Supersingular Isogeny Key Encapsulation (SIKE)
|
|
|
- Laura Preston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supersingular Isogeny Key Encapsulation (SIKE) Reza Azarderakhsh Matthew Campagna Craig Costello Luca De Feo Basil Hess David Jao Brian Koziel Brian LaMacchia Patrick Longa Michael Naehrig Joost Renes Vladimir Soukharev Digital Security Group, Radboud University, Nijmegen 1 February 2018
2 Introduction (generic intro...) 1 / 1
3 A graph-based protocol Alice Bob 2 / 1
4 A graph-based protocol Alice Bob 2 / 1
5 A graph-based protocol 24 Alice 24 Bob 2 / 1
6 A graph-based protocol 24 Alice 24 Bob 2 / 1
7 A graph-based protocol 24 Alice Bob 2 / 1
8 A graph-based protocol 24 Alice Bob 2 / 1
9 A graph-based protocol Alice Bob 66 2 / 1
10 A graph-based protocol Alice Bob 66 2 / 1
11 A graph-based protocol Alice Bob / 1
12 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies 3 / 1
13 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies E 24 E 41 E 66 E 17 E 48 E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
14 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies l-isogeny φ R E 24 E 41 E 66 E 17 E 48 E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
15 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies l-isogeny φ R E 66 {E 24, P 24, Q 24 } E 41 E 17 E 48 E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
16 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies l-isogeny φ R E 66 {E 24, P 24, Q 24 } E 41 E 17 E 48 E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
17 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies l-isogeny φ R E 66 {E 24, P 24, Q 24 } E 41 E 17 E 48 E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
18 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies l-isogeny φ R {E 66, P 66, Q 66 } {E 24, P 24, Q 24 } E 41 E 17 E 48 E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
19 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies l-isogeny φ R {E 66, P 66, Q 66 } {E 24, P 24, Q 24 } E 41 E 17 (1) Choose graph (prime) E 48 E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
20 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies l-isogeny φ R {E 66, P 66, Q 66 } {E 24, P 24, Q 24 } E 41 E 17 E 48 (1) Choose graph (prime) (2) Fix starting curve E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
21 Constructing graphs and walks using isogenies l-isogeny φ R {E 66, P 66, Q 66 } {E 24, P 24, Q 24 } E 41 E 17 E 48 (1) Choose graph (prime) (2) Fix starting curve (3) Fix points E 40 Supersingular elliptic curves 3 / 1
22 Choosing parameters (1) Fix prime p = 2 e2 3 e / 1
23 Choosing parameters (1) Fix prime p = 2 e2 3 e 3 1 (2) Fix starting curve : y 2 = x 3 + x 4 / 1
24 Choosing parameters (1) Fix prime p = 2 e2 3 e 3 1 (2) Fix starting curve : y 2 = x 3 + x (3) Choose smallest points such that [2 e 2 ] = {P 2, Q 2 }, [3 e 3 ] = {P 3, Q 3 } 4 / 1
25 Choosing parameters Only choice to make! How large? (1) Fix prime p = 2 e2 3 e 3 1 (2) Fix starting curve : y 2 = x 3 + x (3) Choose smallest points such that [2 e 2 ] = {P 2, Q 2 }, [3 e 3 ] = {P 3, Q 3 } 4 / 1
26 The SIDH problem {E A, P A, Q A } {P 2, Q 2 } φ A {P 3, Q 3 } φ B {E B, P B, Q B } E AB 5 / 1
27 The SIDH problem {E A, P A, Q A } {P 2, Q 2 } φ A {P 3, Q 3 } φ B {E B, P B, Q B } E AB Prob. 1 (SIDH): Given {E A, P A, Q A } and {E B, P B, Q B }, get E AB 5 / 1
28 The SIDH problem {E A, P A, Q A } {P 2, Q 2 } φ A {P 3, Q 3 } φ B {E B, P B, Q B } E AB Prob. 1 (SIDH): Given {E A, P A, Q A } and {E B, P B, Q B }, get E AB Prob. 2 (SSI*): Given {E A, P A, Q A }, get φ A 5 / 1
29 The SIDH problem {E A, P A, Q A } {P 2, Q 2 } φ A {P 3, Q 3 } φ B {E B, P B, Q B } E AB Prob. 1 (SIDH): Given {E A, P A, Q A } and {E B, P B, Q B }, get E AB Prob. 2 (SSI*): Prob. 3 (SSI): Given {E A, P A, Q A }, get φ A Given E A, get φ A 5 / 1
30 Solving SSI with claw finding algorithms E A 6 / 1
31 Solving SSI with claw finding algorithms E A 6 / 1
32 Solving SSI with claw finding algorithms E A 6 / 1
33 Solving SSI with claw finding algorithms E A 6 / 1
34 Solving SSI with claw finding algorithms E A Complexity of O( deg φ) O( 4 p) classical O( 3 deg φ) O( 6 p) quantum oracle queries 6 / 1
35 Aligning security with the NIST requirements As secure as k-bit AES Classical Quantum AES / 1
36 Aligning security with the NIST requirements As secure as k-bit AES Classical Quantum AES SIKEp / 1
37 Aligning security with the NIST requirements As secure as k-bit AES Classical Quantum AES SIKEp AES SIKEp / 1
38 Aligning security with the NIST requirements As secure as k-bit AES Classical Quantum AES SIKEp AES SIKEp AES SIKEp / 1
39 What is SIKE... PK A K PK B SIDH Passively secure under (SI)CDH 8 / 1
40 What is SIKE... PK A PK A K PK B SIDH Passively secure under (SI)CDH 8 / 1
41 What is SIKE... PK A PK A K K PK B PK B SIDH Passively secure under (SI)CDH 8 / 1
42 What is SIKE... PK A PK A K K PK B PK B C 0 = PK B C 1 = M F (K) SIDH Passively secure under (SI)CDH 8 / 1
43 What is SIKE... PK A PK A K K PK B PK B C 0 = PK B C 1 = M F (K) SIDH Passively secure under (SI)CDH 8 / 1
44 What is SIKE... PK A PK A K K PK B PK B C 0 = PK B C 1 = M F (K) SIDH Passively secure under (SI)CDH ElGamal Passively secure under (SI)CDH in ROM 8 / 1
45 What is SIKE... PK A PK A PK A K K K SIDH PK B Passively secure under (SI)CDH PK B C 0 = PK B C 1 = M F (K) ElGamal Passively secure under (SI)CDH in ROM PK B S = H(M, C 0, C 1 ) 8 / 1
46 What is SIKE... PK A PK A PK A K K K SIDH PK B Passively secure under (SI)CDH PK B C 0 = PK B C 1 = M F (K) ElGamal Passively secure under (SI)CDH in ROM PK B S = H(M, C 0, C 1 ) 8 / 1
47 What is SIKE... PK A PK A PK A K K K SIDH PK B Passively secure under (SI)CDH PK B C 0 = PK B C 1 = M F (K) ElGamal Passively secure under (SI)CDH in ROM PK B S = H(M, C 0, C 1 ) SIKE Actively secure under (SI)CDH in ROM 8 / 1
48 Implementation choices: curve model (1) Model choice: Montgomery 9 / 1
49 Implementation choices: curve model (1) Model choice: Montgomery (2) Only x-coordinates needed (x, ) φ E 1 (f (x), ) deg(f ) = deg(φ) 9 / 1
50 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation (, P 00 ) Order of P 00 is l e = deg(φ 00 ) = l e 10 / 1
51 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation (, P 01 ) P 01 = [l]p 00 Order of P 01 is l e 1 = deg(φ 01 ) = l e 1 10 / 1
