Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
|
|
|
- Norma Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Serial : 5SP_CS_W_Digital Logic_598 Delhi Noida hopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune hubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: info@madeeasy.in Ph: CLSS TEST 289 COMPUTER SCIENCE & IT Subject : Digital Logic Date of test : 5/9/28 nswer Key. (b) 7. (b) 3. (a) 9. (c) 25. (b) 2. (b) 8. (b) 4. (b) 2. (d) 26. (c) 3. (b) 9. (b) 5. (c) 2. (d) 27. (a) 4. (d). (b) 6. (b) 22. (c) 28. (c) 5. (c). (a) 7. (c) 23. (c) 29. (c) 6. (a) 2. (d) 8. (b) 24. (a) 3. (c)
2 CT28 CS Digital Logic 7 Detailed Explanations. (b) Overall MOD = = 6 Lowest frequency is output frequency 2. (b) f out = = 4 khz (54) (4) b b = (3) b or (54) b = (4) b (3) b The expression in decimal number system is (5 b + 4 b ) = (4 b ) ( b + 3 b ) 5b + 4 = 4 (b + 3) b = 2 4 = 8 3. (b) It is a toggle flipflop, the values toggle Q : initial state 4. (d) Excitation table Qn Qn+ J K X X X X 5. (c) Using POS form Z = ( + + C)( + + C) = ( + )( + ) + C = + C = C + ( ) 6. (a) + = ( + ) = + = ( + ) = (+ ) = ( + ) = Thus for F = = ; = and =
3 8 Computer Science & IT 7. (b) 8. (b) x y x y = ( xy + xy) xy = ( xy xy) + ( xy xy) = y( x x) + x( y y) = y + x Y = I SS + I SS + I 2 SS + I 3 SS Y = + () = + = + 9. (b) Essential prime implicant is a prime implicant which is having atleast one minterm which is not the part of any other prime implicant. Using Kmap for the given function we get CD Here total number of prime implicants = 6 and the number of essential prime implicants = 2. (b) S S C Q C C Q = C + C + C + C + C + C + C = Σm (, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) = ΠM(). (a) 422 code is a self complementing code = 9 For a self complementing code system, codeword of 5 = s complement of codeword of 4 5 = 9 4 i.e, 9 s complement of 4. so, codeword of 5 = s complement of () = 2. (d)
4 CT28 CS Digital Logic 9 3. (a) > is possible when either of the following conditions is satisfied. When > i.e., when G = 2. When ( = ) and ( > ) i.e., when E G = So, the oolean expression for G is G = E G + G X Y Z YZ X I I I 2 I 3 Thus solution is option (a). X X 4. (b) T min = minimum clock period required = time delay from the time of active clock edge to the point of time, where the latest change appears at the input of flipflops before the application of next active clock edge. Let us assume active clock edge is applied at t =, then, the latest change in Q appears at t = 5 µs the latest change in Q appears at t = 4 µs the latest change in Q 2 appears at t = 3 µs the latest change in D 2 appears at t = 4 µs the latest change in D appears at t = 8 µs the latest change in D appears at t = µs so T min = µsec f c max = = = khz T µ sec min 5. (c) Given circuit is of 8 to multiplexer. Multiplexer is used to select any one input out of all inputs at a time. Hence, output will be equal to I 5 for a particular combination of selection lines. For D = ; C = ; = combination selects the I 5. lso, we have the given logic function as F = C + D + CD + CD
5 Computer Science & IT So, by substituting D =, C =, and =, We get, F = F = Thus, input to I 5 must be equal to. 6. (b) Given that, T carry = 5 ns and T sum = ns a 2 b 2 a b a b c (initial carry) F.. 2 F.. F.. Final carry c 3 s 2 c 2 s c s From the above circuit we have, T s = ns T s = ( ns + 5 ns) = 5 ns T s 2 = ( ns + ns) = 2 ns Here, we see the final (sum) result will take T = 2 ns maximum rate of addition/sec = 9 T = 2ns = 2 =.5 8 = (c) The output z is connected from inverted outputs of the FFs through ND gate, i.e. z = QQQC = Q + Q + QC Hence, the output z will be high only when all FF s output are zero, i.e. Q = Q = Q C = Let initially z =, then we obtain the truth table for the circuit as CLK number initial Present State Inputs Next State J K J K J + + Q Q Q C C K C Q Q z Q C + It is MOD6 counter. So, output z will be after 6 clock pulses.
