 478, C 5 38, c a 5 4, b 5, c B 5 638, a 5 11, b C , a 5 3, b a 5 4, b 5 30, c A 5 68, B 5 778, c 5 50 Find the area of nabc.. A 5 818, b 5 16, c = a 5 8, b 5 6, c a 5 5, b 5 4, c C , a 5 7, b a 5 16, b 5 33, c B 5 618, a 5, c SURVEYING To measre the width of a river, yo plant a stake at point A on one side of the riverbank, directly across from a tree stmp at point B on the other side of the riverbank. From point A, yo walk 80 meters along the riverbank to point C. Yo find the measre of angle C to be 398. What is the width w of the river? 9. CONSTRUCTION A crane has a 00 foot arm with a lower end that is 5 feet off the grond. The arm has to reach to the top of a bilding that is 160 feet high. At what angle shold the arm be set? 30. NAVIGATION A boat travels 40 miles de west before trning 08 and traveling an additional 5 miles. How far is the boat from its point of departre? Chapter Test 901
6 13 Standardized TEST PREPARATION Scoring Rbric Fll Credit soltion is complete and correct Partial Credit soltion is complete bt has errors, or soltion is withot error bt incomplete No Credit no soltion is given, or soltion makes no sense SHORT RESPONSE QUESTIONS P ROBLEM According to the ADA Accessibility Gidelines, the maximm slope of a wheelchair ramp is 1 :. What is the maximm angle of elevation of an acceptable ramp? What is the angle of elevation of the ramp shown? Does the ramp shown meet the gidelines? Explain yor reasoning. Not drawn to scale Below are sample soltions to the problem. Read each soltion and the comments in ble to see why the sample represents fll credit, partial credit, or no credit. SAMPLE 1: Fll credit soltion The diagram, calclations, and reasoning are correct. The diagram and calclations are correct and clearly explained. A ramp with the maximm acceptable slope is shown. From the diagram, tan 5 1, so 5 tan1 1 ø The maximm angle of elevation is abot The length of the ramp given in the problem is 30 feet. The rise of this ramp is 18 inches, or feet. So, tan and tan ø.868. The ramp s angle of elevation is abot.868. Ramp meeting ADA gidelines 30 ft ft The answer is correct. The ramp given in the problem has an angle of elevation less than the maximm acceptable angle, so the ramp meets the ADA gidelines. SAMPLE : Partial credit soltion The maximm acceptable angle is correctly calclated. The stdent forgot to se the same nits when calclating slope, so the rest of the answers are incorrect. The slope of an acceptable ramp can be at most 1 :, so tan 5 1 where is the maximm angle. Therefore, 5 tan 1 1 ø The maximm angle of elevation for a wheelchair ramp is abot The slope of the ramp given in the problem is 18 30, so tan Therefore, 5 tan 1 18 ø The ramp s angle of elevation is abot The angle of elevation exceeds the maximm acceptable angle of elevation, so the ramp does not meet the gidelines. 90 Chapter 13 Trigonometric Ratios and Fnctions npe-1390.indd 90 10/14/05 4:17:8 PM
7 SAMPLE 3: Partial credit soltion The answer is correct and clearly explained, bt only one of the three qestions is answered. The rise is 18 inches. The rn is 30 feet, x8 or 30 ft p in inches. 18 in. 1 ft 360 in. Yo know the lengths of the sides osite and acent to the angle, so se the tangent ratio. tan x x 5 tan ø.868 The angle of elevation of the ramp given in the problem is abot.868. SAMPLE 4: No credit soltion The stdent confsed slope and angle measre, and did not answer the final qestion. The maximm slope of an acceptable wheelchair ramp is 1 :, so the maximm angle of elevation is 1 ø The slope of the ramp shown in the problem is 18 in. : 30 ft, or 1 : 0, so the angle of elevation is PRACTICE Apply the Scoring Rbric Use the rbric on page 90 to score the soltion to the problem below as fll credit, partial credit, or no credit. Explain yor reasoning. PROBLEM Find the volme of the right trianglar prism shown cm 6 cm 1. To find the prism s volme, mltiply the three given measres: 30(6)(67) 5,060 cm 3. To find the area of the base of the prism, first find the side lengths b and h shown in the diagram. h cm sin b 30 30(sin 678) 5 b cos h 30 30(cos 678) 5 h b Base of prism 7.6 ø b 11.7 ø h The area of the base is 1 bh 5 1 ( 7.6) (11.7) ø cm. The volme of the prism is (area of base)(height) (6) cm 3. Standardized Test Preparation 903 npe-1390.indd /14/05 4:17:34 PM
8 13 Standardized TEST PRACTICE SHORT RESPONSE 1. Kepler s second law states that an imaginary line connecting the center of a planet and the center of the sn sweeps ot eqal areas in eqal time intervals. The diagram below shows the location of Mars in orbit over a ten day period. 4. A tennis player is practicing her serve. She aims for a can placed 57 feet from her in the service box. If she hits the ball when it is 9 feet in the air, what angle mst the path of the ball make with the grond in order for the ball to hit the can s base? Assme the ball travels along a straight line. Explain yor answer. sn AU AU Mars (position 1) Mars (position ) a. Approximate the area Mars swept ot dring this time by finding the area of the triangle formed by the sn and the starting and ending positions of Mars. Give the answer in sqare miles. (Hint: 1 AU is 1 astronomical nit, which is eqal to abot 93 million miles.) b. As a planet moves closer to the sn along its orbit, what does Kepler s law imply abot the planet s speed? Explain.. The wheel of a nicycle completes 6 fll revoltions. a. Throgh what angle, in degrees and radians, has the wheel rotated? b. If the diameter of the wheel is 4 inches, how far does the nicycle travel in 6 wheel revoltions? Explain. 3. The table lists several tools sed to make vertical transitions from one point to a higher point. It also lists the recommended range of angles of elevation for each tool. If a certain task reqires making a vertical transition with a slope of 3, which tool wold be appropriate 5 for the task? Explain yor reasoning. Tool Range of angles Ramp Fixed steps Ladder stairs Portable stairs Fixed ladder The diagrams below show the distances between atoms in a water molecle in liqid and ice forms. The measrements are given in picometers (pm), where 1 pm 5 10 m. Are the obtse angles in the diagrams the same? Explain. 96 pm 101 pm 96 pm 101 pm pm 165 pm Liqid 6. Yo are standing 30 feet from the base of a tree. The angle of elevation from yor eyes to the top of the tree is 708. If the height at eye level is 5 feet, what is the height of the tree to the nearest foot? Explain all of yor steps. 7. Yo kick a soccer ball with an initial velocity of 40 feet per second at an angle of 458. Yor teammate kicks a soccer ball at an angle of 58. With what initial velocity does yor teammate have to kick the ball in order for both of the soccer balls to travel the same horizontal distance? Explain yor reasoning. 8. Find the radis r (in inches) and the central angle (in radians) of a sector with an arc length of 10p inches and an area of 5p 3 3 sqare inches. Explain yor reasoning. Ice 904 Chapter 13 Trigonometric Ratios and Fnctions npe-1390.indd /14/05 4:17:38 PM
