APPENDIX 2. Semiempirical PM3 (Parametrization Method #3) When analytical solutions cannot be obtained, Schrödinger equation may be solved:
|
|
|
- MargaretMargaret Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WRNING NOTICE: The experiments described in these materials are potentially hazardous and require a high level of safety training, special facilities and equipment, and supervision by appropriate individuals. You bear the sole responsibility, liability, and risk for the implementation of such safety procedures and measures. MIT shall have no responsibility, liability, or risk for the content or implementation of any of the material presented. Legal Notice PPENDIX Semiempirical PM3 (Parametrization Method #3). Background information. When analytical solutions cannot be obtained, Schrödinger equation may be solved: (i) (ii) (iii) Numerically. By approximation procedures (perturbation theory, variation theory). The method of self-consistent field (SCF). PM3 is a semiempirical (see below) method that uses parameters from experimental data to simplify calculation. b initio computational methods are based solely on the laws of quantum mechanics and physical constants such as Planck constant, masses and charges of electrons and nuclei and on the speed of light. The SCF method was created by Douglass Hartree and further developed by Vladimir Fock. Molecular orbitals are expressed as a linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCO) : N Φ i = åcµiχµ µ= Φ i are molecular orbitals () Cµi molecular expansion coefficien ts χµ are atomic orbitals The Hartree-Fock and LCO approximations applied to the electronic Schrödinger equation, lead to Roothan-Hall equations: å(f µ - ε i S µ )C i = 0 () In matrix form () can be re-written as: The usual notation convention: Roman subscripts on molecular orbital functions and Greek subscripts on basis functions (pre-defined set such as for, example, atomic orbitals).
2 FC = SCε () F is the Fock matrix (analogous to Hamiltonian in the Schrödinger equation) For closed systems, Fock matrix elements are: where: N N F µ H µ ååp λσ [( )- ( )] (3) λ = σ = H µ is a matrix representing the energy of a single electron in the field of the. In semiempirical methods the is defined as the nuclei and nonvalence electrons. The valence electrons are assumed to move in the potential field of the. H µ = χ µ () H χ () ; H () = - - M Z å ; Z is the atomic number of atom. = r P λσ is the density matrix. The molecular expansion coefficients are summed only over the double occupied molecular orbitals (number in front of summation): occupied MOs * λi i = P λσ = åc C σi (4) The quantities ( ) are two-electron repulsion integrals (representing the coulombic interaction between the cloud of electron and cloud of electron ) χ µ ()χ () χ λ ()χ () dv òò σ r The quantities ( ) are two-electron exchange integrals. It represents the correction required for the Coulomb integral to take into effect the spin correlation. For two electrons with the same spin, the true average repulsion energy will be less than the value of Coulomb integral, because such electrons avoid each other: òò χ ()χ () χ µ σ λ ()χ () dv r S is the overlap matrix; its elements are given by S mn = χ µ () χ () is a diagonal matrix of orbital energies with elements i, the one-electron orbital energy. The Roothan-Hall equations are not linear. The Fock matrix depends on the molecular orbital coefficients, through the density matrix. Its solution requires an iterative process. To begin the calculation, we must pick a preliminary set of wave functions to calculate the Fock operator, for example, wave functions from extended ll electrons are paired.
3 Hückel type methods. In the first cycle a new set of orbitals are generated which become the the starting orbitals for the second cycle. The cycle is repeated until the set of orbitals going through the cycle are returned unchanged. The orbitals are then self-consistent, hence the acronym SCF. The Unrestricted Hartree-Fock method (UHF) allows more freedom because it permits the spatial form of the orbital to depend upon whether the electron has an a or a b spin. B. PM3 method. 3 The two electron repulsion integrals ( ) and ( ) cause most of the trouble. These integrals are particularly difficult to evaluate if the atomic functions c m, etc. are centered on different atoms. The central approximation to reduce the overall computation is to not permit the overlap of atomic orbitals residing on different atomic centers, for example, by a assuming ( )= ms ln ( ). Here ms and ln (Kronecker s delta) equal when the subscripts are equal; otherwise they are zero. Consequently, all three- and four-centers integrals are ignored, as well as two- and onecenter integrals where different atomic orbitals are involved in either of two electrons. In other words, the central approximation to the reduce overall computation is to presume that atomic orbitals residing on different atomic centers do not overlap: ò χ µ χ σ dv = 0. very popular semiempirical, MNDO (modified neglect of diatomic overlap) method was published in 977 by Dewar and Thiel. 4 The second generation of MNDO has been termed M (ustin method #), while the third generation MNDO-PM3, or in short PM3 (parametric method 3). PM3 includes atoms with d orbitals. Parameters for transition metals are based on reproducing known geometries. C. Heat of formation calculation. (You ll use this in.3) The heat of formation of any compound from its elements in their standard state is obtained by adding to the electronic plus nuclear energy, the calculated energy of formation of the gaseous atom from its ion, (E el ()) and the experimental heat of formation for atom, DH f (): DH f = E + E + å E el () + å DH () ee nr f Calculation of the heat of formation: the case of the CH : tomization energy is: E atom =- -E totch + E C + E H = *.90676=7.73 ev=67.7 kcal mol -. 3 Stewart, J. J. P., J. Computer-ided Mol. Design 990, 4,. 4 Dewar, M. J.; Thiel, W. J. m. Chem. Soc. 977, 99, Dewar, M. J.; Zoebisch, E. G.; Healy, E. F.; Stewart, J. J. P. J. m. Chem. Soc. 98, 07,
4 Heat of formation: DH f(c) + * DH f(h) )-E atom = = kcal mol - 4
5 D. Solutions of the self-consistent equations: Read the intial geometry Initial guess at P mn Compute Fock matrix Solve matrix equation Form density matrix Calculate energy No Energy and/or density matrix has converged? Yes Population analysis Finished
The successful wavefunction can be written as a determinant: # 1 (2) # 2 (2) Electrons. This can be generalized to our 2N-electron wavefunction:
 T2. CNDO to AM1: The Semiempirical Molecular Orbital Models The discussion in sections T2.1 T2.3 applies also to ab initio molecular orbital calculations. T2.1 Slater Determinants Consider the general
T2. CNDO to AM1: The Semiempirical Molecular Orbital Models The discussion in sections T2.1 T2.3 applies also to ab initio molecular orbital calculations. T2.1 Slater Determinants Consider the general
AN INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM CHEMISTRY. Mark S. Gordon Iowa State University
 AN INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM CHEMISTRY Mark S. Gordon Iowa State University 1 OUTLINE Theoretical Background in Quantum Chemistry Overview of GAMESS Program Applications 2 QUANTUM CHEMISTRY In principle,
AN INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM CHEMISTRY Mark S. Gordon Iowa State University 1 OUTLINE Theoretical Background in Quantum Chemistry Overview of GAMESS Program Applications 2 QUANTUM CHEMISTRY In principle,
Chem 4502 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi. Lecture 28, December 08, 2014
 Chem 4502 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi Lecture 28, December 08, 2014 Solved Homework Water, H 2 O, involves 2 hydrogen atoms and an oxygen
Chem 4502 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi Lecture 28, December 08, 2014 Solved Homework Water, H 2 O, involves 2 hydrogen atoms and an oxygen
Computational Methods. Chem 561
 Computational Methods Chem 561 Lecture Outline 1. Ab initio methods a) HF SCF b) Post-HF methods 2. Density Functional Theory 3. Semiempirical methods 4. Molecular Mechanics Computational Chemistry " Computational
Computational Methods Chem 561 Lecture Outline 1. Ab initio methods a) HF SCF b) Post-HF methods 2. Density Functional Theory 3. Semiempirical methods 4. Molecular Mechanics Computational Chemistry " Computational
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi. Lecture 27, December 5, 2014
 Chem 4502 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi Lecture 27, December 5, 2014 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C. J.