6 CT28 CS Digital Logic 8. (b) When Q 4 Q 3 is, then CLR =, hence the count goes back to. 9. (c) 2. (d) Q 4 Q3 Q2 Q Q Q 4 Q3 Q2 Q Q Q 4 Q3 Q2 Q Q Thus, counter counts 23, and clears at 24. It s a MOD24 counter. f max = ; nt pd t pd = propagation delay of each flipflop and n = number of flip flops t pd = n = sec sec = nsec 4 25 Clk No. Q Q initial It s a Johnson counter after 4 clock pulses the state (Q Q ) will be () again. 2. (d) The truth table for function f(,, C) is [inverter is on when majority of connection fails] C f The Kmap for f(,, C) is C f(,, C) = + C + C
7 2 Computer Science & IT 22. (c) J K Q Qn Q n + = + + Qn Q n + = + Q n = + Qn n+ 23. (c) Output of the 4 : MUX circuit in Figure is Y = I + I + I 2 + I 3 Output of the circuit in Figure is Y = C = C + C + C + C On comparison I = C I = C I 2 = C = C 24. (a) Using Truth table: I 3 C D S S2 = 2 = 2 2 = 2 3 = 2 = 2 = 2 2 = = 3 > 2 2 = 2 2 = = 4 > = 6 > 2 3 = 2 3 = 3 > = 6 > = 9 > 2 F CD F = F = + C + CD + D + C
8 CT28 CS Digital Logic (b) The kmap has to rearranged as C CD D C F = C + D + C 26. (c) 27. (a) In the circuit, we have S = C = S = ( ) = ( ) + ( ) = + + = + C = ( )( ) = ( + ) = D = QQ 2 = Q+ Q2 D = Q D 2 = Q The truth table for the circuit is obtained below. CLK number initial Present State Q 2 Q Q Inputs D 2 D D Q 2 + Next State Q + Q fter 4 clock pulses, output is Q 2 Q Q = 28. (c) Redrawing the digital circuit 2 2 Y From the figure we get, Y = 2 2 So, Y is XOR of six boolean variables and Y will be when odd number of variable are. Thus there will 6 2 be = 32 cases for the output to be. 2
9 4 Computer Science & IT 29. (c) + + Q Q J K J K Q Q MOD = 3 3. (c) Truth table for output F (X,Y,Z) is shown below Here, X Y Z F F (X, Y, Z) = XYZ + XYZ + XYZ + XYZ = YZ( X + X) + XZ( Y + Y) + XY ( Z + Z) = YZ + XZ + XY Hence, there are total three no. of product terms in the irredundant form of F.
Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
 Serial : S_CS_C_Digital Logic_588 Delhi Noida hopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune hubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -56 CLASS TEST 8-9 COMPUTER SCIENCE & IT Subject : Digital
Serial : S_CS_C_Digital Logic_588 Delhi Noida hopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune hubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -56 CLASS TEST 8-9 COMPUTER SCIENCE & IT Subject : Digital
WORKBOOK. Try Yourself Questions. Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics. Detailed Explanations of
 27 WORKBOOK Detailed Eplanations of Try Yourself Questions Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics Number Systems and Codes T : Solution Converting into decimal number system 2 + 3 + 5 + 8 2 + 4 8 +
27 WORKBOOK Detailed Eplanations of Try Yourself Questions Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics Number Systems and Codes T : Solution Converting into decimal number system 2 + 3 + 5 + 8 2 + 4 8 +
Number Systems 1(Solutions for Vol 1_Classroom Practice Questions)
 Chapter Number Systems (Solutions for Vol _Classroom Practice Questions). ns: (d) 5 x + 44 x = x ( x + x + 5 x )+( x +4 x + 4 x ) = x + x + x x +x+5+x +4x+4 = x + x + x 5x 6 = (x6) (x+ ) = (ase cannot
Chapter Number Systems (Solutions for Vol _Classroom Practice Questions). ns: (d) 5 x + 44 x = x ( x + x + 5 x )+( x +4 x + 4 x ) = x + x + x x +x+5+x +4x+4 = x + x + x 5x 6 = (x6) (x+ ) = (ase cannot
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/79/79145081.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim uestion Paper Solution. (a) Static Hazard Static hazards have two cases: static and static. static- hazard exists when the output variable should
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim uestion Paper Solution. (a) Static Hazard Static hazards have two cases: static and static. static- hazard exists when the output variable should
3. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Use binary numbers with a sign bit and 7 bits for the value
 EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
6 Synchronous State Machine Design
 Design of synchronous counters. Based on the description of the problem, determine the required number n of the FFs - the smallest value of n is such that the number of states N 2 n and the desired counting
Design of synchronous counters. Based on the description of the problem, determine the required number n of the FFs - the smallest value of n is such that the number of states N 2 n and the desired counting
Digital Circuits. 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. Binary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2.
