Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 2018 Elad Alon and Miki Lustig Discussion 5A
|
|
|
- Kerry Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EECS 6B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 208 Elad Alon and Miki Lustig Discussion 5A Transfer Function When we write the transfer function of an arbitrary circuit, it always takes the following form. This is called a rational transfer function. We also like to factor the numerator and denominator, so that they become easier to work with and plot: ( ) H(ω) = z(ω) p(ω) = ( jω)nz0 ( jω) n α n + ( jω) n α n + + jωα + α 0 ( jω) N p0 ( jω) m β m + ( jω) m β m + + jωβ + β 0 ) ) ( jω) N z0 ( + j )( ω + j ω ( + j ω ωz ωz2 ωzn = K ( )( ( ) ( jω) N p0 + j ω ω p + j ω ω p2 ) + j ω ω pm Here, we define the constants ω z as zeros and ω p as poles, and N z0, N p0 are the number of zeros and poles at ω = 0 2 Bode Plots Bode plots provide us with a simple and easy tool to plot these transfer functions by hand. Always remember that Bode plots are an approximation; if you want the precisely correct plots, you need to use numerical methods (like solving using MATLAB or IPython). When we make Bode plots, we plot the frequency on a logarithmic scale, the magnitude on a decibel scale, and the angle in either degrees or radians. We use the decibel because it allows us to break up complex transfer functions into its constituent components. We define the decibel as the following: 20log 0 ( H(ω) ) = H(ω) [db] When making the Bode plot (and plotting using a logarithmic unit), we treat each individual pole and zero independently, and then add them back together at the end. We can use the Bode plot rules to help us plot each of the individual poles and zeros. H(ω) = 0log P out P in = 0log Vout 2 R Vin 2 R = 0log V 2 out V 2 in = 20log V out V in EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A
2 2. Algorithm Given a frequency response H(ω), (a) Break H(ω) into a product of poles and zeros as in the cheat sheet. Appropriately divide terms to reduce H(ω) into one of the given forms. (b) Draw out the Bode plot for each pole and zero in the product above. (c) Add the resulting plots to get the final Bode plot. 2.2 Example Plot the magnitude and phase of the following transfer function using the Bode approximation and a numerical solver and compare the two. H(ω) = ( ) ω 00 + j 000 ( )( ) + j ω + j ω We see zero at 0 3 rad rad s, 2 poles at 06 s and 0 8 rad s, and a constant gain of 00. We start with the constant value, and then move from lowest to highest frequency plotting the poles and zeros as we go. Finally, we add together the plots for each of the individual poles and zeros to give us the final Bode plot. Figure : Plotting of the transfer function magnitude using the Bode approximation Figure 2: Plotting of the transfer function angle using the Bode approximation Finally, comparing the Bode approximation and the precise value calculated via a computer, we can see the Bode approximation is very similar to the exact answer, except for around the pole and zero frequencies (as expected). EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 2
3 H(ω) (db) exact approximation H(ω)( ) exact approximation ω (rad/s) Figure 3: A comparison of Bode vs. exact (numerically computed) answers. Note the agreement between both, except at the pole and zero frequencies. 2.3 Questions. Bode Plots of Transfer Functions To understand the concept of transfer functions and filters with a concrete example, consider the following simple RC circuit. Let the voltage source V S be designated as the input phasor, and let V R and V C designate the two output voltage phasors. R = kω and C = µf. V s V C + + C V R R (a) What is the impedance of a kω resistor? Draw a Bode plot of the impedance of the resistor as a function of frequency. (Don t forget that a Bode plot has both a magnitude plot and a phase plot.) Z R = kω EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 3
4 (b) What is the impedance of a µf capacitor? On the same Bode plot as the last question, sketch the capacitor s impedance as a function of frequency. When is Z C Z R and vice versa? At what ω does Z C = Z R? What is this ω called? Z C Z R approximately when ω < RC. Z C Z R approximately when ω > the corner frequency, or ω c. RC. This ω is called EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 4
5 (c) Now lets look at the impedance voltage divider below. What is the transfer function H(ω) = ṼC ṼS? Z C + V C + + V s V R Z R H(ω) = + jωrc = + j ω 0 3 (d) For the region where Z R Z C, what is the approximate function for ṼC ṼS? At what frequencies is our approximation no longer valid? Sketch the approximate function in the appropreiate region on a Bode magnitude plot. This is valid for ω > RC. Ṽ C Ṽ S Z C Z R EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 5
6 (e) What is the approximate function for V C ṼS when Z C Z R? On the same Bode magnitude plot as before, sketch the this approximate function. Where does this function meet your approximation for when Z R Z C? Ṽ C Ṽ S This is approximately valid for ω < RC. This meets our other approximation at ω = RC. (f) What is the worst case error for our piecewise approximation? On a log-log plot, does this error appear very large? A factor of 2 at ω = RC. The logarithmic nature of Bode plots means that this error doesn t really affect the general shape of the Bode plot. EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 6
7 (g) Approximately what is the phase of ṼC ṼS at ω = 0, 0RC, RC, 0 RC, 000 RC? Connect the dots and sketch a plot of phase vs. time in a phase plot below your magnitude plot to complete your Bode plot for ṼC ṼS. 0,0, 45, 90, 90 EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 7
8 . (h) Draw the Bode plot for ṼR ṼS 2. Bode Plots (a) Derive a transfer function that would result in the following Bode plot. EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 8
9 H(ω) = ( ) 2 + jω ω c (b) Derive a transfer function that would result in the following Bode plot. Hint: 20log 0 2 = 6 j20ω H(ω) = ( ) ( + jω) + jω Bode Plots and Phasors + V in R V 2 x R 0 V out L R I L I R C We found the transfer function of this circuit to be: Using the following values: Plot its magnitude and phase Bode plots. H(ω) = R L + jω L R ( jω)( + jωr 2 C) R 0 = 00Ω,R = kω,l = µh,r 2 = 00kΩ,C = pf EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 9
