Semester II Review part 1
|
|
|
- Charles Dixon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Semester II Review part 1 1. What term is used to identify frequencies higher than our ability to hear? a. Ultrasonic b. Supersonic c. Hypersonic d. Subsonic e. Infrasonic 2. Waves are additive. As a result, a combination of waves at the same frequency that line up on top of each other would be an example of a. Positive wave integration b. Negative wave integration c. In-phase continuum alignment d. Destructive interference e. Constructive interference 3. The speed of sound is totally dependent on the elasticity of the medium. a. True b. False 4. As defined by our textbook, a pulse of low-pressure particles in the transmission of sound is known as a/an a. Compressional wave b. Rarefactional wave c. Bow wave d. Shock wave 5. The top of a wave is known as a. Crest b. Trough c. Base d. Rest e. Wave length 6. The point of a wave that crosses the midpoint of wave as it moves is known as a. Frequency b. Amplitude c. Node d. Antinode
2 7. When discussing the concept of light, how is colour measured? By observing a. Frequency b. Wave length c. Amplitude d. Medium the wave is passing through 8. What term is used to identify the speed of a vehicle that travels faster than the speed of sound? a. Ultrasonic b. Supersonic c. Hypersonic d. Subsonic e. Infrasonic 9. The distance from the midpoint of a wave to the top of the wave is known as a. Frequency b. Amplitude c. Node d. Antinode 10. A bright white light passes you, the frequency of the light pushes against itself along its path. The light leaving you will decrease the frequency that you see and alter the light quality. This is known as a. Amplitude compression b. Red shift c. Rarefaction d. Blue shift 11. The crest and trough are also known as a. Frequency b. Amplitude c. Node d. Antinode 12. What unit is used when referring to frequency? a. Cycles b. Hertz c. Decibels d. Candles
3 13. As discussed in class, the best definition of a wave would be a. A pictorial view of your heart beating b. A rumbling of thunder c. A headache d. Sitting on the dock of a bay e. A disturbance 14. What unit is used when referring to amplitude of light? a. Cycles b. Hertz c. Decibels d. Candles 15. What is the unit of measure for the amplitude of sound? a. Cycles b. Hertz c. Decibels d. Candles 16. When discussing the concept of sound, how is Loudness measured? By observing a. Frequency b. Wave length c. Amplitude d. Medium the wave is passing through 17. When discussing the concept of light, how is brightness measured? By observing a. Frequency b. Wave length c. Amplitude d. Medium the wave is passing through 18. Waves associated with sound are known as a. Longitudinal waves b. Supersonic waves c. Transverse waves d. Hypersonic waves
4 19. Which of the following terms refer to the stationary points on a standing wave along the rest line? a. Antinode b. Crest c. Node d. Trough 20. When a wave source approaches, an observer encounters waves of a higher frequency. As the wave source passes the observer the frequency decreases. This is known as a. Hyperbaric chamber displacement b. Doppler Effect c. Supersonic aberrations d. Bow wave displacement 21. A bright white light approaches you, the frequency of the light pushes against itself along its path. The approaching light will increase the frequency that you see and alter the light quality. This is known as a. Amplitude compression b. Red shift c. Rarefaction d. Blue shift 22. A wave that is incoming (before it bounces off anything) is known as a/an a. Incident wave b. Reflective wave c. Compressional wave d. Royal wave 23.? is when an object moves faster than the speed of sound and is heard as a sonic boom. a. Subsonic waves b. Infrasonic waves c. Shock waves 24. As defined by our text book, when the crest of a sound wave overlaps at the edges by a moving object it produces a v-shaped pattern. The resulting wave is known as a. Compressional wave b. Rarefactional wave c. Bow wave d. Shock wave
5 25. What term used to identify frequencies lower than our ability to hear? a. Ultrasonic b. Supersonic c. Hypersonic d. Subsonic e. Infrasonic 26. As defined by our textbook, a pulse of compressed particles in the transmission of sound is known as a/an a. Compressional wave b. Rarefactional wave c. Bow wave d. Shock wave 27. What term is used to identify the speed of a vehicle that travels slower than the speed of sound? a. Ultrasonic b. Supersonic c. Hypersonic d. Subsonic e. Infrasonic 28. The bottom of a wave is known as a. Crest b. Trough c. Base d. Rest e. Wave length 29. What unit is used when referring to amplitude focusing on sound? a. Cycles b. Hertz c. Decibels d. Candles 30. The distance from one crest to the next crest is known as a. Crest b. Trough c. Base d. Rest e. Wave length
6 31. When discussing the concept of sound, how is pitch measured? By observing a. Frequency b. Wave length c. Amplitude d. Medium the wave is passing through 32. A wave that bounces of an object is known as a/an a. Incident wave b. Reflective wave c. Compressional wave d. Royal wave 33. Waves associated with the electromagnetic spectrum are referred to as a. Longitudinal waves b. Supersonic waves c. Transverse waves d. Hypersonic waves 34. The number of waves per unit of time is known as a. Frequency b. Amplitude c. Node d. Antinode 35. Waves are additive. As a result, a combination of waves at the same frequency that do not line up on top of each other would be an example of a. Positive wave integration b. Negative wave integration c. In-phase continuum alignment d. Destructive interference e. Constructive interference 36. What is the lowest frequency on the Electromagnetic spectrum? a. Radio b. Ultraviolet c. X-rays d. Gamma rays
