Bridging the Gap between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Lang
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bridging the Gap between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Department of Mathematics Oregon State University
2 Mathematics vs. Physics Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary
3 Mathematics vs. Physics Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary
4 Mathematics vs. Physics Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary
5 What are Functions? Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Suppose the temperature on a rectangular slab of metal is given by T(x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) where k is a constant. What is T(r, θ)?
6 What are Functions? Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Suppose the temperature on a rectangular slab of metal is given by T(x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) where k is a constant. What is T(r, θ)? A: T(r, θ) = kr 2
7 What are Functions? Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Suppose the temperature on a rectangular slab of metal is given by T(x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) where k is a constant. What is T(r, θ)? A: T(r, θ) = kr 2 B: T(r, θ) = k(r 2 + θ 2 )
8 What are Functions? Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Suppose the temperature on a rectangular slab of metal is given by T(x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) where k is a constant. What is T(r, θ)? A: T(r, θ) = kr 2 B: T(r, θ) = k(r 2 + θ 2 ) r θ x y
9 What are Functions? Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary MATH T = f (x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) T = g(r, θ) = kr 2
10 What are Functions? Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary MATH T = f (x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) T = g(r, θ) = kr 2 PHYSICS T = T(x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) T = T(r, θ) = kr 2
11 What are Functions? Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary MATH T = f (x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) T = g(r, θ) = kr 2 PHYSICS T = T(x, y) = k(x 2 + y 2 ) T = T(r, θ) = kr 2 Two disciplines separated by a common language...
12 What are Functions? Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Differential Geometry! T(x,y) T (x,y) 1 T(r,θ) T (r,θ) 1 S (x,y) T T(x,y) R 2 R Two disciplines separated by a common language...
13 Mathematics vs. Physics Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Physics is about things. Physicists can t change the problem.
14 Mathematics vs. Physics Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Physics is about things. Physicists can t change the problem. Mathematicians do algebra. Physicists do geometry.
15 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary
16 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Projection: u v = u v cos θ θ u v = u x v x + u y v y
17 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Projection: u v = u v cos θ θ u v = u x v x + u y v y Law of Cosines: ( u v) ( u v) = u u + v v 2 u v u v 2 = u 2 + v 2 2 u v cos θ
18 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Projection: u v = u v cos θ θ u v = u x v x + u y v y Law of Cosines: ( u v) ( u v) = u u + v v 2 u v u v 2 = u 2 + v 2 2 u v cos θ Addition Formulas: u = cos α î + sinαĵ v = cos β î + sinβ ĵ u v = cos(α β)
19 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Find the angle between the diagonal of a cube and the diagonal of one of its faces.
20 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Find the angle between the diagonal of a cube and the diagonal of one of its faces. Algebra: u = î + ĵ + ˆk v = î + ˆk = u v = 2 Geometry: u v = u v cos θ = 3 2 cos θ
21 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Find the angle between the diagonal of a cube and the diagonal of one of its faces. Algebra: u = î + ĵ + ˆk v = î + ˆk = u v = 2 Geometry: u v = u v cos θ = 3 2 cos θ Need both!
22 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary Kerry Browne (Ph.D. 2002)
23 Math vs. Physics Functions Dot Product Dictionary CUPM MAA Committee on the Undergraduate Program in Mathematics Curriculum Guide CRAFTY Subcommittee on Curriculum Renewal Across the First Two Years Voices of the Partner Disciplines
24 Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient The Bridge Project
25 Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient The Bridge Project Differentials (Use what you know!) Multiple representations Symmetry (adapted bases, coordinates) Geometry (vectors, div, grad, curl)
26 Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient The Bridge Project Differentials (Use what you know!) Multiple representations Symmetry (adapted bases, coordinates) Geometry (vectors, div, grad, curl) Small group activities Instructor s guide Online text (
27 Vector Differentials Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient dy ĵ d r dx î d r = dx î + dy ĵ
28 Vector Differentials Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient dy ĵ d r dx î r dφ ˆφ d r dr ˆr d r = dx î + dy ĵ d r = dr ˆr + r dφ ˆφ
29 Vector Differentials Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient dy ĵ d r dx î r dφ ˆφ d r dr ˆr d r = dx î + dy ĵ d r = dr ˆr + r dφ ˆφ ds = d r d A = d r 1 d r 2 da = d r 1 d r 2 dv = (d r 1 d r 2 ) d r 3
30 Gradient Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient
31 Gradient Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient Master Formula: df = f d r
32 Gradient Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient Master Formula: df = f d r f = const = df = 0 = f d r df ds = f d r d r
33 The Hill Bridge Project Vector Differentials Gradient Suppose you are standing on a hill. You have a topographic map, which uses rectangular coordinates (x,y) measured in miles. Your global positioning system says your present location is at one of the points shown. Your guidebook tells you that the height h of the hill in feet above sea level is given by h = a bx 2 cy y 0-5 where a = 5000 ft, b = 30 ft mi 2, and c = 10 ft mi x
34 Coherent Calculus Definition Differentials
35 Coherent Calculus Definition Differentials co-he-rent: logically or aesthetically ordered
36 Coherent Calculus Definition Differentials coherent: logically or aesthetically ordered cal-cu-lus: a method of computation in a special notation
37 Coherent Calculus Definition Differentials coherent: logically or aesthetically ordered calculus: a method of computation in a special notation differential calculus: a branch of mathematics concerned chiefly with the study of the rate of change of functions with respect to their variables especially through the use of derivatives and differentials
38 Differentials Definition Differentials d(u + cv) = du + c dv d(uv) = u dv + v du
39 Differentials Definition Differentials d(u + cv) = du + c dv d(uv) = u dv + v du d (u n ) = nu n 1 du d (e u ) = e u du d(sin u) = cos u du d(cos u) = sinu du d(ln u) = 1 u du
40 Derivatives Definition Differentials Derivatives: f (x) = sin(x) = f (x) = cos(x)
41 Derivatives Definition Differentials Derivatives: d d sinu sinu = du du = cos u
42 Derivatives Definition Differentials Derivatives: Chain rule: d d sinu sinu = du du = cos u h(x) = f ( g(x) ) = h (x) = f ( g(x) ) g (x)
43 Derivatives Definition Differentials Derivatives: Chain rule: d d sinu sinu = du du d d sinu sinu = dx dx = d sinu du = cos u du dx = cos u du dx
44 Derivatives Definition Differentials Derivatives: Chain rule: Inverse functions: d d sinu sinu = du du d d sinu sinu = dx dx = d sinu du = cos u du dx g(x) = f 1 (x) = g (x) = = cos u du dx 1 f ( g(x) )
45 Derivatives Definition Differentials Derivatives: Chain rule: Inverse functions: d d sinu sinu = du du d d sinu sinu = dx dx = d sinu du = cos u du dx = cos u du dx d du lnu = d du q = dq du = 1 du/dq = 1 de q /dq = 1 e q = 1 u
46 Derivatives Definition Differentials Instead of: chain rule related rates implicit differentiation derivatives of inverse functions difficulties of interpretation (units!)