 Digital Circuits 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. inary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2. 11001 = 2 4 + 2 3 + 0 + 0 +2 0 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 25 Digital
Digital Circuits 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. inary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2. 11001 = 2 4 + 2 3 + 0 + 0 +2 0 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 25 Digital
Principles of Computer Architecture. Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic. Chapter Contents
 B-1 Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic B-2 Chapter Contents B.1 Reduction of Combinational Logic and Sequential Logic B.2 Reduction
B-1 Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic B-2 Chapter Contents B.1 Reduction of Combinational Logic and Sequential Logic B.2 Reduction
( c) Give logic symbol, Truth table and circuit diagram for a clocked SR flip-flop. A combinational circuit is defined by the function
 Question Paper Digital Electronics (EE-204-F) MDU Examination May 2015 1. (a) represent (32)10 in (i) BCD 8421 code (ii) Excess-3 code (iii) ASCII code (b) Design half adder using only NAND gates. ( c)
Question Paper Digital Electronics (EE-204-F) MDU Examination May 2015 1. (a) represent (32)10 in (i) BCD 8421 code (ii) Excess-3 code (iii) ASCII code (b) Design half adder using only NAND gates. ( c)
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
Chapter 4. Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. elements. Dr.
 Chapter 4 Dr. Panos Nasiopoulos Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. Sequential: In addition, they include storage elements Combinational
Chapter 4 Dr. Panos Nasiopoulos Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. Sequential: In addition, they include storage elements Combinational
CS221: Digital Design. Dr. A. Sahu. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 CS221: Digital Design Counter&Registers Dr. A. Sahu DeptofComp.Sc.&Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Outline Counter : Synchronous Vs Asynchronous Counter: Finite it State t Machine Mhi A register
CS221: Digital Design Counter&Registers Dr. A. Sahu DeptofComp.Sc.&Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Outline Counter : Synchronous Vs Asynchronous Counter: Finite it State t Machine Mhi A register
KUMARAGURU COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY COIMBATORE
 Estd-1984 KUMARAGURU COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY COIMBATORE 641 006 QUESTION BANK UNIT I PART A ISO 9001:2000 Certified 1. Convert (100001110.010) 2 to a decimal number. 2. Find the canonical SOP for the function
Estd-1984 KUMARAGURU COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY COIMBATORE 641 006 QUESTION BANK UNIT I PART A ISO 9001:2000 Certified 1. Convert (100001110.010) 2 to a decimal number. 2. Find the canonical SOP for the function
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/90/103673562.jpg) . (a) (i) ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H = (FFFF 698) H (ii) (2.3) 4 + (22.3) 4 2 2. 3 2. 3 2 3. 2 (2.3)
. (a) (i) ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H = (FFFF 698) H (ii) (2.3) 4 + (22.3) 4 2 2. 3 2. 3 2 3. 2 (2.3)
Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
 Serial : 4BS_CS_B_Discrete Mathematics_0708 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: 0-452462 CLASS TEST 208-9 COMPUTER SCIENCE
Serial : 4BS_CS_B_Discrete Mathematics_0708 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: 0-452462 CLASS TEST 208-9 COMPUTER SCIENCE
Shift Register Counters
 Shift Register Counters Shift register counter: a shift register with the serial output connected back to the serial input. They are classified as counters because they give a specified sequence of states.
Shift Register Counters Shift register counter: a shift register with the serial output connected back to the serial input. They are classified as counters because they give a specified sequence of states.
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques](/thumbs/90/103932933.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12] Q.1(a) (i) Derive AND gate and OR gate
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12] Q.1(a) (i) Derive AND gate and OR gate
Digital Electronics Circuits 2017
 JSS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY Digital Electronics Circuits (EC37L) Lab in-charge: Dr. Shankraiah Course outcomes: After the completion of laboratory the student will be able to, 1. Simplify, design
JSS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY Digital Electronics Circuits (EC37L) Lab in-charge: Dr. Shankraiah Course outcomes: After the completion of laboratory the student will be able to, 1. Simplify, design
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Review for Final Exam
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Review for Final Exam Mohsen Imani CAPE Please submit your evaluations!!!! RTL design Use the RTL design process to design a system that has
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Review for Final Exam Mohsen Imani CAPE Please submit your evaluations!!!! RTL design Use the RTL design process to design a system that has
Chapter 2. Review of Digital Systems Design
 x 2-4 = 42.625. Chapter 2 Review of Digital Systems Design Numbering Systems Decimal number may be expressed as powers of 10. For example, consider a six digit decimal number 987654, which can be represented
x 2-4 = 42.625. Chapter 2 Review of Digital Systems Design Numbering Systems Decimal number may be expressed as powers of 10. For example, consider a six digit decimal number 987654, which can be represented
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
