This section outlines the methodology used to calculate the wave load and wave wind load values.
|
|
|
- Michael French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., JUNE 2014 AUTOMATIC WAVE LOADS TECHNICAL NOTE CALCULATION O WAVE LOAD VALUES This section outlines the methoology use to calculate the wave loa an wave win loa values. Overview Wave Loa The program calculates the force exerte by a wave at a particular location on a structural object using the following steps. Steps 1 an 2 apply only if the wave water particle velocities an accelerations are calculate from wave theory (i.e., the rom Selecte Wave Theory check box was checke on the Wave Characteristics form; see Defining Wave Loas for more information). Those steps are skippe when user-efine waves are specifie. Note the wave loas are applie to only the portion of the structure that is above the mu line an below the wave surface. 1. Calculate the apparent wave perio. 2. Calculate two-imensional regular wave kinematics (water particle velocities an accelerations) using the selecte wave theory. 3. Use the specifie wave kinematics factor to moify the water particle velocities an accelerations. 4. Calculate the current profile using the specifie current stretching metho. Moify the current velocities using the specifie current blockage factor. 5. Vectorially combine moifie water particle velocities with the moifie current velocities. 6. Determine the section imensions (not incluing marine growth) base on the efine section properties or the wave overwrites. Overview Page 1 of 9
2 7. Determine the amount of marine growth, if any, on the consiere object base on the efine marine growth parameters or the wave overwrites. 8. Determine the rag an inertia coefficients for the consiere object base on the efine rag an inertia coefficient parameters or the wave overwrites. 9. Apply the Morison Equation to calculate the force exerte by the wave at a particular location on the object. 10. Calculate the buoyant forces acting on the object. Wave Win Loa The program calculates the force exerte by a wave win loa at a particular location on a structural object using the following steps. Note that wave win loas are applie only to the portions of the structure that are above the wave surface. 1. Calculate the esign win spee. 2. Determine the section imensions (not incluing marine growth or ice) base on the efine section properties or the wave overwrites. 3. Determine the amount of marine growth, if any, on the consiere object base on the efine marine growth parameters or the wave overwrites. 4. Determine the amount of ice, if any, on the consiere object base on the wave overwrites. Note that if both marine growth an ice is specifie at a location, only the marine growth value is use. 5. Determine the shape coefficient use for win loas for the consiere object base on the efine shape coefficient that applies to all elements or the wave overwrites. 6. Determine the win loa shieling factor, if any, on the consiere object base on the wave overwrites. The win loa on the object is multiplie by this shieling factor. 7. Calculate the win rag at a particular location on the object. Overview Page 2 of 9
3 Apparent Wave Perio The wave perio input in the wave efinition ata oes not inclue the effect of the current. The wave perio use when calculating the wave water particle velocities an accelerations must inclue the effect of the current component in the irection of the wave. The wave perio that inclues the effect of the current is calle the apparent wave perio, T app. The apparent wave perio is calculate by solving a system of three simultaneous nonlinear equations. Those equations, which are ocumente in Section C2.3.1b1 of the commentary of the API Recommene Practice (American Petroleum Institute 2000), are: λ = λ T T app + V I T 2 = 2πλ app g tan (2π / λ) C2.3.1b1 V I = 4π / λ + U c 0 4π ( ) ( ) cosh sinh(4π / λ) λ λ T = Wave length. = Wave perio as input by user (not consiering the current). T app = Apparent wave perio (consiers the current). V I = Effective current spee in the irection of the wave. g = Acceleration ue to gravity. = Elevation reference to the storm water level (positive above storm water level). Apparent Wave Perio Page 3 of 9
4 U c () = Component of steay current profile at elevation in the Wave Kinematics wave irection an not multiplie by the current blockage factor. = Storm water epth. Wave kinematics yiel the wave water particle velocities an accelerations. The velocities an accelerations are calculate from a specifie wave theory or they are user-efine. Regarless of which metho is use to obtain the wave water particle velocities an accelerations, they are then moifie by the wave kinematics factor, which is intene to account for wave irectional spreaing an irregularity in the wave profile shape. The moification consists of multiplying the horiontal velocities an accelerations by the wave kinematics factor. The vertical velocities an accelerations are not moifie. Current Profile The user specifies the current profile (velocity an irection of current as a function of height) from the mu line to the storm water level. The user specifies that either a Linear or a Nonlinear current stretching metho is use to stretch or compress the current to the wave surface at a particular location. The current velocity at a particular location etermine from applying the current stretching technique is multiplie by the current blockage factor to obtain the current velocity that is combine with the wave velocity. Linear Current Stretching Linear current stretching is base on the following equation, which is foun in Section 2.3.1b-5 of the API Recommene Practice (American Petroleum Institute 2000). The equation is solve irectly for '. ' + ) = ( + ) + η ( 2.3.1b-5 Wave Kinematics Page 4 of 9
5 ' = Elevation of the location the water particle current velocity is esire reference to the storm water level (positive above storm water level). = Elevation of the location in the user-specifie current profile the current velocity shoul be obtaine reference to the storm water level (positive above storm water level). η = Elevation of the wave surface irectly above the water particle reference to the storm water level (positive above storm water level). = Storm water epth. Nonlinear Current Stretching Nonlinear current stretching is base on the following equation, which is foun in Section C2.3.1b-5 of the commentary of the API Recommene Practice (American Petroleum Institute 2000). The equation is solve iteratively for '. sinh ' + η sinh ( 2π ( ' + ) / λn ) ( 2π / λ ) = C2.3.1b-5 n ' = Elevation of the location the current velocity is esire reference to the storm water level (positive above storm water level). = Elevation of the location in the user-specifie current profile the current velocity shoul be obtaine reference to the storm water level (positive above storm water level). η = Elevation of the wave surface reference to the storm water level (positive above storm water level). = Storm water epth. η = Wave length. Current Profile Page 5 of 9
6 Morison Equation The Morison equation is use to calculate the force exerte by the wave at a particular location on an object. The equation is given in Section 2.3.1b-10 of the API Recommene Practice (American Petroleum Institute 2000). w = D + I = CD AU U + C 2g m w V g U t = Hyroynamic force per unit length acting normal to the object longituinal axis. D = Drag force per unit length. I = Inertia force per unit length. C D = Drag coefficient. w = Weight ensity of water. g = Gravitational acceleration. A = Projecte area normal to object axis per unit length. or pipes an circles this is the effective iameter of the object, incluing marine growth. or other section types, it is the imension of the sie of the rectangle that encloses the section (incluing marine growth, if any) that is normal to the irection of the loa. V = Displace volume per unit length. or pipes an circles this is π D 2 /4 D is the effective iameter of the object, incluing marine growth. or other section types it is the prouct of the imensions of two ajacent sies of the rectangle that encloses the section (incluing marine growth, if any). U = Component of the water particle velocity acting normal to the axis of the object. Morison Equation Page 6 of 9
