Chapter 5: Measurement of Circles
|
|
|
- Audrey Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5: Measurement of Circles Getting Started, p a) Perimeter, since the word around is used. b) Area, since since the word wrap is used. c) Perimeter, since the word wrap is used. 2. a) 5 cm < 5 m c) m = 1000 mm b) 1 m = 100 cm d) 13 km > 130 m 3. a) perimeter = 4 18 mm = 72 mm area = 18 mm 18 mm = 324 mm 2 b) perimeter = 2 8 m m = 20 m area = 8 m 2 m = 16 m 2 c) perimeter = 5.0 cm cm cm = 18.8 cm area = (5.0 cm 6.0 cm) 2 = 15.0 cm 2 d) perimeter = 12.3 cm cm cm = 29.5 cm area = (6.0 cm 12.3 cm) 2 = 36.9 cm 2 4. perimeter = cm cm = 23.4 cm area = 4.1 cm 7.2 cm = 29.5 cm 2 5. a) For example, the larger rectangle is 3.0 m by 14.1 m, so its area is 3.0 m 14.1 m = 42.3 m 2. The smaller rectangle is 2.0 m by 5.1 m, so its area is 2.0 m 5.1 m = 10.2 m m m 2 The total area is 42.3 m m 2 = 52.5 m 2. b) For example, the larger rectangle is 8.5 m by 3.5 m. Its area is 8.5 m 3.5 m = 29.8 m 2. The smaller rectangle is 4.5 m by 2.0 m. Its area is 4.5 m 2.0 m = 9.0 m m 4.5 m 9.0 m m2 8.5 m 3.5 m The total area is 9.0 m m 2 = 38.8 m 2. c) The large rectangle is 7.0 m 14.0 m. Its area is 7.0 m 14.0 m = 98.0 m 2. The right triangle has a height of 4.0 m and a base of 5.4 m. Its area is (7.0 m 14.0 m) 2 = 10.8 m m mm 2 2 The total area is 98.0 cm cm 2 = m area = (base height) 2 6 cm 2 = (4 cm h) 2 6 cm 2 = 2 cm h 3 cm = h The height of the triangle is 3 cm. 5.3 Calculating Circumference, pp a) C = d cm 16 cm b) C = d cm 14.8 cm 5. a) C = 2 r cm 62.8 cm 63 cm Nelson Mathematics 8 Solutions Manual 5-1
2 b) C = 2 r = m 51.5 m 6. Multiply each diameter by a) C = d cm 14.1 cm b) C = d cm 5.3 cm c) C = d cm 20.1 cm d) C = d m m e) C = d mm 22 mm f) C = d cm 12.6 cm 7. Double each radius to find the diameter, and then multiply the diameter by a) C = 2 r mm 44 mm b) C = 2 r cm cm c) C = 2 r cm 39.6 cm d) C = 2 r cm 56.5 cm e) C = 2 r m m f) C = 2 r m 0.31 m 8. C = d 80 cm cm The circumference of the wheel is about 251 cm. 9. a) For example, to draw a circle using a compass, you need know the radius of the circle. The radius is half the diameter, so since the diameter is 11 cm, the radius must be 11 cm 2 = 5.5 cm. Since the radius is 5.5 cm, you can set your compass to 5.5 cm and draw the circle. 11 cm 5.5 cm b) The circumference is cm 35 cm. 10. Since the line forms the diameter, multiply it by to find the length of the chalk line 11.0 m m The chalk line is about 34.5 m long. 11. clock r = 9.0 cm d = 2 r = cm = 18.0 cm C = 2 r cm 56.5 cm round tea bag r = 1.9 cm d = 2 r = cm = 3.8 cm C = 2 d = cm 11.9 cm circle protractor r = 5.9 cm d = 2 r = cm = 11.8 cm = cm 37.1 cm watch r = d 2 = 36 mm 2 = 18 mm d = 36 mm mm 113 mm sewer cover r = d 2 = 62 cm 2 = 31 cm d = 62 cm cm 195 cm electric fan r = d 2 = 201 mm mm d = 201 mm mm 631 mm 12. The 700 m forms the radius of the circle. So, circumference = 2 r = (2 700 m) m About 4396 m of fencing is needed to enclose the field. 5-2 Chapter 5: Measurement of Circles
3 13. The m is the circumference, which means that the diameter is m m and the radius is half of this, or 6.25 m. The lifeguard must walk 6.25 m from the edge to the centre of the pool. 14. The wheel with a diameter of cm has a circumference of cm cm. The wheel with a diameter of cm has a circumference of cm cm. The difference in circumference is cm cm = 94.2 cm. 15. Since the diameter of each circle is about 9.0 m, the circumference is m. There are 5 circles, so the total length is m = m. 16. diameter of large circle = circumference 37.7 cm cm diameter of large circle diameter of small circle = 12.0 cm 1.5 cm = 10.5 cm distance from outside