UNIT 3 EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS Lesson 4: Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Instruction. Guided Practice Example 1
|
|
|
- Rachel Adele Fowler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guded Practce 3.4. Example 1 Instructon For each equaton, state the number and type of solutons by frst fndng the dscrmnant. x + 3x =.4x x = 3x = x 9x + 1 = 6x 1. Fnd the dscrmnant of x + 3x =. The equaton x + 3x = s n the form ax + bx + c = wth a =, b = 3, and c =. Use the dscrmnant formula. b 4ac Dscrmnant formula (3) 4()( ) Substtute for a, 3 for b, and for c Smplfy. 49 The dscrmnant of x + 3x = s 49. The dscrmnant s postve, so the equaton has two real solutons. U Walch Educaton
2 Instructon. Fnd the dscrmnant of.4x x =. The equaton.4x x = s n the form ax + bx + c = wth a =.4, b = 1, and c =. Use the dscrmnant formula. b 4ac Dscrmnant formula ( 1) 4(.4)() Substtute.4 for a, 1 for b, and for c. ( 1) + Smplfy. 1 The dscrmnant of.4x x = s 1. The dscrmnant s postve, so the equaton has two real solutons. 3. Fnd the dscrmnant of 3x = x. The equaton 3x = x s not n the form ax + bx + c =, so begn by wrtng t n that form. 3x = x 3x x = 3x x + = Orgnal equaton Subtract x from both sdes. Add to both sdes. The equaton 3x x + = s n the form ax + bx + c =, wth a = 3, b =, and c =. Use the dscrmnant formula. b 4ac Dscrmnant formula ( ) 4(3)() Substtute 3 for a, for b, and for c. 4 6 Smplfy. 6 The dscrmnant of 3x = x s 6. The dscrmnant s negatve, so the equaton has two magnary solutons, whch together are a complex conjugate par. Walch Educaton U
3 Instructon 4. Fnd the dscrmnant of 9x + 1 = 6x. The equaton 9x + 1 = 6x s not n the form ax + bx + c =, so begn by wrtng t n that form. 9x + 1 = 6x 9x 6x + 1 = Orgnal equaton Subtract 6x from both sdes. The equaton 9x 6x + 1 = s n the form ax + bx + c = wth a = 9, b = 6, and c = 1. Use the dscrmnant formula. b 4ac Dscrmnant formula ( 6) 4(9)(1) Substtute 9 for a, 6 for b, and 1 for c Smplfy.. The dscrmnant of 9x + 1 = 6x s equal to, so the equaton has one real soluton, whch s a double root. U Walch Educaton
4 Instructon Example Solve by usng a property of square roots. Show that the quadratc formula gves the same solutons. Check your solutons. Explan how the graph of the related functon supports the type of solutons. 1. Determne whch property of square roots to use. There s no x-term, so you can solve the equaton by usng ths property of square roots: If x = a, then x=± a. Orgnal equaton Subtract 6 from both sdes. 1 x = Multply both sdes by. x =± 1 Apply ths property of square roots: If x = a, then x=± a. x=± 1 For any postve real number a, a= a. The solutons to are ± 1. Walch Educaton U
5 Instructon. Wrte the radcal n smplest form. x=± 1 x=± 1 x=± 1 x=± 6 x=± 6 x=± 4 1 x=± 4 1 x=± For any real numbers a and b wth b, Multply by, whch s equal to 1. For any real numbers a and b, a b= ab. Smplfy. Smplfy the denomnator. Factor 6 to show a perfect square factor. For any real numbers a and b, a b= ab. Smplfy. a a =. b b The solutons to, wrtten n smplest form, are 1 and 1. These solutons are a conjugate par and can be wrtten as + 1 and 1. U Walch Educaton
6 Instructon 3. Show that usng the quadratc formula gves the same solutons. The quadratc formula states that f ax + bx + c =, then b b ac x = ±. a Wrte the gven equaton. x + 1= 4 x = ± 4 ( )( 1 ) ( ) x = ± 4 1 x = ± 4 1 x = ± x = ± ±4 1 x = 1 ± 1 x = Multply both sdes by 1, the least common denomnator, to elmnate fractons. Substtute values for a, b, and c: a =, b =, c = 1. Smplfy. For any postve real number a, a= a. Factor 4 to show ts greatest perfect square factor, 16. For any real numbers a and b, ab = a b. Smplfy. The solutons to, found usng the quadratc formula, are 1 and 1, matchng those found n step 1. Walch Educaton U
7 Instructon 4. Check the solutons. Substtute each soluton nto the orgnal equaton,. Check 1 : Check 1 : = = = = ( )+ = ( )+ = = = = = = =. Graph the related quadratc functon f( x)= x + on a graphng calculator. On a TI-83/84: Step 1: Press [Y=]. Step : At Y 1, type n [(][1][ ][][)][X,T,θ,n][x ][+][(][6][ ][][)]. Step 3: Press [WINDOW] to change the vewng wndow. Step 4: At Xmn, enter [( )][9]. Step : At Xmax, enter [9]. Step 6: At Xscl, enter [1]. (contnued) U Walch Educaton
8 Instructon Step 7: At Ymn, enter [( )][6]. Step 8: At Ymax, enter [6]. Step 9: At Yscl, enter [1]. Step 1: Press [GRAPH]. On a TI-Nspre: Step 1: Press the [home] key. Step : Arrow over to the graphng con and press [enter], Step 3: Enter the equaton [(][1][ ][][)][ ][x ][+][(][6][ ][][)] and press [enter]. Step 4: Change the vewng wndow by pressng [menu], then arrow down to number 4: Wndow/Zoom, and clck the center button of the navgaton pad. Step : Choose 1: Wndow Settngs by pressng the center button. Step 6: Enter n the approprate XMn value, [ ][9], then press [tab]. Step 7: Enter the approprate XMax value, [9], then press [tab]. Step 8: Leave the XScale set to auto. Press [tab] twce to navgate to YMn and enter [ ][6]. Step 9: Press [tab] to navgate to YMax. Enter [6]. Press [tab] twce to leave YScale set to auto and to navgate to OK. Step 1: Press [enter] Walch Educaton U3-3.4.
