Research Article Global Dynamics of a Mathematical Model on Smoking
|
|
|
- Elijah Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISRN Applied Mathematics, Article ID , 7 pages Research Article Global Dynamics of a Mathematical Model on Smoking Zainab Alkhudhari, Sarah Al-Sheikh, and Salma Al-Tuwairqi Departmentof Mathematics,KingAbdulaziz University, Jeddah 1551, Saudi Arabia Correspondence should be addressed to Salma Al-Tuwairqi; saltuwairqi@kau.edu.sa Received 17 November 013; Accepted 17 December 013; Published 6 February 014 Academic Editors: A. Bairi and S. W. Gong Copyright 014 Zainab Alkhudhari et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. We derive and analyze a mathematical model of smoking in which the population is divided into four classes: potential smokers, smokers, temporary quitters, and permanent quitters. In this model we study the effect of smokers on temporary quitters. Two equilibria of the model are found: one of them is the smoking-free equilibrium and the other corresponds to the presence of smoking. We examine the local and global stability of both equilibria and we support our results by using numerical simulations. 1. Introduction Tobacco epidemic is one of the biggest public health threats the world has ever faced. It kills up to half of its users. Nearly, each year six million people die from smoking of whom more than 5 million are users and ex-users and more than 600,000 are nonsmokers exposed to second-hand smoke. Tobacco users who die prematurely deprive their families of income, raise the cost of health care, and hinder economic development. In smoking death statistics, there is a death caused by tobacco every 8 seconds; 10% of the adult population who smoke die of tobacco related diseases. The World Health Organization predicts that, by 030, 10 million peoplewilldieeveryyearduetotobaccorelatedillnesses.this makes smoking the biggest killer globally. In Saudi Arabia, the prevalence of current smoking ranges from.4 to 5.3% (median = 17.5%) depending on the age group. The results of a Saudi modern study predicted an increase of smokers number in the country to 10 million smokers by 00. The current number of smokers in Saudi Arabia is approximately 6 million, and they spend around 1 billion Saudi Riyal on smoking annually. Clearly smoking is a prevalent problem among Saudis that requires intervention for eradication. Persistent education of the health hazards related to smoking is recommended particularly at early ages in order to prevent initiation of smoking [1, ]. In 1997, Castillo-Garsow et al. [3] proposed a simple mathematical model for giving up smoking. They considered a system described by the simplified PSQ model with a total constant population which is divided into three classes: potential smokers, that is, people who do not smoke yet but mightbecomesmokersinthefuture(p), smokers (S), and people (former smokers) who have quit smoking permanently (Q). Later, this mathematical model was developed by Sharomi and Gumel (008) [4]; they introduced a new class Q t of smokers who temporarily quit smoking and they described the dynamics of smoking by the following four nonlinear differential equations: dp dt = P βps, ds dt = (+γ)s+βps+αq t, (1) dq t = (+α)q dt t +γ(1 σ) S, dq p = Q dt p +σγs. They concluded that the smoking-free equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable whenever a certain threshold, known as thesmokersgenerationnumber,islessthanunityandunstable if this threshold is greater than unity. The public health implication of this result is that the number of smokers in the community will be effectively controlled (or eliminated) atsteadystateifthethresholdismadetobelessthanunity.
2 ISRN Applied Mathematics Such a control is not feasible if the threshold exceeds unity (a global stability result for the smoking-present equilibrium is provided for a special case). In 011, Lahrouz et al. [5] proved the global stability of the unique smoking-present equilibrium state of the mathematical model developed by Sharomi and Gumel. Also in 011, Zaman [6] derived and analyzed a smoking model taking into account the occasional smokers compartment, and later [7] he extended the model to consider the possibility of quitters becoming smokers again. In 01, Ertürk et al. [8] introduced fractional derivatives into themodelandstudieditnumerically. In this paper, we adopt the model developed and studied in [4, 5] and examine the effect of peer pressure on temporary quitters Q t. By this we mean the effect of smokers on temporary quitters which may be considered as one of the main causes of their relapse. This is done by taking α=αs as a parameter dependent on the pressure of smokers. The aimofthisworkistoanalyzethemodelbyusingstability theory of nonlinear differential equations and supporting the results with numerical simulation. The structure of this paper is organized as follows. In Section, we calculate the smoking generation number, find the equilibria, and investigate their stability. In Section 3, we present numerical simulations to support our results. Finally, we end the paper with a conclusion in Section 4.. Formulation of the Model Let the total population size at time t be denoted by N(t). We divide the populationn(t) into four subclasses: potential smokers (nonsmoker) P(t), smokers S(t), smokers who temporarily quit smoking Q t (t), and smokers who permanently quit smoking Q p (t), suchthatn(t) = P(t) + S(t) + Q t (t) + Q p (t). We describe the dynamics of smoking by the following four nonlinear differential equations: dp dt = P βps, ds dt = (+γ)s+βps+αsq t, dq t = Q dt t αsq t +γ(1 σ) S, dq p = Q dt p +σγs. Here, β is the contact rate between potential smokers and smokers, is the rate of natural death, α is the contact rate between smokers and temporary quitters who revert back to smoking, γ is the rate of quitting smoking, (1 σ)is the fraction of smokers who temporarily quit smoking (at arateγ), and σ is the remaining fraction of smokers who permanently quit smoking (at a rate γ). We assume that the class of potential smokers is increased by the recruitment of individuals at a rate. Inmodel, the total population is constant and P(t), S(t), Q t (t), and Q p (t) are, respectively, the proportions of potential smokers, smokers, temporarily quitters, and permanent quitters where () P(t) + S(t) + Q t (t) + Q p (t) = 1.SincethevariableQ p of model does not appear in the first three equations, we will only consider the subsystem: dp dt = P βps, ds dt = (+γ)s+βps+αsq t, (3) dq t = Q dt t αsq t +γ(1 σ) S. From model 3 we find that dp dt + ds dt + dq t (P+S+Q dt t ). (4) Let N 1 = P + S + Q t ;thenn 1 N 1.Theinitial value problem Φ = Φ,withΦ(0) = N 1 (0), hasthe solution Φ(t) = 1 ce t, and lim t Φ(t) = 1. Therefore, N 1 (t) Φ(t), which implies that lim t sup N 1 (t) 1. Thus, the considered region for model 3 is Γ={(P, S, Q t ) :P+S+Q t 1,P>0,S 0,Q t 0}. (5) All solutions of model 3 are bounded and enter the region Γ. Hence, Γ is positively invariant. That is, every solution of model 3, with initial conditions in Γ, remains there for all t> Equilibria and Smokers Generation Number Setting the right-hand side of the equations in model 3 to zero, we find two equilibria of the model: the smoking-free equilibrium E 0 = (1, 0, 0) and smoking-present equilibrium E =(P,S,Q t ),where P = Q t = and S satisfies the equation +βs, γ (1 σ) S +αs, S +( (β+γβ+α( β)+αγσ) )S βα ( + γσ) (7) + ( + γ β) =0. βα ( + γσ) The smokers generation number R 0 is found by the method of next generation matrix [9, 10]. Let X=(S,Q t,p);thenmodel 3canberewrittenasX = F(X) V(X) such that βps F (X) = [ 0 ], [ 0 ] (8) ( + γ) S αsq t V (X) = [( + α) SQ t γ(1 σ) S]. [ + P + βps ] (6)
