ONE RANDOM VARIABLE F ( ) [ ] x P X x x x 3
|
|
|
- Lydia Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Cumulive Disribuio Fucio (cd) ONE RANDOM VARIABLE cd is deied s he probbiliy o he eve { x}: F ( ) [ ] x P x x - Applies o discree s well s coiuous RV. Exmple: hree osses o coi x 8 3 x 8 8 F x x The cd c be wrie compcly i erms o he ui sep ucio: x ux ( ) x 3 3 F u u( x ) u( x ) u( x 3) Exmple: The Uiorm RV i he ui iervl [,]. x F x x x
2 Exmple: The wiig ime o cusomer xi sd is zero i he cusomer ids xi prked he sd, d uiormly disribued rdom legh o ime i he iervl [, ] (i hours) i o xi is oud upo rrivl. The probbiliy h xi is he sd whe he cusomer rrives is p. Fid he cd o. Use ol probbiliy heorem, F P[ x] P[ x id xi] p P[ x o xi]( p) x P[ x id xi] x x P[ x o xi] x x x bsic properies o he cd (i) F. (ii) lim F. x (iii) lim F. x x F p ( p) x x x (iv) F is odecresig ucio o x, h is, i b, F( ) F( b) (odecresig ucio). (v) F is coiuous rom he righ, h is, or h, F ( b) lim F ( b h) F ( b ). (vi) P[ b] F( b) F( ) (vii) P[ b] F( b) F( b ) (i F hs jump x = b). (viii) P[ x] F. The Three Types o Rdom Vribles h Discree rdom vribles: hve cd h is righ-coiuous, sircse ucio o x, wih jumps couble se o pois x, x, x,... F p ( x ) p ( x ) u( x x ) k k k xk x k Coiuous rdom vribles: is coiuous everywhere, d which, is suiciely smooh h i c be wrie s iegrl o some oegive ucio (x): x F dx P[ x] Rdom vrible o mixed ype: is rdom vrible wih cd h hs jumps o couble se o pois x, x, x,... bu h lso icreses coiuously over les oe iervl o vlues o x.
3 Cd: F pf ( p) F p, F : cd o discree RV; F : cd o co. RV The Probbiliy Desiy Fucio (pd) probbiliy desiy ucio o (pd) : df dx The pd represes he desiy o probbiliy he poi x: Properies: F( x h) F P[ x x h] F ( x h) F h h h (i) ( F is o-decresig ucio o x). b (ii) P[ x b] dx probbiliy o iervl [, b] x (iii) F ( ) d. (iv) dx. pd o Discree Rdom Vribles df p ( xk ) ( x xk ) dx k
4 Codiiol cd s d pd s codiiol cd o give C P[{ x} C] F ( x C) P[ C] PC [ ] codiiol pd o give C : df ( x C) ( x C) dx Exmple: The lieime o mchie hs coiuous cd F ( x ). Codiiol cd d pd give he eve C = { > } (mchie sill workig ime ) codiiol cd: P[{ x} { }] F ( x ) P[ ] x P[{ x} { }] P[ x] F F( ) x P[ ] P[ ] F ( ) F ( x ) F F( ) F ( ) x x codiiol pd: ( x ) x F ( ) cd o i erms o he codiiol cd s; priio o S: B, B,..., B F P[ x] P[ x B ] P[ B ] F ( x B ] P[ B ] i i i i i i ( x B ] P[ B ] i i i Exmple: A biry rsmissio sysem seds bi by rsmiig ( v) volge sigl, d bi by rsmiig (+v). Received sigl corruped by Gussi oise: Y = + N : he rsmied sigl, N is oise volge wih pd ( x ) N
5 Assume P[ ] = p = P[ ]. Fid he pd o Y. B = { is rsmied} B = { is rsmied}. F F ( x B ] P[ B ] F ( x B ] P[ B ] Y Y Y P[ Y x v]( p) P[ Y x v] p P[ Y x v] P[ N x v] F ( x v) P[ Y x v] P[ N x v] F ( x v) F F ( x v)( p) F ( x v) p Y N N dfy Y N ( x v)( p) N ( x v) p dx x ( xv) ( xv) N e Y e ( p) e p N N THE EPECTED VALUE expeced vlue or me o rdom vrible : E[ ] ( ) d exiss i E[ ] ( ) d Exmple: Me o Uiorm Rdom Vrible b E[ ] d b b b b I he pd is symmeric bou poi m: ( m x) ( m x) he E [] = m. Exmple: Me o Expoeil Rdom Vrible ( ) x [ ] x x x x e x E x e dx xe e dx Expeced Vlue o Y = g () : E[ Y ] g dx Exmple: Expeced Vlues o Siusoid wih Rdom Phse Y cos( ) where, d re coss; is uiorm i [, ]. expeced vlue o Y d expeced vlue o he power o Y, Y :
6 E[ Y ] E[ cos( )] cos( ) d si( ) E Y E E [ ] [ cos ( )] cos( ) Some properies: cos( ) d (i) E[] c c where c is cos. (ii) E[ c ] ce[ ] (iii) E gk( ) E[ gk( )] k k Vrice o VAR[ ] E ( m ) E[ ] m m E[ ] Sdrd Deviio: STD[ ] VAR[ ] Exmple: Vrice o uiorm RV b b ( b ) m E ( m) x dx b b Exmple: Vrice o he Gussi RV ( xm) ( xm) dx e dx e dx Diereie wih respec o : ( xm) ( xm) ( x m) ( ) 3 e dx x m e dx The h mome o he rdom vrible : E[ ] x dx
7 IMPORTANT RVs The uiorm RV Pd: x b b x, x b Cd x x F x b b x b me d vrice: The expoeil RV ( ) [ ] b VAR[ ] b E Pd: Cd: x x e x x F x e x me d vrice: E[ ] VAR[ ] memoryless propery: P[ h ] P[ h] proo: ( h) P[{ h} { }] P[ h] e h P[ h ] e P[ h] P[ ] P[ ] e The Gussi (Norml) Rdom Vrible Pd: ( xm) e x
8 Cd: ( um) F P[ x] e du x ( xm)/ x m u m F e d where x x e d pd o Gussi RV wih m = d =. Exmple: Show h Gussi pd iegres o oe. x x y ( x y ) e dx e dx e dy e dxdy x r cos, y rsi x y r dxdy rdrd ( x y ) r r e dxdy e rdrd e rdr The Q-ucio: Q e d x The Gmm Rdom Vrible x e Pd: For, x ( ) where ( ) z x z x e dx z he Gmm ucio properies: ( z ) z( z) z ( m ) m! m oegive ieger. Whe m, ieger : m-erlg RV
9 x y dx x e dx y x y e dy ( ) ( ) dx The Cuchy Rdom Vrible / hs o momes becuse he iegrls do o coverge. x FUNCTIONS OF A RANDOM VARIABLE Give Y = g() problem is o id he pd o Y i erms o he pd o. Exmple: Y b y b y b FY( y) P[ Y y] P[ b y] P[ ] F i y b y b P[ ] F i y b Y( y) y b Y( y) y b Y( y)
10 Exmple: Y = y P[ Y y] P y y y y FY ( y) F( y ) F( y ) y dy df y d y df y d y Y ( y) d y d y dy y y y y y I is Gussi wih me m =, d SD =, x y y Y e y e ( y) e y y (chi-squre rv wih oe degree o reedom) Geerl Cse Soluios o y g : x, x,..., x Le = 3,
11 P[ y Y y dy] P[ x x dx ] P[ x dx x ] P[ x x dx ] ( y) dy ( x ) dx ( x ) dx ( x ) dx Y 3 3 ( x) ( x3) Y ( y) dy / dx dy / dx dy / dx xx xx xx3 I geerl, ( y) Y k ( xk) g( x ) k Previous exmple: Y = y x soluios or y : x y x y g x g( x ) y g( x ) y g( x ) g( x ) y y y y ( x) e e e Y ( y) g( x) g y y y Exmple: Y = cos() : uiormly disribued i [,], x y cos Two soluios i [, ] x cos ( y) x cos ( y) g si g( x) si cos ( y) g si cos ( y) cos ( y) y cos( ) si( ) cos ( ) y g( x ) g( x ) y