10 2.4 Extra Practice. Transfer Function Create a Bode plot of the following transfer function: H(ω) = (( jω) jω + 000)( jω ) 0 ( jω + 000)(( jω) jω + 00) EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 0
11 First of all, we decompose the second-order terms: H(ω) = (( jω) + 00)( jω + 0))( jω ) = ( jω + 0)( jω ) 0 ( jω + 000)(( jω) + 00)( jω + )) 0 ( jω + 000)( jω + ) Then, we convert it to the normal form: H(ω) = 0 ( jω jω 0 + )( ( jω ) + )( jω + ) 20 H(ω) (db) H(ω)( ) ω 2. RLC Circuit In this question, we will take a look at an electrical systems described by second order differential equations and analyze it using the phasor domain. Consider the circuit below where V s is a sinusoidal signal, L = mh, and C = nf: R + V R L + V L + V s V C C (a) Transform the circuit into the phasor domain. Z R = R Z L = jωl Z C = jωc EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A
12 (b) Solve for the transfer function H C (ω) = ṼC Ṽs in terms of R, L, and C. Ṽ C is a voltage divider where the output voltage is taken across the capacitor. Ṽ C = H C (ω) = Z C Ṽ s Z R + Z L + Z C Z C jωc = Z R + Z L + Z C R + jωl + jωc Multiplying the numerator and denominator by jωc gives H C (ω) = ( jω) 2 LC + jωrc + (c) Solve for the transfer function H L (ω) = ṼL Ṽs in terms of R, L, and C. Ṽ L is a voltage divider where the output voltage is taken across the inductor. Z L Ṽ L = Ṽ s Z R + Z L + Z C Z L jωl H L (ω) = = Z R + Z L + Z C R + jωl + jωc Multiplying the numerator and denominator by jωc gives H L (ω) = ( jω) 2 LC ( jω) 2 LC + jωrc + (d) Solve for the transfer function H R (ω) = ṼR Ṽs in terms of R, L, and C. Ṽ R is a voltage divider where the output voltage is taken across the resistor. Z R Ṽ R = Ṽ s Z R + Z L + Z C Z R R H R (ω) = = Z R + Z L + Z C R + jωl + jωc Multiplying the numerator and denominator by jωc gives H R (ω) = (e) Sketch the bode plot for H C. Let R = 2kΩ. jωrc ( jω) 2 LC + jωrc + From part (a) we have, H C (ω) = ( jω) 2 LC + ( jω)rc + = 0 2 ( jω) ( jω) + = ( jω) 2 2( jω) + + (0 6 ) EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 2
13 Hence, we have two poles at ω p = 0 6 and ζ =, and hence we will have a 40 db/dec drop off at ω p. With these parameters, we have the following plot: s EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 3
14 EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 4
15 Figure 4: Bode Plot Cheat Sheet EECS 6B, Fall 208, Discussion 5A 5
EE221 Circuits II. Chapter 14 Frequency Response
 EE22 Circuits II Chapter 4 Frequency Response Frequency Response Chapter 4 4. Introduction 4.2 Transfer Function 4.3 Bode Plots 4.4 Series Resonance 4.5 Parallel Resonance 4.6 Passive Filters 4.7 Active
EE22 Circuits II Chapter 4 Frequency Response Frequency Response Chapter 4 4. Introduction 4.2 Transfer Function 4.3 Bode Plots 4.4 Series Resonance 4.5 Parallel Resonance 4.6 Passive Filters 4.7 Active
EE221 Circuits II. Chapter 14 Frequency Response
 EE22 Circuits II Chapter 4 Frequency Response Frequency Response Chapter 4 4. Introduction 4.2 Transfer Function 4.3 Bode Plots 4.4 Series Resonance 4.5 Parallel Resonance 4.6 Passive Filters 4.7 Active
EE22 Circuits II Chapter 4 Frequency Response Frequency Response Chapter 4 4. Introduction 4.2 Transfer Function 4.3 Bode Plots 4.4 Series Resonance 4.5 Parallel Resonance 4.6 Passive Filters 4.7 Active
Frequency Response. Re ve jφ e jωt ( ) where v is the amplitude and φ is the phase of the sinusoidal signal v(t). ve jφ
 27 Frequency Response Before starting, review phasor analysis, Bode plots... Key concept: small-signal models for amplifiers are linear and therefore, cosines and sines are solutions of the linear differential
27 Frequency Response Before starting, review phasor analysis, Bode plots... Key concept: small-signal models for amplifiers are linear and therefore, cosines and sines are solutions of the linear differential
Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH005/105)
 CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS MATHEMATICS AND ASTRONOMY DIVISION Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH5/15) Analog Electronics Active Filters Copyright c Virgínio de Oliveira Sannibale, 23 (Revision
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS MATHEMATICS AND ASTRONOMY DIVISION Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH5/15) Analog Electronics Active Filters Copyright c Virgínio de Oliveira Sannibale, 23 (Revision
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ. EGR 224 Spring Test II. Michael R. Gustafson II
 'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 224 Spring 2018 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 224 Spring 2018 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any
Solution: K m = R 1 = 10. From the original circuit, Z L1 = jωl 1 = j10 Ω. For the scaled circuit, L 1 = jk m ωl 1 = j10 10 = j100 Ω, Z L
 Problem 9.9 Circuit (b) in Fig. P9.9 is a scaled version of circuit (a). The scaling process may have involved magnitude or frequency scaling, or both simultaneously. If R = kω gets scaled to R = kω, supply
Problem 9.9 Circuit (b) in Fig. P9.9 is a scaled version of circuit (a). The scaling process may have involved magnitude or frequency scaling, or both simultaneously. If R = kω gets scaled to R = kω, supply
AC analysis - many examples
 AC analysis - many examples The basic method for AC analysis:. epresent the AC sources as complex numbers: ( ). Convert resistors, capacitors, and inductors into their respective impedances: resistor Z
AC analysis - many examples The basic method for AC analysis:. epresent the AC sources as complex numbers: ( ). Convert resistors, capacitors, and inductors into their respective impedances: resistor Z
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You may use the equation sheet provided but
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You may use the equation sheet provided but
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ. EGR 224 Spring Test II. Michael R. Gustafson II
 'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 224 Spring 2017 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 224 Spring 2017 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any
EE 40: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 2008: Midterm 2
 EE 4: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 8: Midterm Venkat Anantharam 3/9/8 Total Time Allotted : min Total Points:. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring two pages
EE 4: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 8: Midterm Venkat Anantharam 3/9/8 Total Time Allotted : min Total Points:. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring two pages
Frequency response. Pavel Máša - XE31EO2. XE31EO2 Lecture11. Pavel Máša - XE31EO2 - Frequency response
 Frequency response XE3EO2 Lecture Pavel Máša - Frequency response INTRODUCTION Frequency response describe frequency dependence of output to input voltage magnitude ratio and its phase shift as a function
Frequency response XE3EO2 Lecture Pavel Máša - Frequency response INTRODUCTION Frequency response describe frequency dependence of output to input voltage magnitude ratio and its phase shift as a function
H(s) = 2(s+10)(s+100) (s+1)(s+1000)
 Problem 1 Consider the following transfer function H(s) = 2(s10)(s100) (s1)(s1000) (a) Draw the asymptotic magnitude Bode plot for H(s). Solution: The transfer function is not in standard form to sketch
Problem 1 Consider the following transfer function H(s) = 2(s10)(s100) (s1)(s1000) (a) Draw the asymptotic magnitude Bode plot for H(s). Solution: The transfer function is not in standard form to sketch
EE1-01 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 2013 ANALYSIS OF CIRCUITS. Tuesday, 28 May 10:00 am
 EE1-01 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 2013 ExamHeader: EEE/EIE PART I: MEng, Beng and ACGI ANALYSIS OF CIRCUITS Tuesday, 28 May 10:00 am Time allowed:
EE1-01 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 2013 ExamHeader: EEE/EIE PART I: MEng, Beng and ACGI ANALYSIS OF CIRCUITS Tuesday, 28 May 10:00 am Time allowed:
2. The following diagram illustrates that voltage represents what physical dimension?
 BioE 1310 - Exam 1 2/20/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. A particular voltage divider with 10 V across it consists of two resistors in series. One resistor is 7 KΩ and the other
BioE 1310 - Exam 1 2/20/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. A particular voltage divider with 10 V across it consists of two resistors in series. One resistor is 7 KΩ and the other
Refinements to Incremental Transistor Model
 Refinements to Incremental Transistor Model This section presents modifications to the incremental models that account for non-ideal transistor behavior Incremental output port resistance Incremental changes
Refinements to Incremental Transistor Model This section presents modifications to the incremental models that account for non-ideal transistor behavior Incremental output port resistance Incremental changes
R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits
 P517/617 Lec4, P1 R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits Consider the following RLC series circuit What's R? Simplest way to solve for is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation. X L X C in 0
P517/617 Lec4, P1 R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits Consider the following RLC series circuit What's R? Simplest way to solve for is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation. X L X C in 0
EE348L Lecture 1. EE348L Lecture 1. Complex Numbers, KCL, KVL, Impedance,Steady State Sinusoidal Analysis. Motivation
 EE348L Lecture 1 Complex Numbers, KCL, KVL, Impedance,Steady State Sinusoidal Analysis 1 EE348L Lecture 1 Motivation Example CMOS 10Gb/s amplifier Differential in,differential out, 5 stage dccoupled,broadband
EE348L Lecture 1 Complex Numbers, KCL, KVL, Impedance,Steady State Sinusoidal Analysis 1 EE348L Lecture 1 Motivation Example CMOS 10Gb/s amplifier Differential in,differential out, 5 stage dccoupled,broadband
Dynamic circuits: Frequency domain analysis
 Electronic Circuits 1 Dynamic circuits: Contents Free oscillation and natural frequency Transfer functions Frequency response Bode plots 1 System behaviour: overview 2 System behaviour : review solution
Electronic Circuits 1 Dynamic circuits: Contents Free oscillation and natural frequency Transfer functions Frequency response Bode plots 1 System behaviour: overview 2 System behaviour : review solution
ECE Circuit Theory. Final Examination. December 5, 2008
 ECE 212 H1F Pg 1 of 12 ECE 212 - Circuit Theory Final Examination December 5, 2008 1. Policy: closed book, calculators allowed. Show all work. 2. Work in the provided space. 3. The exam has 3 problems
ECE 212 H1F Pg 1 of 12 ECE 212 - Circuit Theory Final Examination December 5, 2008 1. Policy: closed book, calculators allowed. Show all work. 2. Work in the provided space. 3. The exam has 3 problems
Lecture 4: R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits
 Lecture 4: R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits RLC series circuit: What's V R? Simplest way to solve for V is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation: V X L X C V R = in R R + X C + X L L
Lecture 4: R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits RLC series circuit: What's V R? Simplest way to solve for V is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation: V X L X C V R = in R R + X C + X L L
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits
 Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences E. Alon Final EECS 240 Monday, May 19, 2008 SPRING 2008 You should write your results on the exam
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences E. Alon Final EECS 240 Monday, May 19, 2008 SPRING 2008 You should write your results on the exam
ENGR-4300 Spring 2009 Test 2. Name: SOLUTION. Section: 1(MR 8:00) 2(TF 2:00) 3(MR 6:00) (circle one) Question I (20 points): Question II (20 points):
 ENGR43 Test 2 Spring 29 ENGR43 Spring 29 Test 2 Name: SOLUTION Section: 1(MR 8:) 2(TF 2:) 3(MR 6:) (circle one) Question I (2 points): Question II (2 points): Question III (17 points): Question IV (2 points):