7 37. What phrase is used when mixing frequencies in order to produce a desired colour of light? a. Additive mixing b. Subtractive mixing c. Refractive mixing d. Reflective mixing 38. What type of telescope is represented in the diagram? a. Refractive telescope b. Compound telescope c. Reflective telescope d. Wal Mart Christmas special 39. Who was the American that identified the speed of light and received the Nobel Prize in physics in 1907? a. Olaus Roemer b. Christian Huygens c. Albert Michelson d. Albert Einstein 40. Who identified that light behaved as a particle as well as a wave? a. Olaus Roemer b. Christian Huygens c. Albert Michelson d. Albert Einstein
8 41. What term describes the inability of light to pass through an object? a. Transparent b. Translucent c. Transatlantic d. Opaque 42. The protection from damaging rays which is known to cause skin cancer can be done with an SPF as low as?. a. 50 b. 30 c. 20 d What colour would you see if the coat you are looking at absorbs red, blue, green, orange, and violet? a. Black b. White c. Purple d. Yellow 44. What type of lens is represented in the diagram? a. Concave b. Convex c. Plane (flat) 45. What type of lens is represented in the diagram? a. Concave b. Convex c. Plane (flat)
9 46. In order to see a rainbow, what do you need to make sure? a. The sun is between you and the rain cloud b. The rain cloud is classified as severe c. Make sure you are between 40 0 and 42 0 with the light source behind you d. Make sure the rain is in front of you and the sun is low in the sky 47. Which of the following is not a primary colour of light? a. Red b. Green c. Yellow d. Blue 48. Please identify the umbra in the following diagram A B C D 49. Working as a stage crew for the production of The Fantasticks, you assemble the lighting necessary to reflect the mood of the scene. As a result, you make sure you have plenty lights of Red, Blue and Green in case of a burn-out. You know this because the mixing of lights is a physics principle known as a. Photographic aberrations b. Additive mixing c. Subtractive mixing d. Broadway requirements for productions
10 50. What type of telescope is represented in the diagram? a. Refractive telescope b. Compound telescope c. Reflective telescope d. Amazon Christmas special 51. Please identify the penumbra A. B. C. D. 52. Which of the following is not a primary colour of paint? a. Red b. Green c. Yellow d. Blue 53. The sky is blue because its component particles scatter high frequency light. a. True b. False
11 54. Which of the following is the secondary color for a mixing of red and green light? a. White b. Orange c. Yellow d. Purple 55. Which of the following is the secondary color for a mixing of red and blue paint? a. Green b. Orange c. Yellow d. Purple 56. Which of the following is the secondary color for a mixing of red and yellow paint? a. Green b. Orange c. Cyan d. Purple 57. Mixing paint or other pigments together is allowing us to see colors based on the dyes used. But this type of mixing in physics is known as a. Photographic aberrations b. Additive mixing c. Subtractive mixing d. Broadway requirements for productions 58. A mirage is an image produced by the refraction of light in the Earth s atmosphere. a. True b. False 59. Which theory of light is the photon more consistent with? a. The wave theory b. The particle theory c. The Big Bang theory d. Evolution 60. What happens to the energy of light when it encounters an opaque object? a. It passes straight through b. All energy is reflected off the surface c. All energy is refracted through the material d. It is converted into thermal energy
12 61. Why do smooth metal surfaces make good mirrors? a. They have special powers known only to physicist and chemist b. They reflect most all of the visible light c. The electromagnetic field of the visible light interacts with the metal and is repelled. d. Because it is not rough 62. What is the law of reflection? a. Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of refraction b. Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of normality c. Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection d. Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of incense 63. Standing on the pier at Eagle Mountain lake, what impact does refraction have on items in the water? a. They appear deeper b. There is no difference in their appearance of depth c. They appear shallower 64. If an image can be projected on a screen at AMC theaters, what does this tell you about the theaters projector? a. The projector has at least one convex lens which creates a real image that exhibits converging light rays that are diverging. As a result the image in the projector is upside down. b. The projector has at least one convex lens which creates a real image that exhibits converging light rays that are inverted. As a result the image in the projector is right side up c. The projector has at least one concave lens which creates a real image that exhibits converging light rays that are inverted. As a result the image in the projector is upside down d. The projector has at least one convex lens which creates a real image that exhibits converging light rays that are inverted. As a result the image in the projector is upside down