52 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 02 = [l 2 ]P 00 Order of P 02 is l e 2 (, P 02 ) = deg(φ 02 ) = l e 2 10 / 1
53 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 03 = [l 3 ]P 00 Order of P 03 is l e 3 = deg(φ 03 ) = l e 3 (, P 03 ) 10 / 1
54 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 04 = [l 4 ]P 00 Order of P 04 is l e 4 = deg(φ 04 ) = l e 4 (, P 04 ) 10 / 1
55 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 05 = [l 5 ]P 00 Order of P 05 is l e 5 = deg(φ 05 ) = l e 5 (, P 05 ) 10 / 1
56 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 06 = [l 6 ]P 00 Order of P 06 is l e 6 = deg(φ 06 ) = l e 6 (, P 06 ) 10 / 1
57 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation (E 1, P 10 ) P 10 = φ 00 (P 00 ) Order of P 10 is l e 1 = deg(φ 10 ) = l e 1 10 / 1
58 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 11 = [l]p 10 Order of P 11 is l e 2 (E 1, P 11 ) = deg(φ 11 ) = l e 2 10 / 1
59 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 12 = [l 2 ]P 10 Order of P 12 is l e 3 = deg(φ 12 ) = l e 3 (E 1, P 12 ) 10 / 1
60 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 13 = [l 3 ]P 10 Order of P 13 is l e 4 = deg(φ 13 ) = l e 4 (E 1, P 13 ) 10 / 1
61 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 14 = [l 4 ]P 10 Order of P 14 is l e 5 = deg(φ 14 ) = l e 5 (E 1, P 14 ) 10 / 1
62 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation P 15 = [l 5 ]P 10 Order of P 15 is l e 6 = deg(φ 15 ) = l e 6 (E 1, P 15 ) 10 / 1
63 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation (E 6, P 60 ) 10 / 1
64 Computing isogenies (3) Tree-based isogeny computation 10 / 1
65 Where to begin (4) Starting curve : y 2 = x 3 + x with j = 1728 = Know things about End( ), could help attacks.. 1 = = Defined over F p F p 2 Attack O( p) (with low memory 2 ) = No better way to obtain a random starting curve? 1 Petit 17 2 Delfs, Galbraith / 1
66 Other implementation choices (5) No public-key compression 12 / 1
67 Other implementation choices (5) No public-key compression (6) Sym. functions cshake / 1
68 Final numbers Speed (ms) PK (Kbytes) RSA NIST P Kyber FrodoKEM SIKEp SIKEp SIDHp SIDHp (Numbers from Patrick Longa s RWC 18 talk, measured on different platforms..) 13 / 1
69 Thanks All details can be found at: Post-Quantum-Cryptography/documents/round-1/ submissions/sike.zip All authors: Reza Azarderakhsh, Matthew Campagna, Craig Costello, Luca De Feo, Basil Hess, David Jao, Brian Koziel, Brian LaMacchia, Patrick Longa, Michael Naehrig, Joost Renes, Vladimir Soukharev 14 / 1
Supersingular Isogeny Key Encapsulation
 Supersingular Isogeny Key Encapsulation Presented by David Jao University of Waterloo and evolutionq, Inc. Full list of submitters: Reza Azarderakhsh, FAU Matt Campagna, Amazon Craig Costello, MSR Luca
Supersingular Isogeny Key Encapsulation Presented by David Jao University of Waterloo and evolutionq, Inc. Full list of submitters: Reza Azarderakhsh, FAU Matt Campagna, Amazon Craig Costello, MSR Luca
 https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/people/plonga/ Outline Motivation recap Isogeny-based cryptography The SIDH key exchange protocol The SIKE protocol Authenticated key exchange from supersingular
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/people/plonga/ Outline Motivation recap Isogeny-based cryptography The SIDH key exchange protocol The SIKE protocol Authenticated key exchange from supersingular
You could have invented Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman
 You could have invented Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman Lorenz Panny Technische Universiteit Eindhoven Πλατανιάς, Κρήτη, 11 October 2017 1 / 22 Shor s algorithm 94 Shor s algorithm quantumly breaks
You could have invented Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman Lorenz Panny Technische Universiteit Eindhoven Πλατανιάς, Κρήτη, 11 October 2017 1 / 22 Shor s algorithm 94 Shor s algorithm quantumly breaks
Side-Channel Attacks on Quantum-Resistant Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman
 Side-Channel Attacks on Quantum-Resistant Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman Presenter: Reza Azarderakhsh CEECS Department and I-Sense, Florida Atlantic University razarderakhsh@fau.edu Paper by: Brian
Side-Channel Attacks on Quantum-Resistant Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman Presenter: Reza Azarderakhsh CEECS Department and I-Sense, Florida Atlantic University razarderakhsh@fau.edu Paper by: Brian
An introduction to supersingular isogeny-based cryptography
 An introduction to supersingular isogeny-based cryptography Craig Costello Summer School on Real-World Crypto and Privacy June 8, 2017 Šibenik, Croatia Towards quantum-resistant cryptosystems from supersingular
An introduction to supersingular isogeny-based cryptography Craig Costello Summer School on Real-World Crypto and Privacy June 8, 2017 Šibenik, Croatia Towards quantum-resistant cryptosystems from supersingular
Current trends and challenges in post-quantum cryptography. Steven Galbraith University of Auckland, New Zealand
 Current trends and challenges in post-quantum cryptography University of Auckland, New Zealand Thanks Eric Bach, Joshua Holden, Jen Paulhus, Andrew Shallue, Renate Scheidler, Jonathan Sorenson. Hilary
Current trends and challenges in post-quantum cryptography University of Auckland, New Zealand Thanks Eric Bach, Joshua Holden, Jen Paulhus, Andrew Shallue, Renate Scheidler, Jonathan Sorenson. Hilary
On hybrid SIDH schemes using Edwards and Montgomery curve arithmetic
 On hybrid SIDH schemes using Edwards and Montgomery curve arithmetic Michael Meyer 1,2, Steffen Reith 1, and Fabio Campos 1 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Applied Sciences Wiesbaden 2
On hybrid SIDH schemes using Edwards and Montgomery curve arithmetic Michael Meyer 1,2, Steffen Reith 1, and Fabio Campos 1 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Applied Sciences Wiesbaden 2
Loop-abort faults on supersingular isogeny cryptosystems
 Loop-abort faults on supersingular isogeny cryptosystems Alexandre Gélin Benjamin Wesolowski Laboratoire d Informatique de Paris 6 Sorbonne Universités UPMC, France École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne,