Chem 4502 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi Lecture 27, December 5, 2014 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C. J.
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules
 CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules Lecture 5 The Hartree-Fock method C.-K. Skylaris Learning outcomes Be able to use the variational principle in quantum calculations Be able to construct Fock operators
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules Lecture 5 The Hartree-Fock method C.-K. Skylaris Learning outcomes Be able to use the variational principle in quantum calculations Be able to construct Fock operators
Semiempirical Molecular Orbital Theory
 Semiempirical Molecular Orbital Theory Slater- determinantal wave func:ons and artree- Fock theory Video III.iv Constructing a 1-Electron Wave Function The units of the wave function are such that its
Semiempirical Molecular Orbital Theory Slater- determinantal wave func:ons and artree- Fock theory Video III.iv Constructing a 1-Electron Wave Function The units of the wave function are such that its
Introduction to Hartree-Fock Molecular Orbital Theory
 Introduction to Hartree-Fock Molecular Orbital Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology Origins of Mathematical Modeling in Chemistry Plato (ca. 428-347
Introduction to Hartree-Fock Molecular Orbital Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology Origins of Mathematical Modeling in Chemistry Plato (ca. 428-347
Lecture 5: More about one- Final words about the Hartree-Fock theory. First step above it by the Møller-Plesset perturbation theory.
 Lecture 5: More about one- determinant wave functions Final words about the Hartree-Fock theory. First step above it by the Møller-Plesset perturbation theory. Items from Lecture 4 Could the Koopmans theorem
Lecture 5: More about one- determinant wave functions Final words about the Hartree-Fock theory. First step above it by the Møller-Plesset perturbation theory. Items from Lecture 4 Could the Koopmans theorem
Lecture 4: Hartree-Fock Theory
 Lecture 4: Hartree-Fock Theory One determinant to rule them all, One determinant to find them, One determinant to bring them all and in the darkness bind them Second quantization rehearsal The formalism
Lecture 4: Hartree-Fock Theory One determinant to rule them all, One determinant to find them, One determinant to bring them all and in the darkness bind them Second quantization rehearsal The formalism
Same idea for polyatomics, keep track of identical atom e.g. NH 3 consider only valence electrons F(2s,2p) H(1s)
 XIII 63 Polyatomic bonding -09 -mod, Notes (13) Engel 16-17 Balance: nuclear repulsion, positive e-n attraction, neg. united atom AO ε i applies to all bonding, just more nuclei repulsion biggest at low
XIII 63 Polyatomic bonding -09 -mod, Notes (13) Engel 16-17 Balance: nuclear repulsion, positive e-n attraction, neg. united atom AO ε i applies to all bonding, just more nuclei repulsion biggest at low
Session 1. Introduction to Computational Chemistry. Computational (chemistry education) and/or (Computational chemistry) education
 Session 1 Introduction to Computational Chemistry 1 Introduction to Computational Chemistry Computational (chemistry education) and/or (Computational chemistry) education First one: Use computational tools
Session 1 Introduction to Computational Chemistry 1 Introduction to Computational Chemistry Computational (chemistry education) and/or (Computational chemistry) education First one: Use computational tools
Yingwei Wang Computational Quantum Chemistry 1 Hartree energy 2. 2 Many-body system 2. 3 Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2
 Purdue University CHM 67300 Computational Quantum Chemistry REVIEW Yingwei Wang October 10, 2013 Review: Prof Slipchenko s class, Fall 2013 Contents 1 Hartree energy 2 2 Many-body system 2 3 Born-Oppenheimer
Purdue University CHM 67300 Computational Quantum Chemistry REVIEW Yingwei Wang October 10, 2013 Review: Prof Slipchenko s class, Fall 2013 Contents 1 Hartree energy 2 2 Many-body system 2 3 Born-Oppenheimer
APPENDIX 1 Version of 8/24/05 11:01 AM Simulation of H-NMR without a structure*:
 WARNING NOTICE: The experiments described in these materials are potentially hazardous and require a high level of safety training, special facilities and equipment, and supervision by appropriate individuals.
WARNING NOTICE: The experiments described in these materials are potentially hazardous and require a high level of safety training, special facilities and equipment, and supervision by appropriate individuals.