7 U = The absolute value of U. C M = Inertia coefficient. U t Buoyant orces = Component of the water particle acceleration acting normal to the axis of the object. Buoyant forces are inclue only when so inicate in the wave loa efinition. Buoyant forces are applie only to objects (or portions of objects) that lie above the mu line an below the wave surface. Buoyant forces consist of a uniform projecte Z irection loa applie to objects that are not vertical an concentrate compressive axial forces applie to the ens of all objects. Uniform Loa The magnitue of the uniform loa is calculate as: f = wv f = A uniform loa in the projecte Z irection. w V = Weight ensity of the water. = Displace volume per unit length of the object. or pipes an circles the isplace volume V is calculate as V = π 2 /4, is the iameter incluing marine growth, if any. or other sections V is calculate as V = b, b an are the with an height of a rectangle that woul enclose the section. Concentrate Compressive Loas at Object Ens The magnitue of the concentrate compressive axial loa at each en of each object is calculate as: P = wa h c Buoyant orces Page 7 of 9
8 P w = A concentrate compressive axial loa. = Weight ensity of the water. A c = Cross sectional area to which the loa is applie. h = Height of the water. The magnitue cross-sectional area to which the loa is applie epens on whether the object is flooe. All objects are assume to not be flooe unless the are specifically inicate to be flooe in the wave overwrites. If the object is not flooe, for pipes an circles the cross sectional area A c is calculate as A c = π 2 /4 is the iameter, incluing marine growth, if any. or other sections, A c is calculate as A c = b, b an are the with an height of a rectangle that woul enclose the section. If the object is flooe, the cross-sectional area A c is taken equal to the area specifie for the section property that is assigne to the object. Win Loas The wave win loas are calculate base on Sections 2.3.2b-1 an 2.3.2c of the API Recommene Practice (American Petroleum Institute 2000). Design Win Spee The esign win spee is calculate using the following equations that are taken irectly from the API Recommene Practice. (, t) = U ( ) I t ( ) ln t0 u u the one hour mean win spee U() (ft/sec) at level (ft) is given by: ( ) = U C ln 32.8 U C = U 0 an the turbulence intensity I u () at level is given by: Win Loas Page 8 of 9
9 ( ) = 0.06 [ U ] I u Win Drag orce The win rag force is calculate using the following equation that is taken irectly from the API Recommene Practice. 2 u Cs A 2 = ρ = Win force ρ = Mass ensity of air (slugs/ft 3 ) u = Win spee (ft/sec) C s = Shape coefficient A = Are of element (ft 2 ) Win Loas Page 9 of 9
Table of Common Derivatives By David Abraham
 Prouct an Quotient Rules: Table of Common Derivatives By Davi Abraham [ f ( g( ] = [ f ( ] g( + f ( [ g( ] f ( = g( [ f ( ] g( g( f ( [ g( ] Trigonometric Functions: sin( = cos( cos( = sin( tan( = sec
Prouct an Quotient Rules: Table of Common Derivatives By Davi Abraham [ f ( g( ] = [ f ( ] g( + f ( [ g( ] f ( = g( [ f ( ] g( g( f ( [ g( ] Trigonometric Functions: sin( = cos( cos( = sin( tan( = sec
Physics 2212 K Quiz #2 Solutions Summer 2016
 Physics 1 K Quiz # Solutions Summer 016 I. (18 points) A positron has the same mass as an electron, but has opposite charge. Consier a positron an an electron at rest, separate by a istance = 1.0 nm. What
Physics 1 K Quiz # Solutions Summer 016 I. (18 points) A positron has the same mass as an electron, but has opposite charge. Consier a positron an an electron at rest, separate by a istance = 1.0 nm. What
ARCH 614 Note Set 5 S2012abn. Moments & Supports
 RCH 614 Note Set 5 S2012abn Moments & Supports Notation: = perpenicular istance to a force from a point = name for force vectors or magnitue of a force, as is P, Q, R x = force component in the x irection
RCH 614 Note Set 5 S2012abn Moments & Supports Notation: = perpenicular istance to a force from a point = name for force vectors or magnitue of a force, as is P, Q, R x = force component in the x irection
CE2253- APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING (FOR IV SEMESTER)
 CE5-APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING/UNIT-II/UNIFORM FLOW CE5- APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING (FOR IV SEMESTER) UNIT II- UNIFORM FLOW CE5-APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING/UNIT-II/UNIFORM FLOW CE5- APPLIED HYDRAULIC
CE5-APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING/UNIT-II/UNIFORM FLOW CE5- APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING (FOR IV SEMESTER) UNIT II- UNIFORM FLOW CE5-APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING/UNIT-II/UNIFORM FLOW CE5- APPLIED HYDRAULIC
TEST 2 (PHY 250) Figure Figure P26.21
 TEST 2 (PHY 250) 1. a) Write the efinition (in a full sentence) of electric potential. b) What is a capacitor? c) Relate the electric torque, exerte on a molecule in a uniform electric fiel, with the ipole
TEST 2 (PHY 250) 1. a) Write the efinition (in a full sentence) of electric potential. b) What is a capacitor? c) Relate the electric torque, exerte on a molecule in a uniform electric fiel, with the ipole
Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 2015
 Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 215 I. (17 points) The magnetic fiel at point P ue to a current through the wire is 5. µt into the page. The curve portion of the wire is a semicircle of raius 2.
Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 215 I. (17 points) The magnetic fiel at point P ue to a current through the wire is 5. µt into the page. The curve portion of the wire is a semicircle of raius 2.
23 Implicit differentiation
 23 Implicit ifferentiation 23.1 Statement The equation y = x 2 + 3x + 1 expresses a relationship between the quantities x an y. If a value of x is given, then a corresponing value of y is etermine. For
23 Implicit ifferentiation 23.1 Statement The equation y = x 2 + 3x + 1 expresses a relationship between the quantities x an y. If a value of x is given, then a corresponing value of y is etermine. For
Further Differentiation and Applications
 Avance Higher Notes (Unit ) Prerequisites: Inverse function property; prouct, quotient an chain rules; inflexion points. Maths Applications: Concavity; ifferentiability. Real-Worl Applications: Particle
Avance Higher Notes (Unit ) Prerequisites: Inverse function property; prouct, quotient an chain rules; inflexion points. Maths Applications: Concavity; ifferentiability. Real-Worl Applications: Particle
inflow outflow Part I. Regular tasks for MAE598/494 Task 1
 MAE 494/598, Fall 2016 Project #1 (Regular tasks = 20 points) Har copy of report is ue at the start of class on the ue ate. The rules on collaboration will be release separately. Please always follow the
MAE 494/598, Fall 2016 Project #1 (Regular tasks = 20 points) Har copy of report is ue at the start of class on the ue ate. The rules on collaboration will be release separately. Please always follow the
Calculus in the AP Physics C Course The Derivative
 Limits an Derivatives Calculus in the AP Physics C Course The Derivative In physics, the ieas of the rate change of a quantity (along with the slope of a tangent line) an the area uner a curve are essential.