3 ISRN Applied Mathematics 3 By calculating the Jacobian matrices at E 0,wefindthat where D(F (E 0 )) = [ F ], D(V (E 0)) = [ V 0 J 1 J ], (9) F=[ β 0 ( + γ) 0 ], V=[ ]. (10) 0 0 γ (1 σ) Thus, the next generation matrix is FV 1 =[ β/(+γ) ] and the smokers generation number R 0 is the spectral radius ρ(fv 1 ) = β/( + γ). Next we explore the existence of positive smoking-present equilibrium E of model 3. Equation (7)hassolutionsofthe form where A 1 and A are S 1, = A 1 ± 1 A 1 4A, (11) A 1 = (β+γβ+α( β)+αγσ), βα ( + γσ) A = ( + γ β) βα ( + γσ) = ( + γ) (1 R 0 ). βα ( + γσ) (1) Proof. Evaluating the Jacobian matrix of model 3 at E 0 (using linearization method [11]) gives β 0 J(E 0 )=[ 0 (+γ)+β 0 ]. (14) [ 0 γ(1 σ) ] Thus, the eigenvalues of J(E 0 ) are λ 1 = λ = < 0, λ 3 = ( + γ) + β. Clearlyλ 3 is negative if R 0 <1.Soall eigenvalues are negative if R 0 < 1, and hence E 0 is locally asymptotically stable. If R 0 =1,thenλ 3 =0and E 0 is locally stable. If R 0 >1,thenλ 3 >0which means that there exists a positive eigenvalue. So E 0 is unstable. Next, we investigate the local stability of the positive equilibrium E by using the following lemma. Lemma 3 (see [1 14]). Let M be a 3 3real matrix. If tr(m), det(m), anddet(m [] ) are all negative, then all of the eigenvalues of M have negative real part. M [] in the previous lemma is known as the second additive compound matrix with the following definition. Definition 4 (see [15] (second additive compound matrix)). Let A = (a ij ) be an n nrealmatrix.thesecondadditive compound of A is the matrix A [] =(b ij ) defined as follows: If R 0 >1,thenA <0and A 1 4A >A 1.Sowehave only one positive solution: S = 1 ( A 1 + A 1 4A ). (13) n=:a [] =a 11 +a, a 11 +a a 3 a 13 n=3:a [] = a 3 a 11 +a 33 a 1. a 31 a 1 a +a 33 (15) If R 0 =1,thenA =0and there are no positive solutions. If R 0 <1and β,thena 1 >0and A >0and there are no positive solutions. These results are summarized below. Theorem 1. Model 3 always has the smoking-free equilibrium point E 0 = (1, 0, 0). As for the existence of a smoking-present equilibrium point E, one has three cases: (i) if R 0 <1and β, one has no positive equilibrium point; (ii) if R 0 >1, one has one positive equilibrium point E ; (iii) if R 0 =1, one has no positive equilibrium point. 4. Stability of the Equilibria 4.1. Local Stability. First, we investigate the local stability of E 0 and state the following theorem. Theorem (local stability of E 0 ). If R 0 <1,thesmoking-free equilibrium point E 0 of model 3 is locally asymptotically stable. If R 0 =1, E 0 is locally stable. If R 0 >1, E 0 is unstable. Theorem 5 (local stability of E ). The smoking-present equilibrium E of model 3 is locally asymptotically stable if α β. Proof. Linearizing model 3 at the equilibrium E (P,S,Q t ) gives βs βp 0 J(E )= βs 0 αs. (16) [ 0 αq ] t +γ(1 σ) αs [ ] The second additive compound matrix J [] (E ) is J [] (E ) βs αs 0 = αq t +γ(1 σ) βs αs βp. [ 0 βs αs ] [ ] (17)
4 4 ISRN Applied Mathematics Here tr (J (E )) = βs αs <0, det (J (E )) = βαs (Q t βp S )+(αq t β P S ) βαs (Q t βp S ) +β(q t βp S ), if α β =(βαs +β)(q t +P 1)<0, since P +Q t <1, det (J [] (E )) = ( + βs )[(+βs +αs )(+αs ) +β P S ]+αq t (+αs ) = (+βs )[(+βs +αs )(+αs )] +(αq t β P S ) +S (α Q t β3 P S )<0, if α β. (18) Hence, by previous lemma, E is locally asymptotically stable if α β. 4.. Global Stability. We will examine the global stability of E 0 when β.first,itshouldbenotedthatp<1in Γ for all t>0. Consider the following Lyapunov function [16]: L=S+Q t, dl dt = (+γ)s+βps+αsq t Q t αsq t +γ(1 σ) S ( +β)s Q t 0. (19) We have dl/dt < 0 for β and dl/dt = 0 only if S=0and Q t =0. Therefore, by LaSalle s Invariance Principle [16], every solution to the equations of the model with initial conditions in Γ approaches E 0 as t.wehavethefollowingresult. Theorem 6 (global stability of E 0 ). If β,thene 0 is globally asymptotically stable in Γ. Now we examine the global stability of E by using the following theorem [1, 17] to prove that model 3 has no periodic solutions, homoclinic loops, and oriented phase polygons inside the invariant region. Theorem 7. Let g(p, S, Q t ) = {g 1 (P, S, Q t ), g (P,S,Q t ), g 3 (P, S, Q t )} be a vector field which is piecewise smooth on Γ and which satisfies the conditions g f = 0, (curl g) n<0 in the interior of Γ,wheren is the normal vector to Γ and f=(f 1,f,f 3 ) is a Lipschitz continuous field in the interior of Γ and curl g=( g 3 / S g / Q t ) i ( g 3 / P g 1 / Q t ) j+ ( g / P g 1 / S) k. Then the differential equation system P = f 1, S = f,andq t = f 3 has no periodic solutions, homoclinic loops, and oriented phase polygons inside Γ. Let Γ ={(P,S,Q t ) : P+((+γσ)/)S+Q t =1,P>0,S 0, Q t 0}.OnecaneasilyprovethatΓ Γ, Γ is positively invariant, and E Γ.Thus,westatethefollowingtheorem. Theorem 8. Model 3 has no periodic solutions, homoclinic loops, and oriented phase polygons inside the invariant region Γ. Proof. Let f 1, f, and f 3 denote the right-hand side of equations in model 3, respectively. Using P + (( + γσ)/)s + Q t =1to rewrite f 1, f,andf 3 in the equivalent forms, we have f 1 (P, S) = P βps, f 1 (P, Q t )= P βp[ +γσ (1 P Q t)], f (P, S) = (+γ)s+βps+αs[1 P ( +γσ )S], f (S, Q t )= (+γ)s +β[1 Q t ( +γσ )S]S+αSQ t, f 3 (P, Q t )= Q t [αq t γ(1 σ)][ +γσ (1 P Q t)], f 3 (S, Q t )= Q t αsq t +γ(1 σ) S. Let g=(g 1,g,g 3 ) be a vector field such that g 1 = f 3 (P, Q t ) PQ t α = P(+γσ) + + f (P, S) PS α +γσ + αq t P(+γσ) γ (1 σ) γ (1 σ) PQ t ( + γσ) Q t ( + γσ) γ (1 σ) P(+γσ) + γ P β α P +α(+γσ ) S P +α, g = f 1 (P, S) PS = PS f 3 (S, Q t ) SQ t β+α γ (1 σ) Q t, (0)
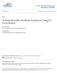
5 ISRN Applied Mathematics 5 Potential smokers P(t) (a) Smokers S(t) (b) 0.14 Temporary quitters Q t (t) Permanent quitters Q p (t) (c) (d) Figure 1: Time plots of model with different initial conditions for R 0 <1. (a) Potential smokers; (b) smokers; (c) temporary quitters; (d) permanent quitters. g 3 = f (S, Q t ) SQ t f 1 (P, Q t ) PQ t ( + γ) = + β β β(+γσ)s Q t Q t Q t +α + β + PQ t Q t Q t ( + γσ) βp Q t ( + γσ) β ( + γσ). (1) Since the alternate forms of f 1, f,andf 3 are equivalent in Γ, then Using the normal vector n = (1, ( + γσ)/, 1) to Γ,we can see that (curl g) n= βγσ γ (1 σ) Q t PQt +γσ P Q t P S αγσ P <0. (3) Hence, model 3 has no periodic solutions, homoclinic loops, and oriented phase polygons inside the invariant region Γ. Consequently,wehavethefollowingresult. So g f=0on Γ. g f=g 1 f 1 +g f +g 3 f 3 = f 3f 1 PQ t f f 1 PS + f 1f PS f 3f SQ t + f f 3 SQ t f 1f 3 PQ t =0. () Theorem 9 (global stability of E ). If R 0 > 1, then the smoking-present equilibrium point E of system (3) is globally asymptotically stable. Proof. We know that, if R 0 > 1 in Γ,thenE 0 is unstable. Also Γ is a positively invariant subset of Γ and the ω limit set of each solution of (3) is a single point in Γ since there is no periodic solutions, homoclinic loops, and oriented phase
6 6 ISRN Applied Mathematics Temporary quitters Q t (t) Potential smokers P(t) (a) Smokers S(t) (b) 0.5 Permanent quitters Q p (t) (c) (d) Figure : Time plots of model with different initial conditions for β α. (a) Potential smokers; (b) smokers; (c) temporary quitters; (d) permanent quitters. polygons inside Γ. Therefore E is globally asymptotically stable. 5. Numerical Simulations In this section, we illustrate some numerical solutions of model for different values of the parameters, and we show that these solutions are in agreement with the qualitative behavior of the solutions. We use the following parameters: = 0.04, γ = 0.3, α = 0.5, andσ = 0.4, withtwo different values of the contact rate between potential smokers and smokers: for R 0 <1we use β = 0. and for β αwe use β = 0.5. Model is simulated for the following different initial values such that P+S+Q t +Q p =1: (1) P(0) = , S(0) = 68, Q t (0) = ,and Q p (0) = ; () P(0) = , S(0) = , Q t (0) = ,and Q p (0) = 0.018; (3) P(0) = , S(0) = , Q t (0) = 566,and Q p (0) = ; (4) P(0) = , S(0) = , Q t (0) = ,and Q p (0) = For R 0 = < 1, Figure 1(a) shows that the number of potential smokers increases and approaches the total population 1. Figure 1(b) shows that the number of the smokers decreases and approaches zero. In Figures 1(c) and 1(d), temporary quitters and permanent quitters increase at first; after that they decrease and approach zero. We see from Figure 1 that, for any initial value, the solution curves tend to the equilibrium E 0,whenR 0 < 1.Hence,modelis locally asymptotically stable about E 0 for the previous set of parameters. In Figure, we use the same parameters and initial values as previously with β = 0.5. Figure (a) shows that the number of potential smokers decreases at first; then it increases and approaches P. Figure (b) shows that the number of smokers increases at first; then it decreases and approaches S.In Figures (c) and (d), temporary quitters and permanent quitters increase at first; after that they decrease and approach Q t and Q p.weseefromfigure that, for any initial value, thesolutioncurvestendtotheequilibriume,whenβ α.