UNIVERSITI TENAGA NASIONAL. College of Information Technology
 UNIVERSITI TENAGA NASIONAL College of Information Technology BACHELOR OF COMPUTER SCIENCE (HONS.) FINAL EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2 2012/2013 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN (CSNB163) January 2013 Time allowed: 3 hours
UNIVERSITI TENAGA NASIONAL College of Information Technology BACHELOR OF COMPUTER SCIENCE (HONS.) FINAL EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2 2012/2013 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN (CSNB163) January 2013 Time allowed: 3 hours
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques](/thumbs/82/86792063.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12]
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12]
Digital Logic Design. Midterm #2
 EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm - igital Logic esign Midterm #2 Problems Points. 5 2. 4 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm
EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm - igital Logic esign Midterm #2 Problems Points. 5 2. 4 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm
 vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN UNIT I : BOOLEAN ALGEBRA AND LOGIC GATES PART - A (2 MARKS) Number
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN UNIT I : BOOLEAN ALGEBRA AND LOGIC GATES PART - A (2 MARKS) Number
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4
 Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4 1. Analyze the latch circuit shown below by obtaining timing diagram for the circuit; include propagation delays. Y This circuit has two external input and one feedback
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4 1. Analyze the latch circuit shown below by obtaining timing diagram for the circuit; include propagation delays. Y This circuit has two external input and one feedback
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page of COE 22: Digital Logic Design (3--3) Term (Fall 22) Final Exam Sunday January
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page of COE 22: Digital Logic Design (3--3) Term (Fall 22) Final Exam Sunday January
CHW 261: Logic Design
 CHW 26: Logic Design Instructors: Prof. Hala Zayed Dr. Ahmed Shalaby http://www.bu.edu.eg/staff/halazayed4 http://bu.edu.eg/staff/ahmedshalaby4# Slide Digital Fundamentals CHAPTER 8 Counters Slide 2 Counting
CHW 26: Logic Design Instructors: Prof. Hala Zayed Dr. Ahmed Shalaby http://www.bu.edu.eg/staff/halazayed4 http://bu.edu.eg/staff/ahmedshalaby4# Slide Digital Fundamentals CHAPTER 8 Counters Slide 2 Counting
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuit Design. t phl. Fig.: Input and output voltage waveforms to define propagation delay times.
![S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuit Design. t phl. Fig.: Input and output voltage waveforms to define propagation delay times. S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuit Design. t phl. Fig.: Input and output voltage waveforms to define propagation delay times.](/thumbs/93/111090909.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital ircuit Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80. Solve following : [20].(a) Explain characteristics of logic families. [5] haracteristics of logic families are
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital ircuit Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80. Solve following : [20].(a) Explain characteristics of logic families. [5] haracteristics of logic families are
Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
 Serial : CH_EE_B_Network Theory_098 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow ndore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: 0-56 CLASS TEST 08-9 ELECTCAL ENGNEENG Subject : Network
Serial : CH_EE_B_Network Theory_098 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow ndore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: 0-56 CLASS TEST 08-9 ELECTCAL ENGNEENG Subject : Network
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis
 Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Standard & Canonical Forms
 1 COE 202- Digital Logic Standard & Canonical Forms Dr. Abdulaziz Y. Barnawi COE Department KFUPM 2 Outline Minterms and Maxterms From truth table to Boolean expression Sum of minterms Product of Maxterms
1 COE 202- Digital Logic Standard & Canonical Forms Dr. Abdulaziz Y. Barnawi COE Department KFUPM 2 Outline Minterms and Maxterms From truth table to Boolean expression Sum of minterms Product of Maxterms
Lecture 9: Digital Electronics
 Introduction: We can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit parameter of interest: nalog: The voltage can
Introduction: We can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit parameter of interest: nalog: The voltage can
CS 121 Digital Logic Design. Chapter 2. Teacher Assistant. Hanin Abdulrahman
 CS 121 Digital Logic Design Chapter 2 Teacher Assistant Hanin Abdulrahman 1 2 Outline 2.2 Basic Definitions 2.3 Axiomatic Definition of Boolean Algebra. 2.4 Basic Theorems and Properties 2.5 Boolean Functions
CS 121 Digital Logic Design Chapter 2 Teacher Assistant Hanin Abdulrahman 1 2 Outline 2.2 Basic Definitions 2.3 Axiomatic Definition of Boolean Algebra. 2.4 Basic Theorems and Properties 2.5 Boolean Functions
Karnaugh Maps (K-Maps)
 Karnaugh Maps (K-Maps) Boolean expressions can be minimized by combining terms P + P = P K-maps minimize equations graphically Put terms to combine close to one another B C C B B C BC BC BC BC BC BC BC
Karnaugh Maps (K-Maps) Boolean expressions can be minimized by combining terms P + P = P K-maps minimize equations graphically Put terms to combine close to one another B C C B B C BC BC BC BC BC BC BC