Limits an Derivatives Calculus in the AP Physics C Course The Derivative In physics, the ieas of the rate change of a quantity (along with the slope of a tangent line) an the area uner a curve are essential.
V = Flow velocity, ft/sec
 1 Drag Coefficient Preiction Chapter 1 The ieal force acting on a surface positione perpenicular to the airflow is equal to a ynamic pressure, enote by q, times the area of that surface. Dynamic pressure
1 Drag Coefficient Preiction Chapter 1 The ieal force acting on a surface positione perpenicular to the airflow is equal to a ynamic pressure, enote by q, times the area of that surface. Dynamic pressure
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. The Virial Theorem and The Poisson Bracket-1
 Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics The Virial Theorem an The Poisson Bracket 1 Introuction In this lecture we will consier two applications of the Hamiltonian. The first, the Virial Theorem, applies to systems
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics The Virial Theorem an The Poisson Bracket 1 Introuction In this lecture we will consier two applications of the Hamiltonian. The first, the Virial Theorem, applies to systems
Prof. Dr. Ibraheem Nasser electric_charhe 9/22/2017 ELECTRIC CHARGE
 ELECTRIC CHARGE Introuction: Orinary matter consists of atoms. Each atom consists of a nucleus, consisting of protons an neutrons, surroune by a number of electrons. In electricity, the electric charge
ELECTRIC CHARGE Introuction: Orinary matter consists of atoms. Each atom consists of a nucleus, consisting of protons an neutrons, surroune by a number of electrons. In electricity, the electric charge
Physics 170 Week 7, Lecture 2
 Physics 170 Week 7, Lecture 2 http://www.phas.ubc.ca/ goronws/170 Physics 170 203 Week 7, Lecture 2 1 Textbook Chapter 12:Section 12.2-3 Physics 170 203 Week 7, Lecture 2 2 Learning Goals: Learn about
Physics 170 Week 7, Lecture 2 http://www.phas.ubc.ca/ goronws/170 Physics 170 203 Week 7, Lecture 2 1 Textbook Chapter 12:Section 12.2-3 Physics 170 203 Week 7, Lecture 2 2 Learning Goals: Learn about
Fill Removal Modeling
 CTES, L.C 9870 ozos Lane Conroe, Texas 77303 phone: (936) 521-2200 fax: (936) 5221-2275 www.ctes.com Fill moval Moeling Subject Matter Authority: Bharath Rao May 10, 1999 Summary Operations involving fill
CTES, L.C 9870 ozos Lane Conroe, Texas 77303 phone: (936) 521-2200 fax: (936) 5221-2275 www.ctes.com Fill moval Moeling Subject Matter Authority: Bharath Rao May 10, 1999 Summary Operations involving fill
Analytic Scaling Formulas for Crossed Laser Acceleration in Vacuum
 October 6, 4 ARDB Note Analytic Scaling Formulas for Crosse Laser Acceleration in Vacuum Robert J. Noble Stanfor Linear Accelerator Center, Stanfor University 575 San Hill Roa, Menlo Park, California 945
October 6, 4 ARDB Note Analytic Scaling Formulas for Crosse Laser Acceleration in Vacuum Robert J. Noble Stanfor Linear Accelerator Center, Stanfor University 575 San Hill Roa, Menlo Park, California 945
THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE
 Journal of Soun an Vibration (1996) 191(3), 397 414 THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE E. M. WEINSTEIN Galaxy Scientific Corporation, 2500 English Creek
Journal of Soun an Vibration (1996) 191(3), 397 414 THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE E. M. WEINSTEIN Galaxy Scientific Corporation, 2500 English Creek
AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WING FLUTTER Revision A
 AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WIN FLUTTER Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com January 8, 000 Introuction Certain aircraft wings have experience violent oscillations uring high spee flight.
AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WIN FLUTTER Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com January 8, 000 Introuction Certain aircraft wings have experience violent oscillations uring high spee flight.
TMA 4195 Matematisk modellering Exam Tuesday December 16, :00 13:00 Problems and solution with additional comments
 Problem F U L W D g m 3 2 s 2 0 0 0 0 2 kg 0 0 0 0 0 0 Table : Dimension matrix TMA 495 Matematisk moellering Exam Tuesay December 6, 2008 09:00 3:00 Problems an solution with aitional comments The necessary
Problem F U L W D g m 3 2 s 2 0 0 0 0 2 kg 0 0 0 0 0 0 Table : Dimension matrix TMA 495 Matematisk moellering Exam Tuesay December 6, 2008 09:00 3:00 Problems an solution with aitional comments The necessary
The Press-Schechter mass function
 The Press-Schechter mass function To state the obvious: It is important to relate our theories to what we can observe. We have looke at linear perturbation theory, an we have consiere a simple moel for
The Press-Schechter mass function To state the obvious: It is important to relate our theories to what we can observe. We have looke at linear perturbation theory, an we have consiere a simple moel for
Section 2.7 Derivatives of powers of functions
 Section 2.7 Derivatives of powers of functions (3/19/08) Overview: In this section we iscuss the Chain Rule formula for the erivatives of composite functions that are forme by taking powers of other functions.
Section 2.7 Derivatives of powers of functions (3/19/08) Overview: In this section we iscuss the Chain Rule formula for the erivatives of composite functions that are forme by taking powers of other functions.