Molecular Simulation I
 Molecular Simulation I Quantum Chemistry Classical Mechanics E = Ψ H Ψ ΨΨ U = E bond +E angle +E torsion +E non-bond Jeffry D. Madura Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry Center for Computational Sciences
Molecular Simulation I Quantum Chemistry Classical Mechanics E = Ψ H Ψ ΨΨ U = E bond +E angle +E torsion +E non-bond Jeffry D. Madura Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry Center for Computational Sciences
Quantum Chemical Simulations and Descriptors. Dr. Antonio Chana, Dr. Mosè Casalegno
 Quantum Chemical Simulations and Descriptors Dr. Antonio Chana, Dr. Mosè Casalegno Classical Mechanics: basics It models real-world objects as point particles, objects with negligible size. The motion
Quantum Chemical Simulations and Descriptors Dr. Antonio Chana, Dr. Mosè Casalegno Classical Mechanics: basics It models real-world objects as point particles, objects with negligible size. The motion
Semi-Empirical MO Methods
 Semi-Empirical MO Methods the high cost of ab initio MO calculations is largely due to the many integrals that need to be calculated (esp. two electron integrals) semi-empirical MO methods start with the
Semi-Empirical MO Methods the high cost of ab initio MO calculations is largely due to the many integrals that need to be calculated (esp. two electron integrals) semi-empirical MO methods start with the
Electronic structure theory: Fundamentals to frontiers. 1. Hartree-Fock theory
 Electronic structure theory: Fundamentals to frontiers. 1. Hartree-Fock theory MARTIN HEAD-GORDON, Department of Chemistry, University of California, and Chemical Sciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley National
Electronic structure theory: Fundamentals to frontiers. 1. Hartree-Fock theory MARTIN HEAD-GORDON, Department of Chemistry, University of California, and Chemical Sciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley National
One-Electron Hamiltonians
 One-Electron Hamiltonians Hartree-Fock and Density Func7onal Theory Christopher J. Cramer @ChemProfCramer 2017 MSSC, July 10, 2017 REVIEW A One-Slide Summary of Quantum Mechanics Fundamental Postulate:
One-Electron Hamiltonians Hartree-Fock and Density Func7onal Theory Christopher J. Cramer @ChemProfCramer 2017 MSSC, July 10, 2017 REVIEW A One-Slide Summary of Quantum Mechanics Fundamental Postulate:
Electronic structure calculations: fundamentals George C. Schatz Northwestern University
 Electronic structure calculations: fundamentals George C. Schatz Northwestern University Electronic Structure (often called Quantum Chemistry) calculations use quantum mechanics to determine the wavefunctions
Electronic structure calculations: fundamentals George C. Schatz Northwestern University Electronic Structure (often called Quantum Chemistry) calculations use quantum mechanics to determine the wavefunctions
CHEM6085: Density Functional Theory Lecture 10
 CHEM6085: Density Functional Theory Lecture 10 1) Spin-polarised calculations 2) Geometry optimisation C.-K. Skylaris 1 Unpaired electrons So far we have developed Kohn-Sham DFT for the case of paired
CHEM6085: Density Functional Theory Lecture 10 1) Spin-polarised calculations 2) Geometry optimisation C.-K. Skylaris 1 Unpaired electrons So far we have developed Kohn-Sham DFT for the case of paired
Close agreement between the orientation dependence of hydrogen bonds observed in protein structures and quantum mechanical calculations
 Close agreement between the orientation dependence of hydrogen bonds observed in protein structures and quantum mechanical calculations Alexandre V. Morozov, Tanja Kortemme, Kiril Tsemekhman, David Baker
Close agreement between the orientation dependence of hydrogen bonds observed in protein structures and quantum mechanical calculations Alexandre V. Morozov, Tanja Kortemme, Kiril Tsemekhman, David Baker
3: Many electrons. Orbital symmetries. l =2 1. m l
 3: Many electrons Orbital symmetries Atomic orbitals are labelled according to the principal quantum number, n, and the orbital angular momentum quantum number, l. Electrons in a diatomic molecule experience
3: Many electrons Orbital symmetries Atomic orbitals are labelled according to the principal quantum number, n, and the orbital angular momentum quantum number, l. Electrons in a diatomic molecule experience
Introduction to Computational Chemistry Computational (chemistry education) and/or. (Computational chemistry) education
 Introduction to Computational Chemistry Computational (chemistry education) and/or (Computational chemistry) education First one: Use computational tools to help increase student understanding of material
Introduction to Computational Chemistry Computational (chemistry education) and/or (Computational chemistry) education First one: Use computational tools to help increase student understanding of material
Semi-Empirical Methods CHEM 430
 Semi-Empirical Methods CHEM 430 Cost, Hartree%Fock, scales,as,n 4,(N=#, basis,funcfons), Due,to,two% electron, integrals, within,fock, matrix, Semi%empirical,cut, cost,by,reducing, number,of, integrals,
Semi-Empirical Methods CHEM 430 Cost, Hartree%Fock, scales,as,n 4,(N=#, basis,funcfons), Due,to,two% electron, integrals, within,fock, matrix, Semi%empirical,cut, cost,by,reducing, number,of, integrals,
On the Uniqueness of Molecular Orbitals and limitations of the MO-model.
 On the Uniqueness of Molecular Orbitals and limitations of the MO-model. The purpose of these notes is to make clear that molecular orbitals are a particular way to represent many-electron wave functions.
On the Uniqueness of Molecular Orbitals and limitations of the MO-model. The purpose of these notes is to make clear that molecular orbitals are a particular way to represent many-electron wave functions.
DFT calculations of NMR indirect spin spin coupling constants
 DFT calculations of NMR indirect spin spin coupling constants Dalton program system Program capabilities Density functional theory Kohn Sham theory LDA, GGA and hybrid theories Indirect NMR spin spin coupling
DFT calculations of NMR indirect spin spin coupling constants Dalton program system Program capabilities Density functional theory Kohn Sham theory LDA, GGA and hybrid theories Indirect NMR spin spin coupling
Born-Oppenheimer Approximation
 Born-Oppenheimer Approximation Adiabatic Assumption: Nuclei move so much more slowly than electron that the electrons that the electrons are assumed to be obtained if the nuclear kinetic energy is ignored,
Born-Oppenheimer Approximation Adiabatic Assumption: Nuclei move so much more slowly than electron that the electrons that the electrons are assumed to be obtained if the nuclear kinetic energy is ignored,
Quantum mechanics can be used to calculate any property of a molecule. The energy E of a wavefunction Ψ evaluated for the Hamiltonian H is,
 Chapter : Molecules Quantum mechanics can be used to calculate any property of a molecule The energy E of a wavefunction Ψ evaluated for the Hamiltonian H is, E = Ψ H Ψ Ψ Ψ 1) At first this seems like
Chapter : Molecules Quantum mechanics can be used to calculate any property of a molecule The energy E of a wavefunction Ψ evaluated for the Hamiltonian H is, E = Ψ H Ψ Ψ Ψ 1) At first this seems like
Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory
 Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology June 2002 Last Revised: June 2003 1 Introduction The purpose of these
Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology June 2002 Last Revised: June 2003 1 Introduction The purpose of these
Lecture 4: methods and terminology, part II
 So theory guys have got it made in rooms free of pollution. Instead of problems with the reflux, they have only solutions... In other words, experimentalists will likely die of cancer From working hard,
So theory guys have got it made in rooms free of pollution. Instead of problems with the reflux, they have only solutions... In other words, experimentalists will likely die of cancer From working hard,
Chem 442 Review for Exam 2. Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative (3D) components.