Loop-abort faults on supersingular isogeny cryptosystems Alexandre Gélin Benjamin Wesolowski Laboratoire d Informatique de Paris 6 Sorbonne Universités UPMC, France École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne,
Faster SeaSign signatures through improved rejection sampling
 Faster SeaSign signatures through improved rejection sampling Thomas Decru 1, Lorenz Panny 2, and Frederik Vercauteren 1 thomas.decru@kuleuven.be, lorenz@yx7.cc, frederik.vercauteren@kuleuven.be 1 imec-cosic,
Faster SeaSign signatures through improved rejection sampling Thomas Decru 1, Lorenz Panny 2, and Frederik Vercauteren 1 thomas.decru@kuleuven.be, lorenz@yx7.cc, frederik.vercauteren@kuleuven.be 1 imec-cosic,
Elliptic curve cryptography in a post-quantum world: the mathematics of isogeny-based cryptography
 Elliptic curve cryptography in a post-quantum world: the mathematics of isogeny-based cryptography Andrew Sutherland MIT Undergraduate Mathematics Association November 29, 2018 Creating a shared secret
Elliptic curve cryptography in a post-quantum world: the mathematics of isogeny-based cryptography Andrew Sutherland MIT Undergraduate Mathematics Association November 29, 2018 Creating a shared secret
Practical Supersingular Isogeny Group Key Agreement
 Practical Supersingular Isogeny Group Key Agreement Reza Azarderakhsh 1, Amir Jalali 1, David Jao 2, and Vladimir Soukharev 3 1 Department of Computer and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Florida
Practical Supersingular Isogeny Group Key Agreement Reza Azarderakhsh 1, Amir Jalali 1, David Jao 2, and Vladimir Soukharev 3 1 Department of Computer and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Florida
A Post-Quantum Digital Signature Scheme based on Supersingular Isogenies
 Post-Quantum Digital Signature Scheme based on Supersingular Isogenies by Youngho Yoo thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree of Master of
Post-Quantum Digital Signature Scheme based on Supersingular Isogenies by Youngho Yoo thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree of Master of
Isogenies in a quantum world
 Isogenies in a quantum world David Jao University of Waterloo September 19, 2011 Summary of main results A. Childs, D. Jao, and V. Soukharev, arxiv:1012.4019 For ordinary isogenous elliptic curves of equal
Isogenies in a quantum world David Jao University of Waterloo September 19, 2011 Summary of main results A. Childs, D. Jao, and V. Soukharev, arxiv:1012.4019 For ordinary isogenous elliptic curves of equal
Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption
 Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption Vladimir Soukharev David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science February 24, 2016 Introduction Bellare and Namprempre in 2008, have shown that
Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption Vladimir Soukharev David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science February 24, 2016 Introduction Bellare and Namprempre in 2008, have shown that
A gentle introduction to isogeny-based cryptography
 A gentle introduction to isogeny-based cryptography Craig Costello Tutorial at SPACE 2016 December 15, 2016 CRRao AIMSCS, Hyderabad, India Part 1: Motivation Part 2: Preliminaries Part 3: Brief SIDH sketch
A gentle introduction to isogeny-based cryptography Craig Costello Tutorial at SPACE 2016 December 15, 2016 CRRao AIMSCS, Hyderabad, India Part 1: Motivation Part 2: Preliminaries Part 3: Brief SIDH sketch
Efficient Finite Field Multiplication for Isogeny Based Post Quantum Cryptography
 Efficient Finite Field Multiplication for Isogeny Based Post Quantum Cryptography Angshuman Karmakar 1 Sujoy Sinha Roy 1 Frederik Vercauteren 1,2 Ingrid Verbauwhede 1 1 COSIC, ESAT KU Leuven and iminds
Efficient Finite Field Multiplication for Isogeny Based Post Quantum Cryptography Angshuman Karmakar 1 Sujoy Sinha Roy 1 Frederik Vercauteren 1,2 Ingrid Verbauwhede 1 1 COSIC, ESAT KU Leuven and iminds
The isogeny cycle seminar
 The isogeny cycle seminar Luca De Feo Université de Versailles & Inria Saclay September 29, 2016, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Elliptic curves Let E : y 2 = x 3 + ax + b be an elliptic curve...
The isogeny cycle seminar Luca De Feo Université de Versailles & Inria Saclay September 29, 2016, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Elliptic curves Let E : y 2 = x 3 + ax + b be an elliptic curve...
Side-Channel Attacks on Quantum-Resistant Supersingular Isogeny Die-Hellman
 Side-Channel Attacks on Quantum-Resistant Supersingular Isogeny Die-Hellman Brian Koziel 1, Reza Azarderakhsh 2, and David Jao 3 1 Texas Instruments, kozielbrian@gmail.com. 2 CEECS Dept and I-SENSE FAU,
Side-Channel Attacks on Quantum-Resistant Supersingular Isogeny Die-Hellman Brian Koziel 1, Reza Azarderakhsh 2, and David Jao 3 1 Texas Instruments, kozielbrian@gmail.com. 2 CEECS Dept and I-SENSE FAU,
Loop-abort faults on supersingular isogeny cryptosystems
 Loop-abort faults on supersingular isogeny cryptosystems Alexandre Gélin 1 and Benjamin Wesolowski 2 1 Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Paris 6, UMR 7606, LIP6, Paris, France alexandre.gelin@lip6.fr 2 École
Loop-abort faults on supersingular isogeny cryptosystems Alexandre Gélin 1 and Benjamin Wesolowski 2 1 Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Paris 6, UMR 7606, LIP6, Paris, France alexandre.gelin@lip6.fr 2 École
ON THE COST OF COMPUTING ISOGENIES BETWEEN SUPERSINGULAR ELLIPTIC CURVES
 ON THE COST OF COMPUTING ISOGENIES BETWEEN SUPERSINGULR ELLIPTIC CURVES GOR DJ, DNIEL CERVNTES-VÁZQUEZ, JESÚS-JVIER CHI-DOMÍNGUEZ, LFRED MENEZES, ND FRNCISCO RODRÍGUEZ-HENRÍQUEZ bstract. The security of
ON THE COST OF COMPUTING ISOGENIES BETWEEN SUPERSINGULR ELLIPTIC CURVES GOR DJ, DNIEL CERVNTES-VÁZQUEZ, JESÚS-JVIER CHI-DOMÍNGUEZ, LFRED MENEZES, ND FRNCISCO RODRÍGUEZ-HENRÍQUEZ bstract. The security of
Post-Snowden Elliptic Curve Cryptography. Patrick Longa Microsoft Research
 Post-Snowden Elliptic Curve Cryptography Patrick Longa Microsoft Research Joppe Bos Craig Costello Michael Naehrig NXP Semiconductors Microsoft Research Microsoft Research June 2013 the Snowden leaks the
Post-Snowden Elliptic Curve Cryptography Patrick Longa Microsoft Research Joppe Bos Craig Costello Michael Naehrig NXP Semiconductors Microsoft Research Microsoft Research June 2013 the Snowden leaks the