ENGR43 Test 2 Spring 29 ENGR43 Spring 29 Test 2 Name: SOLUTION Section: 1(MR 8:) 2(TF 2:) 3(MR 6:) (circle one) Question I (2 points): Question II (2 points): Question III (17 points): Question IV (2 points):
Figure Circuit for Question 1. Figure Circuit for Question 2
 Exercises 10.7 Exercises Multiple Choice 1. For the circuit of Figure 10.44 the time constant is A. 0.5 ms 71.43 µs 2, 000 s D. 0.2 ms 4 Ω 2 Ω 12 Ω 1 mh 12u 0 () t V Figure 10.44. Circuit for Question
Exercises 10.7 Exercises Multiple Choice 1. For the circuit of Figure 10.44 the time constant is A. 0.5 ms 71.43 µs 2, 000 s D. 0.2 ms 4 Ω 2 Ω 12 Ω 1 mh 12u 0 () t V Figure 10.44. Circuit for Question
ECE 201 Fall 2009 Final Exam
 ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2016 Anant Sahai and Michel Maharbiz Midterm 2
 EECS 16B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2016 Anant Sahai and Michel Maharbiz Midterm 2 Exam location: 145 Dwinelle (SIDs ending in 1 and 5) PRINT your student ID: PRINT AND SIGN your
EECS 16B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2016 Anant Sahai and Michel Maharbiz Midterm 2 Exam location: 145 Dwinelle (SIDs ending in 1 and 5) PRINT your student ID: PRINT AND SIGN your
ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam
 ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam December 12, 2013 Circle your division: Division 0101: Furgason (8:30 am) Division 0201: Bermel (9:30 am) Name (Last, First) Purdue ID # There are 18 multiple choice problems
ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam December 12, 2013 Circle your division: Division 0101: Furgason (8:30 am) Division 0201: Bermel (9:30 am) Name (Last, First) Purdue ID # There are 18 multiple choice problems
Test II Michael R. Gustafson II
 'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 224 Spring 2016 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 224 Spring 2016 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ. ECE 110 Fall Test II. Michael R. Gustafson II
 'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ ECE 110 Fall 2016 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any assistance
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ ECE 110 Fall 2016 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any assistance
BIOEN 302, Section 3: AC electronics
 BIOEN 3, Section 3: AC electronics For this section, you will need to have very present the basics of complex number calculus (see Section for a brief overview) and EE5 s section on phasors.. Representation
BIOEN 3, Section 3: AC electronics For this section, you will need to have very present the basics of complex number calculus (see Section for a brief overview) and EE5 s section on phasors.. Representation
Chapter 8: Converter Transfer Functions
 Chapter 8. Converter Transfer Functions 8.1. Review of Bode plots 8.1.1. Single pole response 8.1.2. Single zero response 8.1.3. Right half-plane zero 8.1.4. Frequency inversion 8.1.5. Combinations 8.1.6.
Chapter 8. Converter Transfer Functions 8.1. Review of Bode plots 8.1.1. Single pole response 8.1.2. Single zero response 8.1.3. Right half-plane zero 8.1.4. Frequency inversion 8.1.5. Combinations 8.1.6.
The general form for the transform function of a second order filter is that of a biquadratic (or biquad to the cool kids).
 nd-order filters The general form for the transform function of a second order filter is that of a biquadratic (or biquad to the cool kids). T (s) A p s a s a 0 s b s b 0 As before, the poles of the transfer
nd-order filters The general form for the transform function of a second order filter is that of a biquadratic (or biquad to the cool kids). T (s) A p s a s a 0 s b s b 0 As before, the poles of the transfer
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 8.1. Review of Bode plots Decibels Table 8.1. Expressing magnitudes in decibels G db = 0 log 10
R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 8.1. Review of Bode plots Decibels Table 8.1. Expressing magnitudes in decibels G db = 0 log 10
Basic RL and RC Circuits R-L TRANSIENTS: STORAGE CYCLE. Engineering Collage Electrical Engineering Dep. Dr. Ibrahim Aljubouri
 st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
Today. 1/25/11 Physics 262 Lecture 2 Filters. Active Components and Filters. Homework. Lab 2 this week
 /5/ Physics 6 Lecture Filters Today Basics: Analog versus Digital; Passive versus Active Basic concepts and types of filters Passband, Stopband, Cut-off, Slope, Knee, Decibels, and Bode plots Active Components
/5/ Physics 6 Lecture Filters Today Basics: Analog versus Digital; Passive versus Active Basic concepts and types of filters Passband, Stopband, Cut-off, Slope, Knee, Decibels, and Bode plots Active Components
Electric Circuits I FINAL EXAMINATION
 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I FINAL EXAMINATION Problems Points.. 3. 0 Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no 5//6 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Problem
EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I FINAL EXAMINATION Problems Points.. 3. 0 Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no 5//6 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Problem
Frequency Response part 2 (I&N Chap 12)
 Frequency Response part 2 (I&N Chap 12) Introduction & TFs Decibel Scale & Bode Plots Resonance Scaling Filter Networks Applications/Design Frequency response; based on slides by J. Yan Slide 3.1 Example
Frequency Response part 2 (I&N Chap 12) Introduction & TFs Decibel Scale & Bode Plots Resonance Scaling Filter Networks Applications/Design Frequency response; based on slides by J. Yan Slide 3.1 Example
I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers
 I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers A. Common-Emitter Amplifier: V i SUP i OUT R S V BIAS R L v OUT V Operating Point analysis: 0, R s 0, r o --->, r oc --->, R L ---> Find V BIAS such that I C
I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers A. Common-Emitter Amplifier: V i SUP i OUT R S V BIAS R L v OUT V Operating Point analysis: 0, R s 0, r o --->, r oc --->, R L ---> Find V BIAS such that I C
( s) N( s) ( ) The transfer function will take the form. = s = 2. giving ωo = sqrt(1/lc) = 1E7 [rad/s] ω 01 := R 1. α 1 2 L 1.
