Electromagnetic Energy
|
|
|
- Kory Christiana Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCIENCE GRADE 4 Below Level California Content Standards Physical Sciences: 1.B Physical Sciences: 1.C Physical Sciences: 1.D Physical Sciences: 1.E Physical Sciences: 1.F Investigation and Experimentation: 6.F Electromagnetic Energy FOCUScurriculum Curriculum materials for your content standards 33 Milford Drive, Suite 1, Hudson, OH LOOK INSIDE FOR: California s Academic Content Standards Covered Reproducible Student Book Reproducible English-language Arts Activities
2 Electromagnetic Energy California s Content Standards Met GRADE 4 SCIENCE PHYSICAL SCIENCES: 1 Electricity and magnetism are related effects that have many useful applications in everyday life. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know how to build a simple compass and use it to detect magnetic effects, including Earth s magnetic field. c. Students know electric currents produce magnetic fields and know how to build a simple electromagnet. d. Students know the role of electromagnets in the construction of electric motors, electric generators, and simple devices, such as doorbells and earphones. e. Students know electrically charged objects attract or repel each other. f. Students know that magnets have two poles (north and south) and that like poles repel each other while unlike poles attract each other. INVESTIGATION AND EXPERIMENTATION: 6 Scientific progress is made by asking meaningful questions and conducting careful investigations. As a basis for understanding this concept and addressing the content in the other three strands, students should develop their own questions and perform investigations. Students will: f. Follow a set of written instructions for a scientific investigation. GRADE 4 ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS 1.0 WORD ANALYSIS, FLUENCY, AND SYSTEMATIC VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT Vocabulary and Concept Development 1.2 Apply knowledge of word origins, derivations, synonyms, antonyms, and idioms to determine the meaning of words and phrases. 2.0 READING COMPREHENSION Structural Features of Informational Materials 2.1 Identify structural patterns found in informational text (e.g., compare and contrast, cause and effect, sequential or chronological order, proposition and support) to strengthen comprehension. Comprehension and Analysis of Grade-Level-Appropriate Text 2.2 Use appropriate strategies when reading for different purposes (e.g., full comprehension, location of information, personal enjoyment). Comprehension and Analysis of Grade-Level-Appropriate Text 2.6 Distinguish between cause and effect and between fact and opinion in expository text.
3 SCIENCE GRADE 4 Below Level California Content Standards Physical Sciences: 1.B Physical Sciences: 1.C Physical Sciences: 1.D Physical Sciences: 1.E Physical Sciences: 1.F Investigation and Experimentation: 6.F Student Book Electromagnetic Energy Print pages 5 18 of this PDF for the student book.
4 How to Make the Student Book The student book is contained on pages 5 18 of this PDF. It begins on the next page. To make one student book, or a two-sided master copy that can be photocopied, you will print on both sides of seven sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper. Do a test printout of one book first to familiarize yourself with the procedure. Follow these instructions carefully. First Select the Paper Since you will be printing on both sides of the sheets of paper, select a good quality white paper. We recommend using at least a 22lb sheet. Forth Print ODD Pages When the even pages have printed, flip the stack of pages over to print the odd pages. Place the stack back in your printer. Select print from the file menu again. In your printer s dialogue box, select ODD pages. Click Print to print the odd the pages. Fifth Fold the Book You now have a complete book. Check to be sure the pages are in the correct order with the book s cover as the top page. Then fold the stack of paper in half. Sixth Staple the Book Use an extended-length stapler to staple the pages together. Place three staples in the spine of the book. Second Check Printer Settings Be sure you have the correct page setup settings for your computer and printer. You will print these pages in landscape format. Third Print EVEN Pages Open the PDF of the book you want to print. Select print from your file menu. In your printer s dialogue box enter pages 5 18 to print. Then select EVEN pages only. It is important to print only the EVEN pages first. Click "Print" to print the even pages. (Important note: The first page that prints will be blank. DO NOT discard this page. It will be needed to print the cover in the next step.) Please note that printers vary in how they output pages. Do a test printing with one book and adjust the procedure as necessary. If you want to make a one-sided master copy, print ALL pages 5 18 at once. Then select "one-sided to two-sided" on the copy machine.
5 BL Electromagnetic Energy California s Content Standards Met GRADE 4 SCIENCE PHYSICAL SCIENCES: 1 Electricity and magnetism are related effects that have many useful applications in everyday life. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know how to build a simple compass and use it to detect magnetic effects, including Earth s magnetic field. c. Students know electric currents produce magnetic fields and know how to build a simple electromagnet. d. Students know the role of electromagnets in the construction of electric motors, electric generators, and simple devices, such as doorbells and earphones. e. Students know electrically charged objects attract or repel each other. f. Students know that magnets have two poles (north and south) and that like poles repel each other while unlike poles attract each other. INVESTIGATION AND EXPERIMENTATION: 6 Scientific progress is made by asking meaningful questions and conducting careful investigations. As a basis for understanding this concept and addressing the content in the other three strands, students should develop their own questions and perform investigations. Students will: f. Follow a set of written instructions for a scientific investigation. Electromagnetic Energy by Ken Sibila SCIENCE GRADE 4 California Content Standards Physical Sciences: 1.B Physical Sciences: 1.C Physical Sciences: 1.D Physical Sciences: 1.E Physical Sciences: 1.F Investigation and Experimentation: 6.F GRADE 4 ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS 1.0 WORD ANALYSIS, FLUENCY, AND SYSTEMATIC VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT Vocabulary and Concept Development 1.2 Apply knowledge of word origins, derivations, synonyms, antonyms, and idioms to determine the meaning of words and phrases. 2.0 READING COMPREHENSION Structural Features of Informational Materials 2.1 Identify structural patterns found in informational text (e.g., compare and contrast, cause and effect, sequential or chronological order, proposition and support) to strengthen comprehension. Comprehension and Analysis of Grade-Level-Appropriate Text 2.2 Use appropriate strategies when reading for different purposes (e.g., full comprehension, location of information, personal enjoyment). Comprehension and Analysis of Grade-Level-Appropriate Text 2.6 Distinguish between cause and effect and between fact and opinion in expository text.
