Mathematical Practices
|
|
|
- Audrey Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mathematical Practices 8.MP.1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 8.MP.2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 8.MP.5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 8.MP.6. Attend to precision. 8.MP.7. Look for and make use of structure. 8.MP.8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. 1
2 Unit 1/2 Rational & Irrational Numbers UEQ: How do I determine if a number is real? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.A-N.1.1 Apply concepts of rational and irrational numbers. M08.A-N Determine whether a number is rational or irrational. For rational numbers, show that the decimal expansion terminates or repeats (limit repeating decimals to thousandths). Students can use graphic organizers to show the relationship between the subsets of the real number system. M08.A-N Convert a terminating or repeating decimal into a rational number (limit repeating decimals to thousandths). M08.A-N.1.1. Estimate the value of irrational numbers without a calculator (limit whole number radicand to less than 144). M08.A-N Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare and order irrational numbers. Students can approximate square roots by iterative processes. Approximate the value of 5 to the nearest hundredth. Solution: Students start with a rough estimate based upon perfect squares. falls between 2 and because 5 falls between 2 2 = 4 and 2 = 9. The value will be closer to 2 than to. Students continue the iterative process 5 with the tenths place value. falls between 2.2 and 2. because 5 falls between = 4.84 and 2. 2 = The value is closer to 2.2. Further iteration shows that the value of and is is between 2.2 and 2.24 since is 2
3 Compare 2 and by estimating their values, plotting them on a number line, and making comparative statements. M08.A-N Locate/identify rational and irrational numbers at their approximate locations on a number line. M08.B-E Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of perfect squares (up to and including 12 2 ) and cube roots of perfect cubes (up to and including 5 ) without a calculator. Solution: Statements for the comparison could include: 2 is approximately 0. less than 2 is between the whole numbers 1 and 2 is between 1.7 and 1.8 How do we evaluate square roots without a calculator? How do we evaluate cube roots without a calculator? How do we solve equations involving squares and cubes? Solve Solution: Solve Solution: and 1 x 2 9 x 2 9 x 2 = ± 9 x x x 8 x x = and 27 1
4 Unit Operations with Real Numbers UEQ: What skills are necessary to solve real world problems involving powers? Standards Eligible Content Examples 2 5 = = 1/ = 1/27 M08.B-E.1.1 Represent and use expressions and equations to solve problems involving radicals and integer exponents. M08.B-E Apply one or more properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions without a calculator (with final answers expressed in exponential form with positive exponents). Properties will be provided = = = = 1 16, 000 M08.B-E.1.1. Estimate very large or very small quantities by using numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10, and express how many times larger or smaller one number is than another. M08.B-E Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Express answers in scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology (e.g., interpret 4.7EE9 displayed on a calculator as ). Estimate the population of the United States as x10 8 and the population of the world as 7x10 9, and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. Students can convert decimal forms to scientific notation and apply rules of exponents to simplify expressions. In working with calculators or spreadsheets, it is important that students recognize scientific notation. Students should recognize that the output of 2.45E+2 is 2.45 x 10 2 and.5e-4 is.5 x Students enter scientific notation using E or EE (scientific notation), * (multiplication), and ^ (exponent) symbols. 4
5 Unit 4 Pythagorean Theorem UEQ: How would knowing the properties of a right triangle assist in solving real world situations? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.C-G.2.1 Solve problems involving right triangles by applying the Pythgorean theorem. M08.C-G Apply the converse of the Pythagorean theorem to show a triangle is a right triangle. M08.C-G Apply the Pythagorean theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. (Figures provided for problems in three dimensions will be consistent with Eligible Content in grade 8 and below.) M08.C-G.2.1. Apply the Pythagorean theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system. Students should verify, using a model, that the sum of the squares of the legs is equal to the square of the hypotenuse in a right triangle. Students should also understand that if the sum of the squares of the 2 smaller legs of a triangle is equal to the square of the third leg, then the triangle is a right triangle. Through authentic experiences and exploration, students should use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems. Problems can include working in both two and three dimensions. Students should be familiar with the common Pythagorean triplets. Students will create a right triangle from the two points given (as shown in the diagram below) and then use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between the two given points. 5
6 Unit 5 Transformations UEQ: How can we prove 2-D figures are congruent without using measurement tools? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.C-G.1.1 Apply properties of geometric transformations to verify congruence or similarity. M08.C-G Identify and apply properties of rotations, reflections, and translations. Students need multiple opportunities to explore the transformation of figures so that they can appreciate that points stay the same distance apart and lines stay at the same angle after they have been rotated, reflected, and/or translated. M08.C-G Given two congruent figures, describe a sequence of transformations that exhibits the congruence between them. Is Figure A congruent to Figure A? Explain how you know. Describe the sequence of transformations that results in the transformation of Figure A to Figure A. M08.C-G.1.1. Describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures, using coordinates. A dilation is a transformation that moves each point along a ray emanating from a fixed center, and multiplies distances from the center by a common scale factor. In dilated figures, the dilated figure is similar to its pre-image. Translation: A translation is a transformation of an object that moves the object so that every point of the object moves in the same direction as well as the same distance. In a translation, the translated object is congruent to its pre-image. 6
7 ABC has been translated 7 units to the right and units up. To get from A (1,5) to A (8,8), move A 7 units to the right (from x = 1 to x = 8) and units up (from y = 5 to y = 8). Points B + C also move in the same direction (7 units to the right and units up). Reflection: A reflection is a transformation that flips an object across a line of reflection (in a coordinate grid the line of reflection may be the x or y axis). In a rotation, the rotated object is congruent to its pre-image. When an object is reflected across the y axis, the reflected x coordinate is the opposite of the preimage x coordinate. Rotation: A rotated figure is a figure that has been turned about a fixed point. This is called the center of rotation. A figure can be rotated up to 60. Rotated figures are congruent to their pre-image figures. 7
8 Consider when DEF is rotated 180 clockwise about the origin. The coordinates of DEF are D(2,5), E(2,1), and F(8,1). When rotated 180, D' E' F' has new coordinates D (-2,-5), E (-2,-1) and F (-8,-1). Each coordinate is the opposite of its pre-image. M08.C-G Given two similar two-dimensional figures, describe a sequence of transformations that exhibits the similarity between them. 8.MP.2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 8.MP.4. Model with mathematics. 8.MP.5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 8.MP.6. Attend to precision. 8.MP.7. Look for and make use of structure. How do we identify similar figures? How can we use transformations to show that two figures are similar? Is Figure A similar to Figure A? Explain how you know. Describe the sequence of transformations that results in the transformation of Figure A to Figure A. 8
9 9
10 Unit 6 Similarity and Dilation UEQ: How can we prove 2-D figures are similar without using measurement tools? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.C-G.1.1 Apply properties of geometric transformations to verify congruence or similarity. M08.C-G.1.1. Describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures using coordinates. M08.C-G Given two similar two-dimensional figures, describe a sequence of transformations that exhibits the similarity between them. 10