![( s) N( s) ( ) The transfer function will take the form. = s = 2. giving ωo = sqrt(1/lc) = 1E7 [rad/s] ω 01 := R 1. α 1 2 L 1. ( s) N( s) ( ) The transfer function will take the form. = s = 2. giving ωo = sqrt(1/lc) = 1E7 [rad/s] ω 01 := R 1. α 1 2 L 1.](/thumbs/83/87520964.jpg) Problem ) RLC Parallel Circuit R L C E-4 E-0 V a. What is the resonant frequency of the circuit? The transfer function will take the form N ( ) ( s) N( s) H s R s + α s + ω s + s + o L LC giving ωo sqrt(/lc)
Problem ) RLC Parallel Circuit R L C E-4 E-0 V a. What is the resonant frequency of the circuit? The transfer function will take the form N ( ) ( s) N( s) H s R s + α s + ω s + s + o L LC giving ωo sqrt(/lc)
ECE Spring 2015 Final Exam
 ECE 20100 Spring 2015 Final Exam May 7, 2015 Section (circle below) Jung (1:30) 0001 Qi (12:30) 0002 Peleato (9:30) 0004 Allen (10:30) 0005 Zhu (4:30) 0006 Name PUID Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL
ECE 20100 Spring 2015 Final Exam May 7, 2015 Section (circle below) Jung (1:30) 0001 Qi (12:30) 0002 Peleato (9:30) 0004 Allen (10:30) 0005 Zhu (4:30) 0006 Name PUID Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, pm, Room TBA
 EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
REACTANCE. By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013
 REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
Poles, Zeros, and Frequency Response
 Complex Poles Poles, Zeros, and Frequency esponse With only resistors and capacitors, you're stuck with real poles. If you want complex poles, you need either an op-amp or an inductor as well. Complex
Complex Poles Poles, Zeros, and Frequency esponse With only resistors and capacitors, you're stuck with real poles. If you want complex poles, you need either an op-amp or an inductor as well. Complex
Overview of Bode Plots Transfer function review Piece-wise linear approximations First-order terms Second-order terms (complex poles & zeros)
 Overview of Bode Plots Transfer function review Piece-wise linear approximations First-order terms Second-order terms (complex poles & zeros) J. McNames Portland State University ECE 222 Bode Plots Ver.
Overview of Bode Plots Transfer function review Piece-wise linear approximations First-order terms Second-order terms (complex poles & zeros) J. McNames Portland State University ECE 222 Bode Plots Ver.
Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work Solutions
 Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work s 21.1 Problem 21.11 What is the time constant of the circuit in Figure (21.19). 10 Ω 10 Ω 5.0 Ω 2.0µF 2.0µF 2.0µF 3.0µF Figure 21.19: Given: The circuit
Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work s 21.1 Problem 21.11 What is the time constant of the circuit in Figure (21.19). 10 Ω 10 Ω 5.0 Ω 2.0µF 2.0µF 2.0µF 3.0µF Figure 21.19: Given: The circuit
Time Varying Circuit Analysis
 MAS.836 Sensor Systems for Interactive Environments th Distributed: Tuesday February 16, 2010 Due: Tuesday February 23, 2010 Problem Set # 2 Time Varying Circuit Analysis The purpose of this problem set
MAS.836 Sensor Systems for Interactive Environments th Distributed: Tuesday February 16, 2010 Due: Tuesday February 23, 2010 Problem Set # 2 Time Varying Circuit Analysis The purpose of this problem set
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA
 EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
MODULE-4 RESONANCE CIRCUITS
 Introduction: MODULE-4 RESONANCE CIRCUITS Resonance is a condition in an RLC circuit in which the capacitive and inductive Reactance s are equal in magnitude, there by resulting in purely resistive impedance.
Introduction: MODULE-4 RESONANCE CIRCUITS Resonance is a condition in an RLC circuit in which the capacitive and inductive Reactance s are equal in magnitude, there by resulting in purely resistive impedance.
First and Second Order Circuits. Claudio Talarico, Gonzaga University Spring 2015
 First and Second Order Circuits Claudio Talarico, Gonzaga University Spring 2015 Capacitors and Inductors intuition: bucket of charge q = Cv i = C dv dt Resist change of voltage DC open circuit Store voltage
First and Second Order Circuits Claudio Talarico, Gonzaga University Spring 2015 Capacitors and Inductors intuition: bucket of charge q = Cv i = C dv dt Resist change of voltage DC open circuit Store voltage
Physics 405/505 Digital Electronics Techniques. University of Arizona Spring 2006 Prof. Erich W. Varnes
 Physics 405/505 Digital Electronics Techniques University of Arizona Spring 2006 Prof. Erich W. Varnes Administrative Matters Contacting me I will hold office hours on Tuesday from 1-3 pm Room 420K in
Physics 405/505 Digital Electronics Techniques University of Arizona Spring 2006 Prof. Erich W. Varnes Administrative Matters Contacting me I will hold office hours on Tuesday from 1-3 pm Room 420K in
EEE161 Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory 2
 Dr. Milica Marković Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory page 1 EEE161 Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory 2 Instructor: Dr. Milica Marković Office: Riverside Hall 5026 Email: milica@csus.edu Web:http://gaia.ecs.csus.edu/
Dr. Milica Marković Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory page 1 EEE161 Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory 2 Instructor: Dr. Milica Marković Office: Riverside Hall 5026 Email: milica@csus.edu Web:http://gaia.ecs.csus.edu/
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
DC and AC Impedance of Reactive Elements
 3/6/20 D and A Impedance of Reactive Elements /6 D and A Impedance of Reactive Elements Now, recall from EES 2 the complex impedances of our basic circuit elements: ZR = R Z = jω ZL = jωl For a D signal
3/6/20 D and A Impedance of Reactive Elements /6 D and A Impedance of Reactive Elements Now, recall from EES 2 the complex impedances of our basic circuit elements: ZR = R Z = jω ZL = jωl For a D signal
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.9 Basic Approach Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin & Norton Equivalent Circuits
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.9 Basic Approach Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin & Norton Equivalent Circuits
Handout 11: AC circuit. AC generator
 Handout : AC circuit AC generator Figure compares the voltage across the directcurrent (DC) generator and that across the alternatingcurrent (AC) generator For DC generator, the voltage is constant For
Handout : AC circuit AC generator Figure compares the voltage across the directcurrent (DC) generator and that across the alternatingcurrent (AC) generator For DC generator, the voltage is constant For