6 SCIENCE GRADE 4 California Content Standards Physical Sciences: 1.B Physical Sciences: 1.C Physical Sciences: 1.D Physical Sciences: 1.E Physical Sciences: 1.F Investigation and Experimentation: 6.F Electromagnetic Energy by Ken Sibila FOCUScurriculum Table of Contents Introduction: Electrical Charges Chapter 1: Magnets Magnetic Fields Earth Is a Magnet How a Compass Works Electricity Creates Magnetic Fields Hans Christian Oersted Chapter 2: Electromagnets in Use Glossary To Find Out More Index Curriculum materials for your content standards
7 INTRODUCTION Electrical Charges Everything in the world is made up of tiny pieces called atoms. Inside each atom are even tinier pieces. Some have an electrical charge. Protons have a positive charge. Electrons have a negative charge. Positive charges attract, or pull toward, negative charges. For example, when you rub a balloon against your hair, the tiny pieces move. The balloon picks up electrons and gets a negative charge. The negative electrons in the balloon attract positive particles in the wall. This causes the balloon to stick to the wall. Positive charges and negative charges are opposite. Opposite charges attract! Objects with a negative charge repel, or move away from, other objects with a negative charge. Tie strings to two balloons. Rub each balloon on your hair. Both balloons get a negative charge. Then hold them close together by the strings. The balloons move apart. They repel each other because both charges are negative. Negative charges repel each other. Positive charges repel each other too. Similar charges repel! attract: to make something come closer repel: to make something move away 4 5
8 Magnets are objects that attract certain metals. Magnets also have electrical charges. They attract and repel. Magnets have two ends. These ends of a magnet are called poles. One end is the north pole (N). The other end is the south pole (S). Put opposite poles of two magnets close together. They will pull each other together. Opposite poles attract! Put poles that are the same close together. They will repel each other. Like poles repel! 6 N S N S CHAPTER 1 Magnets Like poles repel each other. N S S N Opposite poles attract each other Try it Yourself! Gather different sizes and shapes of magnets. Place one magnet at the end of this ruler. Place the other magnet a few inches away. Slide the magnet toward the other magnet at the end of the ruler. Record what happens in a journal. S N Distance First magnet Distance 1 Distance 2 Distance 3 S N Second magnet 7
9 Magnetic Fields A magnet has forces that push and pull. The forces surround the magnet with a magnetic field. Where is the force of the magnetic field the strongest? It is strongest at the north and the south pole of the magnet. Earth Is a Magnet Earth is a giant magnet. It also has a magnetic field around it. Like a magnet, the Earth has a north pole and a south pole. The Earth s magnetic field is strongest at the north and south magnetic poles. Magnetic Field of a Magnet Magnetic Field of Earth Where is the magnetic field the strongest? 8 9
10 How a Compass Works A compass is a simple device that can keep people from getting lost. A compass has a magnet called the needle. No matter which way you turn the compass, one end of the needle always point towards the north. The other end always points toward the south. A compass has a magnet. The tip of one end of the magnet is attracted to Earth s north pole. Try It Yourself! You can make your own compass. To create one, you will need the following: Materials craft needle cork or sponge magnet bowl filled with water Procedure 1. Rub the magnet in the same direction along the needle 25 times. S N 2. Place the cork or sponge in the the bowl. Rest the needle on top. 10 device: something made or invented for a special use 3. In which direction does the needle on your compass point? 11
11 Electricity Creates Magnetic Fields When an electric current flows through a wire, the wire has its own weak magnetic field. This magnetic field can be made stronger if the wire is coiled around an iron bar. This creates a temporary magnet called an electromagnet. The electromagnet only has a magnetic field when the electricity flows. If the current is switched off, the electromagnet loses its magnetic field. It is no longer a magnet. Electricity flows through the electromagnet. It then has a magnetic field. Hans Christian Oersted Hans Christian Oersted was a teacher in Denmark. One day in 1819, he set up two demonstrations. First, he was going to show how an electric current heats a wire. Then he was going to show magnetism using a compass. While Oersted was showing how electricity heats a wire, he looked at the compass. He noticed that when the electric current was switched on, the nearby compass needle moved. He discovered that an electric current flowing through a wire could move the needle of a compass. His discovery showed the connection between electricity and magnetism. temporary: lasting only for a short time demonstration: showing how something works 12 13
12 Try It Yourself! You can make your own electromagnet. Materials copper wire with insulation 8d iron nail D battery tape small metal items such as paper clips, and staples compass Procedure 1. Ask an adult to strip the insulation off both ends of the copper wire. 2. Carefully wrap, or coil, the copper wire around the nail ten or more times. 3. Attach one end of the wire to the negative ( ) side of the battery with tape. Attach the other end to the positive side (+). 4. Place the nail close to the small metal objects. Record what happens. 5. Place the compass close to the nail. Move the compass around the nail. Record your findings. 6. Reverse the wires on the battery. Repeat step 3. Record your findings. 7. Disconnect one wire from the battery and repeat steps 3 and 4. Record your findings. N S - BATTERY
13 CHAPTER 2 Electromagnets in Use Diagram of a Classroom Bell Electromagnets Are All Around Us Electromagnets are all around us. The bell on a classroom wall can use an electromagnet. Look at the picture to see how it works. First, someone pushes a button connected to the bell. This sends an electric current to the electromagnet in the bell. Now the electromagnet has a magnetic field. An iron bar with a hammer head is attracted to the magnetic field. This causes the hammer head to strike the bell. Bell Electromagnet Iron bar with hammer head Wires to door bell button Brainstorm a list of things you use or have seen that have an electromagnet
14 The speaker in your classroom is also an electromagnet. Look at the picture below. The speaker has a paper cone, a magnet, and an electromagnet. Magnetic forces between the electromagnet and the magnet push or pull on the paper cone. The movement of the cone forms sound waves. Diagram of a Speaker A motor uses an electromagnet. The electromagnet is surrounded by a magnet. The electromagnet is connected to a rod. The rod allows the electromagnet to spin. When an electric current passes through, the magnetic force causes the electromagnet to spin. Diagram of an Electric Motor Magnet Electromagnet Rod Electromagnet N S To Battery Paper cone Magnet The electromagnet in a speaker helps convert electrical energy into sound energy
15 Try It Yourself! You can make your own electric motor. Materials safety glasses 6 inches of copper wire 1.5 V battery small neodymium disk magnet iron screw with flat head such as a drywall screw Procedure 1. Have an adult strip the insulation off both ends of the wire. 2. Attach the magnet to the flat head of the screw. 3. Hold the battery as shown and place the tip of the screw to the Battery button end of the battery. 20 Screw Magnet 4. Press and hold one end of the wire to the top of the battery. 5. Lightly touch the other end of the wire to the side of the magnet. Caution Objects in this experiment can fly off and hit surrounding areas. Be sure anyone nearby is wearing safety glasses. 6. Record your findings and explain what you observed. 21
16 Glossary attract to make something come closer demonstration showing how something works repel to make something move away temporary lasting only for a short time To Find Out More... Want to learn more about electromagnetic energy? Try these books Electricity and Magnetism (Usborne Understanding Science) by Peter Adamczyk. Usborne Books, Awesome Experiments in Electricity & Magnetism by Michael A. DiSpezio. Sterling, The Science of Electricity & Magnetism: Projects and Experiments With Electricity And Magnets (Tabletop Scientist) by Steve Parker. Heinemann, Access these Web sites Creative Kids at Home magnet.html Energy Kid s Page electricity.html The NASA Sci Files Lab/acts_ electric.html 22 23
17 Index Published by FOCUScurriculum 33 Milford Drive, Suite 1 Hudson, OH compass, 10, 13 doorbell, 16 electric motor, 19 electrical charges, 4 5 magnetic fields, 8 9, 12 Oersted, Hans Christian, 13 speaker, Copyright 2009 FOCUScurriculum Order Number: CASC-42BL Created by Kent Publishing Services, Inc. Designed by Signature Design Group, Inc. No part of the book may be reproduced without purchasing a license from the publisher. To purchase a license to reproduce this book, contact FOCUScurriculum. The publisher takes no responsibility for the use of any of the materials or methods described in this book, nor for the products thereof. 24
18 ENGLISH-LANGUAGE ARTS GRADE 4 Below Level California Content Standards Vocabulary and Concept Development: 1.2 Structural Features of Informational Materials: 2.1 Comprehension and Analysis of Grade-Level-Appropriate Text: 2.2 Comprehension and Analysis of Grade-Level-Appropriate Text: 2.6 English-language Arts Activities Electromagnetic Energy Print pages of this PDF for the reading activities.