11 Unit 7 Understanding Linear Relationships UEQ: How do I use linear patterns to describe real life situations? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.B-E.2.1 Analyze and describe linear relationships between two variables, using slope. M08.B-E Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. Using graphs of experiences that are familiar to student s increases accessibility and supports understanding and interpretation of proportional relationship. Students are expected to both sketch and interpret graphs. Example: Compare the scenarios to determine which represents a greater speed. Include a description of each scenario including the unit rates in your explanation. M08.B-E Use similar right triangles to show and explain why the slope m is the same between any two distinct points on a non-vertical line in the coordinate plane. ACB y = 50x x is time in hours y is distance in miles Explain why is similar to DFE, and deduce that AB has the same slope as BE. Express each line as an equation. 11
12 M08.B-E.2.1. Derive the equation y = mx for a line through the origin and the equation y = mx + b for a line intercepting the vertical axis at b. M08.B-F Construct a function to model a linear relationship between two quantities. Determine the rate of change and initial value of the function from a description of a relationship or from two (x, y) values, including reading these from a table or from a graph. Interpret the rate of change and initial value of a linear function in terms of the situation it models and in terms of its graph or a table of values. 12
13 Unit 8 Solving Linear Equations UEQ: How does modeling & solving linear equations assist in answering real world problems? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.B-E..1 Write, solve, graph, and interpret linear equations in one or two variables, using various methods. M08.B-E..1.1 Write and identify linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x = a, a = a, or a = b results (where a and b are different numbers). When the equation has one solution, the variable has one value that makes the equation true as in 12-4y=16. The only value for y that makes this equation true is -1. When the equation has infinitely many solutions, the equation is true for all real numbers as in 7x + 14 = 7 (x+2). As this equation is simplified, the variable terms cancel leaving 14 = 14 or 0 = 0. Since the expressions are equivalent, the value for the two sides of the equation will be the same regardless which real number is used for the substitution. When an equation has no solutions it is also called an inconsistent equation. This is the case when the two expressions are not equivalent as in 5x - 2 = 5(x+1). When simplifying this equation, students will find that the solution appears to be two numbers that are not equal or -2 = 1. In this case, regardless which real number is used for the substitution, the equation is not true and therefore has no solution. M08.B-E..1.2 Solve linear equations that have rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. 7( m ) y 4 1 y 1
14 Unit 9 Introduction to Functions UEQ: How does determining the relationship between an input and output help to describe the rule of the relation? Standards Eligible Contents Examples M08.B-F.1.1 Define, evaluate, and compare functions displayed algebraically, graphically, or numerically in tables or by verbal descriptions. M08.B-F Determine whether a relation is a function. M08.B-F Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (i.e., algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). Compare the two linear functions listed below and determine which has a negative slope. Function 1: Gift CardSamantha starts with $20 on a gift card for the book store. She spends $.50 per week to buy a magazine. Let y be the amount remaining as a function of the number of weeks, x. x y Function 2: The school bookstore rents graphing calculators for $5 per month. It also collects a nonrefundable fee of $10.00 for the school year. Write the rule for the total cost (c) of renting a calculator as a function of the number of months (m).solution:function 1 is an example of a function whose graph has negative slope. Samantha starts with $20 and spends money each week. The amount of money left on the gift card decreases each week. The graph has a negative slope of -.5, which is the amount the gift card balance decreases with Samantha s weekly magazine purchase. Function 2 is an example of a function whose graph has positive slope. Students pay a yearly nonrefundable fee for renting the calculator and pay $5 for each month they rent the calculator. This function has a positive slope of 5 which is the amount of the monthly rental fee. An equation for Example 2 could be c = 5m
15 Unit 10 Modeling Functions UEQ: How do you compare real world relationships that are represented in different forms? Standards Eligible Contents Examples M08.B-F.2.1 Represent or interpret functional relationships between quantities using tables, graphs, and descriptions. M08.B-F Construct a function to model a linear relationship between two quantities. Determine the rate of change and initial value of the function from a description of a relationship or from two (x, y) values, including reading these from a table or from a graph. Interpret the rate of change and initial value of a linear function in terms of the situation it models and in terms of its graph or a table of values. The table below shows the cost of renting a car. The company charges $45 a day for the car as well as charging a one-time $25 fee for the car s navigation system (GPS).Write an expression for the cost in dollars, c, as a function of the number of days, d. Students might write the equation c = 45d + 25 using the verbal description or by first making a table. Days (d) Cost (c) in dollars Students should recognize that the rate of change is 45 (the cost of renting the car) and that initial cost (the first day charge) also includes paying for the navigation system. Classroom discussion about one time fees vs. recurrent fees will help student s model contextual situations. M08.B-F Describe qualitatively the functional relationship between two quantities by analyzing a graph (e.g., where the function is increasing or decreasing, linear or nonlinear). Sketch or determine a graph that exhibits the qualitative features of a function that has been described verbally. When scuba divers come back to the surface of the water, they need to be careful not to ascend too quickly. Divers should not come to the surface more quickly than a rate of 0.75 ft per second. If the divers start at a depth of 100 feet, the equation d = 0.75t 100 shows the relationship between the time of the ascent in seconds (t) and the distance from the surface in feet (d). Make a table of values showing several times and the corresponding distance of the divers from the surface. Explain what your table shows. How do the values in the table relate to your equation? The graph below shows a student s trip to school. This student walks to his friend s house and, together, they ride a bus to school. The bus stops once before arriving at school. Describe how each part A-E of the graph relates to the story. 15
16 16
17 Unit 11 Systems of Linear Equations UEQ: How can I solve a real world problem that have two unknows? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.B-E..1 Write, solve, graph, and interpret linear equations in one or two variables, using various methods. M08.B-E..1. Interpret solutions to a system of two linear equations in two variables as points of intersection of their graphs, because points of intersection satisfy both equations simultaneously. Systems of linear equations can also have one solution, infinitely many solutions or no solutions. Students will discover these cases as they graph systems of linear equations and solve them algebraically. A system of linear equations whose graphs meet at one point (intersecting lines) has only one solution, the ordered pair representing the point of intersection. A system of linear equations whose graphs do not meet (parallel lines) has no solutions and the slopes of these lines are the same. A system of linear equations whose graphs are coincident (the same line) has infinitely many solutions, the set of ordered pairs representing all the points on the line. M08.B-E..1.4 Solve systems of two linear equations in two variables algebraically, and estimate solutions by graphing the equations. Solve simple cases by inspection. M08.B-E..1.5 Solve real-world and mathematical problems leading to two linear equations in two variables. By making connections between algebraic and graphical solutions and the context of the system of linear equations, students are able to make sense of their solutions. Students need opportunities to work with equations and context that include whole number and/or decimals/fractions. Find x and y using elimination and then using substitution. x + 4y = 7-2x + 8y = 10 Plant A and Plant B are on different watering schedules. This affects their rate of growth. Compare the growth of the two plants to determine when their heights will be the same. Let W = number of weeks Let H = height of the plant after W weeks Plant A Plant B W H W H 0 4 (0,4) 0 2 (0, 1 6 (1,6) 1 6 (1, 2 8 (2,8) 2 10 (2, 10 (,10) 14 (, Given each set of coordinates, graph their corresponding lines. Solution: 17
18 Write an equation that represent the growth rate of Plant A and Plant B. Solution: Plant A H = 2W + 4 Plant B H = 4W + 2 At which week will the plants have the same height? Solution: The plants have the same height after one week. Plant A: H = 2W + 4 Plant B: H = 4W + 2 Plant A: H = 2(1) + 4 Plant B: H = 4(1) + 2 Plant A: H = 6 Plant B: H = 6 After one week, the height of Plant A and Plant B are both 6 inches 18
