and K becoming functions of Mach number i.e.: (3.49)
|
|
|
- Dorthy Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3 Lecture 11 Drag polar 6 Topics Parabolic drag polar at high speeds Guidelines for variations of C Do and K for subsonic jet transport airplanes Variations of C Do and K for a fighter airplane Area ruling 3.4 Drag polar at hypersonic speeds 3.5 Lift to drag ratio 3.6 Other types of drags Cooling drag Base drag External stores drag Leakage drag Trim drag Parabolic drag polar at high speeds The foregoing sections indicate that the drag coefficients of major airplane components change as the Mach number changes from subsonic to supersonic. Consequently, the drag polar of an airplane, being the sum of the drag coefficients of major components, will also undergo changes as Mach number changes from subsonic to supersonic. However, it is observed that the approximation of parabolic polar is still valid at transonic and supersonic speeds, with C D0 and K becoming functions of Mach number i.e.: C D = C (M) + K (M)C 2 D0 L (3.49) Detailed estimation of the drag polar of a subsonic jet airplane is presented in section 2 of Appendix B. Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 1
2 3.3.5 Guidelines for variations of C Do and K for subsonic jet transport airplanes Subsonic jet airplanes are generally designed in a manner that there is no significant wave drag up to the cruise Mach number (M cruise ). Further, the drag polar of the airplane for Mach numbers upto M cruise can be estimated, using the methods for subsonic airplanes. Section 2 of Appendix B illustrates the procedure for estimation of such a polar. However, to calculate the maximum speed in level flight (V max ) or the maximum Mach number M max, guidelines are needed for the increase in C D0 and K beyond M cruise. Such guidelines are obtained in this subsection by using the data on drag polars of B airplane at Mach numbers between 0.7 to Reference 3.18 part VI, chapter 5, gives drag polars of B at M = 0.7, 0.76, 0.82, 0.84, 0.86 and Values of C D and C L corresponding to various Mach numbers were recorded and are shown in Fig.3.29 by symbols. Following the parabolic approximation, these polars were fitted with Eq.(3.49) and C D0 and K were obtained using least square technique. The fitted polars are shown as curves in Fig The values of C D0 and K are given in Table 3.5 and presented in Figs.3.30 a & b. Fig.3.29 Drag polars at different Mach numbers for B Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 2
3 M C D0 K Table 3.5 Variations of C D0 and K with Mach number Fig.3.30a Parameters of drag polar - C D0 for B Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 3
4 Fig.3.30b Parameters of drag polar - K for B It is seen that the drag polar and hence C D0 and K are almost constant up to M = The variations of C D0 and K between M = 0.76 and 0.86, when fitted with polynomial curves, give the following equations (see also Figs.3.30 a & b). C D0 = ( M-0.76)+0.11 (M-0.76)2 (3.50) K= (M-0.76) (M-0.76) 3 (3.51) Note: For M 0.76, C D0 = , K = Based on these trends, the variations of C D0 and K beyond M cruise but upto M cruise are expressed by the following two equations. C D = CDOcr ( M-M cruise ) (M-M cruise ) 2 (3.50 a) K = K cr + (M-M cruise ) (M-M cruise ) 3 (3.51 a) where CDOcr and K cr are the values of C D0 and K at cruise Mach number for the airplane whose V max or M max is required to be calculated. It may be pointed out that the value of in Eq.(3.50) has been replaced by C DOcr in Eq.(3.50a). Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 4
5 This has been done to permit the use of Eq.(3.50a) for different types of airplanes which may have their own values of C DOcr (see section 4.2 of Appendix B). For the same reason the value of in Eq.(3.51) has been replaced by K cr in Eq.(3.51a). Section 4.2 of Appendix B illustrates the application of the guidelines given in this subsection Variations of C D0 and K for a fighter airplane Reference 1.10, chapter 2 has given drag polars of F-15 fighter airplane at M = 0.8, 0.95, 1.2, 1.4 and 2.2.These are shown in Fig These drag polars were also fitted with Eq.(3.49) and C D0 and K were calculated. The variations of C D0 and K are shown in Figs.3.32a & b. It is interesting to note that C D0 has a peak and then decreases, whereas K increases monotonically with Mach number. It may be recalled that the Mach number, at which C D0 has the peak value, depends mainly on the sweep of the wing. Fig.3.31 Drag polars at different Mach numbers for F15 (Reproduced from Ref.1.10, chapter 2 with permission from McGraw-Hill book company) Please note: The origins for polars corresponding to different Mach numbers are shifted. Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 5
6 Fig.3.32a Typical variations of C D0 with Mach number for a fighter airplane Fig.3.32b Typical variations of K with Mach number for a fighter airplane Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 6
7 3.3.7 Area ruling The plan view of supersonic airplanes indicates that the area of cross section of fuselage is decreased in the region where wing is located. This is called area ruling. A brief note on this topic is presented below. It was observed that the transonic wave drag of an airplane is reduced when the distribution of the area of cross section of the airplane, in planes perpendicular to the flow direction, has a smooth variation. In this context, it may be added that the area of cross section of the fuselage generally varies smoothly. However, when the wing is encountered there is an abrupt change in the cross sectional area. This abrupt change is alleviated by reduction in the area of cross section of fuselage in the region where the wing is located. Such a fuselage shape is called Coke-bottle shape. Figure 3.33c illustrates such a modification of fuselage shape. Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 7
8 Fig.3.33 Design for low transonic wave drag (a) Abrupt change in cross sectional area at wing fuselage junction (b) Coke-bottle shape Figure 3.34, based on data in Ref.1.9, chapter 5, indicates the maximum wave drag coefficient, in transonic range, for three configurations viz (i) a body of revolution (ii) a wing-body combination without area ruling and (iii) a wing-body combination with area ruling (Ref. 1.9, chapter 5 may be referred to for further details). Substantial decrease in wave drag coefficient is observed as a result of area ruling. Figure presents a practical application of this principle. Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 8
9 C DWave = Fig.3.34 Maximum transonic wave drag coefficient of three different shapes (a) body of revolution (b) wing-body combination without area ruling (c) wingbody combination with area ruling Fig.3.35 An example of area ruling - SAAB VIGGEN (Adapted from Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 9