19 Synonyms and Antonyms Words that mean the same, such as tiny and small, are synonyms. Words that mean the opposite, such as tiny and large, are antonyms. For example, a synonym for push is shove. Push and shove have the same meaning. An antonym for push is pull. Push and pull have opposite meanings. Write the correct words from the box on the lines. You will use some of the words twice. TRY THE SKILL 5. A synonym for the other end 6. An antonym for repel 7. A synonym for close 8. An antonym for positive attract negative opposite strongest temporary discovered nearby 1. A synonym for found 2. An antonym for same 3. An antonym for weakest 4. A synonym for come closer Find more words in the book that have synonyms and antonyms. Write them on the lines below. Vocabulary and Concept Development, 1.2
20 Sequential Order Sequential order is the order in which things happen. Understanding sequential order can help you understand and remember what you read. You can retell the sequential order. To do this, use words such as, first, then, next, and finally. Read this passage from Electromagnetic Energy. Tie strings to two balloons. Rub each balloon on your hair. Both balloons get a negative charge. Then hold them close together by the strings. The balloons move apart. They repel each other because both charges are negative. What are the steps in this investigation? A graphic organizer can help you identify the steps. Step 1 Tie strings to two balloons. TRY THE SKILL Read this passage from Electromagnetic Energy. How does a bell with an electromagnet work? Retell in sequential order. Use the graphic organizer to help. First, someone pushes a button connected to the bell. This sends an electric current to the electromagnet in the bell. Now the electromagnet has a magnetic field. An iron bar with a hammer head is attracted to the magnetic field. This causes the hammer head to strike the bell. Step 1 Step 2 Step 2 Step 3 Rub each balloon against your hair. Hold the balloons close together. Step 3 Step 4 Structural Features of Informational Materials 2.1
21 Identify a Purpose As you choose something to read, you usually have a purpose in mind, such as these: to gain or understand information to learn how to do something to gather information in order to form an opinion to be entertained For example, you read this book to gain information about electromagnetic energy. You also learned how to perform several experiments another purposes for reading. As you look through books, magazines, and articles, think about your purpose for reading. Choose reading material that matches your purpose. 2. This selection tells how to build an electromagnet. to inform to tell how to do something to persuade to entertain 3. This selection explains the benefits of using electric powered cars. to inform to tell how to do something to persuade to entertain TRY THE SKILL Read the description of each selection. Then identify its main purpose. 1. This selection tells why magnets attract and repel each other. to inform to tell how to do something to persuade to entertain 4. This selection tells about early scientists who investigated magnetism. to inform to tell how to do something to persuade to entertain Comprehension and Analysis of Grade-Level-Appropriate Text, 2.2
22 Distinguish Fact from Opinion TRY THE SKILL A fact can be proved. For example, a scientists can say that an electromagnet only has a magnetic field when the electricity flows through it.. An opinion is what someone believes. For example, a person might say electromagnets waste energy However, other people might disagree with this opinion. Being able to tell facts from opinions makes you a better reader. Opinion sentences often have words such as better, worse, should, difficult, toughest, and easy. Here are more examples: Fact Hans Christian Oersted was a teacher in Denmark. Opinion Hans Christian Oersted made the most important discovery about magnetic fields. Mark each statement below F for fact or O for opinion. 1. Everything in the word is made up of atoms. 2. The experiment testing the strength of two magnets was fun. 3. Objects with a negative charge repel other objects with a negative charge. 4. You should never leave on a trip without a compass. 5. Earth is a giant magnet. 6. Hans Christian Oersted should have known what caused the compass needle to move. 7. A speaker uses an electromagnet to send sound waves. 8. Opposite charges attract. Similar charges repel. On the back of this page, write one fact and one opinion about electromagnetic energy. Comprehension and Analysis of Grade-Level-Appropriate Text, 2.6
23 Answer Key Synonyms and Antonyms 1. discovered 2. opposite 3. strongest 4. attract 5. opposite 6. attract 7. nearby 8. negative Sequential Order Step 1: Someone pushes a button Step 2: An electric current is sent to the electromagnet Step 3: An iron bar with a hammer head is attracted to the magnetic field. Step 4: The hammer head strikes the bell. Identify a Purpose 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. A Distinguish Fact from Opinion 1. F 2. O 3. F 4. O 5. F 6. O 7. O 8. F
Electromagnetic Energy
 SCIENCE GRADE 4 On Level California Content Standards Physical Sciences: 1.B Physical Sciences: 1.C Physical Sciences: 1.D Physical Sciences: 1.E Physical Sciences: 1.F Investigation and Experimentation:
SCIENCE GRADE 4 On Level California Content Standards Physical Sciences: 1.B Physical Sciences: 1.C Physical Sciences: 1.D Physical Sciences: 1.E Physical Sciences: 1.F Investigation and Experimentation:
Electrical Energy. On Level. FOCUScurriculum
 SCIENCE GRADE 4 On Level California Content Standards Physical Sciences: 1.A Physical Sciences: 1.E Physical Sciences: 1.F Physical Sciences: 1.G Electrical Energy FOCUScurriculum Curriculum materials
SCIENCE GRADE 4 On Level California Content Standards Physical Sciences: 1.A Physical Sciences: 1.E Physical Sciences: 1.F Physical Sciences: 1.G Electrical Energy FOCUScurriculum Curriculum materials
MAGNETISM. B.Directions: Answer the following questions with a short answer. You may use the back of this sheet if you need more space.
 1 Pre-Test A. Directions: Circle the word or phrase that completes the sentence. 1. If two bar magnets are brought near each other and they repel, then the poles of the magnets are the same. the poles
1 Pre-Test A. Directions: Circle the word or phrase that completes the sentence. 1. If two bar magnets are brought near each other and they repel, then the poles of the magnets are the same. the poles
Rocks and Minerals. Below Level. FOCUScurriculum
 SCIENCE GRADE 4 Science Content Standards Earth Sciences: 4.A Earth Sciences: 4.B Below Level Rocks and Minerals FOCUScurriculum Curriculum materials for your content standards 33 Milford Drive, Suite
SCIENCE GRADE 4 Science Content Standards Earth Sciences: 4.A Earth Sciences: 4.B Below Level Rocks and Minerals FOCUScurriculum Curriculum materials for your content standards 33 Milford Drive, Suite
Lesson 9: Products of Electricity
 Magnetism and Electricity -> 9: Products of Electricity Getting Started? Big Ideas P What does electrical power produce? P How is electrical power produced? Lesson 9: Products of Electricity & Facts and
Magnetism and Electricity -> 9: Products of Electricity Getting Started? Big Ideas P What does electrical power produce? P How is electrical power produced? Lesson 9: Products of Electricity & Facts and
CLASSROOM KIT ELECTROMAGNETS
 CLASSROOM KIT ELECTROMAGNETS Page 1 1 Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their ideas. The
CLASSROOM KIT ELECTROMAGNETS Page 1 1 Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their ideas. The
ì<(sk$m)=beabid< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Physical Science by Lillian Duggan Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Captions Charts Diagrams Glossary Forms of Energy Scott Foresman Science 6.17 ì
Physical Science by Lillian Duggan Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Captions Charts Diagrams Glossary Forms of Energy Scott Foresman Science 6.17 ì
CLASSROOM VISIT ELECTROMAGNETS
 CLASSROOM VISIT ELECTROMAGNETS Page 1 1 Pre-Outreach Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their
CLASSROOM VISIT ELECTROMAGNETS Page 1 1 Pre-Outreach Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their
Magnetism BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN
 activity 5 Magnetism BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 1 Quarter 1 Activity 5 SC.A.1.1.1 The student knows that objects can be described, classified, and compared by their composition
activity 5 Magnetism BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 1 Quarter 1 Activity 5 SC.A.1.1.1 The student knows that objects can be described, classified, and compared by their composition
Electric and Magnetic Forces
 Imagine that you had two superpowers. Both powers allow you to move things without touching them. You can even move things located on the other side of a wall! One power is the ability to pull something
Imagine that you had two superpowers. Both powers allow you to move things without touching them. You can even move things located on the other side of a wall! One power is the ability to pull something
CLASSROOM KIT MAGNET EXPLORATION
 CLASSROOM KIT MAGNET EXPLORATION Page 1 1 Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their ideas.