EE 209 Spiral 1 Exam Solutions Name:
 EE 29 Spiral Exam Solutions Name:.) Answer the following questions as True or False a.) A 4-to- multiplexer requires at least 4 select lines: true / false b.) An 8-to- mux and no other logic can be used
EE 29 Spiral Exam Solutions Name:.) Answer the following questions as True or False a.) A 4-to- multiplexer requires at least 4 select lines: true / false b.) An 8-to- mux and no other logic can be used
Digital Electronics. Delay Max. FF Rate Power/Gate High Low (ns) (MHz) (mw) (V) (V) Standard TTL (7400)
 P57/67 Lec9, P Digital Electronics Introduction: In electronics we can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit
P57/67 Lec9, P Digital Electronics Introduction: In electronics we can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit
Show that the dual of the exclusive-or is equal to its compliment. 7
 Darshan Institute of ngineering and Technology, Rajkot, Subject: Digital lectronics (2300) GTU Question ank Unit Group Questions Do as directed : I. Given that (6)0 = (00)x, find the value of x. II. dd
Darshan Institute of ngineering and Technology, Rajkot, Subject: Digital lectronics (2300) GTU Question ank Unit Group Questions Do as directed : I. Given that (6)0 = (00)x, find the value of x. II. dd
In Module 3, we have learned about Exclusive OR (XOR) gate. Boolean Expression AB + A B = Y also A B = Y. Logic Gate. Truth table
 Module 8 In Module 3, we have learned about Exclusive OR (XOR) gate. Boolean Expression AB + A B = Y also A B = Y Logic Gate Truth table A B Y 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 In Module 3, we have learned about
Module 8 In Module 3, we have learned about Exclusive OR (XOR) gate. Boolean Expression AB + A B = Y also A B = Y Logic Gate Truth table A B Y 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 In Module 3, we have learned about
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Midterm Information. Instructor: Mohsen Imani. Sources: TSR, Katz, Boriello & Vahid
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
MC9211 Computer Organization
 MC92 Computer Organization Unit : Digital Fundamentals Lesson2 : Boolean Algebra and Simplification (KSB) (MCA) (29-2/ODD) (29 - / A&B) Coverage Lesson2 Introduces the basic postulates of Boolean Algebra
MC92 Computer Organization Unit : Digital Fundamentals Lesson2 : Boolean Algebra and Simplification (KSB) (MCA) (29-2/ODD) (29 - / A&B) Coverage Lesson2 Introduces the basic postulates of Boolean Algebra
TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS PART - I OJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Each Question carries 2 marks. Choose correct or the best alternative in the following: Q.1 The NAN gate output will be low if the two inputs
TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS PART - I OJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Each Question carries 2 marks. Choose correct or the best alternative in the following: Q.1 The NAN gate output will be low if the two inputs
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
COEN 312 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN - LECTURE NOTES Concordia University
 1 OEN 312 DIGIAL SYSEMS DESIGN - LEURE NOES oncordia University hapter 6: Registers and ounters NOE: For more examples and detailed description of the material in the lecture notes, please refer to the
1 OEN 312 DIGIAL SYSEMS DESIGN - LEURE NOES oncordia University hapter 6: Registers and ounters NOE: For more examples and detailed description of the material in the lecture notes, please refer to the
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques s complement 2 s complement 1 s complement
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques s complement 2 s complement 1 s complement S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques s complement 2 s complement 1 s complement](/thumbs/80/82077570.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : Q.(a) (i) () (2) s COMPLEMENT s COMPLEMENT 2s COMPLEMENT 2s COMPLEMENT + Q.(a) (ii) ()
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : Q.(a) (i) () (2) s COMPLEMENT s COMPLEMENT 2s COMPLEMENT 2s COMPLEMENT + Q.(a) (ii) ()
CSE 140 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing. Spring 2008
 CSE 14 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 28 Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate the pages.
CSE 14 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 28 Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate the pages.
Chapter 2 Combinational Logic Circuits
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 2 Combinational Logic Circuits Part 1 Gate Circuits and Boolean Equations Chapter 2 - Part 1 2 Chapter 2 - Part 1 3 Chapter 2 - Part 1 4 Chapter 2 - Part
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 2 Combinational Logic Circuits Part 1 Gate Circuits and Boolean Equations Chapter 2 - Part 1 2 Chapter 2 - Part 1 3 Chapter 2 - Part 1 4 Chapter 2 - Part
ECE 341. Lecture # 3
 ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
Sample Test Paper - I
 Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
DE58/DC58 LOGIC DESIGN DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. In a base-5 number system, 3 digit representations is used. Find out (i) Number of distinct quantities that can be represented.(ii) Representation of highest decimal number in base-5. Since, r=5
Q.2 a. In a base-5 number system, 3 digit representations is used. Find out (i) Number of distinct quantities that can be represented.(ii) Representation of highest decimal number in base-5. Since, r=5
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B](/thumbs/84/91058397.jpg) . (a). (b). (c) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] igital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC = B LHS = ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC But ( ) = = ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( )