10 3.4 Drag polar at hypersonic speeds When the free stream Mach number is more than five, the changes in temperature and pressure behind the shock waves are large and the treatment of the flow has to be different from that at lower Mach numbers. Hence, the flows with Mach number greater than five are termed hypersonic flows. Reference 3.19 may be referred to for details. For the purpose of flight mechanics it may be mentioned that the drag polar at hypersonic speeds is given by the following modified expression (Ref. 1.1, chapter 6). C D = C (M) + K (M)C 3/2 D0 (3.52) L Note that the exponent of the C L term is 1.5 and not Lift to drag ratio The ratio C L / C D is called lift to drag ratio. It is an indicator of the aerodynamic efficiency of the design of the airplane. For a parabolic drag polar C L / C D can be worked out as follows. C D = C D0 +KC L 2 Hence, C D / C L = (C D0 / C L ) +KC L (3.53) Differentiating Eq.(3.53) with C L and equating to zero gives C Lmd which corresponds to minimum of (C D / C L ) or maximum of (C L / C D ). C Lmd = (C D0 / K)1/2 (3.54) C Dmd = C D0 + K (C Lmd ) 2 = 2 C D0 (3.55) (L/D) max = (C Lmd / C Dmd ) = 1 2 C K D0 (3.56) Note: To show that C Lmd corresponds to minimum of (C / C D ), take the second L derivative of the right hand side of Eq.(3.53) and verify that it is greater than zero. 3.6 Other types of drag Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 10
11 Subsections 3.1.1, 3.2.2, , and dealt with the skin friction drag, pressure drag (or form drag), profile drag, interference drag, parasite drag, induced drag, lift dependent drag and wave drag. Following additional types of drags are mentioned briefly to conclude the discussion on this topic Cooling drag The piston engines used in airplanes are air cooled engines. In such engines, a part of free stream air passes over the cooling fins and accessories. This causes some loss of momentum and results in a drag called cooling drag Base drag If the rear end of a body terminates abruptly, the area at the rear is called a base. An abrupt ending causes flow to separate and a low pressure region exists over the base. This causes a pressure drag called base drag External stores drag Presence of external fuel tank, bombs, missiles etc. causes additional parasite drag which is called external stores drag. Antennas, lights etc. also cause parasite drag which is called protuberance drag Leakage drag Air leaking into and out of gaps and holes in the airplane surface causes increase in parasite drag called leakage drag Trim drag In example 1.1 it was shown that to balance the pitching moment about c.g. (M cg ), the horizontal tail which is located behind the wing produces a lift (- L T ) in the downward direction. To compensate for this, the wing needs to produce a lift (L W ) equal to the weight of the airplane plus the downward load on the tail i.e. L W = W + L. Hence, the induced drag of the wing, which depends on L T w, would be more than that when the lift equals weight. This additional drag is called trim drag as the action of making M cg equal to zero is referred to as trimming the airplane. It may be added that a canard surface is located ahead of the wing and the lift on it, to make M cg equal to zero, is in upward direction. Consequently, the lift Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 11
12 produced by the wing is less than the weight of the airplane. SAAB Viggen shown in Fig.3.35, is an example of an airplane with canard. Reference1.15 and internet ( may be consulted for details of this airplane. Dept. of Aerospace Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 12
Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required,
 Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required, minimum thrust required, minimum speed, maximum speed;
Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required, minimum thrust required, minimum speed, maximum speed;
Chapter 5 Lecture 19. Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3. Topics. Chapter-5
 Chapter 5 Lecture 19 Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3 Topics 5.8 Influence of level flight analysis on airplane design 5.9 Steady level flight performance with a given engine 5.10 Steady level
Chapter 5 Lecture 19 Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3 Topics 5.8 Influence of level flight analysis on airplane design 5.9 Steady level flight performance with a given engine 5.10 Steady level
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters 2 Lecture 20 Topics
 Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
9.4 Miscellaneous topics flight limitations, operating envelop and V-n diagram Flight limitations Operating envelop 9.4.
 Chapter 9 Lecture 31 Performance analysis V Manoeuvres 4 Topics 9.4 Miscellaneous topics flight limitations, operating envelop and V-n diagram 9.4.1 Flight limitations 9.4.2 Operating envelop 9.4.3 V-n
Chapter 9 Lecture 31 Performance analysis V Manoeuvres 4 Topics 9.4 Miscellaneous topics flight limitations, operating envelop and V-n diagram 9.4.1 Flight limitations 9.4.2 Operating envelop 9.4.3 V-n
Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide 2
 Chapter 6 Lecture Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide Topics 6.5 Maximum rate of climb and imum angle of climb 6.5. Parameters influencing (R/C) of a jet airplane 6.5. Parameters influencing
Chapter 6 Lecture Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide Topics 6.5 Maximum rate of climb and imum angle of climb 6.5. Parameters influencing (R/C) of a jet airplane 6.5. Parameters influencing
Chapter 8 Performance analysis IV Accelerated level flight and climb (Lecture 27) Keywords: Topics 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Accelerated level flight
 Chapter 8 Performance analysis I Accelerated level flight and climb (Lecture 7) Keywords: Accelerated level flight; accelerated climb; energy height. Topics 8.1 Introduction 8. Accelerated level flight
Chapter 8 Performance analysis I Accelerated level flight and climb (Lecture 7) Keywords: Accelerated level flight; accelerated climb; energy height. Topics 8.1 Introduction 8. Accelerated level flight
MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag. G. Leng, MDTS, NUS
 MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag 2.1. The design of supersonic airfoils For efficient lift generation at subsonic speeds, airfoils look like : So why can t a similar
MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag 2.1. The design of supersonic airfoils For efficient lift generation at subsonic speeds, airfoils look like : So why can t a similar
Chapter 1 Lecture 2. Introduction 2. Topics. Chapter-1
 Chapter 1 Lecture 2 Introduction 2 Topics 1.4 Equilibrium of airplane 1.5 Number of equations of motion for airplane in flight 1.5.1 Degrees of freedom 1.5.2 Degrees of freedom for a rigid airplane 1.6
Chapter 1 Lecture 2 Introduction 2 Topics 1.4 Equilibrium of airplane 1.5 Number of equations of motion for airplane in flight 1.5.1 Degrees of freedom 1.5.2 Degrees of freedom for a rigid airplane 1.6
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics. Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017
 AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
Definitions. Temperature: Property of the atmosphere (τ). Function of altitude. Pressure: Property of the atmosphere (p). Function of altitude.
 Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Chapter 3 Lecture 8. Drag polar 3. Topics. Chapter-3
 Chapter 3 ecture 8 Drag polar 3 Topics 3.2.7 Boundary layer separation, adverse pressure gradient and favourable pressure gradient 3.2.8 Boundary layer transition 3.2.9 Turbulent boundary layer over a
Chapter 3 ecture 8 Drag polar 3 Topics 3.2.7 Boundary layer separation, adverse pressure gradient and favourable pressure gradient 3.2.8 Boundary layer transition 3.2.9 Turbulent boundary layer over a
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics. Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015
 AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40)
 APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40 E.G. TULAPURKARA YASHKUMAR A. VENKATTRAMAN REPORT NO: AE TR 2007-3 APRIL 2007 (REVISED NOVEMBER
APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40 E.G. TULAPURKARA YASHKUMAR A. VENKATTRAMAN REPORT NO: AE TR 2007-3 APRIL 2007 (REVISED NOVEMBER
Chapter 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 7 Lecture 15 Topics
 Chapter 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 7 Lecture 15 Topics 4.12 Introductory remarks on choice of engine 4.13 Engines considered for airplane applications 4.14 Piston engine-propeller
Chapter 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 7 Lecture 15 Topics 4.12 Introductory remarks on choice of engine 4.13 Engines considered for airplane applications 4.14 Piston engine-propeller
Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide 3
 Chapter 6 Lecture 3 Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide 3 Topics 6.6. Climb hydrograph 6.7. Absolute ceiling and service ceiling 6.8 Time to climb 6.9 Steady descent 6.0 Glide 6.0.
Chapter 6 Lecture 3 Performance analysis II Steady climb, descent and glide 3 Topics 6.6. Climb hydrograph 6.7. Absolute ceiling and service ceiling 6.8 Time to climb 6.9 Steady descent 6.0 Glide 6.0.
Chapter 1 Introduction (Lectures 1,2 and 3)
 Chapter 1 Introduction (Lectures 1,2 and 3) Keywords : Importance of stability and control analysis ; brief historical background ; basic concepts static stability, dynamic stability, longitudinal, lateral
Chapter 1 Introduction (Lectures 1,2 and 3) Keywords : Importance of stability and control analysis ; brief historical background ; basic concepts static stability, dynamic stability, longitudinal, lateral
DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum
 DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum SEMESTER I AS5010 Engg. Aerodyn. & Flt. Mech. 3 0 0 3 AS5020 Elements of Gas Dyn. & Propln. 3 0 0 3 AS5030 Aircraft and Aerospace Structures
DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum SEMESTER I AS5010 Engg. Aerodyn. & Flt. Mech. 3 0 0 3 AS5020 Elements of Gas Dyn. & Propln. 3 0 0 3 AS5030 Aircraft and Aerospace Structures
Drag Computation (1)
 Drag Computation (1) Why drag so concerned Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase ( C D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be
Drag Computation (1) Why drag so concerned Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase ( C D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be
Aircraft stability and control Prof: A. K. Ghosh Dept of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Aircraft stability and control Prof: A. K. Ghosh Dept of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture- 05 Stability: Tail Contribution and Static Margin (Refer Slide Time: 00:15)
Aircraft stability and control Prof: A. K. Ghosh Dept of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture- 05 Stability: Tail Contribution and Static Margin (Refer Slide Time: 00:15)
Airfoils and Wings. Eugene M. Cliff
 Airfoils and Wings Eugene M. Cliff 1 Introduction The primary purpose of these notes is to supplement the text material related to aerodynamic forces. We are mainly interested in the forces on wings and
Airfoils and Wings Eugene M. Cliff 1 Introduction The primary purpose of these notes is to supplement the text material related to aerodynamic forces. We are mainly interested in the forces on wings and
Drag (2) Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag
 Drag () Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Multiple Lifting Surfaces Zero Lift Drag :Friction and Form Drag Supersonic
Drag () Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Multiple Lifting Surfaces Zero Lift Drag :Friction and Form Drag Supersonic
MDTS 5734 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 1 : Characteristics of high speed flight. G. Leng, MDTS, NUS
 MDTS 5734 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 1 : Characteristics of high speed flight References Jack N. Nielsen, Missile Aerodynamics, AIAA Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics, v104, 1986 Michael
MDTS 5734 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 1 : Characteristics of high speed flight References Jack N. Nielsen, Missile Aerodynamics, AIAA Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics, v104, 1986 Michael
To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag
 Drag Drag Bookkeeping Drag may be divided into components in several ways: To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag To emphasize the
Drag Drag Bookkeeping Drag may be divided into components in several ways: To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag To emphasize the
Chapter 2 Lecture 7 Longitudinal stick fixed static stability and control 4 Topics
 hapter 2 Lecture 7 Longitudinal stick ixed static stability and control 4 Topics 2.4.6 Revised expression or mcgt 2.4.7 mαt in stick-ixed case 2.5 ontributions o uselage to mcg and mα 2.5.1 ontribution
hapter 2 Lecture 7 Longitudinal stick ixed static stability and control 4 Topics 2.4.6 Revised expression or mcgt 2.4.7 mαt in stick-ixed case 2.5 ontributions o uselage to mcg and mα 2.5.1 ontribution
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
Mechanics of Flight. Warren F. Phillips. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY
 Mechanics of Flight Warren F. Phillips Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Inc. CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments xi xiii 1. Overview of Aerodynamics
Mechanics of Flight Warren F. Phillips Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Inc. CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments xi xiii 1. Overview of Aerodynamics
Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics
 David G. Hull Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics With 125 Figures and 25 Tables y Springer Introduction to Airplane Flight Mechanics 1 1.1 Airframe Anatomy 2 1.2 Engine Anatomy 5 1.3 Equations of
David G. Hull Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics With 125 Figures and 25 Tables y Springer Introduction to Airplane Flight Mechanics 1 1.1 Airframe Anatomy 2 1.2 Engine Anatomy 5 1.3 Equations of
Supersonic Aerodynamics. Methods and Applications
 Supersonic Aerodynamics Methods and Applications Outline Introduction to Supersonic Flow Governing Equations Numerical Methods Aerodynamic Design Applications Introduction to Supersonic Flow What does
Supersonic Aerodynamics Methods and Applications Outline Introduction to Supersonic Flow Governing Equations Numerical Methods Aerodynamic Design Applications Introduction to Supersonic Flow What does
Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments
 Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments The lifting surfaces of a vehicle generally include the wings, the horizontal and vertical tail, and other surfaces such
Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments The lifting surfaces of a vehicle generally include the wings, the horizontal and vertical tail, and other surfaces such
Flight Dynamics and Control. Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege
 Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Previously on AERO0003-1 We developed linearized equations of motion Longitudinal direction
Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Previously on AERO0003-1 We developed linearized equations of motion Longitudinal direction
Compressible Potential Flow: The Full Potential Equation. Copyright 2009 Narayanan Komerath
 Compressible Potential Flow: The Full Potential Equation 1 Introduction Recall that for incompressible flow conditions, velocity is not large enough to cause density changes, so density is known. Thus
Compressible Potential Flow: The Full Potential Equation 1 Introduction Recall that for incompressible flow conditions, velocity is not large enough to cause density changes, so density is known. Thus
Drag Analysis of a Supermarine. Spitfire Mk V at Cruise Conditions
 Introduction to Flight Aircraft Drag Project April 2016 2016 Drag Analysis of a Supermarine Spitfire Mk V at Cruise Conditions Nicholas Conde nicholasconde@gmail.com U66182304 Introduction to Flight Nicholas
Introduction to Flight Aircraft Drag Project April 2016 2016 Drag Analysis of a Supermarine Spitfire Mk V at Cruise Conditions Nicholas Conde nicholasconde@gmail.com U66182304 Introduction to Flight Nicholas
An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond
 An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond Antony Jameson Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV AIAA Paper 2007-0037
An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond Antony Jameson Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV AIAA Paper 2007-0037
Configuration Aerodynamics
 Configuration Aerodynamics William H. Mason Virginia Tech Blacksburg, VA The front cover of the brochure describing the French Exhibit at the Montreal Expo, 1967. January 2018 W.H. Mason CONTENTS i CONTENTS
Configuration Aerodynamics William H. Mason Virginia Tech Blacksburg, VA The front cover of the brochure describing the French Exhibit at the Montreal Expo, 1967. January 2018 W.H. Mason CONTENTS i CONTENTS
The Importance of drag
 Drag Computation The Importance of drag Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase (ΔC D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be taken
Drag Computation The Importance of drag Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase (ΔC D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be taken
The polar for uncambered and cambered airfoils. The angel of attack α
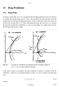 13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
RESEARCH MEMORANDUM FUGHT CHARACTERSSTICS OF A WINGIZSS ROCKET-POWERED MODEL WITH FOUR EXTERNALLY MOUNTED AIR-TO-APR MISSILES,$ Langley.Field, Va.
 3 1176 6 693 i RESEARCH MEMORANDUM FUGHT CHARACTERSSTCS OF A WNGZSS ROCKET-POWERED MODEL 'r- WTH FOUR EXTERNALLY MOUNTED AR-TO-APR MSSLES,$ AT MACH NUMBERS FROM.7 TO 1.6 By Allen B. Henning and Clarence
3 1176 6 693 i RESEARCH MEMORANDUM FUGHT CHARACTERSSTCS OF A WNGZSS ROCKET-POWERED MODEL 'r- WTH FOUR EXTERNALLY MOUNTED AR-TO-APR MSSLES,$ AT MACH NUMBERS FROM.7 TO 1.6 By Allen B. Henning and Clarence
Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations. W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class
 Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class Transonic Aerodynamics History Pre WWII propeller tip speeds limited airplane speed Props did encounter
Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class Transonic Aerodynamics History Pre WWII propeller tip speeds limited airplane speed Props did encounter
Flight Vehicle Terminology
 Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Missile Interceptor EXTROVERT ADVANCED CONCEPT EXPLORATION ADL P Ryan Donnan, Herman Ryals
 EXTROVERT ADVANCED CONCEPT EXPLORATION ADL P- 2011121203 Ryan Donnan, Herman Ryals Georgia Institute of Technology School of Aerospace Engineering Missile Interceptor December 12, 2011 EXTROVERT ADVANCED
EXTROVERT ADVANCED CONCEPT EXPLORATION ADL P- 2011121203 Ryan Donnan, Herman Ryals Georgia Institute of Technology School of Aerospace Engineering Missile Interceptor December 12, 2011 EXTROVERT ADVANCED
Air Loads. Airfoil Geometry. Upper surface. Lower surface
 AE1 Jha Loads-1 Air Loads Airfoil Geometry z LE circle (radius) Chord line Upper surface thickness Zt camber Zc Zl Zu Lower surface TE thickness Camber line line joining the midpoints between upper and
AE1 Jha Loads-1 Air Loads Airfoil Geometry z LE circle (radius) Chord line Upper surface thickness Zt camber Zc Zl Zu Lower surface TE thickness Camber line line joining the midpoints between upper and
F-35: A case study. Eugene Heim Leifur Thor Leifsson Evan Neblett. AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Virginia Tech April 2003
 F-35: A case study Eugene Heim Leifur Thor Leifsson Evan Neblett AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Virginia Tech April 2003 Course: AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Project: A case study of the F-35