13 True (A) or False (B) 65. Electrons and protons have the same charge and therefore attract each other. F 66. Electric charge is neither created nor destroyed, but can be rearranged. T 67. A material is a good insulator if outer electrons of atoms in the material are free to roam around. F 68. When an object is changed by induction, electrons flow from the ground onto the object or from the object to the ground. F 69. Electricity will always do its best to find the easiest way to ground T Multiple Choice 70. Atomic nuclei of almost all atoms consist of a. Only protons b. Protons and neutrons c. Protons and electrons d. Neutrons and electrons 71. The net charge of a non-ionized atom a. Depends only on the number of protons it has b. Depends only on the number of electrons it has c. Is zero d. Usually cannot be determined 72. A positive ion has a. One proton b. More electrons than protons c. More protons than electrons d. A +1 charge always
14 73. Coulomb s law says that the force between any two charges depends a. Directly on the magnitude of the charges b. Inversely on the square of the distance between the charges c. Both of the above are correct d. The answer is not here 74. The common Hydrogen atom consists of a. One proton b. One proton and one electron c. Two protons, one neutron, and two electrons d. One neutron and one electron 75. In a good insulator, electrons are usually a. Free to move around b. Free to move around after an impurity has been added c. Semi-free to move around d. Tightly bound in place 76. The reason a charged balloon will stick to a wall is that a. The charge is slightly sticky and acts like glue b. Electrons transfer back and forth between the wall and the balloon c. Induced opposite charges in the wall are closer than other wall charges d. Balloon material simply sticks to the wall 77. The charge distribution in some molecules is permanently separated in two regions. Such molecules are called a. Ionized molecules b. Electric dipoles c. Insulators d. Coulomb molecules True (A) or False (B) 78. When a charge is placed on an electric field, the charge will experience a force a. T b. F 79. The direction of lines of force shows how large a force will be on a charge placed in an electric field a. T b. F
15 80. Even though a car may be struck by lightning, people inside the car will be safe as long as they do not touch any metal. a. T b. F 81. The energy a charge possesses by virtue of its location is called electrical potential energy a. T b. F 82. The unit of electrical potential energy is the joule. a. T b. F 83. Force vectors always move away from positive charges a. T b. F Multiple Choice 84. How many different kinds of forces would act on a proton placed in both an electric field and a gravitational field? a. One b. Two c. Three d. Four e. None 85. An electric field has a. Magnitude b. Direction c. Both of the above are correct d. The answer is not here 86. The direction of electric field lines shows a. The strength of the field b. The direction of the force on a test positive charge c. The size of the field d. All of the above are correct
16 87. Suppose a hollow metal sphere has a large negative charge on it. The electric field strength inside the sphere is a. Weak and positive b. Large and negative c. Weak and negative d. Zero 88. Suppose you touch a negatively charged object to a metal sphere so that the electrons move from the charged object onto the sphere. After separation of the charged object, electrons on the sphere will be a. Located at the spot where the object touched the sphere b. Bunched together randomly c. Evenly distributed on the sphere d. Fly off the sphere 89. Electrical potential energy is the energy a charged object has because of its a. Position b. Size c. Motion d. Momentum 90. A small positively charged object near a positively charged sphere is moved closer to the sphere. The electrical potential energy of the small object a. Increases b. Decreases c. Stays the same 91. If two negative charges are held close together and then released, the charges will a. Accelerate toward each other b. Accelerate away from each other c. Move at a constant speed away from each other d. Not move at all 92. Which of the following has the potential to move first? a. Proton b. Neutron c. Electron d. Quark
17 93. If an alpha particle with two positive charges and a less massive electron come close together, both will experience an increase in a. Force b. Speed c. Acceleration d. All of the above are correct e. The answer is not here 94. Which of the following best explains why you are safe in an airplane in flight if struck by lightning? a. The charge will spread out around the aircraft and not inside b. There is no ground for the charges to follow c. You are not safe in an airplane! It will crash! d. Only A and B are correct e. There is no correct answer here
Wave Motion and Sound
 Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
Study Guide: Semester Two ( )
 Name Hour Study Guide: Semester Two (2017-2018) Unit 5 Chapter 9 Momentum and its Conservation Chapter 10 Energy, Work and Simple Machines Chapter 11 Energy and its Conservation Vocabulary (define the
Name Hour Study Guide: Semester Two (2017-2018) Unit 5 Chapter 9 Momentum and its Conservation Chapter 10 Energy, Work and Simple Machines Chapter 11 Energy and its Conservation Vocabulary (define the
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves. What is a wave?
 Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Properties of Waves. Before You Read. What are the features of a wave?
 Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
PAP Physics Spring Exam Review
 Class: Date: PAP Physics Spring Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A container of gas is at a pressure of.3 0 5 Pa
Class: Date: PAP Physics Spring Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A container of gas is at a pressure of.3 0 5 Pa
Physics Second Semester Exam Review 2014
 Physics Second Semester Exam Review 2014 Honors and Physics Classes Momentum Inertia in motion. p = mv Must be moving. No velocity, no momentum. Mass and velocity are both directly proportional to momentum.
Physics Second Semester Exam Review 2014 Honors and Physics Classes Momentum Inertia in motion. p = mv Must be moving. No velocity, no momentum. Mass and velocity are both directly proportional to momentum.
Physics Test Review Electrostatics, Electric Fields and Potential Session: Name:
 Physics Test Review lectrostatics, lectric Fields and Potential Session: Name: Multiple hoice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Two unlike
Physics Test Review lectrostatics, lectric Fields and Potential Session: Name: Multiple hoice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Two unlike
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Fineman CP Physics Final Study Guide
 All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The CP Physics
All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The CP Physics
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016
 Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
SABIS End of Year STUDY GUIDE Grade 11 Physics Chapters 25, 27, 28, 29, 32, 33, 34, 35
 Name Section SABIS End of Year STUDY GUIDE Grade 11 Physics Chapters 25, 27, 28, 29, 32, 33, 34, 35 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The
Name Section SABIS End of Year STUDY GUIDE Grade 11 Physics Chapters 25, 27, 28, 29, 32, 33, 34, 35 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The
What does the speed of a wave depend on?
 Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
Light.notebook May 03, 2016
 Unit 4 Light LIGHT.1 Describe the ray model of light. 16.1 LIGHT.2 Predict the effect of distance on light s illuminance. 16.1 LIGHT.3 Explain polarization and the Doppler effect. 16.2 LIGHT.4 Describe
Unit 4 Light LIGHT.1 Describe the ray model of light. 16.1 LIGHT.2 Predict the effect of distance on light s illuminance. 16.1 LIGHT.3 Explain polarization and the Doppler effect. 16.2 LIGHT.4 Describe
Cp physics - Spring Final Review (second semester topics)
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Cp physics - Spring Final Review (second semester topics) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Cp physics - Spring Final Review (second semester topics) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following
Sound Waves. Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium
 Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
Ch Guided Reading Sound and Light
 Name Date Hour Chapter 15 Answer Key Ch.15-18 Guided Reading Sound and Light 1. Compare the speed of sound as it travels within a liquid, a solid, and a gas. Why does the speed of sound differ? Sound travels
Name Date Hour Chapter 15 Answer Key Ch.15-18 Guided Reading Sound and Light 1. Compare the speed of sound as it travels within a liquid, a solid, and a gas. Why does the speed of sound differ? Sound travels
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Energy - the ability to do work or cause change. 1 point
 Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Grade 5. Practice Test. What is Light? How Light Behaves. Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com
 Name Date Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information
Name Date Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information
Saint Lucie County Science Scope and Sequence
 Course: Physics 1 Course Code: 2003380 SEMESTER 2 QUARTER 3 UNIT 7 TOPIC of STUDY: Thermal Energy STANDARDS: 8:Matter, 10: Energy, 12: Motion KEY LEARNING: ~Mathematically relate heat, phase change, energy,
Course: Physics 1 Course Code: 2003380 SEMESTER 2 QUARTER 3 UNIT 7 TOPIC of STUDY: Thermal Energy STANDARDS: 8:Matter, 10: Energy, 12: Motion KEY LEARNING: ~Mathematically relate heat, phase change, energy,
Name Date Class. Electromagnetic Spectrum. Colors
 b e n c h m a r k t e s t : p h y s i c a l s c i e n c e Multiple Choice Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio waves A B C D Gamma rays Long Wavelength
b e n c h m a r k t e s t : p h y s i c a l s c i e n c e Multiple Choice Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio waves A B C D Gamma rays Long Wavelength
Fineman Honors Physics Final Study Guide
 All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The Honors Physics
All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The Honors Physics
CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES
 Name Period CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT WAVES FOLDABLE (blue, green & yellow completely filled in.) /30 /30 2. WS READING GUIDE FOR
Name Period CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT WAVES FOLDABLE (blue, green & yellow completely filled in.) /30 /30 2. WS READING GUIDE FOR
Physics Worksheet Electrostatics, Electric Fields and Potential Section: Name: Electric Charges
 Electric Charges 1. The fundamental rule of all electrical phenomena is: Like charges, opposite charges 2. Thomson s cathode ray experiment proved that: _ 3. Millikan s oil drop experiment proved that:
Electric Charges 1. The fundamental rule of all electrical phenomena is: Like charges, opposite charges 2. Thomson s cathode ray experiment proved that: _ 3. Millikan s oil drop experiment proved that:
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see?
 Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
S2 F1. Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 S2 F1 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which has greater linear speed, a horse near the outside rail of a merry-go-round or
S2 F1 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which has greater linear speed, a horse near the outside rail of a merry-go-round or
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 13 Sound
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Waves Review Checklist Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one
 5.1.1 Oscillating Systems Waves Review Checklist 5.1.2 Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one Four pendulums are built as shown
5.1.1 Oscillating Systems Waves Review Checklist 5.1.2 Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one Four pendulums are built as shown
Physics Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING
 Physics Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Physics Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
PHYSICS CURRICULUM. Unit 1: Measurement and Mathematics
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 PHYSICS CURRICULUM Unit 1: Measurement and Mathematics OVERVIEW Summary Mathematics is an essential tool of physics. This unit will
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 PHYSICS CURRICULUM Unit 1: Measurement and Mathematics OVERVIEW Summary Mathematics is an essential tool of physics. This unit will
Final Worksheet. Equation And Constant Summary
 Equation And Constant Summary Final Worksheet These equations will be provided for you on the final. Know what they mean! Make notes on this page with which to study. v = d t t = d v d=vt If the speed
Equation And Constant Summary Final Worksheet These equations will be provided for you on the final. Know what they mean! Make notes on this page with which to study. v = d t t = d v d=vt If the speed
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
8.01. Determine arc length, angular velocity, and angular acceleration.
 8.01. Determine arc length, angular velocity, and angular acceleration. 8.02 Demonstrate conceptual knowledge of angular momentum and how it is affected by changing rotational velocity and moment of inertia.
8.01. Determine arc length, angular velocity, and angular acceleration. 8.02 Demonstrate conceptual knowledge of angular momentum and how it is affected by changing rotational velocity and moment of inertia.
the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance)
 Vocabulary Terms - Energy energy the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance) heat Heat is a form of energy that flows between two substances
Vocabulary Terms - Energy energy the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance) heat Heat is a form of energy that flows between two substances
MR. HOLL S PHYSICS FACTS MECHANICS. 1) Velocity is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
 MR. HOLL S PHYSICS FACTS MECHANICS 1) Velocity is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. 2) Speed is a scalar quantity that has ONLY magnitude. 3) Distance is a scalar and represents
MR. HOLL S PHYSICS FACTS MECHANICS 1) Velocity is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. 2) Speed is a scalar quantity that has ONLY magnitude. 3) Distance is a scalar and represents
8th Grade Physical Science Review Sheet SOL PS.2 matter # of protons (atomic #) atoms Physical properties Element # of protons (atomic #) chemically
 SOL PS.2 1. Anything that has mass and takes up space? matter 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called? atoms 3. Pure substance made up of only one kind of atom? Element 4. Two or more elements
SOL PS.2 1. Anything that has mass and takes up space? matter 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called? atoms 3. Pure substance made up of only one kind of atom? Element 4. Two or more elements
Course Guide. Introduction... 2
 Introduction... 2 Unit 1: Matter, States, & Interactions Lesson 1: Properties of Matter... 2 Lesson 2: States of Matter... 2 Lesson 3: Matter Particles... 3 Lesson 4: Organization of Matter... 3 Lesson
Introduction... 2 Unit 1: Matter, States, & Interactions Lesson 1: Properties of Matter... 2 Lesson 2: States of Matter... 2 Lesson 3: Matter Particles... 3 Lesson 4: Organization of Matter... 3 Lesson
10.1 Properties of Light
 10.1 Properties of Light Every time you see, you are using light. You can t see anything in complete darkness! Whether you are looking at a light bulb, or a car, or this book, light brings information
10.1 Properties of Light Every time you see, you are using light. You can t see anything in complete darkness! Whether you are looking at a light bulb, or a car, or this book, light brings information
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
P5 Revision Questions
 P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4. Properties of Light
 Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 Properties of Light There are many types of light sources... Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion The Nature of Light Pythagoras A Greek
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 Properties of Light There are many types of light sources... Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion The Nature of Light Pythagoras A Greek
Physics 9e/Cutnell. correlated to the. College Board AP Physics 2 Course Objectives
 correlated to the College Board AP Physics 2 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring Understanding 1.A:
correlated to the College Board AP Physics 2 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring Understanding 1.A:
A motion of particles motion of particles
 PHYSICS 2.3 Externally assessed 4 credits Demonstrate understanding of waves Unit 1: Wave properties Energy transfer Wave motion, in general, is a process in which kinetic energy is transferred from one
PHYSICS 2.3 Externally assessed 4 credits Demonstrate understanding of waves Unit 1: Wave properties Energy transfer Wave motion, in general, is a process in which kinetic energy is transferred from one
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
3/9/2011. Outline Chapter 7 Waves Water Waves Water Waves. Water waves are really circular. They are an example of Mechanical waves.
 Outline Chapter 7 Waves 7-1. Water Waves 7-2. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 7-3. Describing Waves 7-4. Standing Waves 7-5. Sound 7-6. Doppler Effect 7-7. Musical Sounds 7-8. Electromagnetic Waves 7-9.