edge to inside edge = 10.5 cm cm 17. C = d m 28.9 m 18. a) For example, about how far does Earth travel in space every year? Since the radius of orbit is about km, the diameter of orbit must be twice as large, or km. The circumference of the orbit is about 3.14 ( km) km. b) For example, how far has the tire rolled? For each complete rotation, the tire will move a distance equal to its circumference, or cm cm. Since every turn it rolls cm, in 15 turns it will roll cm = cm. 19. Notice that the length of the label is the same as the circumference of the lid. Use 4.0 cm as the diameter and calculate the circumference of the lid. 4.0 cm cm The soup label is about 12.6 cm by 10.0 cm. 20. Separate the perimeter into two parts: two semicircles (or a full circle) of radius 21.7 m, and two straight sections of lengths 56.8 m. The circumference of the full circle is C = d ( m) m The combined length of the straight sections is l = m = m total distance around the track = circumference of circle + length of straight section m m m 21. The red arc is half of the circumference of a circle with the larger diameter. Since the circumference of a circle doubles when the diameter doubles, half of the circumference of the red semi-circle will be equal to the whole circumference of the blue circle. This can be verified algebraically: red arc = larger diameter 2 The larger diameter is equal to twice the smaller diameter, so, red arc = 2 smaller diameter 2 = 2 smaller diameter 2 = smaller diameter = blue circumference The red arc and the blue circle are the same length. Mid-Chapter Review, p radius chord circumference arc diameter 2. From shortest to longest: radius, diameter, circumference. The circumference is about 3.14 times the diameter, which in turn is twice the radius. circumference diameter radius radius diameter circumference 3. An estimate for the circumference of the circle is C 3 3 m 9 m 4. For example, a) about 3 25 cm 75 cm b) about 3 11 m 33 m c) about 3 20 cm 60 cm d) about 3 3 km 9 km Nelson Mathematics 8 Solutions Manual 5-3
4 5. CD case d = 2 r = cm = 12.0 cm r = 6.0 cm C = 2 r = cm 37.7 cm coaster d = 9.0 cm r = d 2 = 9.0 cm cm cm 28.3 cm lock d = 26 mm r = d 2 = 26 mm 2 13 mm mm 82 mm coin d = 2 r = cm = 3.8 cm r = 1.9 cm C = 2 d cm 11.9 cm 6. a) C = d 15 cm cm b) C = d 60 cm cm c) C = d 12.5 cm cm d) C = d 17 cm cm e) C = d 44 cm cm f) C = d 20 cm cm 7. If the diameter of a circle is doubled, the circumference also doubles. For example, the circumference is d, so if the diameter is 2.0 cm, then the circumference is about 2.0 cm cm. If the diameter is 4.0 cm, then the circumference is about 4.0 cm cm, or twice 6.3 cm. d = 2.0 cm C = 6.3 cm d = 4.0 cm C = 12.6 cm 5.5 Calculating Area, pp a) area = r (10.5 cm) cm 2 b) area = r (14 cm 2) (7 cm) cm cm 2 c) area = r (13 cm) cm cm 2 d) area = r (2.8 cm 2) (1.4 cm) cm 2 5. a) area = r (7.3 cm 2) (3.65 cm) cm 2 b) area = r (2 cm) 2 13 cm Chapter 5: Measurement of Circles
5 c) area = r (2.7 cm) cm 2 d) area = r (1.7 cm 2) (0.85 cm) cm 2 6. For example, to estimate: the area of the square outside the circle is 7.0 cm 7.0 cm = 49 cm 2. The area of the square inside the circle is 5.0 cm 5.0 cm = 25 cm 2. The area of the circle is about halfway between these, or about 37 cm 2. To calculate: area = (3.5 cm) cm 2 7. a) area of circle = r (2.3 cm 2) cm 2 b) area of section = area of circle cm cm 2 8. a) 3.14 (4.1 cm) cm 2 b) The area of each section is one third of the total area. area of one section 52.8 cm cm 2 9. a) 3.14 (22.0 cm) cm 2 b) The area of each section is one quarter of the total area. area of one section cm cm a) The area of the square is: A = lw 2 = 10.0 m 10.0 