AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES Introduction
|
|
|
- Edwin Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 3 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES Introduction You are already familiar with some methods of finding perimeters and areas of simple plane figures such as rectangles, squares, parallelograms, triangles and circles from your earlier classes. Many objects that we come across in our daily life are related to the circular shape in some form or the other. Cycle wheels, wheel barrow (thela), dartboard, round cake, papad, drain cover, various designs, bangles, brooches, circular paths, washers, flower beds, etc. are some examples of such objects (see Fig. 1.1). So, the problem of finding perimeters and areas related to circular figures is of great practical importance. In this chapter, we shall begin our discussion with a review of the concepts of perimeter (circumference) and area of a circle and apply this knowledge in finding the areas of two special parts of a circular region (or briefly of a circle) known as sector and segment. We shall also see how to find the areas of some combinations of plane figures involving circles or their parts. Fig. 1.1
2 4 MATHEMATICS 1. Perimeter and Area of a Circle A Review Recall that the distance covered by travelling once around a circle is its perimeter, usually called its circumference. You also know from your earlier classes, that circumference of a circle bears a constant ratio with its diameter. This constant ratio is denoted by the Greek letter π (read as pi ). In other words, or, circumference π diameter circumference π diameter π r (where r is the radius of the circle) πr The great Indian mathematician Aryabhatta (A.D ) gave an approximate value of π. He stated that π 683, which is nearly equal to It is also 0000 interesting to note that using an identity of the great mathematical genius Srinivas Ramanujan ( ) of India, mathematicians have been able to calculate the value of π correct to million places of decimals. As you know from Chapter 1 of Class IX, π is an irrational number and its decimal expansion is non-terminating and non-recurring (non-repeating). However, for practical purposes, we generally take the value of π as or 3.14, approximately. 7 You may also recall that area of a circle is πr, where r is the radius of the circle. Recall that you have verified it in Class VII, by cutting a circle into a number of sectors and rearranging them as shown in Fig. 1.. Fig 1.
3 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 5 You can see that the shape in Fig. 1. (ii) is nearly a rectangle of length 1 πr and breadth r. This suggests that the area of the circle 1 πr r πr. Let us recall the concepts learnt in earlier classes, through an example. Example 1 : The cost of fencing a circular field at the rate of Rs 4 per metre is Rs 580. The field is to be ploughed at the rate of Rs 0.50 per m. Find the cost of ploughing the field (Take π 7 ). Solution : Length of the fence (in metres) Total cost Rate So, circumference of the field 0 m Therefore, if r metres is the radius of the field, then πr 0 or, 7 r 0 or, r i.e., radius of the field is 35 m Therefore, area of the field πr m 5 35 m 7 Now, cost of ploughing 1 m of the field Rs 0.50 So, total cost of ploughing the field Rs Rs 195 EXERCISE 1.1 Unless stated otherwise, use π The radii of two circles are 19 cm and 9 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle which has circumference equal to the sum of the circumferences of the two circles.. The radii of two circles are 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle having area equal to the sum of the areas of the two circles. 3. Fig. 1.3 depicts an archery target marked with its five scoring areas from the centre outwards as Gold, Red, Blue, Black and White. The diameter of the region representing Gold score is 1 cm and each of the other bands is 10.5 cm wide. Find the area of each of the five scoring regions. Fig. 1.3
4 6 MATHEMATICS 4. The wheels of a car are of diameter 80 cm each. How many complete revolutions does each wheel make in 10 minutes when the car is travelling at a speed of 66 km per hour? 5. Tick the correct answer in the following and justify your choice : If the perimeter and the area of a circle are numerically equal, then the radius of the circle is (A) units (B) π units (C) 4 units (D) 7 units 1.3 Areas of Sector and Segment of a Circle You have already come across the terms sector and segment of a circle in your earlier classes. Recall that the portion (or part) of the circular region enclosed by two radii and the corresponding arc is called a sector of the circle and the portion (or part) of the circular region enclosed between a chord and the corresponding arc is called a segment of the circle. Thus, in Fig. 1.4, shaded region OAPB is a sector Fig. 1.4 of the circle with centre O. AOB is called the angle of the sector. Note that in this figure, unshaded region OAQB is also a sector of the circle. For obvious reasons, OAPB is called the minor sector and OAQB is called the major sector. You can also see that angle of the major sector is AOB. Now, look at Fig. 1.5 in which AB is a chord of the circle with centre O. So, shaded region APB is a segment of the circle. You can also note that unshaded region AQB is another segment of the circle formed by the chord AB. For obvious reasons, APB is called the minor segment and AQB is called the major segment. Remark : When we write segment and sector we will mean the minor segment and the minor sector respectively, unless stated otherwise. Now with this knowledge, let us try to find some relations (or formulae) to calculate their areas. Let OAPB be a sector of a circle with centre O and radius r (see Fig. 1.6). Let the degree measure of AOB be θ. You know that area of a circle (in fact of a circular region or disc) is πr. Fig. 1.5 Fig. 1.6
5 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 7 In a way, we can consider this circular region to be a sector forming an angle of (i.e., of degree measure ) at the centre O. Now by applying the Unitary Method, we can arrive at the area of the sector OAPB as follows: When degree measure of the angle at the centre is, area of the sector πr So, when the degree measure of the angle at the centre is 1, area of the πr sector Therefore, when the degree measure of the angle at the centre is θ, area of the πr θ sector θ π r. Thus, we obtain the following relation (or formula) for area of a sector of a circle: θ Area of the sector of angle θ πr, where r is the radius of the circle and θ the angle of the sector in degrees. Now, a natural question arises : Can we find the length of the arc APB corresponding to this sector? Yes. Again, by applying the Unitary Method and taking the whole length of the circle (of angle ) as πr, we can obtain the required θ length of the arc APB as π r. θ So, length of an arc of a sector of angle θ πr. Fig. 1.7 Now let us take the case of the area of the segment APB of a circle with centre O and radius r (see Fig. 1.7). You can see that : Area of the segment APB Area of the sector OAPB Area of Δ OAB θ π r area of Δ OAB Note : From Fig. 1.6 and Fig. 1.7 respectively, you can observe that : Area of the major sector OAQB πr Area of the minor sector OAPB and Area of major segment AQB πr Area of the minor segment APB
6 8 MATHEMATICS Let us now take some examples to understand these concepts (or results). Example : Find the area of the sector of a circle with radius 4 cm and of angle 30. Also, find the area of the corresponding major sector (Use π 3.14). Solution : Given sector is OAPB (see Fig. 1.8). Area of the sector θ πr cm Fig cm 4.19cm (approx.) 3 Area of the corresponding major sector Alternatively, area of the major sector πr area of sector OAPB ( ) cm cm 46.1 cm (approx.) ( θ ) πr Example 3 : Find the area of the segment AYB shown in Fig. 1.9, if radius of the circle is 1 cm and AOB 10. (Use π 7 ) cm cm cm 46.1 cm (approx.) Fig. 1.9
7 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 9 Solution : Area of the segment AYB Area of sector OAYB Area of Δ OAB (1) Now, area of the sector OAYB cm 46 cm () 7 For finding the area of Δ OAB, draw OM AB as shown in Fig Note that OA OB. Therefore, by RHS congruence, Δ AMO Δ BMO. So, M is the mid-point of AB and AOM BOM Let OM x cm So, from Δ OMA, OM OA cos 60 or, x 1 1 cos 60 1 Fig or, x 1 So, OM 1 cm Also, AM OA sin 60 3 So, AM 1 3 cm Therefore, AB AM 1 3 cm 1 3 cm So, area of Δ OAB AB OM 1 3 cm 441 3cm 4 (3) Therefore, area of the segment AYB cm 4 1 (88 1 3)cm 4 [From (1), () and (3)]