47 Derivatives Definition Differentials Instead of: chain rule related rates implicit differentiation derivatives of inverse functions difficulties of interpretation (units!) One coherent idea:
48 Derivatives Definition Differentials Instead of: chain rule related rates implicit differentiation derivatives of inverse functions difficulties of interpretation (units!) One coherent idea: Zap equations with d
49 Derivatives Definition Differentials Instead of: chain rule related rates implicit differentiation derivatives of inverse functions difficulties of interpretation (units!) One coherent idea: Zap equations with d & Corinne A. Manogue, Putting Differentials Back into Calculus, College Math. J., (to apppear).
50 Functions A Radical View of Calculus The central idea in calculus is not the limit. The central idea of derivatives is not slope. The central idea of integrals is not area. The central idea of curves and surfaces is not parameterization. The central representation of a function is not its graph.
51 Functions A Radical View of Calculus The central idea in calculus is not the limit. The central idea of derivatives is not slope. The central idea of integrals is not area. The central idea of curves and surfaces is not parameterization. The central representation of a function is not its graph. The central idea in calculus is the differential. The central idea of derivatives is rate of change. The central idea of integrals is total amount. The central idea of curves and surfaces is use what you know. The central representation of a function is data attached to the domain.
52 SUMMARY Functions
53 SUMMARY Functions I took this class a year ago, and I still remember all of it...
54 Functions
Bridging the Gap between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences
 Bridging the Gap between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Department of Mathematics Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/~tevian Mathematics vs. Physics Math vs. Physics Functions
Bridging the Gap between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Department of Mathematics Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/~tevian Mathematics vs. Physics Math vs. Physics Functions
Teaching Calculus Coherently
 Department of Mathematics Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/ tevian co-he-rent: logically or aesthetically ordered cal-cu-lus: a method of computation in a special notation differential
Department of Mathematics Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/ tevian co-he-rent: logically or aesthetically ordered cal-cu-lus: a method of computation in a special notation differential
The Geometry of Calculus
 Introduction Department of Mathematics Oregon State University http://math.oregonstate.edu/~tevian Introduction Acknowledgments Places: People: Stuart Boersma, Johnner Barrett, Sam Cook, Aaron Wangberg
Introduction Department of Mathematics Oregon State University http://math.oregonstate.edu/~tevian Introduction Acknowledgments Places: People: Stuart Boersma, Johnner Barrett, Sam Cook, Aaron Wangberg
BRIDGING THE GAP between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences
 BRIDGING THE GAP between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University I: Mathematics Physics II: The Bridge Project http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/bridge
BRIDGING THE GAP between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University I: Mathematics Physics II: The Bridge Project http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/bridge
G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences
 the G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/bridge Support Mathematical Association of America Professional
the G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/bridge Support Mathematical Association of America Professional
G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences
 the G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/bridge Support Mathematical Association of America Professional
the G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/bridge Support Mathematical Association of America Professional
THE VECTOR CALCULUS BRIDGE PROJECT
 THE VECTOR CALCULUS BRIDGE PROJECT Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University I: Mathematics Physics II: The Bridge Project III: A Radical View of Calculus Support Oregon State University Department
THE VECTOR CALCULUS BRIDGE PROJECT Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University I: Mathematics Physics II: The Bridge Project III: A Radical View of Calculus Support Oregon State University Department
THE IMPORTANCE OF GEOMETRIC REASONING
 THE IMPORTANCE OF GEOMETRIC REASONING Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University I: Mathematics Physics II: The Bridge Project III: Geometric Visualization QUESTIONS I: Suppose T (x, y) = k(x
THE IMPORTANCE OF GEOMETRIC REASONING Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University I: Mathematics Physics II: The Bridge Project III: Geometric Visualization QUESTIONS I: Suppose T (x, y) = k(x
G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences
 the G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/bridge Support Mathematical Association of America Professional
the G A P between Mathematics and the Physical Sciences Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/bridge Support Mathematical Association of America Professional
THE VECTOR CALCULUS BRIDGE PROJECT
 THE VECTOR CALCULUS BRIDGE PROJECT Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University I: Mathematics Physics II: The Bridge Project III: A Radical View of Calculus Support Mathematical Association of
THE VECTOR CALCULUS BRIDGE PROJECT Tevian Dray & Corinne Manogue Oregon State University I: Mathematics Physics II: The Bridge Project III: A Radical View of Calculus Support Mathematical Association of
BRIDGING THE VECTOR (CALCULUS) GAP
 BRIDGING THE VECTOR (CALCULUS) GAP TEVIAN DRAY Department of Mathematics, Mount Holyoke College, South Hadley, MA 01075 & Department of Mathematics, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331 tevian@math.orst.edu