9 Instructon 6. Explan how the graph of the related quadratc functon, f( x)= x +, supports the type of solutons. The graph of f( x)= x + has no x-ntercepts, whch verfes that the equaton has no real solutons. Example 3 Solve x + 6x 13 = by usng the quadratc formula. Check your solutons. Explan how the graph of the related functon supports the type of solutons. 1. Substtute values for the equaton nto the quadratc formula. b b ac The quadratc formula states that f ax + bx + c =, then x = ±. a x + 6x 13 = s wrtten n the form ax + bx + c = ; therefore, a = 1, b = 6, and c = 13. x + 6x 13 = Orgnal equaton ( )( ) ( ) x = ± x = 6 ± 36 x = 6 ± 16 x = 6 ± 16 x = 6 ± 4 x = 6 ± 4 x= 3± 4 Substtute values for a, b and c nto the formula: a = 1, b = 6, c = 13. Smplfy. For any postve real number a, a= a. Smplfy. The solutons of x + 6x 13 = are 3 + and 3. U Walch Educaton
10 Instructon. Check the solutons. Substtute the solutons nto the orgnal formula. Check 3 + : Check 3 : x + 6x 13 = x + 6x 13 = ( 3+ ) + 6( 3+ ) 13= ( 3 ) + 6( 3 ) 13= ( 3+ ) ( 3+ )+ 6( 3+ ) 13= ( 3 ) ( 3 )+ 6( 3 ) 13= ( )+ 6( 3+ ) 13= ( )+ 6( 3 ) 13= ( )+ 6( 3+ ) 13= ( )+ 6( 3 ) 13= = = = = = = = = 3. Explan how the graph of the related quadratc functon, f(x) = x + 6x 13, supports the type of solutons. y x f(x) = x + 6x 13 8 The graph of f(x) = x + 6x 13 has no x-ntercepts, whch verfes that the equaton x + 6x 13 = has no real solutons, and has two magnary solutons. Walch Educaton U
11 Example 4 Instructon Solve x + 9 = 8x by usng the quadratc formula. Check your solutons. Explan how the graph of the related functon supports the type of solutons. 1. Substtute values for the equaton nto the quadratc formula. b b ac The quadratc formula states that f ax + bx + c =, then x = ±. a x + 9 = 8x Orgnal equaton x + 8x + 9 = x = ± ( )( 9 ) ( ) x = 8 ± x = 8± 8 4 x = 8± 8 4 x = 8± 4 x = 8 ± 4 4 x= ± Add 8x to both sdes to get the form ax + bx + c =. Substtute values for a, b, and c nto the formula: a =, b = 8, c = 9. Smplfy. 4 For any postve real number a, a= a. Smplfy. The solutons of x + 9 = 8x are + and.. Check the solutons. Substtute the solutons nto x + 8x + 9 =. (contnued) U Walch Educaton
12 Instructon Check + : x + 8x + 9 = = = = = = = = Check : x + 8x + 9 = = = = = = = = Walch Educaton U
13 Instructon 3. Explan how the graph of the related quadratc functon, f(x) = x + 8x + 9, supports the type of solutons. y 4 f(x) = x + 8x x The graph of f(x) = x + 8x + 9 has no x-ntercepts, whch verfes that the equaton x + 8x + 9 = has no real solutons, and has two magnary solutons. U Walch Educaton
Complex Numbers. x = B B 2 4AC 2A. or x = x = 2 ± 4 4 (1) (5) 2 (1)
 Complex Numbers If you have not yet encountered complex numbers, you wll soon do so n the process of solvng quadratc equatons. The general quadratc equaton Ax + Bx + C 0 has solutons x B + B 4AC A For
Complex Numbers If you have not yet encountered complex numbers, you wll soon do so n the process of solvng quadratc equatons. The general quadratc equaton Ax + Bx + C 0 has solutons x B + B 4AC A For
Quadratic Formula, Completing the Square, Systems Review Sheet
 Quadratc Formula Completng the Square Systems Revew Sheet 1. Factor the polynomal completely. 6. Use the graph to approxmate the real zeros of the functon. 2. Fnd the real-number solutons of the equaton.
Quadratc Formula Completng the Square Systems Revew Sheet 1. Factor the polynomal completely. 6. Use the graph to approxmate the real zeros of the functon. 2. Fnd the real-number solutons of the equaton.
8.6 The Complex Number System
 8.6 The Complex Number System Earler n the chapter, we mentoned that we cannot have a negatve under a square root, snce the square of any postve or negatve number s always postve. In ths secton we want
8.6 The Complex Number System Earler n the chapter, we mentoned that we cannot have a negatve under a square root, snce the square of any postve or negatve number s always postve. In ths secton we want
Unit 5: Quadratic Equations & Functions
 Date Perod Unt 5: Quadratc Equatons & Functons DAY TOPIC 1 Modelng Data wth Quadratc Functons Factorng Quadratc Epressons 3 Solvng Quadratc Equatons 4 Comple Numbers Smplfcaton, Addton/Subtracton & Multplcaton
Date Perod Unt 5: Quadratc Equatons & Functons DAY TOPIC 1 Modelng Data wth Quadratc Functons Factorng Quadratc Epressons 3 Solvng Quadratc Equatons 4 Comple Numbers Smplfcaton, Addton/Subtracton & Multplcaton
Section 3.6 Complex Zeros
 04 Chapter Secton 6 Comple Zeros When fndng the zeros of polynomals, at some pont you're faced wth the problem Whle there are clearly no real numbers that are solutons to ths equaton, leavng thngs there
04 Chapter Secton 6 Comple Zeros When fndng the zeros of polynomals, at some pont you're faced wth the problem Whle there are clearly no real numbers that are solutons to ths equaton, leavng thngs there
UNIT 4 EXTENDING THE NUMBER SYSTEM Lesson 3: Operating with Complex Numbers Instruction
 Prerequste Sklls Ths lesson requres the use of the followng sklls: understandng that multplyng the numerator and denomnator of a fracton by the same quantty produces an equvalent fracton multplyng complex
Prerequste Sklls Ths lesson requres the use of the followng sklls: understandng that multplyng the numerator and denomnator of a fracton by the same quantty produces an equvalent fracton multplyng complex
Section 8.3 Polar Form of Complex Numbers
 80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Objective To use the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to solve polynomial equations with complex solutions
 5-6 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Content Standards N.CN.7 Solve quadratc equatons wth real coeffcents that have comple solutons. N.CN.8 Etend polnomal denttes to the comple numbers. Also N.CN.9,
5-6 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Content Standards N.CN.7 Solve quadratc equatons wth real coeffcents that have comple solutons. N.CN.8 Etend polnomal denttes to the comple numbers. Also N.CN.9,
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
 COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
Math1110 (Spring 2009) Prelim 3 - Solutions
 Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
332600_08_1.qxp 4/17/08 11:29 AM Page 481
 336_8_.qxp 4/7/8 :9 AM Page 48 8 Complex Vector Spaces 8. Complex Numbers 8. Conjugates and Dvson of Complex Numbers 8.3 Polar Form and DeMovre s Theorem 8.4 Complex Vector Spaces and Inner Products 8.5
336_8_.qxp 4/7/8 :9 AM Page 48 8 Complex Vector Spaces 8. Complex Numbers 8. Conjugates and Dvson of Complex Numbers 8.3 Polar Form and DeMovre s Theorem 8.4 Complex Vector Spaces and Inner Products 8.5
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
UNIT 6 MODELING GEOMETRY Lesson 1: Deriving Equations Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: appling the Pthagorean Theorem representing horizontal and vertical distances in a coordinate plane simplifing square roots writing
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: appling the Pthagorean Theorem representing horizontal and vertical distances in a coordinate plane simplifing square roots writing
A repeated root is a root that occurs more than once in a polynomial function.