m = m 2 b) The area of the circle is: 3.14 (5.0 m) m 2 c) The area of the red area is the difference between the area of the square and the circle. red area = area of square area of circle m m m Use the circumference to determine the radius. Since the circumference is 10.0 cm, the diameter is 10.0 cm cm. The diameter is about 3.2 cm, so the radius is 3.2 cm 2. Use the radius to calculate the area (1.6 cm 2) cm a) The area of the rectangle is 4.0 cm 2.0 cm = 8.0 cm 2. b) The area of the two circles is 2 r 2. A = 2 r (1.0 cm) cm 2 The yellow area is the difference between the area of the rectangle and the circles. So, the yellow area has an area of about 8.0 cm cm cm For example, what area of plastic is needed to make a DVD? Since the large and small diameters are 12.0 cm and 1.5 cm, their radii are 6.0 cm and 0.8 cm. The area of the DVD is the difference in areas between these two circles. Area of outer circle 3.14 (12.0 cm 2) cm 2. Area of hole 3.14 (1.5 cm 2) cm 2 area of DVD = area of outer circle area of hole cm cm cm 2 The area of the DVD is about cm The figure can be separated into two figures, a rectangle and a semicircle. The total area of the figure is the sum of the areas of the rectangle and the semicircle. 5.0 cm 5.0 cm 10.0 cm area of rectangle = length width = 10.0 cm 5.0 cm = 50.0 cm 2 Nelson Mathematics 8 Solutions Manual 5-5
6 area of semicircle = r (5.0 cm) cm 2 total area of figure = area of rectangle + area of semicircle 50.0 cm cm cm The total area of the target is 3.14 (30.0 cm) cm 2 The total target has a radius of 30.0 cm and there are 4 bands of equal width. So the width of each band must be 30.0 cm 4 = 7.5 cm. The area of each band is the difference in areas between the larger and smaller bands. area of small white band = r (7.5 cm ) cm 2 area of small red band = r 2 area of small white band 3.14 (15.0 cm) cm cm cm cm 2 area of large white band = r 2 area of both smaller bands 3.14 (22.5 cm) cm cm cm cm 2 area of large red band = r 2 area of three smaller bands 3.14 (30.0 cm) cm cm cm cm 2 The total area of the red region is the sum of the areas of the two red bands. red area = cm cm 2 = cm a) The total area will be the sum of the area of the square in the middle, plus the area of a full circle with diameter m. The radius of the circle is half of the diameter or m 2 = m. total area of the field = (area of square) + (area of circle) (375.0 m m) (187.5 m) m 2 b) m 2 $1.25/m = $ c) The total perimeter is the sum of the two sides measuring m and the circumference of the circle with diameter m m m m d) m $2.75/m = $ e) Adding both costs for sod and paving stones together, $ $ = $ Solve Problems by Working Backward, pp a) C = 2 r 62.8 cm = 2 r 31.4 cm = r 31.4 cm 3.14 r 10.0 cm r 20.0 cm d 20 cm b) 314 cm r cm 2 r 2 10 cm r 20 cm d 20 cm 5-6 Chapter 5: Measurement of Circles
7 4. Working backward, use the opposite operations. Start with 32. Subtract 12: = 44 Find the opposite: +44 Add 10: 44 + ( 10) = 34 Subtract 12: 34 ( 12) = = 46 The original number is Use the area of the circle to calculate the radius. area of circle = r m r m r m 2 r m r The height of the triangle is equivalent to the diameter of the circle, or m = 10.0 m. 6. a) Use the area to determine the radius of the figure. area of figure = r cm r cm r cm 2 r 2 15 cm r The large circle has a radius of about 15 cm and a diameter of about 30 cm. Since it is divided into three equal sections, each section has a length of about 10 cm. The radius of the small circle is about 10 cm 2 = 5 cm and the radius of the middle circle is about 20 cm 2 = 10 cm. b) circumference of large circle = 2 r cm 94 cm circumference of middle circle = 2 r