19 Unit 12 Volume UEQ: Will understanding volume make your life full? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.C-G..1 Apply volume formulas of cones, cylinder and spheres. M08.C-G..1.1 Apply formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres to solve real-world and mathematical problems. Formulas will be provided. James wanted to plant pansies in his new planter. He wondered how much potting soil he should buy to fill it. Use the measurements in the diagram below to determine the planter s volume. 19
20 Unit 1 Patterns of Association of Data UEQ: How can data displays be used to interpret real life situations? Standards Eligible Content Examples M08.D-S.1.1 Analyze and interpret bivariate data displayed in multiple representations. M08.D-S Construct and interpret scatter plots for bivariate measurement data to investigate patterns of association between two quantities. Describe patterns such as clustering, outliers, positive or negative correlation, linear association, and nonlinear association. Students build on their previous knowledge of scatter plots examine relationships between variables. They analyze scatterplots to determine positive and negative associations, the degree of association, and type of association. Students examine outliers to determine if data points are valid or represent a recording or measurement error. Students can use tools such as those at the National Center for Educational Statistics to create a graph or generate data sets. ( Examples: Data for 10 students Math and Science scores are provided in the chart. Describe the association between the Math and Science scores. Student Math Science Data for 10 students Math scores and the distance they live from school are provided in the table below. Describe the association between the Math scores and the distance they live from school re school (miles) Data from a local fast food restaurant is provided showing the number of staff members and the average time for filling an order are provided in the table below. Describe the association between the number of staff and the average time for filling an order. Number of staff Average time to fill order (seconds) The chart below lists the life expectancy in years for people in the United States every five years from 1970 to What would you expect the life expectancy of a person in the United States to be in 2010, 2015, and 2020 based upon this data? Explain how you determined your values. Date
21 Life Expectancy (in years) M08.D-S For scatter plots that suggest a linear association, identify a line of best fit by judging the closeness of the data points to the line. Draw a line of best fit, paying attention to the closeness of the data points on either side of the line. From the line of best fit, determine an approximate linear equation that models the 25 x 95 given data (about y = 25 Students should recognize that 95 represents the y intercept and represents the slope of the line. Students can use this linear model to solve problems. For example, through substitution, they can use the equation to determine that a student with 4 absences should expect to receive a math score of about 62. They can then compare this value to their line. M08.D-S.1.1. Use the equation of a linear model to solve problems in the context of bivariate measurement data, interpreting the slope and intercept. Given data from students math scores and absences, make a scatterplot. 21
22 CC B.2 Understand that patterns of association can be seen in bivariate data utilizing frequencies. M08.D-S Construct and interpret a two-way table summarizing data on two categorical variables collected from the same subjects. Use relative frequencies calculated for rows or columns to describe possible associations between the two variables. The table illustrates the results when 100 students were asked the survey questions: Do you have a curfew? and Do you have assigned chores? Is there evidence that those who have a curfew also tend to have chores? Solution: Of the students who answered that they had a curfew, 40 had chores and 10 did not. Of the students who answered they did not have a curfew, 10 had chores and 40 did not. From this sample, there appears to be a positive correlation between having a curfew and having chores. 22
Functions MCC8.F.1 MCC8.F.2 MCC8.EE.5 MCC8.EE.6 MCC8.F.3
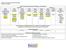 Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade - At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade - At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade
 Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade 1st Semester nd Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit Unit 9 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity Exponents
Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade 1st Semester nd Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit Unit 9 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity Exponents
Functions MCC8.F.1 MCC8.F.2 MCC8.EE.5 MCC8.EE.6 MCC8.F.3
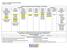 Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
How do I apply concepts of rational and irrational numbers? Concepts Competencies Resources Assessments CC E.1. number system properties.
 M08.A-N The Number System M08.A-N.1 Demonstrate an understanding of rational and irrational numbers. M08.A-N.1.1 Apply concepts of rational and irrational numbers. How do I apply concepts of rational and
M08.A-N The Number System M08.A-N.1 Demonstrate an understanding of rational and irrational numbers. M08.A-N.1.1 Apply concepts of rational and irrational numbers. How do I apply concepts of rational and
Mathematics Grade 8 PA Alternate Eligible Content
 Mathematics Grade 8 PA Content Grade 8 Mathematics Content Approved November 19, 2015 Page 1 PA Reporting Category: M08.A-N The Number System CC.2.1.8.E.1 Distinguish between rational and irrational numbers
Mathematics Grade 8 PA Content Grade 8 Mathematics Content Approved November 19, 2015 Page 1 PA Reporting Category: M08.A-N The Number System CC.2.1.8.E.1 Distinguish between rational and irrational numbers
Pennsylvania System of School Assessment
 Pennsylvania System of School Assessment The Assessment Anchors, as defined by the Eligible Content, are organized into cohesive blueprints, each structured with a common labeling system that can be read
Pennsylvania System of School Assessment The Assessment Anchors, as defined by the Eligible Content, are organized into cohesive blueprints, each structured with a common labeling system that can be read
Eighth Grade - Mathematics Kentucky Core Academic Standards with Targets Student Friendly Targets
 Eighth Grade - Mathematics Kentucky Core Academic Standards with Targets Student Friendly Targets College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Math The 6-8 standards on the following pages define
Eighth Grade - Mathematics Kentucky Core Academic Standards with Targets Student Friendly Targets College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Math The 6-8 standards on the following pages define
Westbrook Public Schools Middle School Mathematics Curriculum Grade 8
 Westbrook Public Schools Middle School Mathematics Curriculum Grade 8 Unit 1: Real Numbers Anticipated Length: 8 weeks Mathematical Practices: (Practices in bold are to be emphasized in the unit.) Mathematical
Westbrook Public Schools Middle School Mathematics Curriculum Grade 8 Unit 1: Real Numbers Anticipated Length: 8 weeks Mathematical Practices: (Practices in bold are to be emphasized in the unit.) Mathematical
New To 8 th Grade: Moved from 8 th Grade:
 New To 8 th Grade: Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x 3 = p, where p is a positive rational number (8.EE.2) Scientific notation, including
New To 8 th Grade: Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x 3 = p, where p is a positive rational number (8.EE.2) Scientific notation, including
Mathematics Grade 8. Prepublication Version, April 2013 California Department of Education 51
 Mathematics In, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a linear
Mathematics In, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a linear
MCS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR 8 th GRADE MATHEMATICS *
 MCS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR 8 th GRADE MATHEMATICS * Examples of Key Advances from Grade 7 to Grade 8 Students build on previous work with proportional relationships, unit rates, and graphing to connect
MCS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR 8 th GRADE MATHEMATICS * Examples of Key Advances from Grade 7 to Grade 8 Students build on previous work with proportional relationships, unit rates, and graphing to connect
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR
 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR Mathematics (CCSSM) Grade 8 Mathematics Grade 8 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR Mathematics (CCSSM) Grade 8 Mathematics Grade 8 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and
Pre-Algebra Curriculum Map Unit 1: The Number System M08.A-N Essential Questions Standards Content Skills Vocabulary
 Unit 1: The Number System M08.A-N Essential Questions Standards Content Skills Vocabulary Why is it helpful to write numbers in different ways? M08.A-N.1.1.1 Determine whether a number is rational or irrational.