9 STATE TEST PRACTICE classzone.com MULTIPLE CHOICE 9. Which angle measre is shown in the diagram? A C p 4 radians B 3p 4 radians 5p 4 radians D 3p radians 10. What is the approximate vale of a in n ABC if A 5 858, B 5 78, and c cm? A 1.0 cm C 5.9 cm y x B 5.4 cm D 11.0 cm 11. What is the reference angle for 3008? A 308 B 608 C 08 D 408 GRIDDED ANSWER. If is an acte angle of a right triangle and sin 5 3, what is the vale of cos? What angle, in degrees, is eqivalent to 5p 6 radians? 14. What is the vale of sin in degrees? 15. What is the area of the triangle, to the nearest tenth of a sqare nit? Let (10, 4) be a point on the terminal side of an angle in standard position. What is the vale of sec? 17. What is the degree measre of angle A in n ABC if a 5 13, b 5 9, and c 5 7? Rond yor answer to the nearest degree. 7 EXTENDED RESPONSE 18. A boat ses 50 feet of rope to drop anchor in a lake. The angle that the rope makes with the bottom of the lake is 08. a. Find the depth of the water. b. The boat moves to deeper water bt still lets ot the same amont of rope when dring anchor. If the horizontal distance from the boat to the anchor is 37 feet, what angle does the rope make with the lake bottom? c. Describe how changes as the boat travels to deeper water with a constant length of anchor rope let ot. Assme the rope is always tat. 19. Yo are making a lampshade ot of fabric for the lamp shown. The pattern for the lampshade is shown in the diagram on the left. a. Use the smaller sector to write an eqation that relates and x. b. Use the larger sector to write an eqation that relates and x c. Solve the system of eqations from parts (a) and (b) to find x and. d. Use the formla for the area of a sector to find the amont of fabric (in sqare inches) that yo will se. 5π in. 14π in. x 10 in. Standardized Test Practice 905 npe-1390.indd /14/05 4:17:4 PM
CC-32 Trigonometric Identities
 CC-32 Common Core State Standards MACC.92.F-TF.3.8 Prove the Pythagorean identity sin2(x) + cos2(x) and se it to find sin(x), cos(x), or tan(x), given sin(x), cos(x), or tan(x), and the qadrant of the
CC-32 Common Core State Standards MACC.92.F-TF.3.8 Prove the Pythagorean identity sin2(x) + cos2(x) and se it to find sin(x), cos(x), or tan(x), given sin(x), cos(x), or tan(x), and the qadrant of the
Trigonometric Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Evaluate trigonometric
4 Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Evaluate trigonometric
Trigonometric ratios:
 0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
Evaluate Inverse Trigonometric Functions. 5p, }} 13p, }}
 13.4 a.1, a.3, 2A.4.C; P.3.A TEKS Evalate Inverse Trigonometri Fntions Before Yo fond vales of trigonometri fntions given angles. Now Yo will find angles given vales of trigonometri fntions. Wh? So o an
13.4 a.1, a.3, 2A.4.C; P.3.A TEKS Evalate Inverse Trigonometri Fntions Before Yo fond vales of trigonometri fntions given angles. Now Yo will find angles given vales of trigonometri fntions. Wh? So o an
m = Average Rate of Change (Secant Slope) Example:
 Average Rate o Change Secant Slope Deinition: The average change secant slope o a nction over a particlar interval [a, b] or [a, ]. Eample: What is the average rate o change o the nction over the interval
Average Rate o Change Secant Slope Deinition: The average change secant slope o a nction over a particlar interval [a, b] or [a, ]. Eample: What is the average rate o change o the nction over the interval
Math 144 Activity #10 Applications of Vectors
 144 p 1 Math 144 Actiity #10 Applications of Vectors In the last actiity, yo were introdced to ectors. In this actiity yo will look at some of the applications of ectors. Let the position ector = a, b
144 p 1 Math 144 Actiity #10 Applications of Vectors In the last actiity, yo were introdced to ectors. In this actiity yo will look at some of the applications of ectors. Let the position ector = a, b
Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle θ? opp. hyp. opp. adj. sec θ = hyp. adj.
 . Right Triangle Trigonometry Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle? Consider one of the acute angles of a right triangle. Ratios of a right triangle s side lengths
. Right Triangle Trigonometry Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle? Consider one of the acute angles of a right triangle. Ratios of a right triangle s side lengths
Lesson 11-5: Trigonometric Ratios
 Math Regents Exam Questions - Pearson Integrated Algebra Lesson 11-5 Page 1 Lesson 11-5: Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Finding Trigonometric Ratios 1. 080414a, P.I. A.A.42 Which ratio represents cos A in
Math Regents Exam Questions - Pearson Integrated Algebra Lesson 11-5 Page 1 Lesson 11-5: Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Finding Trigonometric Ratios 1. 080414a, P.I. A.A.42 Which ratio represents cos A in
Triangles and Vectors
 Chapter 3 Triangles and Vectors As was stated at the start of Chapter 1, trigonometry had its origins in the study of triangles. In fact, the word trigonometry comes from the Greek words for triangle measurement.
Chapter 3 Triangles and Vectors As was stated at the start of Chapter 1, trigonometry had its origins in the study of triangles. In fact, the word trigonometry comes from the Greek words for triangle measurement.