BRIDGING THE VECTOR (CALCULUS) GAP TEVIAN DRAY Department of Mathematics, Mount Holyoke College, South Hadley, MA 01075 & Department of Mathematics, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331 tevian@math.orst.edu
Physics 3323, Fall 2016 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 2016
 Physics 3323, Fall 26 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 26. What s my charge? A spherical region of radius R is filled with a charge distribution that gives rise to an electric field inside of the form E E /R 2
Physics 3323, Fall 26 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 26. What s my charge? A spherical region of radius R is filled with a charge distribution that gives rise to an electric field inside of the form E E /R 2
Problem Solving 1: The Mathematics of 8.02 Part I. Coordinate Systems
 Problem Solving 1: The Mathematics of 8.02 Part I. Coordinate Systems In 8.02 we regularly use three different coordinate systems: rectangular (Cartesian), cylindrical and spherical. In order to become
Problem Solving 1: The Mathematics of 8.02 Part I. Coordinate Systems In 8.02 we regularly use three different coordinate systems: rectangular (Cartesian), cylindrical and spherical. In order to become
Using differentials to bridge the vector calculus gap
 Using differentials to bridge the vector calculus gap Tevian Dray & Corinne A. Manogue Department of Mathematics & Department of Physics Oregon State University Corvallis, OR 97331 tevian@math.orst.edu
Using differentials to bridge the vector calculus gap Tevian Dray & Corinne A. Manogue Department of Mathematics & Department of Physics Oregon State University Corvallis, OR 97331 tevian@math.orst.edu
If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy. du du. If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u
 Section 3 4B The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then f (u) u The Chain Rule with the Power
Section 3 4B The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then f (u) u The Chain Rule with the Power
THE VECTOR CALCULUS GAP:
 THE VECTOR CALCULUS GAP: Mathematics Physics Tevian Dray Department of Mathematics, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA tevian@math.orst.edu Corinne A. Manogue Department of Physics, Oregon
THE VECTOR CALCULUS GAP: Mathematics Physics Tevian Dray Department of Mathematics, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA tevian@math.orst.edu Corinne A. Manogue Department of Physics, Oregon
MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Fall Integrating a vector field over a surface
 MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Fall 2011 Definition Integrating a vector field over a surface We are given a vector field F in space and an oriented surface in the domain of F as shown in the figure below
MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Fall 2011 Definition Integrating a vector field over a surface We are given a vector field F in space and an oriented surface in the domain of F as shown in the figure below
If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy. du du. If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u
 Section 3 4B Lecture The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u The Chain Rule
Section 3 4B Lecture The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u The Chain Rule
ELECTROMAGNETIC CONIC SECTIONS
 ELECTROMAGNETIC CONIC SECTIONS Tevian Dray Department of Mathematics, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331 tevian@math.orst.edu Corinne A. Manogue Department of Physics, Oregon State University,
ELECTROMAGNETIC CONIC SECTIONS Tevian Dray Department of Mathematics, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331 tevian@math.orst.edu Corinne A. Manogue Department of Physics, Oregon State University,
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University. Shari Ultman
 Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Second Order ODEs. Second Order ODEs. In general second order ODEs contain terms involving y, dy But here only consider equations of the form
 Second Order ODEs Second Order ODEs In general second order ODEs contain terms involving y, dy But here only consider equations of the form A d2 y dx 2 + B dy dx + Cy = 0 dx, d2 y dx 2 and F(x). where
Second Order ODEs Second Order ODEs In general second order ODEs contain terms involving y, dy But here only consider equations of the form A d2 y dx 2 + B dy dx + Cy = 0 dx, d2 y dx 2 and F(x). where
Learning Objectives for Math 165
 Learning Objectives for Math 165 Chapter 2 Limits Section 2.1: Average Rate of Change. State the definition of average rate of change Describe what the rate of change does and does not tell us in a given
Learning Objectives for Math 165 Chapter 2 Limits Section 2.1: Average Rate of Change. State the definition of average rate of change Describe what the rate of change does and does not tell us in a given
CURRENT MATERIAL: Vector Calculus.
 Math 275, section 002 (Ultman) Spring 2012 FINAL EXAM REVIEW The final exam will be held on Wednesday 9 May from 8:00 10:00am in our regular classroom. You will be allowed both sides of two 8.5 11 sheets
Math 275, section 002 (Ultman) Spring 2012 FINAL EXAM REVIEW The final exam will be held on Wednesday 9 May from 8:00 10:00am in our regular classroom. You will be allowed both sides of two 8.5 11 sheets
Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 10 1 Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates 1. Summary of Integral Theorems 2. Generalized Coordinates 3. Cartesian Coordinates: Surfaces of Constant
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 10 1 Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates 1. Summary of Integral Theorems 2. Generalized Coordinates 3. Cartesian Coordinates: Surfaces of Constant
Review for the Final Exam
 Math 171 Review for the Final Exam 1 Find the limits (4 points each) (a) lim 4x 2 3; x x (b) lim ( x 2 x x 1 )x ; (c) lim( 1 1 ); x 1 ln x x 1 sin (x 2) (d) lim x 2 x 2 4 Solutions (a) The limit lim 4x
Math 171 Review for the Final Exam 1 Find the limits (4 points each) (a) lim 4x 2 3; x x (b) lim ( x 2 x x 1 )x ; (c) lim( 1 1 ); x 1 ln x x 1 sin (x 2) (d) lim x 2 x 2 4 Solutions (a) The limit lim 4x
Disclaimer: This Final Exam Study Guide is meant to help you start studying. It is not necessarily a complete list of everything you need to know.