Unit 1: The Number System M08.A-N Essential Questions Standards Content Skills Vocabulary Why is it helpful to write numbers in different ways? M08.A-N.1.1.1 Determine whether a number is rational or irrational.
Grade 8 Math Spring 2017 Item Release
 Grade 8 Math Spring 2017 Item Release 1 Grade 8 Reporting Category: Expressions and Equations Question 2 16701 Content Cluster: Investigate patterns of association in bivariate data. Content Standard:
Grade 8 Math Spring 2017 Item Release 1 Grade 8 Reporting Category: Expressions and Equations Question 2 16701 Content Cluster: Investigate patterns of association in bivariate data. Content Standard:
UNIT 1 Unit Title: The Number System Unit Description: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers
 Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: Mathematics Course Name: Grade 8 Math UNIT 1 Unit Title: The Number System Unit Description: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate
Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: Mathematics Course Name: Grade 8 Math UNIT 1 Unit Title: The Number System Unit Description: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate
Middle School Math 3 Grade 8
 Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Middle School Math 3 Grade 8 Table of Contents The Number System 1 Expressions and Equations 1 Functions 3 Geometry 4 Statistics and Probability
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Middle School Math 3 Grade 8 Table of Contents The Number System 1 Expressions and Equations 1 Functions 3 Geometry 4 Statistics and Probability
Grade 8 Yearlong Mathematics Map
 rade 8 Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments NS NS Common Core State Standards Standards
rade 8 Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments NS NS Common Core State Standards Standards
Mathematics: Pre-Algebra Eight
 Mathematics: Pre-Algebra Eight Students in 8 th Grade Pre-Algebra will study expressions and equations using one or two unknown values. Students will be introduced to the concept of a mathematical function
Mathematics: Pre-Algebra Eight Students in 8 th Grade Pre-Algebra will study expressions and equations using one or two unknown values. Students will be introduced to the concept of a mathematical function
Common Core Correlations. Mathematics Grade 8. Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions.
 Common Core Correlations Mathematics Grade 8 BENCHMARK CODE 8.EE.1.1 BENCHMARK Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. SpringBoard Page 72, 73,
Common Core Correlations Mathematics Grade 8 BENCHMARK CODE 8.EE.1.1 BENCHMARK Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. SpringBoard Page 72, 73,
I can Statements Grade 8 Mathematics
 I can Statements Grade 8 Mathematics ! I can Statements Grade 8 Mathematics Unit 1 I can: 8.EE.1 know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. 8.EE.3
I can Statements Grade 8 Mathematics ! I can Statements Grade 8 Mathematics Unit 1 I can: 8.EE.1 know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. 8.EE.3
3 RD 9 WEEKS. EE 1 EE 3 EE 4 EE 7a EE 7b EE 8a EE 8b EE 8c SP 1 SP 2 SP 3 SP 4 F 2 F 3 F 5
 1ST 9 WEEKS 2ND 9 WEEKS 3 RD 9 WEEKS 4 TH 9 WEEKS NS 1 NS 2 EE 2 G 1 G 2 G 3 G 4 G 5 EE 1 G 9 G 6 G 7 G 8 G 5 EE 5 EE 6 F 1 F 2 EE 1 EE 3 EE 4 EE 7a EE 7b EE 8a EE 8b EE 8c SP 1 SP 2 SP 3 SP 4 SP 4 SP
1ST 9 WEEKS 2ND 9 WEEKS 3 RD 9 WEEKS 4 TH 9 WEEKS NS 1 NS 2 EE 2 G 1 G 2 G 3 G 4 G 5 EE 1 G 9 G 6 G 7 G 8 G 5 EE 5 EE 6 F 1 F 2 EE 1 EE 3 EE 4 EE 7a EE 7b EE 8a EE 8b EE 8c SP 1 SP 2 SP 3 SP 4 SP 4 SP
Eighth Grade Mathematics
 Description The Appleton Area School District middle school mathematics program provides students opportunities to develop mathematical skills in thinking and applying problem-solving strategies. The framework
Description The Appleton Area School District middle school mathematics program provides students opportunities to develop mathematical skills in thinking and applying problem-solving strategies. The framework
Grade 8 Common Core Lesson Correlation
 8.NS The Number System Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand
8.NS The Number System Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand
Correlation of Final Common Core Standards (06/02/10) Grade 8 to UCSMP Algebra, 2008
 Correlation of Final Common Core Standards (06/02/10) Grade 8 to UCSMP Algebra, 2008 Final Common Core Standards (06/02/10) Lessons Page References The Number System Know that there are numbers that are
Correlation of Final Common Core Standards (06/02/10) Grade 8 to UCSMP Algebra, 2008 Final Common Core Standards (06/02/10) Lessons Page References The Number System Know that there are numbers that are
BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide
 BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
8.EE.7a; 8.EE.7b 1.3 (Extra) 7 I can rewrite equations to solve for a different variable. 8.EE.7 1.4
 Pre-Algebra Curriculum Map: (122 days) Unit #1: Algebra: Equations and Graphing (15 days) : Big Ideas Chapter 1 s: 8.EE.7a-b 1 I can solve one and two step equations. (1 day) 8.EE.7a; 8.EE.7b 1.1 (Extra)
Pre-Algebra Curriculum Map: (122 days) Unit #1: Algebra: Equations and Graphing (15 days) : Big Ideas Chapter 1 s: 8.EE.7a-b 1 I can solve one and two step equations. (1 day) 8.EE.7a; 8.EE.7b 1.1 (Extra)
MATH GRADE 8 PLD Standard Below Proficient Approaching Proficient Proficient Highly Proficient
 MATH GRADE 8 PLD Standard Below Proficient Approaching Proficient Proficient Highly Proficient The Level 1 student is below proficient The Level 2 student is approaching The Level 3 student is proficient
MATH GRADE 8 PLD Standard Below Proficient Approaching Proficient Proficient Highly Proficient The Level 1 student is below proficient The Level 2 student is approaching The Level 3 student is proficient
Grade 8: Mathematics Curriculum (2010 Common Core) Hamburg School
 Focus Topic:RP Ration & Proportional Relationships TSW = The Student Will TSW compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions, including ratios of lengths, areas and other quantities measured in
Focus Topic:RP Ration & Proportional Relationships TSW = The Student Will TSW compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions, including ratios of lengths, areas and other quantities measured in
AHSAA Homeschool Student Eligibility Exams Mathematics Grade 8
 8.NS 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 8.EE 8.EE.3 8.EE.4 8.EE.5 8.EE.6 AHSAA Homeschool Student Eligibility Exams Mathematics Grade 8 The Number System, Expressions and Equations 40% The Number System Know that there are
8.NS 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 8.EE 8.EE.3 8.EE.4 8.EE.5 8.EE.6 AHSAA Homeschool Student Eligibility Exams Mathematics Grade 8 The Number System, Expressions and Equations 40% The Number System Know that there are