7 ISRN Applied Mathematics 7 Hence, model is locally asymptotically stable about E for the above set of parameters. 6. Discussion and Conclusions In this paper, we presented a mathematical model to analyze the behavior of smoking dynamics in a population with peer pressure effect on temporary quitters Q t.localasymptotic stability for the smoking-free equilibrium state is obtained when the threshold quantity R 0 is less than 1 (i.e., when the contact rate β between potential smokers and smokers is less than the sum of natural death rate and the quitting rate γ). A Lyapunov function is used to show global stability of thesmoking-freeequilibriumwhenthecontactratebetween potential smokers and smokers is less than or equal to the natural death rate (β ). This means that the number of smokers may be controlled by reducing the contact rate β to be less than the natural death rate. On the other hand, if β α (i.e., when the contact rate β between potential smokers and smokers is greater than the contact rate α between smokers andtemporaryquitterswhorevertbacktosmoking),thenthe smoking-present equilibrium state is locally asymptotically stable. By showing that this model has no periodic solutions, homoclinic loops, and oriented phase polygons inside the invariant region Γ,weprovedtheglobalasymptoticstability of E. This means that, if R 0 >1, smoking will persist. Some numerical simulations are performed to illustrate the findings of the analytical results. For R 0 >1, the results show that the smokers population reaches a steady state of approximately 6% of the total population. This model may be extended to include, for example, smokers who after quitting smoking may become potential smokersagain.wemayalsoconsiderthepublichealthimpact ofsmokingrelatedillnessesaswell. Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. [6] G. Zaman, Qualitative behavior of giving up smoking models, Bulletin of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society,vol.34, no., pp , 011. [7] G. Zaman, Optimal campaign in the smoking dynamics, Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, vol. 011, Article ID , 9 pages, 011. [8] V. S. Ertürk, G. Zaman, and S. Momani, A numeric-analytic method for approximating a giving up smoking model containing fractional derivatives, Computers & Mathematics with Applications,vol.64,no.10,pp ,01. [9] P. van den Driessche and J. Watmough, Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission, Mathematical Biosciences,vol.180, pp.9 48,00. [10] F. Brauer, P. van den Driessche, and J. Wu, Mathematical Epidemiology, vol of Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Springer, Berlin, Germany, 008. [11] L. Perko, Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems, vol. 7 of Texts in Applied Mathematics, Springer, New York, NY, USA, [1]L.Cai,X.Li,M.Ghosh,andB.Guo, Stabilityanalysisof an HIV/AIDS epidemic model with treatment, Computational and Applied Mathematics,vol.9,no.1,pp , 009. [13] C. C. McCluskey and P. van den Driessche, Global analysis of two tuberculosis models, Dynamics and Differential Equations,vol.16,no.1,pp ,004. [14] J. Arino, C. C. McCluskey, and P. van den Driessche, Global results for an epidemic model with vaccination that exhibits backward bifurcation, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, vol.64,no.1,pp.60 76,003. [15] X. Ge and M. Arcak, A sufficient condition for additive Dstability and application to reaction-diffusion models, Systems & Control Letters, vol. 58, no , pp , 009. [16] M. W. Hirsch, S. Smale, and R. L. Devaney, Differential Equations, Dynamical Systems, and an Introduction to Chaos, vol. 60 of Pure and Applied Mathematics, Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, nd edition, 004. [17] S. Busenberg and P. van den Driessche, Analysis of a disease transmission model in a population with varying size, Journal of Mathematical Biology,vol.8,no.3,pp.57 70,1990. References [1] M. M. Bassiony, Smoking in Saudi Arabia, Saudi Medical Journal,vol.30,no.7,pp ,009. [] World Health Organization report on tobacco, 01, [3] C. Castillo-Garsow, G. Jordan-Salivia, and A. R. Herrera, Mathematical models for the dynamics of tobacco use, recovery, and relapse, Technical Report Series BU-1505-M, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, [4] O. Sharomi and A. B. Gumel, Curtailing smoking dynamics: a mathematical modeling approach, Applied Mathematics and Computation,vol.195,no.,pp ,008. [5] A. Lahrouz, L. Omari, D. Kiouach, anda. Belmaâti, Deterministic and stochastic stability of a mathematical model of smoking, Statistics & Probability Letters, vol. 81, no. 8, pp , 011.