 Chem 44 Review for Exam Hydrogenic atoms: The Coulomb energy between two point charges Ze and e: V r Ze r Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative
Chem 44 Review for Exam Hydrogenic atoms: The Coulomb energy between two point charges Ze and e: V r Ze r Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative
Hartree-Fock-Roothan Self-Consistent Field Method
 Hartree-Fock-Roothan Self-Consistent Field Method 1. Helium Here is a summary of the derivation of the Hartree-Fock equations presented in class. First consider the ground state of He and start with with
Hartree-Fock-Roothan Self-Consistent Field Method 1. Helium Here is a summary of the derivation of the Hartree-Fock equations presented in class. First consider the ground state of He and start with with
This is called a singlet or spin singlet, because the so called multiplicity, or number of possible orientations of the total spin, which is
 9. Open shell systems The derivation of Hartree-Fock equations (Chapter 7) was done for a special case of a closed shell systems. Closed shell means that each MO is occupied by two electrons with the opposite
9. Open shell systems The derivation of Hartree-Fock equations (Chapter 7) was done for a special case of a closed shell systems. Closed shell means that each MO is occupied by two electrons with the opposite
LUMO + 1 LUMO. Tómas Arnar Guðmundsson Report 2 Reikniefnafræði G
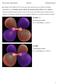 Q1: Display all the MOs for N2 in your report and classify each one of them as bonding, antibonding or non-bonding, and say whether the symmetry of the orbital is σ or π. Sketch a molecular orbital diagram
Q1: Display all the MOs for N2 in your report and classify each one of them as bonding, antibonding or non-bonding, and say whether the symmetry of the orbital is σ or π. Sketch a molecular orbital diagram
Lecture 10. Born-Oppenheimer approximation LCAO-MO application to H + The potential energy surface MOs for diatomic molecules. NC State University
 Chemistry 431 Lecture 10 Diatomic molecules Born-Oppenheimer approximation LCAO-MO application to H + 2 The potential energy surface MOs for diatomic molecules NC State University Born-Oppenheimer approximation
Chemistry 431 Lecture 10 Diatomic molecules Born-Oppenheimer approximation LCAO-MO application to H + 2 The potential energy surface MOs for diatomic molecules NC State University Born-Oppenheimer approximation
VALENCE Hilary Term 2018
 VALENCE Hilary Term 2018 8 Lectures Prof M. Brouard Valence is the theory of the chemical bond Outline plan 1. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Bonding in H + 2 the LCAO approximation 3. Many electron
VALENCE Hilary Term 2018 8 Lectures Prof M. Brouard Valence is the theory of the chemical bond Outline plan 1. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Bonding in H + 2 the LCAO approximation 3. Many electron
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY FOR TRANSITION METALS
 QUANTUM CHEMISTRY FOR TRANSITION METALS Outline I Introduction II Correlation Static correlation effects MC methods DFT III Relativity Generalities From 4 to 1 components Effective core potential Outline
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY FOR TRANSITION METALS Outline I Introduction II Correlation Static correlation effects MC methods DFT III Relativity Generalities From 4 to 1 components Effective core potential Outline
Introduction to Hartree-Fock calculations in Spartan
 EE5 in 2008 Hannes Jónsson Introduction to Hartree-Fock calculations in Spartan In this exercise, you will get to use state of the art software for carrying out calculations of wavefunctions for molecues,
EE5 in 2008 Hannes Jónsson Introduction to Hartree-Fock calculations in Spartan In this exercise, you will get to use state of the art software for carrying out calculations of wavefunctions for molecues,
Chemistry 334 Part 2: Computational Quantum Chemistry
 Chemistry 334 Part 2: Computational Quantum Chemistry 1. Definition Louis Scudiero, Ben Shepler and Kirk Peterson Washington State University January 2006 Computational chemistry is an area of theoretical
Chemistry 334 Part 2: Computational Quantum Chemistry 1. Definition Louis Scudiero, Ben Shepler and Kirk Peterson Washington State University January 2006 Computational chemistry is an area of theoretical
PAPER :8, PHYSICAL SPECTROSCOPY MODULE: 29, MOLECULAR TERM SYMBOLS AND SELECTION RULES FOR DIATOMIC MOLECULES
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 8: Physical Spectroscopy 29: Molecular Term Symbols and Selection Rules for Diatomic Molecules. CHE_P8_M29 TLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 8: Physical Spectroscopy 29: Molecular Term Symbols and Selection Rules for Diatomic Molecules. CHE_P8_M29 TLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning
Quantum Chemistry. NC State University. Lecture 5. The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy
 Quantum Chemistry Lecture 5 The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy NC State University 3.5 Selective absorption and emission by atmospheric gases (source:
Quantum Chemistry Lecture 5 The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy NC State University 3.5 Selective absorption and emission by atmospheric gases (source:
Section 3 Electronic Configurations, Term Symbols, and States
 Section 3 Electronic Configurations, Term Symbols, and States Introductory Remarks- The Orbital, Configuration, and State Pictures of Electronic Structure One of the goals of quantum chemistry is to allow
Section 3 Electronic Configurations, Term Symbols, and States Introductory Remarks- The Orbital, Configuration, and State Pictures of Electronic Structure One of the goals of quantum chemistry is to allow
Handbook of Computational Quantum Chemistry. DAVID B. COOK The Department of Chemistry, University of Sheffield
 Handbook of Computational Quantum Chemistry DAVID B. COOK The Department of Chemistry, University of Sheffield Oxford New York Tokyo OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1998 CONTENTS 1 Mechanics and molecules 1 1.1
Handbook of Computational Quantum Chemistry DAVID B. COOK The Department of Chemistry, University of Sheffield Oxford New York Tokyo OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1998 CONTENTS 1 Mechanics and molecules 1 1.1
2 Electronic structure theory
 Electronic structure theory. Generalities.. Born-Oppenheimer approximation revisited In Sec..3 (lecture 3) the Born-Oppenheimer approximation was introduced (see also, for instance, [Tannor.]). We are
Electronic structure theory. Generalities.. Born-Oppenheimer approximation revisited In Sec..3 (lecture 3) the Born-Oppenheimer approximation was introduced (see also, for instance, [Tannor.]). We are
Part III: The Nuclear Many-Body Problem
 Part III: The Nuclear Many-Body Problem To understand the properties of complex nuclei from first principles Microscopic Valence- Space Interactions Model spaces Many-body perturbation theory (MBPT) Calculating
Part III: The Nuclear Many-Body Problem To understand the properties of complex nuclei from first principles Microscopic Valence- Space Interactions Model spaces Many-body perturbation theory (MBPT) Calculating
MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES
 MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES 6. The theory of molecular orbitals for the description of nanosystems (part II) 6.0. Ab initio methods. Basis functions. Luis A. Monte ro Firmado digitalmente por Luis A.
MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES 6. The theory of molecular orbitals for the description of nanosystems (part II) 6.0. Ab initio methods. Basis functions. Luis A. Monte ro Firmado digitalmente por Luis A.
Electric properties of molecules
 Electric properties of molecules For a molecule in a uniform electric fielde the Hamiltonian has the form: Ĥ(E) = Ĥ + E ˆµ x where we assume that the field is directed along the x axis and ˆµ x is the
Electric properties of molecules For a molecule in a uniform electric fielde the Hamiltonian has the form: Ĥ(E) = Ĥ + E ˆµ x where we assume that the field is directed along the x axis and ˆµ x is the
Spin-Orbit Interactions in Nuclei and Hypernuclei
 Ab-Initio Nuclear Structure Bad Honnef July 29, 2008 Spin-Orbit Interactions in Nuclei and Hypernuclei Wolfram Weise Phenomenology Aspects of Chiral Dynamics and Spin-Orbit Forces Nuclei vs. -Hypernuclei:
Ab-Initio Nuclear Structure Bad Honnef July 29, 2008 Spin-Orbit Interactions in Nuclei and Hypernuclei Wolfram Weise Phenomenology Aspects of Chiral Dynamics and Spin-Orbit Forces Nuclei vs. -Hypernuclei:
EXAM INFORMATION. Radial Distribution Function: B is the normalization constant. d dx. p 2 Operator: Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle:
 EXAM INFORMATION Radial Distribution Function: P() r RDF() r Br R() r B is the normalization constant., p Operator: p ^ d dx Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: n ax n! Integrals: xe dx n1 a x p Particle
EXAM INFORMATION Radial Distribution Function: P() r RDF() r Br R() r B is the normalization constant., p Operator: p ^ d dx Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: n ax n! Integrals: xe dx n1 a x p Particle
Lecture 5. Hartree-Fock Theory. WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Lecture 5 Hartree-Fock Theory WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Particle-number representation: General formalism The simplest starting point for a many-body state is a system of
Lecture 5 Hartree-Fock Theory WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Particle-number representation: General formalism The simplest starting point for a many-body state is a system of
Molecular Orbitals for Ozone
 Molecular Orbitals for Ozone Purpose: In this exercise you will do semi-empirical molecular orbital calculations on ozone with the goal of understanding the molecular orbital print out provided by Spartan
Molecular Orbitals for Ozone Purpose: In this exercise you will do semi-empirical molecular orbital calculations on ozone with the goal of understanding the molecular orbital print out provided by Spartan
Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods VI: more modifications to the NDDO approximations and re-optimization of parameters
 J Mol Model (2013) 19:1 32 DOI 10.1007/s00894-012-1667-x ORIGINAL PAPER Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods VI: more modifications to the NDDO approximations and re-optimization of parameters
J Mol Model (2013) 19:1 32 DOI 10.1007/s00894-012-1667-x ORIGINAL PAPER Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods VI: more modifications to the NDDO approximations and re-optimization of parameters
5.61 Physical Chemistry Final Exam 12/16/09. MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Chemistry Chemistry Physical Chemistry
 5.6 Physical Chemistry Final Exam 2/6/09 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Chemistry Chemistry - 5.6 Physical Chemistry Final Examination () PRINT your name on the cover page. (2) It
5.6 Physical Chemistry Final Exam 2/6/09 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Chemistry Chemistry - 5.6 Physical Chemistry Final Examination () PRINT your name on the cover page. (2) It
Chem 1140; Molecular Modeling
 P. Wipf 1 Chem 1140 $E = -! (q a + q b )" ab S ab + ab!k
P. Wipf 1 Chem 1140 $E = -! (q a + q b )" ab S ab + ab!k
1.2 Rare earth atoms H Ψ=E Ψ, (1.2.1) where the non-relativistic Hamiltonian operator is. H = h2 2m. v ext (r i ) (1.2.
 8 1. ELEMENTS OF RARE EARTH MAGNETISM 1.2 Rare earth atoms The starting point for the understanding of the magnetism of the rare earths is the description of the electronic states, particularly of the
8 1. ELEMENTS OF RARE EARTH MAGNETISM 1.2 Rare earth atoms The starting point for the understanding of the magnetism of the rare earths is the description of the electronic states, particularly of the
0 belonging to the unperturbed Hamiltonian H 0 are known
 Time Independent Perturbation Theory D Perturbation theory is used in two qualitatively different contexts in quantum chemistry. It allows one to estimate (because perturbation theory is usually employed
Time Independent Perturbation Theory D Perturbation theory is used in two qualitatively different contexts in quantum chemistry. It allows one to estimate (because perturbation theory is usually employed
A One-Slide Summary of Quantum Mechanics
 A One-Slide Summary of Quantum Mechanics Fundamental Postulate: O! = a! What is!?! is an oracle! operator wave function (scalar) observable Where does! come from?! is refined Variational Process H! = E!
A One-Slide Summary of Quantum Mechanics Fundamental Postulate: O! = a! What is!?! is an oracle! operator wave function (scalar) observable Where does! come from?! is refined Variational Process H! = E!