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 8 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 3: Equations Topic C: Equations in Two Variables and Their Graphs (Continued) This topic focuses on extending the
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 8 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 3: Equations Topic C: Equations in Two Variables and Their Graphs (Continued) This topic focuses on extending the
Pre-Algebra 8 Overview
 Pre-Algebra 8 Overview Pre-Algebra 8 content is organized into five domains for focused study as outlined below in the column to the left. The Pre-Algebra 8 domains listed in bold print on the shaded bars
Pre-Algebra 8 Overview Pre-Algebra 8 content is organized into five domains for focused study as outlined below in the column to the left. The Pre-Algebra 8 domains listed in bold print on the shaded bars
Sequence of Grade 8 Modules Aligned with the Standards
 Sequence of Grade 8 Modules Aligned with the Standards Module 1: The Number System and Properties of Exponents Module 2: Congruence Module 3: Similarity Module 4: Linear Equations Module 5: Examples of
Sequence of Grade 8 Modules Aligned with the Standards Module 1: The Number System and Properties of Exponents Module 2: Congruence Module 3: Similarity Module 4: Linear Equations Module 5: Examples of
Days 1-2: Perfect Squares/ Perfect Cubes Days 3-4: Square Roots of Perfect Squares /Cube Roots of
 Common Core 8 Math Regular Pacing Guide Unit & Days Objectives Topic Performance Tasks QUARTER 1 PACING GUIDE Unit 1: Number Sense-Squares, Square Roots, Cubes & Cube Roots 8.EE.2 Use square root and cube
Common Core 8 Math Regular Pacing Guide Unit & Days Objectives Topic Performance Tasks QUARTER 1 PACING GUIDE Unit 1: Number Sense-Squares, Square Roots, Cubes & Cube Roots 8.EE.2 Use square root and cube
IA_CCSS_Math Math (2011) Grade 8
 IA_CCSS_Math Math (2011) Grade 8 8 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association
IA_CCSS_Math Math (2011) Grade 8 8 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map. Mathematics. GSE 8 th Grade
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
DRAFT EAST POINSETT CO. SCHOOL DIST. - GRADE 8 MATH
 Module 1 - Math Test: 10/8/2015 Work with radicals and integer exponents. 8.EE.1 8.EE.2 * 8.EE.3 * 8.EE.4 * Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions.
Module 1 - Math Test: 10/8/2015 Work with radicals and integer exponents. 8.EE.1 8.EE.2 * 8.EE.3 * 8.EE.4 * Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions.
Middle School Math Solution: Course 3
 Ohio 8.MP MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES The s for Mathematical Practice describe the skills that mathematics educators should seek to develop in their students. The descriptions of the mathematical practices
Ohio 8.MP MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES The s for Mathematical Practice describe the skills that mathematics educators should seek to develop in their students. The descriptions of the mathematical practices
Diocese of Erie Mathematics Curriculum Eighth Grade August 2012
 The Number System 8.NS Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers 1 1. Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. 1 2. Understand informally
The Number System 8.NS Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers 1 1. Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. 1 2. Understand informally
First Six Weeks Math Standards Sequence Grade 8 Domain Cluster Standard Dates The Number System
 First Six Weeks Math Stards Sequence Grade 8 Domain Cluster Stard Dates The Number System The Number System Know that there are numbers that are not rational, approximate them by rational numbers. Know
First Six Weeks Math Stards Sequence Grade 8 Domain Cluster Stard Dates The Number System The Number System Know that there are numbers that are not rational, approximate them by rational numbers. Know
GRADE 8. Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers.
 GRADE 8 Students will: The Number System Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. 1. Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand
GRADE 8 Students will: The Number System Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. 1. Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand
CORRELATION OF STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT PRENTICE HALL COURSE 3 MATHEMATICS
 CORRELATION OF STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT PRENTICE HALL COURSE 3 MATHEMATICS The following shows the alignment of Prentice Hall Course 3 Common to the Grade 8 Common Core State Standards for Mathematics.
CORRELATION OF STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT PRENTICE HALL COURSE 3 MATHEMATICS The following shows the alignment of Prentice Hall Course 3 Common to the Grade 8 Common Core State Standards for Mathematics.
SCOPE AND SEQUENCE CHART
 GSE MATH 8 SCOPE AND SEQUENCE CHART Unit Name Unit Description Georgia Standards of Excellence Unit 1 Exponents and Equations Unit 1: Students explore and understand numbers that are not rational (irrational
GSE MATH 8 SCOPE AND SEQUENCE CHART Unit Name Unit Description Georgia Standards of Excellence Unit 1 Exponents and Equations Unit 1: Students explore and understand numbers that are not rational (irrational
Repeated Reasoning. Reason A & Q. Make sense. Construct & Critique. Model Tools Precision Structure NS
 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a linear equation,
In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a linear equation,
PA Core Standards For Mathematics Curriculum Framework Grade Level 8
 PA Core Standards For Mathematics Grade Level How is mathematics used to quantify, Rational Distinguish between rational CC.2.1..E.1 among numbers can be compare, represent, and model Numbers and and irrational
PA Core Standards For Mathematics Grade Level How is mathematics used to quantify, Rational Distinguish between rational CC.2.1..E.1 among numbers can be compare, represent, and model Numbers and and irrational
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map. Mathematics. GSE 8 th Grade
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Grade 8 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition 2014
 Correlation to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Grade 8 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition 2014 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition
Correlation to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Grade 8 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition 2014 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition
I can demonstrate for rational numbers that the decimal expansion repeats eventually.