NEON-SIDH: Ecient Implementation of Supersingular Isogeny Die-Hellman Key Exchange Protocol on ARM
 NEON-SIDH: Ecient Implementation of Supersingular Isogeny Die-Hellman Key Exchange Protocol on ARM Brian Koziel 1, Amir Jalali 2, Reza Azarderakhsh 3, David Jao 4, and Mehran Mozaari-Kermani 5 1 Texas
NEON-SIDH: Ecient Implementation of Supersingular Isogeny Die-Hellman Key Exchange Protocol on ARM Brian Koziel 1, Amir Jalali 2, Reza Azarderakhsh 3, David Jao 4, and Mehran Mozaari-Kermani 5 1 Texas
Efficient compression of SIDH public keys
 Efficient compression of SIDH public keys Craig Costello 1, David Jao 2,3, atrick Longa 1, Michael Naehrig 1, Joost Renes 4, and David Urbanik 2 1 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA {craigco,plonga,mnaehrig}@microsoft.com
Efficient compression of SIDH public keys Craig Costello 1, David Jao 2,3, atrick Longa 1, Michael Naehrig 1, Joost Renes 4, and David Urbanik 2 1 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA {craigco,plonga,mnaehrig}@microsoft.com
CSIDH: An Efficient Post-Quantum Commutative Group Action
 CSIDH: An Efficient Post-Quantum Commutative Group Action Wouter Castryck 1, Tanja Lange 2, Chloe Martindale 2, Lorenz Panny 2, and Joost Renes 3 wouter.castryck@esat.kuleuven.be, tanja@hyperelliptic.org,
CSIDH: An Efficient Post-Quantum Commutative Group Action Wouter Castryck 1, Tanja Lange 2, Chloe Martindale 2, Lorenz Panny 2, and Joost Renes 3 wouter.castryck@esat.kuleuven.be, tanja@hyperelliptic.org,
Genus Two Isogeny Cryptography
 Genus Two Isogeny Cryptography E.V. Flynn 1 and Yan Bo Ti 2 1 Mathematical Institute, Oxford University, UK. flynn@maths.ox.ac.uk 2 Mathematics Department, University of Auckland, NZ. yanbo.ti@gmail.com
Genus Two Isogeny Cryptography E.V. Flynn 1 and Yan Bo Ti 2 1 Mathematical Institute, Oxford University, UK. flynn@maths.ox.ac.uk 2 Mathematics Department, University of Auckland, NZ. yanbo.ti@gmail.com
Digital Signatures. p1.
 Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Efficient algorithms for supersingular isogeny
 Efficient algorithms for supersingular isogeny Diffie-Hellman Craig Costello, Patrick Longa, and Michael Naehrig Microsoft Research, US bstract. We propose a new suite of algorithms that significantly
Efficient algorithms for supersingular isogeny Diffie-Hellman Craig Costello, Patrick Longa, and Michael Naehrig Microsoft Research, US bstract. We propose a new suite of algorithms that significantly
Quantum-resistant cryptography
 Quantum-resistant cryptography Background: In quantum computers, states are represented as vectors in a Hilbert space. Quantum gates act on the space and allow us to manipulate quantum states with combination
Quantum-resistant cryptography Background: In quantum computers, states are represented as vectors in a Hilbert space. Quantum gates act on the space and allow us to manipulate quantum states with combination
Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography Real World Issues
 Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography Real World Issues Michael Naehrig Cryptography Research Group Microsoft Research UW Number Theory Seminar Seattle, 28 April 2015 Elliptic Curve Cryptography 1985:
Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography Real World Issues Michael Naehrig Cryptography Research Group Microsoft Research UW Number Theory Seminar Seattle, 28 April 2015 Elliptic Curve Cryptography 1985:
Quantum Security Analysis of CSIDH and Ordinary Isogeny-based Schemes
 Quantum Security Analysis of CSIDH and Ordinary Isogeny-based Schemes Xavier Bonnetain 1,2 and André Schrottenloher 2 1 Sorbonne Université, Collège Doctoral, F-75005 Paris, France 2 Inria, France Abstract.
Quantum Security Analysis of CSIDH and Ordinary Isogeny-based Schemes Xavier Bonnetain 1,2 and André Schrottenloher 2 1 Sorbonne Université, Collège Doctoral, F-75005 Paris, France 2 Inria, France Abstract.
A Generic Hybrid Encryption Construction in the Quantum Random Oracle Model
 A Generic Hybrid Encryption Construction in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Presented by: Angela Robinson Department of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Atlantic University April 4, 2018 Motivation Quantum-resistance
A Generic Hybrid Encryption Construction in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Presented by: Angela Robinson Department of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Atlantic University April 4, 2018 Motivation Quantum-resistance
FPGA-BASED ACCELERATOR FOR POST-QUANTUM SIGNATURE SCHEME SPHINCS-256
 IMES FPGA-BASED ACCELERATOR FOR POST-QUANTUM SIGNATURE SCHEME SPHINCS-256 Dorian Amiet 1, Andreas Curiger 2 and Paul Zbinden 1 1 HSR Hochschule für Technik, Rapperswil, Switzerland 2 Securosys SA, Zürich,
IMES FPGA-BASED ACCELERATOR FOR POST-QUANTUM SIGNATURE SCHEME SPHINCS-256 Dorian Amiet 1, Andreas Curiger 2 and Paul Zbinden 1 1 HSR Hochschule für Technik, Rapperswil, Switzerland 2 Securosys SA, Zürich,
Efficient Finite Field Multiplication for Isogeny Based Post Quantum Cryptography
 Efficient Finite Field Multiplication for Isogeny Based Post Quantum Cryptography Angshuman Karmakar 1, Sujoy Sinha Roy 1, Frederik Vercauteren 1,2, and Ingrid Verbauwhede 1 1 KU Leuven ESAT/COSIC and
Efficient Finite Field Multiplication for Isogeny Based Post Quantum Cryptography Angshuman Karmakar 1, Sujoy Sinha Roy 1, Frederik Vercauteren 1,2, and Ingrid Verbauwhede 1 1 KU Leuven ESAT/COSIC and
A Post-Quantum Digital Signature Scheme Based on Supersingular Isogenies
 Post-Quantum Digital Signature Scheme ased on Supersingular Isogenies Youngho Yoo 1, Reza zarderakhsh 3, mir Jalali 3, David Jao 1,2, and Vladimir Soukharev 4 1 University of Waterloo, {yh2yoo,djao}@uwaterloo.ca
Post-Quantum Digital Signature Scheme ased on Supersingular Isogenies Youngho Yoo 1, Reza zarderakhsh 3, mir Jalali 3, David Jao 1,2, and Vladimir Soukharev 4 1 University of Waterloo, {yh2yoo,djao}@uwaterloo.ca
18 Seconds to Key Exchange: Limitations of Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman on Embedded Devices
 18 Seconds to Key Exchange: Limitations of Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman on Embedded Devices Philipp Koppermann 1, Eduard Pop 1, Johann Heyszl 1, and Georg Sigl 1,2 1 Fraunhofer Institute for pplied