 Disclaimer: This is meant to help you start studying. It is not necessarily a complete list of everything you need to know. The MTH 234 final exam mainly consists of standard response questions where students
Disclaimer: This is meant to help you start studying. It is not necessarily a complete list of everything you need to know. The MTH 234 final exam mainly consists of standard response questions where students
Coordinate systems and vectors in three spatial dimensions
 PHYS2796 Introduction to Modern Physics (Spring 2015) Notes on Mathematics Prerequisites Jim Napolitano, Department of Physics, Temple University January 7, 2015 This is a brief summary of material on
PHYS2796 Introduction to Modern Physics (Spring 2015) Notes on Mathematics Prerequisites Jim Napolitano, Department of Physics, Temple University January 7, 2015 This is a brief summary of material on
2t t dt.. So the distance is (t2 +6) 3/2
 Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review
 2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review September 10, 2018 These notes are to help you through the math used in this class. This is just a refresher, so if you never learned one of these topics you should look more
2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review September 10, 2018 These notes are to help you through the math used in this class. This is just a refresher, so if you never learned one of these topics you should look more
Let s Do This Once. Folding Vector Calculus into Multivariable Calculus Using Geometry and Language. Aaron Wangberg
 Folding Vector Calculus into Multivariable Calculus Using Geometry and Language Department of Mathematics Winona State University Annual Summer Meeting of the Mathematical Association of America, 2008
Folding Vector Calculus into Multivariable Calculus Using Geometry and Language Department of Mathematics Winona State University Annual Summer Meeting of the Mathematical Association of America, 2008
Introduction and Vectors Lecture 1
 1 Introduction Introduction and Vectors Lecture 1 This is a course on classical Electromagnetism. It is the foundation for more advanced courses in modern physics. All physics of the modern era, from quantum
1 Introduction Introduction and Vectors Lecture 1 This is a course on classical Electromagnetism. It is the foundation for more advanced courses in modern physics. All physics of the modern era, from quantum
Solution to Homework 1. Vector Analysis (P201)
 Solution to Homework 1. Vector Analysis (P1) Q1. A = 3î + ĵ ˆk, B = î + 3ĵ + 4ˆk, C = 4î ĵ 6ˆk. The sides AB, BC and AC are, AB = 4î ĵ 6ˆk AB = 7.48 BC = 5î + 5ĵ + 1ˆk BC = 15 1.5 CA = î 3ĵ 4ˆk CA = 6
Solution to Homework 1. Vector Analysis (P1) Q1. A = 3î + ĵ ˆk, B = î + 3ĵ + 4ˆk, C = 4î ĵ 6ˆk. The sides AB, BC and AC are, AB = 4î ĵ 6ˆk AB = 7.48 BC = 5î + 5ĵ + 1ˆk BC = 15 1.5 CA = î 3ĵ 4ˆk CA = 6
MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Fall Integration over a curve
 dr dr y MATH 28 Multivariate Calculus Fall 211 Integration over a curve Given a curve C in the plane or in space, we can (conceptually) break it into small pieces each of which has a length ds. In some
dr dr y MATH 28 Multivariate Calculus Fall 211 Integration over a curve Given a curve C in the plane or in space, we can (conceptually) break it into small pieces each of which has a length ds. In some
MATH H53 : Final exam
 MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
College of the Holy Cross MATH 133, Calculus With Fundamentals 1 Solutions for Final Examination Friday, December 15
 College of the Holy Cross MATH 33, Calculus With Fundamentals Solutions for Final Examination Friday, December 5 I. The graph y = f(x) is given in light blue. Match each equation with one of the numbered
College of the Holy Cross MATH 33, Calculus With Fundamentals Solutions for Final Examination Friday, December 5 I. The graph y = f(x) is given in light blue. Match each equation with one of the numbered
Brief Review of Vector Algebra
 APPENDIX Brief Review of Vector Algebra A.0 Introduction Vector algebra is used extensively in computational mechanics. The student must thus understand the concepts associated with this subject. The current
APPENDIX Brief Review of Vector Algebra A.0 Introduction Vector algebra is used extensively in computational mechanics. The student must thus understand the concepts associated with this subject. The current
7a3 2. (c) πa 3 (d) πa 3 (e) πa3
 1.(6pts) Find the integral x, y, z d S where H is the part of the upper hemisphere of H x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = a 2 above the plane z = a and the normal points up. ( 2 π ) Useful Facts: cos = 1 and ds = ±a sin
1.(6pts) Find the integral x, y, z d S where H is the part of the upper hemisphere of H x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = a 2 above the plane z = a and the normal points up. ( 2 π ) Useful Facts: cos = 1 and ds = ±a sin
Find the indicated derivative. 1) Find y(4) if y = 3 sin x. A) y(4) = 3 cos x B) y(4) = 3 sin x C) y(4) = - 3 cos x D) y(4) = - 3 sin x
 Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
Note: Every graph is a level set (why?). But not every level set is a graph. Graphs must pass the vertical line test. (Level sets may or may not.
 Curves in R : Graphs vs Level Sets Graphs (y = f(x)): The graph of f : R R is {(x, y) R y = f(x)} Example: When we say the curve y = x, we really mean: The graph of the function f(x) = x That is, we mean
Curves in R : Graphs vs Level Sets Graphs (y = f(x)): The graph of f : R R is {(x, y) R y = f(x)} Example: When we say the curve y = x, we really mean: The graph of the function f(x) = x That is, we mean
CURRENT MATERIAL: Vector Calculus.