 Grade 8 Math Length of Class: School Year Program/Text Used: Competency 1: The Number Systems - Students will demonstrate the ability to know that there are numbers that are not rational and approximate
Grade 8 Math Length of Class: School Year Program/Text Used: Competency 1: The Number Systems - Students will demonstrate the ability to know that there are numbers that are not rational and approximate
8 th Grade Math Instructional Guide. 1 st Quarter Expressions and Equations (Exponents) and the Number System. 8 th Math Draft 6/7/16 1
 8 th Grade Math Instructional Guide Students should continue to develop proficiency with the Common Core s for Mathematical 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
8 th Grade Math Instructional Guide Students should continue to develop proficiency with the Common Core s for Mathematical 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M MATHEMATICS Integrated Algebra 8
 B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M MATHEMATICS Integrated Algebra 8 Book/Quarter ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC FOCUS STANDARDS & SKILLS Looking for Pythagoras (Quarter 1) Square and Cube
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M MATHEMATICS Integrated Algebra 8 Book/Quarter ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC FOCUS STANDARDS & SKILLS Looking for Pythagoras (Quarter 1) Square and Cube
8 th Grade Remediation Guide
 8 th Grade Remediation Guide Focused remediation helps target the skills students need to more quickly access and practice on-grade level content. This chart is a reference guide for teachers to help them
8 th Grade Remediation Guide Focused remediation helps target the skills students need to more quickly access and practice on-grade level content. This chart is a reference guide for teachers to help them
Common Core State Standards with California Additions 1 Standards Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program. Grade Eight Mathematics
 Common Core State s with California Additions 1 s Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program Grade Eight Mathematics Publisher 8.NS 1. 8.NS 2. Language Primary Supporting THE NUMBER SYSTEM Know that there are
Common Core State s with California Additions 1 s Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program Grade Eight Mathematics Publisher 8.NS 1. 8.NS 2. Language Primary Supporting THE NUMBER SYSTEM Know that there are
Middle School Math Course 3. Correlation of the ALEKS course Middle School Math Course 3 to the Common Core State Standards for Grade 8 (2010)
 Middle School Math Course 3 Correlation of the ALEKS course Middle School Math Course 3 to the Common Core State Standards for Grade 8 (2010) 8.NS: The Number System 8.NS.A.1: 8.NS.A.2: = ALEKS course
Middle School Math Course 3 Correlation of the ALEKS course Middle School Math Course 3 to the Common Core State Standards for Grade 8 (2010) 8.NS: The Number System 8.NS.A.1: 8.NS.A.2: = ALEKS course
CK-12 Middle School Math Grade 8
 CK-12 Middle School Math aligned with COMMON CORE MATH STATE STANDARDS INITIATIVE Middle School Standards for Math Content Common Core Math Standards for CK-12 Middle School Math The Number System (8.NS)
CK-12 Middle School Math aligned with COMMON CORE MATH STATE STANDARDS INITIATIVE Middle School Standards for Math Content Common Core Math Standards for CK-12 Middle School Math The Number System (8.NS)
Achievement Level Descriptors Mathematics Grade 8
 Achievement Level Descriptors Mathematics Grade 8 ALD Standard Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Policy demonstrate a below satisfactory level of success with the challenging content of the Florida Standards.
Achievement Level Descriptors Mathematics Grade 8 ALD Standard Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Policy demonstrate a below satisfactory level of success with the challenging content of the Florida Standards.
April 2016 Draft. DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1. eureka math.org 2016 Great Minds
 DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Grade 8 April 2016 Draft DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1 Grade 8 Mathematics The majority
DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Grade 8 April 2016 Draft DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1 Grade 8 Mathematics The majority
GRADE 8 MATH Curriculum Map
 GRADE 8 MATH Curriculum Map Unit #1 (26 days) ~5 weeks Expressions and Equations Analyze and solve linear equations. Simplify linear expressions utilizing the distributive property and collecting like
GRADE 8 MATH Curriculum Map Unit #1 (26 days) ~5 weeks Expressions and Equations Analyze and solve linear equations. Simplify linear expressions utilizing the distributive property and collecting like
Grade 8 Mathematics Performance Level Descriptors
 Limited A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Grade 8 Mathematics. A student at this level has an emerging ability to formulate and reason
Limited A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Grade 8 Mathematics. A student at this level has an emerging ability to formulate and reason
Mathematics Grade 8 focuses on three critical areas:
 Mathematics Grade 8 focuses on three critical areas: (1) Students use linear equations and systems of linear equations to represent, analyze, and solve a variety of problems. Students recognize equations
Mathematics Grade 8 focuses on three critical areas: (1) Students use linear equations and systems of linear equations to represent, analyze, and solve a variety of problems. Students recognize equations
EXPAND expressions and equations by using the. combining like terms
 Course: Grade 8 Mathematics Year: 2013 2014 Teachers: MaryAnn Valentino, Cheryl Flanagan Unit 1: Equations Approximate Time Frame: # of Weeks 8.EE.7. Solve linear equations in one variable. a. Give examples
Course: Grade 8 Mathematics Year: 2013 2014 Teachers: MaryAnn Valentino, Cheryl Flanagan Unit 1: Equations Approximate Time Frame: # of Weeks 8.EE.7. Solve linear equations in one variable. a. Give examples
Pittsburg Unified School District. Math 8 CCSS. Teaching Guide for Mathematics Common Core Curriculum REVISED
 Pittsburg Unified School District Math 8 CCSS Teaching Guide for Mathematics Common Core Curriculum 2015-2016 REVISED 7.31.15 Benchmark 1 (21% of standards/20 Q) Unit 1: 8.G.1a, b, c 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.G.4
Pittsburg Unified School District Math 8 CCSS Teaching Guide for Mathematics Common Core Curriculum 2015-2016 REVISED 7.31.15 Benchmark 1 (21% of standards/20 Q) Unit 1: 8.G.1a, b, c 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.G.4
Grade 8. Concepts and Procedures. The Number System. Expressions and Equations
 Grade 8 Concepts and Procedures The Number System Target A: Know that there are numbers that are not rational and approximate them by rational numbers. identify pi as not rational, classify numbers as
Grade 8 Concepts and Procedures The Number System Target A: Know that there are numbers that are not rational and approximate them by rational numbers. identify pi as not rational, classify numbers as
Arkansas Mathematics Standards Grade
 Arkansas Mathematics Standards Grade 8 2016 The Number System AR.Math.Content.8.NS.A.1 Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers Know that numbers that
Arkansas Mathematics Standards Grade 8 2016 The Number System AR.Math.Content.8.NS.A.1 Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers Know that numbers that
Skills available for New York eighth grade math standards
 Skills available for New York eighth grade math standards Standards are in bold, followed by a list of the IXL math skills that are aligned to that standard. Students can practice these skills online at
Skills available for New York eighth grade math standards Standards are in bold, followed by a list of the IXL math skills that are aligned to that standard. Students can practice these skills online at
Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum
 Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum The Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop in
Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum The Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop in
MD College and Career Ready Standards: Grade 8 Math
 8.NS The Number System 8.NS.A Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. 8.NS.A.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand
8.NS The Number System 8.NS.A Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. 8.NS.A.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand
8 th Grade Math. Units of Study. Overview
 8 th Grade Math Overview Course Description: In this class students will learn the rest of the essentials necessary for them to move forward into Algebra at the High School level. The class will teach
8 th Grade Math Overview Course Description: In this class students will learn the rest of the essentials necessary for them to move forward into Algebra at the High School level. The class will teach
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 A Correlation of To the for Mathematics Table of Contents The Number System... 1 Expressions and Equations... 1 Functions... 4 Geometry... 5 Statistics and Probability... 7 Standards for Mathematical Practices...
A Correlation of To the for Mathematics Table of Contents The Number System... 1 Expressions and Equations... 1 Functions... 4 Geometry... 5 Statistics and Probability... 7 Standards for Mathematical Practices...