18 Seconds to Key Exchange: Limitations of Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman on Embedded Devices Philipp Koppermann 1, Eduard Pop 1, Johann Heyszl 1, and Georg Sigl 1,2 1 Fraunhofer Institute for pplied
Secure Oblivious Transfer from Semi-Commutative Masking
 Secure Oblivious Transfer from Semi-Commutative Masking Cyprien Delpech de Saint Guilhem 1,2, Emmanuela Orsini 1, Christophe Petit 3, and Nigel P. Smart 1,2 1 imec-cosic, KU Leuven, Belgium 2 Dept Computer
Secure Oblivious Transfer from Semi-Commutative Masking Cyprien Delpech de Saint Guilhem 1,2, Emmanuela Orsini 1, Christophe Petit 3, and Nigel P. Smart 1,2 1 imec-cosic, KU Leuven, Belgium 2 Dept Computer
Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model
 Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) - TU Darmstadt, Germany June, 21st, 2012 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) - TU Darmstadt, Germany June, 21st, 2012 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
From NewHope to Kyber. Peter Schwabe April 7, 2017
 From NewHope to Kyber Peter Schwabe peter@cryptojedi.org https://cryptojedi.org April 7, 2017 In the past, people have said, maybe it s 50 years away, it s a dream, maybe it ll happen sometime. I used
From NewHope to Kyber Peter Schwabe peter@cryptojedi.org https://cryptojedi.org April 7, 2017 In the past, people have said, maybe it s 50 years away, it s a dream, maybe it ll happen sometime. I used
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 11 February 21, 2013 CPSC 467b, Lecture 11 1/27 Discrete Logarithm Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange ElGamal Key Agreement Primitive Roots
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 11 February 21, 2013 CPSC 467b, Lecture 11 1/27 Discrete Logarithm Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange ElGamal Key Agreement Primitive Roots
Identification Protocols and Signature Schemes Based on Supersingular Isogeny Problems
 Identification Protocols and Signature Schemes Based on Supersingular Isogeny Problems Steven D. Galbraith 1, Christophe Petit 2, and Javier Silva 3 1 Mathematics Department, University of Auckland, NZ.
Identification Protocols and Signature Schemes Based on Supersingular Isogeny Problems Steven D. Galbraith 1, Christophe Petit 2, and Javier Silva 3 1 Mathematics Department, University of Auckland, NZ.
Asymmetric Pairings. Alfred Menezes (joint work with S. Chatterjee, D. Hankerson & E. Knapp)
 Asymmetric Pairings Alfred Menezes (joint work with S. Chatterjee, D. Hankerson & E. Knapp) 1 Overview In their 2006 paper "Pairings for cryptographers", Galbraith, Paterson and Smart identified three
Asymmetric Pairings Alfred Menezes (joint work with S. Chatterjee, D. Hankerson & E. Knapp) 1 Overview In their 2006 paper "Pairings for cryptographers", Galbraith, Paterson and Smart identified three
Overview. Public Key Algorithms II
 Public Key Algorithms II Dr. Arjan Durresi Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70810 Durresi@csc.lsu.Edu These slides are available at: http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~durresi/csc4601-04/ Louisiana State
Public Key Algorithms II Dr. Arjan Durresi Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70810 Durresi@csc.lsu.Edu These slides are available at: http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~durresi/csc4601-04/ Louisiana State
Post-quantum key exchange based on Lattices
 Post-quantum key exchange based on Lattices Joppe W. Bos Romanian Cryptology Days Conference Cybersecurity in a Post-quantum World September 20, 2017, Bucharest 1. NXP Semiconductors Operations in > 35
Post-quantum key exchange based on Lattices Joppe W. Bos Romanian Cryptology Days Conference Cybersecurity in a Post-quantum World September 20, 2017, Bucharest 1. NXP Semiconductors Operations in > 35
Faster Algorithms for Isogeny Problems using Torsion Point Images
 Faster Algorithms for Isogeny Problems using Torsion Point Images Christophe Petit School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham Abstract. There is a recent trend in cryptography to construct protocols
Faster Algorithms for Isogeny Problems using Torsion Point Images Christophe Petit School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham Abstract. There is a recent trend in cryptography to construct protocols
CRYSTALS Kyber and Dilithium. Peter Schwabe February 7, 2018
 CRYSTALS Kyber and Dilithium Peter Schwabe peter@cryptojedi.org https://cryptojedi.org February 7, 2018 Crypto today 5 building blocks for a secure channel Symmetric crypto Block or stream cipher (e.g.,
CRYSTALS Kyber and Dilithium Peter Schwabe peter@cryptojedi.org https://cryptojedi.org February 7, 2018 Crypto today 5 building blocks for a secure channel Symmetric crypto Block or stream cipher (e.g.,
Practical, Quantum-Secure Key Exchange from LWE
 Practical, Quantum-Secure Key Exchange from LWE Douglas Stebila 4 th ETSI/IQC Workshop on Quantum-Safe Cryptography September 21, 2016 Acknowledgements Collaborators Joppe Bos Craig Costello and Michael
Practical, Quantum-Secure Key Exchange from LWE Douglas Stebila 4 th ETSI/IQC Workshop on Quantum-Safe Cryptography September 21, 2016 Acknowledgements Collaborators Joppe Bos Craig Costello and Michael
Security Issues in Cloud Computing Modern Cryptography II Asymmetric Cryptography
 Security Issues in Cloud Computing Modern Cryptography II Asymmetric Cryptography Peter Schwabe October 21 and 28, 2011 So far we assumed that Alice and Bob both have some key, which nobody else has. How
Security Issues in Cloud Computing Modern Cryptography II Asymmetric Cryptography Peter Schwabe October 21 and 28, 2011 So far we assumed that Alice and Bob both have some key, which nobody else has. How
Hard and Easy Problems for Supersingular Isogeny Graphs
 Hard and Easy Problems for Supersingular Isogeny Graphs Christophe Petit and Kristin Lauter University of Birmingham, Microsoft Research February 21, 2018 Abstract We consider the endomorphism ring computation
Hard and Easy Problems for Supersingular Isogeny Graphs Christophe Petit and Kristin Lauter University of Birmingham, Microsoft Research February 21, 2018 Abstract We consider the endomorphism ring computation
Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 4)
 Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 4) Review of Last Lecture Blockciphers Review of DES Attacks on Blockciphers Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Modes of Operation MACs and Hashes Message
Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 4) Review of Last Lecture Blockciphers Review of DES Attacks on Blockciphers Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Modes of Operation MACs and Hashes Message
Introduction to Quantum Safe Cryptography. ENISA September 2018
 Introduction to Quantum Safe Cryptography ENISA September 2018 Introduction This talk will introduce the mathematical background of the most popular PQC primitives Code-based Lattice-based Multivariate
Introduction to Quantum Safe Cryptography ENISA September 2018 Introduction This talk will introduce the mathematical background of the most popular PQC primitives Code-based Lattice-based Multivariate
ON ISOGENY GRAPHS OF SUPERSINGULAR ELLIPTIC CURVES OVER FINITE FIELDS
 ON ISOGENY GRAPHS OF SUPERSINGULAR ELLIPTIC CURVES OVER FINITE FIELDS GORA ADJ, OMRAN AHMADI, AND ALFRED MENEZES Abstract. We study the isogeny graphs of supersingular elliptic curves over finite fields,
ON ISOGENY GRAPHS OF SUPERSINGULAR ELLIPTIC CURVES OVER FINITE FIELDS GORA ADJ, OMRAN AHMADI, AND ALFRED MENEZES Abstract. We study the isogeny graphs of supersingular elliptic curves over finite fields,
Part 2 LWE-based cryptography
 Part 2 LWE-based cryptography Douglas Stebila SAC Summer School Université d'ottawa August 14, 2017 https://www.douglas.stebila.ca/research/presentations Funding acknowledgements: SAC Summer School 2017-08-14
Part 2 LWE-based cryptography Douglas Stebila SAC Summer School Université d'ottawa August 14, 2017 https://www.douglas.stebila.ca/research/presentations Funding acknowledgements: SAC Summer School 2017-08-14
Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 4)
 Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 4) Review of Last Lecture Blockciphers Review of DES Attacks on Blockciphers Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Modes of Operation MACs and Hashes Message
Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 4) Review of Last Lecture Blockciphers Review of DES Attacks on Blockciphers Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Modes of Operation MACs and Hashes Message
A quantum algorithm for computing isogenies between supersingular elliptic curves
 A quantum algorithm for computing isogenies between supersingular elliptic curves Jean-François Biasse 1,2, David Jao 1, and Anirudh Sankar 1 1 Department of Combinatorics and Optimization 2 Institute
A quantum algorithm for computing isogenies between supersingular elliptic curves Jean-François Biasse 1,2, David Jao 1, and Anirudh Sankar 1 1 Department of Combinatorics and Optimization 2 Institute
On the CCA1-Security of Elgamal and Damgård s Elgamal
 On the CCA1-Security of Elgamal and Damgård s Elgamal Cybernetica AS, Estonia Tallinn University, Estonia October 21, 2010 Outline I Motivation 1 Motivation 2 3 Motivation Three well-known security requirements
On the CCA1-Security of Elgamal and Damgård s Elgamal Cybernetica AS, Estonia Tallinn University, Estonia October 21, 2010 Outline I Motivation 1 Motivation 2 3 Motivation Three well-known security requirements
Winter 2011 Josh Benaloh Brian LaMacchia
 Winter 2011 Josh Benaloh Brian LaMacchia Fun with Public-Key Tonight we ll Introduce some basic tools of public-key crypto Combine the tools to create more powerful tools Lay the ground work for substantial
Winter 2011 Josh Benaloh Brian LaMacchia Fun with Public-Key Tonight we ll Introduce some basic tools of public-key crypto Combine the tools to create more powerful tools Lay the ground work for substantial
Public Key Cryptography
 Public Key Cryptography Introduction Public Key Cryptography Unlike symmetric key, there is no need for Alice and Bob to share a common secret Alice can convey her public key to Bob in a public communication:
Public Key Cryptography Introduction Public Key Cryptography Unlike symmetric key, there is no need for Alice and Bob to share a common secret Alice can convey her public key to Bob in a public communication:
II. Digital signatures
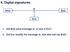 II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
Faster Cryptographic Hash Function From Supersingular Isogeny Graphs
 Faster Cryptographic Hash Function From Supersingular Isogeny Graphs Javad Doliskani, Geovandro C. C. F. Pereira and Paulo S. L. M. Barreto Abstract. We propose a variant of the CGL hash [5] that is significantly
Faster Cryptographic Hash Function From Supersingular Isogeny Graphs Javad Doliskani, Geovandro C. C. F. Pereira and Paulo S. L. M. Barreto Abstract. We propose a variant of the CGL hash [5] that is significantly
Foundations. P =! NP oneway function signature schemes Trapdoor oneway function PKC, IBS IBE
 Foundations P =! NP oneway function signature schemes Trapdoor oneway function PKC, IBS IBE NP problems: IF, DL, Knapsack Hardness of these problems implies the security of cryptosytems? 2 Relations of
Foundations P =! NP oneway function signature schemes Trapdoor oneway function PKC, IBS IBE NP problems: IF, DL, Knapsack Hardness of these problems implies the security of cryptosytems? 2 Relations of
Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers
 Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers Computer Security Lecture 7 David Aspinall School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 31st January 2011 Outline Background RSA Diffie-Hellman ElGamal Summary Outline
Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers Computer Security Lecture 7 David Aspinall School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 31st January 2011 Outline Background RSA Diffie-Hellman ElGamal Summary Outline
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography
 Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Message Authentication Codes (MACs)
 Message Authentication Codes (MACs) Tung Chou Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands October 8, 2015 1 / 22 About Me 2 / 22 About Me Tung Chou (Tony) 2 / 22 About Me Tung Chou (Tony) Ph.D.
Message Authentication Codes (MACs) Tung Chou Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands October 8, 2015 1 / 22 About Me 2 / 22 About Me Tung Chou (Tony) 2 / 22 About Me Tung Chou (Tony) Ph.D.