CLASSROOM KIT MAGNET EXPLORATION Page 1 1 Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their ideas.
Tracking Weather Patterns
 SCIENCE GRADE 5 Science Content Standards Earth Sciences: 4.C Earth Sciences: 4.D Below Level Tracking Weather Patterns F O C UScurriculum LOOK INSIDE FOR: California s Academic Content Standards Covered
SCIENCE GRADE 5 Science Content Standards Earth Sciences: 4.C Earth Sciences: 4.D Below Level Tracking Weather Patterns F O C UScurriculum LOOK INSIDE FOR: California s Academic Content Standards Covered
Magnetism and Electricity
 Magnetism and Electricity UNIT 7 Student Reader E3 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 7 Page 1 2016 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of a girl with her hair standing straight up. This
Magnetism and Electricity UNIT 7 Student Reader E3 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 7 Page 1 2016 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of a girl with her hair standing straight up. This
Magnetism and Electricity Unit Design Rev9.08 Grade 5
 Magnetism and Electricity Unit Design Rev9.08 Grade 5 RI Statements of Enduring Knowledge - (Established Goals): PS 1 Energy is necessary for change to occur in matter. Energy can be stored, transferred,
Magnetism and Electricity Unit Design Rev9.08 Grade 5 RI Statements of Enduring Knowledge - (Established Goals): PS 1 Energy is necessary for change to occur in matter. Energy can be stored, transferred,
MAGNETS: A FIRST LOOK Grade Levels: K-4 17 minutes AIMS MULTIMEDIA Instructional Graphics Enclosed
 DESCRIPTION #8721 MAGNETS: A FIRST LOOK Grade Levels: K-4 17 minutes AIMS MULTIMEDIA 2000 2 Instructional Graphics Enclosed Introduces the basic principles of magnets. Discusses what they do and do not
DESCRIPTION #8721 MAGNETS: A FIRST LOOK Grade Levels: K-4 17 minutes AIMS MULTIMEDIA 2000 2 Instructional Graphics Enclosed Introduces the basic principles of magnets. Discusses what they do and do not
AGN. discover how. discoveries. Science.
 AGN NETISM RADE ASSESSMENT PACKET A comprehensive course that teaches the big ideas behind Maxwell s Principles. You ll discover how to detectt magnetic poles and magnetic fields, learn about electromagnetismm
AGN NETISM RADE ASSESSMENT PACKET A comprehensive course that teaches the big ideas behind Maxwell s Principles. You ll discover how to detectt magnetic poles and magnetic fields, learn about electromagnetismm
Electricity in Progress
 Electricity in Progress GRADE LEVELS: Grades 4th - 8th CONCEPT: Explore the history of electricity through two 15 minutes shows, a 30 minute hands on exploration and a 30 experience in the Progress exhibition
Electricity in Progress GRADE LEVELS: Grades 4th - 8th CONCEPT: Explore the history of electricity through two 15 minutes shows, a 30 minute hands on exploration and a 30 experience in the Progress exhibition
Activity One Force, Mass, and Acceleration
 Steps Activity One Force, Mass, and Acceleration This activity may be done alone or with a partner. FOR THIS ACTIVITY, you will need: Rocks of different sizes. (Use rocks that are all the same kind of
Steps Activity One Force, Mass, and Acceleration This activity may be done alone or with a partner. FOR THIS ACTIVITY, you will need: Rocks of different sizes. (Use rocks that are all the same kind of
Embedded Assessment Notes
 Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
Magnets attract some metals but not others
 Electricity and Magnetism Junior Science Magnets attract some metals but not others Some objects attract iron and steel. They are called magnets. Magnetic materials have the ability to attract some materials
Electricity and Magnetism Junior Science Magnets attract some metals but not others Some objects attract iron and steel. They are called magnets. Magnetic materials have the ability to attract some materials
Vocabulary. Magnet. a material that can create magnetic effects by itself. Electromagnet
 Vocabulary Term Magnet Definition a material that can create magnetic effects by itself Electromagnet Magnets created by electric current flowing in wires. A simple electromagnet is a coil of wire wrapped
Vocabulary Term Magnet Definition a material that can create magnetic effects by itself Electromagnet Magnets created by electric current flowing in wires. A simple electromagnet is a coil of wire wrapped
9. Which of the following is the correct relationship among power, current, and voltage?. a. P = I/V c. P = I x V b. V = P x I d.
 Name: Electricity and Magnetism Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Resistance is measured in a unit called the. a. ohm c. ampere b. coulomb d. volt 2. The statement
Name: Electricity and Magnetism Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Resistance is measured in a unit called the. a. ohm c. ampere b. coulomb d. volt 2. The statement
Activity 1: Evidence of Interactions
 UNIT 1 CHAPTER 2 Activity 1: Evidence of Interactions Name Date Class Key Questions Chapter Activity I Think Fill in the evidence of the following interactions. Demonstration A Time Interval: while the
UNIT 1 CHAPTER 2 Activity 1: Evidence of Interactions Name Date Class Key Questions Chapter Activity I Think Fill in the evidence of the following interactions. Demonstration A Time Interval: while the
LESSON 1: Exploring Static Electric Effects
 UNIT SE LESSON 1: Exploring Static Electric Effects Purpose and Materials Needed In the previous unit you explored some magnetic effects and then went on to develop a model that explains these effects
UNIT SE LESSON 1: Exploring Static Electric Effects Purpose and Materials Needed In the previous unit you explored some magnetic effects and then went on to develop a model that explains these effects
3rd Grade Motion and Stability
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction from patterns
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction from patterns
Review: Magnetism and Electromagnetism
 Review: Magnetism and Electromagnetism Multiple Choice: Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement. 1. Magnetism is a force of a. gravity. b. weight. c. voltage. d. attraction
Review: Magnetism and Electromagnetism Multiple Choice: Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement. 1. Magnetism is a force of a. gravity. b. weight. c. voltage. d. attraction
What are some properties of interactions involving electrified objects?