8 30 MATHEMATICS EXERCISE 1. Unless stated otherwise, use π Find the area of a sector of a circle with radius 6 cm if angle of the sector is 60.. Find the area of a quadrant of a circle whose circumference is cm. 3. The length of the minute hand of a clock is 14 cm. Find the area swept by the minute hand in 5 minutes. 4. A chord of a circle of radius 10 cm subtends a right angle at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding : (i) minor segment (ii) major sector. (Use π 3.14) 5. In a circle of radius 1 cm, an arc subtends an angle of 60 at the centre. Find: (i) the length of the arc (ii) area of the sector formed by the arc (iii) area of the segment formed by the corresponding chord 6. A chord of a circle of radius 15 cm subtends an angle of 60 at the centre. Find the areas of the corresponding minor and major segments of the circle. (Use π 3.14 and ) 7. A chord of a circle of radius 1 cm subtends an angle of 10 at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding segment of the circle. (Use π 3.14 and ) 8. A horse is tied to a peg at one corner of a square shaped grass field of side 15 m by means of a 5 m long rope (see Fig. 1.11). Find (i) the area of that part of the field in which the horse can graze. (ii) the increase in the grazing area if the rope were 10 m long instead of 5 m. (Use π 3.14) 9. A brooch is made with silver wire in the form of a circle with diameter 35 mm. The wire is also used in making 5 diameters which divide the circle into 10 equal sectors as shown in Fig Find : (i) the total length of the silver wire required. (ii) the area of each sector of the brooch. Fig Fig. 1.1
9 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES An umbrella has 8 ribs which are equally spaced (see Fig. 1.13). Assuming umbrella to be a flat circle of radius 45 cm, find the area between the two consecutive ribs of the umbrella. 11. A car has two wipers which do not overlap. Each wiper has a blade of length 5 cm sweeping through an angle of 115. Find the total area cleaned at each sweep of the blades. Fig To warn ships for underwater rocks, a lighthouse spreads a red coloured light over a sector of angle 80 to a distance of 16.5 km. Find the area of the sea over which the ships are warned. (Use π 3.14) 13. A round table cover has six equal designs as shown in Fig If the radius of the cover is 8 cm, find the cost of making the designs at the rate of Rs 0.35 per cm. (Use 3 1.7) 14. Tick the correct answer in the following : Fig Area of a sector of angle p (in degrees) of a circle with radius R is p (A) π R (B) 180 p π R (C) R 180 p π (D) p π R Areas of Combinations of Plane Figures So far, we have calculated the areas of different figures separately. Let us now try to calculate the areas of some combinations of plane figures. We come across these types of figures in our daily life and also in the form of various interesting designs. Flower beds, drain covers, window designs, designs on table covers, are some of such examples. We illustrate the process of calculating areas of these figures through some examples. Example 4 : In Fig. 1.15, two circular flower beds have been shown on two sides of a square lawn ABCD of side 56 m. If the centre of each circular flower bed is the point of intersection O of the diagonals of the square lawn, find the sum of the areas of the lawn and the flower beds. Fig. 1.15
10 3 MATHEMATICS Solution : Area of the square lawn ABCD m (1) Let OA OB x metres So, x + x 56 or, x or, x 8 56 () Now, area of sector OAB Also, area of Δ OAB 90 π x 1 4 πx m [From ()] (3) m 4 ( AOB 90 ) (4) So, area of flower bed AB m [From (3) and (4)] m m (5) 4 7 Similarly, area of the other flower bed m (6) 4 7 Therefore, total area m [From (1), (5) and (6)] m m 403m 7
11 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 33 Alternative Solution : Total area Area of sector OAB + Area of sector ODC + Area of Δ OAD + Area of Δ OBC m m ( 14 14)m m 403 m Example 5 : Find the area of the shaded region in Fig. 1.16, where ABCD is a square of side 14 cm. Solution : Area of square ABCD cm 196 cm Diameter of each circle 14 cm 7cm So, radius of each circle 7 cm Fig So, area of one circle πr 7 7 cm cm 4 cm Therefore, area of the four circles 77 4 cm 154 cm Hence, area of the shaded region ( ) cm 4 cm.
12 34 MATHEMATICS Example 6 : Find the area of the shaded design in Fig. 1.17, where ABCD is a square of side 10 cm and semicircles are drawn with each side of the square as diameter. (Use π 3.14) Fig Fig Solution : Let us mark the four unshaded regions as I, II, III and IV (see Fig. 1.18). Area of I + Area of III Area of ABCD Areas of two semicircles of each of radius 5 cm π 5 cm ( ) cm ( ) cm 1.5 cm Similarly, Area of II + Area of IV 1.5 cm So, area of the shaded design Area of ABCD Area of (I + II + III + IV) ( ) cm (100 43) cm 57 cm Unless stated otherwise, use π 7 EXERCISE Find the area of the shaded region in Fig. 1.19, if PQ 4 cm, PR 7 cm and O is the centre of the circle. Fig. 1.19
13 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 35. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig. 1.0, if radii of the two concentric circles with centre O are 7 cm and 14 cm respectively and AOC 40. Fig. 1.0 Fig Find the area of the shaded region in Fig. 1.1, if ABCD is a square of side 14 cm and APD and BPC are semicircles. 4. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig. 1., where a circular arc of radius 6 cm has been drawn with vertex O of an equilateral triangle OAB of side 1 cm as centre. Fig. 1. Fig From each corner of a square of side 4 cm a quadrant of a circle of radius 1 cm is cut and also a circle of diameter cm is cut as shown in Fig Find the area of the remaining portion of the square. 6. In a circular table cover of radius 3 cm, a design is formed leaving an equilateral triangle ABC in the middle as shown in Fig Find the area of the design (shaded region). Fig. 1.4
14 36 MATHEMATICS 7. In Fig. 1.5, ABCD is a square of side 14 cm. With centres A, B, C and D, four circles are drawn such that each circle touch externally two of the remaining three circles. Find the area of the shaded region. Fig Fig. 1.6 depicts a racing track whose left and right ends are semicircular. Fig. 1.6 The distance between the two inner parallel line segments is 60 m and they are each 106 m long. If the track is 10 m wide, find : (i) the distance around the track along its inner edge (ii) the area of the track. 9. In Fig. 1.7, AB and CD are two diameters of a circle (with centre O) perpendicular to each other and OD is the diameter of the smaller circle. If OA 7 cm, find the area of the shaded region. 10. The area of an equilateral triangle ABC is cm. With each vertex of the triangle as centre, a circle is drawn with radius equal to half the length of the side of the triangle (see Fig. 1.8). Find the area of the shaded region. (Use π 3.14 and ) Fig. 1.7 Fig. 1.8
15 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES On a square handkerchief, nine circular designs each of radius 7 cm are made (see Fig. 1.9). Find the area of the remaining portion of the handkerchief. Fig. 1.9 Fig In Fig. 1.30, OACB is a quadrant of a circle with centre O and radius 3.5 cm. If OD cm, find the area of the (i) quadrant OACB, (ii) shaded region. 13. In Fig. 1.31, a square OABC is inscribed in a quadrant OPBQ. If OA 0 cm, find the area of the shaded region. (Use π 3.14) Fig Fig AB and CD are respectively arcs of two concentric circles of radii 1 cm and 7 cm and centre O (see Fig. 1.3). If AOB 30, find the area of the shaded region. 15. In Fig. 1.33, ABC is a quadrant of a circle of radius 14 cm and a semicircle is drawn with BC as diameter. Find the area of the shaded region. Fig. 1.33
16 38 MATHEMATICS 16. Calculate the area of the designed region in Fig common between the two quadrants of circles of radius 8 cm each. Fig Summary In this chapter, you have studied the following points : 1. Circumference of a circle π r.. Area of a circle π r. 3. Length of an arc of a sector of a circle with radius r and angle with degree measure θ is θ π r θ 4. Area of a sector of a circle with radius r and angle with degrees measure θ is π r 5. Area of segment of a circle Area of the corresponding sector Area of the corresponding triangle.