cm 63 cm circumference of small circle = 2 r cm 31 cm c) Green area = area of small circle = r (5 cm) 2 79 cm 2 Purple area = area of middle circle area of small circle r 2 79 cm 2 (10 cm) cm cm 2 Blue area = area of large circle area of middle circle cm cm 2 7. If she increases the amount of weight that she lifts by 2 kg each week, then by the 10th week, that is, after 9 weeks, 2 kg 9 = 18 kg more than she started out with. Since she is now lifting 120 kg, she must have started out by lifting 120 kg 18 kg = 102 kg. 8. For example, to find the original shape, double the figure 5 times: 9. a) The circle is drawn around the square, so the diagonal of the square is equal to the diameter of the circle. 5.0 m 7.1 m 25 m 2 The square has an area of 25.0 m 2, which means the square has side lengths that measure 25.0 m 2 = 5.0 m. The square is 5.0 m by 5.0 m. By Pythagoras, c 2 = a 2 + b 2 c 2 = (5.0 m) 2 + (5.0 m) 2 c 2 = 50.0 m 2 c 7.1 m The diagonal of this square will be about 7.1 m. b) From part a), you know the diameter of the circle is about 7.1 m. The circumference will be m 22.3 m. 10. i) For example, if the wheel rolls 20.5 m, how many times has it rotated? Since the circumference is m, you need to find out how many times divides Since m m, the wheel has rotated 8 times. Nelson Mathematics 8 Solutions Manual 5-7
8 ii) For example, about how long are the spokes on this bicycle wheel? If the circumference is cm, then the diameter is cm. So, the radius is 40.8 cm, which is also the length of the spokes. iii) For example, if the wheel lies flat on a driveway, how much area does it cover? Since the radius is 40.8 cm, the wheel covers an area of 3.14 (40.8 cm) cm Use the area of the circle covered by the sprinkler to determine the radius. 283 m 2 = r m r 2 90 r 2 9 m r The sprinkler can spray about 9 m. 12. The diameter of the coin is 2.8 cm, so its radius is 2.8 cm 2 = 1.4 cm. The total area of the coin is: 3.14 (1.4 cm) cm 2 area of nickel rim = area of coin area of copper centre 6.2 cm cm cm 2 Chapter Self-Test, p diameter arc chord 6.5 cm 2. a) The amount to cover is required. This is the area. b) This is a space that needs to be covered, so it is area. c) Since it is the border, it is a circumference. d) The frame around is needed, so it is circumference. 3. Divide the diameter by a) C = 2 r km 15.7 km b) C= 2 r cm 163 cm c) C = d cm 9.4 cm d) C = d cm 66 cm 5. a) 3.14 (2 cm) 2 13 cm 2 b) 3.14 (11 cm 2) 2 95 cm 2 c) 3.14 (5.7 cm 2) cm 2 d) 3.14 (6.2 cm) cm 2 6. a) total area = 15.0 m 15.0 m = m 2 b) area of circle = r (7.5 m) m 2 c) area of blue region = total area area of circle m m m 2 7. To determine the area of the orange region, subtract the area of the small circle from the area of the large circle. area of large circle = r (4.5 cm 2) cm 2 radius of small circle = 4.5 cm cm 0.8 cm area of small circle = r (0.8 cm) cm Chapter 5: Measurement of Circles
9 area of orange region = area of large circle area of small circle 15.9 cm cm cm 2 8. Separate the shaded area into two parts. 4.0 cm 8.0 cm The rectangle has an area of 4.0 cm 8.0 cm = 32.0 cm 2. The semicircle has a radius of 4.0 cm. A = r (4.0 cm) cm 2 The total area is about 25.1 cm cm 2 = 57.1 cm a) The area required is the area of the rectangle minus the area of the circle. area of park = area of rectangle area of pool = (l w) ( r 2 ) (6.0 m 14.0 m) 3.14 (2.5 m) m 2 b) The fence will need to be as long as the circumference of the circle with radius 2.5 m, or m 15.7 m. 10. a) area of circle = r cm r cm r 2 36 cm 2 r 2 6 cm r The radius of the circle is 6 cm. Once you know the radius (or diameter), you can draw the circle. 