 Math 275, section 002 (Ultman) Fall 2011 FINAL EXAM REVIEW The final exam will be held on Wednesday 14 December from 10:30am 12:30pm in our regular classroom. You will be allowed both sides of an 8.5 11
Math 275, section 002 (Ultman) Fall 2011 FINAL EXAM REVIEW The final exam will be held on Wednesday 14 December from 10:30am 12:30pm in our regular classroom. You will be allowed both sides of an 8.5 11
Major Ideas in Calc 3 / Exam Review Topics
 Major Ideas in Calc 3 / Exam Review Topics Here are some highlights of the things you should know to succeed in this class. I can not guarantee that this list is exhaustive!!!! Please be sure you are able
Major Ideas in Calc 3 / Exam Review Topics Here are some highlights of the things you should know to succeed in this class. I can not guarantee that this list is exhaustive!!!! Please be sure you are able
UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE
 Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Review Sheet for the Final
 Review Sheet for the Final Math 6-4 4 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
Review Sheet for the Final Math 6-4 4 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
Vector Calculus handout
 Vector Calculus handout The Fundamental Theorem of Line Integrals Theorem 1 (The Fundamental Theorem of Line Integrals). Let C be a smooth curve given by a vector function r(t), where a t b, and let f
Vector Calculus handout The Fundamental Theorem of Line Integrals Theorem 1 (The Fundamental Theorem of Line Integrals). Let C be a smooth curve given by a vector function r(t), where a t b, and let f
6 Div, grad curl and all that
 6 Div, grad curl and all that 6.1 Fundamental theorems for gradient, divergence, and curl Figure 1: Fundamental theorem of calculus relates df/dx over[a, b] and f(a), f(b). You will recall the fundamental
6 Div, grad curl and all that 6.1 Fundamental theorems for gradient, divergence, and curl Figure 1: Fundamental theorem of calculus relates df/dx over[a, b] and f(a), f(b). You will recall the fundamental
Review problems for the final exam Calculus III Fall 2003
 Review problems for the final exam alculus III Fall 2003 1. Perform the operations indicated with F (t) = 2t ı 5 j + t 2 k, G(t) = (1 t) ı + 1 t k, H(t) = sin(t) ı + e t j a) F (t) G(t) b) F (t) [ H(t)
Review problems for the final exam alculus III Fall 2003 1. Perform the operations indicated with F (t) = 2t ı 5 j + t 2 k, G(t) = (1 t) ı + 1 t k, H(t) = sin(t) ı + e t j a) F (t) G(t) b) F (t) [ H(t)
2.8 Linear Approximations and Differentials
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 294: Calculus I Dr. Marcel B. Finan 2.8 Linear Approximations and Differentials In this section we approximate graphs by tangent lines which we refer to as tangent line approximations.
Arkansas Tech University MATH 294: Calculus I Dr. Marcel B. Finan 2.8 Linear Approximations and Differentials In this section we approximate graphs by tangent lines which we refer to as tangent line approximations.
Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions)
 Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions). Set up (but do not evaluate) an integral for the surface area of the surface f(x, y) x 2 y y over the region x, y 4. We have that the surface are is
Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions). Set up (but do not evaluate) an integral for the surface area of the surface f(x, y) x 2 y y over the region x, y 4. We have that the surface are is
One side of each sheet is blank and may be used as scratch paper.
 Math 244 Spring 2017 (Practice) Final 5/11/2017 Time Limit: 2 hours Name: No calculators or notes are allowed. One side of each sheet is blank and may be used as scratch paper. heck your answers whenever
Math 244 Spring 2017 (Practice) Final 5/11/2017 Time Limit: 2 hours Name: No calculators or notes are allowed. One side of each sheet is blank and may be used as scratch paper. heck your answers whenever
Math 3435 Homework Set 11 Solutions 10 Points. x= 1,, is in the disk of radius 1 centered at origin
 Math 45 Homework et olutions Points. ( pts) The integral is, x + z y d = x + + z da 8 6 6 where is = x + z 8 x + z = 4 o, is the disk of radius centered on the origin. onverting to polar coordinates then
Math 45 Homework et olutions Points. ( pts) The integral is, x + z y d = x + + z da 8 6 6 where is = x + z 8 x + z = 4 o, is the disk of radius centered on the origin. onverting to polar coordinates then
Math 212-Lecture 8. The chain rule with one independent variable
 Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
The Geometry of Relativity
 Department of Mathematics Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/~tevian Differential Geometry Definition A topological manifold is a second countable Housdorff space that is locally homeomorphic
Department of Mathematics Oregon State University http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/~tevian Differential Geometry Definition A topological manifold is a second countable Housdorff space that is locally homeomorphic
Final Exam December 20, 2011
 Final Exam December 20, 2011 Math 420 - Ordinary Differential Equations No credit will be given for answers without mathematical or logical justification. Simplify answers as much as possible. Leave solutions
Final Exam December 20, 2011 Math 420 - Ordinary Differential Equations No credit will be given for answers without mathematical or logical justification. Simplify answers as much as possible. Leave solutions
Final Problem Set. 2. Use the information in #1 to show a solution to the differential equation ), where k and L are constants and e c L be
 Final Problem Set Name A. Show the steps for each of the following problems. 1. Show 1 1 1 y y L y y(1 ) L.. Use the information in #1 to show a solution to the differential equation dy y ky(1 ), where
Final Problem Set Name A. Show the steps for each of the following problems. 1. Show 1 1 1 y y L y y(1 ) L.. Use the information in #1 to show a solution to the differential equation dy y ky(1 ), where
Summary for Vector Calculus and Complex Calculus (Math 321) By Lei Li
 Summary for Vector alculus and omplex alculus (Math 321) By Lei Li 1 Vector alculus 1.1 Parametrization urves, surfaces, or volumes can be parametrized. Below, I ll talk about 3D case. Suppose we use e
Summary for Vector alculus and omplex alculus (Math 321) By Lei Li 1 Vector alculus 1.1 Parametrization urves, surfaces, or volumes can be parametrized. Below, I ll talk about 3D case. Suppose we use e
2.12: Derivatives of Exp/Log (cont d) and 2.15: Antiderivatives and Initial Value Problems
 2.12: Derivatives of Exp/Log (cont d) and 2.15: Antiderivatives and Initial Value Problems Mathematics 3 Lecture 14 Dartmouth College February 03, 2010 Derivatives of the Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
2.12: Derivatives of Exp/Log (cont d) and 2.15: Antiderivatives and Initial Value Problems Mathematics 3 Lecture 14 Dartmouth College February 03, 2010 Derivatives of the Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Math 1 Lecture 22. Dartmouth College. Monday