Class X Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles Maths
 Exercise 12.1 Question 1: The radii of two circles are 19 cm and 9 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle which has circumference equal to the sum of the circumferences of the two circles. Radius
Exercise 12.1 Question 1: The radii of two circles are 19 cm and 9 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle which has circumference equal to the sum of the circumferences of the two circles. Radius
Area Related to Circle Exercise 2
 1 Area Related to Circle Exercise 2 Things to Remember Length of the arc of angle θ = (θ/360) 2πr Unless stated otherwise, use π =22/7. Question 1 Find the area of a sector of a circle with radius 6 cm
1 Area Related to Circle Exercise 2 Things to Remember Length of the arc of angle θ = (θ/360) 2πr Unless stated otherwise, use π =22/7. Question 1 Find the area of a sector of a circle with radius 6 cm
AREA RELATED TO CIRCLES
 CHAPTER 11 AREA RELATED TO CIRCLES (A) Main Concepts and Results Perimeters and areas of simple closed figures. Circumference and area of a circle. Area of a circular path (i.e., ring). Sector of a circle
CHAPTER 11 AREA RELATED TO CIRCLES (A) Main Concepts and Results Perimeters and areas of simple closed figures. Circumference and area of a circle. Area of a circular path (i.e., ring). Sector of a circle
AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES
 HPTER 1 Points to Remember : RES RELTE T IRLES 1. circle is a collection of points which moves in a plane in such a way that its distance from a fixed point always remains the same. The fixed point is
HPTER 1 Points to Remember : RES RELTE T IRLES 1. circle is a collection of points which moves in a plane in such a way that its distance from a fixed point always remains the same. The fixed point is
CIRCLES MODULE - 3 OBJECTIVES EXPECTED BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE. Circles. Geometry. Notes
 Circles MODULE - 3 15 CIRCLES You are already familiar with geometrical figures such as a line segment, an angle, a triangle, a quadrilateral and a circle. Common examples of a circle are a wheel, a bangle,
Circles MODULE - 3 15 CIRCLES You are already familiar with geometrical figures such as a line segment, an angle, a triangle, a quadrilateral and a circle. Common examples of a circle are a wheel, a bangle,
ieducation.com Tangents given as follows. the circle. contact. There are c) Secant:
 h Tangents and Secants to the Circle A Line and a circle: let us consider a circle and line say AB. There can be three possibilities given as follows. a) Non-intersecting line: The line AB and the circle
h Tangents and Secants to the Circle A Line and a circle: let us consider a circle and line say AB. There can be three possibilities given as follows. a) Non-intersecting line: The line AB and the circle
MINIMUM LEVEL LEARNING MATERIAL
 MATHEMATICS MINIMUM LEVEL LEARNING MATERIAL for CLASS X 018 19 Prepared by M. S. KUMARSWAMY, TGT(MATHS) M. Sc. Gold Medallist (Elect.), B. Ed. Kendriya Vidyalaya gachibowli DEDICATED TO MY FATHER LATE
MATHEMATICS MINIMUM LEVEL LEARNING MATERIAL for CLASS X 018 19 Prepared by M. S. KUMARSWAMY, TGT(MATHS) M. Sc. Gold Medallist (Elect.), B. Ed. Kendriya Vidyalaya gachibowli DEDICATED TO MY FATHER LATE
COMMON UNITS OF PERIMITER ARE METRE
 MENSURATION BASIC CONCEPTS: 1.1 PERIMETERS AND AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES: PERIMETER AND AREA The perimeter of a plane figure is the total length of its boundary. The area of a plane figure is the amount of
MENSURATION BASIC CONCEPTS: 1.1 PERIMETERS AND AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES: PERIMETER AND AREA The perimeter of a plane figure is the total length of its boundary. The area of a plane figure is the amount of
CIRCULAR MEASURE - SECTORS AND SEGMENTS
 Mathematics Revision Guides Circular Measure Page 1 of M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier CIRCULAR MEASURE - SECTORS AND SEGMENTS Version: 3. Date: -10-014 Mathematics
Mathematics Revision Guides Circular Measure Page 1 of M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier CIRCULAR MEASURE - SECTORS AND SEGMENTS Version: 3. Date: -10-014 Mathematics
Downloaded from AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES
 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES #,&#,&#!#'&*(#6$&#)(,,#&()!,&&!!&###&#%#&#&.,.&#$#*&.*- 1. In the adjoining figure ABC right angled triangle right angled at A. Semi circles are drawn on the sides of the triangle
AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES #,&#,&#!#'&*(#6$&#)(,,#&()!,&&!!&###&#%#&#&.,.&#$#*&.*- 1. In the adjoining figure ABC right angled triangle right angled at A. Semi circles are drawn on the sides of the triangle
CIRCLE PROPERTIES M.K. HOME TUITION. Mathematics Revision Guides. Level: GCSE Foundation Tier
 Mathematics Revision Guides Circle Properties Page 1 of 5 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier CIRCLE PROPERTIES Version:.1 Date: 8-10-01 Mathematics Revision Guides
Mathematics Revision Guides Circle Properties Page 1 of 5 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier CIRCLE PROPERTIES Version:.1 Date: 8-10-01 Mathematics Revision Guides
CHAPTER 11 AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES
 CHAPTER 11 AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES EXERCISE 45, Page 106 1. Find the angles p and q in diagram (a) below. p = 180-75 = 105 (interior opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal) q = 180-105 - 40 = 35.