 UNIT SE Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Exploring Static Electric Effects Purpose In the previous unit you explored some magnetic effects and then went on to develop a model that explains these effects in
UNIT SE Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Exploring Static Electric Effects Purpose In the previous unit you explored some magnetic effects and then went on to develop a model that explains these effects in
24 Magnetic Fields BIGIDEA Write the Big Idea for this chapter.
 24 Magnetic Fields BIGIDEA Write the Big Idea for this chapter. Use the What I Know column to list the things you know about the Big Idea. Then list the questions you have about the Big Idea in the What
24 Magnetic Fields BIGIDEA Write the Big Idea for this chapter. Use the What I Know column to list the things you know about the Big Idea. Then list the questions you have about the Big Idea in the What
3rd Grade. Forces and Motion Review. Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106. Slide 4 / 106. Slide 3 / 106. Slide 5 / 106. Slide 6 / 106. Motion and Stability
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Slide 4 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Slide 4 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction
The complete lesson plan for this topic is included below.
 Home Connection Parent Information: Magnets provide a simple way to explore force with children. The power of a magnet is somewhat like magic to them and requires exploration to understand. When forces
Home Connection Parent Information: Magnets provide a simple way to explore force with children. The power of a magnet is somewhat like magic to them and requires exploration to understand. When forces
Introduction & Chapter 1: Matter
 Section 1 WHAT IS MATTER? Introduction & Chapter 1: Matter Use pages 3 5 of the student text to complete the worksheet. Choose the Answer. Circle the answer that correctly completes each sentence. 1. Matter
Section 1 WHAT IS MATTER? Introduction & Chapter 1: Matter Use pages 3 5 of the student text to complete the worksheet. Choose the Answer. Circle the answer that correctly completes each sentence. 1. Matter
Electric Charge and Electric Forces
 CHAPTER 19 Electricity LESSON 1 Electric Charge and Electric Forces What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column
CHAPTER 19 Electricity LESSON 1 Electric Charge and Electric Forces What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column
Cabrillo College Physics 10L. LAB 8 Magnetism. Read Hewitt Chapter 24
 Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 8 Magnetism Read Hewitt Chapter 24 What to learn and explore Magnetic forces are very closely related to electric forces--for example, they share the property that
Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 8 Magnetism Read Hewitt Chapter 24 What to learn and explore Magnetic forces are very closely related to electric forces--for example, they share the property that
Physical Science V2 Science course from Educational Options. Lesson 9: Electricity & Magnetism. Objectives. Introduction. What Is Electricity?
 Lesson 9: Electricity - Physical Science V2 - Browse All Courseware - Stars Suite http://secure.starssuite.com/sshome.asp?action=702&course=92&item=5793 Page 1 of 9 Thursday, February 17, 2011 Lisa Edmonds@Silver
Lesson 9: Electricity - Physical Science V2 - Browse All Courseware - Stars Suite http://secure.starssuite.com/sshome.asp?action=702&course=92&item=5793 Page 1 of 9 Thursday, February 17, 2011 Lisa Edmonds@Silver
Tracking Weather Patterns
 SCIENCE GRADE 5 California Content Standards Earth Sciences: 4.C Earth Sciences: 4.D On Level Tracking Weather Patterns F O C UScurriculum LOOK INSIDE FOR: California s Academic Content Standards Covered
SCIENCE GRADE 5 California Content Standards Earth Sciences: 4.C Earth Sciences: 4.D On Level Tracking Weather Patterns F O C UScurriculum LOOK INSIDE FOR: California s Academic Content Standards Covered
Electrostatics. Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility - Office of Science Education
 Electrostatics Electrostatics What happens to Different objects when they are electrically charged? 1. In this experiment, a device called a Van de Graaff generator will be used to place extra electrons
Electrostatics Electrostatics What happens to Different objects when they are electrically charged? 1. In this experiment, a device called a Van de Graaff generator will be used to place extra electrons
Transfer of Forces Classwork
 Transfer of Forces Classwork 1. Describe what a force is. 2. List at least four forces that are observed in nature. 3. How are forces transferred between two objects if they are not in contact? 4. Describe
Transfer of Forces Classwork 1. Describe what a force is. 2. List at least four forces that are observed in nature. 3. How are forces transferred between two objects if they are not in contact? 4. Describe
Reading Question 24.1
 Reading Question 24.1 A compass in a magnetic field will line up A. With the north pole pointing in the direction of the magnetic field. B. With the north pole pointing opposite the direction of the magnetic
Reading Question 24.1 A compass in a magnetic field will line up A. With the north pole pointing in the direction of the magnetic field. B. With the north pole pointing opposite the direction of the magnetic
7.2. Electric Force 7-2A. What Is the Attraction to Water? Words to Know. Find Out ACTIVITY. Materials. What Did You Find Out?
 7.2 Electric Force Electric force acts on objects even if they are not touching. Objects with the same charge repel each other. Objects with opposite charges attract each other. Neutral objects are attracted
7.2 Electric Force Electric force acts on objects even if they are not touching. Objects with the same charge repel each other. Objects with opposite charges attract each other. Neutral objects are attracted
> What happens when the poles of two magnets are brought close together? > Two like poles repel each other. Two unlike poles attract each other.
 CHAPTER OUTLINE Section 1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields Key Idea questions > What happens when the poles of two magnets are brought close together? > What causes a magnet to attract or repel another magnet?
CHAPTER OUTLINE Section 1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields Key Idea questions > What happens when the poles of two magnets are brought close together? > What causes a magnet to attract or repel another magnet?
Electric Charge and Force
 CHAPTER 17 21 SECTION Electricity Electric Charge and Force KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the different kinds of electric charge? How do materials become electrically
CHAPTER 17 21 SECTION Electricity Electric Charge and Force KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the different kinds of electric charge? How do materials become electrically
BSA Electricity Merit Badge. Electricity Merit Badge Basic Electricity
 Electricity Merit Badge Basic Electricity This Electricity course was put together to be presented in 6 classes. It should take about 5 hours. That is if each student has individual tools. Otherwise if
Electricity Merit Badge Basic Electricity This Electricity course was put together to be presented in 6 classes. It should take about 5 hours. That is if each student has individual tools. Otherwise if
9.5 Making an Electric Motor. Grade 9 Activity Plan
 9.5 Making an Electric Motor Grade 9 Activity Plan Reviews and Updates 9.5 Electric Motor Objectives: 1. To know more about force fields and be able to outline the difference between field and contact
9.5 Making an Electric Motor Grade 9 Activity Plan Reviews and Updates 9.5 Electric Motor Objectives: 1. To know more about force fields and be able to outline the difference between field and contact
8.5 Snake Charming & Making an Electroscope (Static Electricity) Grade 8 Activity Plan
 8.5 Snake Charming & Making an Electroscope (Static Electricity) Grade 8 Activity Plan Reviews and Updates 2 8.5 Snake Charming and Making an Electroscope Objectives: 1. To demonstrate the attraction that
8.5 Snake Charming & Making an Electroscope (Static Electricity) Grade 8 Activity Plan Reviews and Updates 2 8.5 Snake Charming and Making an Electroscope Objectives: 1. To demonstrate the attraction that
Magnetism. Magnets and Magnetic Fields S N
 Magnetism Magnets and Magnetic Fields What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Magnetism Magnets and Magnetic Fields What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
*We studied the following types of En.: Potential and kinetic EX of potential is Chemical EX of kinetic is Temperature Another Ex of kinetic En is:
 *We studied the following types of En.: Potential and kinetic EX of potential is Chemical EX of kinetic is Temperature Another Ex of kinetic En is: *Electrical Energy also called Electricity - ( the result
*We studied the following types of En.: Potential and kinetic EX of potential is Chemical EX of kinetic is Temperature Another Ex of kinetic En is: *Electrical Energy also called Electricity - ( the result
Unit 3P.1: Forces, magnets and springs.