Fairfield Public Schools
 Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools Pre-Algebra 8 Pre-Algebra 8 BOE Approved 05/21/2013 1 PRE-ALGEBRA 8 Critical Areas of Focus In the Pre-Algebra 8 course, instructional time should focus on three critical
Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools Pre-Algebra 8 Pre-Algebra 8 BOE Approved 05/21/2013 1 PRE-ALGEBRA 8 Critical Areas of Focus In the Pre-Algebra 8 course, instructional time should focus on three critical
Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards
 Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Course 3 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations Ch. 1 Equations 29 days: 9/5/17 10/13/17 2. Transformational
Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Course 3 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations Ch. 1 Equations 29 days: 9/5/17 10/13/17 2. Transformational
Connected Mathematics Project 3 (CMP3) 2014
 s Map for a Basic Grade Level Program San Diego Unified School District Connected Mathematics Project 3 (CMP3) 2014 Common Core State s with California Additions Grade 8 Mathematics Common Core State s
s Map for a Basic Grade Level Program San Diego Unified School District Connected Mathematics Project 3 (CMP3) 2014 Common Core State s with California Additions Grade 8 Mathematics Common Core State s
3A: Solving linear equations, understanding rate of change.
 Grade/Subject Unit Title Grade 8/ Mathematics Unit 3: Linear Relationships 3A: Solving linear equations, understanding rate of change. 3B: Systems of Equations Overview of Unit Pacing In this unit, students
Grade/Subject Unit Title Grade 8/ Mathematics Unit 3: Linear Relationships 3A: Solving linear equations, understanding rate of change. 3B: Systems of Equations Overview of Unit Pacing In this unit, students
Standards to Topics. Louisiana Student Standards for Mathematics Mathematics 8 Grade 8
 Standards to Topics Louisiana Student Standards for Mathematics Mathematics 8 8.NS.A.01 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal
Standards to Topics Louisiana Student Standards for Mathematics Mathematics 8 8.NS.A.01 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal
A TRADITION of EXCELLENCE A VISION for TOMORROW
 Pre-Algebra Grade 8 The Number System To successfully complete Grade 8 Pre-Algebra, the learner will Cluster: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers.
Pre-Algebra Grade 8 The Number System To successfully complete Grade 8 Pre-Algebra, the learner will Cluster: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers.
GRADE 8 MATH Curriculum Map
 GRADE 8 MATH Curriculum Map Unit #1 Analyze and solve linear equations. ~5 weeks Expressions and Equations Simplify linear expressions utilizing the distributive property and collecting like terms. (8.EE.7)
GRADE 8 MATH Curriculum Map Unit #1 Analyze and solve linear equations. ~5 weeks Expressions and Equations Simplify linear expressions utilizing the distributive property and collecting like terms. (8.EE.7)
GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester
 GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester Unit 1 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity MGSE8.G.1 MGSE8.G.2 MGSE8.G.3 MGSE8.G.4 MGSE8.G.5 Unit 2 Exponents MGSE8.EE1
GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester Unit 1 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity MGSE8.G.1 MGSE8.G.2 MGSE8.G.3 MGSE8.G.4 MGSE8.G.5 Unit 2 Exponents MGSE8.EE1
Mathematics Pacing. Instruction 9/9-10/18/13 Assessment 10/21-10/25/13 Remediation 10/28 11/1/13. # STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES CCSS Resources
 CONTENT AREA: Grade 8 Mathematics Unit 1 Instruction 9/9-10/18/13 Assessment 10/21-10/25/13 Remediation 10/28 11/1/13 UNIT NAME: The Number System # STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES CCSS Resources 1 2 3 4 5
CONTENT AREA: Grade 8 Mathematics Unit 1 Instruction 9/9-10/18/13 Assessment 10/21-10/25/13 Remediation 10/28 11/1/13 UNIT NAME: The Number System # STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES CCSS Resources 1 2 3 4 5
, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1
 2017.18, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical
2017.18, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical
Grade 8 envisionmath SY
 Topics Days in Cycle Dates Grade 8 envisionmath2.0 2017-2018 SY Benchmark Cycle 1 Benchmark Cycle 2 Benchmark Cycle 3 Cycle 4 September 5 - October 31 BM Window Nov 1-17 November 2 - January 26 BM Window
Topics Days in Cycle Dates Grade 8 envisionmath2.0 2017-2018 SY Benchmark Cycle 1 Benchmark Cycle 2 Benchmark Cycle 3 Cycle 4 September 5 - October 31 BM Window Nov 1-17 November 2 - January 26 BM Window
BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide UNIT 7.1: THE NUMBER SYSTEM
 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content Accelerated 7th Grade BPS Suggested Planning Guide BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving
Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content Accelerated 7th Grade BPS Suggested Planning Guide BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving
Alabama Course of Study Mathematics
 A Correlation of Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 2 (CMP2) with Common Core Investigations Grade 8 to the Alabama Course of Study Mathematics Grade 8 The Number System Know that there are numbers that
A Correlation of Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 2 (CMP2) with Common Core Investigations Grade 8 to the Alabama Course of Study Mathematics Grade 8 The Number System Know that there are numbers that
Math 8 Common Core. Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools
 Math 8 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 7 Common Core This course continues the trajectory towards a more
Math 8 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 7 Common Core This course continues the trajectory towards a more
Grade 8 Big Ideas SY
 Topics and Chapters/Units Days in Cycle Dates Grade 8 Big Ideas 2017-2018 SY Benchmark Cycle 1 Benchmark Cycle 2 Benchmark Cycle 3 Cycle 4 September 5 - October 31 BM Window Nov 1-17 November 2 - January
Topics and Chapters/Units Days in Cycle Dates Grade 8 Big Ideas 2017-2018 SY Benchmark Cycle 1 Benchmark Cycle 2 Benchmark Cycle 3 Cycle 4 September 5 - October 31 BM Window Nov 1-17 November 2 - January
Test Blueprint ATI AzMERIT Math 08 Gr. CBAS #1 TE AZ-8.NS THE NUMBER SYSTEM. 6.7% on Test. # on AP. % on Test. # on Test
 Blueprint 2016-17 ATI AzMERIT Math 08 Gr. CBAS #1 TE AZ-8.NS THE NUMBER SYSTEM 6.7 Page 1 AZ-8.NS.A.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number
Blueprint 2016-17 ATI AzMERIT Math 08 Gr. CBAS #1 TE AZ-8.NS THE NUMBER SYSTEM 6.7 Page 1 AZ-8.NS.A.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number
Mathematics Grade 8 focuses on three critical areas:
 Mathematics Grade 8 focuses on three critical areas: (1) Students use linear equations and systems of linear equations to represent, analyze, and solve a variety of problems. Students recognize equations
Mathematics Grade 8 focuses on three critical areas: (1) Students use linear equations and systems of linear equations to represent, analyze, and solve a variety of problems. Students recognize equations
I can calculate percent of change. I can calculate percent increases (sales tax, tip/gratuity, commission, fees, markup, etc ).