CHAPTER 11 AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES EXERCISE 45, Page 106 1. Find the angles p and q in diagram (a) below. p = 180-75 = 105 (interior opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal) q = 180-105 - 40 = 35.
CHAPTER 10 CIRCLES Introduction
 168 MATHEMATICS CIRCLES CHAPTER 10 10.1 Introduction You may have come across many objects in daily life, which are round in shape, such as wheels of a vehicle, bangles, dials of many clocks, coins of
168 MATHEMATICS CIRCLES CHAPTER 10 10.1 Introduction You may have come across many objects in daily life, which are round in shape, such as wheels of a vehicle, bangles, dials of many clocks, coins of
Chapter (Circle) * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in
 Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Core Mathematics 2 Radian Measures
 Core Mathematics 2 Radian Measures Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Radian Measures 1 Radian Measures Radian measure, including use for arc length and area of sector.
Core Mathematics 2 Radian Measures Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Radian Measures 1 Radian Measures Radian measure, including use for arc length and area of sector.
CBSE CLASS X MATH -SOLUTION Therefore, 0.6, 0.25 and 0.3 are greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1.
 CBSE CLASS X MATH -SOLUTION 011 Q1 The probability of an event is always greater than or equal to zero and less than or equal to one. Here, 3 5 = 0.6 5% = 5 100 = 0.5 Therefore, 0.6, 0.5 and 0.3 are greater
CBSE CLASS X MATH -SOLUTION 011 Q1 The probability of an event is always greater than or equal to zero and less than or equal to one. Here, 3 5 = 0.6 5% = 5 100 = 0.5 Therefore, 0.6, 0.5 and 0.3 are greater
10. Circles. Q 5 O is the centre of a circle of radius 5 cm. OP AB and OQ CD, AB CD, AB = 6 cm and CD = 8 cm. Determine PQ. Marks (2) Marks (2)
 10. Circles Q 1 True or False: It is possible to draw two circles passing through three given non-collinear points. Mark (1) Q 2 State the following statement as true or false. Give reasons also.the perpendicular
10. Circles Q 1 True or False: It is possible to draw two circles passing through three given non-collinear points. Mark (1) Q 2 State the following statement as true or false. Give reasons also.the perpendicular
MATHEMATICS. MINIMUM LEVEL MATERIAL for CLASS X Project Planned By Honourable Shri D. Manivannan Deputy Commissioner, KVS RO Hyderabad
 MATHEMATICS MINIMUM LEVEL MATERIAL for CLASS X 017 18 Project Planned By Honourable Shri D. Manivannan Deputy Commissioner, KVS RO Hyderabad Prepared by M. S. KUMARSWAMY, TGT(MATHS) M. Sc. Gold Medallist
MATHEMATICS MINIMUM LEVEL MATERIAL for CLASS X 017 18 Project Planned By Honourable Shri D. Manivannan Deputy Commissioner, KVS RO Hyderabad Prepared by M. S. KUMARSWAMY, TGT(MATHS) M. Sc. Gold Medallist
It is known that the length of the tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is equal.
 CBSE -MATHS-SET 1-2014 Q1. The first three terms of an AP are 3y-1, 3y+5 and 5y+1, respectively. We need to find the value of y. We know that if a, b and c are in AP, then: b a = c b 2b = a + c 2 (3y+5)
CBSE -MATHS-SET 1-2014 Q1. The first three terms of an AP are 3y-1, 3y+5 and 5y+1, respectively. We need to find the value of y. We know that if a, b and c are in AP, then: b a = c b 2b = a + c 2 (3y+5)
Possible C2 questions from past papers P1 P3
 Possible C2 questions from past papers P1 P3 Source of the original question is given in brackets, e.g. [P1 January 2001 Question 1]; a question which has been edited is indicated with an asterisk, e.g.
Possible C2 questions from past papers P1 P3 Source of the original question is given in brackets, e.g. [P1 January 2001 Question 1]; a question which has been edited is indicated with an asterisk, e.g.
Full Question Paper Maths, X Class
 Full Question Paper Maths, X Class Time: 3 Hrs MM: 80 Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The questions paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A,B,C and D. Section A comprises
Full Question Paper Maths, X Class Time: 3 Hrs MM: 80 Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The questions paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A,B,C and D. Section A comprises
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER Summative Assessment II Class-X ( ) Mathematics. Time Allowed: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 90
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER Summative Assessment II Class-X (2016 17) Mathematics Time Allowed: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of31
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER Summative Assessment II Class-X (2016 17) Mathematics Time Allowed: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of31
CBSE CLASS X MATH
 CBSE CLASS X MATH - 2011 Q.1) Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event? A. 1.5 B. 3 5 C. 25% D. 0.3 Q.2 The mid-point of segment AB is the point P (0, 4). If the Coordinates of B are
CBSE CLASS X MATH - 2011 Q.1) Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event? A. 1.5 B. 3 5 C. 25% D. 0.3 Q.2 The mid-point of segment AB is the point P (0, 4). If the Coordinates of B are
MATHEMATICS. IMPORTANT FORMULAE AND CONCEPTS for. Summative Assessment -II. Revision CLASS X Prepared by
 MATHEMATICS IMPORTANT FORMULAE AND CONCEPTS for Summative Assessment -II Revision CLASS X 06 7 Prepared by M. S. KUMARSWAMY, TGT(MATHS) M. Sc. Gold Medallist (Elect.), B. Ed. Kendriya Vidyalaya GaCHiBOWli
MATHEMATICS IMPORTANT FORMULAE AND CONCEPTS for Summative Assessment -II Revision CLASS X 06 7 Prepared by M. S. KUMARSWAMY, TGT(MATHS) M. Sc. Gold Medallist (Elect.), B. Ed. Kendriya Vidyalaya GaCHiBOWli
CIRCLES, CHORDS AND TANGENTS
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE CIRCLES, CHORDS AND TANGENTS KCSE 1989 2012 Form 3 Mathematics Working Space 1. 1989 Q24 P2 The figure below represents the cross section of a metal bar. C A 4cm M 4cm B The
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE CIRCLES, CHORDS AND TANGENTS KCSE 1989 2012 Form 3 Mathematics Working Space 1. 1989 Q24 P2 The figure below represents the cross section of a metal bar. C A 4cm M 4cm B The
Grade 9 Geometry-Overall
 ID : au-9-geometry-overall [1] Grade 9 Geometry-Overall For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) A chord of a circle is equal to its radius. Find the angle subtended by
ID : au-9-geometry-overall [1] Grade 9 Geometry-Overall For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) A chord of a circle is equal to its radius. Find the angle subtended by
UNIT 13 Areas: CSEC Revision Test
 Area of square 64 cm (4 marks) MEP Jamaica: STRAND E : 1. The shaded square has sides of length 1 cm. It is enlarged a number of times as shown. Complete the table. Length of side of square 1 cm cm 3 cm
Area of square 64 cm (4 marks) MEP Jamaica: STRAND E : 1. The shaded square has sides of length 1 cm. It is enlarged a number of times as shown. Complete the table. Length of side of square 1 cm cm 3 cm
2012 GCSE Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved
 2012 GCSE Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved www.gcsemathstutor.com This book is under copyright to GCSE Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents angles
2012 GCSE Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved www.gcsemathstutor.com This book is under copyright to GCSE Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents angles
Introduction Circle Some terms related with a circle
 141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
7. Find the value of If (a+1) and (a-1) are the factors of p(a)= a 3 x+2a 2 +2a - y, find x and y
 AJANTA PUBLIC SCHOOL ASSIGNMENT (MATHS) SESSION 2018-19 CLASS - IX 1. Are the following Statements are True or False, also give reasons? (i) zero is a rational number (ii) Zero is natural number (iii)
AJANTA PUBLIC SCHOOL ASSIGNMENT (MATHS) SESSION 2018-19 CLASS - IX 1. Are the following Statements are True or False, also give reasons? (i) zero is a rational number (ii) Zero is natural number (iii)
Geometry Honors Homework
 Geometry Honors Homework pg. 1 12-1 Practice Form G Tangent Lines Algebra Assume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. 2. 3. The circle
Geometry Honors Homework pg. 1 12-1 Practice Form G Tangent Lines Algebra Assume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. 2. 3. The circle
Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles
 Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles 1. Joe had a bet with Mr. Federer saying that if Federer can solve the following problem in one minute, Joe would be his slave for a whole month. The problem
Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles 1. Joe had a bet with Mr. Federer saying that if Federer can solve the following problem in one minute, Joe would be his slave for a whole month. The problem
21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle.