 Unit 3P.1:. Size and direction of forces Magnets Springs Science skills: Making and using models Classifying Observing By the end of this unit you should be able to: Recognise that a force acts in a particular
Unit 3P.1:. Size and direction of forces Magnets Springs Science skills: Making and using models Classifying Observing By the end of this unit you should be able to: Recognise that a force acts in a particular
Forces LAB. PART 1: Mapping the Magnetic Field-Invisible Forces. 1. BACKGROUND INFORMATION (what is a magnetic field?): 2. ASK A QUESTION (Aim):
 DUE DATE: Name: Forces LAB PART 1: Mapping the Magnetic Field-Invisible Forces 1. BACKGROUND INFORMATION (what is a magnetic field?): 2. ASK A QUESTION (Aim): 3. HYPOTHESIS (Use if, then, and because statement):
DUE DATE: Name: Forces LAB PART 1: Mapping the Magnetic Field-Invisible Forces 1. BACKGROUND INFORMATION (what is a magnetic field?): 2. ASK A QUESTION (Aim): 3. HYPOTHESIS (Use if, then, and because statement):
IF A NUCLEUS IS FULL OF POSITIVELY CHARGED PROTONS, WHY DOESN T IT FLY APART?
 IF A NUCLEUS IS FULL OF POSITIVELY CHARGED PROTONS, WHY DOESN T IT FLY APART? An introduction to the fundamental forces that control our world. Remembering that like charges repel each other, you may have
IF A NUCLEUS IS FULL OF POSITIVELY CHARGED PROTONS, WHY DOESN T IT FLY APART? An introduction to the fundamental forces that control our world. Remembering that like charges repel each other, you may have
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) Poles Apart: Electro-magnetic Attraction & Repulsion Bruce Jackson Grade Level 4th Standards Connection(s) Physical Science: Electricity/magnetism:
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) Poles Apart: Electro-magnetic Attraction & Repulsion Bruce Jackson Grade Level 4th Standards Connection(s) Physical Science: Electricity/magnetism:
Magnetism and Gravity
 Imagine that you had two superpowers. Both powers allow you to move things without touching them. You can even move things located on the other side of a wall! One power is the ability to pull anything
Imagine that you had two superpowers. Both powers allow you to move things without touching them. You can even move things located on the other side of a wall! One power is the ability to pull anything
Magnets. Grade Level: 1 3
 Magnets Grade Level: 1 3 Teacher Guidelines page 1 Instructional Pages pages 2 3 Activity Page page 4 Practice Page page 5 Homework Page page 6 Answer Key pages 7 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Distribute the
Magnets Grade Level: 1 3 Teacher Guidelines page 1 Instructional Pages pages 2 3 Activity Page page 4 Practice Page page 5 Homework Page page 6 Answer Key pages 7 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Distribute the
Lesson Plan: Electric Circuits (~130 minutes) Concepts
 Lesson Plan: Electric Circuits (~130 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity is the flow of electric charge (electrons). 2. Electric Charge is a property of subatomic particles. 3. Current is the movement of
Lesson Plan: Electric Circuits (~130 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity is the flow of electric charge (electrons). 2. Electric Charge is a property of subatomic particles. 3. Current is the movement of
GRADE 7: Physical processes 3. UNIT 7P.3 8 hours. Magnetism. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 7: Physical processes 3 Magnetism UNIT 7P.3 8 hours About this unit This unit is the third of five units on physical processes for Grade 7. It builds on Unit 6P.1 and leads on to work on electromagnets
GRADE 7: Physical processes 3 Magnetism UNIT 7P.3 8 hours About this unit This unit is the third of five units on physical processes for Grade 7. It builds on Unit 6P.1 and leads on to work on electromagnets
Jeopardy. Circuits. Electricity. Terms. Magnets This N That Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200
 Jeopardy Magnets This N That Circuits Terms Electricity Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
Jeopardy Magnets This N That Circuits Terms Electricity Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
Photo Credits: All images Harcourt
 CXEGA09ALR1X_OL16.indd 2 3/2/07 6:19:50 PM Photo Credits: All images Harcourt If you have received these materials as examination copies free of charge, Harcourt School Publishers retains title to the
CXEGA09ALR1X_OL16.indd 2 3/2/07 6:19:50 PM Photo Credits: All images Harcourt If you have received these materials as examination copies free of charge, Harcourt School Publishers retains title to the
Chapter 18 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 18 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The region around a magnet in which magnetic forces
Chapter 18 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The region around a magnet in which magnetic forces
Tracking Weather Patterns
 SCIENCE GRADE 5 Science Content Standards Earth Sciences: 4.C Earth Sciences: 4.D On Level Tracking Weather Patterns F O C UScurriculum LOOK INSIDE FOR: California s Academic Content Standards Covered
SCIENCE GRADE 5 Science Content Standards Earth Sciences: 4.C Earth Sciences: 4.D On Level Tracking Weather Patterns F O C UScurriculum LOOK INSIDE FOR: California s Academic Content Standards Covered
What Materials Are Attracted to Magnets?
 What Materials Are Attracted to Magnets? Focus: Students test a variety of materials to discover which materials are magnetic. Specific Curriculum Outcomes Students will be expected to: 40.0 identify familiar
What Materials Are Attracted to Magnets? Focus: Students test a variety of materials to discover which materials are magnetic. Specific Curriculum Outcomes Students will be expected to: 40.0 identify familiar
HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE. Physical Science 7: Electricity & Magnetism
 HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE Physical Science 7: Electricity & Magnetism WILLMAR PUBLIC SCHOOL 2013-2014 EDITION CHAPTER 7 Electricity & Magnatism In this chapter you will: 1. Analyze factors that affect the strength
HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE Physical Science 7: Electricity & Magnetism WILLMAR PUBLIC SCHOOL 2013-2014 EDITION CHAPTER 7 Electricity & Magnatism In this chapter you will: 1. Analyze factors that affect the strength
Magnetic Attraction and Electromagnetism. Spring 2011
 Magnetic Attraction and Electromagnetism Spring 2011 The Nature of Magnetism Magnets are found everywhere doorbells, TV s, computers Magnets were discovered in a region in Greece called.you guessed it
Magnetic Attraction and Electromagnetism Spring 2011 The Nature of Magnetism Magnets are found everywhere doorbells, TV s, computers Magnets were discovered in a region in Greece called.you guessed it
2. How do electrically charged objects affect neutral objects when they come in contact?
 North arolina Testing Program EO Physical Science Sample Items Goal 4 1. When a plastic rod is rubbed with fur, the plastic rod becomes negatively charged. Which statement explains the charge transfer
North arolina Testing Program EO Physical Science Sample Items Goal 4 1. When a plastic rod is rubbed with fur, the plastic rod becomes negatively charged. Which statement explains the charge transfer
Educator Guide: Electromagnetism
 Educator Guide: Electromagnetism This document is a resource for teachers whose classes are participating in the Museum of Science s Electromagnetism Traveling Program. The information in this document
Educator Guide: Electromagnetism This document is a resource for teachers whose classes are participating in the Museum of Science s Electromagnetism Traveling Program. The information in this document
Written by Ruth M. Young, M.S. Ed.