Math 116 First Midterm October 14, 2009
 Math 116 First Midterm October 14, 9 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instrctor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam ntil yo are told to do so.. This exam has 1 pages inclding this cover. There are 9 problems. Note
Math 116 First Midterm October 14, 9 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instrctor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam ntil yo are told to do so.. This exam has 1 pages inclding this cover. There are 9 problems. Note
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Practice Test - Chapter 4
 Find the value of x. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. An acute angle measure and the length of the hypotenuse are given, so the sine function can be used to find the length of the side opposite.
Find the value of x. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. An acute angle measure and the length of the hypotenuse are given, so the sine function can be used to find the length of the side opposite.
Pre-calculus Notes: Chapter 5 The Trigonometric Functions. Use the word bank below to fill in the blanks below. You may use each term only once.
 Name: Pre-calculus Notes: Chapter 5 The Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Angles and Degree Measure Use the word bank below to fill in the blanks below. You may use each term only once. degree vertex negative
Name: Pre-calculus Notes: Chapter 5 The Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Angles and Degree Measure Use the word bank below to fill in the blanks below. You may use each term only once. degree vertex negative
CK- 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 1.1 Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse 1. 194. 6. 5 4. c = 10 5. 4 10 6. 6 5 7. Yes 8. No 9. No 10. Yes 11. No 1. No 1 1 1. ( b+ a)( a+ b) ( a + ab+ b ) 1 1 1 14. ab + c ( ab + c ) 15. Students must
1.1 Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse 1. 194. 6. 5 4. c = 10 5. 4 10 6. 6 5 7. Yes 8. No 9. No 10. Yes 11. No 1. No 1 1 1. ( b+ a)( a+ b) ( a + ab+ b ) 1 1 1 14. ab + c ( ab + c ) 15. Students must
Algebra II Standard Term 4 Review packet Test will be 60 Minutes 50 Questions
 Algebra II Standard Term Review packet 2017 NAME Test will be 0 Minutes 0 Questions DIRECTIONS: Solve each problem, choose the correct answer, and then fill in the corresponding oval on your answer document.
Algebra II Standard Term Review packet 2017 NAME Test will be 0 Minutes 0 Questions DIRECTIONS: Solve each problem, choose the correct answer, and then fill in the corresponding oval on your answer document.
2. Pythagorean Theorem:
 Chapter 4 Applications of Trigonometric Functions 4.1 Right triangle trigonometry; Applications 1. A triangle in which one angle is a right angle (90 0 ) is called a. The side opposite the right angle
Chapter 4 Applications of Trigonometric Functions 4.1 Right triangle trigonometry; Applications 1. A triangle in which one angle is a right angle (90 0 ) is called a. The side opposite the right angle
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Overview: 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure 4.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry 4.4 Trigonometric Functions of Any Angle 4.5 Graphs
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Overview: 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure 4.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry 4.4 Trigonometric Functions of Any Angle 4.5 Graphs
3.4-Miscellaneous Equations
 .-Miscellaneos Eqations Factoring Higher Degree Polynomials: Many higher degree polynomials can be solved by factoring. Of particlar vale is the method of factoring by groping, however all types of factoring
.-Miscellaneos Eqations Factoring Higher Degree Polynomials: Many higher degree polynomials can be solved by factoring. Of particlar vale is the method of factoring by groping, however all types of factoring
Solve Trigonometric Equations. Solve a trigonometric equation
 14.4 a.5, a.6, A..A; P.3.D TEKS Before Now Solve Trigonometric Equations You verified trigonometric identities. You will solve trigonometric equations. Why? So you can solve surface area problems, as in
14.4 a.5, a.6, A..A; P.3.D TEKS Before Now Solve Trigonometric Equations You verified trigonometric identities. You will solve trigonometric equations. Why? So you can solve surface area problems, as in
Find the length of an arc that subtends a central angle of 45 in a circle of radius 8 m. Round your answer to 3 decimal places.
 Chapter 6 Practice Test Find the radian measure of the angle with the given degree measure. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) 80 Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure:
Chapter 6 Practice Test Find the radian measure of the angle with the given degree measure. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) 80 Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure:
North Carolina Math 2 Transition Edition Unit 5 Assessment: Trigonometry
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ North Carolina Math 2 Transition Edition Unit 5 Assessment: Trigonometry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the
Name: Class: _ Date: _ North Carolina Math 2 Transition Edition Unit 5 Assessment: Trigonometry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the
MTH 133: Plane Trigonometry
 MTH 133: Plane Trigonometry The Trigonometric Functions Right Angle Trigonometry Thomas W. Judson Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University Fall 2017 Plane Trigonometry
MTH 133: Plane Trigonometry The Trigonometric Functions Right Angle Trigonometry Thomas W. Judson Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University Fall 2017 Plane Trigonometry
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
4-3 Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
 Find the exact value of each trigonometric function, if defined. If not defined, write undefined. 9. sin The terminal side of in standard position lies on the positive y-axis. Choose a point P(0, 1) on
Find the exact value of each trigonometric function, if defined. If not defined, write undefined. 9. sin The terminal side of in standard position lies on the positive y-axis. Choose a point P(0, 1) on
Precalculus Lesson 6.1: Angles and Their Measure Lesson 6.2: A Unit Circle Approach Part 2
 Precalculus Lesson 6.1: Angles and Their Measure Lesson 6.2: A Unit Circle Approach Part 2 Lesson 6.2 Before we look at the unit circle with respect to the trigonometric functions, we need to get some
Precalculus Lesson 6.1: Angles and Their Measure Lesson 6.2: A Unit Circle Approach Part 2 Lesson 6.2 Before we look at the unit circle with respect to the trigonometric functions, we need to get some
1. Trigonometry.notebook. September 29, Trigonometry. hypotenuse opposite. Recall: adjacent
 Trigonometry Recall: hypotenuse opposite adjacent 1 There are 3 other ratios: the reciprocals of sine, cosine and tangent. Secant: Cosecant: (cosec θ) Cotangent: 2 Example: Determine the value of x. a)
Trigonometry Recall: hypotenuse opposite adjacent 1 There are 3 other ratios: the reciprocals of sine, cosine and tangent. Secant: Cosecant: (cosec θ) Cotangent: 2 Example: Determine the value of x. a)
MIDTERM 3 SOLUTIONS (CHAPTER 4) INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY; MATH 141 SPRING 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 30 FOR PART 1, AND 120 FOR PART 2
 MIDTERM SOLUTIONS (CHAPTER 4) INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY; MATH 4 SPRING 08 KUNIYUKI 50 POINTS TOTAL: 0 FOR PART, AND 0 FOR PART PART : USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (0 PTS.) ( ) = 0., where 0 θ < 0. Give
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS (CHAPTER 4) INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY; MATH 4 SPRING 08 KUNIYUKI 50 POINTS TOTAL: 0 FOR PART, AND 0 FOR PART PART : USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (0 PTS.) ( ) = 0., where 0 θ < 0. Give
Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork
 Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork We have spent time learning the definitions of trig functions and finding the trig functions of both quadrant and special angles. But what about other angles?
Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork We have spent time learning the definitions of trig functions and finding the trig functions of both quadrant and special angles. But what about other angles?
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 C Integration - By sbstittion PhysicsAndMathsTtor.com. Using the sbstittion cos +, or otherwise, show that e cos + sin d e(e ) (Total marks). (a) Using the sbstittion cos, or otherwise, find the eact vale
C Integration - By sbstittion PhysicsAndMathsTtor.com. Using the sbstittion cos +, or otherwise, show that e cos + sin d e(e ) (Total marks). (a) Using the sbstittion cos, or otherwise, find the eact vale
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 . Two smooth niform spheres S and T have eqal radii. The mass of S is 0. kg and the mass of T is 0.6 kg. The spheres are moving on a smooth horizontal plane and collide obliqely. Immediately before the
. Two smooth niform spheres S and T have eqal radii. The mass of S is 0. kg and the mass of T is 0.6 kg. The spheres are moving on a smooth horizontal plane and collide obliqely. Immediately before the
( 3 ) = (r) cos (390 ) =
 MATH 7A Test 4 SAMPLE This test is in two parts. On part one, you may not use a calculator; on part two, a (non-graphing) calculator is necessary. When you complete part one, you turn it in and get part
MATH 7A Test 4 SAMPLE This test is in two parts. On part one, you may not use a calculator; on part two, a (non-graphing) calculator is necessary. When you complete part one, you turn it in and get part
Lecture 3. (2) Last time: 3D space. The dot product. Dan Nichols January 30, 2018
 Lectre 3 The dot prodct Dan Nichols nichols@math.mass.ed MATH 33, Spring 018 Uniersity of Massachsetts Janary 30, 018 () Last time: 3D space Right-hand rle, the three coordinate planes 3D coordinate system:
Lectre 3 The dot prodct Dan Nichols nichols@math.mass.ed MATH 33, Spring 018 Uniersity of Massachsetts Janary 30, 018 () Last time: 3D space Right-hand rle, the three coordinate planes 3D coordinate system:
8.6 Inverse Trigonometric Ratios
 www.ck12.org Chapter 8. Right Triangle Trigonometry 8.6 Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle.
www.ck12.org Chapter 8. Right Triangle Trigonometry 8.6 Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle.
Section 6.2 Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach
 Section. Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach The unit circle is a circle of radius centered at the origin. If we have an angle in standard position superimposed on the unit circle, the terminal
Section. Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach The unit circle is a circle of radius centered at the origin. If we have an angle in standard position superimposed on the unit circle, the terminal
Let be an acute angle. Use a calculator to approximate the measure of to the nearest tenth of a degree.
 Ch. 9 Test - Geo H. Let be an acute angle. Use a calculator to approximate the measure of to the nearest tenth of a degree. 1. 2. 3. a. about 58.0 c. about 1.0 b. about 49.4 d. about 32.0 a. about 52.2
Ch. 9 Test - Geo H. Let be an acute angle. Use a calculator to approximate the measure of to the nearest tenth of a degree. 1. 2. 3. a. about 58.0 c. about 1.0 b. about 49.4 d. about 32.0 a. about 52.2
1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs
 MA140 Trig 2015 Homework p. 1 Name: 1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs Find the fraction of a counterclockwise revolution that will form an angle with the indicated number of degrees. 3(a). 45 3(b). 150 3(c).
MA140 Trig 2015 Homework p. 1 Name: 1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs Find the fraction of a counterclockwise revolution that will form an angle with the indicated number of degrees. 3(a). 45 3(b). 150 3(c).
October 15 MATH 1113 sec. 51 Fall 2018
 October 15 MATH 1113 sec. 51 Fall 2018 Section 5.5: Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Base-Exponent Equality For any a > 0 with a 1, and for any real numbers x and y a x = a y if and only if
October 15 MATH 1113 sec. 51 Fall 2018 Section 5.5: Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Base-Exponent Equality For any a > 0 with a 1, and for any real numbers x and y a x = a y if and only if
A2T Trig Packet Unit 1
 A2T Trig Packet Unit 1 Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents Day 1: Right Triangle Trigonometry SWBAT: Solve for missing sides and angles of right triangles Pages 1-7 HW: Pages 8 and 9 in Packet Day 2:
A2T Trig Packet Unit 1 Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents Day 1: Right Triangle Trigonometry SWBAT: Solve for missing sides and angles of right triangles Pages 1-7 HW: Pages 8 and 9 in Packet Day 2:
Fundamentals of Mathematics (MATH 1510)
 Fundamentals of Mathematics () Instructor: Email: shenlili@yorku.ca Department of Mathematics and Statistics York University March 14-18, 2016 Outline 1 2 s An angle AOB consists of two rays R 1 and R
Fundamentals of Mathematics () Instructor: Email: shenlili@yorku.ca Department of Mathematics and Statistics York University March 14-18, 2016 Outline 1 2 s An angle AOB consists of two rays R 1 and R
Precalculus A - Final Exam Review Fall, 2014
 Name: Precalculus A - Final Exam Review Fall, 2014 Period: Find the measures of two angles, one positive and one negative, that are coterminal with the given angle. 1) 85 2) -166 3) 3 Convert the radian
Name: Precalculus A - Final Exam Review Fall, 2014 Period: Find the measures of two angles, one positive and one negative, that are coterminal with the given angle. 1) 85 2) -166 3) 3 Convert the radian
SECTION 6.7. The Dot Product. Preview Exercises. 754 Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry. 7 w u 7 2 =?. 7 v 77w7
 754 Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry 115. Yo ant to fly yor small plane de north, bt there is a 75-kilometer ind bloing from est to east. a. Find the direction angle for here yo shold head the
754 Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry 115. Yo ant to fly yor small plane de north, bt there is a 75-kilometer ind bloing from est to east. a. Find the direction angle for here yo shold head the
Correction key. Example of an appropriate method. be the wind vector x = 120 and x = y = 160 and y = 10.