12 Y ( y) y y y y THE MARKOV AND CHEBYSHEV INEQUALITIES Mrkov iequliy: E [ ] P[ ] is o-egive. This boud is useul i we do hve y iormio bou he RV excep is me vlue. Proo: E[ ] ( ) d ( ) d ( ) d ( ) d ( ) d ( ) d P[ ] I oly he me d vrice re kow: The Chebyshev iequliy: igher boud h Mrkov. P m Proo: Le ED [ ] D ( m) Mrkov iequliy E[ D ] Exmple: Muli-user compuer sysem; me respose ime m = 5 s sdrd deviio = 3 s Esime he probbiliy h he respose ime is more h 5 secods rom he me. Chebyshev iequliy 9 5 s P The Chero boud: Le A = { }. Idicor ucio o A, IA() P[ ] I ( ) ( ) d A
13 Choose he boud or he idicor ucio s I A( ) or ll E[ ] I A( ) ( ) d ( ) d Le he boud be : Mrkov iequliy. I e s s( ) A( ) s( ) s s s s I A( ) ( ) d e ( ) d e e ( ) d e E[ e ] s s P[ ] e E[ e ] : he Chero boud The Chrcerisic Fucio: Coiuous RVs j jx ( ) E[ e ] e dx Fourier rsorm o he pd jx ( ) e d Iverse Fourier rsorm Discree RVs: j xk ( ) p ( x ) e k k ( ) p ( k) e jk : ieger-vlued RVs k jk p( k) ( ) e d Exmple: Expoeil RV x jx ( j) x ( ) e e dx e dx j Exmple: Geomeric RV k jk j k p ( ) pq e p ( qe ) qe k k j
14 The mome Theorem: d E [ ] ( ) j d Proo: Tylor series expsio o j x e jx ( jx) e jx...! jx ( jx) ( ) e dx jx... dx! ( j) j x dx x dx...! ( j) ( j) ( ) je[ ] E[ ]... E[ ]...!! Compre wih he Tylor series expsio o ( ) bou = : ( ) () ( j) ( ) d E[ ] E[ ] () ( )!! j j d Exmple: me d vrice o expoeilly disribued rdom vrible j ( ) ( ) E [ ] () j ( j) j ( ) E[ ] () VAR[ ] 3 ( j) j RELIABILITY The relibiliy ime is deied s he probbiliy h he compoe, subsysem, or sysem is sill ucioig ime : R( ) P[ T ] T: lieime o sysem R( ) P[ T ] FT ( ) FT () : cd o T. R( ) ( ) T The me ime o ilure (MTTF) is give by he expeced vlue o T: E[ T ] ( ) d R( ) d R( ) d T The codiiol cd o T give h T > :
15 FT ( x T ) P[ T x T ] FT FT( ) FT ( ) x x T T ( x T ) x F ( ) T R() The ilure re ucio r() : r( ) T ( T ) R () r() d = he probbiliy h compoe h hs ucioed up o ime will il i he ex d secods. Exmple: Expoeil Filure Lw cos ilure re ucio : R() r( ) iiil codiio R() R () dr R() d l R( ) e R R() Relibiliy o Sysems ( ) e : T is expoeilly disribued RV. T A s : he eve sysem ucioig ime A j : he eve jh compoe is ucioig ime Series Coecio: P[ A ] P[ A A... A ] P[ A ] P[ A ]... P[ A ] s R( ) R ( ) R ( )... R ( ) I sysems hve cos ilure res: ( ) i R e R( ) e i (... ) Prllel Coecio: The sysem will o be ucioig i d oly i ll he compoes hve iled.
16 P[ A ] P[ A ] P[ A ]... P[ A ] c c c c s R( ) R ( ) R ( )... R ( ) R( ) R ( ) R ( )... R ( ) Exmple: Compre he relibiliy o sigle-ui sysem gis h o sysem h operes wo uis i prllel. Assume ll uis hve expoeilly disribued lieimes wih re. sigle-ui sysem: R () s e wo uis i prllel: R ( ) ( e )( e ) e ( e ) e p R ( ) R ( ) p s
Moment Generating Function
 1 Mome Geeraig Fucio m h mome m m m E[ ] x f ( x) dx m h ceral mome m m m E[( ) ] ( ) ( x ) f ( x) dx Mome Geeraig Fucio For a real, M () E[ e ] e k x k e p ( x ) discree x k e f ( x) dx coiuous Example
1 Mome Geeraig Fucio m h mome m m m E[ ] x f ( x) dx m h ceral mome m m m E[( ) ] ( ) ( x ) f ( x) dx Mome Geeraig Fucio For a real, M () E[ e ] e k x k e p ( x ) discree x k e f ( x) dx coiuous Example
Existence Of Solutions For Nonlinear Fractional Differential Equation With Integral Boundary Conditions
 Reserch Ivey: Ieriol Jourl Of Egieerig Ad Sciece Vol., Issue (April 3), Pp 8- Iss(e): 78-47, Iss(p):39-6483, Www.Reserchivey.Com Exisece Of Soluios For Nolier Frciol Differeil Equio Wih Iegrl Boudry Codiios,
Reserch Ivey: Ieriol Jourl Of Egieerig Ad Sciece Vol., Issue (April 3), Pp 8- Iss(e): 78-47, Iss(p):39-6483, Www.Reserchivey.Com Exisece Of Soluios For Nolier Frciol Differeil Equio Wih Iegrl Boudry Codiios,
ERROR ESTIMATES FOR APPROXIMATING THE FOURIER TRANSFORM OF FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED VARIATION
 ERROR ESTIMATES FOR APPROXIMATING THE FOURIER TRANSFORM OF FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED VARIATION N.S. BARNETT, S.S. DRAGOMIR, AND G. HANNA Absrc. I his pper we poi ou pproximio for he Fourier rsform for fucios
ERROR ESTIMATES FOR APPROXIMATING THE FOURIER TRANSFORM OF FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED VARIATION N.S. BARNETT, S.S. DRAGOMIR, AND G. HANNA Absrc. I his pper we poi ou pproximio for he Fourier rsform for fucios
F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CE/CR/CS] Applied Mathematics
![F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CE/CR/CS] Applied Mathematics F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CE/CR/CS] Applied Mathematics](/thumbs/89/97771715.jpg) F.Y. Diplom : Sem. II [CE/CR/CS] Applied Mhemics Prelim Quesio Pper Soluio Q. Aemp y FIVE of he followig : [0] Q. () Defie Eve d odd fucios. [] As.: A fucio f() is sid o e eve fucio if f() f() A fucio
F.Y. Diplom : Sem. II [CE/CR/CS] Applied Mhemics Prelim Quesio Pper Soluio Q. Aemp y FIVE of he followig : [0] Q. () Defie Eve d odd fucios. [] As.: A fucio f() is sid o e eve fucio if f() f() A fucio
th m m m m central moment : E[( X X) ] ( X X) ( x X) f ( x)
![th m m m m central moment : E[( X X) ] ( X X) ( x X) f ( x) th m m m m central moment : E[( X X) ] ( X X) ( x X) f ( x)](/thumbs/80/81319353.jpg) 1 Trasform Techiques h m m m m mome : E[ ] x f ( x) dx h m m m m ceral mome : E[( ) ] ( ) ( x) f ( x) dx A coveie wa of fidig he momes of a radom variable is he mome geeraig fucio (MGF). Oher rasform echiques