 Managing Editor Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Illustrators Howard Chaney Bruce Hedges Cover Artist Lesley Palmer Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Art Director CJae Froshay
Managing Editor Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Illustrators Howard Chaney Bruce Hedges Cover Artist Lesley Palmer Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Art Director CJae Froshay
Electricity. Year 10 Science
 Electricity Year 10 Science What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? A stationary electrical charge that is built up on the
Electricity Year 10 Science What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? A stationary electrical charge that is built up on the
Magnets SPI Success Criteria:
 Magnets SPI 0807.12.3 Distinguish among the Earth s magnetic field, a magnet, and the fields that surround a magnet and an electromagnet. Success Criteria: 1. I can explain the properties of any magnetic
Magnets SPI 0807.12.3 Distinguish among the Earth s magnetic field, a magnet, and the fields that surround a magnet and an electromagnet. Success Criteria: 1. I can explain the properties of any magnetic
2. How do electrically charged objects affect neutral objects when they come in contact?
 North arolina Testing Program EO Physical Science Sample Items Goal 4 1. When a plastic rod is rubbed with fur, the plastic rod becomes negatively charged. Which statement explains the charge transfer
North arolina Testing Program EO Physical Science Sample Items Goal 4 1. When a plastic rod is rubbed with fur, the plastic rod becomes negatively charged. Which statement explains the charge transfer
ELECTROMAGNETISM The study of the relationship between electricity and magnetism is called
 ELECTROMAGNETISM The study of the relationship between electricity and magnetism is called Electromagnetism Before, 1819 it was believed that there was no connection between electricity and magnetism.
ELECTROMAGNETISM The study of the relationship between electricity and magnetism is called Electromagnetism Before, 1819 it was believed that there was no connection between electricity and magnetism.
Revision Sheet grade 4
 Revision Sheet grade 4 Materials for the final exam grade 4 : 1- Science book (pages 484 to 528). 2- The final revision sheet and the copy book. 3- The science booklet. Prepared by: Miss Tamara Al. Majali
Revision Sheet grade 4 Materials for the final exam grade 4 : 1- Science book (pages 484 to 528). 2- The final revision sheet and the copy book. 3- The science booklet. Prepared by: Miss Tamara Al. Majali
Exploring the Poles (Without Leaving Your Classroom!)
 Exploring the Poles (Without Leaving Your Classroom!) Computer 37 Magnets have north and south poles. Do you think that the poles of differently shaped magnets are in different places? In this activity,
Exploring the Poles (Without Leaving Your Classroom!) Computer 37 Magnets have north and south poles. Do you think that the poles of differently shaped magnets are in different places? In this activity,
Pre-Lab Questions. Physics 1BL MAGNETISM Spring 2010
 In this lab, you will focus on the concepts of magnetism and magnetic fields and the interaction between flowing charges (electric current) and magnetic fields. You will find this material in Chapter 19
In this lab, you will focus on the concepts of magnetism and magnetic fields and the interaction between flowing charges (electric current) and magnetic fields. You will find this material in Chapter 19
Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of:
 Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Potential Energy Electric Potential Energy Electric Circuit Current Voltage Resistance Coulomb Notes 7.1: Electrostatic Force This lesson
Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Potential Energy Electric Potential Energy Electric Circuit Current Voltage Resistance Coulomb Notes 7.1: Electrostatic Force This lesson
GRADE 5: Physical processes 4. UNIT 5P.4 5 hours. Magnetic forces. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 5: Physical processes 4 Magnetic forces UNIT 5P.4 5 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of five units on physical processes for Grade 5. The unit is designed to guide your planning and
GRADE 5: Physical processes 4 Magnetic forces UNIT 5P.4 5 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of five units on physical processes for Grade 5. The unit is designed to guide your planning and
Basic electromagnetism and electromagnetic induction
 Basic electromagnetism and electromagnetic induction This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Basic electromagnetism and electromagnetic induction This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
DRAFT. Activity 16, Electromagnetic Induction! Science & Global Issues: Global Energy & Power! from! 2014 The Regents of the University of California!
 Activity 16, Electromagnetic Induction! from! Science & Global Issues: Global Energy & Power! This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. ESI 0352453.
Activity 16, Electromagnetic Induction! from! Science & Global Issues: Global Energy & Power! This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. ESI 0352453.
Grade 2 Hands on Science Forces and Magnets
 Grade 2 Hands on Science Forces and Magnets Objectives: to discuss and demonstrate "what is a force?" and to demonstrate the "push and pull" forces produced by a magnet. Safety: Remind students of general
Grade 2 Hands on Science Forces and Magnets Objectives: to discuss and demonstrate "what is a force?" and to demonstrate the "push and pull" forces produced by a magnet. Safety: Remind students of general
Electromagnetism Review Sheet
 Electromagnetism Review Sheet Electricity Atomic basics: Particle name Charge location protons electrons neutrons + in the nucleus - outside of the nucleus neutral in the nucleus What would happen if two
Electromagnetism Review Sheet Electricity Atomic basics: Particle name Charge location protons electrons neutrons + in the nucleus - outside of the nucleus neutral in the nucleus What would happen if two
1103 Period 19: Magnetic Forces and Electromagnets
 Name Section 1103 Period 19: Magnetic Forces and Electromagnets Caution: Our class activities use strong magnets. While these magnets are not dangerous to your health, they can permanently damage objects
Name Section 1103 Period 19: Magnetic Forces and Electromagnets Caution: Our class activities use strong magnets. While these magnets are not dangerous to your health, they can permanently damage objects
Ontario Science and Technology Curriculum 1999 Strand: Matter and Materials Topic: Magnetic and Charged Materials Grade: 3
 Name: Ontario Science and Technology Curriculum 1999 Strand: Matter and Materials Topic: Magnetic and Charged Materials Grade: 3 Goggled Science, 2001 All rights reserved Developed by T. Tasker May be
Name: Ontario Science and Technology Curriculum 1999 Strand: Matter and Materials Topic: Magnetic and Charged Materials Grade: 3 Goggled Science, 2001 All rights reserved Developed by T. Tasker May be
A Deeper Look at Electricity A First Look at Magnets. NBSP Physical Science Institute Tuesday July 23, 2002
 A Deeper Look at Electricity A First Look at Magnets NBSP Physical Science Institute Tuesday July 23, 2002 1 Currents: Thinking Deeper Our model for current so far: The current in a circuit depends on
A Deeper Look at Electricity A First Look at Magnets NBSP Physical Science Institute Tuesday July 23, 2002 1 Currents: Thinking Deeper Our model for current so far: The current in a circuit depends on
Grade 3 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1. Force and Motion. Overview
 Grade 3 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Force and Motion Overview Number of instructional days: 8 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Use observations of magnets in relation to other objects to describe
Grade 3 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Force and Motion Overview Number of instructional days: 8 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Use observations of magnets in relation to other objects to describe
Introduction to Electricity
 ENERGY USE AND DELIVERY LESSON PLAN 3.1 Introduction to Electricity This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools)
ENERGY USE AND DELIVERY LESSON PLAN 3.1 Introduction to Electricity This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools)
Opening. Monster Guard. Grades 1-3. Teacher s Guide
 Teacher s Guide PLEASE NOTE: Students must complete the Initiation section of the Monster Guard app before they begin this activity, in order to gain access to the Earthquake training mission. Opening
Teacher s Guide PLEASE NOTE: Students must complete the Initiation section of the Monster Guard app before they begin this activity, in order to gain access to the Earthquake training mission. Opening
Electricity and magnetism. Verifying the Lenz Law by measuring the electric current flowing through a coil created by an external magnetic field
 Verifying the Lenz Law by measuring the electric current flowing through a coil created by an external magnetic field Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices Electricity
Verifying the Lenz Law by measuring the electric current flowing through a coil created by an external magnetic field Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices Electricity
Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law
 Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law Objective: To learn how excess charge is created and transferred. To measure the electrostatic force between two objects as a function of their electrical charges and their
Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law Objective: To learn how excess charge is created and transferred. To measure the electrostatic force between two objects as a function of their electrical charges and their
1. The Sun directly provides. A water energy B wind energy C heat energy D electrical energy
 1. The Sun directly provides A water energy B wind energy C heat energy D electrical energy 2. What is the Sun doing in this picture? F Burning away the clouds in the sky G Drying up the plant roots H
1. The Sun directly provides A water energy B wind energy C heat energy D electrical energy 2. What is the Sun doing in this picture? F Burning away the clouds in the sky G Drying up the plant roots H
13.5 Conductor in a Magnetic Field The Motor Principle
 13.5 Conductor in a Magnetic ield igure 1 Determining the force on an electric conductor in a magnetic field Magnetic field of the permanent magnet Magnetic field of the current-carrying conductor (c)
13.5 Conductor in a Magnetic ield igure 1 Determining the force on an electric conductor in a magnetic field Magnetic field of the permanent magnet Magnetic field of the current-carrying conductor (c)
STATIC ELECTRICITY. II. Directions:Answer the following questions with short answers. Use the back of this sheet to write your answers.