Homwork AC circuits. due Friday Oct 8, 2017
 Homwork AC circuits due Friday Oct 8, 2017 Validate your answers (show your work) using a Matlab Live Script and Simulink models. Include these computations and models with your homework. 1 Problem 1 Worksheet
Homwork AC circuits due Friday Oct 8, 2017 Validate your answers (show your work) using a Matlab Live Script and Simulink models. Include these computations and models with your homework. 1 Problem 1 Worksheet
ECE3050 Assignment 7
 ECE3050 Assignment 7. Sketch and label the Bode magnitude and phase plots for the transfer functions given. Use loglog scales for the magnitude plots and linear-log scales for the phase plots. On the magnitude
ECE3050 Assignment 7. Sketch and label the Bode magnitude and phase plots for the transfer functions given. Use loglog scales for the magnitude plots and linear-log scales for the phase plots. On the magnitude
Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8. θ (radians) θ (degrees) cos θ sin θ π/ /2 1/2 π/4 45 2/2 2/2 π/3 60 1/2 3/2 π/
 Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8 Trigonometric Identities ( cos(θ) = cos(θ) sin(θ) = sin(θ) sin(θ) = cos θ π ) 2 Cosines and Sines of common angles Euler s Formula θ (radians) θ (degrees)
Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8 Trigonometric Identities ( cos(θ) = cos(θ) sin(θ) = sin(θ) sin(θ) = cos θ π ) 2 Cosines and Sines of common angles Euler s Formula θ (radians) θ (degrees)
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
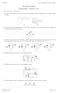 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Learnabout Electronics - AC Theory
 Learnabout Electronics - AC Theory Facts & Formulae for AC Theory www.learnabout-electronics.org Contents AC Wave Values... 2 Capacitance... 2 Charge on a Capacitor... 2 Total Capacitance... 2 Inductance...
Learnabout Electronics - AC Theory Facts & Formulae for AC Theory www.learnabout-electronics.org Contents AC Wave Values... 2 Capacitance... 2 Charge on a Capacitor... 2 Total Capacitance... 2 Inductance...
Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis. Phasors
 Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis Lecture 6, 0/07/05 OUTLINE Phasor ReCap Capacitor/Inductor Example Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis with Complex Impedance Phasor
Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis Lecture 6, 0/07/05 OUTLINE Phasor ReCap Capacitor/Inductor Example Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis with Complex Impedance Phasor
EE221 - Practice for the Midterm Exam
 EE1 - Practice for the Midterm Exam 1. Consider this circuit and corresponding plot of the inductor current: Determine the values of L, R 1 and R : L = H, R 1 = Ω and R = Ω. Hint: Use the plot to determine
EE1 - Practice for the Midterm Exam 1. Consider this circuit and corresponding plot of the inductor current: Determine the values of L, R 1 and R : L = H, R 1 = Ω and R = Ω. Hint: Use the plot to determine
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors
 Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
2nd-order filters. EE 230 second-order filters 1
 nd-order filters Second order filters: Have second order polynomials in the denominator of the transfer function, and can have zeroth-, first-, or second-order polyinomials in the numerator. Use two reactive
nd-order filters Second order filters: Have second order polynomials in the denominator of the transfer function, and can have zeroth-, first-, or second-order polyinomials in the numerator. Use two reactive
Homework Assignment 11
 Homework Assignment Question State and then explain in 2 3 sentences, the advantage of switched capacitor filters compared to continuous-time active filters. (3 points) Continuous time filters use resistors
Homework Assignment Question State and then explain in 2 3 sentences, the advantage of switched capacitor filters compared to continuous-time active filters. (3 points) Continuous time filters use resistors
K.K. Gan L3: R-L-C AC Circuits. amplitude. Volts. period. -Vo
 Lecture 3: R-L-C AC Circuits AC (Alternative Current): Most of the time, we are interested in the voltage at a point in the circuit will concentrate on voltages here rather than currents. We encounter
Lecture 3: R-L-C AC Circuits AC (Alternative Current): Most of the time, we are interested in the voltage at a point in the circuit will concentrate on voltages here rather than currents. We encounter
Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits
 Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits 1 Single Phase Parallel A.C. Circuits (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) n parallel a.c. circuits similar
Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits 1 Single Phase Parallel A.C. Circuits (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) n parallel a.c. circuits similar
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Almost all electrical systems, whether signal or power, operate with alternating currents and voltages. We have seen that when any circuit is disturbed (switched on or
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Almost all electrical systems, whether signal or power, operate with alternating currents and voltages. We have seen that when any circuit is disturbed (switched on or
EKT 119 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT II. Chapter 3: Frequency Response of AC Circuit Sem2 2015/2016 Dr. Mohd Rashidi Che Beson
 EKT 9 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT II Chapter 3: Frequency Response of AC Circuit Sem 05/06 Dr. Mohd Rashidi Che Beson TRANSFER FUNCTION (TF Frequency response can be obtained by using transfer function. DEFINITION:
EKT 9 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT II Chapter 3: Frequency Response of AC Circuit Sem 05/06 Dr. Mohd Rashidi Che Beson TRANSFER FUNCTION (TF Frequency response can be obtained by using transfer function. DEFINITION:
CHAPTER 7 : BODE PLOTS AND GAIN ADJUSTMENTS COMPENSATION
 CHAPTER 7 : BODE PLOTS AND GAIN ADJUSTMENTS COMPENSATION Objectives Students should be able to: Draw the bode plots for first order and second order system. Determine the stability through the bode plots.
CHAPTER 7 : BODE PLOTS AND GAIN ADJUSTMENTS COMPENSATION Objectives Students should be able to: Draw the bode plots for first order and second order system. Determine the stability through the bode plots.
ELEC 2501 AB. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock midterm UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the midterm in 3 hour(s). Work on your own. Keep your notes and textbook closed. Attempt every question.