 Math 1 Lecture 22 Dartmouth College Monday 10-31-16 Contents Reminders/Announcements Last Time Implicit Differentiation Derivatives of Inverse Functions Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions Examish
Math 1 Lecture 22 Dartmouth College Monday 10-31-16 Contents Reminders/Announcements Last Time Implicit Differentiation Derivatives of Inverse Functions Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions Examish
Math 23b Practice Final Summer 2011
 Math 2b Practice Final Summer 211 1. (1 points) Sketch or describe the region of integration for 1 x y and interchange the order to dy dx dz. f(x, y, z) dz dy dx Solution. 1 1 x z z f(x, y, z) dy dx dz
Math 2b Practice Final Summer 211 1. (1 points) Sketch or describe the region of integration for 1 x y and interchange the order to dy dx dz. f(x, y, z) dz dy dx Solution. 1 1 x z z f(x, y, z) dy dx dz
f(x 0 + h) f(x 0 ) h slope of secant line = m sec
 Derivatives Using limits, we can define the slope of a tangent line to a function. When given a function f(x), and given a point P (x 0, f(x 0 )) on f, if we want to find the slope of the tangent line
Derivatives Using limits, we can define the slope of a tangent line to a function. When given a function f(x), and given a point P (x 0, f(x 0 )) on f, if we want to find the slope of the tangent line
MATH 1501G1/G2/G3 Test II Fall 2006
 MATH 50G/G2/G3 Test II Fall 2006 Name: GTid (9xxxxxxxx): Instructor: Mitchel T. Keller Teaching Assistant and Section: There are 6 questions on this exam on 4 pages (not counting this coverpage). Answer
MATH 50G/G2/G3 Test II Fall 2006 Name: GTid (9xxxxxxxx): Instructor: Mitchel T. Keller Teaching Assistant and Section: There are 6 questions on this exam on 4 pages (not counting this coverpage). Answer
Chapter 12 Overview: Review of All Derivative Rules
 Chapter 12 Overview: Review of All Derivative Rules The emphasis of the previous chapters was graphing the families of functions as they are viewed (mostly) in Analytic Geometry, that is, with traits.
Chapter 12 Overview: Review of All Derivative Rules The emphasis of the previous chapters was graphing the families of functions as they are viewed (mostly) in Analytic Geometry, that is, with traits.
MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Fall Integrating a vector field over a curve
 MATH 280 Multivariate alculus Fall 2012 Definition Integrating a vector field over a curve We are given a vector field F and an oriented curve in the domain of F as shown in the figure on the left below.
MATH 280 Multivariate alculus Fall 2012 Definition Integrating a vector field over a curve We are given a vector field F and an oriented curve in the domain of F as shown in the figure on the left below.
Chapter 6: Vector Analysis
 Chapter 6: Vector Analysis We use derivatives and various products of vectors in all areas of physics. For example, Newton s 2nd law is F = m d2 r. In electricity dt 2 and magnetism, we need surface and
Chapter 6: Vector Analysis We use derivatives and various products of vectors in all areas of physics. For example, Newton s 2nd law is F = m d2 r. In electricity dt 2 and magnetism, we need surface and
Math review. Math review
 Math review 1 Math review 3 1 series approximations 3 Taylor s Theorem 3 Binomial approximation 3 sin(x), for x in radians and x close to zero 4 cos(x), for x in radians and x close to zero 5 2 some geometry
Math review 1 Math review 3 1 series approximations 3 Taylor s Theorem 3 Binomial approximation 3 sin(x), for x in radians and x close to zero 4 cos(x), for x in radians and x close to zero 5 2 some geometry
Solutions for the Practice Final - Math 23B, 2016
 olutions for the Practice Final - Math B, 6 a. True. The area of a surface is given by the expression d, and since we have a parametrization φ x, y x, y, f x, y with φ, this expands as d T x T y da xy
olutions for the Practice Final - Math B, 6 a. True. The area of a surface is given by the expression d, and since we have a parametrization φ x, y x, y, f x, y with φ, this expands as d T x T y da xy
Chapter 2: Differentiation
 Chapter 2: Differentiation Spring 2018 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 82 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Chapter 2: Differentiation Spring 2018 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 82 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
The Derivative. Appendix B. B.1 The Derivative of f. Mappings from IR to IR
 Appendix B The Derivative B.1 The Derivative of f In this chapter, we give a short summary of the derivative. Specifically, we want to compare/contrast how the derivative appears for functions whose domain
Appendix B The Derivative B.1 The Derivative of f In this chapter, we give a short summary of the derivative. Specifically, we want to compare/contrast how the derivative appears for functions whose domain
Core Mathematics 3 Differentiation
 http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics Differentiation C differentiation Page Differentiation C Specifications. By the end of this unit you should be able to : Use chain rule to find the derivative
http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics Differentiation C differentiation Page Differentiation C Specifications. By the end of this unit you should be able to : Use chain rule to find the derivative
MATH 1241 FINAL EXAM FALL 2012 Part I, No Calculators Allowed
 MATH 11 FINAL EXAM FALL 01 Part I, No Calculators Allowed 1. Evaluate the limit: lim x x x + x 1. (a) 0 (b) 0.5 0.5 1 Does not exist. Which of the following is the derivative of g(x) = x cos(3x + 1)? (a)
MATH 11 FINAL EXAM FALL 01 Part I, No Calculators Allowed 1. Evaluate the limit: lim x x x + x 1. (a) 0 (b) 0.5 0.5 1 Does not exist. Which of the following is the derivative of g(x) = x cos(3x + 1)? (a)
Dr. Allen Back. Dec. 3, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back Dec. 3, 2014 forms are sums of wedge products of the basis 1-forms dx, dy, and dz. They are kinds of tensors generalizing ordinary scalar functions and vector fields. They have a skew-symmetry
Dr. Allen Back Dec. 3, 2014 forms are sums of wedge products of the basis 1-forms dx, dy, and dz. They are kinds of tensors generalizing ordinary scalar functions and vector fields. They have a skew-symmetry
Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals
 A. Line Integrals MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOY Department of Physics Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals The line integral of a scalar function f ( xyz),, along a path C is
A. Line Integrals MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOY Department of Physics Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals The line integral of a scalar function f ( xyz),, along a path C is
Differentiation Review, Part 1 (Part 2 follows; there are answers at the end of each part.)