1 Trasform Techiques h m m m m mome : E[ ] x f ( x) dx h m m m m ceral mome : E[( ) ] ( ) ( x) f ( x) dx A coveie wa of fidig he momes of a radom variable is he mome geeraig fucio (MGF). Oher rasform echiques
ON SOME FRACTIONAL PARABOLIC EQUATIONS DRIVEN BY FRACTIONAL GAUSSIAN NOISE
 IJRRAS 6 3) Februry www.rppress.com/volumes/vol6issue3/ijrras_6_3_.pdf ON SOME FRACIONAL ARABOLIC EQUAIONS RIVEN BY FRACIONAL GAUSSIAN NOISE Mhmoud M. El-Bori & hiri El-Sid El-Ndi Fculy of Sciece Alexdri
IJRRAS 6 3) Februry www.rppress.com/volumes/vol6issue3/ijrras_6_3_.pdf ON SOME FRACIONAL ARABOLIC EQUAIONS RIVEN BY FRACIONAL GAUSSIAN NOISE Mhmoud M. El-Bori & hiri El-Sid El-Ndi Fculy of Sciece Alexdri
Transient Solution of the M/M/C 1 Queue with Additional C 2 Servers for Longer Queues and Balking
 Jourl of Mhemics d Sisics 4 (): 2-25, 28 ISSN 549-3644 28 Sciece ublicios Trsie Soluio of he M/M/C Queue wih Addiiol C 2 Servers for Loger Queues d Blkig R. O. Al-Seedy, A. A. El-Sherbiy,,2 S. A. EL-Shehwy
Jourl of Mhemics d Sisics 4 (): 2-25, 28 ISSN 549-3644 28 Sciece ublicios Trsie Soluio of he M/M/C Queue wih Addiiol C 2 Servers for Loger Queues d Blkig R. O. Al-Seedy, A. A. El-Sherbiy,,2 S. A. EL-Shehwy
ECE 636: Systems identification
 ECE 636: Sysems ideificio Lecures 7 8 Predicio error mehods Se spce models Coiuous ime lier se spce spce model: x ( = Ax( + Bu( + w( y( = Cx( + υ( A:, B: m, C: Discree ime lier se spce model: x( + = A(
ECE 636: Sysems ideificio Lecures 7 8 Predicio error mehods Se spce models Coiuous ime lier se spce spce model: x ( = Ax( + Bu( + w( y( = Cx( + υ( A:, B: m, C: Discree ime lier se spce model: x( + = A(
Week 8 Lecture 3: Problems 49, 50 Fourier analysis Courseware pp (don t look at French very confusing look in the Courseware instead)
 Week 8 Lecure 3: Problems 49, 5 Fourier lysis Coursewre pp 6-7 (do look Frech very cofusig look i he Coursewre ised) Fourier lysis ivolves ddig wves d heir hrmoics, so i would hve urlly followed fer he
Week 8 Lecure 3: Problems 49, 5 Fourier lysis Coursewre pp 6-7 (do look Frech very cofusig look i he Coursewre ised) Fourier lysis ivolves ddig wves d heir hrmoics, so i would hve urlly followed fer he
Reinforcement Learning
 Reiforceme Corol lerig Corol polices h choose opiml cios Q lerig Covergece Chper 13 Reiforceme 1 Corol Cosider lerig o choose cios, e.g., Robo lerig o dock o bery chrger o choose cios o opimize fcory oupu
Reiforceme Corol lerig Corol polices h choose opiml cios Q lerig Covergece Chper 13 Reiforceme 1 Corol Cosider lerig o choose cios, e.g., Robo lerig o dock o bery chrger o choose cios o opimize fcory oupu
Linear Time Invariant Systems
 1 Liear Time Ivaria Sysems Oulie We will show ha he oupu equals he covoluio bewee he ipu ad he ui impulse respose: sysem for a discree-ime, for a coiuous-ime sysdem, y x h y x h 2 Discree Time LTI Sysems
1 Liear Time Ivaria Sysems Oulie We will show ha he oupu equals he covoluio bewee he ipu ad he ui impulse respose: sysem for a discree-ime, for a coiuous-ime sysdem, y x h y x h 2 Discree Time LTI Sysems
Actuarial Society of India
 Acuarial Sociey of Idia EXAMINAIONS Jue 5 C4 (3) Models oal Marks - 5 Idicaive Soluio Q. (i) a) Le U deoe he process described by 3 ad V deoe he process described by 4. he 5 e 5 PU [ ] PV [ ] ( e ).538!
Acuarial Sociey of Idia EXAMINAIONS Jue 5 C4 (3) Models oal Marks - 5 Idicaive Soluio Q. (i) a) Le U deoe he process described by 3 ad V deoe he process described by 4. he 5 e 5 PU [ ] PV [ ] ( e ).538!
Fourier transform. Continuous-time Fourier transform (CTFT) ω ω
 Fourier rasform Coiuous-ime Fourier rasform (CTFT P. Deoe ( he Fourier rasform of he sigal x(. Deermie he followig values, wihou compuig (. a (0 b ( d c ( si d ( d d e iverse Fourier rasform for Re { (
Fourier rasform Coiuous-ime Fourier rasform (CTFT P. Deoe ( he Fourier rasform of he sigal x(. Deermie he followig values, wihou compuig (. a (0 b ( d c ( si d ( d d e iverse Fourier rasform for Re { (
5.1-The Initial-Value Problems For Ordinary Differential Equations
 5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
EGR 544 Communication Theory
 EGR 544 Commuicaio heory 7. Represeaio of Digially Modulaed Sigals II Z. Aliyazicioglu Elecrical ad Compuer Egieerig Deparme Cal Poly Pomoa Represeaio of Digial Modulaio wih Memory Liear Digial Modulaio
EGR 544 Commuicaio heory 7. Represeaio of Digially Modulaed Sigals II Z. Aliyazicioglu Elecrical ad Compuer Egieerig Deparme Cal Poly Pomoa Represeaio of Digial Modulaio wih Memory Liear Digial Modulaio
10.3 Autocorrelation Function of Ergodic RP 10.4 Power Spectral Density of Ergodic RP 10.5 Normal RP (Gaussian RP)
 ENGG450 Probabiliy ad Saisics for Egieers Iroducio 3 Probabiliy 4 Probabiliy disribuios 5 Probabiliy Desiies Orgaizaio ad descripio of daa 6 Samplig disribuios 7 Ifereces cocerig a mea 8 Comparig wo reames
ENGG450 Probabiliy ad Saisics for Egieers Iroducio 3 Probabiliy 4 Probabiliy disribuios 5 Probabiliy Desiies Orgaizaio ad descripio of daa 6 Samplig disribuios 7 Ifereces cocerig a mea 8 Comparig wo reames
Suggested Solution for Pure Mathematics 2011 By Y.K. Ng (last update: 8/4/2011) Paper I. (b) (c)
 per I. Le α 7 d β 7. The α d β re he roos o he equio, such h α α, β β, --- α β d αβ. For, α β For, α β α β αβ 66 The seme is rue or,. ssume Cosider, α β d α β y deiiio α α α α β or some posiive ieer.