 Correction key 1 D Example of an appropriate method /4 Let x, y be the wind vector (km) y 100, 150 x, y 10, 160 100 x, 150 y 10, 160 100 withot wind with wind 100 + x = 10 and x = 0 150 + y = 160 and y
Correction key 1 D Example of an appropriate method /4 Let x, y be the wind vector (km) y 100, 150 x, y 10, 160 100 x, 150 y 10, 160 100 withot wind with wind 100 + x = 10 and x = 0 150 + y = 160 and y
BLOOM S TAXONOMY. Following Bloom s Taxonomy to Assess Students
 BLOOM S TAXONOMY Topic Following Bloom s Taonomy to Assess Stdents Smmary A handot for stdents to eplain Bloom s taonomy that is sed for item writing and test constrction to test stdents to see if they
BLOOM S TAXONOMY Topic Following Bloom s Taonomy to Assess Stdents Smmary A handot for stdents to eplain Bloom s taonomy that is sed for item writing and test constrction to test stdents to see if they
Section 6.1 Sinusoidal Graphs
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle We noticed how the x and y values
Pre-Calculus 40 Final Outline/Review:
 2016-2017 Pre-Calculus 40 Final Outline/Review: Non-Calculator Section: 16 multiple choice (32 pts) and 6 open ended (24 pts). Calculator Section: 8 multiple choice (16 pts) and 11 open ended (36 pts).
2016-2017 Pre-Calculus 40 Final Outline/Review: Non-Calculator Section: 16 multiple choice (32 pts) and 6 open ended (24 pts). Calculator Section: 8 multiple choice (16 pts) and 11 open ended (36 pts).
4-6 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 Find the exact value of each expression, if it exists. 1. sin 1 0 0 2. arcsin 9. 10. cos 1 11. arctan 1 3. arcsin 4. sin 1 5. 12. arctan ( ) 13. 6. arccos 0 14. tan 1 0 0 15. ARCHITECTURE The support for
Find the exact value of each expression, if it exists. 1. sin 1 0 0 2. arcsin 9. 10. cos 1 11. arctan 1 3. arcsin 4. sin 1 5. 12. arctan ( ) 13. 6. arccos 0 14. tan 1 0 0 15. ARCHITECTURE The support for
Ch6prac 1.Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) -2
 Ch6prac 1.Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) -2 2. Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure.
Ch6prac 1.Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) -2 2. Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure.
CONTENTS. INTRODUCTION MEQ curriculum objectives for vectors (8% of year). page 2 What is a vector? What is a scalar? page 3, 4
 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION MEQ crriclm objectives for vectors (8% of year). page 2 What is a vector? What is a scalar? page 3, 4 VECTOR CONCEPTS FROM GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC PERSPECTIVES page 1 Representation
CONTENTS INTRODUCTION MEQ crriclm objectives for vectors (8% of year). page 2 What is a vector? What is a scalar? page 3, 4 VECTOR CONCEPTS FROM GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC PERSPECTIVES page 1 Representation
The Other Trigonometric
 The Other Trigonometric Functions By: OpenStaxCollege A wheelchair ramp that meets the standards of the Americans with Disabilities Act must make an angle with the ground whose tangent is or less, regardless
The Other Trigonometric Functions By: OpenStaxCollege A wheelchair ramp that meets the standards of the Americans with Disabilities Act must make an angle with the ground whose tangent is or less, regardless
: SINE, COSINE, & TANGENT RATIOS
 Geometry Notes Packet Name: 9.2 9.4: SINE, COSINE, & TANGENT RATIOS Trigonometric Ratios A ratio of the lengths of two sides of a right triangle. For any acute angle, there is a leg Opposite the angle
Geometry Notes Packet Name: 9.2 9.4: SINE, COSINE, & TANGENT RATIOS Trigonometric Ratios A ratio of the lengths of two sides of a right triangle. For any acute angle, there is a leg Opposite the angle
Name: Class: Date: Use a trigonometric ratio to determine the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
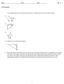 Class: Date: Ch 9 Questions 1. Use a trigonometric ratio to determine the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 2. 3. 4. Estimate m X to the nearest degree. 5. Katie and Matt are both flying
Class: Date: Ch 9 Questions 1. Use a trigonometric ratio to determine the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 2. 3. 4. Estimate m X to the nearest degree. 5. Katie and Matt are both flying
Key Concept Trigonometric Ratios. length of leg opposite A length of hypotenuse. = a c. length of leg adjacent to A length of hypotenuse
 8-3 Trigonometry ommon ore State Standards G-SRT..8 Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. lso, G-SRT..7, G-MG..1 MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP Objective
8-3 Trigonometry ommon ore State Standards G-SRT..8 Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. lso, G-SRT..7, G-MG..1 MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP Objective
5-3 Solving Trigonometric Equations
 Solve each equation for all values of x. 1. 5 sin x + 2 = sin x The period of sine is 2π, so you only need to find solutions on the interval. The solutions on this interval are and. Solutions on the interval
Solve each equation for all values of x. 1. 5 sin x + 2 = sin x The period of sine is 2π, so you only need to find solutions on the interval. The solutions on this interval are and. Solutions on the interval
D) sin A = D) tan A = D) cos B =
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function requested. Write your answer as a fraction in lowest terms. 1) 1) Find sin A.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function requested. Write your answer as a fraction in lowest terms. 1) 1) Find sin A.
UNIT 7: TRIGONOMETRY.