PREPARATION OF THE NATIONAL MAGNETIC FIELD STANDARD IN CROATIA
 n IMEKO TC 11 International Symposium METROLOGICAL INFRASTRUCTURE June 15-17, 11, Cavtat, Dubrovni Riviera, Croatia PREPARATION OF THE NATIONAL MAGNETIC FIELD STANDARD IN CROATIA A. Pavić 1, L.Ferović,
n IMEKO TC 11 International Symposium METROLOGICAL INFRASTRUCTURE June 15-17, 11, Cavtat, Dubrovni Riviera, Croatia PREPARATION OF THE NATIONAL MAGNETIC FIELD STANDARD IN CROATIA A. Pavić 1, L.Ferović,
19 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Ordinary Differential Equations, and Control
 19 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Orinary Differential Equations, an Control This section introuces eigenvalues an eigenvectors of a matrix, an iscusses the role of the eigenvalues in etermining the behavior
19 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Orinary Differential Equations, an Control This section introuces eigenvalues an eigenvectors of a matrix, an iscusses the role of the eigenvalues in etermining the behavior
Thermal conductivity of graded composites: Numerical simulations and an effective medium approximation
 JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 34 (999)5497 5503 Thermal conuctivity of grae composites: Numerical simulations an an effective meium approximation P. M. HUI Department of Physics, The Chinese University
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 34 (999)5497 5503 Thermal conuctivity of grae composites: Numerical simulations an an effective meium approximation P. M. HUI Department of Physics, The Chinese University
12.5. Differentiation of vectors. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Differentiation of vectors 12.5 Introuction The area known as vector calculus is use to moel mathematically a vast range of engineering phenomena incluing electrostatics, electromagnetic fiels, air flow
Differentiation of vectors 12.5 Introuction The area known as vector calculus is use to moel mathematically a vast range of engineering phenomena incluing electrostatics, electromagnetic fiels, air flow
6. Friction and viscosity in gasses
 IR2 6. Friction an viscosity in gasses 6.1 Introuction Similar to fluis, also for laminar flowing gases Newtons s friction law hols true (see experiment IR1). Using Newton s law the viscosity of air uner
IR2 6. Friction an viscosity in gasses 6.1 Introuction Similar to fluis, also for laminar flowing gases Newtons s friction law hols true (see experiment IR1). Using Newton s law the viscosity of air uner
Quantum Search on the Spatial Grid
 Quantum Search on the Spatial Gri Matthew D. Falk MIT 2012, 550 Memorial Drive, Cambrige, MA 02139 (Date: December 11, 2012) This paper explores Quantum Search on the two imensional spatial gri. Recent
Quantum Search on the Spatial Gri Matthew D. Falk MIT 2012, 550 Memorial Drive, Cambrige, MA 02139 (Date: December 11, 2012) This paper explores Quantum Search on the two imensional spatial gri. Recent
MATH2231-Differentiation (2)
 -Differentiation () The Beginnings of Calculus The prime occasion from which arose my iscovery of the metho of the Characteristic Triangle, an other things of the same sort, happene at a time when I ha
-Differentiation () The Beginnings of Calculus The prime occasion from which arose my iscovery of the metho of the Characteristic Triangle, an other things of the same sort, happene at a time when I ha
Vectors in two dimensions
 Vectors in two imensions Until now, we have been working in one imension only The main reason for this is to become familiar with the main physical ieas like Newton s secon law, without the aitional complication
Vectors in two imensions Until now, we have been working in one imension only The main reason for this is to become familiar with the main physical ieas like Newton s secon law, without the aitional complication
Problem 1 (20 points)
 ME 309 Fall 01 Exam 1 Name: C Problem 1 0 points Short answer questions. Each question is worth 5 points. Don t spen too long writing lengthy answers to these questions. Don t use more space than is given.
ME 309 Fall 01 Exam 1 Name: C Problem 1 0 points Short answer questions. Each question is worth 5 points. Don t spen too long writing lengthy answers to these questions. Don t use more space than is given.
To understand how scrubbers work, we must first define some terms.
 SRUBBERS FOR PARTIE OETION Backgroun To unerstan how scrubbers work, we must first efine some terms. Single roplet efficiency, η, is similar to single fiber efficiency. It is the fraction of particles
SRUBBERS FOR PARTIE OETION Backgroun To unerstan how scrubbers work, we must first efine some terms. Single roplet efficiency, η, is similar to single fiber efficiency. It is the fraction of particles
Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm
 Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm 1. Maxwell s Equations Quasi-statics o a An air core, N turn, cylinrical solenoi of length an raius a, carries a current I Io cos t. a. Using Ampere s Law, etermine
Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm 1. Maxwell s Equations Quasi-statics o a An air core, N turn, cylinrical solenoi of length an raius a, carries a current I Io cos t. a. Using Ampere s Law, etermine
Introduction to Mechanics Work and Energy
 Introuction to Mechanics Work an Energy Lana Sherian De Anza College Mar 15, 2018 Last time non-uniform circular motion an tangential acceleration energy an work Overview energy work a more general efinition
Introuction to Mechanics Work an Energy Lana Sherian De Anza College Mar 15, 2018 Last time non-uniform circular motion an tangential acceleration energy an work Overview energy work a more general efinition
1 Definition of the derivative
 Math 20A - Calculus by Jon Rogawski Chapter 3 - Differentiation Prepare by Jason Gais Definition of the erivative Remark.. Recall our iscussion of tangent lines from way back. We now rephrase this in terms
Math 20A - Calculus by Jon Rogawski Chapter 3 - Differentiation Prepare by Jason Gais Definition of the erivative Remark.. Recall our iscussion of tangent lines from way back. We now rephrase this in terms
1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Electrostatics 1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity. A soli conucting sphere is given a positive charge Q.
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Electrostatics 1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity. A soli conucting sphere is given a positive charge Q.
Math Notes on differentials, the Chain Rule, gradients, directional derivative, and normal vectors
 Math 18.02 Notes on ifferentials, the Chain Rule, graients, irectional erivative, an normal vectors Tangent plane an linear approximation We efine the partial erivatives of f( xy, ) as follows: f f( x+
Math 18.02 Notes on ifferentials, the Chain Rule, graients, irectional erivative, an normal vectors Tangent plane an linear approximation We efine the partial erivatives of f( xy, ) as follows: f f( x+
05 The Continuum Limit and the Wave Equation
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Founations of Wave Phenomena Physics, Department of 1-1-2004 05 The Continuum Limit an the Wave Equation Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University,
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Founations of Wave Phenomena Physics, Department of 1-1-2004 05 The Continuum Limit an the Wave Equation Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University,
Angles-Only Orbit Determination Copyright 2006 Michel Santos Page 1