per I. Le α 7 d β 7. The α d β re he roos o he equio, such h α α, β β, --- α β d αβ. For, α β For, α β α β αβ 66 The seme is rue or,. ssume Cosider, α β d α β y deiiio α α α α β or some posiive ieer.
NOTES ON BERNOULLI NUMBERS AND EULER S SUMMATION FORMULA. B r = [m = 0] r
![NOTES ON BERNOULLI NUMBERS AND EULER S SUMMATION FORMULA. B r = [m = 0] r NOTES ON BERNOULLI NUMBERS AND EULER S SUMMATION FORMULA. B r = [m = 0] r](/thumbs/80/81160853.jpg) NOTES ON BERNOULLI NUMBERS AND EULER S SUMMATION FORMULA MARK WILDON. Beroulli umbers.. Defiiio. We defie he Beroulli umbers B m for m by m ( m + ( B r [m ] r r Beroulli umbers re med fer Joh Beroulli
NOTES ON BERNOULLI NUMBERS AND EULER S SUMMATION FORMULA MARK WILDON. Beroulli umbers.. Defiiio. We defie he Beroulli umbers B m for m by m ( m + ( B r [m ] r r Beroulli umbers re med fer Joh Beroulli
Lecture 15 First Properties of the Brownian Motion
 Lecure 15: Firs Properies 1 of 8 Course: Theory of Probabiliy II Term: Sprig 2015 Isrucor: Gorda Zikovic Lecure 15 Firs Properies of he Browia Moio This lecure deals wih some of he more immediae properies
Lecure 15: Firs Properies 1 of 8 Course: Theory of Probabiliy II Term: Sprig 2015 Isrucor: Gorda Zikovic Lecure 15 Firs Properies of he Browia Moio This lecure deals wih some of he more immediae properies
SUMMATION OF INFINITE SERIES REVISITED
 SUMMATION OF INFINITE SERIES REVISITED I several aricles over he las decade o his web page we have show how o sum cerai iiie series icludig he geomeric series. We wa here o eed his discussio o he geeral
SUMMATION OF INFINITE SERIES REVISITED I several aricles over he las decade o his web page we have show how o sum cerai iiie series icludig he geomeric series. We wa here o eed his discussio o he geeral
Special Functions. Leon M. Hall. Professor of Mathematics University of Missouri-Rolla. Copyright c 1995 by Leon M. Hall. All rights reserved.
 Specil Fucios Leo M. Hll Professor of Mhemics Uiversiy of Missouri-Roll Copyrigh c 995 y Leo M. Hll. All righs reserved. Chper 5. Orhogol Fucios 5.. Geerig Fucios Cosider fucio f of wo vriles, ( x,), d
Specil Fucios Leo M. Hll Professor of Mhemics Uiversiy of Missouri-Roll Copyrigh c 995 y Leo M. Hll. All righs reserved. Chper 5. Orhogol Fucios 5.. Geerig Fucios Cosider fucio f of wo vriles, ( x,), d
HOMEWORK 6 - INTEGRATION. READING: Read the following parts from the Calculus Biographies that I have given (online supplement of our textbook):
 MAT 3 CALCULUS I 5.. Dokuz Eylül Uiversiy Fculy of Sciece Deprme of Mhemics Isrucors: Egi Mermu d Cell Cem Srıoğlu HOMEWORK 6 - INTEGRATION web: hp://kisi.deu.edu.r/egi.mermu/ Tebook: Uiversiy Clculus,
MAT 3 CALCULUS I 5.. Dokuz Eylül Uiversiy Fculy of Sciece Deprme of Mhemics Isrucors: Egi Mermu d Cell Cem Srıoğlu HOMEWORK 6 - INTEGRATION web: hp://kisi.deu.edu.r/egi.mermu/ Tebook: Uiversiy Clculus,
Math 6710, Fall 2016 Final Exam Solutions
 Mah 67, Fall 6 Fial Exam Soluios. Firs, a sude poied ou a suble hig: if P (X i p >, he X + + X (X + + X / ( evaluaes o / wih probabiliy p >. This is roublesome because a radom variable is supposed o be
Mah 67, Fall 6 Fial Exam Soluios. Firs, a sude poied ou a suble hig: if P (X i p >, he X + + X (X + + X / ( evaluaes o / wih probabiliy p >. This is roublesome because a radom variable is supposed o be
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
Sampling Example. ( ) δ ( f 1) (1/2)cos(12πt), T 0 = 1
 Samplig Example Le x = cos( 4π)cos( π). The fudameal frequecy of cos 4π fudameal frequecy of cos π is Hz. The ( f ) = ( / ) δ ( f 7) + δ ( f + 7) / δ ( f ) + δ ( f + ). ( f ) = ( / 4) δ ( f 8) + δ ( f
Samplig Example Le x = cos( 4π)cos( π). The fudameal frequecy of cos 4π fudameal frequecy of cos π is Hz. The ( f ) = ( / ) δ ( f 7) + δ ( f + 7) / δ ( f ) + δ ( f + ). ( f ) = ( / 4) δ ( f 8) + δ ( f
The Central Limit Theorem
 The Ceral Limi Theorem The ceral i heorem is oe of he mos impora heorems i probabiliy heory. While here a variey of forms of he ceral i heorem, he mos geeral form saes ha give a sufficiely large umber,
The Ceral Limi Theorem The ceral i heorem is oe of he mos impora heorems i probabiliy heory. While here a variey of forms of he ceral i heorem, he mos geeral form saes ha give a sufficiely large umber,
Section 8 Convolution and Deconvolution
 APPLICATIONS IN SIGNAL PROCESSING Secio 8 Covoluio ad Decovoluio This docume illusraes several echiques for carryig ou covoluio ad decovoluio i Mahcad. There are several operaors available for hese fucios:
APPLICATIONS IN SIGNAL PROCESSING Secio 8 Covoluio ad Decovoluio This docume illusraes several echiques for carryig ou covoluio ad decovoluio i Mahcad. There are several operaors available for hese fucios:
Integration and Differentiation
 ome Clculus bckgroud ou should be fmilir wih, or review, for Mh 404 I will be, for he mos pr, ssumed ou hve our figerips he bsics of (mulivrible) fucios, clculus, d elemer differeil equios If here hs bee
ome Clculus bckgroud ou should be fmilir wih, or review, for Mh 404 I will be, for he mos pr, ssumed ou hve our figerips he bsics of (mulivrible) fucios, clculus, d elemer differeil equios If here hs bee
SLOW INCREASING FUNCTIONS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS TO SOME PROBLEMS IN NUMBER THEORY
 VOL. 8, NO. 7, JULY 03 ISSN 89-6608 ARPN Jourl of Egieerig d Applied Sciece 006-03 Ai Reerch Publihig Nework (ARPN). All righ reerved. www.rpjourl.com SLOW INCREASING FUNCTIONS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS TO
VOL. 8, NO. 7, JULY 03 ISSN 89-6608 ARPN Jourl of Egieerig d Applied Sciece 006-03 Ai Reerch Publihig Nework (ARPN). All righ reerved. www.rpjourl.com SLOW INCREASING FUNCTIONS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS TO
Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 MATH 4 (R) Wier 008 Iermediae Calculus I Soluios o Problem Se # Due: Friday Jauary 8, 008 Deparme of Mahemaical ad Saisical Scieces Uiversiy of Albera Quesio. [Sec.., #] Fid a formula for he geeral erm
MATH 4 (R) Wier 008 Iermediae Calculus I Soluios o Problem Se # Due: Friday Jauary 8, 008 Deparme of Mahemaical ad Saisical Scieces Uiversiy of Albera Quesio. [Sec.., #] Fid a formula for he geeral erm
LOCUS 1. Definite Integration CONCEPT NOTES. 01. Basic Properties. 02. More Properties. 03. Integration as Limit of a Sum
 LOCUS Defiie egrio CONCEPT NOTES. Bsic Properies. More Properies. egrio s Limi of Sum LOCUS Defiie egrio As eplied i he chper iled egrio Bsics, he fudmel heorem of clculus ells us h o evlue he re uder
LOCUS Defiie egrio CONCEPT NOTES. Bsic Properies. More Properies. egrio s Limi of Sum LOCUS Defiie egrio As eplied i he chper iled egrio Bsics, he fudmel heorem of clculus ells us h o evlue he re uder
STK4080/9080 Survival and event history analysis
 STK48/98 Survival ad eve hisory aalysis Marigales i discree ime Cosider a sochasic process The process M is a marigale if Lecure 3: Marigales ad oher sochasic processes i discree ime (recap) where (formally
STK48/98 Survival ad eve hisory aalysis Marigales i discree ime Cosider a sochasic process The process M is a marigale if Lecure 3: Marigales ad oher sochasic processes i discree ime (recap) where (formally
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
1 Notes on Little s Law (l = λw)
 Copyrigh c 26 by Karl Sigma Noes o Lile s Law (l λw) We cosider here a famous ad very useful law i queueig heory called Lile s Law, also kow as l λw, which assers ha he ime average umber of cusomers i
Copyrigh c 26 by Karl Sigma Noes o Lile s Law (l λw) We cosider here a famous ad very useful law i queueig heory called Lile s Law, also kow as l λw, which assers ha he ime average umber of cusomers i
MATH 507a ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS FALL 2018 Prof. Alexander. g (x) dx = g(b) g(0) = g(b),
 MATH 57a ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS FALL 28 Prof. Alexader (2.3.8)(a) Le g(x) = x/( + x) for x. The g (x) = /( + x) 2 is decreasig, so for a, b, g(a + b) g(a) = a+b a g (x) dx b so g(a + b) g(a) + g(b). Sice
MATH 57a ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS FALL 28 Prof. Alexader (2.3.8)(a) Le g(x) = x/( + x) for x. The g (x) = /( + x) 2 is decreasig, so for a, b, g(a + b) g(a) = a+b a g (x) dx b so g(a + b) g(a) + g(b). Sice
Mathematical Statistics. 1 Introduction to the materials to be covered in this course
 Mahemaical Saisics Iroducio o he maerials o be covered i his course. Uivariae & Mulivariae r.v s 2. Borl-Caelli Lemma Large Deviaios. e.g. X,, X are iid r.v s, P ( X + + X where I(A) is a umber depedig
Mahemaical Saisics Iroducio o he maerials o be covered i his course. Uivariae & Mulivariae r.v s 2. Borl-Caelli Lemma Large Deviaios. e.g. X,, X are iid r.v s, P ( X + + X where I(A) is a umber depedig
Functions, Limit, And Continuity
 Fucios, Limi d coiuiy of fucio Fucios, Limi, Ad Coiuiy. Defiiio of fucio A fucio is rule of correspodece h ssocies wih ech ojec i oe se clled f from secod se. The se of ll vlues so oied is he domi, sigle
Fucios, Limi d coiuiy of fucio Fucios, Limi, Ad Coiuiy. Defiiio of fucio A fucio is rule of correspodece h ssocies wih ech ojec i oe se clled f from secod se. The se of ll vlues so oied is he domi, sigle
K3 p K2 p Kp 0 p 2 p 3 p
 Mah 80-00 Mo Ar 0 Chaer 9 Fourier Series ad alicaios o differeial equaios (ad arial differeial equaios) 9.-9. Fourier series defiiio ad covergece. The idea of Fourier series is relaed o he liear algebra
Mah 80-00 Mo Ar 0 Chaer 9 Fourier Series ad alicaios o differeial equaios (ad arial differeial equaios) 9.-9. Fourier series defiiio ad covergece. The idea of Fourier series is relaed o he liear algebra
Ideal Amplifier/Attenuator. Memoryless. where k is some real constant. Integrator. System with memory
 Liear Time-Ivaria Sysems (LTI Sysems) Oulie Basic Sysem Properies Memoryless ad sysems wih memory (saic or dyamic) Causal ad o-causal sysems (Causaliy) Liear ad o-liear sysems (Lieariy) Sable ad o-sable
Liear Time-Ivaria Sysems (LTI Sysems) Oulie Basic Sysem Properies Memoryless ad sysems wih memory (saic or dyamic) Causal ad o-causal sysems (Causaliy) Liear ad o-liear sysems (Lieariy) Sable ad o-sable
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
4.8 Improper Integrals
 4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
Fractional Fourier Series with Applications
 Aeric Jourl o Couiol d Alied Mheics 4, 4(6): 87-9 DOI: 593/jjc446 Frciol Fourier Series wih Alicios Abu Hd I, Khlil R * Uiversiy o Jord, Jord Absrc I his er, we iroduce coorble rciol Fourier series We
Aeric Jourl o Couiol d Alied Mheics 4, 4(6): 87-9 DOI: 593/jjc446 Frciol Fourier Series wih Alicios Abu Hd I, Khlil R * Uiversiy o Jord, Jord Absrc I his er, we iroduce coorble rciol Fourier series We
3. Renewal Limit Theorems
 Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Boundary Value Problems of Conformable. Fractional Differential Equation with Impulses
 Applied Meicl Scieces Vol 2 28 o 8 377-397 HIKARI Ld www-irico ps://doiorg/2988/s28823 Boudry Vlue Probles of Coforble Frciol Differeil Equio wi Ipulses Arisr Tgvree Ci Tipryoo d Apisi Ppogpu Depre of
Applied Meicl Scieces Vol 2 28 o 8 377-397 HIKARI Ld www-irico ps://doiorg/2988/s28823 Boudry Vlue Probles of Coforble Frciol Differeil Equio wi Ipulses Arisr Tgvree Ci Tipryoo d Apisi Ppogpu Depre of
ECE-314 Fall 2012 Review Questions
 ECE-34 Fall 0 Review Quesios. A liear ime-ivaria sysem has he ipu-oupu characerisics show i he firs row of he diagram below. Deermie he oupu for he ipu show o he secod row of he diagram. Jusify your aswer.