Theoretical Chemistry - Level II - Practical Class Molecular Orbitals in Diatomics
 Theoretical Chemistry - Level II - Practical Class Molecular Orbitals in Diatomics Problem 1 Draw molecular orbital diagrams for O 2 and O 2 +. E / ev dioxygen molecule, O 2 dioxygenyl cation, O 2 + 25
Theoretical Chemistry - Level II - Practical Class Molecular Orbitals in Diatomics Problem 1 Draw molecular orbital diagrams for O 2 and O 2 +. E / ev dioxygen molecule, O 2 dioxygenyl cation, O 2 + 25
Handbook of Computational Quantum Chemistry
 Handbook of Computational Quantum Chemistry David B. Cook Dept. of Chemistry University of Sheffield DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. Mineola, New York F Contents 1 Mechanics and molecules 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5
Handbook of Computational Quantum Chemistry David B. Cook Dept. of Chemistry University of Sheffield DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. Mineola, New York F Contents 1 Mechanics and molecules 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules
 CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules Lecture 4 Molecular orbitals C.-K. Skylaris Learning outcomes Be able to manipulate expressions involving spin orbitals and molecular orbitals Be able to write down
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules Lecture 4 Molecular orbitals C.-K. Skylaris Learning outcomes Be able to manipulate expressions involving spin orbitals and molecular orbitals Be able to write down
University of Michigan Physics Department Graduate Qualifying Examination
 Name: University of Michigan Physics Department Graduate Qualifying Examination Part II: Modern Physics Saturday 17 May 2014 9:30 am 2:30 pm Exam Number: This is a closed book exam, but a number of useful
Name: University of Michigan Physics Department Graduate Qualifying Examination Part II: Modern Physics Saturday 17 May 2014 9:30 am 2:30 pm Exam Number: This is a closed book exam, but a number of useful
Lecture 9. Hartree Fock Method and Koopman s Theorem
 Lecture 9 Hartree Fock Method and Koopman s Theorem Ψ(N) is approximated as a single slater determinant Φ of N orthogonal One electron spin-orbitals. One electron orbital φ i = φ i (r) χ i (σ) χ i (σ)
Lecture 9 Hartree Fock Method and Koopman s Theorem Ψ(N) is approximated as a single slater determinant Φ of N orthogonal One electron spin-orbitals. One electron orbital φ i = φ i (r) χ i (σ) χ i (σ)
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules
 CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules Lecture 3 The Born-Oppenheimer approximation C.-K. Skylaris Learning outcomes Separate molecular Hamiltonians to electronic and nuclear parts according to the Born-Oppenheimer
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules Lecture 3 The Born-Oppenheimer approximation C.-K. Skylaris Learning outcomes Separate molecular Hamiltonians to electronic and nuclear parts according to the Born-Oppenheimer
ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF MAGNESIUM OXIDE
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(3), 2010, 1749-1756 ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF MAGNESIUM OXIDE P. N. PIYUSH and KANCHAN LATA * Department of Chemistry, B. N. M. V. College, Sahugarh, MADHIPUR (Bihar) INDIA ABSTRACT
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(3), 2010, 1749-1756 ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF MAGNESIUM OXIDE P. N. PIYUSH and KANCHAN LATA * Department of Chemistry, B. N. M. V. College, Sahugarh, MADHIPUR (Bihar) INDIA ABSTRACT
Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics
 Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics A Virtual Laboratory by Milad Hobbi Mobarhan Thesis for the degree of Master of Science Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences University of Oslo June 2014 cba This work
Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics A Virtual Laboratory by Milad Hobbi Mobarhan Thesis for the degree of Master of Science Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences University of Oslo June 2014 cba This work
AB INITIO METHODS IN COMPUTATIONAL QUANTUM CHEMISTRY
 AB INITIO METHODS IN COMPUTATIONAL QUANTUM CHEMISTRY Aneesh. M.H A theoretical study on the regioselectivity of electrophilic reactions of heterosubstituted allyl systems Thesis. Department of Chemistry,
AB INITIO METHODS IN COMPUTATIONAL QUANTUM CHEMISTRY Aneesh. M.H A theoretical study on the regioselectivity of electrophilic reactions of heterosubstituted allyl systems Thesis. Department of Chemistry,
Chemistry 3502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2003 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 25, November 5, 2003
 Chemistry 3502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2003 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 25, November 5, 2003 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Chemistry 3502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2003 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 25, November 5, 2003 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy
 Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy Molecular Orbital Theory: A Review - LCAO approximaton & AO overlap - Variation Principle & Secular Determinant - Homonuclear Diatomic MOs - Energy Levels, Bond Order
Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy Molecular Orbital Theory: A Review - LCAO approximaton & AO overlap - Variation Principle & Secular Determinant - Homonuclear Diatomic MOs - Energy Levels, Bond Order
Lecture 6. Fermion Pairing. WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Lecture 6 Fermion Pairing WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Experimental indications for Cooper-Pairing Solid state physics: Pairing of electrons near the Fermi surface with antiparallel
Lecture 6 Fermion Pairing WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Experimental indications for Cooper-Pairing Solid state physics: Pairing of electrons near the Fermi surface with antiparallel
Conical Intersections. Spiridoula Matsika
 Conical Intersections Spiridoula Matsika The Born-Oppenheimer approximation Energy TS Nuclear coordinate R ν The study of chemical systems is based on the separation of nuclear and electronic motion The
Conical Intersections Spiridoula Matsika The Born-Oppenheimer approximation Energy TS Nuclear coordinate R ν The study of chemical systems is based on the separation of nuclear and electronic motion The
Lecture 15 From molecules to solids
 Lecture 15 From molecules to solids Background In the last two lectures, we explored quantum mechanics of multi-electron atoms the subject of atomic physics. In this lecture, we will explore how these
Lecture 15 From molecules to solids Background In the last two lectures, we explored quantum mechanics of multi-electron atoms the subject of atomic physics. In this lecture, we will explore how these
Answers Quantum Chemistry NWI-MOL406 G. C. Groenenboom and G. A. de Wijs, HG00.307, 8:30-11:30, 21 jan 2014
 Answers Quantum Chemistry NWI-MOL406 G. C. Groenenboom and G. A. de Wijs, HG00.307, 8:30-11:30, 21 jan 2014 Question 1: Basis sets Consider the split valence SV3-21G one electron basis set for formaldehyde
Answers Quantum Chemistry NWI-MOL406 G. C. Groenenboom and G. A. de Wijs, HG00.307, 8:30-11:30, 21 jan 2014 Question 1: Basis sets Consider the split valence SV3-21G one electron basis set for formaldehyde
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 17, March 1, 2006
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 17, March 1, 2006 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C. J.