 21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle. 22. Prove that If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, then
21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle. 22. Prove that If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, then
Grade 9 Circles. Answer the questions. For more such worksheets visit
 ID : ae-9-circles [1] Grade 9 Circles For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Two circles with centres O and O intersect at two points A and B. A line PQ is drawn parallel
ID : ae-9-circles [1] Grade 9 Circles For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Two circles with centres O and O intersect at two points A and B. A line PQ is drawn parallel
I.G.C.S.E. Area. You can access the solutions from the end of each question
 I.G.C.S.E. Area Index: Please click on the question number you want Question Question Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 Question 9 You can access the solutions from the
I.G.C.S.E. Area Index: Please click on the question number you want Question Question Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 Question 9 You can access the solutions from the
Class X Delhi Math Set-3 Section A
 Class X Delhi Math Set-3 Section A 1. The angle of depression of a car, standing on the ground, from the top of a 75 m high tower, is 30. The distance of the car from the base of the tower (in m.) is:
Class X Delhi Math Set-3 Section A 1. The angle of depression of a car, standing on the ground, from the top of a 75 m high tower, is 30. The distance of the car from the base of the tower (in m.) is:
CHAPTER 1 NUMBER SYSTEMS. 1.1 Introduction
 N UMBER S YSTEMS NUMBER SYSTEMS CHAPTER. Introduction In your earlier classes, you have learnt about the number line and how to represent various types of numbers on it (see Fig..). Fig.. : The number
N UMBER S YSTEMS NUMBER SYSTEMS CHAPTER. Introduction In your earlier classes, you have learnt about the number line and how to represent various types of numbers on it (see Fig..). Fig.. : The number
Lesson 2B: Thales Theorem
 Lesson 2B: Thales Theorem Learning Targets o I can identify radius, diameter, chords, central circles, inscribed circles and semicircles o I can explain that an ABC is a right triangle, then A, B, and
Lesson 2B: Thales Theorem Learning Targets o I can identify radius, diameter, chords, central circles, inscribed circles and semicircles o I can explain that an ABC is a right triangle, then A, B, and
(D) (A) Q.3 To which of the following circles, the line y x + 3 = 0 is normal at the point ? 2 (A) 2
 CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
Grade 9 Circles. Answer t he quest ions. For more such worksheets visit
 ID : th-9-circles [1] Grade 9 Circles For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral such that AB is a diameter of the circle circumscribing it
ID : th-9-circles [1] Grade 9 Circles For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral such that AB is a diameter of the circle circumscribing it
If x = 180 then the arc subtended by x is a semicircle which we know has length πr. Now we argue that:
 Arclength Consider a circle of radius r and an angle of x degrees as shown in the figure below. The segment of the circle opposite the angle x is called the arc subtended by x. We need a formula for its
Arclength Consider a circle of radius r and an angle of x degrees as shown in the figure below. The segment of the circle opposite the angle x is called the arc subtended by x. We need a formula for its
1 / 22
 CBSE-XII-017 EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Paper & Solution Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 90 General Instructions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 31 questions divided into
CBSE-XII-017 EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Paper & Solution Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 90 General Instructions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 31 questions divided into
 Fill in the blanks Chapter 10 Circles Exercise 10.1 Question 1: (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle. (exterior/ interior) (ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater
Fill in the blanks Chapter 10 Circles Exercise 10.1 Question 1: (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle. (exterior/ interior) (ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 1. The diagram above shows the sector OA of a circle with centre O, radius 9 cm and angle 0.7 radians. Find the length of the arc A. Find the area of the sector OA. The line AC shown in the diagram above
1. The diagram above shows the sector OA of a circle with centre O, radius 9 cm and angle 0.7 radians. Find the length of the arc A. Find the area of the sector OA. The line AC shown in the diagram above
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AS level Mathematics Core mathematics 2 - C2 2015-2016 Name: Page C2 workbook contents Algebra Differentiation Integration Coordinate Geometry Logarithms Geometric series Series
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AS level Mathematics Core mathematics 2 - C2 2015-2016 Name: Page C2 workbook contents Algebra Differentiation Integration Coordinate Geometry Logarithms Geometric series Series
Page 1 of 15. Website: Mobile:
 Exercise 10.2 Question 1: From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of Q from the centre is 25 cm. The radius of the circle is (A) 7 cm (B) 12 cm (C) 15 cm (D) 24.5
Exercise 10.2 Question 1: From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of Q from the centre is 25 cm. The radius of the circle is (A) 7 cm (B) 12 cm (C) 15 cm (D) 24.5
"Full Coverage": Non-Right Angled Triangles
 "Full Coverage": Non-Right Angled Triangles This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated
"Full Coverage": Non-Right Angled Triangles This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
x n+1 = ( x n + ) converges, then it converges to α. [2]
![x n+1 = ( x n + ) converges, then it converges to α. [2] x n+1 = ( x n + ) converges, then it converges to α. [2]](/thumbs/92/110299841.jpg) 1 A Level - Mathematics P 3 ITERATION ( With references and answers) [ Numerical Solution of Equation] Q1. The equation x 3 - x 2 6 = 0 has one real root, denoted by α. i) Find by calculation the pair
1 A Level - Mathematics P 3 ITERATION ( With references and answers) [ Numerical Solution of Equation] Q1. The equation x 3 - x 2 6 = 0 has one real root, denoted by α. i) Find by calculation the pair