. (a). (b). (c) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] igital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC = B LHS = ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC But ( ) = = ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( )
CHAPTER * 2-2.* Pearson Education Limited Problem Solutions, Global Edition Chapter 2. Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem
 HPTER 2 2-.* a) XYZ = X + Y + Z Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem Pearson Education Limited 206. X Y Z XYZ XYZ X + Y + Z 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 b) X + YZ = ( X + Y) ( X + Z) The Second
HPTER 2 2-.* a) XYZ = X + Y + Z Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem Pearson Education Limited 206. X Y Z XYZ XYZ X + Y + Z 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 b) X + YZ = ( X + Y) ( X + Z) The Second
Synchronous Sequential Logic
 1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number:
 Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 08/06/2016
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 08/06/2016
Reg. No. Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Second Semester. Computer Science and Engineering
 Sp 6 Reg. No. Question Paper Code : 27156 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN (Common
Sp 6 Reg. No. Question Paper Code : 27156 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN (Common
CHAPTER 7. Exercises 17/ / /2 2 0
 CHAPTER 7 Exercises E7. (a) For the whole part, we have: Quotient Remainders 23/2 /2 5 5/2 2 2/2 0 /2 0 Reading the remainders in reverse order, we obtain: 23 0 = 0 2 For the fractional part we have 2
CHAPTER 7 Exercises E7. (a) For the whole part, we have: Quotient Remainders 23/2 /2 5 5/2 2 2/2 0 /2 0 Reading the remainders in reverse order, we obtain: 23 0 = 0 2 For the fractional part we have 2
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 6 - Combinational Logic Introduction A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output variables. The logic gates accept
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 6 - Combinational Logic Introduction A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output variables. The logic gates accept
Name. ECE-200 Intelligent Systems
 Name Spring 2003 EE-200 Intelligent Systems Pracice Final Solution ll problems have the same weight Problem 1. We are working with a multiplexor that is to switch between four sources (inputs), each one
Name Spring 2003 EE-200 Intelligent Systems Pracice Final Solution ll problems have the same weight Problem 1. We are working with a multiplexor that is to switch between four sources (inputs), each one
PART-A. 2. Expand ASCII and BCD ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange BCD Binary Coded Decimal
 PART-A 1. What is radix? Give the radix for binary, octal, decimal and hexadecimal Radix is the total number of digits used in a particular number system Binary - 2 (0,1) Octal - 8 (0 to 7) Decimal - 10
PART-A 1. What is radix? Give the radix for binary, octal, decimal and hexadecimal Radix is the total number of digits used in a particular number system Binary - 2 (0,1) Octal - 8 (0 to 7) Decimal - 10
Digital Circuits ECS 371
 Digital Circuits ECS 371 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 18 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Monday 9:00-10:30, 1:30-3:30 Tuesday 10:30-11:30 1 Announcement Reading Assignment: Chapter 7: 7-1,
Digital Circuits ECS 371 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 18 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Monday 9:00-10:30, 1:30-3:30 Tuesday 10:30-11:30 1 Announcement Reading Assignment: Chapter 7: 7-1,
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Design at the Register Transfer Level
 Week-7 Design at the Register Transfer Level Algorithmic State Machines Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) q Our design methodologies do not scale well to real-world problems. q 232 - Logic Design / Algorithmic
Week-7 Design at the Register Transfer Level Algorithmic State Machines Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) q Our design methodologies do not scale well to real-world problems. q 232 - Logic Design / Algorithmic
Unit 2 Session - 6 Combinational Logic Circuits
 Objectives Unit 2 Session - 6 Combinational Logic Circuits Draw 3- variable and 4- variable Karnaugh maps and use them to simplify Boolean expressions Understand don t Care Conditions Use the Product-of-Sums
Objectives Unit 2 Session - 6 Combinational Logic Circuits Draw 3- variable and 4- variable Karnaugh maps and use them to simplify Boolean expressions Understand don t Care Conditions Use the Product-of-Sums
Digital Circuits and Systems
 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems 4 Sequential Circuits page 1 of 11 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Section 4 Sequential Circuits 4.1 Overview of Sequential Circuits: Definition The circuit whose
EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems 4 Sequential Circuits page 1 of 11 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Section 4 Sequential Circuits 4.1 Overview of Sequential Circuits: Definition The circuit whose
 / M Morris Mano Digital Design Ahmad_911@hotmailcom / / / / wwwuqucscom Binary Systems Introduction - Digital Systems - The Conversion Between Numbering Systems - From Binary To Decimal - Octet To Decimal
/ M Morris Mano Digital Design Ahmad_911@hotmailcom / / / / wwwuqucscom Binary Systems Introduction - Digital Systems - The Conversion Between Numbering Systems - From Binary To Decimal - Octet To Decimal