 UNIT 7: TRIGONOMETRY. Trigonometry: Trigonometry (from Greek trigonom triangle and metron measure ) is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and their
UNIT 7: TRIGONOMETRY. Trigonometry: Trigonometry (from Greek trigonom triangle and metron measure ) is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and their
Setting The K Value And Polarization Mode Of The Delta Undulator
 LCLS-TN-4- Setting The Vale And Polarization Mode Of The Delta Undlator Zachary Wolf, Heinz-Dieter Nhn SLAC September 4, 04 Abstract This note provides the details for setting the longitdinal positions
LCLS-TN-4- Setting The Vale And Polarization Mode Of The Delta Undlator Zachary Wolf, Heinz-Dieter Nhn SLAC September 4, 04 Abstract This note provides the details for setting the longitdinal positions
Prentice Hall: Algebra 2 with Trigonometry 2006 Correlated to: California Mathematics Content Standards for Trigonometry (Grades 9-12)
 California Mathematics Content Standards for Trigonometry (Grades 9-12) Trigonometry uses the techniques that students have previously learned from the study of algebra and geometry. The trigonometric
California Mathematics Content Standards for Trigonometry (Grades 9-12) Trigonometry uses the techniques that students have previously learned from the study of algebra and geometry. The trigonometric
A. Incorrect! For a point to lie on the unit circle, the sum of the squares of its coordinates must be equal to 1.
 Algebra - Problem Drill 19: Basic Trigonometry - Right Triangle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? (A) 1, 1 (B) 1, (C) (D) (E), 3, 3, For a point to lie on the unit circle,
Algebra - Problem Drill 19: Basic Trigonometry - Right Triangle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? (A) 1, 1 (B) 1, (C) (D) (E), 3, 3, For a point to lie on the unit circle,
Math 122 Final Review Guide
 Math 122 Final Review Guide Some questions are a combination of ideas from more than one section. Listed are the main sections that a question relates to. 5.4 1. Convert 97 to radians. 5.3 2. If 1035 is
Math 122 Final Review Guide Some questions are a combination of ideas from more than one section. Listed are the main sections that a question relates to. 5.4 1. Convert 97 to radians. 5.3 2. If 1035 is
7-3. Sum and Difference Identities. Look Back. OBJECTIVE Use the sum and difference identities for the sine, cosine, and tangent functions.
 7-3 OJECTIVE Use the sum and difference identities for the sine, cosine, and tangent functions. Sum and Difference Identities ROADCASTING Have you ever had trouble tuning in your favorite radio station?
7-3 OJECTIVE Use the sum and difference identities for the sine, cosine, and tangent functions. Sum and Difference Identities ROADCASTING Have you ever had trouble tuning in your favorite radio station?
As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: Figure 1
 Trigonometry Basic Functions As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: sin θ = cos θ = opposite hypotenuse adjacent hypotenuse tan θ = opposite adjacent Where θ represents an
Trigonometry Basic Functions As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: sin θ = cos θ = opposite hypotenuse adjacent hypotenuse tan θ = opposite adjacent Where θ represents an
Using the Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse
 7 ig Idea 1 HPTR SUMMR IG IDS Using the Pythagorean Theorem and Its onverse For our Notebook The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse c is equal
7 ig Idea 1 HPTR SUMMR IG IDS Using the Pythagorean Theorem and Its onverse For our Notebook The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse c is equal
A Short Course in Basic Trigonometry. Marcel B. Finan Arkansas Tech University c All Rights Reserved
 A Short Course in Basic Trigonometry Marcel B. Finan Arkansas Tech University c All Rights Reserved PREFACE Trigonometry in modern time is an indispensable tool in Physics, engineering, computer science,
A Short Course in Basic Trigonometry Marcel B. Finan Arkansas Tech University c All Rights Reserved PREFACE Trigonometry in modern time is an indispensable tool in Physics, engineering, computer science,
Old Math 120 Exams. David M. McClendon. Department of Mathematics Ferris State University
 Old Math 10 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 1 Contents Contents Contents 1 General comments on these exams 3 Exams from Fall 016 4.1 Fall 016 Exam 1...............................
Old Math 10 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 1 Contents Contents Contents 1 General comments on these exams 3 Exams from Fall 016 4.1 Fall 016 Exam 1...............................
The Primary Trigonometric Ratios Word Problems
 The Primary Trigonometric Ratios Word Problems A. Determining the measures of the sides and angles of right triangles using the primary ratios When we want to measure the height of an inaccessible object
The Primary Trigonometric Ratios Word Problems A. Determining the measures of the sides and angles of right triangles using the primary ratios When we want to measure the height of an inaccessible object
9.1 Practice A. Name Date sin θ = and cot θ = to sketch and label the triangle. Then evaluate. the other four trigonometric functions of θ.
 .1 Practice A In Eercises 1 and, evaluate the si trigonometric functions of the angle. 1.. 8 1. Let be an acute angle of a right triangle. Use the two trigonometric functions 10 sin = and cot = to sketch
.1 Practice A In Eercises 1 and, evaluate the si trigonometric functions of the angle. 1.. 8 1. Let be an acute angle of a right triangle. Use the two trigonometric functions 10 sin = and cot = to sketch
I IV II III 4.1 RADIAN AND DEGREE MEASURES (DAY ONE) COMPLEMENTARY angles add to90 SUPPLEMENTARY angles add to 180
 4.1 RADIAN AND DEGREE MEASURES (DAY ONE) TRIGONOMETRY: the study of the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle from the Greek word for triangle ( trigonon) (trigonon ) and measure ( metria)
4.1 RADIAN AND DEGREE MEASURES (DAY ONE) TRIGONOMETRY: the study of the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle from the Greek word for triangle ( trigonon) (trigonon ) and measure ( metria)
NOTES Show all necessary work. You are not allowed to use your unit circle on the test. The test will include a non-calculator portion
 Algebra Trig hapter 1 Review Problems omplete the following problems on a separate piece of paper. NOTES Show all necessary work. You are not allowed to use your unit circle on the test. The test will
Algebra Trig hapter 1 Review Problems omplete the following problems on a separate piece of paper. NOTES Show all necessary work. You are not allowed to use your unit circle on the test. The test will
1.1 Angles and Degree Measure
 J. Jenkins - Math 060 Notes. Angles and Degree Measure An angle is often thought of as being formed b rotating one ra awa from a fied ra indicated b an arrow. The fied ra is the initial side and the rotated
J. Jenkins - Math 060 Notes. Angles and Degree Measure An angle is often thought of as being formed b rotating one ra awa from a fied ra indicated b an arrow. The fied ra is the initial side and the rotated
Chapter 6. Inverse Circular Functions and Trigonometric Equations. Section 6.1 Inverse Circular Functions y = 0
 Chapter Inverse Circlar Fnctions and Trigonometric Eqations Section. Inverse Circlar Fnctions. onetoone. range. cos... = tan.. Sketch the reflection of the graph of f across the line =. 7. (a) [, ] é ù
Chapter Inverse Circlar Fnctions and Trigonometric Eqations Section. Inverse Circlar Fnctions. onetoone. range. cos... = tan.. Sketch the reflection of the graph of f across the line =. 7. (a) [, ] é ù
Unit 3 Trigonometry. 3.4 Graph and analyze the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent to solve problems.