Outline Chapter 7 Waves 7-1. Water Waves 7-2. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 7-3. Describing Waves 7-4. Standing Waves 7-5. Sound 7-6. Doppler Effect 7-7. Musical Sounds 7-8. Electromagnetic Waves 7-9.
Matter mass space atoms solid, a liquid, a gas, or plasm elements compounds mixtures atoms Compounds chemically combined Mixtures not chemically
 SOL PS.2 THE NATURE OF MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. Matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, a gas, or plasma. Matter
SOL PS.2 THE NATURE OF MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. Matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, a gas, or plasma. Matter
Physics Worksheet Sound and Light Section: Name:
 Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
Physics I Spring Final Review
 Name Period Physics I Spring Final Review Know all symbols and units! Know the these two constants: g = 9.8m/s 2 and c = 3x10 8 m/s Study old worksheets, notes, quizzes, labs, tests, & test reviews. If
Name Period Physics I Spring Final Review Know all symbols and units! Know the these two constants: g = 9.8m/s 2 and c = 3x10 8 m/s Study old worksheets, notes, quizzes, labs, tests, & test reviews. If
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
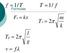 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
The Nature of Light and Matter 1 Light
 The Nature of Light and Matter 1 Light ASTR 103 4/06/2016 1 Basic properties: The Nature of Light Light travels in a straight line. Most surfaces reflect light. Amount of reflection depends on the medium.
The Nature of Light and Matter 1 Light ASTR 103 4/06/2016 1 Basic properties: The Nature of Light Light travels in a straight line. Most surfaces reflect light. Amount of reflection depends on the medium.
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Chapter 11. Preview. Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER
 SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
Light is an electromagnetic wave (EM)
 What is light? Light is a form of energy. Light travels in a straight line Light speed is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s Light is carried by photons Light can travel through a vacuum Light is a transverse wave Light is
What is light? Light is a form of energy. Light travels in a straight line Light speed is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s Light is carried by photons Light can travel through a vacuum Light is a transverse wave Light is
Page # Physics 103: Lecture 26 Sound. Lecture 26, Preflight 2. Lecture 26, Preflight 1. Producing a Sound Wave. Sound from a Tuning Fork
 Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS
 JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS (PHYSICS 2013) 1. What is the correct ascending order for frequencies of the following radiations? (1) Visible (2) X-rays (3) Ultra-violet (4) Radio waves (a) 1,3,2.4 (b) 3,2.4,1
JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS (PHYSICS 2013) 1. What is the correct ascending order for frequencies of the following radiations? (1) Visible (2) X-rays (3) Ultra-violet (4) Radio waves (a) 1,3,2.4 (b) 3,2.4,1
Modern Physics, Waves, Electricity
 Name: Date: 1. Metal sphere has a charge of +12 elementary charges and identical sphere has a charge of +16 elementary charges. fter the two spheres are brought into contact, the charge on sphere is 4.
Name: Date: 1. Metal sphere has a charge of +12 elementary charges and identical sphere has a charge of +16 elementary charges. fter the two spheres are brought into contact, the charge on sphere is 4.
Physics Fundamentals Study Guide
 Physics Fundamentals Study Guide Items to gather: 1. Any colorful helpful unit sheets 2. All Friday quizzes 3. All free responses from tests On the Day of the Final: May Items to bring: 1. Calculator (using
Physics Fundamentals Study Guide Items to gather: 1. Any colorful helpful unit sheets 2. All Friday quizzes 3. All free responses from tests On the Day of the Final: May Items to bring: 1. Calculator (using
Fluorescence. Incandescence. Electric. Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence. Combustion
 Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion Pythagoras A Greek philosopher Believed light was beams of tiny particles The eyes could detect these particles and see
Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion Pythagoras A Greek philosopher Believed light was beams of tiny particles The eyes could detect these particles and see
to calculate gravitational force. d - Know how changes in mass or distance affect the gravitational force between two objects.
 PHYSICS 2 ND SEMESTER REVIEW Semester Test Notes: - You may use a 5 x 8 index card (NO LARGER) with equations, diagrams, and notes. - Your index card will be turned in with your test. - Most constants
PHYSICS 2 ND SEMESTER REVIEW Semester Test Notes: - You may use a 5 x 8 index card (NO LARGER) with equations, diagrams, and notes. - Your index card will be turned in with your test. - Most constants
Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light
 Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light Key Terms: Microscope, telescope, amplitude, crest, energy, force, frequency, hertz, medium, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, reflection,
Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light Key Terms: Microscope, telescope, amplitude, crest, energy, force, frequency, hertz, medium, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, reflection,
Pearson Interactive Science: Physical Science 2013 CPO Science Link Correlation
 Pearson Interactive Science: Physical Science 2013 CPO Science Link Correlation Interactive Science: Physical Science Chapter 1 - Introduction to Matter Lesson 1 - Describing Matter matter, substance,
Pearson Interactive Science: Physical Science 2013 CPO Science Link Correlation Interactive Science: Physical Science Chapter 1 - Introduction to Matter Lesson 1 - Describing Matter matter, substance,
Academic Physics Spring Semester Final Review
 Spring Semester Final Review The Final will be 70 multiple choice questions. This review is intended to be a review and not all inclusive. You must study your notes, labs, quizzes and tests in order to
Spring Semester Final Review The Final will be 70 multiple choice questions. This review is intended to be a review and not all inclusive. You must study your notes, labs, quizzes and tests in order to
LIGHT. Question. Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light.
 LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
Give some examples of a Noncontact force
 What is a vector quantity? What is a scalar quantity? What do physicists mean by the term displacement? State Newton s third law of motion. What is the unit of Force What is meant by the term Contact force
What is a vector quantity? What is a scalar quantity? What do physicists mean by the term displacement? State Newton s third law of motion. What is the unit of Force What is meant by the term Contact force
Name Class Date. What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic spectrum? How can electromagnetic waves be used?
 CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
Study Guide for Physics 1100 Final Exam
 Study Guide for Physics 1100 Final Exam Dr. Fazzini s Physics 1100 Final Exam will take place on Wednesday, May 16 th, 2018 from 9:00AM-10:50AM in Room BIC-3535. Click on the Detailed Class Information
Study Guide for Physics 1100 Final Exam Dr. Fazzini s Physics 1100 Final Exam will take place on Wednesday, May 16 th, 2018 from 9:00AM-10:50AM in Room BIC-3535. Click on the Detailed Class Information
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Science Curriculum Matrix
 Science Curriculum Matrix Physics Version 1.0 beta June 2, 2008 This curriculum (core matrix) document will eventually become part of the Science Curriculum Matrix. We envision the Science Curriculum Matrix
Science Curriculum Matrix Physics Version 1.0 beta June 2, 2008 This curriculum (core matrix) document will eventually become part of the Science Curriculum Matrix. We envision the Science Curriculum Matrix
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220. Final Exam. Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total)
 Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Unit 6 Forces in Nature gravity; Law of Universal Gravitation; current; series/parallel circuits; magnets; electromagnets
 8 th grade Physical Science comprehensive study guide Unit 2 Nature of Matter atoms/molecules; atomic models; physical/chemical properties; physical/chemical changes; types of bonds; periodic table; states
8 th grade Physical Science comprehensive study guide Unit 2 Nature of Matter atoms/molecules; atomic models; physical/chemical properties; physical/chemical changes; types of bonds; periodic table; states
CAMI - Science. CAPS - Physics Links Grade 10
 CAMI - Science CAPS - Physics Links Grade 10 TERM 1 TOPICS CONTENT, CONCEPTS & SKILLS CAMI - KEYSTROKES Transverse pulses on a string or spring Pulse, amplitude Define a pulse Define a transverse pulse
CAMI - Science CAPS - Physics Links Grade 10 TERM 1 TOPICS CONTENT, CONCEPTS & SKILLS CAMI - KEYSTROKES Transverse pulses on a string or spring Pulse, amplitude Define a pulse Define a transverse pulse
Fluids density Pascal s principle (pressure vs. depth) Equation of continuity Buoyant force Bernoulli s (pressure, velocity, depth)
 Final Exam All Finals week in the testing center. 50 multiple choice questions. Equations on the back of the test. Calculators are allowed on the test. There is a practice test in the packet. Exam 1 Review
Final Exam All Finals week in the testing center. 50 multiple choice questions. Equations on the back of the test. Calculators are allowed on the test. There is a practice test in the packet. Exam 1 Review
Republic of Somaliland. Somaliland National Examination Board. Form Four. Physics Examination. June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS
 Name..... Total Score School... Roll No... Republic of Somaliland Form Four Physics Examination June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS Plus 10 minutes for reading through the paper Total time 2 Hours and 10 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS
Name..... Total Score School... Roll No... Republic of Somaliland Form Four Physics Examination June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS Plus 10 minutes for reading through the paper Total time 2 Hours and 10 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS
Light. Mike Maloney Physics, SHS
 Light Mike Maloney Physics, SHS 1 Light What is LIGHT? WHERE DOES IT COME FROM? 2003 Mike Maloney 2 What is Light? Light is a wave, or rather acts like a wave. How do we know since we cannot see it? We
Light Mike Maloney Physics, SHS 1 Light What is LIGHT? WHERE DOES IT COME FROM? 2003 Mike Maloney 2 What is Light? Light is a wave, or rather acts like a wave. How do we know since we cannot see it? We
PHYSICS PRACTICAL (CBSE) - X
 PHYSICS PRACTICAL (CBSE) - X Scientific Terminology / Definitions Absolute refractive index (m) : It is the refractive index of the medium with respect to air or vacuum. Amplitude (A) : It is the maximum
PHYSICS PRACTICAL (CBSE) - X Scientific Terminology / Definitions Absolute refractive index (m) : It is the refractive index of the medium with respect to air or vacuum. Amplitude (A) : It is the maximum
The Final Exam (Exam 4) will be on FRIDAY MAY 11 From 3 5 PM in LR1 VAN