Cryptography in the Quantum Era. Tomas Rosa and Jiri Pavlu Cryptology and Biometrics Competence Centre, Raiffeisen BANK International
 Cryptography in the Quantum Era Tomas Rosa and Jiri Pavlu Cryptology and Biometrics Competence Centre, Raiffeisen BANK International Postulate #1: Qubit state belongs to Hilbert space of dimension 2 ψ
Cryptography in the Quantum Era Tomas Rosa and Jiri Pavlu Cryptology and Biometrics Competence Centre, Raiffeisen BANK International Postulate #1: Qubit state belongs to Hilbert space of dimension 2 ψ
Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures
 Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures v 1. Introduction to Public-key Cryptography 2. Example of Public-key Algorithm: Diffie- Hellman Key Exchange Scheme 3. RSA Encryption and Digital
Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures v 1. Introduction to Public-key Cryptography 2. Example of Public-key Algorithm: Diffie- Hellman Key Exchange Scheme 3. RSA Encryption and Digital
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16. Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange
 ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16 Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16 Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants. COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from
 Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Efficient Application of Countermeasures for Elliptic Curve Cryptography
 Efficient Application of Countermeasures for Elliptic Curve Cryptography Vladimir Soukharev, Ph.D. Basil Hess, Ph.D. InfoSec Global Inc. May 19, 2017 Outline Introduction Brief Summary of ECC Arithmetic
Efficient Application of Countermeasures for Elliptic Curve Cryptography Vladimir Soukharev, Ph.D. Basil Hess, Ph.D. InfoSec Global Inc. May 19, 2017 Outline Introduction Brief Summary of ECC Arithmetic
How to Use Short Basis : Trapdoors for Hard Lattices and new Cryptographic Constructions
 Presentation Article presentation, for the ENS Lattice Based Crypto Workgroup http://www.di.ens.fr/~pnguyen/lbc.html, 30 September 2009 How to Use Short Basis : Trapdoors for http://www.cc.gatech.edu/~cpeikert/pubs/trap_lattice.pdf
Presentation Article presentation, for the ENS Lattice Based Crypto Workgroup http://www.di.ens.fr/~pnguyen/lbc.html, 30 September 2009 How to Use Short Basis : Trapdoors for http://www.cc.gatech.edu/~cpeikert/pubs/trap_lattice.pdf
Public Key Compression and Modulus Switching for Fully Homomorphic Encryption over the Integers
 Public Key Compression and Modulus Switching for Fully Homomorphic Encryption over the Integers Jean-Sébastien Coron, David Naccache and Mehdi Tibouchi University of Luxembourg & ENS & NTT EUROCRYPT, 2012-04-18
Public Key Compression and Modulus Switching for Fully Homomorphic Encryption over the Integers Jean-Sébastien Coron, David Naccache and Mehdi Tibouchi University of Luxembourg & ENS & NTT EUROCRYPT, 2012-04-18
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 11 October 7, 2015 CPSC 467, Lecture 11 1/37 Digital Signature Algorithms Signatures from commutative cryptosystems Signatures from
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 11 October 7, 2015 CPSC 467, Lecture 11 1/37 Digital Signature Algorithms Signatures from commutative cryptosystems Signatures from
2. Cryptography 2.5. ElGamal cryptosystems and Discrete logarithms
 CRYPTOGRAPHY 19 Cryptography 5 ElGamal cryptosystems and Discrete logarithms Definition Let G be a cyclic group of order n and let α be a generator of G For each A G there exists an uniue 0 a n 1 such
CRYPTOGRAPHY 19 Cryptography 5 ElGamal cryptosystems and Discrete logarithms Definition Let G be a cyclic group of order n and let α be a generator of G For each A G there exists an uniue 0 a n 1 such
Efficient Implementation of Cryptographic pairings. Mike Scott Dublin City University
 Efficient Implementation of Cryptographic pairings Mike Scott Dublin City University First Steps To do Pairing based Crypto we need two things l Efficient algorithms l Suitable elliptic curves We have
Efficient Implementation of Cryptographic pairings Mike Scott Dublin City University First Steps To do Pairing based Crypto we need two things l Efficient algorithms l Suitable elliptic curves We have
Ma/CS 6a Class 4: Primality Testing
 Ma/CS 6a Class 4: Primality Testing By Adam Sheffer Reminder: Euler s Totient Function Euler s totient φ(n) is defined as follows: Given n N, then φ n = x 1 x < n and GCD x, n = 1. In more words: φ n is
Ma/CS 6a Class 4: Primality Testing By Adam Sheffer Reminder: Euler s Totient Function Euler s totient φ(n) is defined as follows: Given n N, then φ n = x 1 x < n and GCD x, n = 1. In more words: φ n is
Lecture Notes, Week 6
 YALE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Week 6 (rev. 3) Professor M. J. Fischer February 15 & 17, 2005 1 RSA Security Lecture Notes, Week 6 Several
YALE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Week 6 (rev. 3) Professor M. J. Fischer February 15 & 17, 2005 1 RSA Security Lecture Notes, Week 6 Several
communication complexity lower bounds yield data structure lower bounds
 communication complexity lower bounds yield data structure lower bounds Implementation of a database - D: D represents a subset S of {...N} 2 3 4 Access to D via "membership queries" - Q for each i, can
communication complexity lower bounds yield data structure lower bounds Implementation of a database - D: D represents a subset S of {...N} 2 3 4 Access to D via "membership queries" - Q for each i, can
Cryptography and Network Security Prof. D. Mukhopadhyay Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Cryptography and Network Security Prof. D. Mukhopadhyay Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 33 The Diffie-Hellman Problem
Cryptography and Network Security Prof. D. Mukhopadhyay Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 33 The Diffie-Hellman Problem
Practice Assignment 2 Discussion 24/02/ /02/2018
 German University in Cairo Faculty of MET (CSEN 1001 Computer and Network Security Course) Dr. Amr El Mougy 1 RSA 1.1 RSA Encryption Practice Assignment 2 Discussion 24/02/2018-29/02/2018 Perform encryption
German University in Cairo Faculty of MET (CSEN 1001 Computer and Network Security Course) Dr. Amr El Mougy 1 RSA 1.1 RSA Encryption Practice Assignment 2 Discussion 24/02/2018-29/02/2018 Perform encryption
Digital Signatures from Strong RSA without Prime Genera7on. David Cash Rafael Dowsley Eike Kiltz
 Digital Signatures from Strong RSA without Prime Genera7on David Cash Rafael Dowsley Eike Kiltz Digital Signatures Digital signatures are one of mostly deployed cryptographic primi7ves. Digital Signatures
Digital Signatures from Strong RSA without Prime Genera7on David Cash Rafael Dowsley Eike Kiltz Digital Signatures Digital signatures are one of mostly deployed cryptographic primi7ves. Digital Signatures
Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 5)
 Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 5) Prof. Dr. Michael Backes 13.01.2017 February 17 th Special Lecture! 45 Minutes Your Choice 1. Automotive Security 2. Smartphone Security 3. Side Channel
Introduction to Cybersecurity Cryptography (Part 5) Prof. Dr. Michael Backes 13.01.2017 February 17 th Special Lecture! 45 Minutes Your Choice 1. Automotive Security 2. Smartphone Security 3. Side Channel
SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS. CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography
 SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 8 of Trappe and Washington DIGITAL SIGNATURES message sig 1. How do we bind
SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 8 of Trappe and Washington DIGITAL SIGNATURES message sig 1. How do we bind
Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography: An Eciency and Security Analysis
 Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography: An Eciency and Security Analysis Joppe W. Bos, Craig Costello, Patrick Longa and Michael Naehrig Microsoft Research, USA Abstract. We select a set of elliptic
Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography: An Eciency and Security Analysis Joppe W. Bos, Craig Costello, Patrick Longa and Michael Naehrig Microsoft Research, USA Abstract. We select a set of elliptic
SJÄLVSTÄNDIGA ARBETEN I MATEMATIK
 SJÄLVSTÄNDIG RBETEN I MTEMTIK MTEMTISK INSTITUTIONEN, STOCKHOLMS UNIVERSITET Post-Quantum Cryptography: Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange av Erik Thormarker 2017 - No 42 MTEMTISK INSTITUTIONEN,
SJÄLVSTÄNDIG RBETEN I MTEMTIK MTEMTISK INSTITUTIONEN, STOCKHOLMS UNIVERSITET Post-Quantum Cryptography: Supersingular Isogeny Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange av Erik Thormarker 2017 - No 42 MTEMTISK INSTITUTIONEN,
1 Number Theory Basics
 ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
Digital Signatures. Adam O Neill based on
 Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Lecture 22: RSA Encryption. RSA Encryption
 Lecture 22: Recall: RSA Assumption We pick two primes uniformly and independently at random p, q $ P n We define N = p q We shall work over the group (Z N, ), where Z N is the set of all natural numbers
Lecture 22: Recall: RSA Assumption We pick two primes uniformly and independently at random p, q $ P n We define N = p q We shall work over the group (Z N, ), where Z N is the set of all natural numbers
8 Elliptic Curve Cryptography
 8 Elliptic Curve Cryptography 8.1 Elliptic Curves over a Finite Field For the purposes of cryptography, we want to consider an elliptic curve defined over a finite field F p = Z/pZ for p a prime. Given
8 Elliptic Curve Cryptography 8.1 Elliptic Curves over a Finite Field For the purposes of cryptography, we want to consider an elliptic curve defined over a finite field F p = Z/pZ for p a prime. Given
Public-Key Identification Schemes based on Multivariate Quadratic Polynomials
 Public-Key Identification Schemes based on Multivariate Quadratic Polynomials Koichi Sakumoto, Taizo Shirai, Harunaga Hiwatari from Tokyo, Japan Sony Corporation @CRYPTO2011 Motivation Finding a new alternative
Public-Key Identification Schemes based on Multivariate Quadratic Polynomials Koichi Sakumoto, Taizo Shirai, Harunaga Hiwatari from Tokyo, Japan Sony Corporation @CRYPTO2011 Motivation Finding a new alternative
CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security. Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography
 CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography 1 Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange 2 Diffie-Hellman Protocol For negotiating a shared secret key using only public communication
CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography 1 Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange 2 Diffie-Hellman Protocol For negotiating a shared secret key using only public communication
µkummer: efficient hyperelliptic signatures and key exchange on microcontrollers
 µkummer: efficient hyperelliptic signatures and key exchange on microcontrollers Joost Renes 1 Peter Schwabe 1 Benjamin Smith 2 Lejla Batina 1 1 Digital Security Group, Radboud University, The Netherlands
µkummer: efficient hyperelliptic signatures and key exchange on microcontrollers Joost Renes 1 Peter Schwabe 1 Benjamin Smith 2 Lejla Batina 1 1 Digital Security Group, Radboud University, The Netherlands
Introduction to Elliptic Curve Cryptography. Anupam Datta
 Introduction to Elliptic Curve Cryptography Anupam Datta 18-733 Elliptic Curve Cryptography Public Key Cryptosystem Duality between Elliptic Curve Cryptography and Discrete Log Based Cryptography Groups
Introduction to Elliptic Curve Cryptography Anupam Datta 18-733 Elliptic Curve Cryptography Public Key Cryptosystem Duality between Elliptic Curve Cryptography and Discrete Log Based Cryptography Groups
Efficient and Secure Algorithms for GLV-Based Scalar Multiplication and Their Implementation on GLV-GLS Curves
 Efficient and Secure Algorithms for GLV-Based Scalar Multiplication and Their Implementation on GLV-GLS Curves SESSION ID: CRYP-T07 Patrick Longa Microsoft Research http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/people/plonga/
Efficient and Secure Algorithms for GLV-Based Scalar Multiplication and Their Implementation on GLV-GLS Curves SESSION ID: CRYP-T07 Patrick Longa Microsoft Research http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/people/plonga/
On the complexity of computing discrete logarithms in the field F
 On the complexity of computing discrete logarithms in the field F 3 6 509 Francisco Rodríguez-Henríquez CINVESTAV-IPN Joint work with: Gora Adj Alfred Menezes Thomaz Oliveira CINVESTAV-IPN University of
On the complexity of computing discrete logarithms in the field F 3 6 509 Francisco Rodríguez-Henríquez CINVESTAV-IPN Joint work with: Gora Adj Alfred Menezes Thomaz Oliveira CINVESTAV-IPN University of
Cryptography and Security Final Exam
 Cryptography and Security Final Exam Serge Vaudenay 17.1.2017 duration: 3h no documents allowed, except one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes a pocket calculator is allowed communication devices are not
Cryptography and Security Final Exam Serge Vaudenay 17.1.2017 duration: 3h no documents allowed, except one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes a pocket calculator is allowed communication devices are not
5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall
 5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall Homework 2 Reference Solution 1. This is about the RSA common modulus problem. Consider that two users A and B use the same modulus n = 146171 for the RSA encryption.
5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall Homework 2 Reference Solution 1. This is about the RSA common modulus problem. Consider that two users A and B use the same modulus n = 146171 for the RSA encryption.
Arithmétique et Cryptographie Asymétrique
 Arithmétique et Cryptographie Asymétrique Laurent Imbert CNRS, LIRMM, Université Montpellier 2 Journée d inauguration groupe Sécurité 23 mars 2010 This talk is about public-key cryptography Why did mathematicians
Arithmétique et Cryptographie Asymétrique Laurent Imbert CNRS, LIRMM, Université Montpellier 2 Journée d inauguration groupe Sécurité 23 mars 2010 This talk is about public-key cryptography Why did mathematicians
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography. Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017
 COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Previously Digital Signatures Algorithms: Gen() à (sk,pk) Sign(sk,m) à σ Ver(pk,m,σ) à 0/1 Correctness: Pr[Ver(pk,m,Sign(sk,m))=1:
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Previously Digital Signatures Algorithms: Gen() à (sk,pk) Sign(sk,m) à σ Ver(pk,m,σ) à 0/1 Correctness: Pr[Ver(pk,m,Sign(sk,m))=1:
The McEliece Cryptosystem Resists Quantum Fourier Sampling Attack
 The McEliece Cryptosystem Resists Quantum Fourier Sampling Attack Cristopher Moore University of New Mexico and the Santa Fe Institute Joint work with Hang Dinh, University of Connecticut / Indiana, South
The McEliece Cryptosystem Resists Quantum Fourier Sampling Attack Cristopher Moore University of New Mexico and the Santa Fe Institute Joint work with Hang Dinh, University of Connecticut / Indiana, South
Asymmetric Encryption
 -3 s s Encryption Comp Sci 3600 Outline -3 s s 1-3 2 3 4 5 s s Outline -3 s s 1-3 2 3 4 5 s s Function Using Bitwise XOR -3 s s Key Properties for -3 s s The most important property of a hash function
-3 s s Encryption Comp Sci 3600 Outline -3 s s 1-3 2 3 4 5 s s Outline -3 s s 1-3 2 3 4 5 s s Function Using Bitwise XOR -3 s s Key Properties for -3 s s The most important property of a hash function
Optimal Eta Pairing on Supersingular Genus-2 Binary Hyperelliptic Curves
 CT-RSA 2012 February 29th, 2012 Optimal Eta Pairing on Supersingular Genus-2 Binary Hyperelliptic Curves Joint work with: Nicolas Estibals CARAMEL project-team, LORIA, Université de Lorraine / CNRS / INRIA,
CT-RSA 2012 February 29th, 2012 Optimal Eta Pairing on Supersingular Genus-2 Binary Hyperelliptic Curves Joint work with: Nicolas Estibals CARAMEL project-team, LORIA, Université de Lorraine / CNRS / INRIA,