 Unit 2A, Lesson 3.3 Finding Zeros Synthetic division, along with your knowledge of end behavior and turning points, can be used to identify the x-intercepts of a polynomial function. This information allows
Unit 2A, Lesson 3.3 Finding Zeros Synthetic division, along with your knowledge of end behavior and turning points, can be used to identify the x-intercepts of a polynomial function. This information allows
y i x P vap 10 A T SOLUTION TO HOMEWORK #7 #Problem
 SOLUTION TO HOMEWORK #7 #roblem 1 10.1-1 a. In order to solve ths problem, we need to know what happens at the bubble pont; at ths pont, the frst bubble s formed, so we can assume that all of the number
SOLUTION TO HOMEWORK #7 #roblem 1 10.1-1 a. In order to solve ths problem, we need to know what happens at the bubble pont; at ths pont, the frst bubble s formed, so we can assume that all of the number
Solution of Linear System of Equations and Matrix Inversion Gauss Seidel Iteration Method
 Soluton of Lnear System of Equatons and Matr Inverson Gauss Sedel Iteraton Method It s another well-known teratve method for solvng a system of lnear equatons of the form a + a22 + + ann = b a2 + a222
Soluton of Lnear System of Equatons and Matr Inverson Gauss Sedel Iteraton Method It s another well-known teratve method for solvng a system of lnear equatons of the form a + a22 + + ann = b a2 + a222
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Fall 13 Midterm, October 31
 Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Fall 13 Mdterm, October 31 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Fall 13 Mdterm, October 31 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Statistics MINITAB - Lab 2
 Statstcs 20080 MINITAB - Lab 2 1. Smple Lnear Regresson In smple lnear regresson we attempt to model a lnear relatonshp between two varables wth a straght lne and make statstcal nferences concernng that
Statstcs 20080 MINITAB - Lab 2 1. Smple Lnear Regresson In smple lnear regresson we attempt to model a lnear relatonshp between two varables wth a straght lne and make statstcal nferences concernng that
Physics 4B. A positive value is obtained, so the current is counterclockwise around the circuit.
 Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Winter 16 Final, March 16, 2016
 ME140 - Lnear rcuts - Wnter 16 Fnal, March 16, 2016 Instructons () The exam s open book. You may use your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator wth no communcaton capabltes. () You have
ME140 - Lnear rcuts - Wnter 16 Fnal, March 16, 2016 Instructons () The exam s open book. You may use your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator wth no communcaton capabltes. () You have
THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructions
 THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructons by George Hardgrove Chemstry Department St. Olaf College Northfeld, MN 55057 hardgrov@lars.acc.stolaf.edu Copyrght George
THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructons by George Hardgrove Chemstry Department St. Olaf College Northfeld, MN 55057 hardgrov@lars.acc.stolaf.edu Copyrght George
Pre-Calculus Summer Assignment
 Pre-Calculus Summer Assgnment Dear Future Pre-Calculus Student, Congratulatons on our successful completon of Algebra! Below ou wll fnd the summer assgnment questons. It s assumed that these concepts,
Pre-Calculus Summer Assgnment Dear Future Pre-Calculus Student, Congratulatons on our successful completon of Algebra! Below ou wll fnd the summer assgnment questons. It s assumed that these concepts,
APPENDIX 2 FITTING A STRAIGHT LINE TO OBSERVATIONS
 Unversty of Oulu Student Laboratory n Physcs Laboratory Exercses n Physcs 1 1 APPEDIX FITTIG A STRAIGHT LIE TO OBSERVATIOS In the physcal measurements we often make a seres of measurements of the dependent
Unversty of Oulu Student Laboratory n Physcs Laboratory Exercses n Physcs 1 1 APPEDIX FITTIG A STRAIGHT LIE TO OBSERVATIOS In the physcal measurements we often make a seres of measurements of the dependent
Complex Numbers Alpha, Round 1 Test #123
 Complex Numbers Alpha, Round Test #3. Wrte your 6-dgt ID# n the I.D. NUMBER grd, left-justfed, and bubble. Check that each column has only one number darkened.. In the EXAM NO. grd, wrte the 3-dgt Test
Complex Numbers Alpha, Round Test #3. Wrte your 6-dgt ID# n the I.D. NUMBER grd, left-justfed, and bubble. Check that each column has only one number darkened.. In the EXAM NO. grd, wrte the 3-dgt Test
Complex Numbers, Signals, and Circuits
 Complex Numbers, Sgnals, and Crcuts 3 August, 009 Complex Numbers: a Revew Suppose we have a complex number z = x jy. To convert to polar form, we need to know the magntude of z and the phase of z. z =
Complex Numbers, Sgnals, and Crcuts 3 August, 009 Complex Numbers: a Revew Suppose we have a complex number z = x jy. To convert to polar form, we need to know the magntude of z and the phase of z. z =
CALCULUS CLASSROOM CAPSULES
 CALCULUS CLASSROOM CAPSULES SESSION S86 Dr. Sham Alfred Rartan Valley Communty College salfred@rartanval.edu 38th AMATYC Annual Conference Jacksonvlle, Florda November 8-, 202 2 Calculus Classroom Capsules
CALCULUS CLASSROOM CAPSULES SESSION S86 Dr. Sham Alfred Rartan Valley Communty College salfred@rartanval.edu 38th AMATYC Annual Conference Jacksonvlle, Florda November 8-, 202 2 Calculus Classroom Capsules
Table of Contents. Unit 6: Modeling Geometry. Answer Key...AK-1. Introduction... v
 These materials ma not be reproduced for an purpose. The reproduction of an part for an entire school or school sstem is strictl prohibited. No part of this publication ma be transmitted, stored, or recorded
These materials ma not be reproduced for an purpose. The reproduction of an part for an entire school or school sstem is strictl prohibited. No part of this publication ma be transmitted, stored, or recorded
Be true to your work, your word, and your friend.