 Angles-Only Orbit Determination Copyright 6 Michel Santos Page 1 Abstract This ocument presents a re-erivation of the Gauss an Laplace Angles-Only Methos for Initial Orbit Determination. It keeps close
Angles-Only Orbit Determination Copyright 6 Michel Santos Page 1 Abstract This ocument presents a re-erivation of the Gauss an Laplace Angles-Only Methos for Initial Orbit Determination. It keeps close
Calculus BC Section II PART A A GRAPHING CALCULATOR IS REQUIRED FOR SOME PROBLEMS OR PARTS OF PROBLEMS
 Calculus BC Section II PART A A GRAPHING CALCULATOR IS REQUIRED FOR SOME PROBLEMS OR PARTS OF PROBLEMS. An isosceles triangle, whose base is the interval from (0, 0) to (c, 0), has its verte on the graph
Calculus BC Section II PART A A GRAPHING CALCULATOR IS REQUIRED FOR SOME PROBLEMS OR PARTS OF PROBLEMS. An isosceles triangle, whose base is the interval from (0, 0) to (c, 0), has its verte on the graph
Physics 505 Electricity and Magnetism Fall 2003 Prof. G. Raithel. Problem Set 3. 2 (x x ) 2 + (y y ) 2 + (z + z ) 2
 Physics 505 Electricity an Magnetism Fall 003 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 3 Problem.7 5 Points a): Green s function: Using cartesian coorinates x = (x, y, z), it is G(x, x ) = 1 (x x ) + (y y ) + (z z
Physics 505 Electricity an Magnetism Fall 003 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 3 Problem.7 5 Points a): Green s function: Using cartesian coorinates x = (x, y, z), it is G(x, x ) = 1 (x x ) + (y y ) + (z z
Summary: Differentiation
 Techniques of Differentiation. Inverse Trigonometric functions The basic formulas (available in MF5 are: Summary: Differentiation ( sin ( cos The basic formula can be generalize as follows: Note: ( sin
Techniques of Differentiation. Inverse Trigonometric functions The basic formulas (available in MF5 are: Summary: Differentiation ( sin ( cos The basic formula can be generalize as follows: Note: ( sin
Torque OBJECTIVE INTRODUCTION APPARATUS THEORY
 Torque OBJECTIVE To verify the rotational an translational conitions for equilibrium. To etermine the center of ravity of a rii boy (meter stick). To apply the torque concept to the etermination of an
Torque OBJECTIVE To verify the rotational an translational conitions for equilibrium. To etermine the center of ravity of a rii boy (meter stick). To apply the torque concept to the etermination of an
Ch.7 #4 7,11,12,18 21,24 27
 Ch.7 #4 7,,,8,4 7 4. Picture the Problem: The farmhan pushes the hay horizontally. 88 N Strategy: Multiply the force by the istance because in this case the two point along the same irection. 3.9 m Solution:
Ch.7 #4 7,,,8,4 7 4. Picture the Problem: The farmhan pushes the hay horizontally. 88 N Strategy: Multiply the force by the istance because in this case the two point along the same irection. 3.9 m Solution:
water adding dye partial mixing homogenization time
 iffusion iffusion is a process of mass transport that involves the movement of one atomic species into another. It occurs by ranom atomic jumps from one position to another an takes place in the gaseous,
iffusion iffusion is a process of mass transport that involves the movement of one atomic species into another. It occurs by ranom atomic jumps from one position to another an takes place in the gaseous,
Fluid Pressure and Fluid Force
 SECTION 7.7 Flui Pressure an Flui Force 07 Section 7.7 Flui Pressure an Flui Force Fin flui pressure an flui force. Flui Pressure an Flui Force Swimmers know that the eeper an object is submerge in a flui,
SECTION 7.7 Flui Pressure an Flui Force 07 Section 7.7 Flui Pressure an Flui Force Fin flui pressure an flui force. Flui Pressure an Flui Force Swimmers know that the eeper an object is submerge in a flui,
Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 9
 9A. Vectors an Forces Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 9. F = 5 sin 5.9 an F = 5 cos 5 4.8.. a. By the Pythagorean theorem, the length of the vector from to (, ) is + = 5. So the magnitue of the force
9A. Vectors an Forces Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 9. F = 5 sin 5.9 an F = 5 cos 5 4.8.. a. By the Pythagorean theorem, the length of the vector from to (, ) is + = 5. So the magnitue of the force
cosh x sinh x So writing t = tan(x/2) we have 6.4 Integration using tan(x/2) 2t 1 + t 2 cos x = 1 t2 sin x =
 6.4 Integration using tan/ We will revisit the ouble angle ientities: sin = sin/ cos/ = tan/ sec / = tan/ + tan / cos = cos / sin / tan = = tan / sec / tan/ tan /. = tan / + tan / So writing t = tan/ we
6.4 Integration using tan/ We will revisit the ouble angle ientities: sin = sin/ cos/ = tan/ sec / = tan/ + tan / cos = cos / sin / tan = = tan / sec / tan/ tan /. = tan / + tan / So writing t = tan/ we
Example 1. Examples for walls are available on our Web page: Columns
 Portlan Cement Association Page 1 o 9 Te ollowing examples illustrate te esign metos presente in te article Timesaving Design Ais or Reinorce Concrete, Part 3: an Walls, by Davi A. Fanella, wic appeare
Portlan Cement Association Page 1 o 9 Te ollowing examples illustrate te esign metos presente in te article Timesaving Design Ais or Reinorce Concrete, Part 3: an Walls, by Davi A. Fanella, wic appeare
Related Rates. Introduction. We are familiar with a variety of mathematical or quantitative relationships, especially geometric ones.
 Relate Rates Introuction We are familiar with a variety of mathematical or quantitative relationships, especially geometric ones For example, for the sies of a right triangle we have a 2 + b 2 = c 2 or
Relate Rates Introuction We are familiar with a variety of mathematical or quantitative relationships, especially geometric ones For example, for the sies of a right triangle we have a 2 + b 2 = c 2 or
On Using Unstable Electrohydraulic Valves for Control
 Kailash Krishnaswamy Perry Y. Li Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Minnesota, 111 Church St. SE, Minneapolis, MN 55455 e-mail: kk,pli @me.umn.eu On Using Unstable Electrohyraulic Valves
Kailash Krishnaswamy Perry Y. Li Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Minnesota, 111 Church St. SE, Minneapolis, MN 55455 e-mail: kk,pli @me.umn.eu On Using Unstable Electrohyraulic Valves
Math 11 Fall 2016 Section 1 Monday, September 19, Definition: A vector parametric equation for the line parallel to vector v = x v, y v, z v
 Math Fall 06 Section Monay, September 9, 06 First, some important points from the last class: Definition: A vector parametric equation for the line parallel to vector v = x v, y v, z v passing through
Math Fall 06 Section Monay, September 9, 06 First, some important points from the last class: Definition: A vector parametric equation for the line parallel to vector v = x v, y v, z v passing through
SIMULATION OF POROUS MEDIUM COMBUSTION IN ENGINES
 SIMULATION OF POROUS MEDIUM COMBUSTION IN ENGINES Jan Macek, Miloš Polášek Czech Technical University in Prague, Josef Božek Research Center Introuction Improvement of emissions from reciprocating internal
SIMULATION OF POROUS MEDIUM COMBUSTION IN ENGINES Jan Macek, Miloš Polášek Czech Technical University in Prague, Josef Božek Research Center Introuction Improvement of emissions from reciprocating internal
Math Chapter 2 Essentials of Calculus by James Stewart Prepared by Jason Gaddis
 Math 231 - Chapter 2 Essentials of Calculus by James Stewart Prepare by Jason Gais Chapter 2 - Derivatives 21 - Derivatives an Rates of Change Definition A tangent to a curve is a line that intersects
Math 231 - Chapter 2 Essentials of Calculus by James Stewart Prepare by Jason Gais Chapter 2 - Derivatives 21 - Derivatives an Rates of Change Definition A tangent to a curve is a line that intersects
Schrödinger s equation.