8 Advances in Operations Research Advances in Decision Sciences Mathematical Problems in Engineering Algebra Probability and Statistics The Scientific World Journal International Differential Equations Submit your manuscripts at International Advances in Combinatorics Mathematical Physics Complex Analysis International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Stochastic Analysis Abstract and Applied Analysis International Mathematics Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Discrete Mathematics Applied Mathematics Function Spaces Optimization
The E ect of Occasional Smokers on the Dynamics of a Smoking Model
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 25, 1207-1222 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2014.46120 The E ect of Occasional Smokers on the Dynamics of a Smoking Model
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 25, 1207-1222 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2014.46120 The E ect of Occasional Smokers on the Dynamics of a Smoking Model
Smoking as Epidemic: Modeling and Simulation Study
 American Journal of Applied Mathematics 2017; 5(1): 31-38 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajam doi: 10.11648/j.ajam.20170501.14 ISSN: 2330-0043 (Print); ISSN: 2330-006X (Online) Smoking as Epidemic:
American Journal of Applied Mathematics 2017; 5(1): 31-38 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajam doi: 10.11648/j.ajam.20170501.14 ISSN: 2330-0043 (Print); ISSN: 2330-006X (Online) Smoking as Epidemic:
Thursday. Threshold and Sensitivity Analysis
 Thursday Threshold and Sensitivity Analysis SIR Model without Demography ds dt di dt dr dt = βsi (2.1) = βsi γi (2.2) = γi (2.3) With initial conditions S(0) > 0, I(0) > 0, and R(0) = 0. This model can
Thursday Threshold and Sensitivity Analysis SIR Model without Demography ds dt di dt dr dt = βsi (2.1) = βsi γi (2.2) = γi (2.3) With initial conditions S(0) > 0, I(0) > 0, and R(0) = 0. This model can
GlobalStabilityofStificrsImpactonMemeTransmissionModel. Global Stability of Stificrs Impact on Meme Transmission Model
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: F Mathematics and Decision Sciences Volume 14 Issue 6 Version 1. Year 14 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: F Mathematics and Decision Sciences Volume 14 Issue 6 Version 1. Year 14 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
Stability Analysis of an HIV/AIDS Epidemic Model with Screening
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 66, 351-373 Stability Analysis of an HIV/AIDS Epidemic Model with Screening Sarah Al-Sheikh Department of Mathematics King Abdulaziz University Jeddah,
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 66, 351-373 Stability Analysis of an HIV/AIDS Epidemic Model with Screening Sarah Al-Sheikh Department of Mathematics King Abdulaziz University Jeddah,
Mathematical Model of Tuberculosis Spread within Two Groups of Infected Population
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 43, 2131-2140 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2016.63130 Mathematical Model of Tuberculosis Spread within Two Groups of Infected
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 43, 2131-2140 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2016.63130 Mathematical Model of Tuberculosis Spread within Two Groups of Infected
Mathematical Analysis of Epidemiological Models III
 Intro Computing R Complex models Mathematical Analysis of Epidemiological Models III Jan Medlock Clemson University Department of Mathematical Sciences 27 July 29 Intro Computing R Complex models What
Intro Computing R Complex models Mathematical Analysis of Epidemiological Models III Jan Medlock Clemson University Department of Mathematical Sciences 27 July 29 Intro Computing R Complex models What
Research Article Propagation of Computer Virus under Human Intervention: A Dynamical Model
 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and ociety Volume 2012, Article ID 106950, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/106950 Research Article Propagation of Computer Virus under Human Intervention: A Dynamical Model Chenquan
Discrete Dynamics in Nature and ociety Volume 2012, Article ID 106950, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/106950 Research Article Propagation of Computer Virus under Human Intervention: A Dynamical Model Chenquan
Stability of SEIR Model of Infectious Diseases with Human Immunity
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 6 (2017), pp. 1811 1819 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/gjpam.htm Stability of SEIR Model of Infectious
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 6 (2017), pp. 1811 1819 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/gjpam.htm Stability of SEIR Model of Infectious
STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A GENERAL SIR EPIDEMIC MODEL
 VFAST Transactions on Mathematics http://vfast.org/index.php/vtm@ 2013 ISSN: 2309-0022 Volume 1, Number 1, May-June, 2013 pp. 16 20 STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A GENERAL SIR EPIDEMIC MODEL Roman Ullah 1, Gul
VFAST Transactions on Mathematics http://vfast.org/index.php/vtm@ 2013 ISSN: 2309-0022 Volume 1, Number 1, May-June, 2013 pp. 16 20 STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A GENERAL SIR EPIDEMIC MODEL Roman Ullah 1, Gul
Research Article Modeling Computer Virus and Its Dynamics
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 213, Article ID 842614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/842614 Research Article Modeling Computer Virus and Its Dynamics Mei Peng, 1 Xing He, 2 Junjian
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 213, Article ID 842614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/842614 Research Article Modeling Computer Virus and Its Dynamics Mei Peng, 1 Xing He, 2 Junjian
Introduction: What one must do to analyze any model Prove the positivity and boundedness of the solutions Determine the disease free equilibrium
 Introduction: What one must do to analyze any model Prove the positivity and boundedness of the solutions Determine the disease free equilibrium point and the model reproduction number Prove the stability
Introduction: What one must do to analyze any model Prove the positivity and boundedness of the solutions Determine the disease free equilibrium point and the model reproduction number Prove the stability
Global Analysis of an Epidemic Model with Nonmonotone Incidence Rate
 Global Analysis of an Epidemic Model with Nonmonotone Incidence Rate Dongmei Xiao Department of Mathematics, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 00030, China E-mail: xiaodm@sjtu.edu.cn and Shigui Ruan
Global Analysis of an Epidemic Model with Nonmonotone Incidence Rate Dongmei Xiao Department of Mathematics, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 00030, China E-mail: xiaodm@sjtu.edu.cn and Shigui Ruan
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Effect of Personal Hygiene Campaign on the Transmission Model of Hepatitis A
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 9(13) Special 15, Pages: 67-73 ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: wwwajbaswebcom Effect of Personal Hygiene
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 9(13) Special 15, Pages: 67-73 ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: wwwajbaswebcom Effect of Personal Hygiene
Global Analysis of an SEIRS Model with Saturating Contact Rate 1
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 80, 3991-4003 Global Analysis of an SEIRS Model with Saturating Contact Rate 1 Shulin Sun a, Cuihua Guo b, and Chengmin Li a a School of Mathematics and
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 80, 3991-4003 Global Analysis of an SEIRS Model with Saturating Contact Rate 1 Shulin Sun a, Cuihua Guo b, and Chengmin Li a a School of Mathematics and
GLOBAL STABILITY OF A VACCINATION MODEL WITH IMMIGRATION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2015 (2015), No. 92, pp. 1 10. SSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu GLOBAL STABLTY
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2015 (2015), No. 92, pp. 1 10. SSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu GLOBAL STABLTY
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences
 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com A SIR Transmission Model of Political Figure Fever 1 Benny Yong and 2 Nor Azah Samat 1
AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com A SIR Transmission Model of Political Figure Fever 1 Benny Yong and 2 Nor Azah Samat 1
Simple Mathematical Model for Malaria Transmission
 Journal of Advances in Mathematics and Computer Science 25(6): 1-24, 217; Article no.jamcs.37843 ISSN: 2456-9968 (Past name: British Journal of Mathematics & Computer Science, Past ISSN: 2231-851) Simple
Journal of Advances in Mathematics and Computer Science 25(6): 1-24, 217; Article no.jamcs.37843 ISSN: 2456-9968 (Past name: British Journal of Mathematics & Computer Science, Past ISSN: 2231-851) Simple
Analysis of SIR Mathematical Model for Malaria disease with the inclusion of Infected Immigrants
 IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 14, Issue 5 Ver. I (Sep - Oct 218), PP 1-21 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of SIR Mathematical Model for Malaria disease
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 14, Issue 5 Ver. I (Sep - Oct 218), PP 1-21 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of SIR Mathematical Model for Malaria disease
Global Stability of a Computer Virus Model with Cure and Vertical Transmission
 International Journal of Research Studies in Computer Science and Engineering (IJRSCSE) Volume 3, Issue 1, January 016, PP 16-4 ISSN 349-4840 (Print) & ISSN 349-4859 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Global
International Journal of Research Studies in Computer Science and Engineering (IJRSCSE) Volume 3, Issue 1, January 016, PP 16-4 ISSN 349-4840 (Print) & ISSN 349-4859 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Global
Mathematical Analysis of Visceral Leishmaniasis Model