 Chemstry 13 NT Be true to your work, your word, and your frend. Henry Davd Thoreau 1 Chem 13 NT Chemcal Equlbrum Module Usng the Equlbrum Constant Interpretng the Equlbrum Constant Predctng the Drecton
Chemstry 13 NT Be true to your work, your word, and your frend. Henry Davd Thoreau 1 Chem 13 NT Chemcal Equlbrum Module Usng the Equlbrum Constant Interpretng the Equlbrum Constant Predctng the Drecton
Problem Solving in Math (Math 43900) Fall 2013
 Problem Solvng n Math (Math 43900) Fall 2013 Week four (September 17) solutons Instructor: Davd Galvn 1. Let a and b be two nteger for whch a b s dvsble by 3. Prove that a 3 b 3 s dvsble by 9. Soluton:
Problem Solvng n Math (Math 43900) Fall 2013 Week four (September 17) solutons Instructor: Davd Galvn 1. Let a and b be two nteger for whch a b s dvsble by 3. Prove that a 3 b 3 s dvsble by 9. Soluton:
Solutions to Problem Set 6
 Solutons to Problem Set 6 Problem 6. (Resdue theory) a) Problem 4.7.7 Boas. n ths problem we wll solve ths ntegral: x sn x x + 4x + 5 dx: To solve ths usng the resdue theorem, we study ths complex ntegral:
Solutons to Problem Set 6 Problem 6. (Resdue theory) a) Problem 4.7.7 Boas. n ths problem we wll solve ths ntegral: x sn x x + 4x + 5 dx: To solve ths usng the resdue theorem, we study ths complex ntegral:
November 5, 2002 SE 180: Earthquake Engineering SE 180. Final Project
 SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
1 Matrix representations of canonical matrices
 1 Matrx representatons of canoncal matrces 2-d rotaton around the orgn: ( ) cos θ sn θ R 0 = sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the x-axs: R x = 1 0 0 0 cos θ sn θ 0 sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the y-axs:
1 Matrx representatons of canoncal matrces 2-d rotaton around the orgn: ( ) cos θ sn θ R 0 = sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the x-axs: R x = 1 0 0 0 cos θ sn θ 0 sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the y-axs:
For all questions, answer choice E) NOTA" means none of the above answers is correct.
 0 MA Natonal Conventon For all questons, answer choce " means none of the above answers s correct.. In calculus, one learns of functon representatons that are nfnte seres called power 3 4 5 seres. For
0 MA Natonal Conventon For all questons, answer choce " means none of the above answers s correct.. In calculus, one learns of functon representatons that are nfnte seres called power 3 4 5 seres. For
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Winter 16 Midterm, February 5
 Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Wnter 16 Mdterm, February 5 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Wnter 16 Mdterm, February 5 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Chapter Newton s Method
 Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
DISCRIMINANTS AND RAMIFIED PRIMES. 1. Introduction A prime number p is said to be ramified in a number field K if the prime ideal factorization
 DISCRIMINANTS AND RAMIFIED PRIMES KEITH CONRAD 1. Introducton A prme number p s sad to be ramfed n a number feld K f the prme deal factorzaton (1.1) (p) = po K = p e 1 1 peg g has some e greater than 1.
DISCRIMINANTS AND RAMIFIED PRIMES KEITH CONRAD 1. Introducton A prme number p s sad to be ramfed n a number feld K f the prme deal factorzaton (1.1) (p) = po K = p e 1 1 peg g has some e greater than 1.
= = = (a) Use the MATLAB command rref to solve the system. (b) Let A be the coefficient matrix and B be the right-hand side of the system.
 Chapter Matlab Exercses Chapter Matlab Exercses. Consder the lnear system of Example n Secton.. x x x y z y y z (a) Use the MATLAB command rref to solve the system. (b) Let A be the coeffcent matrx and
Chapter Matlab Exercses Chapter Matlab Exercses. Consder the lnear system of Example n Secton.. x x x y z y y z (a) Use the MATLAB command rref to solve the system. (b) Let A be the coeffcent matrx and
Introduction to Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium, part 2. Raoult s Law:
 CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
Advanced Circuits Topics - Part 1 by Dr. Colton (Fall 2017)
 Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
THE CHINESE REMAINDER THEOREM. We should thank the Chinese for their wonderful remainder theorem. Glenn Stevens
 THE CHINESE REMAINDER THEOREM KEITH CONRAD We should thank the Chnese for ther wonderful remander theorem. Glenn Stevens 1. Introducton The Chnese remander theorem says we can unquely solve any par of
THE CHINESE REMAINDER THEOREM KEITH CONRAD We should thank the Chnese for ther wonderful remander theorem. Glenn Stevens 1. Introducton The Chnese remander theorem says we can unquely solve any par of
U.C. Berkeley CS294: Beyond Worst-Case Analysis Luca Trevisan September 5, 2017
 U.C. Berkeley CS94: Beyond Worst-Case Analyss Handout 4s Luca Trevsan September 5, 07 Summary of Lecture 4 In whch we ntroduce semdefnte programmng and apply t to Max Cut. Semdefnte Programmng Recall that
U.C. Berkeley CS94: Beyond Worst-Case Analyss Handout 4s Luca Trevsan September 5, 07 Summary of Lecture 4 In whch we ntroduce semdefnte programmng and apply t to Max Cut. Semdefnte Programmng Recall that
C/CS/Phy191 Problem Set 3 Solutions Out: Oct 1, 2008., where ( 00. ), so the overall state of the system is ) ( ( ( ( 00 ± 11 ), Φ ± = 1
 C/CS/Phy9 Problem Set 3 Solutons Out: Oct, 8 Suppose you have two qubts n some arbtrary entangled state ψ You apply the teleportaton protocol to each of the qubts separately What s the resultng state obtaned
C/CS/Phy9 Problem Set 3 Solutons Out: Oct, 8 Suppose you have two qubts n some arbtrary entangled state ψ You apply the teleportaton protocol to each of the qubts separately What s the resultng state obtaned
Mathematics Intersection of Lines
 a place of mnd F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Currculum and Pedagog Mathematcs Intersecton of Lnes Scence and Mathematcs Educaton Research Group Supported b UBC Teachng and Learnng Enhancement
a place of mnd F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Currculum and Pedagog Mathematcs Intersecton of Lnes Scence and Mathematcs Educaton Research Group Supported b UBC Teachng and Learnng Enhancement
Kinematics in 2-Dimensions. Projectile Motion
 Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
18.781: Solution to Practice Questions for Final Exam
 18.781: Soluton to Practce Questons for Fnal Exam 1. Fnd three solutons n postve ntegers of x 6y = 1 by frst calculatng the contnued fracton expanson of 6. Soluton: We have 1 6=[, ] 6 6+ =[, ] 1 =[,, ]=[,,
18.781: Soluton to Practce Questons for Fnal Exam 1. Fnd three solutons n postve ntegers of x 6y = 1 by frst calculatng the contnued fracton expanson of 6. Soluton: We have 1 6=[, ] 6 6+ =[, ] 1 =[,, ]=[,,
( ) 1/ 2. ( P SO2 )( P O2 ) 1/ 2.
 Chemstry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Problem Set 9 Solutons. The followng chemcal reacton converts sulfur doxde to sulfur troxde. SO ( g) + O ( g) SO 3 ( l). (a.) Wrte the expresson for K eq for ths reacton.
Chemstry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Problem Set 9 Solutons. The followng chemcal reacton converts sulfur doxde to sulfur troxde. SO ( g) + O ( g) SO 3 ( l). (a.) Wrte the expresson for K eq for ths reacton.
First day August 1, Problems and Solutions
 FOURTH INTERNATIONAL COMPETITION FOR UNIVERSITY STUDENTS IN MATHEMATICS July 30 August 4, 997, Plovdv, BULGARIA Frst day August, 997 Problems and Solutons Problem. Let {ε n } n= be a sequence of postve
FOURTH INTERNATIONAL COMPETITION FOR UNIVERSITY STUDENTS IN MATHEMATICS July 30 August 4, 997, Plovdv, BULGARIA Frst day August, 997 Problems and Solutons Problem. Let {ε n } n= be a sequence of postve
LECTURE 9 CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS
 LECURE 9 CANONICAL CORRELAION ANALYSIS Introducton he concept of canoncal correlaton arses when we want to quantfy the assocatons between two sets of varables. For example, suppose that the frst set of
LECURE 9 CANONICAL CORRELAION ANALYSIS Introducton he concept of canoncal correlaton arses when we want to quantfy the assocatons between two sets of varables. For example, suppose that the frst set of
1 (1 + ( )) = 1 8 ( ) = (c) Carrying out the Taylor expansion, in this case, the series truncates at second order:
 68A Solutons to Exercses March 05 (a) Usng a Taylor expanson, and notng that n 0 for all n >, ( + ) ( + ( ) + ) We can t nvert / because there s no Taylor expanson around 0 Lets try to calculate the nverse
68A Solutons to Exercses March 05 (a) Usng a Taylor expanson, and notng that n 0 for all n >, ( + ) ( + ( ) + ) We can t nvert / because there s no Taylor expanson around 0 Lets try to calculate the nverse
Assignment 4 Solutions
 Assgnment 4 Solutons Tmothy Vs February 3, 2006 3-3-2 We have n 25, 0.04, P MT 100, and we need to fnd F V. F V P MT (1 + )n 1 100 (1 + 0.04)2 5 1 0.04 4164.59 3-3-6 We have F V 8000, n 30, 0.03, and we
Assgnment 4 Solutons Tmothy Vs February 3, 2006 3-3-2 We have n 25, 0.04, P MT 100, and we need to fnd F V. F V P MT (1 + )n 1 100 (1 + 0.04)2 5 1 0.04 4164.59 3-3-6 We have F V 8000, n 30, 0.03, and we
ACTM State Calculus Competition Saturday April 30, 2011
 ACTM State Calculus Competton Saturday Aprl 30, 2011 ACTM State Calculus Competton Sprng 2011 Page 1 Instructons: For questons 1 through 25, mark the best answer choce on the answer sheet provde Afterward
ACTM State Calculus Competton Saturday Aprl 30, 2011 ACTM State Calculus Competton Sprng 2011 Page 1 Instructons: For questons 1 through 25, mark the best answer choce on the answer sheet provde Afterward
Analytical Chemistry Calibration Curve Handout
 I. Quck-and Drty Excel Tutoral Analytcal Chemstry Calbraton Curve Handout For those of you wth lttle experence wth Excel, I ve provded some key technques that should help you use the program both for problem
I. Quck-and Drty Excel Tutoral Analytcal Chemstry Calbraton Curve Handout For those of you wth lttle experence wth Excel, I ve provded some key technques that should help you use the program both for problem
However, since P is a symmetric idempotent matrix, of P are either 0 or 1 [Eigen-values
 Fall 007 Soluton to Mdterm Examnaton STAT 7 Dr. Goel. [0 ponts] For the general lnear model = X + ε, wth uncorrelated errors havng mean zero and varance σ, suppose that the desgn matrx X s not necessarly
Fall 007 Soluton to Mdterm Examnaton STAT 7 Dr. Goel. [0 ponts] For the general lnear model = X + ε, wth uncorrelated errors havng mean zero and varance σ, suppose that the desgn matrx X s not necessarly
Lectures - Week 4 Matrix norms, Conditioning, Vector Spaces, Linear Independence, Spanning sets and Basis, Null space and Range of a Matrix
 Lectures - Week 4 Matrx norms, Condtonng, Vector Spaces, Lnear Independence, Spannng sets and Bass, Null space and Range of a Matrx Matrx Norms Now we turn to assocatng a number to each matrx. We could
Lectures - Week 4 Matrx norms, Condtonng, Vector Spaces, Lnear Independence, Spannng sets and Bass, Null space and Range of a Matrx Matrx Norms Now we turn to assocatng a number to each matrx. We could
Newton s Method for One - Dimensional Optimization - Theory
 Numercal Methods Newton s Method for One - Dmensonal Optmzaton - Theory For more detals on ths topc Go to Clck on Keyword Clck on Newton s Method for One- Dmensonal Optmzaton You are free to Share to copy,
Numercal Methods Newton s Method for One - Dmensonal Optmzaton - Theory For more detals on ths topc Go to Clck on Keyword Clck on Newton s Method for One- Dmensonal Optmzaton You are free to Share to copy,
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Fall 10 Midterm, October 28
 M140 - Lnear rcuts - Fall 10 Mdterm, October 28 nstructons () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
M140 - Lnear rcuts - Fall 10 Mdterm, October 28 nstructons () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Important Instructions to the Examiners:
 Summer 0 Examnaton Subject & Code: asc Maths (70) Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructons to the Examners: ) The Answers should be examned by key words and not as word-to-word as gven n the model
Summer 0 Examnaton Subject & Code: asc Maths (70) Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructons to the Examners: ) The Answers should be examned by key words and not as word-to-word as gven n the model
Introduction to Complex Numbers
 Introducton to Complex Numbers Let s revew the varous classfcaton of number we have encountered Number Systems Natural Numbers (Postve Integers) {1,, 3, 4, } Whole Numbers (Postve Integers plus zero) {0,
Introducton to Complex Numbers Let s revew the varous classfcaton of number we have encountered Number Systems Natural Numbers (Postve Integers) {1,, 3, 4, } Whole Numbers (Postve Integers plus zero) {0,
Difference Equations
 Dfference Equatons c Jan Vrbk 1 Bascs Suppose a sequence of numbers, say a 0,a 1,a,a 3,... s defned by a certan general relatonshp between, say, three consecutve values of the sequence, e.g. a + +3a +1
Dfference Equatons c Jan Vrbk 1 Bascs Suppose a sequence of numbers, say a 0,a 1,a,a 3,... s defned by a certan general relatonshp between, say, three consecutve values of the sequence, e.g. a + +3a +1
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Rao IIT Academy/ SSC - Board Exam 2018 / Mathematics Code-A / QP + Solutions JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS SSC - BOARD
 Rao IIT Academy/ SSC - Board Exam 08 / Mathematcs Code-A / QP + Solutons JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS SSC - BOARD - 08 Date: 0.03.08 MATHEMATICS - PAPER- - SOLUTIONS Q. Attempt any FIVE of
Rao IIT Academy/ SSC - Board Exam 08 / Mathematcs Code-A / QP + Solutons JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS SSC - BOARD - 08 Date: 0.03.08 MATHEMATICS - PAPER- - SOLUTIONS Q. Attempt any FIVE of
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 PhscsAndMathsTutor.com phscsandmathstutor.com June 005 5. The random varable X has probablt functon k, = 1,, 3, P( X = ) = k ( + 1), = 4, 5, where k s a constant. (a) Fnd the value of k. (b) Fnd the eact
PhscsAndMathsTutor.com phscsandmathstutor.com June 005 5. The random varable X has probablt functon k, = 1,, 3, P( X = ) = k ( + 1), = 4, 5, where k s a constant. (a) Fnd the value of k. (b) Fnd the eact
1. relation between exp. function and IUF
 Dualty Dualty n consumer theory II. relaton between exp. functon and IUF - straghtforward: have m( p, u mn'd value of expendture requred to attan a gven level of utlty, gven a prce vector; u ( p, M max'd
Dualty Dualty n consumer theory II. relaton between exp. functon and IUF - straghtforward: have m( p, u mn'd value of expendture requred to attan a gven level of utlty, gven a prce vector; u ( p, M max'd
Lecture 10 Support Vector Machines II
 Lecture 10 Support Vector Machnes II 22 February 2016 Taylor B. Arnold Yale Statstcs STAT 365/665 1/28 Notes: Problem 3 s posted and due ths upcomng Frday There was an early bug n the fake-test data; fxed
Lecture 10 Support Vector Machnes II 22 February 2016 Taylor B. Arnold Yale Statstcs STAT 365/665 1/28 Notes: Problem 3 s posted and due ths upcomng Frday There was an early bug n the fake-test data; fxed
(2mn, m 2 n 2, m 2 + n 2 )
 MATH 16T Homewk Solutons 1. Recall that a natural number n N s a perfect square f n = m f some m N. a) Let n = p α even f = 1,,..., k. be the prme factzaton of some n. Prove that n s a perfect square f
MATH 16T Homewk Solutons 1. Recall that a natural number n N s a perfect square f n = m f some m N. a) Let n = p α even f = 1,,..., k. be the prme factzaton of some n. Prove that n s a perfect square f
WINTER 2017 EXAMINATION
 (ISO/IEC - 700-00 Certfed) WINTER 07 EXAMINATION Model wer ject Code: Important Instructons to Eamners: ) The answers should be eamned by key words and not as word-to-word as gven n the model answer scheme.
(ISO/IEC - 700-00 Certfed) WINTER 07 EXAMINATION Model wer ject Code: Important Instructons to Eamners: ) The answers should be eamned by key words and not as word-to-word as gven n the model answer scheme.
9. Complex Numbers. 1. Numbers revisited. 2. Imaginary number i: General form of complex numbers. 3. Manipulation of complex numbers
 9. Comple Numbers. Numbers revsted. Imagnar number : General form of comple numbers 3. Manpulaton of comple numbers 4. The Argand dagram 5. The polar form for comple numbers 9.. Numbers revsted We saw
9. Comple Numbers. Numbers revsted. Imagnar number : General form of comple numbers 3. Manpulaton of comple numbers 4. The Argand dagram 5. The polar form for comple numbers 9.. Numbers revsted We saw
At right: Closeups of the graphs of. with WINDOW settings Xmin=-1, Xmax=1, Xscl=0.1, Ymin=-1, Ymax=1, Yscl=0.1
 Know the graphs of f(x) = x n for n = odd, positive: 1, 3, 5, The Domain is All Real Numbers, (, ), or R. The Range is All Real Numbers, (, ), or R. It is an Odd function because f( x) = f(x). It is symmetric
Know the graphs of f(x) = x n for n = odd, positive: 1, 3, 5, The Domain is All Real Numbers, (, ), or R. The Range is All Real Numbers, (, ), or R. It is an Odd function because f( x) = f(x). It is symmetric
Math 217 Fall 2013 Homework 2 Solutions
 Math 17 Fall 013 Homework Solutons Due Thursday Sept. 6, 013 5pm Ths homework conssts of 6 problems of 5 ponts each. The total s 30. You need to fully justfy your answer prove that your functon ndeed has
Math 17 Fall 013 Homework Solutons Due Thursday Sept. 6, 013 5pm Ths homework conssts of 6 problems of 5 ponts each. The total s 30. You need to fully justfy your answer prove that your functon ndeed has
THE SUMMATION NOTATION Ʃ
 Sngle Subscrpt otaton THE SUMMATIO OTATIO Ʃ Most of the calculatons we perform n statstcs are repettve operatons on lsts of numbers. For example, we compute the sum of a set of numbers, or the sum of the
Sngle Subscrpt otaton THE SUMMATIO OTATIO Ʃ Most of the calculatons we perform n statstcs are repettve operatons on lsts of numbers. For example, we compute the sum of a set of numbers, or the sum of the
LINEAR REGRESSION MODELS W4315
 LINEAR REGRESSION MODELS W4315 HOMEWORK ANSWERS February 15, 010 Instructor: Frank Wood 1. (0 ponts) In the fle problem1.txt (accessble on professor s webste), there are 500 pars of data, where the frst
LINEAR REGRESSION MODELS W4315 HOMEWORK ANSWERS February 15, 010 Instructor: Frank Wood 1. (0 ponts) In the fle problem1.txt (accessble on professor s webste), there are 500 pars of data, where the frst
,, MRTS is the marginal rate of technical substitution
 Mscellaneous Notes on roducton Economcs ompled by eter F Orazem September 9, 00 I Implcatons of conve soquants Two nput case, along an soquant 0 along an soquant Slope of the soquant,, MRTS s the margnal
Mscellaneous Notes on roducton Economcs ompled by eter F Orazem September 9, 00 I Implcatons of conve soquants Two nput case, along an soquant 0 along an soquant Slope of the soquant,, MRTS s the margnal
The Geometry of Logit and Probit
 The Geometry of Logt and Probt Ths short note s meant as a supplement to Chapters and 3 of Spatal Models of Parlamentary Votng and the notaton and reference to fgures n the text below s to those two chapters.
The Geometry of Logt and Probt Ths short note s meant as a supplement to Chapters and 3 of Spatal Models of Parlamentary Votng and the notaton and reference to fgures n the text below s to those two chapters.
AS-Level Maths: Statistics 1 for Edexcel
 1 of 6 AS-Level Maths: Statstcs 1 for Edecel S1. Calculatng means and standard devatons Ths con ndcates the slde contans actvtes created n Flash. These actvtes are not edtable. For more detaled nstructons,
1 of 6 AS-Level Maths: Statstcs 1 for Edecel S1. Calculatng means and standard devatons Ths con ndcates the slde contans actvtes created n Flash. These actvtes are not edtable. For more detaled nstructons,
Physics 443, Solutions to PS 7
 Physcs 443, Solutons to PS 7. Grffths 4.50 The snglet confguraton state s χ ) χ + χ χ χ + ) where that second equaton defnes the abbrevated notaton χ + and χ. S a ) S ) b χ â S )ˆb S ) χ In sphercal coordnates
Physcs 443, Solutons to PS 7. Grffths 4.50 The snglet confguraton state s χ ) χ + χ χ χ + ) where that second equaton defnes the abbrevated notaton χ + and χ. S a ) S ) b χ â S )ˆb S ) χ In sphercal coordnates
APPENDIX A Some Linear Algebra
 APPENDIX A Some Lnear Algebra The collecton of m, n matrces A.1 Matrces a 1,1,..., a 1,n A = a m,1,..., a m,n wth real elements a,j s denoted by R m,n. If n = 1 then A s called a column vector. Smlarly,
APPENDIX A Some Lnear Algebra The collecton of m, n matrces A.1 Matrces a 1,1,..., a 1,n A = a m,1,..., a m,n wth real elements a,j s denoted by R m,n. If n = 1 then A s called a column vector. Smlarly,
How Strong Are Weak Patents? Joseph Farrell and Carl Shapiro. Supplementary Material Licensing Probabilistic Patents to Cournot Oligopolists *
 How Strong Are Weak Patents? Joseph Farrell and Carl Shapro Supplementary Materal Lcensng Probablstc Patents to Cournot Olgopolsts * September 007 We study here the specal case n whch downstream competton
How Strong Are Weak Patents? Joseph Farrell and Carl Shapro Supplementary Materal Lcensng Probablstc Patents to Cournot Olgopolsts * September 007 We study here the specal case n whch downstream competton
Causal Diamonds. M. Aghili, L. Bombelli, B. Pilgrim
 Causal Damonds M. Aghl, L. Bombell, B. Plgrm Introducton The correcton to volume of a causal nterval due to curvature of spacetme has been done by Myrhem [] and recently by Gbbons & Solodukhn [] and later
Causal Damonds M. Aghl, L. Bombell, B. Plgrm Introducton The correcton to volume of a causal nterval due to curvature of spacetme has been done by Myrhem [] and recently by Gbbons & Solodukhn [] and later
Radar Trackers. Study Guide. All chapters, problems, examples and page numbers refer to Applied Optimal Estimation, A. Gelb, Ed.
 Radar rackers Study Gude All chapters, problems, examples and page numbers refer to Appled Optmal Estmaton, A. Gelb, Ed. Chapter Example.0- Problem Statement wo sensors Each has a sngle nose measurement
Radar rackers Study Gude All chapters, problems, examples and page numbers refer to Appled Optmal Estmaton, A. Gelb, Ed. Chapter Example.0- Problem Statement wo sensors Each has a sngle nose measurement
Workshop: Approximating energies and wave functions Quantum aspects of physical chemistry
 Workshop: Approxmatng energes and wave functons Quantum aspects of physcal chemstry http://quantum.bu.edu/pltl/6/6.pdf Last updated Thursday, November 7, 25 7:9:5-5: Copyrght 25 Dan Dll (dan@bu.edu) Department
Workshop: Approxmatng energes and wave functons Quantum aspects of physcal chemstry http://quantum.bu.edu/pltl/6/6.pdf Last updated Thursday, November 7, 25 7:9:5-5: Copyrght 25 Dan Dll (dan@bu.edu) Department
(c) (cos θ + i sin θ) 5 = cos 5 θ + 5 cos 4 θ (i sin θ) + 10 cos 3 θ(i sin θ) cos 2 θ(i sin θ) 3 + 5cos θ (i sin θ) 4 + (i sin θ) 5 (A1)
 . (a) (cos θ + sn θ) = cos θ + cos θ( sn θ) + cos θ(sn θ) + (sn θ) = cos θ cos θ sn θ + ( cos θ sn θ sn θ) (b) from De Movre s theorem (cos θ + sn θ) = cos θ + sn θ cos θ + sn θ = (cos θ cos θ sn θ) +
. (a) (cos θ + sn θ) = cos θ + cos θ( sn θ) + cos θ(sn θ) + (sn θ) = cos θ cos θ sn θ + ( cos θ sn θ sn θ) (b) from De Movre s theorem (cos θ + sn θ) = cos θ + sn θ cos θ + sn θ = (cos θ cos θ sn θ) +
Chapter 8: Further Applications of Trigonometry
 Secton 8. Polar Form of Complex Numbers 1 Chapter 8: Further Applcatons of Trgonometry In ths chapter, we wll explore addtonal applcatons of trgonometry. We wll begn wth an extenson of the rght trangle
Secton 8. Polar Form of Complex Numbers 1 Chapter 8: Further Applcatons of Trgonometry In ths chapter, we wll explore addtonal applcatons of trgonometry. We wll begn wth an extenson of the rght trangle
Section 8.1 Exercises
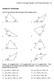 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Kernel Methods and SVMs Extension
 Kernel Methods and SVMs Extenson The purpose of ths document s to revew materal covered n Machne Learnng 1 Supervsed Learnng regardng support vector machnes (SVMs). Ths document also provdes a general
Kernel Methods and SVMs Extenson The purpose of ths document s to revew materal covered n Machne Learnng 1 Supervsed Learnng regardng support vector machnes (SVMs). Ths document also provdes a general
The Fourier Transform
 e Processng ourer Transform D The ourer Transform Effcent Data epresentaton Dscrete ourer Transform - D Contnuous ourer Transform - D Eamples + + + Jean Baptste Joseph ourer Effcent Data epresentaton Data
e Processng ourer Transform D The ourer Transform Effcent Data epresentaton Dscrete ourer Transform - D Contnuous ourer Transform - D Eamples + + + Jean Baptste Joseph ourer Effcent Data epresentaton Data
Recursion and growth estimates in quantum field theory
 Recurson and growth estmates n quantum feld theory Karen Yeats Boston Unversty Aprl 9, 2007 Johns Hopns Unversty Some recursve equatons Start n the mddle γ (x) = γ (x)( rx x )γ (x) γ,n = p(n) ( rj )γ,j
Recurson and growth estmates n quantum feld theory Karen Yeats Boston Unversty Aprl 9, 2007 Johns Hopns Unversty Some recursve equatons Start n the mddle γ (x) = γ (x)( rx x )γ (x) γ,n = p(n) ( rj )γ,j
Homework 9 Solutions. 1. (Exercises from the book, 6 th edition, 6.6, 1-3.) Determine the number of distinct orderings of the letters given:
 Homework 9 Solutons PROBLEM ONE 1 (Exercses from the book, th edton,, 1-) Determne the number of dstnct orderngs of the letters gven: (a) GUIDE Soluton: 5! (b) SCHOOL Soluton:! (c) SALESPERSONS Soluton:
Homework 9 Solutons PROBLEM ONE 1 (Exercses from the book, th edton,, 1-) Determne the number of dstnct orderngs of the letters gven: (a) GUIDE Soluton: 5! (b) SCHOOL Soluton:! (c) SALESPERSONS Soluton:
Modelli Clamfim Equazioni differenziali 7 ottobre 2013
 CLAMFIM Bologna Modell 1 @ Clamfm Equazon dfferenzal 7 ottobre 2013 professor Danele Rtell danele.rtell@unbo.t 1/18? Ordnary Dfferental Equatons A dfferental equaton s an equaton that defnes a relatonshp
CLAMFIM Bologna Modell 1 @ Clamfm Equazon dfferenzal 7 ottobre 2013 professor Danele Rtell danele.rtell@unbo.t 1/18? Ordnary Dfferental Equatons A dfferental equaton s an equaton that defnes a relatonshp
CHEM 112 Exam 3 Practice Test Solutions
 CHEM 11 Exam 3 Practce Test Solutons 1A No matter what temperature the reacton takes place, the product of [OH-] x [H+] wll always equal the value of w. Therefore, f you take the square root of the gven
CHEM 11 Exam 3 Practce Test Solutons 1A No matter what temperature the reacton takes place, the product of [OH-] x [H+] wll always equal the value of w. Therefore, f you take the square root of the gven
A summation on Bernoulli numbers
 Journal of Number Theory 111 (005 37 391 www.elsever.com/locate/jnt A summaton on Bernoull numbers Kwang-Wu Chen Department of Mathematcs and Computer Scence Educaton, Tape Muncpal Teachers College, No.
Journal of Number Theory 111 (005 37 391 www.elsever.com/locate/jnt A summaton on Bernoull numbers Kwang-Wu Chen Department of Mathematcs and Computer Scence Educaton, Tape Muncpal Teachers College, No.
Chemical Engineering Department University of Washington
 Chemcal Engneerng Department Unversty of Washngton ChemE 60 - Exam I July 4, 003 - Mass Flow Rate of Steam Through a Turbne (5 onts) Steam enters a turbne at 70 o C and.8 Ma and leaves at 00 ka wth a qualty
Chemcal Engneerng Department Unversty of Washngton ChemE 60 - Exam I July 4, 003 - Mass Flow Rate of Steam Through a Turbne (5 onts) Steam enters a turbne at 70 o C and.8 Ma and leaves at 00 ka wth a qualty
CHEM 112 Exam 3 Practice Test Solutions
 CHEM 11 Exam 3 Practce Test Solutons 1A No matter what temperature the reacton takes place, the product of [OH-] x [H+] wll always equal the value of w. Therefore, f you take the square root of the gven
CHEM 11 Exam 3 Practce Test Solutons 1A No matter what temperature the reacton takes place, the product of [OH-] x [H+] wll always equal the value of w. Therefore, f you take the square root of the gven
Foundations of Arithmetic
 Foundatons of Arthmetc Notaton We shall denote the sum and product of numbers n the usual notaton as a 2 + a 2 + a 3 + + a = a, a 1 a 2 a 3 a = a The notaton a b means a dvdes b,.e. ac = b where c s an
Foundatons of Arthmetc Notaton We shall denote the sum and product of numbers n the usual notaton as a 2 + a 2 + a 3 + + a = a, a 1 a 2 a 3 a = a The notaton a b means a dvdes b,.e. ac = b where c s an
A new Approach for Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 , ISSN 974-57X (Onlne), ISSN 974-5718 (Prnt), Vol. ; Issue No. 1; Year 14, Copyrght 13-14 by CESER PUBLICATIONS A new Approach for Solvng Lnear Ordnary Dfferental Equatons Fawz Abdelwahd Department of
, ISSN 974-57X (Onlne), ISSN 974-5718 (Prnt), Vol. ; Issue No. 1; Year 14, Copyrght 13-14 by CESER PUBLICATIONS A new Approach for Solvng Lnear Ordnary Dfferental Equatons Fawz Abdelwahd Department of
Poisson brackets and canonical transformations
 rof O B Wrght Mechancs Notes osson brackets and canoncal transformatons osson Brackets Consder an arbtrary functon f f ( qp t) df f f f q p q p t But q p p where ( qp ) pq q df f f f p q q p t In order
rof O B Wrght Mechancs Notes osson brackets and canoncal transformatons osson Brackets Consder an arbtrary functon f f ( qp t) df f f f q p q p t But q p p where ( qp ) pq q df f f f p q q p t In order
IMGS-261 Solutions to Homework #9
 IMGS-6 Solutons to Homework #9. For f [] SINC [] sn[π], use the modulaton theorem to evaluate and sketch π the Fourer transform of f [] f [] f [] (f []) Soluton: We know that F{RECT []} SINC [] so we use
IMGS-6 Solutons to Homework #9. For f [] SINC [] sn[π], use the modulaton theorem to evaluate and sketch π the Fourer transform of f [] f [] f [] (f []) Soluton: We know that F{RECT []} SINC [] so we use
Lecture 6/7 (February 10/12, 2014) DIRAC EQUATION. The non-relativistic Schrödinger equation was obtained by noting that the Hamiltonian 2
 P470 Lecture 6/7 (February 10/1, 014) DIRAC EQUATION The non-relatvstc Schrödnger equaton was obtaned by notng that the Hamltonan H = P (1) m can be transformed nto an operator form wth the substtutons
P470 Lecture 6/7 (February 10/1, 014) DIRAC EQUATION The non-relatvstc Schrödnger equaton was obtaned by notng that the Hamltonan H = P (1) m can be transformed nto an operator form wth the substtutons
Publication 2006/01. Transport Equations in Incompressible. Lars Davidson
 Publcaton 2006/01 Transport Equatons n Incompressble URANS and LES Lars Davdson Dvson of Flud Dynamcs Department of Appled Mechancs Chalmers Unversty of Technology Göteborg, Sweden, May 2006 Transport
Publcaton 2006/01 Transport Equatons n Incompressble URANS and LES Lars Davdson Dvson of Flud Dynamcs Department of Appled Mechancs Chalmers Unversty of Technology Göteborg, Sweden, May 2006 Transport
8.1 Arc Length. What is the length of a curve? How can we approximate it? We could do it following the pattern we ve used before
 .1 Arc Length hat s the length of a curve? How can we approxmate t? e could do t followng the pattern we ve used before Use a sequence of ncreasngly short segments to approxmate the curve: As the segments
.1 Arc Length hat s the length of a curve? How can we approxmate t? e could do t followng the pattern we ve used before Use a sequence of ncreasngly short segments to approxmate the curve: As the segments
Root Locus Techniques
 Root Locu Technque ELEC 32 Cloed-Loop Control The control nput u t ynthezed baed on the a pror knowledge of the ytem plant, the reference nput r t, and the error gnal, e t The control ytem meaure the output,
Root Locu Technque ELEC 32 Cloed-Loop Control The control nput u t ynthezed baed on the a pror knowledge of the ytem plant, the reference nput r t, and the error gnal, e t The control ytem meaure the output,