F-35: A case study Eugene Heim Leifur Thor Leifsson Evan Neblett AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Virginia Tech April 2003 Course: AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Project: A case study of the F-35
LONGITUDINAL STABILITY AND TRIM OF AN ARIANE 5 FLY-BACK BOOSTER
 12th AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies 1-19 December 23, Norfolk, Virginia AIAA 23-7 LONGITUDINAL STABILITY AND TRIM OF AN ARIANE FLY-BACK BOOSTER Th. Eggers DLR,
12th AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies 1-19 December 23, Norfolk, Virginia AIAA 23-7 LONGITUDINAL STABILITY AND TRIM OF AN ARIANE FLY-BACK BOOSTER Th. Eggers DLR,
High Speed Aerodynamics. Copyright 2009 Narayanan Komerath
 Welcome to High Speed Aerodynamics 1 Lift, drag and pitching moment? Linearized Potential Flow Transformations Compressible Boundary Layer WHAT IS HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS? Airfoil section? Thin airfoil
Welcome to High Speed Aerodynamics 1 Lift, drag and pitching moment? Linearized Potential Flow Transformations Compressible Boundary Layer WHAT IS HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS? Airfoil section? Thin airfoil
Applied Aerodynamics - I
 Applied Aerodynamics - I o Course Contents (Tentative) Introductory Thoughts Historical Perspective Flow Similarity Aerodynamic Coefficients Sources of Aerodynamic Forces Fundamental Equations & Principles
Applied Aerodynamics - I o Course Contents (Tentative) Introductory Thoughts Historical Perspective Flow Similarity Aerodynamic Coefficients Sources of Aerodynamic Forces Fundamental Equations & Principles
Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows
 Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows Prandtl-Glauert-Goethert Transformation Potential equation: 1 If we choose and Laplace eqn. The transformation has stretched the x co-ordinate by 2 Values of at corresponding
Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows Prandtl-Glauert-Goethert Transformation Potential equation: 1 If we choose and Laplace eqn. The transformation has stretched the x co-ordinate by 2 Values of at corresponding
Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes Boeing Commercial Airplane Group, Seattle, Washington, 98124
 AIAA--2007-0684 Pressures and Drag Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near Sonic Speeds Including the Effects of Viscosity and Wind Tunnel Walls Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig
AIAA--2007-0684 Pressures and Drag Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near Sonic Speeds Including the Effects of Viscosity and Wind Tunnel Walls Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig
An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond
 45 th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, January 8 11, 2007, Reno, Nevada An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond Antony Jameson Department of Aeronautics
45 th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, January 8 11, 2007, Reno, Nevada An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond Antony Jameson Department of Aeronautics
Aerodynamics Simulation of Hypersonic Waverider Vehicle
 Modern Applied Science February, 9 Aerodynamics Simulation of Hypersonic Waverider Vehicle Dingyi Wu & Hong Xiao School of Power and Energy Northwestern Polytechnical University PO box 85, Xian, Shaanxi,
Modern Applied Science February, 9 Aerodynamics Simulation of Hypersonic Waverider Vehicle Dingyi Wu & Hong Xiao School of Power and Energy Northwestern Polytechnical University PO box 85, Xian, Shaanxi,
DRAG PREDICTION AND VALIDATION OF STANDARD M549, 155mm PROJECTILE
 DRAG PREDICTION AND VALIDATION OF STANDARD M549, 155mm PROJECTILE 1 Kiran Torangatti, 2 Dr.Basawaraj 1 Research Scholar, Department of Aerospace Propulsion and Technology, VTU-CPGS Bangalore -560018,Karnataka,
DRAG PREDICTION AND VALIDATION OF STANDARD M549, 155mm PROJECTILE 1 Kiran Torangatti, 2 Dr.Basawaraj 1 Research Scholar, Department of Aerospace Propulsion and Technology, VTU-CPGS Bangalore -560018,Karnataka,
Lecture1: Characteristics of Hypersonic Atmosphere
 Module 1: Hypersonic Atmosphere Lecture1: Characteristics of Hypersonic Atmosphere 1.1 Introduction Hypersonic flight has special traits, some of which are seen in every hypersonic flight. Presence of
Module 1: Hypersonic Atmosphere Lecture1: Characteristics of Hypersonic Atmosphere 1.1 Introduction Hypersonic flight has special traits, some of which are seen in every hypersonic flight. Presence of
Aircraft Performance, Stability and control with experiments in Flight. Questions
 Aircraft Performance, Stability and control with experiments in Flight Questions Q. If only the elevator size of a given aircraft is decreased; keeping horizontal tail area unchanged; then the aircraft
Aircraft Performance, Stability and control with experiments in Flight Questions Q. If only the elevator size of a given aircraft is decreased; keeping horizontal tail area unchanged; then the aircraft
Sample question paper Model answers * AE 1301 Flight dynamics B.E./B.Tech Degree examination, November / December Anna University.
 Sample question paper Model answers * AE 1301 Flight dynamics B.E./B.Tech Degree examination, November / December 006. Anna University. Time: 3 hours Answer ALL questions Part A- (10 x = 0 marks) Maximum:
Sample question paper Model answers * AE 1301 Flight dynamics B.E./B.Tech Degree examination, November / December 006. Anna University. Time: 3 hours Answer ALL questions Part A- (10 x = 0 marks) Maximum:
AERO-STRUCTURAL MDO OF A SPAR-TANK-TYPE WING FOR AIRCRAFT CONCEPTUAL DESIGN
 1 26th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES AERO-STRUCTURAL MDO OF A SPAR-TANK-TYPE WING FOR AIRCRAFT CONCEPTUAL DESIGN Paulo R. Caixeta Jr., Álvaro M. Abdalla, Flávio D. Marques, Fernando
1 26th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES AERO-STRUCTURAL MDO OF A SPAR-TANK-TYPE WING FOR AIRCRAFT CONCEPTUAL DESIGN Paulo R. Caixeta Jr., Álvaro M. Abdalla, Flávio D. Marques, Fernando
Improved Method for Prediction of Attainable Wing Leading-Edge Thrust
 NASA Technical Paper 3557 Improved Method for Prediction of Attainable Wing Leading-Edge Thrust Harry W. Carlson Lockheed Engineering & Sciences Company Hampton, Virginia Marcus O. McElroy and Wendy B.