 vol. 1 (2017), Article I 101263, 16 pages doi:10.11131/2017/101263 AgiAl Publishing House http://www.agialpress.com/ Research Article Mathematical Analysis of Visceral Leishmaniasis Model F. Boukhalfa,
vol. 1 (2017), Article I 101263, 16 pages doi:10.11131/2017/101263 AgiAl Publishing House http://www.agialpress.com/ Research Article Mathematical Analysis of Visceral Leishmaniasis Model F. Boukhalfa,
Modeling and Global Stability Analysis of Ebola Models
 Modeling and Global Stability Analysis of Ebola Models T. Stoller Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Physics Wichita State University REU July 27, 2016 T. Stoller REU 1 / 95 Outline Background
Modeling and Global Stability Analysis of Ebola Models T. Stoller Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Physics Wichita State University REU July 27, 2016 T. Stoller REU 1 / 95 Outline Background
GLOBAL STABILITY OF SIR MODELS WITH NONLINEAR INCIDENCE AND DISCONTINUOUS TREATMENT
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2015 (2015), No. 304, pp. 1 8. SSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu GLOBAL STABLTY
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2015 (2015), No. 304, pp. 1 8. SSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu GLOBAL STABLTY
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Effect of Education Campaign on Transmission Model of Conjunctivitis
 ISSN:99-878 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com ffect of ducation Campaign on Transmission Model of Conjunctivitis Suratchata Sangthongjeen, Anake Sudchumnong
ISSN:99-878 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com ffect of ducation Campaign on Transmission Model of Conjunctivitis Suratchata Sangthongjeen, Anake Sudchumnong
Mathematical Analysis of Epidemiological Models: Introduction
 Mathematical Analysis of Epidemiological Models: Introduction Jan Medlock Clemson University Department of Mathematical Sciences 8 February 2010 1. Introduction. The effectiveness of improved sanitation,
Mathematical Analysis of Epidemiological Models: Introduction Jan Medlock Clemson University Department of Mathematical Sciences 8 February 2010 1. Introduction. The effectiveness of improved sanitation,
Research Article A Hamilton-Poisson Model of the Chen-Lee System
 Applied Mathematics Volume 1, Article ID 4848, 11 pages doi:1.1155/1/4848 Research Article A Hamilton-Poisson Model of the Chen-Lee System Camelia Pop Arieşanu Department of Mathematics, Politehnica University
Applied Mathematics Volume 1, Article ID 4848, 11 pages doi:1.1155/1/4848 Research Article A Hamilton-Poisson Model of the Chen-Lee System Camelia Pop Arieşanu Department of Mathematics, Politehnica University
Research Article Applying GG-Convex Function to Hermite-Hadamard Inequalities Involving Hadamard Fractional Integrals
 International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 4, Article ID 3635, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/4/3635 Research Article Applying GG-Convex Function to Hermite-Hadamard Inequalities
International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 4, Article ID 3635, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/4/3635 Research Article Applying GG-Convex Function to Hermite-Hadamard Inequalities
3 Stability and Lyapunov Functions
 CDS140a Nonlinear Systems: Local Theory 02/01/2011 3 Stability and Lyapunov Functions 3.1 Lyapunov Stability Denition: An equilibrium point x 0 of (1) is stable if for all ɛ > 0, there exists a δ > 0 such
CDS140a Nonlinear Systems: Local Theory 02/01/2011 3 Stability and Lyapunov Functions 3.1 Lyapunov Stability Denition: An equilibrium point x 0 of (1) is stable if for all ɛ > 0, there exists a δ > 0 such
LAW OF LARGE NUMBERS FOR THE SIRS EPIDEMIC
 LAW OF LARGE NUMBERS FOR THE SIRS EPIDEMIC R. G. DOLGOARSHINNYKH Abstract. We establish law of large numbers for SIRS stochastic epidemic processes: as the population size increases the paths of SIRS epidemic
LAW OF LARGE NUMBERS FOR THE SIRS EPIDEMIC R. G. DOLGOARSHINNYKH Abstract. We establish law of large numbers for SIRS stochastic epidemic processes: as the population size increases the paths of SIRS epidemic
A Mathematical Analysis on the Transmission Dynamics of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Yk j N k j
 North Carolina Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 3, Pages 7 20 (Accepted June 23, 2017, published June 30, 2017 ISSN 2380-7539 A Mathematical Analysis on the Transmission Dynamics of Neisseria
North Carolina Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 3, Pages 7 20 (Accepted June 23, 2017, published June 30, 2017 ISSN 2380-7539 A Mathematical Analysis on the Transmission Dynamics of Neisseria
Behavior Stability in two SIR-Style. Models for HIV
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 4, 2010, no. 9, 427-434 Behavior Stability in two SIR-Style Models for HIV S. Seddighi Chaharborj 2,1, M. R. Abu Bakar 2, I. Fudziah 2 I. Noor Akma 2, A. H. Malik 2,
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 4, 2010, no. 9, 427-434 Behavior Stability in two SIR-Style Models for HIV S. Seddighi Chaharborj 2,1, M. R. Abu Bakar 2, I. Fudziah 2 I. Noor Akma 2, A. H. Malik 2,
Research Article Remarks on Asymptotic Centers and Fixed Points
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2010, Article ID 247402, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/247402 Research Article Remarks on Asymptotic Centers and Fixed Points A. Kaewkhao 1 and K. Sokhuma 2 1 Department
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2010, Article ID 247402, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/247402 Research Article Remarks on Asymptotic Centers and Fixed Points A. Kaewkhao 1 and K. Sokhuma 2 1 Department
The death of an epidemic
 LECTURE 2 Equilibrium Stability Analysis & Next Generation Method The death of an epidemic In SIR equations, let s divide equation for dx/dt by dz/ dt:!! dx/dz = - (β X Y/N)/(γY)!!! = - R 0 X/N Integrate
LECTURE 2 Equilibrium Stability Analysis & Next Generation Method The death of an epidemic In SIR equations, let s divide equation for dx/dt by dz/ dt:!! dx/dz = - (β X Y/N)/(γY)!!! = - R 0 X/N Integrate
Research Article Remarks on the Regularity Criterion of the Navier-Stokes Equations with Nonlinear Damping
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 15, Article ID 194, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/15/194 Research Article Remarks on the Regularity Criterion of the Navier-Stokes Equations with Nonlinear
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 15, Article ID 194, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/15/194 Research Article Remarks on the Regularity Criterion of the Navier-Stokes Equations with Nonlinear
Research Article Asymptotic Behavior of the Solutions of System of Difference Equations of Exponential Form
 Difference Equations Article ID 936302 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/936302 Research Article Asymptotic Behavior of the Solutions of System of Difference Equations of Exponential Form Vu Van Khuong
Difference Equations Article ID 936302 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/936302 Research Article Asymptotic Behavior of the Solutions of System of Difference Equations of Exponential Form Vu Van Khuong
Qualitative Analysis of a Discrete SIR Epidemic Model
 ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 05 Issue, 03 March 2015 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Qualitative Analysis of a Discrete SIR Epidemic Model A. George Maria Selvam 1, D.
ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 05 Issue, 03 March 2015 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Qualitative Analysis of a Discrete SIR Epidemic Model A. George Maria Selvam 1, D.
A Delayed HIV Infection Model with Specific Nonlinear Incidence Rate and Cure of Infected Cells in Eclipse Stage
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 216, no. 43, 2121-213 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.216.63128 A Delayed HIV Infection Model with Specific Nonlinear Incidence Rate and
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 216, no. 43, 2121-213 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.216.63128 A Delayed HIV Infection Model with Specific Nonlinear Incidence Rate and
GLOBAL DYNAMICS OF A MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF TUBERCULOSIS
 CANADIAN APPIED MATHEMATICS QUARTERY Volume 13, Number 4, Winter 2005 GOBA DYNAMICS OF A MATHEMATICA MODE OF TUBERCUOSIS HONGBIN GUO ABSTRACT. Mathematical analysis is carried out for a mathematical model
CANADIAN APPIED MATHEMATICS QUARTERY Volume 13, Number 4, Winter 2005 GOBA DYNAMICS OF A MATHEMATICA MODE OF TUBERCUOSIS HONGBIN GUO ABSTRACT. Mathematical analysis is carried out for a mathematical model
Research Article Global Attractivity of a Higher-Order Difference Equation
 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 2012, Article ID 930410, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2012/930410 Research Article Global Attractivity of a Higher-Order Difference Equation R. Abo-Zeid Department
Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 2012, Article ID 930410, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2012/930410 Research Article Global Attractivity of a Higher-Order Difference Equation R. Abo-Zeid Department
GLOBAL STABILITY OF THE ENDEMIC EQUILIBRIUM OF A TUBERCULOSIS MODEL WITH IMMIGRATION AND TREATMENT
 CANADIAN APPLIED MATHEMATICS QUARTERLY Volume 19, Number 1, Spring 2011 GLOBAL STABILITY OF THE ENDEMIC EQUILIBRIUM OF A TUBERCULOSIS MODEL WITH IMMIGRATION AND TREATMENT HONGBIN GUO AND MICHAEL Y. LI
CANADIAN APPLIED MATHEMATICS QUARTERLY Volume 19, Number 1, Spring 2011 GLOBAL STABILITY OF THE ENDEMIC EQUILIBRIUM OF A TUBERCULOSIS MODEL WITH IMMIGRATION AND TREATMENT HONGBIN GUO AND MICHAEL Y. LI
Impact of Case Detection and Treatment on the Spread of HIV/AIDS: a Mathematical Study
 Malaysian Journal of Mathematical Sciences (3): 33 347 (8) MALAYSIA JOURAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIECES Journal homepage: http://einspemupmedumy/journal Impact of Case Detection and Treatment on the Spread