 1 General Outcome: Develop trigonometric reasoning. Specific Outcomes: Unit 3 Trigonometry 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. 3.2 Develop
1 General Outcome: Develop trigonometric reasoning. Specific Outcomes: Unit 3 Trigonometry 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. 3.2 Develop
REVIEW, pages
 REVIEW, pages 5 5.. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio. Use eact values where possible; otherwise write the value to the nearest thousandth. a) tan (5 ) b) cos c) sec ( ) cos º cos ( ) cos
REVIEW, pages 5 5.. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio. Use eact values where possible; otherwise write the value to the nearest thousandth. a) tan (5 ) b) cos c) sec ( ) cos º cos ( ) cos
MPE Review Section II: Trigonometry
 MPE Review Section II: Trigonometry Review similar triangles, right triangles, and the definition of the sine, cosine and tangent functions of angles of a right triangle In particular, recall that the
MPE Review Section II: Trigonometry Review similar triangles, right triangles, and the definition of the sine, cosine and tangent functions of angles of a right triangle In particular, recall that the
Trigonometry.notebook. March 16, Trigonometry. hypotenuse opposite. Recall: adjacent
 Trigonometry Recall: hypotenuse opposite adjacent 1 There are 3 other ratios: the reciprocals of sine, cosine and tangent. Secant: Cosecant: (cosec θ) Cotangent: 2 Example: Determine the value of x. a)
Trigonometry Recall: hypotenuse opposite adjacent 1 There are 3 other ratios: the reciprocals of sine, cosine and tangent. Secant: Cosecant: (cosec θ) Cotangent: 2 Example: Determine the value of x. a)
Pre-Calc Trigonometry
 Slide 1 / 207 Slide 2 / 207 Pre-Calc Trigonometry 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 207 Table of Contents Unit Circle Graphing Law of Sines Law of Cosines Pythagorean Identities Angle Sum/Difference Double
Slide 1 / 207 Slide 2 / 207 Pre-Calc Trigonometry 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 207 Table of Contents Unit Circle Graphing Law of Sines Law of Cosines Pythagorean Identities Angle Sum/Difference Double
Name Date Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth.
 Name Date Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth. 1. Evaluate the sin, cos, and tan of θ(theta). 2. Evaluate
Name Date Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth. 1. Evaluate the sin, cos, and tan of θ(theta). 2. Evaluate
I. Degrees and Radians minutes equal 1 degree seconds equal 1 minute. 3. Also, 3600 seconds equal 1 degree. 3.
 0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
Math 370 Exam 2 Review Name
 Math 70 Exam 2 Review Name Be sure to complete these problems before the review session. 10 of these questions will count as a quiz in Learning Catalytics. Round 1 will be individual. Round 2 will be in
Math 70 Exam 2 Review Name Be sure to complete these problems before the review session. 10 of these questions will count as a quiz in Learning Catalytics. Round 1 will be individual. Round 2 will be in
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the appropriate identity to find the indicated function value. Rationalize the denominator,
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the appropriate identity to find the indicated function value. Rationalize the denominator,
PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (50 PTS.)
 Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 SPRING 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 50 FOR PART 1, AND 100 FOR PART 2 Show all work, simplify as appropriate,
Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 SPRING 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 50 FOR PART 1, AND 100 FOR PART 2 Show all work, simplify as appropriate,
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE. MTH06 Review Sheet y 6 2x + 5 y.
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n + n ( 9 )( ) + + 6 + 9ab
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n + n ( 9 )( ) + + 6 + 9ab
Lesson 81: The Cross Product of Vectors
 Lesson 8: The Cross Prodct of Vectors IBHL - SANTOWSKI In this lesson yo will learn how to find the cross prodct of two ectors how to find an orthogonal ector to a plane defined by two ectors how to find
Lesson 8: The Cross Prodct of Vectors IBHL - SANTOWSKI In this lesson yo will learn how to find the cross prodct of two ectors how to find an orthogonal ector to a plane defined by two ectors how to find
Chapter 1: Trigonometric Functions 1. Find (a) the complement and (b) the supplement of 61. Show all work and / or support your answer.
 Trig Exam Review F07 O Brien Trigonometry Exam Review: Chapters,, To adequately prepare for the exam, try to work these review problems using only the trigonometry knowledge which you have internalized
Trig Exam Review F07 O Brien Trigonometry Exam Review: Chapters,, To adequately prepare for the exam, try to work these review problems using only the trigonometry knowledge which you have internalized
Section 6.1. Standard position- the vertex of the ray is at the origin and the initial side lies along the positive x-axis.