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock midterm UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the midterm in 3 hour(s). Work on your own. Keep your notes and textbook closed. Attempt every question.
15 n=0. zz = re jθ re jθ = r 2. (b) For division and multiplication, it is handy to use the polar representation: z = rejθ. = z 1z 2.
 Professor Fearing EECS0/Problem Set v.0 Fall 06 Due at 4 pm, Fri. Sep. in HW box under stairs (st floor Cory) Reading: EE6AB notes. This problem set should be review of material from EE6AB. (Please note,
Professor Fearing EECS0/Problem Set v.0 Fall 06 Due at 4 pm, Fri. Sep. in HW box under stairs (st floor Cory) Reading: EE6AB notes. This problem set should be review of material from EE6AB. (Please note,
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Self-paced Course
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Self-paced Course MODULE 26 APPLICATIONS TO ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS Module Topics 1. Complex numbers and alternating currents 2. Complex impedance 3.
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Self-paced Course MODULE 26 APPLICATIONS TO ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS Module Topics 1. Complex numbers and alternating currents 2. Complex impedance 3.
Lecture 37: Frequency response. Context
 EECS 05 Spring 004, Lecture 37 Lecture 37: Frequency response Prof J. S. Smith EECS 05 Spring 004, Lecture 37 Context We will figure out more of the design parameters for the amplifier we looked at in
EECS 05 Spring 004, Lecture 37 Lecture 37: Frequency response Prof J. S. Smith EECS 05 Spring 004, Lecture 37 Context We will figure out more of the design parameters for the amplifier we looked at in
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
8.1.6 Quadratic pole response: resonance
 8.1.6 Quadratic pole response: resonance Example G(s)= v (s) v 1 (s) = 1 1+s L R + s LC L + Second-order denominator, of the form 1+a 1 s + a s v 1 (s) + C R Two-pole low-pass filter example v (s) with
8.1.6 Quadratic pole response: resonance Example G(s)= v (s) v 1 (s) = 1 1+s L R + s LC L + Second-order denominator, of the form 1+a 1 s + a s v 1 (s) + C R Two-pole low-pass filter example v (s) with
EE40 Lecture 11 Josh Hug 7/19/2010
 EE40 Lecture Josh 7/9/200 Logistical Things Lab 4 tomorrow Lab 5 (active filter lab) on Wednesday Prototype for future lab for EE40 Prelab is very short, sorry. Please give us our feedback Google docs
EE40 Lecture Josh 7/9/200 Logistical Things Lab 4 tomorrow Lab 5 (active filter lab) on Wednesday Prototype for future lab for EE40 Prelab is very short, sorry. Please give us our feedback Google docs
1.3 Sinusoidal Steady State
 1.3 Sinusoidal Steady State Electromagnetics applications can be divided into two broad classes: Time-domain: Excitation is not sinusoidal (pulsed, broadband, etc.) Ultrawideband communications Pulsed
1.3 Sinusoidal Steady State Electromagnetics applications can be divided into two broad classes: Time-domain: Excitation is not sinusoidal (pulsed, broadband, etc.) Ultrawideband communications Pulsed
Adjoint networks and other elements of circuit theory. E416 4.Adjoint networks
 djoint networks and other elements of circuit theory One-port reciprocal networks one-port network is reciprocal if: V I I V = Where and are two different tests on the element Example: a linear impedance
djoint networks and other elements of circuit theory One-port reciprocal networks one-port network is reciprocal if: V I I V = Where and are two different tests on the element Example: a linear impedance
EECS 105: FALL 06 FINAL
 University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Jan M. Rabaey TuTh 2-3:30 Wednesday December 13, 12:30-3:30pm EECS 105: FALL 06 FINAL NAME Last
University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Jan M. Rabaey TuTh 2-3:30 Wednesday December 13, 12:30-3:30pm EECS 105: FALL 06 FINAL NAME Last
ECE 255, Frequency Response
 ECE 255, Frequency Response 19 April 2018 1 Introduction In this lecture, we address the frequency response of amplifiers. This was touched upon briefly in our previous lecture in Section 7.5 of the textbook.
ECE 255, Frequency Response 19 April 2018 1 Introduction In this lecture, we address the frequency response of amplifiers. This was touched upon briefly in our previous lecture in Section 7.5 of the textbook.
1 Phasors and Alternating Currents
 Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Review of DC Electric Circuit. DC Electric Circuits Examples (source:
 Review of DC Electric Circuit DC Electric Circuits Examples (source: http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dcex.html) 1 Review - DC Electric Circuit Multisim Circuit Simulation DC Circuit
Review of DC Electric Circuit DC Electric Circuits Examples (source: http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dcex.html) 1 Review - DC Electric Circuit Multisim Circuit Simulation DC Circuit
EE40 Lec 13. Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/13/2009. Reading: Hambley Chapter Chapter 14.10,14.5
 EE4 Lec 13 Filter and eonance Pro. Nathan Cheung 1/13/9 eading: Hambley Chapter 6.6-6.8 Chapter 14.1,14.5 Slide 1 Common Filter Traner Function v. Freq H ( ) H( ) Low Pa High Pa Frequency H ( ) H ( ) Frequency
EE4 Lec 13 Filter and eonance Pro. Nathan Cheung 1/13/9 eading: Hambley Chapter 6.6-6.8 Chapter 14.1,14.5 Slide 1 Common Filter Traner Function v. Freq H ( ) H( ) Low Pa High Pa Frequency H ( ) H ( ) Frequency
Single-Time-Constant (STC) Circuits This lecture is given as a background that will be needed to determine the frequency response of the amplifiers.
 Single-Time-Constant (STC) Circuits This lecture is given as a background that will be needed to determine the frequency response of the amplifiers. Objectives To analyze and understand STC circuits with
Single-Time-Constant (STC) Circuits This lecture is given as a background that will be needed to determine the frequency response of the amplifiers. Objectives To analyze and understand STC circuits with
Electric Circuits I Final Examination
 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points. 4. 3. Total 38 Was the exam fair? yes no //3 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Problem 4 points
EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points. 4. 3. Total 38 Was the exam fair? yes no //3 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Problem 4 points
Use of a Notch Filter in a Tuned Mode for LISA.