 Differentiation Review 1 Name Differentiation Review, Part 1 (Part 2 follows; there are answers at the end of each part.) Derivatives Review: Summary of Rules Each derivative rule is summarized for you
Differentiation Review 1 Name Differentiation Review, Part 1 (Part 2 follows; there are answers at the end of each part.) Derivatives Review: Summary of Rules Each derivative rule is summarized for you
Two dimensional oscillator and central forces
 Two dimensional oscillator and central forces September 4, 04 Hooke s law in two dimensions Consider a radial Hooke s law force in -dimensions, F = kr where the force is along the radial unit vector and
Two dimensional oscillator and central forces September 4, 04 Hooke s law in two dimensions Consider a radial Hooke s law force in -dimensions, F = kr where the force is along the radial unit vector and
SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 10550
 SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 0550. Find the critical numbers of f(x) = 6 x2 x /3. We have f (x) = 3 x 3 x 2/3 = [ x 5/3 ] 3 x 2/3. So x = 0 is a critical point. For x 0, the equation f (x) = 0 can be written
SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 0550. Find the critical numbers of f(x) = 6 x2 x /3. We have f (x) = 3 x 3 x 2/3 = [ x 5/3 ] 3 x 2/3. So x = 0 is a critical point. For x 0, the equation f (x) = 0 can be written
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not
 Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
x + ye z2 + ze y2, y + xe z2 + ze x2, z and where T is the
 1.(8pts) Find F ds where F = x + ye z + ze y, y + xe z + ze x, z and where T is the T surface in the pictures. (The two pictures are two views of the same surface.) The boundary of T is the unit circle
1.(8pts) Find F ds where F = x + ye z + ze y, y + xe z + ze x, z and where T is the T surface in the pictures. (The two pictures are two views of the same surface.) The boundary of T is the unit circle
Directional Derivatives in the Plane
 Directional Derivatives in the Plane P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Directional Derivatives in the Plane April 10, 2017 1 / 30 Directional Derivatives in the Plane Let z =
Directional Derivatives in the Plane P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Directional Derivatives in the Plane April 10, 2017 1 / 30 Directional Derivatives in the Plane Let z =
Differentiation. Timur Musin. October 10, University of Freiburg 1 / 54
 Timur Musin University of Freiburg October 10, 2014 1 / 54 1 Limit of a Function 2 2 / 54 Literature A. C. Chiang and K. Wainwright, Fundamental methods of mathematical economics, Irwin/McGraw-Hill, Boston,
Timur Musin University of Freiburg October 10, 2014 1 / 54 1 Limit of a Function 2 2 / 54 Literature A. C. Chiang and K. Wainwright, Fundamental methods of mathematical economics, Irwin/McGraw-Hill, Boston,
Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS : Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Integrals / 7 The Substitution Method Idea: To replace a relatively
Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS : Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Integrals / 7 The Substitution Method Idea: To replace a relatively
MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010
 MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010 Please print the following information: Name: Instructor: Student ID: Section/Time: The MATH 1241 Final Exam consists of three parts. You have three hours for the
MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010 Please print the following information: Name: Instructor: Student ID: Section/Time: The MATH 1241 Final Exam consists of three parts. You have three hours for the
Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes
 Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes Implicit Differentiation and Related Rates Why? We have learned how to take derivatives of functions, and we have seen many applications of this. However
Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes Implicit Differentiation and Related Rates Why? We have learned how to take derivatives of functions, and we have seen many applications of this. However
Chapter 2: Differentiation
 Chapter 2: Differentiation Winter 2016 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 75 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Chapter 2: Differentiation Winter 2016 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 75 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Math 20C. Lecture Examples. Section 14.5, Part 1. Directional derivatives and gradient vectors in the plane
 Math 0C. Lecture Examples. (8/7/08) Section 4.5, Part. Directional derivatives and gradient vectors in the plane The x-derivative f x (a,b) is the derivative of f at (a,b) in the direction of the unit
Math 0C. Lecture Examples. (8/7/08) Section 4.5, Part. Directional derivatives and gradient vectors in the plane The x-derivative f x (a,b) is the derivative of f at (a,b) in the direction of the unit
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION TUTORIAL 2 ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION TUTORIAL ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION CONTENTS Function of a Function Differentiation of a Sum Differentiation of a Proct Differentiation of a Quotient Turning Points
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION TUTORIAL ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION CONTENTS Function of a Function Differentiation of a Sum Differentiation of a Proct Differentiation of a Quotient Turning Points
Review for the First Midterm Exam
 Review for the First Midterm Exam Thomas Morrell 5 pm, Sunday, 4 April 9 B9 Van Vleck Hall For the purpose of creating questions for this review session, I did not make an effort to make any of the numbers
Review for the First Midterm Exam Thomas Morrell 5 pm, Sunday, 4 April 9 B9 Van Vleck Hall For the purpose of creating questions for this review session, I did not make an effort to make any of the numbers
MATHS 267 Answers to Stokes Practice Dr. Jones
 MATH 267 Answers to tokes Practice Dr. Jones 1. Calculate the flux F d where is the hemisphere x2 + y 2 + z 2 1, z > and F (xz + e y2, yz, z 2 + 1). Note: the surface is open (doesn t include any of the
MATH 267 Answers to tokes Practice Dr. Jones 1. Calculate the flux F d where is the hemisphere x2 + y 2 + z 2 1, z > and F (xz + e y2, yz, z 2 + 1). Note: the surface is open (doesn t include any of the
MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Spring Derivatives of vector fields: divergence and curl
 MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Spring 2011 Vector fields in the plane Derivatives of vector fields: divergence and curl Given a planar vector field F P x, y î + Qx, y ĵ, we can consider the partial derivatives.
MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Spring 2011 Vector fields in the plane Derivatives of vector fields: divergence and curl Given a planar vector field F P x, y î + Qx, y ĵ, we can consider the partial derivatives.
Sec. 1.1: Basics of Vectors
 Sec. 1.1: Basics of Vectors Notation for Euclidean space R n : all points (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) in n-dimensional space. Examples: 1. R 1 : all points on the real number line. 2. R 2 : all points (x 1, x
Sec. 1.1: Basics of Vectors Notation for Euclidean space R n : all points (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) in n-dimensional space. Examples: 1. R 1 : all points on the real number line. 2. R 2 : all points (x 1, x
Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution
 Name: Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and that it
Name: Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and that it
Math 221 Exam III (50 minutes) Friday April 19, 2002 Answers
 Math Exam III (5 minutes) Friday April 9, Answers I. ( points.) Fill in the boxes as to complete the following statement: A definite integral can be approximated by a Riemann sum. More precisely, if a
Math Exam III (5 minutes) Friday April 9, Answers I. ( points.) Fill in the boxes as to complete the following statement: A definite integral can be approximated by a Riemann sum. More precisely, if a
FINAL EXAM CALCULUS 2. Name PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS
 FINAL EXAM CALCULUS MATH 00 FALL 08 Name PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS Please answer all of the questions, and show your work. You must explain your answers to get credit. You will be graded on the clarity of
FINAL EXAM CALCULUS MATH 00 FALL 08 Name PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS Please answer all of the questions, and show your work. You must explain your answers to get credit. You will be graded on the clarity of
CALCULUS III THE CHAIN RULE, DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES, AND GRADIENT
 CALCULUS III THE CHAIN RULE, DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES, AND GRADIENT MATH 20300 DD & ST2 prepared by Antony Foster Department of Mathematics (office: NAC 6-273) The City College of The City University of
CALCULUS III THE CHAIN RULE, DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES, AND GRADIENT MATH 20300 DD & ST2 prepared by Antony Foster Department of Mathematics (office: NAC 6-273) The City College of The City University of
Math 20C Homework 2 Partial Solutions
 Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key
 Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key 1. a) P = 4s (definition of perimeter and square) b) P = l + w (definition of perimeter and rectangle) c) P = a + b + c (definition of perimeter and triangle)
Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key 1. a) P = 4s (definition of perimeter and square) b) P = l + w (definition of perimeter and rectangle) c) P = a + b + c (definition of perimeter and triangle)
1 Antiderivatives graphically and numerically
 Math B - Calculus by Hughes-Hallett, et al. Chapter 6 - Constructing antiderivatives Prepared by Jason Gaddis Antiderivatives graphically and numerically Definition.. The antiderivative of a function f
Math B - Calculus by Hughes-Hallett, et al. Chapter 6 - Constructing antiderivatives Prepared by Jason Gaddis Antiderivatives graphically and numerically Definition.. The antiderivative of a function f
Example. Evaluate. 3x 2 4 x dx.
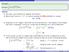 3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
Dr. Allen Back. Sep. 10, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back Sep. 10, 2014 The chain rule in multivariable calculus is in some ways very simple. But it can lead to extremely intricate sorts of relationships (try thermodynamics in physical chemistry...
Dr. Allen Back Sep. 10, 2014 The chain rule in multivariable calculus is in some ways very simple. But it can lead to extremely intricate sorts of relationships (try thermodynamics in physical chemistry...
Partial Derivatives for Math 229. Our puropose here is to explain how one computes partial derivatives. We will not attempt
 Partial Derivatives for Math 229 Our puropose here is to explain how one computes partial derivatives. We will not attempt to explain how they arise or why one would use them; that is left to other courses
Partial Derivatives for Math 229 Our puropose here is to explain how one computes partial derivatives. We will not attempt to explain how they arise or why one would use them; that is left to other courses
3.1 Derivative Formulas for Powers and Polynomials
 3.1 Derivative Formulas for Powers and Polynomials First, recall that a derivative is a function. We worked very hard in 2.2 to interpret the derivative of a function visually. We made the link, in Ex.
3.1 Derivative Formulas for Powers and Polynomials First, recall that a derivative is a function. We worked very hard in 2.2 to interpret the derivative of a function visually. We made the link, in Ex.
 1 Solving equations 1.1 Kick off with CAS 1. Polynomials 1. Trigonometric symmetry properties 1.4 Trigonometric equations and general solutions 1.5 Literal and simultaneous equations 1.6 Review 1.1 Kick
1 Solving equations 1.1 Kick off with CAS 1. Polynomials 1. Trigonometric symmetry properties 1.4 Trigonometric equations and general solutions 1.5 Literal and simultaneous equations 1.6 Review 1.1 Kick