 Physics 342 Lecture 5 Schröinger s Equation Lecture 5 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wenesay, February 3r, 2010 Toay we iscuss Schröinger s equation an show that it supports the basic interpretation of
Physics 342 Lecture 5 Schröinger s Equation Lecture 5 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wenesay, February 3r, 2010 Toay we iscuss Schröinger s equation an show that it supports the basic interpretation of
Solution. ANSWERS - AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Kinematics. Answer
 NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Practice Kinematics Solution nswer 1. Total istance = 60 miles, total time = 1.5 hours; average spee = total istance/total time 2. rea boune by the curve is the isplacement
NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Practice Kinematics Solution nswer 1. Total istance = 60 miles, total time = 1.5 hours; average spee = total istance/total time 2. rea boune by the curve is the isplacement
Lecture 1b. Differential operators and orthogonal coordinates. Partial derivatives. Divergence and divergence theorem. Gradient. A y. + A y y dy. 1b.
 b. Partial erivatives Lecture b Differential operators an orthogonal coorinates Recall from our calculus courses that the erivative of a function can be efine as f ()=lim 0 or using the central ifference
b. Partial erivatives Lecture b Differential operators an orthogonal coorinates Recall from our calculus courses that the erivative of a function can be efine as f ()=lim 0 or using the central ifference
The influence of the equivalent hydraulic diameter on the pressure drop prediction of annular test section
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science an Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The influence of the equivalent hyraulic iameter on the pressure rop preiction of annular test section To cite this article: A
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science an Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The influence of the equivalent hyraulic iameter on the pressure rop preiction of annular test section To cite this article: A
Numerical Integrator. Graphics
 1 Introuction CS229 Dynamics Hanout The question of the week is how owe write a ynamic simulator for particles, rigi boies, or an articulate character such as a human figure?" In their SIGGRPH course notes,
1 Introuction CS229 Dynamics Hanout The question of the week is how owe write a ynamic simulator for particles, rigi boies, or an articulate character such as a human figure?" In their SIGGRPH course notes,
Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan
 Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan 6 Wave equation: solution In this lecture we will solve the wave equation on the entire real line x R. This correspons to a string of infinite
Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan 6 Wave equation: solution In this lecture we will solve the wave equation on the entire real line x R. This correspons to a string of infinite
PH 132 Exam 1 Spring Student Name. Student Number. Lab/Recitation Section Number (11,,36)
 PH 13 Exam 1 Spring 010 Stuent Name Stuent Number ab/ecitation Section Number (11,,36) Instructions: 1. Fill out all of the information requeste above. Write your name on each page.. Clearly inicate your
PH 13 Exam 1 Spring 010 Stuent Name Stuent Number ab/ecitation Section Number (11,,36) Instructions: 1. Fill out all of the information requeste above. Write your name on each page.. Clearly inicate your
4.2 First Differentiation Rules; Leibniz Notation
 .. FIRST DIFFERENTIATION RULES; LEIBNIZ NOTATION 307. First Differentiation Rules; Leibniz Notation In this section we erive rules which let us quickly compute the erivative function f (x) for any polynomial
.. FIRST DIFFERENTIATION RULES; LEIBNIZ NOTATION 307. First Differentiation Rules; Leibniz Notation In this section we erive rules which let us quickly compute the erivative function f (x) for any polynomial
Single Arm, Centrifugal, Water Turbine for Low Head and Low Flow Application: Part 1- Theory and Design
 Energy an Power 2018, 8(2): 51-55 DOI: 10.5923/j.ep.20180802.03 Single Arm, Centrifugal, Water Turbine for Low ea an Low Flow Application: Part 1- Theory an Design Kiplangat C. Kononen 1, Augustine B.
Energy an Power 2018, 8(2): 51-55 DOI: 10.5923/j.ep.20180802.03 Single Arm, Centrifugal, Water Turbine for Low ea an Low Flow Application: Part 1- Theory an Design Kiplangat C. Kononen 1, Augustine B.
PERMANENT MAGNETS CHAPTER MAGNETIC POLES AND BAR MAGNETS
 CHAPTER 6 PERAET AGET 6. AGETIC POLE AD BAR AGET We have seen that a small current-loop carrying a current i, prouces a magnetic fiel B o 4 ji ' at an axial point. Here p ia is the magnetic ipole moment
CHAPTER 6 PERAET AGET 6. AGETIC POLE AD BAR AGET We have seen that a small current-loop carrying a current i, prouces a magnetic fiel B o 4 ji ' at an axial point. Here p ia is the magnetic ipole moment
Recommendations: Part 7: Transient Creep for service and accident conditions
 Materials an Structures/Matériaux et Constructions, Vol. 31, June 1998, pp 290-295 RILEM TECHNICAL COMMITTEES RILEM TC 129-MHT: TEST METHODS FOR MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CONCRETE AT HIGH TEMPERATURES Recommenations:
Materials an Structures/Matériaux et Constructions, Vol. 31, June 1998, pp 290-295 RILEM TECHNICAL COMMITTEES RILEM TC 129-MHT: TEST METHODS FOR MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CONCRETE AT HIGH TEMPERATURES Recommenations:
Exercise 1. Exercise 2.
 Exercise. Magnitue Galaxy ID Ultraviolet Green Re Infrare A Infrare B 9707296462088.56 5.47 5.4 4.75 4.75 97086278435442.6.33 5.36 4.84 4.58 2255030735995063.64.8 5.88 5.48 5.4 56877420209795 9.52.6.54.08
Exercise. Magnitue Galaxy ID Ultraviolet Green Re Infrare A Infrare B 9707296462088.56 5.47 5.4 4.75 4.75 97086278435442.6.33 5.36 4.84 4.58 2255030735995063.64.8 5.88 5.48 5.4 56877420209795 9.52.6.54.08
ME 141. Engineering Mechanics
 ME 141 Engineering Mechanics Lecture : Statics of particles Ahma Shahei Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.b, shakil6791@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.b/sshakil
ME 141 Engineering Mechanics Lecture : Statics of particles Ahma Shahei Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.b, shakil6791@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.b/sshakil
General Data. Types of bearings 6. Standardization and interchangeability 12. Dimensions and part numbers 14. Bearing manufacturing precision 18
 General ata Types of bearings 6 efinitions 6 Vocabulary 8 Capabilities 9 Stanarization an interchangeability 12 The Stanars 12 Interchangeability 12 imensions an part numbers 14 General esignations 14
General ata Types of bearings 6 efinitions 6 Vocabulary 8 Capabilities 9 Stanarization an interchangeability 12 The Stanars 12 Interchangeability 12 imensions an part numbers 14 General esignations 14
2.20 Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 3
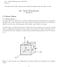 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.7 Stress Tensor 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 1.7.1 Stress Tensor τ ij
2.20 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.7 Stress Tensor 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 1.7.1 Stress Tensor τ ij
Problem Solving 4 Solutions: Magnetic Force, Torque, and Magnetic Moments
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 004 Problem Solving 4 Solutions: Magnetic Force, Torque, an Magnetic Moments OJECTIVES 1. To start with the magnetic force on a moving