NASA Technical Paper 3557 Improved Method for Prediction of Attainable Wing Leading-Edge Thrust Harry W. Carlson Lockheed Engineering & Sciences Company Hampton, Virginia Marcus O. McElroy and Wendy B.
Compressible Flow. Professor Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer Spacecraft Propulsion Specialist
 Compressible Flow Professor Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer Spacecraft Propulsion Specialist What is Compressible Flow? Compressible Flow is a type of flow in which the density can not be treated as constant.
Compressible Flow Professor Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer Spacecraft Propulsion Specialist What is Compressible Flow? Compressible Flow is a type of flow in which the density can not be treated as constant.
Concept: AERODYNAMICS
 1 Concept: AERODYNAMICS 2 Narayanan Komerath 3 4 Keywords: Flow Potential Flow Lift, Drag, Dynamic Pressure, Irrotational, Mach Number, Reynolds Number, Incompressible 5 6 7 1. Definition When objects
1 Concept: AERODYNAMICS 2 Narayanan Komerath 3 4 Keywords: Flow Potential Flow Lift, Drag, Dynamic Pressure, Irrotational, Mach Number, Reynolds Number, Incompressible 5 6 7 1. Definition When objects
Rotor reference axis
 Rotor reference axis So far we have used the same reference axis: Z aligned with the rotor shaft Y perpendicular to Z and along the blade (in the rotor plane). X in the rotor plane and perpendicular do
Rotor reference axis So far we have used the same reference axis: Z aligned with the rotor shaft Y perpendicular to Z and along the blade (in the rotor plane). X in the rotor plane and perpendicular do
ME 6139: High Speed Aerodynamics
 Dr. A.B.M. Toufique Hasan Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, BUET Lecture-01 04 November 2017 teacher.buet.ac.bd/toufiquehasan/ toufiquehasan@me.buet.ac.bd 1 Aerodynamics is the study of dynamics
Dr. A.B.M. Toufique Hasan Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, BUET Lecture-01 04 November 2017 teacher.buet.ac.bd/toufiquehasan/ toufiquehasan@me.buet.ac.bd 1 Aerodynamics is the study of dynamics
Aircraft Stability and Control Prof. A.K.Ghosh Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institution of Technology-Kanpur
 Aircraft Stability and Control Prof. A.K.Ghosh Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institution of Technology-Kanpur Problems Stability Tail Contribution Completed We were trying to understand whatever
Aircraft Stability and Control Prof. A.K.Ghosh Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institution of Technology-Kanpur Problems Stability Tail Contribution Completed We were trying to understand whatever
Introduction to Atmospheric Flight. Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD)
 Introduction to Atmospheric Flight Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) What is Atmospheric Flight? There are many different ways in which Aerospace engineering is associated with atmospheric flight concepts.
Introduction to Atmospheric Flight Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) What is Atmospheric Flight? There are many different ways in which Aerospace engineering is associated with atmospheric flight concepts.
University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005
 University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005 Answer both questions. Question 1 is worth 30 marks and question
University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005 Answer both questions. Question 1 is worth 30 marks and question
Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD
 Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD http://www.aerospaceweb.org/aircraft/research/x35/pics.shtml David Hall Sangeon Chun David Andrews Center of Gravity Estimation.5873 Conventional
Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD http://www.aerospaceweb.org/aircraft/research/x35/pics.shtml David Hall Sangeon Chun David Andrews Center of Gravity Estimation.5873 Conventional
Development of a Wave Drag Prediction Tool for the Conceptual Design Phase
 Master of Science Thesis Development of a Wave Drag Prediction Tool for the Conceptual Design Phase July 14th, 15 Faculty of Aerospace Engineering - Delft University of Technology J. Vargas Development
Master of Science Thesis Development of a Wave Drag Prediction Tool for the Conceptual Design Phase July 14th, 15 Faculty of Aerospace Engineering - Delft University of Technology J. Vargas Development
Entry Aerodynamics MARYLAND U N I V E R S I T Y O F. Entry Aerodynamics. ENAE Launch and Entry Vehicle Design
 Atmospheric Regimes on Entry Basic fluid parameters Definition of Mean Free Path Rarified gas Newtonian flow Continuum Newtonian flow (hypersonics) 2014 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
Atmospheric Regimes on Entry Basic fluid parameters Definition of Mean Free Path Rarified gas Newtonian flow Continuum Newtonian flow (hypersonics) 2014 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
External Forced Convection. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 External Forced Convection Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Drag and Heat Transfer in External flow Fluid flow over solid bodies is responsible
External Forced Convection Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Drag and Heat Transfer in External flow Fluid flow over solid bodies is responsible
AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERIZATION OF A CANARD GUIDED ARTILLERY PROJECTILE
 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit 8-11 January 27, Reno, Nevada AIAA 27-672 AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERIZATION OF A CANARD GUIDED ARTILLERY PROJECTILE Wei-Jen Su 1, Curtis Wilson 2, Tony Farina
45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit 8-11 January 27, Reno, Nevada AIAA 27-672 AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERIZATION OF A CANARD GUIDED ARTILLERY PROJECTILE Wei-Jen Su 1, Curtis Wilson 2, Tony Farina
Technology of Rocket
 Technology of Rocket Parts of Rocket There are four major parts of rocket Structural system Propulsion system Guidance system Payload system Structural system The structural system of a rocket includes
Technology of Rocket Parts of Rocket There are four major parts of rocket Structural system Propulsion system Guidance system Payload system Structural system The structural system of a rocket includes
External Flow and Boundary Layer Concepts
 1 2 Lecture (8) on Fayoum University External Flow and Boundary Layer Concepts By Dr. Emad M. Saad Mechanical Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical
1 2 Lecture (8) on Fayoum University External Flow and Boundary Layer Concepts By Dr. Emad M. Saad Mechanical Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical
Experimental Aerodynamics. Experimental Aerodynamics
 Lecture 6: Slender Body Aerodynamics G. Dimitriadis Slender bodies! Wings are only one of the types of body that can be tested in a wind tunnel.! Although wings play a crucial role in aeronautical applications
Lecture 6: Slender Body Aerodynamics G. Dimitriadis Slender bodies! Wings are only one of the types of body that can be tested in a wind tunnel.! Although wings play a crucial role in aeronautical applications
FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS
 *A \ FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS Second Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Professor of Aerospace Engineering University of Maryland H ' McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas
*A \ FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS Second Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Professor of Aerospace Engineering University of Maryland H ' McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas
RECENT near-sonic and low-sonic boom transport aircraft
 JOURNAL OF AIRCRAFT Vol. 44, No. 6, November December 2007 Aerodynamic Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near-Sonic Speeds Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes The Boeing
JOURNAL OF AIRCRAFT Vol. 44, No. 6, November December 2007 Aerodynamic Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near-Sonic Speeds Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes The Boeing
Introduction to Flight
 l_ Introduction to Flight Fifth Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator for Aerodynamics, National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution Professor Emeritus University of Maryland Me Graw Higher Education
l_ Introduction to Flight Fifth Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator for Aerodynamics, National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution Professor Emeritus University of Maryland Me Graw Higher Education
Chapter 2 Earth s atmosphere (Lectures 4 and 5)
 Chapter 2 Earth s atmosphere (Lectures 4 and 5) Keywords: Earth s atmosphere; International standard atmosphere; geopotential altitude; stability of atmosphere. Topics 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Earth s atmosphere
Chapter 2 Earth s atmosphere (Lectures 4 and 5) Keywords: Earth s atmosphere; International standard atmosphere; geopotential altitude; stability of atmosphere. Topics 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Earth s atmosphere
What is the crack propagation rate for 7075-T6 aluminium alloy.
 - 130 - APPENDIX 4A 100 QUESTIONS BASED ON SOURCE DOCUMENTS LISTED IN APPENDIX 4B 20-06 Magnitude of reductions in heat transfer on the nose region of a body when ablation of the surface takes place. (PI2002)
- 130 - APPENDIX 4A 100 QUESTIONS BASED ON SOURCE DOCUMENTS LISTED IN APPENDIX 4B 20-06 Magnitude of reductions in heat transfer on the nose region of a body when ablation of the surface takes place. (PI2002)
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. #03 Jet Engine Basic Performance Parameters We are talking
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. #03 Jet Engine Basic Performance Parameters We are talking
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES
 ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BY AENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2016 Special 10(6): pages 79-88 Open Access Journal Effect of Variable
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BY AENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2016 Special 10(6): pages 79-88 Open Access Journal Effect of Variable
Transonic Flutter Prediction of Supersonic Jet Trainer with Various External Store Configurations
 Transonic Flutter Prediction of Supersonic Jet Trainer with Various External Store Configurations In Lee * Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, 305-701, Korea Hyuk-Jun Kwon Agency
Transonic Flutter Prediction of Supersonic Jet Trainer with Various External Store Configurations In Lee * Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, 305-701, Korea Hyuk-Jun Kwon Agency
the pitot static measurement equal to a constant C which is to take into account the effect of viscosity and so on.
 Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module -2 Lecture - 27 Measurement of Fluid Velocity We have been
Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module -2 Lecture - 27 Measurement of Fluid Velocity We have been
FLIGHT DYNAMICS. Robert F. Stengel. Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford
 FLIGHT DYNAMICS Robert F. Stengel Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford Preface XV Chapter One Introduction 1 1.1 ELEMENTS OF THE AIRPLANE 1 Airframe Components 1 Propulsion Systems 4 1.2 REPRESENTATIVE
FLIGHT DYNAMICS Robert F. Stengel Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford Preface XV Chapter One Introduction 1 1.1 ELEMENTS OF THE AIRPLANE 1 Airframe Components 1 Propulsion Systems 4 1.2 REPRESENTATIVE
Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows
 Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows Modo U. P, Chukwuneke J. L, Omenyi Sam 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka,
Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows Modo U. P, Chukwuneke J. L, Omenyi Sam 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka,
MODIFICATION OF AERODYNAMIC WING LOADS BY FLUIDIC DEVICES
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 21, No. 2 2014 MODIFICATION OF AERODYNAMIC WING LOADS BY FLUIDIC DEVICES Institute of Aviation Department of Aerodynamics and Flight Mechanics Krakowska
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 21, No. 2 2014 MODIFICATION OF AERODYNAMIC WING LOADS BY FLUIDIC DEVICES Institute of Aviation Department of Aerodynamics and Flight Mechanics Krakowska
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL
 24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL MR Soltani*, Ali R Davari** *Associate Professor, **PhD Student
24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL MR Soltani*, Ali R Davari** *Associate Professor, **PhD Student
Trim 2D. Holly Lewis University of Colorado Center for Aerospace Structures April 29, 2004
 rim D Holly Lewis University of Colorado Center for Aerospace Structures April 9 004 Overview rimming an Aircraft in D Forces and Moments AERO-rimD Assumptions Capabilities Results Conclusions Future wor
rim D Holly Lewis University of Colorado Center for Aerospace Structures April 9 004 Overview rimming an Aircraft in D Forces and Moments AERO-rimD Assumptions Capabilities Results Conclusions Future wor
Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I
 Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I Current Catalog Data: AE 3610 Aerodynamics I Credit: 4 hours A study of incompressible aerodynamics of flight vehicles with emphasis on combined application of theory
Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I Current Catalog Data: AE 3610 Aerodynamics I Credit: 4 hours A study of incompressible aerodynamics of flight vehicles with emphasis on combined application of theory
Nose Cone & Fin Optimization
 Nose Cone & Fin Optimization Tripoli Minnesota Gary Stroick January 2011 Purpose Focus is on drag optimization to maximize rocket performance! Copyright 2011 by Off We Go Rocketry 2 Agenda Definitions
Nose Cone & Fin Optimization Tripoli Minnesota Gary Stroick January 2011 Purpose Focus is on drag optimization to maximize rocket performance! Copyright 2011 by Off We Go Rocketry 2 Agenda Definitions
CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING
 28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING Sun Tae Kim*, Youngtae Kim**, Tae Kyu Reu* *Agency for Defense Development,
28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING Sun Tae Kim*, Youngtae Kim**, Tae Kyu Reu* *Agency for Defense Development,
Chapter 7: External Forced Convection
 Chapter 7: External Forced Convection Yoav Peles Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Chapter 7: External Forced Convection Yoav Peles Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
/ m U) β - r dr/dt=(n β / C) β+ (N r /C) r [8+8] (c) Effective angle of attack. [4+6+6]
![/ m U) β - r dr/dt=(n β / C) β+ (N r /C) r [8+8] (c) Effective angle of attack. [4+6+6] / m U) β - r dr/dt=(n β / C) β+ (N r /C) r [8+8] (c) Effective angle of attack. [4+6+6]](/thumbs/91/105418625.jpg) Code No: R05322101 Set No. 1 1. (a) Explain the following terms with examples i. Stability ii. Equilibrium. (b) Comment upon the requirements of stability of a i. Military fighter aircraft ii. Commercial
Code No: R05322101 Set No. 1 1. (a) Explain the following terms with examples i. Stability ii. Equilibrium. (b) Comment upon the requirements of stability of a i. Military fighter aircraft ii. Commercial
WALL ROUGHNESS EFFECTS ON SHOCK BOUNDARY LAYER INTERACTION FLOWS
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
EFFECT OF ATMOSPHERIC ALTITUDE ON THE DRAG OF WING AT SUBSONIC AND SUPERSONIC SPEEDS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 6 th EURECA 2016 Special Issue May (2017) 71-83 School of Engineering, Taylor s University EFFECT OF ATMOSPHERIC ALTITUDE ON THE DRAG OF WING AT SUBSONIC AND
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 6 th EURECA 2016 Special Issue May (2017) 71-83 School of Engineering, Taylor s University EFFECT OF ATMOSPHERIC ALTITUDE ON THE DRAG OF WING AT SUBSONIC AND
ACTIVE CONTROL OF BASE PRESSURE IN SUDDENLY EXPANDED FLOW FOR AREA RATIO 4.84
 ACTIVE CONTROL OF BASE PRESSURE IN SUDDENLY EXPANDED FLOW FOR AREA RATIO 4.84 MAUGHAL AHMED ALI BAIG Research Scholar Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad, A.P, India & Assistant Professor,
ACTIVE CONTROL OF BASE PRESSURE IN SUDDENLY EXPANDED FLOW FOR AREA RATIO 4.84 MAUGHAL AHMED ALI BAIG Research Scholar Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad, A.P, India & Assistant Professor,
Transonic Tunnel Tests on a 6% Thick, Warped 5S Sweptback-Wing Model
 L R. & M. No. 3385 MINISTRY OF AVIATION AERONAUTICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL REPORTS AND MEMORANDA Transonic Tunnel Tests on a 6% Thick, Warped 5S Sweptback-Wing Model By A. B. HAINES, B.Sc., and J. C. M. JONES,
L R. & M. No. 3385 MINISTRY OF AVIATION AERONAUTICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL REPORTS AND MEMORANDA Transonic Tunnel Tests on a 6% Thick, Warped 5S Sweptback-Wing Model By A. B. HAINES, B.Sc., and J. C. M. JONES,
4 Compressible Fluid Dynamics
 4 Compressible Fluid Dynamics 4. Compressible flow definitions Compressible flow describes the behaviour of fluids that experience significant variations in density under the application of external pressures.
4 Compressible Fluid Dynamics 4. Compressible flow definitions Compressible flow describes the behaviour of fluids that experience significant variations in density under the application of external pressures.
Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Topic 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1 Flow Past a Circular Cylinder Re = 10,000 and Mach approximately zero Mach = 0.45 Mach = 0.64 Pictures are from An Album of Fluid Motion by Van Dyke Flow Past
Topic 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1 Flow Past a Circular Cylinder Re = 10,000 and Mach approximately zero Mach = 0.45 Mach = 0.64 Pictures are from An Album of Fluid Motion by Van Dyke Flow Past
I. Introduction. external compression. supersonic flow. II. Design Criteria
 Design Optimization of High Speed Inlets Doyle D Knight Dept of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Rutgers - The State University of New Jersey New Brunswick, NJ 08903 knight@soemailrutgersedu I Introduction
Design Optimization of High Speed Inlets Doyle D Knight Dept of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Rutgers - The State University of New Jersey New Brunswick, NJ 08903 knight@soemailrutgersedu I Introduction
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 Introduction to Aerospace Engineering 5. Aircraft Performance 5.1 Equilibrium Flight In order to discuss performance, stability, and control, we must first establish the concept of equilibrium flight.
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering 5. Aircraft Performance 5.1 Equilibrium Flight In order to discuss performance, stability, and control, we must first establish the concept of equilibrium flight.
= 390 ( R). Then, for a given edge Mach number, M e., and ratio of wall temperature to adiabatic wall temperature T W = T W. T AW = T e 2 M e 2
 D-32 Applied Computational Aerodynamics D.5 Program FRICTION FRICTION provides an estimate of laminar and turbulent skin friction suitable for use in aircraft preliminary design. It is an entirely new
D-32 Applied Computational Aerodynamics D.5 Program FRICTION FRICTION provides an estimate of laminar and turbulent skin friction suitable for use in aircraft preliminary design. It is an entirely new
Royal Aeronautical Society 2016 Applied Aerodynamics Conference Tuesday 19 th Thursday 21 st July Science Centre, Bristol, UK
 Assessment and validation of aerodynamic performance results for a Natural Laminar Flow transonic wing tested in cryogenic conditions via simulation of turbulent wedges in CFD. Royal Aeronautical Society
Assessment and validation of aerodynamic performance results for a Natural Laminar Flow transonic wing tested in cryogenic conditions via simulation of turbulent wedges in CFD. Royal Aeronautical Society