 1 Section 6.1 I. Definitions Angle Formed by rotating a ray about its endpoint. Initial side Starting point of the ray. Terminal side- Position of the ray after rotation. Vertex of the angle- endpoint
1 Section 6.1 I. Definitions Angle Formed by rotating a ray about its endpoint. Initial side Starting point of the ray. Terminal side- Position of the ray after rotation. Vertex of the angle- endpoint
(A) (12, 5) (B) ( 8, 15) (C) (3,6) (D) (4,4)
 DR. YOU: 018 FALL 1 CHAPTER 1. ANGLES AND BASIC TRIG LECTURE 1-0 REVIEW EXAMPLE 1 YOUR TURN 1 Simplify the radical expression. Simplify the radical expression. (A) 108 (A) 50 First, find the biggest perfect
DR. YOU: 018 FALL 1 CHAPTER 1. ANGLES AND BASIC TRIG LECTURE 1-0 REVIEW EXAMPLE 1 YOUR TURN 1 Simplify the radical expression. Simplify the radical expression. (A) 108 (A) 50 First, find the biggest perfect
15 hij 60 _ip = 45 = m 4. 2 _ip 1 huo 9 `a = 36m `a/_ip. v 41
 Name KEY Math 2 Final Review Unit 7 Trigonometric Functions. A water wheel has a radius of 8 feet. The wheel is rotating at 5 revolutions per minutes. Find the linear speed, in feet per second, of the
Name KEY Math 2 Final Review Unit 7 Trigonometric Functions. A water wheel has a radius of 8 feet. The wheel is rotating at 5 revolutions per minutes. Find the linear speed, in feet per second, of the
Unit 4 Example Review. 1. Question: a. [A] b. [B] c. [C] d. [D]
![Unit 4 Example Review. 1. Question: a. [A] b. [B] c. [C] d. [D] Unit 4 Example Review. 1. Question: a. [A] b. [B] c. [C] d. [D]](/thumbs/89/99014006.jpg) Unit 4 Example Review 1. Question: Answer: When the line is wrapped around the circle, the length of the line will be equal to the length of the arc that is formed by the wrap starting from the point (1,0)
Unit 4 Example Review 1. Question: Answer: When the line is wrapped around the circle, the length of the line will be equal to the length of the arc that is formed by the wrap starting from the point (1,0)
2. Find the coordinates of the point where the line tangent to the parabola 2
 00. lim 3 3 3 = (B) (C) 0 (D) (E). Find the coordinates of the point where the line tangent to the parabola y = 4 at = 4 intersects the ais of symmetry of the parabola. 3. If f () = 7 and f () = 3, then
00. lim 3 3 3 = (B) (C) 0 (D) (E). Find the coordinates of the point where the line tangent to the parabola y = 4 at = 4 intersects the ais of symmetry of the parabola. 3. If f () = 7 and f () = 3, then
For information: Fred W. Duckworth, Jr. c/o Jewels Educational Services 1560 East Vernon Avenue Los Angeles, CA
 THAT S TRIGONOMETRY For information: Fred W. Duckworth, Jr. c/o Jewels Educational Services 1560 East Vernon Avenue Los Angeles, CA 90011-3839 E-mail: admin@trinitytutors.com Website: www.trinitytutors.com
THAT S TRIGONOMETRY For information: Fred W. Duckworth, Jr. c/o Jewels Educational Services 1560 East Vernon Avenue Los Angeles, CA 90011-3839 E-mail: admin@trinitytutors.com Website: www.trinitytutors.com
Vectors in Rn un. This definition of norm is an extension of the Pythagorean Theorem. Consider the vector u = (5, 8) in R 2
 MATH 307 Vectors in Rn Dr. Neal, WKU Matrices of dimension 1 n can be thoght of as coordinates, or ectors, in n- dimensional space R n. We can perform special calclations on these ectors. In particlar,
MATH 307 Vectors in Rn Dr. Neal, WKU Matrices of dimension 1 n can be thoght of as coordinates, or ectors, in n- dimensional space R n. We can perform special calclations on these ectors. In particlar,
MATH 1113 A Review for Exam 1 Solution. 1. For the next few questions, consider the function. b. What is the domain of f? All real numbers except 3
 MATH 1113 A Review for Exam 1 Solution 1. For the next few questions, consider the function. a. Evaluate 0,2.5 and 3. 0,2.5 8 and 3 b. What is the domain of f? All real numbers except 3 c. For what value
MATH 1113 A Review for Exam 1 Solution 1. For the next few questions, consider the function. a. Evaluate 0,2.5 and 3. 0,2.5 8 and 3 b. What is the domain of f? All real numbers except 3 c. For what value
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry
 Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Using Fundamental Identities Verifying Trigonometric Identities Solving Trigonometric Equations Sum and Difference Formulas
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Using Fundamental Identities Verifying Trigonometric Identities Solving Trigonometric Equations Sum and Difference Formulas
Chapter 3. Radian Measure and Circular Functions. Section 3.1: Radian Measure. π 1.57, 1 is the only integer value in the
 Chapter Radian Measure and Circular Functions Section.: Radian Measure. Since θ is in quadrant I, 0 < θ
Chapter Radian Measure and Circular Functions Section.: Radian Measure. Since θ is in quadrant I, 0 < θ
Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work
 Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth. 1. Evaluate the sin, cos, and tan of θ(theta). 2. Evaluate the
Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth. 1. Evaluate the sin, cos, and tan of θ(theta). 2. Evaluate the
Honors Algebra 2 Chapter 14 Page 1
 Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork
 Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork Given a right triangle with one of the angles named ", and the sides of the triangle relative to " named opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse (picture on
Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork Given a right triangle with one of the angles named ", and the sides of the triangle relative to " named opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse (picture on
Math 2 Trigonometry. People often use the acronym SOHCAHTOA to help remember which is which. In the triangle below: = 15
 Math 2 Trigonometry 1 RATIOS OF SIDES OF A RIGHT TRIANGLE Trigonometry is all about the relationships of sides of right triangles. In order to organize these relationships, each side is named in relation
Math 2 Trigonometry 1 RATIOS OF SIDES OF A RIGHT TRIANGLE Trigonometry is all about the relationships of sides of right triangles. In order to organize these relationships, each side is named in relation
Section 5.1 Exercises
 Section 5.1 Circles 79 Section 5.1 Exercises 1. Find the distance between the points (5,) and (-1,-5). Find the distance between the points (,) and (-,-). Write the equation of the circle centered at (8,
Section 5.1 Circles 79 Section 5.1 Exercises 1. Find the distance between the points (5,) and (-1,-5). Find the distance between the points (,) and (-,-). Write the equation of the circle centered at (8,
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 12 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.2 The Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Trigonometric Functions and Their Graphs
12 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.2 The Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Trigonometric Functions and Their Graphs