Malaysian Journal of Mathematical Sciences (3): 33 347 (8) MALAYSIA JOURAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIECES Journal homepage: http://einspemupmedumy/journal Impact of Case Detection and Treatment on the Spread
Dynamics of a Networked Connectivity Model of Waterborne Disease Epidemics
 Dynamics of a Networked Connectivity Model of Waterborne Disease Epidemics A. Edwards, D. Mercadante, C. Retamoza REU Final Presentation July 31, 214 Overview Background on waterborne diseases Introduction
Dynamics of a Networked Connectivity Model of Waterborne Disease Epidemics A. Edwards, D. Mercadante, C. Retamoza REU Final Presentation July 31, 214 Overview Background on waterborne diseases Introduction
Stability Analysis of an SVIR Epidemic Model with Non-linear Saturated Incidence Rate
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 215, no. 23, 1145-1158 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.215.41164 Stability Analysis of an SVIR Epidemic Model with Non-linear Saturated
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 215, no. 23, 1145-1158 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.215.41164 Stability Analysis of an SVIR Epidemic Model with Non-linear Saturated
Delay SIR Model with Nonlinear Incident Rate and Varying Total Population
 Delay SIR Model with Nonlinear Incident Rate Varying Total Population Rujira Ouncharoen, Salinthip Daengkongkho, Thongchai Dumrongpokaphan, Yongwimon Lenbury Abstract Recently, models describing the behavior
Delay SIR Model with Nonlinear Incident Rate Varying Total Population Rujira Ouncharoen, Salinthip Daengkongkho, Thongchai Dumrongpokaphan, Yongwimon Lenbury Abstract Recently, models describing the behavior
Stability Analysis of a SIS Epidemic Model with Standard Incidence
 tability Analysis of a I Epidemic Model with tandard Incidence Cruz Vargas-De-León Received 19 April 2011; Accepted 19 Octuber 2011 leoncruz82@yahoo.com.mx Abstract In this paper, we study the global properties
tability Analysis of a I Epidemic Model with tandard Incidence Cruz Vargas-De-León Received 19 April 2011; Accepted 19 Octuber 2011 leoncruz82@yahoo.com.mx Abstract In this paper, we study the global properties
GLOBAL ASYMPTOTIC STABILITY OF A DIFFUSIVE SVIR EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH IMMIGRATION OF INDIVIDUALS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 16 (16), No. 8, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu GLOBAL ASYMPTOTIC STABILITY OF A DIFFUSIVE SVIR
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 16 (16), No. 8, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu GLOBAL ASYMPTOTIC STABILITY OF A DIFFUSIVE SVIR
Research Article A Two-Grid Method for Finite Element Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 212, Article ID 391918, 11 pages doi:1.1155/212/391918 Research Article A Two-Grid Method for Finite Element Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations Chuanjun Chen
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 212, Article ID 391918, 11 pages doi:1.1155/212/391918 Research Article A Two-Grid Method for Finite Element Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations Chuanjun Chen
Research Article Convex Polyhedron Method to Stability of Continuous Systems with Two Additive Time-Varying Delay Components
 Applied Mathematics Volume 202, Article ID 689820, 3 pages doi:0.55/202/689820 Research Article Convex Polyhedron Method to Stability of Continuous Systems with Two Additive Time-Varying Delay Components
Applied Mathematics Volume 202, Article ID 689820, 3 pages doi:0.55/202/689820 Research Article Convex Polyhedron Method to Stability of Continuous Systems with Two Additive Time-Varying Delay Components
Research Article Solvability for a Coupled System of Fractional Integrodifferential Equations with m-point Boundary Conditions on the Half-Line
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 24, Article ID 29734, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/29734 Research Article Solvability for a Coupled System of Fractional Integrodifferential Equations with m-point
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 24, Article ID 29734, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/29734 Research Article Solvability for a Coupled System of Fractional Integrodifferential Equations with m-point
Research Article Adaptive Control of Chaos in Chua s Circuit
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 2011, Article ID 620946, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2011/620946 Research Article Adaptive Control of Chaos in Chua s Circuit Weiping Guo and Diantong Liu Institute
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 2011, Article ID 620946, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2011/620946 Research Article Adaptive Control of Chaos in Chua s Circuit Weiping Guo and Diantong Liu Institute
Research Article On the Stability Property of the Infection-Free Equilibrium of a Viral Infection Model
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume, Article ID 644, 9 pages doi:.55//644 Research Article On the Stability Property of the Infection-Free Equilibrium of a Viral
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume, Article ID 644, 9 pages doi:.55//644 Research Article On the Stability Property of the Infection-Free Equilibrium of a Viral
Research Article Some New Explicit Values of Quotients of Ramanujan s Theta Functions and Continued Fractions
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Article ID 534376 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/04/534376 Research Article Some New Explicit Values of Quotients of Ramanujan s Theta Functions and
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Article ID 534376 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/04/534376 Research Article Some New Explicit Values of Quotients of Ramanujan s Theta Functions and
Research Article Bessel Equation in the Semiunbounded Interval x [x 0, ]: Solving in the Neighbourhood of an Irregular Singular Point
![Research Article Bessel Equation in the Semiunbounded Interval x [x 0, ]: Solving in the Neighbourhood of an Irregular Singular Point Research Article Bessel Equation in the Semiunbounded Interval x [x 0, ]: Solving in the Neighbourhood of an Irregular Singular Point](/thumbs/83/88729813.jpg) International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 6826482, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6826482 Research Article Bessel Equation in the Semiunbounded Interval x [x 0,
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 6826482, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6826482 Research Article Bessel Equation in the Semiunbounded Interval x [x 0,
Dynamics of Disease Spread. in a Predator-Prey System
 Advanced Studies in Biology, vol. 6, 2014, no. 4, 169-179 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/asb.2014.4845 Dynamics of Disease Spread in a Predator-Prey System Asrul Sani 1, Edi Cahyono
Advanced Studies in Biology, vol. 6, 2014, no. 4, 169-179 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/asb.2014.4845 Dynamics of Disease Spread in a Predator-Prey System Asrul Sani 1, Edi Cahyono
Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission
 Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission P. van den Driessche a,1 and James Watmough b,2, a Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University
Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission P. van den Driessche a,1 and James Watmough b,2, a Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University
Research Article On the Idempotent Solutions of a Kind of Operator Equations
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 0, Article ID 84665, pages doi:0.540/0/84665 Research Article On the Idempotent Solutions of a Kind of Operator Equations Chun Yuan
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 0, Article ID 84665, pages doi:0.540/0/84665 Research Article On the Idempotent Solutions of a Kind of Operator Equations Chun Yuan
Introduction to SEIR Models
 Department of Epidemiology and Public Health Health Systems Research and Dynamical Modelling Unit Introduction to SEIR Models Nakul Chitnis Workshop on Mathematical Models of Climate Variability, Environmental
Department of Epidemiology and Public Health Health Systems Research and Dynamical Modelling Unit Introduction to SEIR Models Nakul Chitnis Workshop on Mathematical Models of Climate Variability, Environmental
Optimal control of vaccination and treatment for an SIR epidemiological model
 ISSN 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 8 (22) No. 3, pp. 94-24 Optimal control of vaccination and treatment for an SIR epidemiological model Tunde Tajudeen Yusuf, Francis
ISSN 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 8 (22) No. 3, pp. 94-24 Optimal control of vaccination and treatment for an SIR epidemiological model Tunde Tajudeen Yusuf, Francis
Research Article The Stability of Gauss Model Having One-Prey and Two-Predators
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2012, Article ID 219640, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/219640 Research Article The Stability of Gauss Model Having One-Prey and Two-Predators A. Farajzadeh, 1 M. H. Rahmani
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2012, Article ID 219640, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/219640 Research Article The Stability of Gauss Model Having One-Prey and Two-Predators A. Farajzadeh, 1 M. H. Rahmani
Accepted Manuscript. Backward Bifurcations in Dengue Transmission Dynamics. S.M. Garba, A.B. Gumel, M.R. Abu Bakar
 Accepted Manuscript Backward Bifurcations in Dengue Transmission Dynamics S.M. Garba, A.B. Gumel, M.R. Abu Bakar PII: S0025-5564(08)00073-4 DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2008.05.002 Reference: MBS 6860 To appear
Accepted Manuscript Backward Bifurcations in Dengue Transmission Dynamics S.M. Garba, A.B. Gumel, M.R. Abu Bakar PII: S0025-5564(08)00073-4 DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2008.05.002 Reference: MBS 6860 To appear
Research Article Coefficient Estimates for Two New Subclasses of Biunivalent Functions with respect to Symmetric Points