 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29:006 SPRING 2012 PRACTICE EXAM 4 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29:006 SPRING 2012 PRACTICE EXAM 4 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Experiment #4 Nature of Light: Telescope and Microscope and Spectroscope
 Experiment #4 Nature of Light: Telescope and Microscope and Spectroscope In this experiment, we are going to learn the basic principles of the telescope and the microscope that make it possible for us
Experiment #4 Nature of Light: Telescope and Microscope and Spectroscope In this experiment, we are going to learn the basic principles of the telescope and the microscope that make it possible for us
2007 Oct 9 Light, Tools of Astronomy Page 1 of 5
 Light Waves, Tools of Astronomy I. Vibrations and waves A. Wiggle in time is a vibration needs elapsed time to occur B. Wave is created by vibration exists over space and time C. Types 1. Sound wave needs
Light Waves, Tools of Astronomy I. Vibrations and waves A. Wiggle in time is a vibration needs elapsed time to occur B. Wave is created by vibration exists over space and time C. Types 1. Sound wave needs
WAVES AND RADIATION. 1 Measuring the focal length of a lens. Topic 7 Physics. The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens.
 1 Measuring the focal length of a lens The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens. Which of these is the correct distance for the focal length? A from the window to the lens B from the
1 Measuring the focal length of a lens The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens. Which of these is the correct distance for the focal length? A from the window to the lens B from the
Photochemical principles
 Chapter 1 Photochemical principles Dr. Suzan A. Khayyat 1 Photochemistry Photochemistry is concerned with the absorption, excitation and emission of photons by atoms, atomic ions, molecules, molecular
Chapter 1 Photochemical principles Dr. Suzan A. Khayyat 1 Photochemistry Photochemistry is concerned with the absorption, excitation and emission of photons by atoms, atomic ions, molecules, molecular
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST
 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
Waves ~ Learning Guide
 Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: AP REVIEW 3 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. For a mass hanging from a spring, the maximum displacement the
Name: Class: Date: AP REVIEW 3 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. For a mass hanging from a spring, the maximum displacement the
Curriculum Map-- Kings School District Honors Physics
 Curriculum Map-- Kings School District Honors Physics Big ideas Essential Questions Content Skills/Standards Assessment + Criteria Activities/Resources Motion of an object can be described by its position,
Curriculum Map-- Kings School District Honors Physics Big ideas Essential Questions Content Skills/Standards Assessment + Criteria Activities/Resources Motion of an object can be described by its position,
Physics Study Notes Lesson 20 Sound and Light 1 The Origin of Sound vibrations longitudinal waves infrasonic ultrasonic 2 Sound in Air Compression
 1 The Origin of Sound a. All sounds are produced by the vibrations of material objects. b. The original vibration stimulates the vibration of something larger or more massive, and then this vibrating material
1 The Origin of Sound a. All sounds are produced by the vibrations of material objects. b. The original vibration stimulates the vibration of something larger or more massive, and then this vibrating material
Section 1: The Science of Energy¹
 SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
National 3 Waves and Radiation
 What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
UNIT II. Energy Transfer of Energy. Chapter 2: Energy Transfers
 UNIT II Energy Transfer of Energy Chapter 2: Energy Transfers The ability of matter to do work or make things happen is known as Energy. There are various forms of energy. Kinetic energy is the energy
UNIT II Energy Transfer of Energy Chapter 2: Energy Transfers The ability of matter to do work or make things happen is known as Energy. There are various forms of energy. Kinetic energy is the energy
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
DEFINITIONS. Linear Motion. Conservation of Momentum. Vectors and Scalars. Circular Motion. Newton s Laws of Motion
 DEFINITIONS Linear Motion Mass: The mass of a body is the amount of matter in it. Displacement: The displacement of a body from a point is its distance from a point in a given direction. Velocity: The
DEFINITIONS Linear Motion Mass: The mass of a body is the amount of matter in it. Displacement: The displacement of a body from a point is its distance from a point in a given direction. Velocity: The
Chapter 4 - Light. Name: Block:
 Chapter 4 Notes: Light Name: Block: Properties of Waves Waves are a repeating disturbance or movement that energy through matter or space without causing any displacement of material Features of a wave:
Chapter 4 Notes: Light Name: Block: Properties of Waves Waves are a repeating disturbance or movement that energy through matter or space without causing any displacement of material Features of a wave:
