Find the area of the triangle. You try: D C. Determine whether each of the following statements is true or false. Solve for the variables.
|
|
|
- Pearl Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide ind the area of the triangle D or all right triangles, a + b c where c is the length of the hpotenuse. 5 4 a + b c 9 + b 5 + b 5 b 5 b 44 b 9 he area of a triangle bh ( 9 )( ) ( 9) ( 6) rea of D sq. un. D. rea of D 6 sq. un. he area of the triangle is 54 square units. G.SR. Solve for the variables his is a triangle. Using theorem: leg leg 9 hpotenuse legi 9i 9 Using leg:leg:hp. ratios: leg leg 9 9 :: leg hp a b J b L 45. JKL is a right scalene triangle. rea of JKL 5 sq. un. D. Perimeter of JKL ( + ) a 0 K 0 0 un. G.SR.. Page of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
2 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 3 Solve for the variables. m n p 60 n X Z his is a triangle. Using theorem: hpotenuse i 4 m m ( short leg ) Using short leg:long leg:hpotenuse ratios: short leg : hp. : 3 : hp.: long leg. m X 30. n 6. n 6 3 ( long leg ) ( short leg ) i 3 n i 3 n 3 m 4 m n n 4 3 D. p 3 E. rea of XZ 4 3 sq. un. m n 3 We can check our answer using the Pthagorean theorem: a + b c ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )( ) G.SR.. Page of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
3 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 4 Solve for the variables in the diagram. Round answers to the nearest tenth z he sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 0 : m + m + m M. 75 L 5 z We can use right triangle trigonometr to solve for and z... sin 5 tan 5 opposite sinθ hpotenuse sin sin 64 adjacent cosθ hpotenuse z cos cos 64 z D. z sin 5 E. <. 3.9 z We can check our answer using the tangent ratio. opposite tanθ adjacent tan 64 z. tan hese values are etremel close and we should epect some error on the right side of the equation because. and 3.9 were alread rounded values. G.SR. Page 3 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
4 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 5 Solve for the variables in the diagram. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 5 X 7 w 9 n a c m Z Using the Pthagorean heorem: 7 + n X n 5 Z + n 49 n 7 n 7 n.5 We can use right triangle trigonometr to solve for a b setting up an equation using the sine function: +. n m m tan opposite sinθ hpotenuse 7 sin a 7 sin ( sin a ) sin a D. 5 n tan + 5 c E. cos n sin m a 39.5 We can solve for w since the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 0 : m X + m + m Z w 0 w w 50.5 w 50.5 G.SR. Page 4 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
5 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 6 Solve for the variables in the diagram. hen find the area of the triangle. Round answers to the nearest tenth. c z 6 z his is not a right triangle, so we are going to have to use the law of sines or the law of cosines. Since we don t know an of the side lengths across from a known angle measure, we are going to have to use law of cosines using angle : c a + b ab cos ( )( ) c cos 60 c cos 60. is an acute scalene triangle. sin 30 sin 70 c 00 96cos 60 c 00 96cos 60 c 7.. sin 30 sin 70 z fter finding, we can use the law of sines to find the other variables. sin sin sin a b c D. 64 z z cos 70 + E. rea of 4 sin 70 sin sin b c sin z sin sin z sin z 0.70 ( z ) ( ) sin sin sin 0.70 z 46. z 46. sin sin a c sin sin sin z 0.0 sin z ( z ) ( ) sin sin sin z 73.7 z 73.7 rea: rea absin rea ( 6 )( ) sin 60 rea 4sin 60 rea 0. herefore the area of the triangle is 0. square units. G.SR.9, G.SR.0, G.SR. Page 5 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
6 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 7 List as man properties as ou can about a rectangle. Since it is a parallelogram: 7 Determine which characteristic(s) are true for the quadrilaterals listed below: oth pairs of opposite sides are parallel oth pairs of opposite sides are congruent Opposite angles are congruent onsecutive angles are supplementar Diagonals bisect each other Unique to a rectangle: ll angles are congruent ( 90 ) he diagonals are congruent G.O. Parallelogram Rhombus Isosceles rapezoid. Onl one pair of parallel lines. ll sides are congruent. he diagonals bisect each other D. he diagonals are congruent ) ame as man special quadrilaterals as ou can. rapezoid, Isosceles rapezoid, Parallelogram, Rhombus, Rectangle, Square, and Kite. ame all the quadrilaterals that have the propert listed. ) oth pairs of opposite angles are congruent ) ame all the quadrilaterals that have perpendicular diagonals? Rhombus, Square, and Kite. 3) ame all the quadrilaterals whose opposite angles are congruent? ) Diagonals bisect angles Parallelogram, Rhombus, Rectangle, and Square. 3) Onl one diagonal bisects the other. G.O. Page 6 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
7 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 9 Use the given information to answer the questions below. Given: D is an isosceles trapezoid D 9 Use the given information to answer the questions below. Given: WXZ is a square M M X a) Which segment is congruent to? D W b) Which segment is congruent to D? D Z c) Which angle is congruent to D? D D d) ame three angles that are congruent to M. a) ame three segments that are congruent to W. b) ame five angles that are congruent to Z. M M DM DM c) ame five angles that are congruent to WZ. d) ame three triangles that are congruent to WZ. G.O. Page 7 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
8 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 0 Prove that quadrilateral D is a rectangle given the coordinates of,,, and D.,, 3 7,0 D 5,4 ( ), ( ), ( ), ( ) D 0 Given: J ( 5, 4), K ( 5, ), L(,5 ), M ( 3,), and (, ) -. KLM is a rhombus.. KLM is a square.. JKL is a parallelogram. D. JKLM is a trapezoid. - Slope of 3 D Slope of 6 4 Slope of + 4 Slope of D + oth pairs of opposite sides have the same slope making them parallel. herefore, D is a parallelogram - onsecutive sides have opposite reciprocal slopes making them perpendicular. his shows that all the interior angles are right angles making D a rectangle. - G.O. Page of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
9 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide Write the equation of the circle with the given information in standard form and graph. enter: ( 3,0) Diameter: 0 units Since the diameter is 0 units, then the radius would be 5 units. 5 (, ) Given: enter: (, 4) Point on the circle: ( 0, ) ( 3,0). he radius of the circle is 9 units. he equation of the circle is ( ) ( ) Using the formula for the standard equation of a h k : circle with center (, ) ( h) + ( k ) r ( ( )) ( ) ( ) Using the distance formula: ( ) ( ) + d ( ( )) ( ) ( ) ( ) n equation of a concentric circle is ( ) ( ) D. nother point on the circle is ( 3, ). Graph the center first and then graph the points up, down, left, and right 5 units from the center and then graph the circle through those 4 points G.GPE. Page 9 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
10 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide Write the equation of the circle with the given information in standard form and graph. + + Given the equation: he equation is not in standard form, h + k r. We have to complete the square ( ) ( ) for and for to put the equation in standard form: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ow the equation is in the standard form for a circle and we can see the center is ( 4, ) and r 9, which means the radius would have to be 3 units. Graph the center first and then graph the points up, down, left, and right 3 units from the center and then graph the circle through those 4 points.. he radius of the circle is units.. he center of the circle is ( 6, 3).. he equation of the circle is ( ) ( ) D. nother point on the circle is (, 3). E. Graph of the given equation: G.GPE. Page 0 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
11 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 3 Write the equation of a parabola with a focus 0, 4 and a directri of 4. of ( ) - V : ( 0, 4) - parabola is the set of points, (, ) d d (, ), equidistant from a line (directri) and a point not on the line (focus). D : 4 3 Write the equation of a parabola with a 0, 4 and a directri of. verte of ( ). he parabola opens upward.. he equation is ( ) 4.. he equation is ( ) D. he focus is (,4). E. Graph: 4. Using the formula for a vertical parabola: Verte: ( 0,0 ) ocus: ( 0, 4) p 4 p 4 (opens down) ( ) ( ) 4 p k h Using the definition: d d ( ) ( ( )) ( ) ( 4 ) + ( + 4) ( )( ) ( ) G.GPE. Page of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
12 lameda USD Geometr 4 Use the diagram and given information to find the measures of the following angles and arcs. Given: G is tangent to O. G a) m m + m m m m 0 b) med me + med + md md 0 + med med med 0 c) m m ( me + m ) m ( ) m ( 90 ) m 45 d) m D m D md m D me + med m D ( ) m D ( 30 ) m D 65 e) m G m G ( m md) m G ( 0 30 ) m G ( 50 ) m G 5 0 E ( ) OR D O tangent is perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangenc. m G + m G + m G 0 m G m G m G 5 G.. 4 enchmark Stud Guide Given: KP is tangent to 00 J 30 O.. 40 H O. m KL 65. KLO is an equilateral triangle. D. mm 9 K E. m JH 30. m HM 9 M L 9 P Page of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
13 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 5 Use the diagram and given information to find the measures of the following angles and arcs. Given: O 5 Given: JK is tangent to J M O. 40 K O O z w D a) m he measure of the central angle is equal to the arc it intercepts. herefore m O m and m 90. b) md md md + m md md 30 c) m he measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the arc it intercepts: m m m ( 90 ) m 45 d) m D m D m m D ( 0 ) m D 90 e) m D md md + md md 40 md m D md m D ( 40 ) m D 0 statements must be true... z. w D. + z 90 E. w + z 0 L G.. Page 3 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
14 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 6 Use the diagram and given information to find the measures of the following angles and segments below. Given: O 6 Given: O, M K I 60 H J O E 53 5 O 6 L K a) m E Since the diameter bisects D, then D. herefore m E 90 b) m m m m md m m OD m ( 53 ) m 6.5 c) OE Since O is a radius, then O 5. If E, then that would make OE 3. d) D Since OED is a right triangle we can use Pthagorean theorem to find ED: 3 + ED ED 5 ED 6 ED 4 Since the diameter is perpendicular to a chord, it bisects the chord. herefore E ED 4 and D. e) E Since is a right triangle we can use Pthagorean theorem to find : D. OM. MK 0. HK 4 4 D. IJ OH E. mml 90. mmhl 0 M G.. Page 4 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
15 lameda USD Geometr 7 Use the diagram to find the lengths of the segments below. S 6 a) S angent segments from a common eternal point are congruent: S S b) VM S 6 If two chords intersect in the interior of a circle, then the product of the lengths of the segments of one chord is equal to the product of the lengths of the segments of the other chord: VM imx ZM imw c) PW Let n equal the length of PW V 0 7 P Z M W VM i4 i7 VM i4 i7 4 4 iii7 VM i7 VM 4 If a secant segment and a tangent segment share an endpoint outside a circle, then the product of the lengths of the secant segment and its eternal segment equals the square of the length of the tangent segment: PW ipz ( VP) ( ) ( 0) n( n + 5) 00 ni n 4 n + 5n 00 n + 5n 00 0 ( n + 0)( n 5) 0 ( n + 0) 0 or ( n 5) 0 n 0 or n 5 X Since PW is a length, then it must be positive and therefore PW5. G.O.9 7 enchmark Stud Guide Use the diagram and given information to find the values of the variables. Given: P is tangent to O, H G M w DP is tangent to O.. w D. z 6 E D 6 4 End of Stud Guide z P Page 5 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
16 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide ou r Solutions: rea of D sq. un sin 5 tan 5 D. rea of D 6 sq. un. D. z sin 5. a b. JKL is a right scalene triangle. rea of JKL 5 sq. un. D. Perimeter of JKL ( + ) 0 0 un. 5 E. < +. n m m tan 3. m X 30. D. 5 n tan + 5 c E. cos n sin m. n 6. n 6 3 D. p 3 E. rea of XZ 4 3 sq. un. Page 6 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
17 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 6 9 a) ame three segments that are congruent to W.. is an acute scalene triangle X,, Z.. sin 30 sin 70 sin 30 sin 70 z b) ame five angles that are congruent to Z. n five of the following angles: X, X, XW, WX, WZ, ZW, Z D. 64 z z cos 70 + E. rea of 4 sin 70 c) ame five angles that are congruent to WZ. WX, XWZ, XZ, WX, X, Z, WZ 7 Parallelogram Rhombus, Isosceles rapezoid, D d) ame three triangles that are congruent to WZ. WZ, XZ, ZX, WX, XZW, WX, ZXW ) oth pairs of opposite angles are congruent Parallelogram, rhombus, rectangle and square. 0 ) Diagonals bisect angles Rhombus and square. 3) Onl one diagonal bisects the other. Kite. KLM is a rhombus.. KLM is a square.. JKL is a parallelogram. D. JKLM is a trapezoid. Page 7 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
18 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 3. he radius of the circle is 9 units. he parabola opens upward.. he equation of the circle is ( ) ( ) n equation of a concentric circle is ( ) ( ). he equation is ( ) 4.. he equation is ( ) D. he focus is (,4). 4. D. nother point on the circle is ( 3, ). E. Graph:. he radius of the circle is units. -. he center of the circle is ( 6, 3).. he equation of the circle is ( ) ( ) D. nother point on the circle is (, 3). E. Graph of the given equation: m KL 65. KLO is an equilateral triangle. - D. mm 9 E. m JH 30. m HM 9 - Page of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
19 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 5.. z. w D. + z 90 E. w + z 0 6. OM. MK 0. HK 4 4 D. IJ OH E. mml 90. mmhl 0 7. w D. z 6 Page 9 of 9 M@WUSD (USD) 0/5/4
Given: You try: Given: Prove: ABC ADC. Prove: ABE DCE. 1. Given 1. AB AD BC DC. 2. AC AC 2. Reflexive Prop. of. 3. ABC ADC 3. SSS Post.
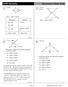 US Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 1 Given: 1 Given: Prove: Statements 1. 1. Given Reasons.. Refleive Prop. of 3. 3. SSS Post Prove: G.O.1 etermine whether the following statements are rue or alse. ) ) ) )
US Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 1 Given: 1 Given: Prove: Statements 1. 1. Given Reasons.. Refleive Prop. of 3. 3. SSS Post Prove: G.O.1 etermine whether the following statements are rue or alse. ) ) ) )
The Coordinate Plane. Circles and Polygons on the Coordinate Plane. LESSON 13.1 Skills Practice. Problem Set
 LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
Name Score Period Date. m = 2. Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement.
 Chapter 6 Review Geometry Name Score Period Date Solve the proportion. 3 5 1. = m 1 3m 4 m = 2. 12 n = n 3 n = Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement. 7 x 7? 3. 12
Chapter 6 Review Geometry Name Score Period Date Solve the proportion. 3 5 1. = m 1 3m 4 m = 2. 12 n = n 3 n = Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement. 7 x 7? 3. 12
Special Mathematics Notes
 Special Mathematics Notes Tetbook: Classroom Mathematics Stds 9 & 10 CHAPTER 6 Trigonometr Trigonometr is a stud of measurements of sides of triangles as related to the angles, and the application of this
Special Mathematics Notes Tetbook: Classroom Mathematics Stds 9 & 10 CHAPTER 6 Trigonometr Trigonometr is a stud of measurements of sides of triangles as related to the angles, and the application of this
Reteaching , or 37.5% 360. Geometric Probability. Name Date Class
 Name ate lass Reteaching Geometric Probability INV 6 You have calculated probabilities of events that occur when coins are tossed and number cubes are rolled. Now you will learn about geometric probability.
Name ate lass Reteaching Geometric Probability INV 6 You have calculated probabilities of events that occur when coins are tossed and number cubes are rolled. Now you will learn about geometric probability.
10-1 Study Guide and Intervention
 opyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of he McGraw-Hill ompanies, Inc. NM I 10-1 tudy Guide and Intervention ircles and ircumference arts of ircles circle consists of all points in a plane that are
opyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of he McGraw-Hill ompanies, Inc. NM I 10-1 tudy Guide and Intervention ircles and ircumference arts of ircles circle consists of all points in a plane that are
Name: GEOMETRY: EXAM (A) A B C D E F G H D E. 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane?
 GMTRY: XM () Name: 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane? ) none ) one ) two ) three 2. How many edges does a heagonal prism have? ) 6 ) 12 ) 18 ) 2. Name the intersection of planes Q and
GMTRY: XM () Name: 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane? ) none ) one ) two ) three 2. How many edges does a heagonal prism have? ) 6 ) 12 ) 18 ) 2. Name the intersection of planes Q and
0611ge. Geometry Regents Exam Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below.
 0611ge 1 Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below. In the diagram below, A B C is a transformation of ABC, and A B C is a transformation of A B C. Which two sets of construction marks, labeled I,
0611ge 1 Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below. In the diagram below, A B C is a transformation of ABC, and A B C is a transformation of A B C. Which two sets of construction marks, labeled I,
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
Geometry: A Complete Course
 eometry: omplete ourse with rigonometry) odule - tudent Worket Written by: homas. lark Larry. ollins 4/2010 or ercises 20 22, use the diagram below. 20. ssume is a rectangle. a) f is 6, find. b) f is,
eometry: omplete ourse with rigonometry) odule - tudent Worket Written by: homas. lark Larry. ollins 4/2010 or ercises 20 22, use the diagram below. 20. ssume is a rectangle. a) f is 6, find. b) f is,
0610ge. Geometry Regents Exam The diagram below shows a right pentagonal prism.
 0610ge 1 In the diagram below of circle O, chord AB chord CD, and chord CD chord EF. 3 The diagram below shows a right pentagonal prism. Which statement must be true? 1) CE DF 2) AC DF 3) AC CE 4) EF CD
0610ge 1 In the diagram below of circle O, chord AB chord CD, and chord CD chord EF. 3 The diagram below shows a right pentagonal prism. Which statement must be true? 1) CE DF 2) AC DF 3) AC CE 4) EF CD
Study Guide. Exploring Circles. Example: Refer to S for Exercises 1 6.
 9 1 Eploring ircles A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point in the plane called the center. Various parts of a circle are labeled in the figure at the
9 1 Eploring ircles A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point in the plane called the center. Various parts of a circle are labeled in the figure at the
Exercise Set 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios
 Eercise Set.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Answer the following. 9. 1. If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the opposite those sides are also congruent. 2. If two angles
Eercise Set.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Answer the following. 9. 1. If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the opposite those sides are also congruent. 2. If two angles
Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2018 GEOMETRY
 Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2018 GEOMETRY Table of Contents Content Summary and Answer Key... iii Question 4: Question and Scoring Guidelines... 1 Question 4: Sample Response... 4 Question 8:
Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2018 GEOMETRY Table of Contents Content Summary and Answer Key... iii Question 4: Question and Scoring Guidelines... 1 Question 4: Sample Response... 4 Question 8:
SM2H Unit 6 Circle Notes
 Name: Period: SM2H Unit 6 Circle Notes 6.1 Circle Vocabulary, Arc and Angle Measures Circle: All points in a plane that are the same distance from a given point, called the center of the circle. Chord:
Name: Period: SM2H Unit 6 Circle Notes 6.1 Circle Vocabulary, Arc and Angle Measures Circle: All points in a plane that are the same distance from a given point, called the center of the circle. Chord:
Geometry Honors Homework
 Geometry Honors Homework pg. 1 12-1 Practice Form G Tangent Lines Algebra Assume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. 2. 3. The circle
Geometry Honors Homework pg. 1 12-1 Practice Form G Tangent Lines Algebra Assume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. 2. 3. The circle
C=2πr C=πd. Chapter 10 Circles Circles and Circumference. Circumference: the distance around the circle
 10.1 Circles and Circumference Chapter 10 Circles Circle the locus or set of all points in a plane that are A equidistant from a given point, called the center When naming a circle you always name it by
10.1 Circles and Circumference Chapter 10 Circles Circle the locus or set of all points in a plane that are A equidistant from a given point, called the center When naming a circle you always name it by
Example 1: Finding angle measures: I ll do one: We ll do one together: You try one: ML and MN are tangent to circle O. Find the value of x
 Ch 1: Circles 1 1 Tangent Lines 1 Chords and Arcs 1 3 Inscribed Angles 1 4 Angle Measures and Segment Lengths 1 5 Circles in the coordinate plane 1 1 Tangent Lines Focused Learning Target: I will be able
Ch 1: Circles 1 1 Tangent Lines 1 Chords and Arcs 1 3 Inscribed Angles 1 4 Angle Measures and Segment Lengths 1 5 Circles in the coordinate plane 1 1 Tangent Lines Focused Learning Target: I will be able
Chapter 3 Summary 3.1. Determining the Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Squares on the Coordinate Plane. Example
 Chapter Summar Ke Terms bases of a trapezoid (.) legs of a trapezoid (.) composite figure (.5).1 Determining the Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Squares on the Coordinate Plane The perimeter or area
Chapter Summar Ke Terms bases of a trapezoid (.) legs of a trapezoid (.) composite figure (.5).1 Determining the Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Squares on the Coordinate Plane The perimeter or area
Geometry Note Cards EXAMPLE:
 Geometry Note Cards EXAMPLE: Lined Side Word and Explanation Blank Side Picture with Statements Sections 12-4 through 12-5 1) Theorem 12-3 (p. 790) 2) Theorem 12-14 (p. 790) 3) Theorem 12-15 (p. 793) 4)
Geometry Note Cards EXAMPLE: Lined Side Word and Explanation Blank Side Picture with Statements Sections 12-4 through 12-5 1) Theorem 12-3 (p. 790) 2) Theorem 12-14 (p. 790) 3) Theorem 12-15 (p. 793) 4)
Geometry Final Review. Chapter 1. Name: Per: Vocab. Example Problems
 Geometry Final Review Name: Per: Vocab Word Acute angle Adjacent angles Angle bisector Collinear Line Linear pair Midpoint Obtuse angle Plane Pythagorean theorem Ray Right angle Supplementary angles Complementary
Geometry Final Review Name: Per: Vocab Word Acute angle Adjacent angles Angle bisector Collinear Line Linear pair Midpoint Obtuse angle Plane Pythagorean theorem Ray Right angle Supplementary angles Complementary
Geometry Rules! Chapter 8 Notes
 Geometr Rules! Chapter 8 Notes - 1 - Notes #6: The Pthagorean Theorem (Sections 8.2, 8.3) A. The Pthagorean Theorem Right Triangles: Triangles with right angle Hpotenuse: the side across from the angle
Geometr Rules! Chapter 8 Notes - 1 - Notes #6: The Pthagorean Theorem (Sections 8.2, 8.3) A. The Pthagorean Theorem Right Triangles: Triangles with right angle Hpotenuse: the side across from the angle
0110ge. Geometry Regents Exam Which expression best describes the transformation shown in the diagram below?
 0110ge 1 In the diagram below of trapezoid RSUT, RS TU, X is the midpoint of RT, and V is the midpoint of SU. 3 Which expression best describes the transformation shown in the diagram below? If RS = 30
0110ge 1 In the diagram below of trapezoid RSUT, RS TU, X is the midpoint of RT, and V is the midpoint of SU. 3 Which expression best describes the transformation shown in the diagram below? If RS = 30
Chapter 12 Practice Test
 hapter 12 Practice Test Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ssume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. is the center of the circle.
hapter 12 Practice Test Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ssume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. is the center of the circle.
Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments. Geometry. Assessment 2 ASSESSMENT CODE LA08_G_T2_TST_31241
 Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments Assessment 2 2008 2009 Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments LA08_G_T2_TST_31241 ASSESSMENT ODE 1100209 The test items contained
Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments Assessment 2 2008 2009 Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments LA08_G_T2_TST_31241 ASSESSMENT ODE 1100209 The test items contained
Circles. II. Radius - a segment with one endpoint the center of a circle and the other endpoint on the circle.
 Circles Circles and Basic Terminology I. Circle - the set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point (called the center) in the plane. Circles are named by their center. II.
Circles Circles and Basic Terminology I. Circle - the set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point (called the center) in the plane. Circles are named by their center. II.
Name: Class: Date: c. WZ XY and XW YZ. b. WZ ZY and XW YZ. d. WN NZ and YN NX
 Class: Date: 2nd Semester Exam Review - Geometry CP 1. Complete this statement: A polygon with all sides the same length is said to be. a. regular b. equilateral c. equiangular d. convex 3. Which statement
Class: Date: 2nd Semester Exam Review - Geometry CP 1. Complete this statement: A polygon with all sides the same length is said to be. a. regular b. equilateral c. equiangular d. convex 3. Which statement
Answers. Chapter 9 A92. Angles Theorem (Thm. 5.6) then XZY. Base Angles Theorem (Thm. 5.6) 5, 2. then WV WZ;
 9 9. M, 0. M ( 9, 4) 7. If WZ XZ, then ZWX ZXW ; Base Angles Theorem (Thm..6). M 9,. M ( 4, ) 74. If XZ XY, then XZY Y; Base Angles Theorem (Thm..6). M, 4. M ( 9, ) 7. If V WZV, then WV WZ; Converse of
9 9. M, 0. M ( 9, 4) 7. If WZ XZ, then ZWX ZXW ; Base Angles Theorem (Thm..6). M 9,. M ( 4, ) 74. If XZ XY, then XZY Y; Base Angles Theorem (Thm..6). M, 4. M ( 9, ) 7. If V WZV, then WV WZ; Converse of
0114ge. Geometry Regents Exam 0114
 0114ge 1 The midpoint of AB is M(4, 2). If the coordinates of A are (6, 4), what are the coordinates of B? 1) (1, 3) 2) (2, 8) 3) (5, 1) 4) (14, 0) 2 Which diagram shows the construction of a 45 angle?
0114ge 1 The midpoint of AB is M(4, 2). If the coordinates of A are (6, 4), what are the coordinates of B? 1) (1, 3) 2) (2, 8) 3) (5, 1) 4) (14, 0) 2 Which diagram shows the construction of a 45 angle?
GEOMETRY ADDITIONAL PRACTICE ITEMS
 GEOMETRY ADDITIONAL PRACTICE ITEMS Geometry Additional Practice Items This section has two parts. The first part is a set of 4 sample items for Geometry. The second part contains a table that shows for
GEOMETRY ADDITIONAL PRACTICE ITEMS Geometry Additional Practice Items This section has two parts. The first part is a set of 4 sample items for Geometry. The second part contains a table that shows for
Section 6.2 Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach
 Section. Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach The unit circle is a circle of radius centered at the origin. If we have an angle in standard position superimposed on the unit circle, the terminal
Section. Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach The unit circle is a circle of radius centered at the origin. If we have an angle in standard position superimposed on the unit circle, the terminal
Theorem 1.2 (Converse of Pythagoras theorem). If the lengths of the sides of ABC satisfy a 2 + b 2 = c 2, then the triangle has a right angle at C.
 hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a + b = c. roof. b a a 3 b b 4 b a b 4 1 a a 3
hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a + b = c. roof. b a a 3 b b 4 b a b 4 1 a a 3
Common Core Readiness Assessment 3
 Common Core Readiness ssessment 3 1. B 3. Find the value of x. D E 2y24 y15 C y13 2x If you know that DE y C, and that D and E are midpoints, which of the following justifies that C 5 2DE? Triangle Midsegment
Common Core Readiness ssessment 3 1. B 3. Find the value of x. D E 2y24 y15 C y13 2x If you know that DE y C, and that D and E are midpoints, which of the following justifies that C 5 2DE? Triangle Midsegment
9.3. Practice C For use with pages Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle.
 LESSON 9.3 NAME DATE For use with pages 543 549 Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle. 1. 21 2. 3. 75 6 2 2 17 72 63 66 16 2 4. 110 5. 4.3 6. 96 2 4.4 10 3 3 4.5 Decide whether the numbers can
LESSON 9.3 NAME DATE For use with pages 543 549 Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle. 1. 21 2. 3. 75 6 2 2 17 72 63 66 16 2 4. 110 5. 4.3 6. 96 2 4.4 10 3 3 4.5 Decide whether the numbers can
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition. GEOMETRY and MEASUREMENT GRADE 7-8
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition INSTRUCTIONS GEOMETRY and MEASUREMENT GRADE 7-8 Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes Mark your
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition INSTRUCTIONS GEOMETRY and MEASUREMENT GRADE 7-8 Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes Mark your
0811ge. Geometry Regents Exam BC, AT = 5, TB = 7, and AV = 10.
 0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 1) 9 2) 8 3) 3 4) 6 2 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 4 Pentagon PQRST has PQ parallel to TS. After a translation
0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 1) 9 2) 8 3) 3 4) 6 2 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 4 Pentagon PQRST has PQ parallel to TS. After a translation
2013 ACTM Regional Geometry Exam
 2013 TM Regional Geometry Exam In each of the following choose the EST answer and record your choice on the answer sheet provided. To insure correct scoring, be sure to make all erasures completely. The
2013 TM Regional Geometry Exam In each of the following choose the EST answer and record your choice on the answer sheet provided. To insure correct scoring, be sure to make all erasures completely. The
Q.2 A, B and C are points in the xy plane such that A(1, 2) ; B (5, 6) and AC = 3BC. Then. (C) 1 1 or
 STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
Integrated Math II. IM2.1.2 Interpret given situations as functions in graphs, formulas, and words.
 Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
0809ge. Geometry Regents Exam Based on the diagram below, which statement is true?
 0809ge 1 Based on the diagram below, which statement is true? 3 In the diagram of ABC below, AB AC. The measure of B is 40. 1) a b ) a c 3) b c 4) d e What is the measure of A? 1) 40 ) 50 3) 70 4) 100
0809ge 1 Based on the diagram below, which statement is true? 3 In the diagram of ABC below, AB AC. The measure of B is 40. 1) a b ) a c 3) b c 4) d e What is the measure of A? 1) 40 ) 50 3) 70 4) 100
0113ge. Geometry Regents Exam In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC?
 0113ge 1 If MNP VWX and PM is the shortest side of MNP, what is the shortest side of VWX? 1) XV ) WX 3) VW 4) NP 4 In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC? In circle
0113ge 1 If MNP VWX and PM is the shortest side of MNP, what is the shortest side of VWX? 1) XV ) WX 3) VW 4) NP 4 In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC? In circle
Math 3 Unit Skills Checklist
 Unit 1 Modeling with Statistics Use Normal Distributions Math 3 Unit Skills Checklist Describe the characteristics of a standard normal curve. Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it
Unit 1 Modeling with Statistics Use Normal Distributions Math 3 Unit Skills Checklist Describe the characteristics of a standard normal curve. Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C. eight D. ten 3. The sum of the interior
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C. eight D. ten 3. The sum of the interior
TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS
 The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS Thursday, January 26, 1989-1:1.5 to 4:1.5 p.m., only The last page of the booklet is the answer sheet. Fold
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS Thursday, January 26, 1989-1:1.5 to 4:1.5 p.m., only The last page of the booklet is the answer sheet. Fold
9. AD = 7; By the Parallelogram Opposite Sides Theorem (Thm. 7.3), AD = BC. 10. AE = 7; By the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem (Thm. 7.6), AE = EC.
 3. Sample answer: Solve 5x = 3x + 1; opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent; es; You could start b setting the two parts of either diagonal equal to each other b the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem
3. Sample answer: Solve 5x = 3x + 1; opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent; es; You could start b setting the two parts of either diagonal equal to each other b the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Mathematics Grades Adopted Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
 , VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 2, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 3,, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 5 Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 State: Georgia Common Core Standards Subject: Mathematics
, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 2, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 3,, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 5 Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 State: Georgia Common Core Standards Subject: Mathematics
Common Core Readiness Assessment 4
 ommon ore Readiness ssessment 4 1. Use the diagram and the information given to complete the missing element of the two-column proof. 2. Use the diagram and the information given to complete the missing
ommon ore Readiness ssessment 4 1. Use the diagram and the information given to complete the missing element of the two-column proof. 2. Use the diagram and the information given to complete the missing
Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1
 Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1 ALGEBRA I A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student
Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1 ALGEBRA I A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student
Conic Section: Circles
 Conic Section: Circles Circle, Center, Radius A circle is defined as the set of all points that are the same distance awa from a specific point called the center of the circle. Note that the circle consists
Conic Section: Circles Circle, Center, Radius A circle is defined as the set of all points that are the same distance awa from a specific point called the center of the circle. Note that the circle consists
Geometry. A. Right Triangle. Legs of a right triangle : a, b. Hypotenuse : c. Altitude : h. Medians : m a, m b, m c. Angles :,
 Geometry A. Right Triangle Legs of a right triangle : a, b Hypotenuse : c Altitude : h Medians : m a, m b, m c Angles :, Radius of circumscribed circle : R Radius of inscribed circle : r Area : S 1. +
Geometry A. Right Triangle Legs of a right triangle : a, b Hypotenuse : c Altitude : h Medians : m a, m b, m c Angles :, Radius of circumscribed circle : R Radius of inscribed circle : r Area : S 1. +
( ) ( ) Geometry Team Solutions FAMAT Regional February = 5. = 24p.
 . A 6 6 The semi perimeter is so the perimeter is 6. The third side of the triangle is 7. Using Heron s formula to find the area ( )( )( ) 4 6 = 6 6. 5. B Draw the altitude from Q to RP. This forms a 454590
. A 6 6 The semi perimeter is so the perimeter is 6. The third side of the triangle is 7. Using Heron s formula to find the area ( )( )( ) 4 6 = 6 6. 5. B Draw the altitude from Q to RP. This forms a 454590
10-3 Arcs and Chords. ALGEBRA Find the value of x.
 ALGEBRA Find the value of x. 1. Arc ST is a minor arc, so m(arc ST) is equal to the measure of its related central angle or 93. and are congruent chords, so the corresponding arcs RS and ST are congruent.
ALGEBRA Find the value of x. 1. Arc ST is a minor arc, so m(arc ST) is equal to the measure of its related central angle or 93. and are congruent chords, so the corresponding arcs RS and ST are congruent.
Arkansas Council of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State Competition Geometry Exam. B. 28 (5x-41) 3 m (2x+25)
 rkansas ouncil of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State ompetition Geometry Exam For questions 1 through 25, mark your answer choice on the answer sheet provided. (Figures may not be drawn to scale.) fter
rkansas ouncil of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State ompetition Geometry Exam For questions 1 through 25, mark your answer choice on the answer sheet provided. (Figures may not be drawn to scale.) fter
Chapter (Circle) * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in
 Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Mathematics Trigonometry: Unit Circle
 a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
+2 u, 2s ) [D] ( r+ t + u, 2s )
![+2 u, 2s ) [D] ( r+ t + u, 2s ) +2 u, 2s ) [D] ( r+ t + u, 2s )](/thumbs/74/70220114.jpg) 1. Isosceles trapezoid JKLM has legs JK and LM, and base KL. If JK = 3x + 6, KL = 9x 3, and LM = 7x 9. Find the value of x. [A] 15 4 [] 3 4 [] 3 [] 3 4. Which best describes the relationship between the
1. Isosceles trapezoid JKLM has legs JK and LM, and base KL. If JK = 3x + 6, KL = 9x 3, and LM = 7x 9. Find the value of x. [A] 15 4 [] 3 4 [] 3 [] 3 4. Which best describes the relationship between the
Chapter 1. Some Basic Theorems. 1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
 hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a 2 + b 2 = c 2. roof. b a a 3 2 b 2 b 4 b a b
hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a 2 + b 2 = c 2. roof. b a a 3 2 b 2 b 4 b a b
absolute value The distance of a number from zero on a real number line.
 G L O S S A R Y A absolute value The distance of a number from zero on a real number line. acute angle An angle whose measure is less than 90. acute triangle A triangle in which each of the three interior
G L O S S A R Y A absolute value The distance of a number from zero on a real number line. acute angle An angle whose measure is less than 90. acute triangle A triangle in which each of the three interior
Content Guidelines Overview
 Content Guidelines Overview The Pearson Video Challenge is open to all students, but all video submissions must relate to set of predetermined curriculum areas and topics. In the following pages the selected
Content Guidelines Overview The Pearson Video Challenge is open to all students, but all video submissions must relate to set of predetermined curriculum areas and topics. In the following pages the selected
9-12 Mathematics Vertical Alignment ( )
 Algebra I Algebra II Geometry Pre- Calculus U1: translate between words and algebra -add and subtract real numbers -multiply and divide real numbers -evaluate containing exponents -evaluate containing
Algebra I Algebra II Geometry Pre- Calculus U1: translate between words and algebra -add and subtract real numbers -multiply and divide real numbers -evaluate containing exponents -evaluate containing
MATH TOURNAMENT 2012 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS
 MATH TOURNAMENT 0 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS. Consider the eperiment of throwing two 6 sided fair dice, where, the faces are numbered from to 6. What is the probability of the event that the sum of the values
MATH TOURNAMENT 0 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS. Consider the eperiment of throwing two 6 sided fair dice, where, the faces are numbered from to 6. What is the probability of the event that the sum of the values
Answers. Chapter10 A Start Thinking. and 4 2. Sample answer: no; It does not pass through the center.
 hapter10 10.1 Start Thinking 6. no; is not a right triangle because the side lengths do not satisf the Pthagorean Theorem (Thm. 9.1). 1. (3, ) 7. es; is a right triangle because the side lengths satisf
hapter10 10.1 Start Thinking 6. no; is not a right triangle because the side lengths do not satisf the Pthagorean Theorem (Thm. 9.1). 1. (3, ) 7. es; is a right triangle because the side lengths satisf
Integrated Mathematics II
 Integrated Mathematics II This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Integrated Mathematics II This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? A. (1,10) B. (2,7) C. (3,5) D. (4,3) E.
 April 9, 01 Standards: MM1Ga, MM1G1b Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? (1,10) B. (,7) C. (,) (,) (,1). Points P, Q, R, and S lie on a line
April 9, 01 Standards: MM1Ga, MM1G1b Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? (1,10) B. (,7) C. (,) (,) (,1). Points P, Q, R, and S lie on a line
1 = 1, b d and c d. Chapter 7. Worked-Out Solutions Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 357) Slope of line b:
 hapter 7 aintaining athematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 = 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 = 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) 7 = 1 7 1 x = 3 1 = 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5)
hapter 7 aintaining athematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 = 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 = 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) 7 = 1 7 1 x = 3 1 = 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5)
Chapter-wise questions
 hapter-wise questions ircles 1. In the given figure, is circumscribing a circle. ind the length of. 3 15cm 5 2. In the given figure, is the center and. ind the radius of the circle if = 18 cm and = 3cm
hapter-wise questions ircles 1. In the given figure, is circumscribing a circle. ind the length of. 3 15cm 5 2. In the given figure, is the center and. ind the radius of the circle if = 18 cm and = 3cm
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 11.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name ate Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to ircles Vocabulary Identify an instance of each term in the diagram. 1. circle X T 2. center of the circle H I
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name ate Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to ircles Vocabulary Identify an instance of each term in the diagram. 1. circle X T 2. center of the circle H I
Arcs and Inscribed Angles of Circles
 Arcs and Inscribed Angles of Circles Inscribed angles have: Vertex on the circle Sides are chords (Chords AB and BC) Angle ABC is inscribed in the circle AC is the intercepted arc because it is created
Arcs and Inscribed Angles of Circles Inscribed angles have: Vertex on the circle Sides are chords (Chords AB and BC) Angle ABC is inscribed in the circle AC is the intercepted arc because it is created
Chapter 10. Properties of Circles
 Chapter 10 Properties of Circles 10.1 Use Properties of Tangents Objective: Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Essential Question: how can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Terminology:
Chapter 10 Properties of Circles 10.1 Use Properties of Tangents Objective: Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Essential Question: how can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Terminology:
1 st Preparatory. Part (1)
 Part (1) (1) omplete: 1) The square is a rectangle in which. 2) in a parallelogram in which m ( ) = 60, then m ( ) =. 3) The sum of measures of the angles of the quadrilateral equals. 4) The ray drawn
Part (1) (1) omplete: 1) The square is a rectangle in which. 2) in a parallelogram in which m ( ) = 60, then m ( ) =. 3) The sum of measures of the angles of the quadrilateral equals. 4) The ray drawn
Practice Test Student Answer Document
 Practice Test Student Answer Document Record your answers by coloring in the appropriate bubble for the best answer to each question. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
Practice Test Student Answer Document Record your answers by coloring in the appropriate bubble for the best answer to each question. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
For math conventions used on the GRE, refer to this link:
 GRE Review ISU Student Success Center Quantitative Workshop One Quantitative Section: Overview Your test will include either two or three 35-minute quantitative sections. There will be 20 questions in
GRE Review ISU Student Success Center Quantitative Workshop One Quantitative Section: Overview Your test will include either two or three 35-minute quantitative sections. There will be 20 questions in
A List of Definitions and Theorems
 Metropolitan Community College Definition 1. Two angles are called complements if the sum of their measures is 90. Two angles are called supplements if the sum of their measures is 180. Definition 2. One
Metropolitan Community College Definition 1. Two angles are called complements if the sum of their measures is 90. Two angles are called supplements if the sum of their measures is 180. Definition 2. One
So, PQ is about 3.32 units long Arcs and Chords. ALGEBRA Find the value of x.
 ALGEBRA Find the value of x. 1. Arc ST is a minor arc, so m(arc ST) is equal to the measure of its related central angle or 93. and are congruent chords, so the corresponding arcs RS and ST are congruent.
ALGEBRA Find the value of x. 1. Arc ST is a minor arc, so m(arc ST) is equal to the measure of its related central angle or 93. and are congruent chords, so the corresponding arcs RS and ST are congruent.
0811ge. Geometry Regents Exam
 0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 1) 9 ) 8 3) 3 4) 6 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 4 Pentagon PQRST has PQ parallel to TS. After a translation
0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 1) 9 ) 8 3) 3 4) 6 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 4 Pentagon PQRST has PQ parallel to TS. After a translation
GEOMETRY & MEASUREMENT
 GEOMETRY & MESUREMENT 1 1. The measure for a stud for a wall must be 72. Which of the following studs is allowed? 4 a. 72.7 in b. 72.31 in c. 71.81 in d. 71.2 in 2. t a bolt manufacturing company, 6 bolts
GEOMETRY & MESUREMENT 1 1. The measure for a stud for a wall must be 72. Which of the following studs is allowed? 4 a. 72.7 in b. 72.31 in c. 71.81 in d. 71.2 in 2. t a bolt manufacturing company, 6 bolts
Section 5.1. Perimeter and Area
 Section 5.1 Perimeter and Area Perimeter and Area The perimeter of a closed plane figure is the distance around the figure. The area of a closed plane figure is the number of non-overlapping squares of
Section 5.1 Perimeter and Area Perimeter and Area The perimeter of a closed plane figure is the distance around the figure. The area of a closed plane figure is the number of non-overlapping squares of
1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1
 1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1 3 As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F'. y = x 2 + 2x
1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1 3 As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F'. y = x 2 + 2x
Unit 10 Geometry Circles. NAME Period
 Unit 10 Geometry Circles NAME Period 1 Geometry Chapter 10 Circles ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** 1. (10-1) Circles and Circumference
Unit 10 Geometry Circles NAME Period 1 Geometry Chapter 10 Circles ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** 1. (10-1) Circles and Circumference
UNIT 5 SIMILARITY, RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY, AND PROOF Unit Assessment
 Unit 5 ircle the letter of the best answer. 1. line segment has endpoints at (, 5) and (, 11). point on the segment has a distance that is 1 of the length of the segment from endpoint (, 5). What are the
Unit 5 ircle the letter of the best answer. 1. line segment has endpoints at (, 5) and (, 11). point on the segment has a distance that is 1 of the length of the segment from endpoint (, 5). What are the
Geometry Final Exam Review
 Name: Date: Period: Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Fill in the flow chart below with the properties that belong to each polygon. 2. Find the measure of each numbered angle: 3. Find the value of x 4. Calculate
Name: Date: Period: Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Fill in the flow chart below with the properties that belong to each polygon. 2. Find the measure of each numbered angle: 3. Find the value of x 4. Calculate
02)
 GRE / GMATmath,! abscissa, scalene, intercept, markup, such that, break even. abscissa. (4, 2) 4abscissa, 2ordinate absolute value acre add adjacent angles altitude ; angle () acute angle (90 ) right angle
GRE / GMATmath,! abscissa, scalene, intercept, markup, such that, break even. abscissa. (4, 2) 4abscissa, 2ordinate absolute value acre add adjacent angles altitude ; angle () acute angle (90 ) right angle
ACTM Regional Geometry Exam 2009
 TM Regional Geometry xam 009 In each of the following questions choose the best answer and bubble the corresponding letter on the answer sheet. Note: The geometric figures on this exam are not necessarily
TM Regional Geometry xam 009 In each of the following questions choose the best answer and bubble the corresponding letter on the answer sheet. Note: The geometric figures on this exam are not necessarily
Common Core Edition Table of Contents
 Common Core Edition Table of Contents ALGEBRA 1 Chapter 1 Foundations for Algebra 1-1 Variables and Expressions 1-2 Order of Operations and Evaluating Expressions 1-3 Real Numbers and the Number Line 1-4
Common Core Edition Table of Contents ALGEBRA 1 Chapter 1 Foundations for Algebra 1-1 Variables and Expressions 1-2 Order of Operations and Evaluating Expressions 1-3 Real Numbers and the Number Line 1-4
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 9.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Meeting Friends The Distance Formula Vocabular Define the term in our own words. 1. Distance Formula Problem Set Archaeologists map the location of
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Meeting Friends The Distance Formula Vocabular Define the term in our own words. 1. Distance Formula Problem Set Archaeologists map the location of
Geometry Cumulative Review
 Geometry Cumulative Review Name 1. Find a pattern for the sequence. Use the pattern to show the next term. 1, 3, 9, 27,... A. 81 B. 45 C. 41 D. 36 2. If EG = 42, find the value of y. A. 5 B. C. 6 D. 7
Geometry Cumulative Review Name 1. Find a pattern for the sequence. Use the pattern to show the next term. 1, 3, 9, 27,... A. 81 B. 45 C. 41 D. 36 2. If EG = 42, find the value of y. A. 5 B. C. 6 D. 7
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
Pythagoras Theorem and Its Applications
 Lecture 10 Pythagoras Theorem and Its pplications Theorem I (Pythagoras Theorem) or a right-angled triangle with two legs a, b and hypotenuse c, the sum of squares of legs is equal to the square of its
Lecture 10 Pythagoras Theorem and Its pplications Theorem I (Pythagoras Theorem) or a right-angled triangle with two legs a, b and hypotenuse c, the sum of squares of legs is equal to the square of its
Page 1 Central Angles & Arc Measures
 Geometry/Trig Unit 8 ll bout ircles! Name: ate: Page 1 entral ngles & rc Measures Example 1: JK is a diameter of ircle. Name two examples for each: K Minor rc:, Major rc:, M Semicircle:, Name Pair of djacent
Geometry/Trig Unit 8 ll bout ircles! Name: ate: Page 1 entral ngles & rc Measures Example 1: JK is a diameter of ircle. Name two examples for each: K Minor rc:, Major rc:, M Semicircle:, Name Pair of djacent
0112ge. Geometry Regents Exam Line n intersects lines l and m, forming the angles shown in the diagram below.
 Geometry Regents Exam 011 011ge 1 Line n intersects lines l and m, forming the angles shown in the diagram below. 4 In the diagram below, MATH is a rhombus with diagonals AH and MT. Which value of x would
Geometry Regents Exam 011 011ge 1 Line n intersects lines l and m, forming the angles shown in the diagram below. 4 In the diagram below, MATH is a rhombus with diagonals AH and MT. Which value of x would
PRACTICE TEST 1 Math Level IC
 SOLID VOLUME OTHER REFERENCE DATA Right circular cone L = cl V = volume L = lateral area r = radius c = circumference of base h = height l = slant height Sphere S = 4 r 2 V = volume r = radius S = surface
SOLID VOLUME OTHER REFERENCE DATA Right circular cone L = cl V = volume L = lateral area r = radius c = circumference of base h = height l = slant height Sphere S = 4 r 2 V = volume r = radius S = surface
Answer Key. 7.1 Tangent Ratio. Chapter 7 Trigonometry. CK-12 Geometry Honors Concepts 1. Answers
 7.1 Tangent Ratio 1. Right triangles with 40 angles have two pairs of congruent angles and therefore are similar. This means that the ratio of the opposite leg to adjacent leg is constant for all 40 right
7.1 Tangent Ratio 1. Right triangles with 40 angles have two pairs of congruent angles and therefore are similar. This means that the ratio of the opposite leg to adjacent leg is constant for all 40 right
TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS
 The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS Tuesday, June 16,1987-1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only The last page of the booklet is the answer sheet. Fold the last
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS Tuesday, June 16,1987-1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only The last page of the booklet is the answer sheet. Fold the last
Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3. Topic 1 : Equation of a circle
 Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3 Topic 1 : Equation of a circle Equation with center (0,0) and radius r Equation with center (h,k) and radius r ( ) ( ) 1. The endpoints of a diameter
Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3 Topic 1 : Equation of a circle Equation with center (0,0) and radius r Equation with center (h,k) and radius r ( ) ( ) 1. The endpoints of a diameter
Grade 11 Pre-Calculus Mathematics (1999) Grade 11 Pre-Calculus Mathematics (2009)
 Use interval notation (A-1) Plot and describe data of quadratic form using appropriate scales (A-) Determine the following characteristics of a graph of a quadratic function: y a x p q Vertex Domain and
Use interval notation (A-1) Plot and describe data of quadratic form using appropriate scales (A-) Determine the following characteristics of a graph of a quadratic function: y a x p q Vertex Domain and
MHR Principles of Mathematics 10 Solutions 1
 Course Review Note: Length and angle measures may vary slightly due to rounding. Course Review Question Page 8 a) Let l represent the length and w represent the width, then l + w 0. n+ q b) If n represents
Course Review Note: Length and angle measures may vary slightly due to rounding. Course Review Question Page 8 a) Let l represent the length and w represent the width, then l + w 0. n+ q b) If n represents
Introduction - Geometry
 L I F O R N I S T N R S T E S T Introduction - The following released test questions are taken from the Standards Test. This test is one of the alifornia Standards Tests administered as part of the Standardized
L I F O R N I S T N R S T E S T Introduction - The following released test questions are taken from the Standards Test. This test is one of the alifornia Standards Tests administered as part of the Standardized
3 = 1, a c, a d, b c, and b d.
 hapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) = 1 7 7 1 x = 3 1 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5) =
hapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) = 1 7 7 1 x = 3 1 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5) =
The focus of SECONDARY Mathematics II Critical Area 1: Critical Area 2: Critical Area 3: Critical Area 4: Critica l Area 5: Critical Area 6:
 The focus of SECONDARY Mathematics II is on quadratic expressions, equations, and functions; comparing their characteristics and behavior to those of linear and exponential relationships from Secondary
The focus of SECONDARY Mathematics II is on quadratic expressions, equations, and functions; comparing their characteristics and behavior to those of linear and exponential relationships from Secondary
Algebra II/Geometry Curriculum Guide Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA
 Algebra II/Geometry Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Algebra II/Geometry Prerequisite: Successful completion of Algebra 1 Part 2 K Algebra II/Geometry is intended for students who have successfully
Algebra II/Geometry Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Algebra II/Geometry Prerequisite: Successful completion of Algebra 1 Part 2 K Algebra II/Geometry is intended for students who have successfully