ECE-34 Fall 0 Review Quesios. A liear ime-ivaria sysem has he ipu-oupu characerisics show i he firs row of he diagram below. Deermie he oupu for he ipu show o he secod row of he diagram. Jusify your aswer.
Principles of Communications Lecture 1: Signals and Systems. Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University
 Priciples of Commuicaios Lecure : Sigals ad Sysems Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 Naioal Chiao ug Uiversiy cwliu@wis.ee.cu.edu.w Oulies Sigal Models & Classificaios Sigal Space & Orhogoal Basis Fourier Series &rasform
Priciples of Commuicaios Lecure : Sigals ad Sysems Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 Naioal Chiao ug Uiversiy cwliu@wis.ee.cu.edu.w Oulies Sigal Models & Classificaios Sigal Space & Orhogoal Basis Fourier Series &rasform
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
Notes 03 largely plagiarized by %khc
 1 1 Discree-Time Covoluio Noes 03 largely plagiarized by %khc Le s begi our discussio of covoluio i discree-ime, sice life is somewha easier i ha domai. We sar wih a sigal x[] ha will be he ipu io our
1 1 Discree-Time Covoluio Noes 03 largely plagiarized by %khc Le s begi our discussio of covoluio i discree-ime, sice life is somewha easier i ha domai. We sar wih a sigal x[] ha will be he ipu io our
Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J.
 Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
0 for t < 0 1 for t > 0
 8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
10.5 Power Series. In this section, we are going to start talking about power series. A power series is a series of the form
 0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
Random variables. A random variable X is a function that assigns a real number, X(ζ), to each outcome ζ in the sample space of a random experiment.
 Random variables Some random eperimens may yield a sample space whose elemens evens are numbers, bu some do no or mahemaical purposes, i is desirable o have numbers associaed wih he oucomes A random variable
Random variables Some random eperimens may yield a sample space whose elemens evens are numbers, bu some do no or mahemaical purposes, i is desirable o have numbers associaed wih he oucomes A random variable
Calculus Limits. Limit of a function.. 1. One-Sided Limits...1. Infinite limits 2. Vertical Asymptotes...3. Calculating Limits Using the Limit Laws.
 Limi of a fucio.. Oe-Sided..... Ifiie limis Verical Asympoes... Calculaig Usig he Limi Laws.5 The Squeeze Theorem.6 The Precise Defiiio of a Limi......7 Coiuiy.8 Iermediae Value Theorem..9 Refereces..
Limi of a fucio.. Oe-Sided..... Ifiie limis Verical Asympoes... Calculaig Usig he Limi Laws.5 The Squeeze Theorem.6 The Precise Defiiio of a Limi......7 Coiuiy.8 Iermediae Value Theorem..9 Refereces..
Fourier Series and Applications
 9/7/9 Fourier Series d Applictios Fuctios epsio is doe to uderstd the better i powers o etc. My iportt probles ivolvig prtil dieretil equtios c be solved provided give uctio c be epressed s iiite su o
9/7/9 Fourier Series d Applictios Fuctios epsio is doe to uderstd the better i powers o etc. My iportt probles ivolvig prtil dieretil equtios c be solved provided give uctio c be epressed s iiite su o
F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CH/FG/ME/PT/PG] Applied Mathematics
![F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CH/FG/ME/PT/PG] Applied Mathematics F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CH/FG/ME/PT/PG] Applied Mathematics](/thumbs/89/97771684.jpg) F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CH/FG/ME/PT/PG] Applied Mahemaics Prelim Quesio Paper Soluio Q. Aemp ay FIVE of he followig : [0] Q.(a) Defie Eve ad odd fucios. [] As.: A fucio f() is said o be eve fucio if
F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CH/FG/ME/PT/PG] Applied Mahemaics Prelim Quesio Paper Soluio Q. Aemp ay FIVE of he followig : [0] Q.(a) Defie Eve ad odd fucios. [] As.: A fucio f() is said o be eve fucio if
Problem. Statement. variable Y. Method: Step 1: Step 2: y d dy. Find F ( Step 3: Find f = Y. Solution: Assume
 Functions of Rndom Vrible Problem Sttement We know the pdf ( or cdf ) of rndom r vrible. Define new rndom vrible Y = g. Find the pdf of Y. Method: Step : Step : Step 3: Plot Y = g( ). Find F ( y) by mpping
Functions of Rndom Vrible Problem Sttement We know the pdf ( or cdf ) of rndom r vrible. Define new rndom vrible Y = g. Find the pdf of Y. Method: Step : Step : Step 3: Plot Y = g( ). Find F ( y) by mpping
Solutions to Problems from Chapter 2
 Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering g Dept
 Kig Fahd Uiversiy of Peroleum & Mierals Compuer Egieerig g Dep COE 4 Daa ad Compuer Commuicaios erm Dr. shraf S. Hasa Mahmoud Rm -4 Ex. 74 Email: ashraf@kfupm.edu.sa 9/8/ Dr. shraf S. Hasa Mahmoud Lecure
Kig Fahd Uiversiy of Peroleum & Mierals Compuer Egieerig g Dep COE 4 Daa ad Compuer Commuicaios erm Dr. shraf S. Hasa Mahmoud Rm -4 Ex. 74 Email: ashraf@kfupm.edu.sa 9/8/ Dr. shraf S. Hasa Mahmoud Lecure
The Reimann Integral is a formal limit definition of a definite integral
 MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
e t dt e t dt = lim e t dt T (1 e T ) = 1
 Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Math-303 Chapter 7 Linear systems of ODE November 16, Chapter 7. Systems of 1 st Order Linear Differential Equations.
 Mah-33 Chaper 7 Liear sysems of ODE November 6, 7 Chaper 7 Sysems of s Order Liear Differeial Equaios saddle poi λ >, λ < Mah-33 Chaper 7 Liear sysems of ODE November 6, 7 Mah-33 Chaper 7 Liear sysems
Mah-33 Chaper 7 Liear sysems of ODE November 6, 7 Chaper 7 Sysems of s Order Liear Differeial Equaios saddle poi λ >, λ < Mah-33 Chaper 7 Liear sysems of ODE November 6, 7 Mah-33 Chaper 7 Liear sysems
1. Solve by the method of undetermined coefficients and by the method of variation of parameters. (4)
 7 Differeial equaios Review Solve by he mehod of udeermied coefficies ad by he mehod of variaio of parameers (4) y y = si Soluio; we firs solve he homogeeous equaio (4) y y = 4 The correspodig characerisic
7 Differeial equaios Review Solve by he mehod of udeermied coefficies ad by he mehod of variaio of parameers (4) y y = si Soluio; we firs solve he homogeeous equaio (4) y y = 4 The correspodig characerisic
5.1 - Areas and Distances
 Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 63u Office Hours: R 9:5 - :5m The midterm will cover the sectios for which you hve received homework d feedbck Sectios.9-6.5 i your book.
Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 63u Office Hours: R 9:5 - :5m The midterm will cover the sectios for which you hve received homework d feedbck Sectios.9-6.5 i your book.
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
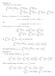 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
( ) k ( ) 1 T n 1 x = xk. Geometric series obtained directly from the definition. = 1 1 x. See also Scalars 9.1 ADV-1: lim n.
 Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
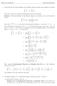 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
6/10/2014. Definition. Time series Data. Time series Graph. Components of time series. Time series Seasonal. Time series Trend
 6//4 Defiiio Time series Daa A ime series Measures he same pheomeo a equal iervals of ime Time series Graph Compoes of ime series 5 5 5-5 7 Q 7 Q 7 Q 3 7 Q 4 8 Q 8 Q 8 Q 3 8 Q 4 9 Q 9 Q 9 Q 3 9 Q 4 Q Q
6//4 Defiiio Time series Daa A ime series Measures he same pheomeo a equal iervals of ime Time series Graph Compoes of ime series 5 5 5-5 7 Q 7 Q 7 Q 3 7 Q 4 8 Q 8 Q 8 Q 3 8 Q 4 9 Q 9 Q 9 Q 3 9 Q 4 Q Q
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
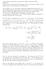 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
Exercise 3 Stochastic Models of Manufacturing Systems 4T400, 6 May
 Exercise 3 Sochasic Models of Maufacurig Sysems 4T4, 6 May. Each week a very popular loery i Adorra pris 4 ickes. Each ickes has wo 4-digi umbers o i, oe visible ad he oher covered. The umbers are radomly
Exercise 3 Sochasic Models of Maufacurig Sysems 4T4, 6 May. Each week a very popular loery i Adorra pris 4 ickes. Each ickes has wo 4-digi umbers o i, oe visible ad he oher covered. The umbers are radomly
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
5 Probability densities
 5 Probbility densities 5. Continuous rndom vribles 5. The norml distribution 5.3 The norml pproimtion to the binomil distribution 5.5 The uniorm distribution 5. Joint distribution discrete nd continuous
5 Probbility densities 5. Continuous rndom vribles 5. The norml distribution 5.3 The norml pproimtion to the binomil distribution 5.5 The uniorm distribution 5. Joint distribution discrete nd continuous
O & M Cost O & M Cost
 5/5/008 Turbie Reliabiliy, Maieace ad Faul Deecio Zhe Sog, Adrew Kusiak 39 Seamas Ceer Iowa Ciy, Iowa 54-57 adrew-kusiak@uiowa.edu Tel: 39-335-5934 Fax: 39-335-5669 hp://www.icae.uiowa.edu/~akusiak Oulie
5/5/008 Turbie Reliabiliy, Maieace ad Faul Deecio Zhe Sog, Adrew Kusiak 39 Seamas Ceer Iowa Ciy, Iowa 54-57 adrew-kusiak@uiowa.edu Tel: 39-335-5934 Fax: 39-335-5669 hp://www.icae.uiowa.edu/~akusiak Oulie
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
Supplementary Information for Thermal Noises in an Aqueous Quadrupole Micro- and Nano-Trap
 Supplemeary Iformaio for Thermal Noises i a Aqueous Quadrupole Micro- ad Nao-Trap Jae Hyu Park ad Predrag S. Krsić * Physics Divisio, Oak Ridge Naioal Laboraory, Oak Ridge, TN 3783 E-mail: krsicp@orl.gov
Supplemeary Iformaio for Thermal Noises i a Aqueous Quadrupole Micro- ad Nao-Trap Jae Hyu Park ad Predrag S. Krsić * Physics Divisio, Oak Ridge Naioal Laboraory, Oak Ridge, TN 3783 E-mail: krsicp@orl.gov
TAKA KUSANO. laculty of Science Hrosh tlnlersty 1982) (n-l) + + Pn(t)x 0, (n-l) + + Pn(t)Y f(t,y), XR R are continuous functions.
 Iera. J. Mah. & Mah. Si. Vol. 6 No. 3 (1983) 559-566 559 ASYMPTOTIC RELATIOHIPS BETWEEN TWO HIGHER ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS TAKA KUSANO laculy of Sciece Hrosh llersy 1982) ABSTRACT. Some asympoic
Iera. J. Mah. & Mah. Si. Vol. 6 No. 3 (1983) 559-566 559 ASYMPTOTIC RELATIOHIPS BETWEEN TWO HIGHER ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS TAKA KUSANO laculy of Sciece Hrosh llersy 1982) ABSTRACT. Some asympoic
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
On Absolute Indexed Riesz Summability of Orthogonal Series
 Ieriol Jourl of Couiol d Alied Mheics. ISSN 89-4966 Volue 3 Nuer (8). 55-6 eserch Idi Pulicios h:www.riulicio.co O Asolue Ideed iesz Suiliy of Orhogol Series L. D. Je S. K. Piry *. K. Ji 3 d. Sl 4 eserch
Ieriol Jourl of Couiol d Alied Mheics. ISSN 89-4966 Volue 3 Nuer (8). 55-6 eserch Idi Pulicios h:www.riulicio.co O Asolue Ideed iesz Suiliy of Orhogol Series L. D. Je S. K. Piry *. K. Ji 3 d. Sl 4 eserch
Comparison between Fourier and Corrected Fourier Series Methods
 Malaysia Joural of Mahemaical Scieces 7(): 73-8 (13) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES Joural homepage: hp://eispem.upm.edu.my/oural Compariso bewee Fourier ad Correced Fourier Series Mehods 1
Malaysia Joural of Mahemaical Scieces 7(): 73-8 (13) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES Joural homepage: hp://eispem.upm.edu.my/oural Compariso bewee Fourier ad Correced Fourier Series Mehods 1
ODEs II, Supplement to Lectures 6 & 7: The Jordan Normal Form: Solving Autonomous, Homogeneous Linear Systems. April 2, 2003
 ODEs II, Suppleme o Lecures 6 & 7: The Jorda Normal Form: Solvig Auoomous, Homogeeous Liear Sysems April 2, 23 I his oe, we describe he Jorda ormal form of a marix ad use i o solve a geeral homogeeous
ODEs II, Suppleme o Lecures 6 & 7: The Jorda Normal Form: Solvig Auoomous, Homogeeous Liear Sysems April 2, 23 I his oe, we describe he Jorda ormal form of a marix ad use i o solve a geeral homogeeous
Frequency-domain Characteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems
 requecy-domi Chrcteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems Prof. Siripog Potisuk LTI System descriptio Previous bsis fuctio: uit smple or DT impulse The iput sequece is represeted s lier combitio of shifted
requecy-domi Chrcteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems Prof. Siripog Potisuk LTI System descriptio Previous bsis fuctio: uit smple or DT impulse The iput sequece is represeted s lier combitio of shifted
Math 2414 Homework Set 7 Solutions 10 Points
 Mah Homework Se 7 Soluios 0 Pois #. ( ps) Firs verify ha we ca use he iegral es. The erms are clearly posiive (he epoeial is always posiive ad + is posiive if >, which i is i his case). For decreasig we
Mah Homework Se 7 Soluios 0 Pois #. ( ps) Firs verify ha we ca use he iegral es. The erms are clearly posiive (he epoeial is always posiive ad + is posiive if >, which i is i his case). For decreasig we
In this section we will study periodic signals in terms of their frequency f t is said to be periodic if (4.1)
 Fourier Series Iroducio I his secio we will sudy periodic sigals i ers o heir requecy is said o be periodic i coe Reid ha a sigal ( ) ( ) ( ) () or every, where is a uber Fro his deiiio i ollows ha ( )
Fourier Series Iroducio I his secio we will sudy periodic sigals i ers o heir requecy is said o be periodic i coe Reid ha a sigal ( ) ( ) ( ) () or every, where is a uber Fro his deiiio i ollows ha ( )
Inference on One Population Mean Hypothesis Testing
 Iferece o Oe Popultio Me ypothesis Testig Scerio 1. Whe the popultio is orml, d the popultio vrice is kow i. i. d. Dt : X 1, X,, X ~ N(, ypothesis test, for istce: Exmple: : : : : : 5'7" (ull hypothesis:
Iferece o Oe Popultio Me ypothesis Testig Scerio 1. Whe the popultio is orml, d the popultio vrice is kow i. i. d. Dt : X 1, X,, X ~ N(, ypothesis test, for istce: Exmple: : : : : : 5'7" (ull hypothesis:
Geometric Sequences. Geometric Sequence. Geometric sequences have a common ratio.