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 004 Problem Solving 4 Solutions: Magnetic Force, Torque, an Magnetic Moments OJECTIVES 1. To start with the magnetic force on a moving
Lectures - Week 10 Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations (ODES) First Order Linear ODEs
 Lectures - Week 10 Introuction to Orinary Differential Equations (ODES) First Orer Linear ODEs When stuying ODEs we are consiering functions of one inepenent variable, e.g., f(x), where x is the inepenent
Lectures - Week 10 Introuction to Orinary Differential Equations (ODES) First Orer Linear ODEs When stuying ODEs we are consiering functions of one inepenent variable, e.g., f(x), where x is the inepenent
Placement and tuning of resonance dampers on footbridges
 Downloae from orbit.tu.k on: Jan 17, 19 Placement an tuning of resonance ampers on footbriges Krenk, Steen; Brønen, Aners; Kristensen, Aners Publishe in: Footbrige 5 Publication ate: 5 Document Version
Downloae from orbit.tu.k on: Jan 17, 19 Placement an tuning of resonance ampers on footbriges Krenk, Steen; Brønen, Aners; Kristensen, Aners Publishe in: Footbrige 5 Publication ate: 5 Document Version
Distribution Restriction Statement Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
 CECW-ED Engineer Manual 1110-2-2104 Department of the Army U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 20314-1000 Engineering an Design STRENGTH DESIGN FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES Distribution
CECW-ED Engineer Manual 1110-2-2104 Department of the Army U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 20314-1000 Engineering an Design STRENGTH DESIGN FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES Distribution
ACCELERATION, FORCE, MOMENTUM, ENERGY : solutions to higher level questions
 ACCELERATION, FORCE, MOMENTUM, ENERGY : solutions to higher level questions 015 Question 1 (a) (i) State Newton s secon law of motion. Force is proportional to rate of change of momentum (ii) What is the
ACCELERATION, FORCE, MOMENTUM, ENERGY : solutions to higher level questions 015 Question 1 (a) (i) State Newton s secon law of motion. Force is proportional to rate of change of momentum (ii) What is the
FLUID MECHANICS UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS. May/June Examination for the degree of. BEng/ MEng Civil Engineering. Time allowed: 2 hours
 This question paper consists of printe pages, each of which is ientifie by the Coe Number CIVE 4 UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS May/June Examination for the egree of BEng/ MEng Civil Engineering FLUID MECANICS Time
This question paper consists of printe pages, each of which is ientifie by the Coe Number CIVE 4 UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS May/June Examination for the egree of BEng/ MEng Civil Engineering FLUID MECANICS Time
INTRODUCTION & PHASE SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION & PHASE SYSTEM Dr. Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 1.1 Geotechnical Engineering Why? 1. We are unable to buil castles in air (yet)! 2. Almost every structure
INTRODUCTION & PHASE SYSTEM Dr. Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 1.1 Geotechnical Engineering Why? 1. We are unable to buil castles in air (yet)! 2. Almost every structure
Final Exam Study Guide and Practice Problems Solutions
 Final Exam Stuy Guie an Practice Problems Solutions Note: These problems are just some of the types of problems that might appear on the exam. However, to fully prepare for the exam, in aition to making
Final Exam Stuy Guie an Practice Problems Solutions Note: These problems are just some of the types of problems that might appear on the exam. However, to fully prepare for the exam, in aition to making
Automobile manual transmission
 Design of Shaft A shaft is a rotating member usually of circular crosssection (soli or hollow), which is use to transmit power an rotational motion. Axles are non rotating member. Elements such as gears,
Design of Shaft A shaft is a rotating member usually of circular crosssection (soli or hollow), which is use to transmit power an rotational motion. Axles are non rotating member. Elements such as gears,
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2017 Official Lecture Notes Note 13
 EES 6A Designing Information Devices an Systems I Spring 27 Official Lecture Notes Note 3 Touchscreen Revisite We ve seen how a resistive touchscreen works by using the concept of voltage iviers. Essentially,
EES 6A Designing Information Devices an Systems I Spring 27 Official Lecture Notes Note 3 Touchscreen Revisite We ve seen how a resistive touchscreen works by using the concept of voltage iviers. Essentially,
Additional Exercises for Chapter 10
 Aitional Eercises for Chapter 0 About the Eponential an Logarithm Functions 6. Compute the area uner the graphs of i. f() =e over the interval [ 3, ]. ii. f() =e over the interval [, 4]. iii. f() = over
Aitional Eercises for Chapter 0 About the Eponential an Logarithm Functions 6. Compute the area uner the graphs of i. f() =e over the interval [ 3, ]. ii. f() =e over the interval [, 4]. iii. f() = over
APPROXIMATE SOLUTION FOR TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSFER IN STATIC TURBULENT HE II. B. Baudouy. CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/STCM Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France
 APPROXIMAE SOLUION FOR RANSIEN HEA RANSFER IN SAIC URBULEN HE II B. Bauouy CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/SCM 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Ceex, France ABSRAC Analytical solution in one imension of the heat iffusion equation
APPROXIMAE SOLUION FOR RANSIEN HEA RANSFER IN SAIC URBULEN HE II B. Bauouy CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/SCM 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Ceex, France ABSRAC Analytical solution in one imension of the heat iffusion equation
Tutorial 1 Differentiation
 Tutorial 1 Differentiation What is Calculus? Calculus 微積分 Differential calculus Differentiation 微分 y lim 0 f f The relation of very small changes of ifferent quantities f f y y Integral calculus Integration
Tutorial 1 Differentiation What is Calculus? Calculus 微積分 Differential calculus Differentiation 微分 y lim 0 f f The relation of very small changes of ifferent quantities f f y y Integral calculus Integration
Linear First-Order Equations
 5 Linear First-Orer Equations Linear first-orer ifferential equations make up another important class of ifferential equations that commonly arise in applications an are relatively easy to solve (in theory)
5 Linear First-Orer Equations Linear first-orer ifferential equations make up another important class of ifferential equations that commonly arise in applications an are relatively easy to solve (in theory)
Study on aero-acoustic structural interactions in fan-ducted system
 Stuy on aero-acoustic structural interactions in fan-ucte system Yan-kei CHIANG 1 ; Yat-sze CHOY ; Li CHENG 3 ; Shiu-keung TANG 4 1,, 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University,
Stuy on aero-acoustic structural interactions in fan-ucte system Yan-kei CHIANG 1 ; Yat-sze CHOY ; Li CHENG 3 ; Shiu-keung TANG 4 1,, 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University,
A 3D SEDIMENT TRANSPORT MODEL FOR COMBINED WAVE-CURRENT FLOWS
 A 3D SEDIMENT TRANSPORT MODEL FOR COMBINED WAVE-CURRENT FLOWS Peifeng Ma 1 an Ole Secher Masen Accurate preiction of current velocity an bottom shear stress, which both can be significantly influence by
A 3D SEDIMENT TRANSPORT MODEL FOR COMBINED WAVE-CURRENT FLOWS Peifeng Ma 1 an Ole Secher Masen Accurate preiction of current velocity an bottom shear stress, which both can be significantly influence by