Trigonometry. Sin θ Cos θ Tan θ Cot θ Sec θ Cosec θ. Sin = = cos = = tan = = cosec = sec = 1. cot = sin. cos. tan
 Trigonometry Trigonometry is one of the most interesting chapters of Quantitative Aptitude section. Basically, it is a part of SSC and other bank exams syllabus. We will tell you the easy method to learn
Trigonometry Trigonometry is one of the most interesting chapters of Quantitative Aptitude section. Basically, it is a part of SSC and other bank exams syllabus. We will tell you the easy method to learn
Unit Circle: The unit circle has radius 1 unit and is centred at the origin on the Cartesian plane. POA
 The Unit Circle Unit Circle: The unit circle has radius 1 unit and is centred at the origin on the Cartesian plane THE EQUATION OF THE UNIT CIRCLE Consider any point P on the unit circle with coordinates
The Unit Circle Unit Circle: The unit circle has radius 1 unit and is centred at the origin on the Cartesian plane THE EQUATION OF THE UNIT CIRCLE Consider any point P on the unit circle with coordinates
CHAPTER 1 BASIC ARITHMETIC
 CHAPTER 1 BASIC ARITHMETIC EXERCISE 1, Page 4 1. Evaluate 67 kg 8 kg + 4 kg without using a calculator 67 kg 8 kg + 4 kg = 67 kg + 4 kg 8 kg = 101 kg 8 kg = 19 kg. Evaluate 851 mm 7 mm without using a
CHAPTER 1 BASIC ARITHMETIC EXERCISE 1, Page 4 1. Evaluate 67 kg 8 kg + 4 kg without using a calculator 67 kg 8 kg + 4 kg = 67 kg + 4 kg 8 kg = 101 kg 8 kg = 19 kg. Evaluate 851 mm 7 mm without using a
QUANTITATIVE APTITUDE
 SBI Probationery Officers QUANTITATIVE APTITUDE Mensuration (Plane Figures) Mensuration is one of the branches of mathematics. This means measurement. It is being done in our life in many situations. Here,
SBI Probationery Officers QUANTITATIVE APTITUDE Mensuration (Plane Figures) Mensuration is one of the branches of mathematics. This means measurement. It is being done in our life in many situations. Here,
(b) Show that sin 2 =. 9 (c) Find the exact value of cos 2. (Total 6 marks)
 IB SL Trig Review. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate the size of PQˆ R ; the area of triangle PQR.. The following diagram shows a triangle ABC, where AĈB is 90, AB =, AC
IB SL Trig Review. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate the size of PQˆ R ; the area of triangle PQR.. The following diagram shows a triangle ABC, where AĈB is 90, AB =, AC
10.5 Areas of Circles and Sectors
 10.5. Areas of Circles and Sectors www.ck12.org 10.5 Areas of Circles and Sectors Learning Objectives Find the area of circles, sectors, and segments. Review Queue Find the area of the shaded region in
10.5. Areas of Circles and Sectors www.ck12.org 10.5 Areas of Circles and Sectors Learning Objectives Find the area of circles, sectors, and segments. Review Queue Find the area of the shaded region in
1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle.
 Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
e x for x 0. Find the coordinates of the point of inflexion and justify that it is a point of inflexion. (Total 7 marks)
 Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Math 9 Chapter 8 Practice Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Math 9 Chapter 8 Practice Test Short Answer 1. O is the centre of this circle and point Q is a point of tangency. Determine the value of t. If necessary, give your answer to the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Math 9 Chapter 8 Practice Test Short Answer 1. O is the centre of this circle and point Q is a point of tangency. Determine the value of t. If necessary, give your answer to the
Total number of printed pages : MATHEMATICS
 Total number of printed pages : 6 Total marks : 80 016 MATHEMATICS NB-T/M Time : 3 hours General Instructions: i) Approximately 15 minutes is allotted to read the question paper and revise the answers.
Total number of printed pages : 6 Total marks : 80 016 MATHEMATICS NB-T/M Time : 3 hours General Instructions: i) Approximately 15 minutes is allotted to read the question paper and revise the answers.
3. AD is a diameter of a circle and AB is a chord. If AD = 34 cm, AB = 30 cm, the distance of AB from the centre of the circle is:
 Solved Paper 2 Class 9 th, Mathematics, SA 2 Time: 3hours Max. Marks 90 General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Draw neat labeled diagram wherever necessary to explain your answer. 3.
Solved Paper 2 Class 9 th, Mathematics, SA 2 Time: 3hours Max. Marks 90 General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Draw neat labeled diagram wherever necessary to explain your answer. 3.
MATHEMATICS. MINIMUM LEVEL MATERIAL for CLASS X
 MATHEMATICS MINIMUM LEVEL MATERIAL for CLASS X 07 8 Project Planned By Honourable Shri D. Manivannan Deputy Commissioner,KVS RO Hyderabad & Guided By Honourable Shri E. Krishna Murthy Principal, KV Gachibowli,
MATHEMATICS MINIMUM LEVEL MATERIAL for CLASS X 07 8 Project Planned By Honourable Shri D. Manivannan Deputy Commissioner,KVS RO Hyderabad & Guided By Honourable Shri E. Krishna Murthy Principal, KV Gachibowli,
Objective Mathematics
 . A tangent to the ellipse is intersected by a b the tangents at the etremities of the major ais at 'P' and 'Q' circle on PQ as diameter always passes through : (a) one fied point two fied points (c) four
. A tangent to the ellipse is intersected by a b the tangents at the etremities of the major ais at 'P' and 'Q' circle on PQ as diameter always passes through : (a) one fied point two fied points (c) four
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. accurately drawn. x + 2. x + 4. x + 2
 1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
Sample Question Paper Mathematics First Term (SA - I) Class IX. Time: 3 to 3 ½ hours
 Sample Question Paper Mathematics First Term (SA - I) Class IX Time: 3 to 3 ½ hours M.M.:90 General Instructions (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided
Sample Question Paper Mathematics First Term (SA - I) Class IX Time: 3 to 3 ½ hours M.M.:90 General Instructions (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided
Solutionbank C2 Edexcel Modular Mathematics for AS and A-Level
 file://c:\users\buba\kaz\ouba\c_rev_a_.html Eercise A, Question Epand and simplify ( ) 5. ( ) 5 = + 5 ( ) + 0 ( ) + 0 ( ) + 5 ( ) + ( ) 5 = 5 + 0 0 + 5 5 Compare ( + ) n with ( ) n. Replace n by 5 and
file://c:\users\buba\kaz\ouba\c_rev_a_.html Eercise A, Question Epand and simplify ( ) 5. ( ) 5 = + 5 ( ) + 0 ( ) + 0 ( ) + 5 ( ) + ( ) 5 = 5 + 0 0 + 5 5 Compare ( + ) n with ( ) n. Replace n by 5 and
chapter 1 vector geometry solutions V Consider the parallelogram shown alongside. Which of the following statements are true?
 chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (10.1)
 Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (10.1) Question 1: Fill in the blanks (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle. (exterior/interior) (ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater
Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (10.1) Question 1: Fill in the blanks (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle. (exterior/interior) (ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater
UNIT 6. BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle. The Circle
 UNIT 6 BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle The Circle 1 Questions How are perimeter and area related? How are the areas of polygons and circles
UNIT 6 BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle The Circle 1 Questions How are perimeter and area related? How are the areas of polygons and circles
Ch 10 Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the diagram shown, the measure of ADC is a. 55 b. 70 c. 90 d. 180 2. What is the measure
Ch 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the diagram shown, the measure of ADC is a. 55 b. 70 c. 90 d. 180 2. What is the measure
SAMPLE PAPER 3 (SA II) Mathematics CLASS : X. Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90
 1 SAMPLE PAPER 3 (SA II) MRS.KIRAN WANGNOO Mathematics CLASS : X Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90 General Instruction:- 1. All questions are Compulsory. 1. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided
1 SAMPLE PAPER 3 (SA II) MRS.KIRAN WANGNOO Mathematics CLASS : X Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90 General Instruction:- 1. All questions are Compulsory. 1. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided
CDS-I 2019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C)
 1 CDS-I 019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C) Direction: Consider the following for the next three (03) items : A cube is inscribed in a sphere. A right circular cylinder is within the cube touching all the
1 CDS-I 019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C) Direction: Consider the following for the next three (03) items : A cube is inscribed in a sphere. A right circular cylinder is within the cube touching all the
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 09 Class-X ( ) Mathematics
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 09 Class-X (2017 18) Mathematics Time allowed: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 09 Class-X (2017 18) Mathematics Time allowed: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided
PRACTICE QUESTIONS CLASS IX: CHAPTER 4 LINEAR EQUATION IN TWO VARIABLES
 PRACTICE QUESTIONS CLASS IX: CHAPTER 4 LINEAR EQUATION IN TWO VARIABLES 1. Find the value of k, if x =, y = 1 is a solution of the equation x + 3y = k.. Find the points where the graph of the equation
PRACTICE QUESTIONS CLASS IX: CHAPTER 4 LINEAR EQUATION IN TWO VARIABLES 1. Find the value of k, if x =, y = 1 is a solution of the equation x + 3y = k.. Find the points where the graph of the equation
Class IX Chapter 1 Number Sustems Maths
 Class IX Chapter 1 Number Sustems Maths Exercise 1.1 Question Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form 0? and q, where p and q are integers Yes. Zero is a rational number as it can be represented
Class IX Chapter 1 Number Sustems Maths Exercise 1.1 Question Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form 0? and q, where p and q are integers Yes. Zero is a rational number as it can be represented
MATHEMATICS STANDARD IX TAMILNADU TEXTBOOK CORPORATION COLLEGE ROAD, CHENNAI
 MATHEMATICS STANDARD IX Untouchability is a sin Untouchability is a crime Untouchability is inhuman TAMILNADU TEXTBOOK CORPORATION COLLEGE ROAD, CHENNAI 600 006. Government of Tamilnadu First Edition 00
MATHEMATICS STANDARD IX Untouchability is a sin Untouchability is a crime Untouchability is inhuman TAMILNADU TEXTBOOK CORPORATION COLLEGE ROAD, CHENNAI 600 006. Government of Tamilnadu First Edition 00
Real-World Problems: Circles
 11.3 Real-World Problems: Circles Lesson Objectives Solve real-world problems involving area and circumference of circles. Solve real-world problems involving semicircles, quadrants, and composite figures.
11.3 Real-World Problems: Circles Lesson Objectives Solve real-world problems involving area and circumference of circles. Solve real-world problems involving semicircles, quadrants, and composite figures.
221 MATH REFRESHER session 3 SAT2015_P06.indd 221 4/23/14 11:39 AM
 Math Refresher Session 3 1 Area, Perimeter, and Volume Problems Area, Perimeter, and Volume 301. Formula Problems. Here, you are given certain data about one or more geometric figures, and you are asked
Math Refresher Session 3 1 Area, Perimeter, and Volume Problems Area, Perimeter, and Volume 301. Formula Problems. Here, you are given certain data about one or more geometric figures, and you are asked
Example 1 Give the degree measure of the angle shown on the circle.
 Section 5. Angles 307 Section 5. Angles Because many applications involving circles also involve q rotation of the circle, it is natural to introduce a measure for the rotation, or angle, between two rays
Section 5. Angles 307 Section 5. Angles Because many applications involving circles also involve q rotation of the circle, it is natural to introduce a measure for the rotation, or angle, between two rays
(A) 50 (B) 40 (C) 90 (D) 75. Circles. Circles <1M> 1.It is possible to draw a circle which passes through three collinear points (T/F)
 Circles 1.It is possible to draw a circle which passes through three collinear points (T/F) 2.The perpendicular bisector of two chords intersect at centre of circle (T/F) 3.If two arcs of a circle
Circles 1.It is possible to draw a circle which passes through three collinear points (T/F) 2.The perpendicular bisector of two chords intersect at centre of circle (T/F) 3.If two arcs of a circle
Summative Assesment-II TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER II MATHEMATICS CLASS X
 Summative Assesment-II TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER II MATHEMATICS CLASS X MM 80 TIME : 3-3 / hrs. GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:. All questions are compulsory.. The question paper is divided into four sections Section
Summative Assesment-II TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER II MATHEMATICS CLASS X MM 80 TIME : 3-3 / hrs. GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:. All questions are compulsory.. The question paper is divided into four sections Section
EXERCISE 10.1 EXERCISE 10.2
 NCERT Class 9 Solved Questions for Chapter: Circle 10 NCERT 10 Class CIRCLES 9 Solved Questions for Chapter: Circle EXERCISE 10.1 Q.1. Fill in the blanks : (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle.
NCERT Class 9 Solved Questions for Chapter: Circle 10 NCERT 10 Class CIRCLES 9 Solved Questions for Chapter: Circle EXERCISE 10.1 Q.1. Fill in the blanks : (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle.