6 cm b) To calculate the diameter of a circle, divide the circumference by. d = C 17.0 cm cm 5.4 cm 11. Use the area to find the radius m 2 = r m r m 2 r m r Now calculate the circumference. C = 2 r m 17.6 m So, 17.6 m of fencing are needed. Chapter Review, p The circle with the radius of 10.0 cm will have a diameter of 20.0 cm, so you can identify both circles by their size. The larger circle (2) has a radius of 10.0 cm and the smaller circle (1) has the diameter of 10.0 cm. 2. The circumference is just over 3 times as long as the diameter. The exact ratio is a special number called (pi). When doing mental math, it is often useful to use 3 as an approximate value of and then round your answer up. When doing calculations, it is useful to approximate the value of to be a) C = 2 r cm 16.3 cm b) C = d cm 94 cm c) C = d km 3.8 km d) C = d cm 26.1 cm 4. Think of the boardwalk as the diameter of the circular wetlands area and the hiking path as its circumference. The length of the hiking path is m 157 m. 5. For example, you can sketch the pool. Draw a square on the outside of the pool that has side lengths the same as the diameter. Estimate the area of this square. Draw a square inside the pool and estimate the area of this square. The area of the pool is about halfway between the areas of the outside square and the inside square. Nelson Mathematics 8 Solutions Manual 5-9
10 6. a) 3.14 (50 km 2) km 2 b) A= r (2 mm) 2 13 mm 2 c) 3.14 (6.5 cm) cm 2 d) A= r (11.0 m 2) m 2 7. The pool s circumference is m, so its diameter is about m m. The radius is half of that, or about 4.00 m. area = r (4.00 m) m 2 8. Every turn of the wheel will move the bicycle forward by a distance equal to its circumference, in this case 197 cm. Calculate the radius. C = 2 r C 2 = r 197 cm 2 = r 31 cm r Use the radius to determine the area covered by the wheel. area covered = r (31 cm) cm 2 9. a) area of square = 12.0 m 12.0 m = m 2 b) area of a quarter circle = r (6.0 m) m 2 c) area of 4 white sections = m 2 = m 2 d) The area of the red region is the area of the square minus the four areas of the white sections. A = m m 2 = 30.8 m a) 5.7 cm b) If the circle has an area of 452 cm 2, then the radius can be determined. area of circle = r cm r cm r cm 2 r 2 12 cm r Once you know the radius (or diameter), you can draw the circle. 12 cm c) d = C 34.5 cm cm 11.0 cm 5-10 Chapter 5: Measurement of Circles
Chapter 8. Chapter 8 Opener. Section 8.1. Big Ideas Math Red Accelerated Worked-Out Solutions 4 7 = = 4 49 = = 39 = = 3 81 = 243
 Chapter 8 Opener Try It Yourself (p. 35). trapezoids. circles Large Perimeter Diameter Small Perimeter Diameter Average of Ratios 3. trapezoid, triangle. triangles 5. rectangle, triangle 6. rectangle,
Chapter 8 Opener Try It Yourself (p. 35). trapezoids. circles Large Perimeter Diameter Small Perimeter Diameter Average of Ratios 3. trapezoid, triangle. triangles 5. rectangle, triangle 6. rectangle,
Angles and Transformations - Ms Buerckner
 Angles and Transformations - Ms Buerckner Question 1 The marked angle is: a revolution a reflex angle Question 2 This rectangle has: four right angles four obtuse angles four acute angles Question 3 Each
Angles and Transformations - Ms Buerckner Question 1 The marked angle is: a revolution a reflex angle Question 2 This rectangle has: four right angles four obtuse angles four acute angles Question 3 Each
CHAPTER 11 AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES
 CHAPTER 11 AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES EXERCISE 45, Page 106 1. Find the angles p and q in diagram (a) below. p = 180-75 = 105 (interior opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal) q = 180-105 - 40 = 35.