Gate-Level Minimization
 Gate-Level Minimization Dr. Bassem A. Abdullah Computer and Systems Department Lectures Prepared by Dr.Mona Safar, Edited and Lectured by Dr.Bassem A. Abdullah Outline 1. The Map Method 2. Four-variable
Gate-Level Minimization Dr. Bassem A. Abdullah Computer and Systems Department Lectures Prepared by Dr.Mona Safar, Edited and Lectured by Dr.Bassem A. Abdullah Outline 1. The Map Method 2. Four-variable
EE40 Lec 15. Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits
 EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) State any two Boolean laws. (Any 2 laws 1 mark each)
 Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 27 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 27 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Principles of Digital Techniques
 MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Principles of Digital Techniques Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Principles of Digital Techniques Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS
 DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Introduction Logic Gates Boolean Algebra Map Specification Combinational Circuits Flip-Flops Sequential Circuits Memory Components Integrated Circuits Digital Computers 2 LOGIC GATES
DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Introduction Logic Gates Boolean Algebra Map Specification Combinational Circuits Flip-Flops Sequential Circuits Memory Components Integrated Circuits Digital Computers 2 LOGIC GATES
CHAPTER * 6-2. a) 3-input NAND gate b) 4-input NOR gate * Pearson Education, Inc. a) F = (A + B) C D. b) G = (A + B) (C + D)
 HPTER 6 6-.* a) = ( + ) b) G = ( + ) ( + ) 200 Pearson Education, Inc. 6-2. a) 3-input NN gate b) 4-input NOR gate +V +V 6-3. 6 inputs 6 inputs 6 inputs 6-4.* The longest path is from input or. 0.073 ns
HPTER 6 6-.* a) = ( + ) b) G = ( + ) ( + ) 200 Pearson Education, Inc. 6-2. a) 3-input NN gate b) 4-input NOR gate +V +V 6-3. 6 inputs 6 inputs 6 inputs 6-4.* The longest path is from input or. 0.073 ns
Chap 2. Combinational Logic Circuits
 Overview 2 Chap 2. Combinational Logic Circuits Spring 24 Part Gate Circuits and Boolean Equations Binary Logic and Gates Boolean Algebra Standard Forms Part 2 Circuit Optimization Two-Level Optimization
Overview 2 Chap 2. Combinational Logic Circuits Spring 24 Part Gate Circuits and Boolean Equations Binary Logic and Gates Boolean Algebra Standard Forms Part 2 Circuit Optimization Two-Level Optimization
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC - 27001-2005 Certified) Subject Code: 12069 SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC - 27001-2005 Certified) Subject Code: 12069 SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should
Lab 3 Revisited. Zener diodes IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1
 Lab 3 Revisited Zener diodes R C 6.091 IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1 Lab 3 Revisited +15 Voltage regulators 555 timers 270 1N758 0.1uf 5K pot V+ V- 2N2222 0.1uf V o. V CC V Vin s = 5 V Vc V c Vs 1 e t = RC Threshold
Lab 3 Revisited Zener diodes R C 6.091 IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1 Lab 3 Revisited +15 Voltage regulators 555 timers 270 1N758 0.1uf 5K pot V+ V- 2N2222 0.1uf V o. V CC V Vin s = 5 V Vc V c Vs 1 e t = RC Threshold
Lecture 6: Manipulation of Algebraic Functions, Boolean Algebra, Karnaugh Maps
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 6: Manipulation of Algebraic Functions, Boolean Algebra, Karnaugh Maps Prof. YingLi Tian Feb. 21/26, 2019 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 6: Manipulation of Algebraic Functions, Boolean Algebra, Karnaugh Maps Prof. YingLi Tian Feb. 21/26, 2019 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York
Appendix A: Digital Logic. Principles of Computer Architecture. Principles of Computer Architecture by M. Murdocca and V. Heuring
 - Principles of Computer rchitecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring 999 M. Murdocca and V. Heuring -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties
- Principles of Computer rchitecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring 999 M. Murdocca and V. Heuring -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties
Total Time = 90 Minutes, Total Marks = 100. Total /10 /25 /20 /10 /15 /20
 University of Waterloo Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering E&CE 223 Digital Circuits and Systems Midterm Examination Instructor: M. Sachdev October 30th, 2006 Total Time = 90 Minutes, Total
University of Waterloo Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering E&CE 223 Digital Circuits and Systems Midterm Examination Instructor: M. Sachdev October 30th, 2006 Total Time = 90 Minutes, Total
Written reexam with solutions for IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 14/
 Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
PG - TRB UNIT-X- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS. POLYTECHNIC-TRB MATERIALS
 SRIMAAN COACHING CENTRE-PG-TRB-PHYSICS- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS-STUDY MATERIAL-CONTACT: 8072230063 SRIMAAN PG - TRB PHYSICS UNIT-X- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS POLYTECHNIC-TRB MATERIALS MATHS/COMPUTER SCIENCE/IT/ECE/EEE
SRIMAAN COACHING CENTRE-PG-TRB-PHYSICS- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS-STUDY MATERIAL-CONTACT: 8072230063 SRIMAAN PG - TRB PHYSICS UNIT-X- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS POLYTECHNIC-TRB MATERIALS MATHS/COMPUTER SCIENCE/IT/ECE/EEE
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic
 Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
Lecture 6: Gate Level Minimization Syed M. Mahmud, Ph.D ECE Department Wayne State University