 Function Spaces Volume 2015 Article ID 145242 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/145242 Research Article Coefficient Estimates for Two New Subclasses of Biunivalent Functions with respect to Symmetric
Function Spaces Volume 2015 Article ID 145242 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/145242 Research Article Coefficient Estimates for Two New Subclasses of Biunivalent Functions with respect to Symmetric
Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 653914, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/653914 Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 653914, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/653914 Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
Solving Separable Nonlinear Equations Using LU Factorization
 Western Washington University Western CEDAR Mathematics College of Science and Engineering 03 Solving Separable Nonlinear Equations Using LU Factorization Yun-Qiu Shen Western Washington University, yunqiu.shen@wwu.edu
Western Washington University Western CEDAR Mathematics College of Science and Engineering 03 Solving Separable Nonlinear Equations Using LU Factorization Yun-Qiu Shen Western Washington University, yunqiu.shen@wwu.edu
Research Article A Half-Inverse Problem for Impulsive Dirac Operator with Discontinuous Coefficient
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 213, Article ID 18189, 4 pages http://d.doi.org/1.1155/213/18189 Research Article A Half-Inverse Problem for Impulsive Dirac Operator with Discontinuous Coefficient
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 213, Article ID 18189, 4 pages http://d.doi.org/1.1155/213/18189 Research Article A Half-Inverse Problem for Impulsive Dirac Operator with Discontinuous Coefficient
Research Article Numerical Integration and Synchronization for the 3-Dimensional Metriplectic Volterra System
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume, Article ID 769, pages doi:.55//769 Research Article Numerical Integration and Synchronization for the -Dimensional Metriplectic Volterra System Gheorghe Ivan,
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume, Article ID 769, pages doi:.55//769 Research Article Numerical Integration and Synchronization for the -Dimensional Metriplectic Volterra System Gheorghe Ivan,
Stability Analysis of Plankton Ecosystem Model. Affected by Oxygen Deficit
 Applied Mathematical Sciences Vol 9 2015 no 81 4043-4052 HIKARI Ltd wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/1012988/ams201553255 Stability Analysis of Plankton Ecosystem Model Affected by Oxygen Deficit Yuriska
Applied Mathematical Sciences Vol 9 2015 no 81 4043-4052 HIKARI Ltd wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/1012988/ams201553255 Stability Analysis of Plankton Ecosystem Model Affected by Oxygen Deficit Yuriska
Research Article Almost Periodic Viscosity Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Boundary Value Problems Volume 29, Article ID 873526, 15 pages doi:1.1155/29/873526 Research Article Almost Periodic Viscosity Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Boundary Value Problems Volume 29, Article ID 873526, 15 pages doi:1.1155/29/873526 Research Article Almost Periodic Viscosity Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations
MODELING THE SPREAD OF DENGUE FEVER BY USING SIR MODEL. Hor Ming An, PM. Dr. Yudariah Mohammad Yusof
 MODELING THE SPREAD OF DENGUE FEVER BY USING SIR MODEL Hor Ming An, PM. Dr. Yudariah Mohammad Yusof Abstract The establishment and spread of dengue fever is a complex phenomenon with many factors that
MODELING THE SPREAD OF DENGUE FEVER BY USING SIR MODEL Hor Ming An, PM. Dr. Yudariah Mohammad Yusof Abstract The establishment and spread of dengue fever is a complex phenomenon with many factors that
Research Article Existence and Uniqueness of Homoclinic Solution for a Class of Nonlinear Second-Order Differential Equations
 Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 615303, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/615303 Research Article Existence and Uniqueness of Homoclinic Solution for a Class of Nonlinear Second-Order Differential
Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 615303, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/615303 Research Article Existence and Uniqueness of Homoclinic Solution for a Class of Nonlinear Second-Order Differential
Research Article Hopf Bifurcation Analysis and Anticontrol of Hopf Circles of the Rössler-Like System
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume, Article ID 3487, 6 pages doi:.55//3487 Research Article Hopf Bifurcation Analysis and Anticontrol of Hopf Circles of the Rössler-Like System Ranchao Wu and Xiang Li
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume, Article ID 3487, 6 pages doi:.55//3487 Research Article Hopf Bifurcation Analysis and Anticontrol of Hopf Circles of the Rössler-Like System Ranchao Wu and Xiang Li
Research Article Chaos Control on a Duopoly Game with Homogeneous Strategy
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 16, Article ID 74185, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/16/74185 Publication Year 16 Research Article Chaos Control on a Duopoly
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 16, Article ID 74185, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/16/74185 Publication Year 16 Research Article Chaos Control on a Duopoly
Research Article Applications of Differential Subordination for Argument Estimates of Multivalent Analytic Functions
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 04, Article ID 63470, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/04/63470 search Article Applications of Differential Subordination for Argument Estimates of Multivalent Analytic
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 04, Article ID 63470, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/04/63470 search Article Applications of Differential Subordination for Argument Estimates of Multivalent Analytic
Research Article Existence for Elliptic Equation Involving Decaying Cylindrical Potentials with Subcritical and Critical Exponent
 International Differential Equations Volume 2015, Article ID 494907, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/494907 Research Article Existence for Elliptic Equation Involving Decaying Cylindrical Potentials
International Differential Equations Volume 2015, Article ID 494907, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/494907 Research Article Existence for Elliptic Equation Involving Decaying Cylindrical Potentials
Research Article Stability Switches and Hopf Bifurcations in a Second-Order Complex Delay Equation
 Hindawi Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 017, Article ID 679879, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/017/679879 Research Article Stability Switches and Hopf Bifurcations in a Second-Order Complex
Hindawi Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 017, Article ID 679879, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/017/679879 Research Article Stability Switches and Hopf Bifurcations in a Second-Order Complex
Research Article Hamilton-Poisson Realizations for the Lü System
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 011, Article ID 8435, 13 pages doi:10.1155/011/8435 Research Article Hamilton-Poisson Realizations for the Lü System Camelia Pop, 1 Camelia Petrişor, 1 and Dumitru
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 011, Article ID 8435, 13 pages doi:10.1155/011/8435 Research Article Hamilton-Poisson Realizations for the Lü System Camelia Pop, 1 Camelia Petrişor, 1 and Dumitru
Mathematical Modeling Applied to Understand the Dynamical Behavior of HIV Infection
 Open Journal of Modelling and Simulation, 217, 5, 145-157 http://wwwscirporg/journal/ojmsi ISSN Online: 2327-426 ISSN Print: 2327-418 Mathematical Modeling Applied to Understand the Dynamical Behavior
Open Journal of Modelling and Simulation, 217, 5, 145-157 http://wwwscirporg/journal/ojmsi ISSN Online: 2327-426 ISSN Print: 2327-418 Mathematical Modeling Applied to Understand the Dynamical Behavior
Research Article A New Class of Meromorphic Functions Associated with Spirallike Functions
 Applied Mathematics Volume 202, Article ID 49497, 2 pages doi:0.55/202/49497 Research Article A New Class of Meromorphic Functions Associated with Spirallike Functions Lei Shi, Zhi-Gang Wang, and Jing-Ping
Applied Mathematics Volume 202, Article ID 49497, 2 pages doi:0.55/202/49497 Research Article A New Class of Meromorphic Functions Associated with Spirallike Functions Lei Shi, Zhi-Gang Wang, and Jing-Ping
Research Article A Generalization of a Class of Matrices: Analytic Inverse and Determinant
 Advances in Numerical Analysis Volume 2011, Article ID 593548, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/593548 Research Article A Generalization of a Class of Matrices: Analytic Inverse and Determinant F. N. Valvi Department
Advances in Numerical Analysis Volume 2011, Article ID 593548, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/593548 Research Article A Generalization of a Class of Matrices: Analytic Inverse and Determinant F. N. Valvi Department
KingSaudBinAbdulazizUniversityforHealthScience,Riyadh11481,SaudiArabia. Correspondence should be addressed to Raghib Abu-Saris;
 Chaos Volume 26, Article ID 49252, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/26/49252 Research Article On Matrix Projective Synchronization and Inverse Matrix Projective Synchronization for Different and Identical
Chaos Volume 26, Article ID 49252, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/26/49252 Research Article On Matrix Projective Synchronization and Inverse Matrix Projective Synchronization for Different and Identical
Research Article Partial Pole Placement in LMI Region
 Control Science and Engineering Article ID 84128 5 pages http://dxdoiorg/11155/214/84128 Research Article Partial Pole Placement in LMI Region Liuli Ou 1 Shaobo Han 2 Yongji Wang 1 Shuai Dong 1 and Lei
Control Science and Engineering Article ID 84128 5 pages http://dxdoiorg/11155/214/84128 Research Article Partial Pole Placement in LMI Region Liuli Ou 1 Shaobo Han 2 Yongji Wang 1 Shuai Dong 1 and Lei
Mathematical Analysis of HIV/AIDS Prophylaxis Treatment Model