CHAPTER 11 AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES EXERCISE 45, Page 106 1. Find the angles p and q in diagram (a) below. p = 180-75 = 105 (interior opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal) q = 180-105 - 40 = 35.
Math Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 7-4.2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the circumference of this circle. Leave π in your answer. 12 m A) m B) m C) m D) 12 m 2.
Math 7-4.2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the circumference of this circle. Leave π in your answer. 12 m A) m B) m C) m D) 12 m 2.
CIRCULAR MEASURE - SECTORS AND SEGMENTS
 Mathematics Revision Guides Circular Measure Page 1 of M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier CIRCULAR MEASURE - SECTORS AND SEGMENTS Version: 3. Date: -10-014 Mathematics
Mathematics Revision Guides Circular Measure Page 1 of M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier CIRCULAR MEASURE - SECTORS AND SEGMENTS Version: 3. Date: -10-014 Mathematics
Section A Labelling Parts of Circles Grade G
 Name: Teacher Assessment Section A Labelling Parts of Grade G 1. Here is a list of words that are connected with circles. centre radius chord diameter circumference tangent Label the four boxes on this
Name: Teacher Assessment Section A Labelling Parts of Grade G 1. Here is a list of words that are connected with circles. centre radius chord diameter circumference tangent Label the four boxes on this
Section 4.2: Radians, Arc Length, and the Area of a Sector
 CHAPTER 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 4.: Radians, Arc Length, and the Area of a Sector Measure of an Angle Formulas for Arc Length and Sector Area Measure of an Angle Degree Measure: 368 SECTION 4.
CHAPTER 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 4.: Radians, Arc Length, and the Area of a Sector Measure of an Angle Formulas for Arc Length and Sector Area Measure of an Angle Degree Measure: 368 SECTION 4.
Real-World Problems: Circles
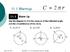
 11.3 Real-World Problems: Circles Lesson Objectives Solve real-world problems involving area and circumference of circles. Solve real-world problems involving semicircles, quadrants, and composite figures.
11.3 Real-World Problems: Circles Lesson Objectives Solve real-world problems involving area and circumference of circles. Solve real-world problems involving semicircles, quadrants, and composite figures.
Park Forest Math Team. Meet #4. Geometry. Self-study Packet
 Park Forest Math Team Meet #4 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : ngle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number Theory:
Park Forest Math Team Meet #4 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : ngle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number Theory:
AREA RELATED TO CIRCLES
 CHAPTER 11 AREA RELATED TO CIRCLES (A) Main Concepts and Results Perimeters and areas of simple closed figures. Circumference and area of a circle. Area of a circular path (i.e., ring). Sector of a circle
CHAPTER 11 AREA RELATED TO CIRCLES (A) Main Concepts and Results Perimeters and areas of simple closed figures. Circumference and area of a circle. Area of a circular path (i.e., ring). Sector of a circle
Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure?
 Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure? 1. Estimate the side length of a square that has a 9 cm long diagonal. 2. Select all quantities that are proportional to the diagonal length of a square. A.
Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure? 1. Estimate the side length of a square that has a 9 cm long diagonal. 2. Select all quantities that are proportional to the diagonal length of a square. A.
1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle.
 Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Skill 3: Multiplication of fractions and decimals. 3.5, 3 times; 1.2, 2.6 times; 4.2, 3.14 times;
 Circle Geometry (not on syllabus) Pre-requisites: Perimeter and Area Direct Proportion Multiplication of Fractions Topics: Parts of a Circle -Vocabulary Relationships between diameter and radius Relationship
Circle Geometry (not on syllabus) Pre-requisites: Perimeter and Area Direct Proportion Multiplication of Fractions Topics: Parts of a Circle -Vocabulary Relationships between diameter and radius Relationship
Algebra Mat: Working Towards Year 6
 Algebra Mat: Working Towards Year 6 at 3 and adds 3 each time. 5, 10, 15, 20, Use simple formulae. The perimeter of a rectangle = a + a + b + b a = a b = 2, cd = 6, find 2 different pairs of numbers for
Algebra Mat: Working Towards Year 6 at 3 and adds 3 each time. 5, 10, 15, 20, Use simple formulae. The perimeter of a rectangle = a + a + b + b a = a b = 2, cd = 6, find 2 different pairs of numbers for
Circles. Parts of a Circle: Vocabulary. Arc : Part of a circle defined by a chord or two radii. It is a part of the whole circumference.
 Page 1 Circles Parts of a Circle: Vocabulary Arc : Part of a circle defined by a chord or two radii. It is a part of the whole circumference. Area of a disc : The measure of the surface of a disc. Think
Page 1 Circles Parts of a Circle: Vocabulary Arc : Part of a circle defined by a chord or two radii. It is a part of the whole circumference. Area of a disc : The measure of the surface of a disc. Think
Integers include positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero. When we add two integers, the sign of the sum depends on the sign of both addends.
 Adding Integers Reteaching 31 Math Course 3, Lesson 31 Integers include positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero. When we add two integers, the sign of the sum depends on the sign of both addends.
Adding Integers Reteaching 31 Math Course 3, Lesson 31 Integers include positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero. When we add two integers, the sign of the sum depends on the sign of both addends.
CIRCLE PROPERTIES M.K. HOME TUITION. Mathematics Revision Guides. Level: GCSE Foundation Tier
 Mathematics Revision Guides Circle Properties Page 1 of 5 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier CIRCLE PROPERTIES Version:.1 Date: 8-10-01 Mathematics Revision Guides
Mathematics Revision Guides Circle Properties Page 1 of 5 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier CIRCLE PROPERTIES Version:.1 Date: 8-10-01 Mathematics Revision Guides
Mid-Chapter Quiz: Lessons 10-1 through Refer to. 1. Name the circle. SOLUTION: The center of the circle is A. Therefore, the circle is ANSWER:
 Refer to. 1. Name the circle. The center of the circle is A. Therefore, the circle is 2. Name a diameter. ; since is a chord that passes through the center, it is a diameter. 3. Name a chord that is not
Refer to. 1. Name the circle. The center of the circle is A. Therefore, the circle is 2. Name a diameter. ; since is a chord that passes through the center, it is a diameter. 3. Name a chord that is not
Name Period Date. GEO2.2: Area of Circles Derive the area formula for circles. Solve application problems that involve areas of circles.
 Name Period Date GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT Student Pages for Packet 2: Circles GEO2.1 Circumference Use multiple representations to explore the relationship between the diameter and the circumference of
Name Period Date GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT Student Pages for Packet 2: Circles GEO2.1 Circumference Use multiple representations to explore the relationship between the diameter and the circumference of
Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure?
 Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure? Let s see how accurately we can measure. 1.1: Estimating a Percentage A student got 16 out of 21 questions correct on a quiz. Use mental estimation to answer
Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure? Let s see how accurately we can measure. 1.1: Estimating a Percentage A student got 16 out of 21 questions correct on a quiz. Use mental estimation to answer
For Exercises 1 4, identify the part of the circle drawn in red as its circumference, diameter, or radius. Then, measure that part in centimeters.
 A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications For Exercises 1 4, identify the part of the circle drawn in red as its circumference, diameter, or radius. Then, measure that part in centimeters.
A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications For Exercises 1 4, identify the part of the circle drawn in red as its circumference, diameter, or radius. Then, measure that part in centimeters.