 Lecture 6: Gate Level Minimization Syed M. Mahmud, Ph.D ECE Department Wayne State University Original Source: Aby K George, ECE Department, Wayne State University Contents The Map method Two variable
Lecture 6: Gate Level Minimization Syed M. Mahmud, Ph.D ECE Department Wayne State University Original Source: Aby K George, ECE Department, Wayne State University Contents The Map method Two variable
Chapter 4: Combinational Logic Solutions to Problems: [1, 5, 9, 12, 19, 23, 30, 33]
![Chapter 4: Combinational Logic Solutions to Problems: [1, 5, 9, 12, 19, 23, 30, 33] Chapter 4: Combinational Logic Solutions to Problems: [1, 5, 9, 12, 19, 23, 30, 33]](/thumbs/81/84077758.jpg) Chapter 4: Combinational Logic Solutions to Problems: [, 5, 9, 2, 9, 23, 3, 33] Problem: 4- Consider the combinational circuit shown in Fig. P4-. (a) Derive the Boolean expressions for T through T 4. Evaluate
Chapter 4: Combinational Logic Solutions to Problems: [, 5, 9, 2, 9, 23, 3, 33] Problem: 4- Consider the combinational circuit shown in Fig. P4-. (a) Derive the Boolean expressions for T through T 4. Evaluate
10/12/2016. An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Eventually, the States Form a Loop
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
Computer Science Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001
 Computer Science 03 60 265 Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001 Dr. Robert D. Kent and Dr. Alioune Ngom Last Name: First Name: Student Number: INSTRUCTIONS EXAM DURATION IS 3 HOURs. CALCULATORS,
Computer Science 03 60 265 Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001 Dr. Robert D. Kent and Dr. Alioune Ngom Last Name: First Name: Student Number: INSTRUCTIONS EXAM DURATION IS 3 HOURs. CALCULATORS,
Digital Electronics Final Examination. Part A
 Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /50 Converted Score: /40 Page 1 of 13 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select
Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /50 Converted Score: /40 Page 1 of 13 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select
Review: Designing with FSM. EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec09 Counters Outline.
 Review: Designing with FSM EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lec09 Counters 9-28-04 David Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
Review: Designing with FSM EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lec09 Counters 9-28-04 David Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
Combinational Logic. Mantıksal Tasarım BBM231. section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan
 Combinational Logic Mantıksal Tasarım BBM23 section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan Classification. Combinational no memory outputs depends on only the present inputs expressed by Boolean functions 2. Sequential
Combinational Logic Mantıksal Tasarım BBM23 section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan Classification. Combinational no memory outputs depends on only the present inputs expressed by Boolean functions 2. Sequential
Roger L. Tokheim. Chapter 8 Counters Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
 Digital Electronics Principles & Applications Sixth Edition Roger L. Tokheim Chapter 8 Counters 2003 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill INTRODUCTION Overview of Counters Characteristics of Counters Ripple Up Counter
Digital Electronics Principles & Applications Sixth Edition Roger L. Tokheim Chapter 8 Counters 2003 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill INTRODUCTION Overview of Counters Characteristics of Counters Ripple Up Counter
Problem Set 9 Solutions
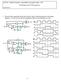 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1
 EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1 FF s and some Definitions Clock Input: FF s are controlled by a trigger or Clock signal. All FF s have a clock input. If a device which attempts to do a FF s task does not
EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1 FF s and some Definitions Clock Input: FF s are controlled by a trigger or Clock signal. All FF s have a clock input. If a device which attempts to do a FF s task does not
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 28 Combinational Building Blocks Lecture 5: Announcements Lab 2 prelab due tomorrow HW due Friday HW 2 to be posted on Thursday Lecture 4 to be replayed
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 28 Combinational Building Blocks Lecture 5: Announcements Lab 2 prelab due tomorrow HW due Friday HW 2 to be posted on Thursday Lecture 4 to be replayed
04. What is the Mod number of the counter circuit shown below? Assume initially reset.
 . Which of the following is the state diagram for the Meale machine shown below. 4. What is the Mod number of the counter circuit shown below? Assume initiall reset. input CLK D output D D a. b. / / /
. Which of the following is the state diagram for the Meale machine shown below. 4. What is the Mod number of the counter circuit shown below? Assume initiall reset. input CLK D output D D a. b. / / /
Chapter 4. Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Q: Examine the relationship between X and the Next state. How would you describe this circuit? A: An inverter which is synched with a clock signal.
 /2/2 OF 7 Next, let s reverse engineer a T-Flip flop Prob. (Pg 529) Note that whenever T is equal to, there is a state change, otherwise, there isn t. In this circuit, (x) determines whether the output
/2/2 OF 7 Next, let s reverse engineer a T-Flip flop Prob. (Pg 529) Note that whenever T is equal to, there is a state change, otherwise, there isn t. In this circuit, (x) determines whether the output