Construction of the Electronic Radial Wave Functions and Probability Distributions of Hydrogen-like Systems
 Construction of the Electronic Raial Wave Functions an Probability Distributions of Hyrogen-like Systems Thomas S. Kuntzleman, Department of Chemistry Spring Arbor University, Spring Arbor MI 498 tkuntzle@arbor.eu
Construction of the Electronic Raial Wave Functions an Probability Distributions of Hyrogen-like Systems Thomas S. Kuntzleman, Department of Chemistry Spring Arbor University, Spring Arbor MI 498 tkuntzle@arbor.eu
θ x = f ( x,t) could be written as
 9. Higher orer PDEs as systems of first-orer PDEs. Hyperbolic systems. For PDEs, as for ODEs, we may reuce the orer by efining new epenent variables. For example, in the case of the wave equation, (1)
9. Higher orer PDEs as systems of first-orer PDEs. Hyperbolic systems. For PDEs, as for ODEs, we may reuce the orer by efining new epenent variables. For example, in the case of the wave equation, (1)
Gyroscopic matrices of the right beams and the discs
 Titre : Matrice gyroscopique es poutres roites et es i[...] Date : 15/07/2014 Page : 1/16 Gyroscopic matrices of the right beams an the iscs Summary: This ocument presents the formulation of the matrices
Titre : Matrice gyroscopique es poutres roites et es i[...] Date : 15/07/2014 Page : 1/16 Gyroscopic matrices of the right beams an the iscs Summary: This ocument presents the formulation of the matrices
Both the ASME B and the draft VDI/VDE 2617 have strengths and
 Choosing Test Positions for Laser Tracker Evaluation an Future Stanars Development ala Muralikrishnan 1, Daniel Sawyer 1, Christopher lackburn 1, Steven Phillips 1, Craig Shakarji 1, E Morse 2, an Robert
Choosing Test Positions for Laser Tracker Evaluation an Future Stanars Development ala Muralikrishnan 1, Daniel Sawyer 1, Christopher lackburn 1, Steven Phillips 1, Craig Shakarji 1, E Morse 2, an Robert
Chapter 2 Lagrangian Modeling
 Chapter 2 Lagrangian Moeling The basic laws of physics are use to moel every system whether it is electrical, mechanical, hyraulic, or any other energy omain. In mechanics, Newton s laws of motion provie
Chapter 2 Lagrangian Moeling The basic laws of physics are use to moel every system whether it is electrical, mechanical, hyraulic, or any other energy omain. In mechanics, Newton s laws of motion provie
Math 1271 Solutions for Fall 2005 Final Exam
 Math 7 Solutions for Fall 5 Final Eam ) Since the equation + y = e y cannot be rearrange algebraically in orer to write y as an eplicit function of, we must instea ifferentiate this relation implicitly
Math 7 Solutions for Fall 5 Final Eam ) Since the equation + y = e y cannot be rearrange algebraically in orer to write y as an eplicit function of, we must instea ifferentiate this relation implicitly
Sph4c Chapter 2 Simple Machines LoRusso
 Sph4c Chapter Simple Machines orusso Machine: A machine is any evice that helps us perform a task. hey are esigne to achieve at least one of five main functions Change energy from one form to another.
Sph4c Chapter Simple Machines orusso Machine: A machine is any evice that helps us perform a task. hey are esigne to achieve at least one of five main functions Change energy from one form to another.
R is the radius of the sphere and v is the sphere s secular velocity. The
 Chapter. Thermal energy: a minnow, an E. Coli an ubiquinone a) Consier a minnow using its fins to swim aroun in water. The minnow must o work against the viscosity of the water in orer to make progress.
Chapter. Thermal energy: a minnow, an E. Coli an ubiquinone a) Consier a minnow using its fins to swim aroun in water. The minnow must o work against the viscosity of the water in orer to make progress.
Paper ID:63, Page 1 TORQUE RESEARCH OF SINGLE SCREW EXPANDERS ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Paper ID:63, Page 1 TORQUE RESEARCH OF SINGLE SCREW EXPANDERS Ruiping Zhi 1 *, Yuting Wu 1, Yeqiang Zhang 1, Biao Lei, Wei Wang 1, Guoqiang Li 1 an Chongfang Ma 1 Key Laboratory of Enhance Heat Transfer
Paper ID:63, Page 1 TORQUE RESEARCH OF SINGLE SCREW EXPANDERS Ruiping Zhi 1 *, Yuting Wu 1, Yeqiang Zhang 1, Biao Lei, Wei Wang 1, Guoqiang Li 1 an Chongfang Ma 1 Key Laboratory of Enhance Heat Transfer
Calculus I Sec 2 Practice Test Problems for Chapter 4 Page 1 of 10
 Calculus I Sec 2 Practice Test Problems for Chapter 4 Page 1 of 10 This is a set of practice test problems for Chapter 4. This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems
Calculus I Sec 2 Practice Test Problems for Chapter 4 Page 1 of 10 This is a set of practice test problems for Chapter 4. This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems
Situation awareness of power system based on static voltage security region
 The 6th International Conference on Renewable Power Generation (RPG) 19 20 October 2017 Situation awareness of power system base on static voltage security region Fei Xiao, Zi-Qing Jiang, Qian Ai, Ran
The 6th International Conference on Renewable Power Generation (RPG) 19 20 October 2017 Situation awareness of power system base on static voltage security region Fei Xiao, Zi-Qing Jiang, Qian Ai, Ran
The Long Span Problem in the Analysis of Conductor Vibration Damping
 770 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 5, NO., APRIL 000 The Long Span Problem in the Analysis of Conuctor Vibration Damping Charles B. Rawlins, Fellow, IEEE Abstract In analysis of vibration amping
770 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 5, NO., APRIL 000 The Long Span Problem in the Analysis of Conuctor Vibration Damping Charles B. Rawlins, Fellow, IEEE Abstract In analysis of vibration amping
American Society of Agricultural Engineers PAPER NO PRAIRIE RAINFALL,CHARACTERISTICS
 - PAPER NO. 79-2108 PRAIRIE RAINFALL,CHARACTERISTICS G.E. Dyck an D.M. Gray Research Engineer an Chairman Division of Hyrology University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canaa For presentation
- PAPER NO. 79-2108 PRAIRIE RAINFALL,CHARACTERISTICS G.E. Dyck an D.M. Gray Research Engineer an Chairman Division of Hyrology University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canaa For presentation
d dx But have you ever seen a derivation of these results? We ll prove the first result below. cos h 1
 Lecture 5 Some ifferentiation rules Trigonometric functions (Relevant section from Stewart, Seventh Eition: Section 3.3) You all know that sin = cos cos = sin. () But have you ever seen a erivation of
Lecture 5 Some ifferentiation rules Trigonometric functions (Relevant section from Stewart, Seventh Eition: Section 3.3) You all know that sin = cos cos = sin. () But have you ever seen a erivation of
1.2 - Stress Tensor Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 3
 13.021 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2004 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.2 - Stress Tensor 13.021 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 Stress Tensor τ ij:. The
13.021 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2004 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.2 - Stress Tensor 13.021 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 Stress Tensor τ ij:. The
Some vector algebra and the generalized chain rule Ross Bannister Data Assimilation Research Centre, University of Reading, UK Last updated 10/06/10
 Some vector algebra an the generalize chain rule Ross Bannister Data Assimilation Research Centre University of Reaing UK Last upate 10/06/10 1. Introuction an notation As we shall see in these notes the
Some vector algebra an the generalize chain rule Ross Bannister Data Assimilation Research Centre University of Reaing UK Last upate 10/06/10 1. Introuction an notation As we shall see in these notes the