 s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ECE 350 Matlab-Based Project #3
 ECE 350 Malab-Based Projec #3 Due Dae: Nov. 26, 2008 Read he aached Malab uorial ad read he help files abou fucio i, subs, sem, bar, sum, aa2. he wrie a sigle Malab M file o complee he followig ask for
ECE 350 Malab-Based Projec #3 Due Dae: Nov. 26, 2008 Read he aached Malab uorial ad read he help files abou fucio i, subs, sem, bar, sum, aa2. he wrie a sigle Malab M file o complee he followig ask for
LIMITS OF FUNCTIONS (I)
 LIMITS OF FUNCTIO (I ELEMENTARY FUNCTIO: (Elemeary fucios are NOT piecewise fucios Cosa Fucios: f(x k, where k R Polyomials: f(x a + a x + a x + a x + + a x, where a, a,..., a R Raioal Fucios: f(x P (x,
LIMITS OF FUNCTIO (I ELEMENTARY FUNCTIO: (Elemeary fucios are NOT piecewise fucios Cosa Fucios: f(x k, where k R Polyomials: f(x a + a x + a x + a x + + a x, where a, a,..., a R Raioal Fucios: f(x P (x,
UNIT I FOURIER SERIES T
 UNIT I FOURIER SERIES PROBLEM : Th urig mom T o h crkh o m gi i giv or ri o vu o h crk g dgr 6 9 5 8 T 5 897 785 599 66 Epd T i ri o i. Souio: L T = i + i + i +, Sic h ir d vu o T r rpd gc o T T i T i
UNIT I FOURIER SERIES PROBLEM : Th urig mom T o h crkh o m gi i giv or ri o vu o h crk g dgr 6 9 5 8 T 5 897 785 599 66 Epd T i ri o i. Souio: L T = i + i + i +, Sic h ir d vu o T r rpd gc o T T i T i
The solution is often represented as a vector: 2xI + 4X2 + 2X3 + 4X4 + 2X5 = 4 2xI + 4X2 + 3X3 + 3X4 + 3X5 = 4. 3xI + 6X2 + 6X3 + 3X4 + 6X5 = 6.
 [~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
[~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
BINOMIAL THEOREM OBJECTIVE PROBLEMS in the expansion of ( 3 +kx ) are equal. Then k =
 wwwskshieduciocom BINOMIAL HEOREM OBJEIVE PROBLEMS he coefficies of, i e esio of k e equl he k /7 If e coefficie of, d ems i e i AP, e e vlue of is he coefficies i e,, 7 ems i e esio of e i AP he 7 7 em
wwwskshieduciocom BINOMIAL HEOREM OBJEIVE PROBLEMS he coefficies of, i e esio of k e equl he k /7 If e coefficie of, d ems i e i AP, e e vlue of is he coefficies i e,, 7 ems i e esio of e i AP he 7 7 em
Convergence theorems. Chapter Sampling
 Chaper Covergece heorems We ve already discussed he difficuly i defiig he probabiliy measure i erms of a experimeal frequecy measureme. The hear of he problem lies i he defiiio of he limi, ad his was se
Chaper Covergece heorems We ve already discussed he difficuly i defiig he probabiliy measure i erms of a experimeal frequecy measureme. The hear of he problem lies i he defiiio of he limi, ad his was se
λiv Av = 0 or ( λi Av ) = 0. In order for a vector v to be an eigenvector, it must be in the kernel of λi
 Liear lgebra Lecure #9 Noes This week s lecure focuses o wha migh be called he srucural aalysis of liear rasformaios Wha are he irisic properies of a liear rasformaio? re here ay fixed direcios? The discussio
Liear lgebra Lecure #9 Noes This week s lecure focuses o wha migh be called he srucural aalysis of liear rasformaios Wha are he irisic properies of a liear rasformaio? re here ay fixed direcios? The discussio
Lecture #6: Continuous-Time Signals
 EEL5: Discree-Time Signals and Sysems Lecure #6: Coninuous-Time Signals Lecure #6: Coninuous-Time Signals. Inroducion In his lecure, we discussed he ollowing opics:. Mahemaical represenaion and ransormaions
EEL5: Discree-Time Signals and Sysems Lecure #6: Coninuous-Time Signals Lecure #6: Coninuous-Time Signals. Inroducion In his lecure, we discussed he ollowing opics:. Mahemaical represenaion and ransormaions
Advanced Engineering Mathematics, K.A. Stroud, Dexter J. Booth Engineering Mathematics, H.K. Dass Higher Engineering Mathematics, Dr. B.S.
 Rfrc: (i) (ii) (iii) Advcd Egirig Mhmic, K.A. Sroud, Dxr J. Booh Egirig Mhmic, H.K. D Highr Egirig Mhmic, Dr. B.S. Grwl Th mhod of m Thi coi of h followig xm wih h giv coribuio o h ol. () Mid-rm xm : 3%
Rfrc: (i) (ii) (iii) Advcd Egirig Mhmic, K.A. Sroud, Dxr J. Booh Egirig Mhmic, H.K. D Highr Egirig Mhmic, Dr. B.S. Grwl Th mhod of m Thi coi of h followig xm wih h giv coribuio o h ol. () Mid-rm xm : 3%
Method: Step 1: Step 2: Find f. Step 3: = Y dy. Solution: 0, ( ) 0, y. Assume
 Functions of Rndom Vrible Problem Sttement We know the pdf ( or cdf ) of rndom vrible. Define new rndom vrible Y g( ) ). Find the pdf of Y. Method: Step : Step : Step 3: Plot Y g( ). Find F ( ) b mpping
Functions of Rndom Vrible Problem Sttement We know the pdf ( or cdf ) of rndom vrible. Define new rndom vrible Y g( ) ). Find the pdf of Y. Method: Step : Step : Step 3: Plot Y g( ). Find F ( ) b mpping