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 18, 893-902 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2018.8689 Mathematical Analysis of HIV/AIDS Prophylaxis Treatment Model F. K. Tireito,
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 18, 893-902 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2018.8689 Mathematical Analysis of HIV/AIDS Prophylaxis Treatment Model F. K. Tireito,
Sensitivity and Stability Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus Model with Non-Cytolytic Cure Process and Logistic Hepatocyte Growth
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 12, Number 3 2016), pp. 2297 2312 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/gjpam.htm Sensitivity and Stability Analysis
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 12, Number 3 2016), pp. 2297 2312 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/gjpam.htm Sensitivity and Stability Analysis
Research Article A Note about the General Meromorphic Solutions of the Fisher Equation
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering, Article ID 793834, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/793834 Research Article A Note about the General Meromorphic Solutions of the Fisher Equation Jian-ming Qi, Qiu-hui
Mathematical Problems in Engineering, Article ID 793834, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/793834 Research Article A Note about the General Meromorphic Solutions of the Fisher Equation Jian-ming Qi, Qiu-hui
New results on the existences of solutions of the Dirichlet problem with respect to the Schrödinger-prey operator and their applications
 Chen Zhang Journal of Inequalities Applications 2017 2017:143 DOI 10.1186/s13660-017-1417-9 R E S E A R C H Open Access New results on the existences of solutions of the Dirichlet problem with respect
Chen Zhang Journal of Inequalities Applications 2017 2017:143 DOI 10.1186/s13660-017-1417-9 R E S E A R C H Open Access New results on the existences of solutions of the Dirichlet problem with respect
The Fractional-order SIR and SIRS Epidemic Models with Variable Population Size
 Math. Sci. Lett. 2, No. 3, 195-200 (2013) 195 Mathematical Sciences Letters An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/msl/020308 The Fractional-order SIR and SIRS Epidemic Models with Variable
Math. Sci. Lett. 2, No. 3, 195-200 (2013) 195 Mathematical Sciences Letters An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/msl/020308 The Fractional-order SIR and SIRS Epidemic Models with Variable
Research Article Strong Convergence of a Projected Gradient Method
 Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 410137, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2012/410137 Research Article Strong Convergence of a Projected Gradient Method Shunhou Fan and Yonghong Yao Department of Mathematics,
Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 410137, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2012/410137 Research Article Strong Convergence of a Projected Gradient Method Shunhou Fan and Yonghong Yao Department of Mathematics,
Research Article Fixed Point Theorems of Quasicontractions on Cone Metric Spaces with Banach Algebras
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2013, Article ID 187348, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187348 Research Article Fixed Point Theorems of Quasicontractions on Cone Metric Spaces with Banach
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2013, Article ID 187348, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187348 Research Article Fixed Point Theorems of Quasicontractions on Cone Metric Spaces with Banach
Analysis of a model for hepatitis C virus transmission that includes the effects of vaccination and waning immunity
 Analysis of a model for hepatitis C virus transmission that includes the effects of vaccination and waning immunity Daniah Tahir Uppsala University Department of Mathematics 7516 Uppsala Sweden daniahtahir@gmailcom
Analysis of a model for hepatitis C virus transmission that includes the effects of vaccination and waning immunity Daniah Tahir Uppsala University Department of Mathematics 7516 Uppsala Sweden daniahtahir@gmailcom
Demographic impact and controllability of malaria in an SIS model with proportional fatality
 Demographic impact and controllability of malaria in an SIS model with proportional fatality Muntaser Safan 1 Ahmed Ghazi Mathematics Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, 35516 Mansoura,
Demographic impact and controllability of malaria in an SIS model with proportional fatality Muntaser Safan 1 Ahmed Ghazi Mathematics Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, 35516 Mansoura,
Research Article The Dirichlet Problem on the Upper Half-Space
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2012, Article ID 203096, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/203096 Research Article The Dirichlet Problem on the Upper Half-Space Jinjin Huang 1 and Lei Qiao 2 1 Department of
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2012, Article ID 203096, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/203096 Research Article The Dirichlet Problem on the Upper Half-Space Jinjin Huang 1 and Lei Qiao 2 1 Department of
Research Article Solvability of a Class of Integral Inclusions
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 212, Article ID 21327, 12 pages doi:1.1155/212/21327 Research Article Solvability of a Class of Integral Inclusions Ying Chen and Shihuang Hong Institute of Applied
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 212, Article ID 21327, 12 pages doi:1.1155/212/21327 Research Article Solvability of a Class of Integral Inclusions Ying Chen and Shihuang Hong Institute of Applied
Research Article Unicity of Entire Functions concerning Shifts and Difference Operators
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 204, Article ID 38090, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/38090 Research Article Unicity of Entire Functions concerning Shifts and Difference Operators Dan Liu, Degui
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 204, Article ID 38090, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/38090 Research Article Unicity of Entire Functions concerning Shifts and Difference Operators Dan Liu, Degui
Research Article Modelling Blood and Pulmonary Pressure for Solving a Performance Optimal Problem for Sportsmen
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 470143, 16 pages doi:10.5402/2012/470143 Research Article Modelling Blood and Pulmonary Pressure for Solving a
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 470143, 16 pages doi:10.5402/2012/470143 Research Article Modelling Blood and Pulmonary Pressure for Solving a
Global Stability of SEIRS Models in Epidemiology
 Global Stability of SRS Models in pidemiology M. Y. Li, J. S. Muldowney, and P. van den Driessche Department of Mathematics and Statistics Mississippi State University, Mississippi State, MS 39762 Department
Global Stability of SRS Models in pidemiology M. Y. Li, J. S. Muldowney, and P. van den Driessche Department of Mathematics and Statistics Mississippi State University, Mississippi State, MS 39762 Department
Research Article Convergence Theorems for Infinite Family of Multivalued Quasi-Nonexpansive Mappings in Uniformly Convex Banach Spaces
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2012, Article ID 435790, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/435790 Research Article Convergence Theorems for Infinite Family of Multivalued Quasi-Nonexpansive Mappings in Uniformly
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2012, Article ID 435790, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/435790 Research Article Convergence Theorems for Infinite Family of Multivalued Quasi-Nonexpansive Mappings in Uniformly
Research Article A Note on the Central Limit Theorems for Dependent Random Variables
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Probability and Statistics Volume 22, Article ID 92427, pages doi:.542/22/92427 Research Article A Note on the Central Limit Theorems for Dependent Random
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Probability and Statistics Volume 22, Article ID 92427, pages doi:.542/22/92427 Research Article A Note on the Central Limit Theorems for Dependent Random
Research Article On Behavior of Solution of Degenerated Hyperbolic Equation
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 124936, 10 pages doi:10.5402/2012/124936 Research Article On Behavior of Solution of Degenerated Hyperbolic Equation
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 124936, 10 pages doi:10.5402/2012/124936 Research Article On Behavior of Solution of Degenerated Hyperbolic Equation
Research Article An Inverse Eigenvalue Problem for Jacobi Matrices
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 2011 Article ID 571781 11 pages doi:10.1155/2011/571781 Research Article An Inverse Eigenvalue Problem for Jacobi Matrices Zhengsheng Wang 1 and Baoiang Zhong
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 2011 Article ID 571781 11 pages doi:10.1155/2011/571781 Research Article An Inverse Eigenvalue Problem for Jacobi Matrices Zhengsheng Wang 1 and Baoiang Zhong
Research Article Translative Packing of Unit Squares into Squares
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 01, Article ID 61301, 7 pages doi:10.1155/01/61301 Research Article Translative Packing of Unit Squares into Squares Janusz Januszewski Institute
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 01, Article ID 61301, 7 pages doi:10.1155/01/61301 Research Article Translative Packing of Unit Squares into Squares Janusz Januszewski Institute
Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread
 Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread Julien Arino Centre for Research on Inner City Health St Michael s Hospital Toronto On leave from Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba Julien Arino@umanitoba.ca
Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread Julien Arino Centre for Research on Inner City Health St Michael s Hospital Toronto On leave from Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba Julien Arino@umanitoba.ca