No Calc. 1 p (seen anywhere) 1 p. 1 p. No Calc. (b) Find an expression for cos 140. (c) Find an expression for tan (a) (i) sin 140 = p A1 N1
 IBSL /4 IB REVIEW: Trig KEY (0points). Let p = sin 40 and q = cos 0. Give your answers to the following in terms of p and/or q. (a) Write down an expression for (i) sin 40; (ii) cos 70. (b) Find an expression
IBSL /4 IB REVIEW: Trig KEY (0points). Let p = sin 40 and q = cos 0. Give your answers to the following in terms of p and/or q. (a) Write down an expression for (i) sin 40; (ii) cos 70. (b) Find an expression
Free GK Alerts- JOIN OnlineGK to AREA FUNDEMENTAL CONCEPTS. 2.Sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
 Free GK Alerts- JOIN OnlineGK to 9870807070 24.AREA FUNDEMENTAL CONCEPTS I.RESULTS ON TRIANGLES: 1.Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. 2.Sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the
Free GK Alerts- JOIN OnlineGK to 9870807070 24.AREA FUNDEMENTAL CONCEPTS I.RESULTS ON TRIANGLES: 1.Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. 2.Sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the
WARM UP. Sunday, November 16, 2014
 WARM UP Sunday, November 16, 2014 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Use properties of circles to derive the formula for sector area. Determine arc length and arc measure for given central and inscribed angle
WARM UP Sunday, November 16, 2014 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Use properties of circles to derive the formula for sector area. Determine arc length and arc measure for given central and inscribed angle
CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Mathematics
 CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Mathematics Board Question Paper 2014 Set 2 Time: 3 hrs Max. Marks: 90 Note: Please check that this question paper contains 15 printed pages. Code number given
CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Mathematics Board Question Paper 2014 Set 2 Time: 3 hrs Max. Marks: 90 Note: Please check that this question paper contains 15 printed pages. Code number given
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE
 QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
G.C.B.5: Arc Length 1
 Regents Exam Questions G.C.B.5: Arc Length www.jmap.org Name: G.C.B.5: Arc Length The diagram below shows circle O with radii OA and OB. The measure of angle AOB is 0, and the length of a radius is inches.
Regents Exam Questions G.C.B.5: Arc Length www.jmap.org Name: G.C.B.5: Arc Length The diagram below shows circle O with radii OA and OB. The measure of angle AOB is 0, and the length of a radius is inches.
Exercise 10.1 Question 1: Fill in the blanks (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle. (exterior/ interior)
 Exercise 10.1 Question 1: Fill in the blanks (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle. (exterior/ interior) (ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater than its radius lies
Exercise 10.1 Question 1: Fill in the blanks (i) The centre of a circle lies in of the circle. (exterior/ interior) (ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater than its radius lies
DESIGN OF THE QUESTION PAPER Mathematics Class X
 SET-I DESIGN OF THE QUESTION PAPER Mathematics Class X Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 80 Weightage and the distribution of marks over different dimensions of the question shall be as follows: (A) Weightage
SET-I DESIGN OF THE QUESTION PAPER Mathematics Class X Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 80 Weightage and the distribution of marks over different dimensions of the question shall be as follows: (A) Weightage
AREAS OF PARALLELOGRAMS AND TRIANGLES
 AREAS OF PARALLELOGRAMS AND TRIANGLES Main Concepts and Results: The area of a closed plane figure is the measure of the region inside the figure: Fig.1 The shaded parts (Fig.1) represent the regions whose
AREAS OF PARALLELOGRAMS AND TRIANGLES Main Concepts and Results: The area of a closed plane figure is the measure of the region inside the figure: Fig.1 The shaded parts (Fig.1) represent the regions whose
Free Sample set of investigative questions
 Free Sample set of investigative questions SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS: Year Contents Unit Topic : Combinatorics Task : Extended investigation: Relationships in Pascal s Triangle 3 Task : In-class investigation:
Free Sample set of investigative questions SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS: Year Contents Unit Topic : Combinatorics Task : Extended investigation: Relationships in Pascal s Triangle 3 Task : In-class investigation:
MATHEMATICS ( CANDIDATES WITH PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) ( CANDIDATES WITHOUT PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT )
 Total No. of Printed Pages 6 X/5/M 0 5 MATHEMATICS ( CANDIDATES WITH PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) Full Marks : 80 Pass Marks : 4 ( CANDIDATES WITHOUT PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) Full Marks : 00
Total No. of Printed Pages 6 X/5/M 0 5 MATHEMATICS ( CANDIDATES WITH PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) Full Marks : 80 Pass Marks : 4 ( CANDIDATES WITHOUT PRACTICALS/INTERNAL ASSESSMENT ) Full Marks : 00
ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Maths (2016) Solution
 ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Maths (016) Solution SECTION A 1. (a) Let f(x) x x kx 5 Using remainder theorem, f() 7 () () k() 5 7 (8) (4) k() 5 7 16 1 k 5 7 k 16 1 5 7 k 6 k 1 (b) A = 9A + MI A 9A mi...
ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Maths (016) Solution SECTION A 1. (a) Let f(x) x x kx 5 Using remainder theorem, f() 7 () () k() 5 7 (8) (4) k() 5 7 16 1 k 5 7 k 16 1 5 7 k 6 k 1 (b) A = 9A + MI A 9A mi...
Question 1: Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p, where p and q are integers and q 0?
 Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (.) Question : Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p, where p and q are integers and q 0? q Solution : Consider the definition of a rational number.
Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (.) Question : Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p, where p and q are integers and q 0? q Solution : Consider the definition of a rational number.
CBSE CLASS-10 MARCH 2018
 CBSE CLASS-10 MARCH 2018 MATHEMATICS Time : 2.30 hrs QUESTION & ANSWER Marks : 80 General Instructions : i. All questions are compulsory ii. This question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
CBSE CLASS-10 MARCH 2018 MATHEMATICS Time : 2.30 hrs QUESTION & ANSWER Marks : 80 General Instructions : i. All questions are compulsory ii. This question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
Trans Web Educational Services Pvt. Ltd B 147,1st Floor, Sec-6, NOIDA, UP
 Solved Examples Example 1: Find the equation of the circle circumscribing the triangle formed by the lines x + y = 6, 2x + y = 4, x + 2y = 5. Method 1. Consider the equation (x + y 6) (2x + y 4) + λ 1
Solved Examples Example 1: Find the equation of the circle circumscribing the triangle formed by the lines x + y = 6, 2x + y = 4, x + 2y = 5. Method 1. Consider the equation (x + y 6) (2x + y 4) + λ 1
April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
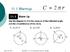 11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
Circles Unit Test. Secondary Math II
 Circles Unit Test Secondary Math II 1. Which pair of circles described are congruent to each other? Circle M has a radius of 6 m; Circle N has a diameter of 10 m. Circle J has a circumference of in; Circle
Circles Unit Test Secondary Math II 1. Which pair of circles described are congruent to each other? Circle M has a radius of 6 m; Circle N has a diameter of 10 m. Circle J has a circumference of in; Circle
Part (1) Second : Trigonometry. Tan
 Part (1) Second : Trigonometry (1) Complete the following table : The angle Ratio 42 12 \ Sin 0.3214 Cas 0.5321 Tan 2.0625 (2) Complete the following : 1) 46 36 \ 24 \\ =. In degrees. 2) 44.125 = in degrees,
Part (1) Second : Trigonometry (1) Complete the following table : The angle Ratio 42 12 \ Sin 0.3214 Cas 0.5321 Tan 2.0625 (2) Complete the following : 1) 46 36 \ 24 \\ =. In degrees. 2) 44.125 = in degrees,