 RATIO & PROPORTIONAL RELATIONSHIPS 7.RP.: Use proportional relationships to solve multistep ratio and percent problems. Examples: simple interest, tax, markups and markdowns, gratuities and commissions,
RATIO & PROPORTIONAL RELATIONSHIPS 7.RP.: Use proportional relationships to solve multistep ratio and percent problems. Examples: simple interest, tax, markups and markdowns, gratuities and commissions,
PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form
 PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form Course Title: Math 8 Course Number/CBED Number: Grade Levels: Length of Course: Eighth Grade One Year Credit: 10 Meets Graduation Requirements:
PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form Course Title: Math 8 Course Number/CBED Number: Grade Levels: Length of Course: Eighth Grade One Year Credit: 10 Meets Graduation Requirements:
Grade 8 Big Ideas + HMH Algebra SY
 Topics and Chapters/Units Days in Dates Grade 8 Big Ideas + HMH Algebra 1 2017-2018 SY Benchmark 1 Benchmark 2 Benchmark 3 4 September 5 - October 31 BM Window Nov 1-17 November 2 - January 26 BM Window
Topics and Chapters/Units Days in Dates Grade 8 Big Ideas + HMH Algebra 1 2017-2018 SY Benchmark 1 Benchmark 2 Benchmark 3 4 September 5 - October 31 BM Window Nov 1-17 November 2 - January 26 BM Window
Horizontal Progression Recommendations
 Greater Albany Public Schools 8 th Grade Math CCSS Pacing Guide Horizontal Progression Recommendations 4 2 Solving Equations 8EE7a-b, 8NS1, 8EE2 5 3 Triangles & Angles with Pythagorean Theorem 6 (5) (end
Greater Albany Public Schools 8 th Grade Math CCSS Pacing Guide Horizontal Progression Recommendations 4 2 Solving Equations 8EE7a-b, 8NS1, 8EE2 5 3 Triangles & Angles with Pythagorean Theorem 6 (5) (end
Common Core State Standard I Can Statements 8 th Grade Mathematics. The Number System (NS)
 CCSS Key: The Number System (NS) Expressions & Equations (EE) Functions (F) Geometry (G) Statistics & Probability (SP) Common Core State Standard I Can Statements 8 th Grade Mathematics 8.NS.1. Understand
CCSS Key: The Number System (NS) Expressions & Equations (EE) Functions (F) Geometry (G) Statistics & Probability (SP) Common Core State Standard I Can Statements 8 th Grade Mathematics 8.NS.1. Understand
Lee County Schools Curriculum Road Map Pre-Algebra
 Quarter 1 Rational Numbers, Repeating Decimals, Terminating Decimals 1 Numbers & Operations 2 Radicals & Integer Exponents 1 8.NS.1 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 8.EE.1 Know that numbers that are not rational
Quarter 1 Rational Numbers, Repeating Decimals, Terminating Decimals 1 Numbers & Operations 2 Radicals & Integer Exponents 1 8.NS.1 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 8.EE.1 Know that numbers that are not rational
Math 8 CCSS Guide. Unit 1 Variables, Expressions and Equations (Chapters 1, 2 and 5)
 Math 8 CCSS Guide Unit 1 Variables, Expressions and Equations (Chapters 1, 2 and 5) 1.1 Expressions and Variables 1.2 Powers and exponents 1.3 Review Order of operations and variables 1.8 The Coordinate
Math 8 CCSS Guide Unit 1 Variables, Expressions and Equations (Chapters 1, 2 and 5) 1.1 Expressions and Variables 1.2 Powers and exponents 1.3 Review Order of operations and variables 1.8 The Coordinate
Oakwood City School District Grade Eight Mathematics. Grade Eight Mathematics
 Grade Eight Course Description In Grade Eight, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling and association
Grade Eight Course Description In Grade Eight, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling and association
Five District Partnership 1
 Five District Partnership 1 Grade 8 Math Year-Long Plan Overview Standards Shorthand Description Sept-Oct Nov-Dec Jan-Feb Mar-Apr May-June 8.NS.1 Rational numbers & decimal expansions X 8.NS.2 Irrational
Five District Partnership 1 Grade 8 Math Year-Long Plan Overview Standards Shorthand Description Sept-Oct Nov-Dec Jan-Feb Mar-Apr May-June 8.NS.1 Rational numbers & decimal expansions X 8.NS.2 Irrational
Grade 8 Curriculum Map Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)
 TIME FRAME September (18 days) UNIT/CONCEPT S Course 3A Content Chapter 1: Exponents CORE GOALS & SKILLS Big Idea : You can use exponential notation to represent repeated multiplication of the same factor
TIME FRAME September (18 days) UNIT/CONCEPT S Course 3A Content Chapter 1: Exponents CORE GOALS & SKILLS Big Idea : You can use exponential notation to represent repeated multiplication of the same factor
8.G.1. Illustrative Mathematics Unit 1. 8.G.1a 8.G.2 8.G.3. 8.G.1c. Illustrative Mathematics Unit 2 8.G.2
 Illustrative Mathematics Unit 3 Illustrative Mathematics Unit 2 Illustrative Mathematics Unit 1 8.G.1 8.G.1a 8.G.1b 8.G.1c 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.G.1 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.EE.5 8.EE.6 1st Nine Weeks Rigid Transformations
Illustrative Mathematics Unit 3 Illustrative Mathematics Unit 2 Illustrative Mathematics Unit 1 8.G.1 8.G.1a 8.G.1b 8.G.1c 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.G.1 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.EE.5 8.EE.6 1st Nine Weeks Rigid Transformations
Math 8 Advanced Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Curriculum Map
 Semester 1 Standards for Mathematical Practice 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of
Semester 1 Standards for Mathematical Practice 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of
Textbook: Chapter 1 Lesson 1
 8 th Grade Math Curriculum Map **Calculators may be used all year on Assessments** Segment 1 6 Weeks Number System [8-NS1] Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally
8 th Grade Math Curriculum Map **Calculators may be used all year on Assessments** Segment 1 6 Weeks Number System [8-NS1] Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally
Agile Mind Mathematics 8 Scope & Sequence for Common Core State Standards, DRAFT
 Engaging problem-solving situations and effective strategies including appropriate use of tools, proportional reasoning, multiple representations, language and measurement are evident throughout this course.
Engaging problem-solving situations and effective strategies including appropriate use of tools, proportional reasoning, multiple representations, language and measurement are evident throughout this course.
AIMS Common Core Math Standards Alignment
 AIMS Common Core Math Standards Alignment Eighth Grade The Number System (8.NS) 8.NS.A Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. 1. Know that numbers
AIMS Common Core Math Standards Alignment Eighth Grade The Number System (8.NS) 8.NS.A Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. 1. Know that numbers
Common Core Math Units Grade 8
 Sequenced Units for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics Prior to, students have written and interpreted expressions, solved equations and inequalities, explored quantitative relationships between
Sequenced Units for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics Prior to, students have written and interpreted expressions, solved equations and inequalities, explored quantitative relationships between