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 17, March 1, 2006 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C. J.
We can keep track of the mixing of the 2s and 2p orbitals in beryllium as follows:
 We can keep track of the mixing of the 2s and 2p orbitals in beryllium as follows: The beryllium sp orbitals overlap with hydrogen Is orbitals (the hydrogen's electrons are shown in the above orbital diagram
We can keep track of the mixing of the 2s and 2p orbitals in beryllium as follows: The beryllium sp orbitals overlap with hydrogen Is orbitals (the hydrogen's electrons are shown in the above orbital diagram
AM1/d Parameters for Magnesium in Metalloenzymes
 1050 J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 1050-1056 AM1/d Parameters for Magnesium in Metalloenzymes Petra Imhof, Frank Noé, Stefan Fischer, and Jeremy C. Smith*, Computational Molecular Biophysics and Computational
1050 J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 1050-1056 AM1/d Parameters for Magnesium in Metalloenzymes Petra Imhof, Frank Noé, Stefan Fischer, and Jeremy C. Smith*, Computational Molecular Biophysics and Computational
Application of electrostatic Solvent Models to the Electronic Spectrum of Mesityl Oxide
 Journal of Basrah Researches ((Sciences Volume 38. Number 1. ((2012 vailable online at: www.basra-science journal.org 2695 1817 ISSN pplication of electrostatic Solvent Models to the Electronic Spectrum
Journal of Basrah Researches ((Sciences Volume 38. Number 1. ((2012 vailable online at: www.basra-science journal.org 2695 1817 ISSN pplication of electrostatic Solvent Models to the Electronic Spectrum
Solid State Theory: Band Structure Methods
 Solid State Theory: Band Structure Methods Lilia Boeri Wed., 11:15-12:45 HS P3 (PH02112) http://itp.tugraz.at/lv/boeri/ele/ Plan of the Lecture: DFT1+2: Hohenberg-Kohn Theorem and Kohn and Sham equations.
Solid State Theory: Band Structure Methods Lilia Boeri Wed., 11:15-12:45 HS P3 (PH02112) http://itp.tugraz.at/lv/boeri/ele/ Plan of the Lecture: DFT1+2: Hohenberg-Kohn Theorem and Kohn and Sham equations.
Preliminary Quantum Questions
 Preliminary Quantum Questions Thomas Ouldridge October 01 1. Certain quantities that appear in the theory of hydrogen have wider application in atomic physics: the Bohr radius a 0, the Rydberg constant
Preliminary Quantum Questions Thomas Ouldridge October 01 1. Certain quantities that appear in the theory of hydrogen have wider application in atomic physics: the Bohr radius a 0, the Rydberg constant
Reactivity and Organocatalysis. (Adalgisa Sinicropi and Massimo Olivucci)
 Reactivity and Organocatalysis (Adalgisa Sinicropi and Massimo Olivucci) The Aldol Reaction - O R 1 O R 1 + - O O OH * * H R 2 R 1 R 2 The (1957) Zimmerman-Traxler Transition State Counterion (e.g. Li
Reactivity and Organocatalysis (Adalgisa Sinicropi and Massimo Olivucci) The Aldol Reaction - O R 1 O R 1 + - O O OH * * H R 2 R 1 R 2 The (1957) Zimmerman-Traxler Transition State Counterion (e.g. Li
The Overhauser Instability
 The Overhauser Instability Zoltán Radnai and Richard Needs TCM Group ESDG Talk 14th February 2007 Typeset by FoilTEX Introduction Hartree-Fock theory and Homogeneous Electron Gas Noncollinear spins and
The Overhauser Instability Zoltán Radnai and Richard Needs TCM Group ESDG Talk 14th February 2007 Typeset by FoilTEX Introduction Hartree-Fock theory and Homogeneous Electron Gas Noncollinear spins and
Walter Kohn was awarded with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1998 for his development of the density functional theory.
 Walter Kohn was awarded with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1998 for his development of the density functional theory. Walter Kohn receiving his Nobel Prize from His Majesty the King at the Stockholm
Walter Kohn was awarded with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1998 for his development of the density functional theory. Walter Kohn receiving his Nobel Prize from His Majesty the King at the Stockholm
Chem 452 Exam III April 8, Cover Sheet Closed Book, Closed Notes
 Last Name: First Name: PSU ID#: (last 4 digit) Chem 452 Exam III April 8, 2009 Cover Sheet Closed Book, Closed Notes There are 6 problems. The point value of each part of each problem is indicated. Useful
Last Name: First Name: PSU ID#: (last 4 digit) Chem 452 Exam III April 8, 2009 Cover Sheet Closed Book, Closed Notes There are 6 problems. The point value of each part of each problem is indicated. Useful
( ) + ( ) + ( ) = 0.00
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 32, April 14, 2006 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 32, April 14, 2006 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Physical Chemistry II Recommended Problems Chapter 12( 23)
 Physical Chemistry II Recommended Problems Chapter 1( 3) Chapter 1(3) Problem. Overlap of two 1s orbitals recprobchap1.odt 1 Physical Chemistry II Recommended Problems, Chapter 1(3), continued Chapter
Physical Chemistry II Recommended Problems Chapter 1( 3) Chapter 1(3) Problem. Overlap of two 1s orbitals recprobchap1.odt 1 Physical Chemistry II Recommended Problems, Chapter 1(3), continued Chapter
Quantum Mechanical Simulations
 Quantum Mechanical Simulations Prof. Yan Wang Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332, U.S.A. yan.wang@me.gatech.edu Topics Quantum Monte Carlo Hartree-Fock
Quantum Mechanical Simulations Prof. Yan Wang Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332, U.S.A. yan.wang@me.gatech.edu Topics Quantum Monte Carlo Hartree-Fock
( ( ; R H = 109,677 cm -1
 CHAPTER 9 Atomic Structure and Spectra I. The Hydrogenic Atoms (one electron species). H, He +1, Li 2+, A. Clues from Line Spectra. Reminder: fundamental equations of spectroscopy: ε Photon = hν relation
CHAPTER 9 Atomic Structure and Spectra I. The Hydrogenic Atoms (one electron species). H, He +1, Li 2+, A. Clues from Line Spectra. Reminder: fundamental equations of spectroscopy: ε Photon = hν relation
CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I
 CHEM-UA 7: Advanced General Chemistry I I. LINEAR COMBINATION OF ATOMIC ORBITALS Linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) is a simple method of quantum chemistry that yields a qualitative picture of
CHEM-UA 7: Advanced General Chemistry I I. LINEAR COMBINATION OF ATOMIC ORBITALS Linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) is a simple method of quantum chemistry that yields a qualitative picture of
Oslo node. Highly accurate calculations benchmarking and extrapolations
 Oslo node Highly accurate calculations benchmarking and extrapolations Torgeir Ruden, with A. Halkier, P. Jørgensen, J. Olsen, W. Klopper, J. Gauss, P. Taylor Explicitly correlated methods Pål Dahle, collaboration
Oslo node Highly accurate calculations benchmarking and extrapolations Torgeir Ruden, with A. Halkier, P. Jørgensen, J. Olsen, W. Klopper, J. Gauss, P. Taylor Explicitly correlated methods Pål Dahle, collaboration
Instructor background for the discussion points of Section 2
 Supplementary Information for: Orbitals Some fiction and some facts Jochen Autschbach Department of Chemistry State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY 14260 3000, USA Instructor background for
Supplementary Information for: Orbitals Some fiction and some facts Jochen Autschbach Department of Chemistry State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY 14260 3000, USA Instructor background for
SCF calculation on HeH +
 SCF calculation on HeH + Markus Meuwly Department of Chemistry, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland Abstract This document describes the main steps involved in carrying out a SCF calculation on the
SCF calculation on HeH + Markus Meuwly Department of Chemistry, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland Abstract This document describes the main steps involved in carrying out a SCF calculation on the
Simulation Methods II
 Simulation Methods II Maria Fyta Institute for Computational Physics Universität Stuttgart Summer Term 2018 SM II - contents First principles methods Hartree-Fock and beyond Density-funtional-theory Ab
Simulation Methods II Maria Fyta Institute for Computational Physics Universität Stuttgart Summer Term 2018 SM II - contents First principles methods Hartree-Fock and beyond Density-funtional-theory Ab
Lecture 30 Chapter 10 Sections 1-2. Orbital overlap = bonding Molecular orbitals Hybrid orbitals
 Lecture 30 Chapter 10 Sections 1-2 Orbital overlap = bonding Molecular orbitals Hybrid orbitals Announcements CAPA #17 due tomorrow Seminar Friday 3:00 Seminar Tuesday 11:00 Bond Lengths and Energies Bond
Lecture 30 Chapter 10 Sections 1-2 Orbital overlap = bonding Molecular orbitals Hybrid orbitals Announcements CAPA #17 due tomorrow Seminar Friday 3:00 Seminar Tuesday 11:00 Bond Lengths and Energies Bond
Be H. Delocalized Bonding. Localized Bonding. σ 2. σ 1. Two (sp-1s) Be-H σ bonds. The two σ bonding MO s in BeH 2. MO diagram for BeH 2
 The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
Exchange Mechanisms. Erik Koch Institute for Advanced Simulation, Forschungszentrum Jülich. lecture notes:
 Exchange Mechanisms Erik Koch Institute for Advanced Simulation, Forschungszentrum Jülich lecture notes: www.cond-mat.de/events/correl Magnetism is Quantum Mechanical QUANTUM MECHANICS THE KEY TO UNDERSTANDING
Exchange Mechanisms Erik Koch Institute for Advanced Simulation, Forschungszentrum Jülich lecture notes: www.cond-mat.de/events/correl Magnetism is Quantum Mechanical QUANTUM MECHANICS THE KEY TO UNDERSTANDING
4πε. me 1,2,3,... 1 n. H atom 4. in a.u. atomic units. energy: 1 a.u. = ev distance 1 a.u. = Å
 H atom 4 E a me =, n=,,3,... 8ε 0 0 π me e e 0 hn ε h = = 0.59Å E = me (4 πε ) 4 e 0 n n in a.u. atomic units E = r = Z n nao Z = e = me = 4πε = 0 energy: a.u. = 7. ev distance a.u. = 0.59 Å General results
H atom 4 E a me =, n=,,3,... 8ε 0 0 π me e e 0 hn ε h = = 0.59Å E = me (4 πε ) 4 e 0 n n in a.u. atomic units E = r = Z n nao Z = e = me = 4πε = 0 energy: a.u. = 7. ev distance a.u. = 0.59 Å General results
We also deduced that transformations between Slater determinants are always of the form
 .3 Hartree-Fock The Hartree-Fock method assumes that the true N-body ground state wave function can be approximated by a single Slater determinant and minimizes the energy among all possible choices of
.3 Hartree-Fock The Hartree-Fock method assumes that the true N-body ground state wave function can be approximated by a single Slater determinant and minimizes the energy among all possible choices of
Chemistry 6 (9 am section) Spring Covalent Bonding
 Chemistry 6 (9 am section) Spring 000 Covalent Bonding The stability of the bond in molecules such as H, O, N and F is associated with a sharing (equal) of the VALENCE ELECTRONS between the BONDED ATOMS.
Chemistry 6 (9 am section) Spring 000 Covalent Bonding The stability of the bond in molecules such as H, O, N and F is associated with a sharing (equal) of the VALENCE ELECTRONS between the BONDED ATOMS.
Bonding in Molecules Prof John McGrady Michaelmas Term 2009
 Bonding in Molecules Prof John McGrady Michaelmas Term 2009 6 lectures building on material presented in Introduction to Molecular Orbitals (HT Year 1). Provides a basis for analysing the shapes, properties,
Bonding in Molecules Prof John McGrady Michaelmas Term 2009 6 lectures building on material presented in Introduction to Molecular Orbitals (HT Year 1). Provides a basis for analysing the shapes, properties,
Density Functional Theory - II part
 Density Functional Theory - II part antonino.polimeno@unipd.it Overview From theory to practice Implementation Functionals Local functionals Gradient Others From theory to practice From now on, if not
Density Functional Theory - II part antonino.polimeno@unipd.it Overview From theory to practice Implementation Functionals Local functionals Gradient Others From theory to practice From now on, if not