 1 Pre-Test I. Directions: Circle the word that completes the sentence. 1. The "building blocks of matter" are called neutrons atoms electrons. 2. When charged objects jump apart we say they each other.
1 Pre-Test I. Directions: Circle the word that completes the sentence. 1. The "building blocks of matter" are called neutrons atoms electrons. 2. When charged objects jump apart we say they each other.
ELECTRICITY. This chain is similar to the fire fighter's bucket brigades in olden times. But
 ELECTRICITY Electricity figures everywhere in our lives. Electricity lights up our homes, cooks our food, powers our computers, television sets, and other electronic devices. Electricity from batteries
ELECTRICITY Electricity figures everywhere in our lives. Electricity lights up our homes, cooks our food, powers our computers, television sets, and other electronic devices. Electricity from batteries
Magnetism. and its applications
 Magnetism and its applications Laws of Magnetism 1) Like magnetic poles repel, and 2) unlike poles attract. Magnetic Direction and Strength Law 3 - Magnetic force, either attractive or repelling varies
Magnetism and its applications Laws of Magnetism 1) Like magnetic poles repel, and 2) unlike poles attract. Magnetic Direction and Strength Law 3 - Magnetic force, either attractive or repelling varies
Generating Electricity. Outreach Program Lesson Plan
 Outreach Program Lesson Plan WAAW Foundation is non-profit organization dedicated to bringing hands-on STEM education to girls all over Africa. Our Mission: To increase the pipeline of African women in
Outreach Program Lesson Plan WAAW Foundation is non-profit organization dedicated to bringing hands-on STEM education to girls all over Africa. Our Mission: To increase the pipeline of African women in
CLASSROOM VISIT MAGNETISM IN CHEMISTRY
 CLASSROOM VISIT MAGNETISM IN CHEMISTRY Page 1 1 Pre-Outreach Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify
CLASSROOM VISIT MAGNETISM IN CHEMISTRY Page 1 1 Pre-Outreach Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify
AP Physics-B ElectroStatics Electric Charges: Subatomic Particles and Electricity: atoms subatomic particles protons neutrons electrons nucleus
 AP Physics-B ElectroStatics Electric Charges: It made my hair stand on end! Perhaps you are familiar with this expression, which is often used to describe a frightening or startling experience. According
AP Physics-B ElectroStatics Electric Charges: It made my hair stand on end! Perhaps you are familiar with this expression, which is often used to describe a frightening or startling experience. According
4.4 Electricity & Magnetism
 4.4 Electricity & Magnetism Enduring Understanding: Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed. Magnetic energy can be transferred and transformed. Essential Question: How is energy transferred
4.4 Electricity & Magnetism Enduring Understanding: Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed. Magnetic energy can be transferred and transformed. Essential Question: How is energy transferred
Electricity and Electromagnetism SOL review Scan for a brief video. A. Law of electric charges.
 A. Law of electric charges. Electricity and Electromagnetism SOL review Scan for a brief video The law of electric charges states that like charges repel and opposite charges attract. Because protons and
A. Law of electric charges. Electricity and Electromagnetism SOL review Scan for a brief video The law of electric charges states that like charges repel and opposite charges attract. Because protons and
Batteries, Bulbs and Switches. Understanding Batteries
 Exploring Physics Electricity Magnetism -- the CD-ROM by M. Chrasekhar, R. Litherl J. Geib: Correlation of Unit Concepts with California State Science Stards Electricity Bulbs Switches Understing Batteries
Exploring Physics Electricity Magnetism -- the CD-ROM by M. Chrasekhar, R. Litherl J. Geib: Correlation of Unit Concepts with California State Science Stards Electricity Bulbs Switches Understing Batteries
Ellie gets charged about Electricity!
 SCIENCE ALLIANCE Ellie gets charged about Electricity! by Carole Marsh 2008 Carole Marsh Permission is hereby granted to the individual purchaser or classroom teacher to reproduce materials in this book
SCIENCE ALLIANCE Ellie gets charged about Electricity! by Carole Marsh 2008 Carole Marsh Permission is hereby granted to the individual purchaser or classroom teacher to reproduce materials in this book
To teach students how to make and use magnetic compasses. To help students understand the science behind how magnetic compasses work
 Title: The Cardinal Points Suitable for: All churches Curriculum Links: Science, History and RE Lesson Aims: To teach students how to make and use magnetic compasses To help students understand the science
Title: The Cardinal Points Suitable for: All churches Curriculum Links: Science, History and RE Lesson Aims: To teach students how to make and use magnetic compasses To help students understand the science
Particle symbol. electron negative outside nucleus e
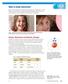 What Is Static Electricity? Have you ever had your hair stand up after putting on, or taking off, a sweater (Figure 1)? Or have you perhaps noticed that a balloon placed near your head will attract your
What Is Static Electricity? Have you ever had your hair stand up after putting on, or taking off, a sweater (Figure 1)? Or have you perhaps noticed that a balloon placed near your head will attract your
Joy of Science Discovering the matters and the laws of the universe
 Joy of Science Discovering the matters and the laws of the universe Key Words Universe, Energy, Quantum mechanics, Chemical reaction, Structure of matter Unless otherwise noted, copied pictures are taken
Joy of Science Discovering the matters and the laws of the universe Key Words Universe, Energy, Quantum mechanics, Chemical reaction, Structure of matter Unless otherwise noted, copied pictures are taken