 Use of a Notch Filter in a Tuned Mode for LISA. Giorgio Fontana September 00 Abstract. During interferometric measurements the proof mass must be free from any controlling force within a given observation
Use of a Notch Filter in a Tuned Mode for LISA. Giorgio Fontana September 00 Abstract. During interferometric measurements the proof mass must be free from any controlling force within a given observation
Network Graphs and Tellegen s Theorem
 Networ Graphs and Tellegen s Theorem The concepts of a graph Cut sets and Kirchhoff s current laws Loops and Kirchhoff s voltage laws Tellegen s Theorem The concepts of a graph The analysis of a complex
Networ Graphs and Tellegen s Theorem The concepts of a graph Cut sets and Kirchhoff s current laws Loops and Kirchhoff s voltage laws Tellegen s Theorem The concepts of a graph The analysis of a complex
LECTURE 21: Butterworh & Chebeyshev BP Filters. Part 1: Series and Parallel RLC Circuits On NOT Again
 LECTURE : Butterworh & Chebeyshev BP Filters Part : Series and Parallel RLC Circuits On NOT Again. RLC Admittance/Impedance Transfer Functions EXAMPLE : Series RLC. H(s) I out (s) V in (s) Y in (s) R Ls
LECTURE : Butterworh & Chebeyshev BP Filters Part : Series and Parallel RLC Circuits On NOT Again. RLC Admittance/Impedance Transfer Functions EXAMPLE : Series RLC. H(s) I out (s) V in (s) Y in (s) R Ls
Electric Circuits I Final Examination
 The University of Toledo s8fs_elci7.fm - EECS:300 Electric Circuits I Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points.. 3. Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s8fs_elci7.fm
The University of Toledo s8fs_elci7.fm - EECS:300 Electric Circuits I Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points.. 3. Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s8fs_elci7.fm
Response of Second-Order Systems
 Unit 3 Response of SecondOrder Systems In this unit, we consider the natural and step responses of simple series and parallel circuits containing inductors, capacitors and resistors. The equations which
Unit 3 Response of SecondOrder Systems In this unit, we consider the natural and step responses of simple series and parallel circuits containing inductors, capacitors and resistors. The equations which
Alternating Current (AC) Circuits
 Alternating Current (AC) Circuits We have been talking about DC circuits Constant currents and voltages Resistors Linear equations Now we introduce AC circuits Time-varying currents and voltages Resistors,
Alternating Current (AC) Circuits We have been talking about DC circuits Constant currents and voltages Resistors Linear equations Now we introduce AC circuits Time-varying currents and voltages Resistors,
Frequency Response Prof. Ali M. Niknejad Prof. Rikky Muller
 EECS 105 Spring 2017, Module 4 Frequency Response Prof. Ali M. Niknejad Department of EECS Announcements l HW9 due on Friday 2 Review: CD with Current Mirror 3 Review: CD with Current Mirror 4 Review:
EECS 105 Spring 2017, Module 4 Frequency Response Prof. Ali M. Niknejad Department of EECS Announcements l HW9 due on Friday 2 Review: CD with Current Mirror 3 Review: CD with Current Mirror 4 Review:
Filters and Tuned Amplifiers
 Filters and Tuned Amplifiers Essential building block in many systems, particularly in communication and instrumentation systems Typically implemented in one of three technologies: passive LC filters,
Filters and Tuned Amplifiers Essential building block in many systems, particularly in communication and instrumentation systems Typically implemented in one of three technologies: passive LC filters,
EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain.
![EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain. EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain.](/thumbs/95/123488230.jpg) Name If you have any questions ask them. Remember to include all units on your answers (V, A, etc). Clearly indicate your answers. All angles must be in the range 0 to +180 or 0 to 180 degrees. 1) [6 pts]
Name If you have any questions ask them. Remember to include all units on your answers (V, A, etc). Clearly indicate your answers. All angles must be in the range 0 to +180 or 0 to 180 degrees. 1) [6 pts]
Review of Linear Time-Invariant Network Analysis
 D1 APPENDIX D Review of Linear Time-Invariant Network Analysis Consider a network with input x(t) and output y(t) as shown in Figure D-1. If an input x 1 (t) produces an output y 1 (t), and an input x
D1 APPENDIX D Review of Linear Time-Invariant Network Analysis Consider a network with input x(t) and output y(t) as shown in Figure D-1. If an input x 1 (t) produces an output y 1 (t), and an input x
6.1 Introduction
 6. Introduction A.C Circuits made up of resistors, inductors and capacitors are said to be resonant circuits when the current drawn from the supply is in phase with the impressed sinusoidal voltage. Then.
6. Introduction A.C Circuits made up of resistors, inductors and capacitors are said to be resonant circuits when the current drawn from the supply is in phase with the impressed sinusoidal voltage. Then.
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis 9 Assessment Problems AP 9. [a] V = 70/ 40 V [b] 0 sin(000t +20 ) = 0 cos(000t 70 ).. I = 0/ 70 A [c] I =5/36.87 + 0/ 53.3 =4+j3+6 j8 =0 j5 =.8/ 26.57 A [d] sin(20,000πt
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis 9 Assessment Problems AP 9. [a] V = 70/ 40 V [b] 0 sin(000t +20 ) = 0 cos(000t 70 ).. I = 0/ 70 A [c] I =5/36.87 + 0/ 53.3 =4+j3+6 j8 =0 j5 =.8/ 26.57 A [d] sin(20,000πt
Complex Numbers Review
 Complex Numbers view ference: Mary L. Boas, Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences Chapter 2 & 4 George Arfken, Mathematical Methods for Physicists Chapter 6 The real numbers (denoted R) are incomplete
Complex Numbers view ference: Mary L. Boas, Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences Chapter 2 & 4 George Arfken, Mathematical Methods for Physicists Chapter 6 The real numbers (denoted R) are incomplete