If x = 180 then the arc subtended by x is a semicircle which we know has length πr. Now we argue that:
 Arclength Consider a circle of radius r and an angle of x degrees as shown in the figure below. The segment of the circle opposite the angle x is called the arc subtended by x. We need a formula for its
Arclength Consider a circle of radius r and an angle of x degrees as shown in the figure below. The segment of the circle opposite the angle x is called the arc subtended by x. We need a formula for its
Curvaceous Circles BUT IT DOES WORK! Yep we can still relate the formula for the area of a circle to the formula for the area of a rectangle
 Curvaceous Circles So our running theme on our worksheets has been that all the formulas for calculating the area of various shapes comes back to relating that shape to a rectangle. But how can that possibly
Curvaceous Circles So our running theme on our worksheets has been that all the formulas for calculating the area of various shapes comes back to relating that shape to a rectangle. But how can that possibly
Introduction Circle Some terms related with a circle
 141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
221 MATH REFRESHER session 3 SAT2015_P06.indd 221 4/23/14 11:39 AM
 Math Refresher Session 3 1 Area, Perimeter, and Volume Problems Area, Perimeter, and Volume 301. Formula Problems. Here, you are given certain data about one or more geometric figures, and you are asked
Math Refresher Session 3 1 Area, Perimeter, and Volume Problems Area, Perimeter, and Volume 301. Formula Problems. Here, you are given certain data about one or more geometric figures, and you are asked
AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES
 HPTER 1 Points to Remember : RES RELTE T IRLES 1. circle is a collection of points which moves in a plane in such a way that its distance from a fixed point always remains the same. The fixed point is
HPTER 1 Points to Remember : RES RELTE T IRLES 1. circle is a collection of points which moves in a plane in such a way that its distance from a fixed point always remains the same. The fixed point is
Pre-Algebra Homework 10 Geometry: Solutions
 Pre-Algebra Homework 10 Geometry: Solutions Use π = 3 for your calculations 1. I am building a ramp. The length of the ramp along the ground is 12 meters and it s 5 meters high and 5 meters wide. I want
Pre-Algebra Homework 10 Geometry: Solutions Use π = 3 for your calculations 1. I am building a ramp. The length of the ramp along the ground is 12 meters and it s 5 meters high and 5 meters wide. I want
Lesson 9. Exit Ticket Sample Solutions ( )= ( ) The arc length of is (. ) or.. Homework Problem Set Sample Solutions S.79
 Exit Ticket Sample Solutions 1. Find the arc length of. ( )= ()() ( )=. ( ) = The arc length of is (. ) or.. Homework Problem Set Sample Solutions S.79 1. and are points on the circle of radius, and the
Exit Ticket Sample Solutions 1. Find the arc length of. ( )= ()() ( )=. ( ) = The arc length of is (. ) or.. Homework Problem Set Sample Solutions S.79 1. and are points on the circle of radius, and the
GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS. Marks shown in brackets for each question (2)
 MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20 Legend used
MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20 Legend used
Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles
 Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles 1. Joe had a bet with Mr. Federer saying that if Federer can solve the following problem in one minute, Joe would be his slave for a whole month. The problem
Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles 1. Joe had a bet with Mr. Federer saying that if Federer can solve the following problem in one minute, Joe would be his slave for a whole month. The problem
Chapter 3: Graphs and Equations CHAPTER 3: GRAPHS AND EQUATIONS. Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
 Chapter 3: Graphs and Equations CHAPTER 3: GRAPHS AND EQUATIONS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Graphs and Equations Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Notes:
Chapter 3: Graphs and Equations CHAPTER 3: GRAPHS AND EQUATIONS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Graphs and Equations Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Notes:
2017 OHMIO Individual Competition
 2017 OHMIO Individual Competition 1. On a winter hike with friends (all of whom were wearing either a scarlet or gray hat), I saw twice as many scarlet hats as gray. That s silly, said a friend. I see
2017 OHMIO Individual Competition 1. On a winter hike with friends (all of whom were wearing either a scarlet or gray hat), I saw twice as many scarlet hats as gray. That s silly, said a friend. I see
Meet #4. Math League SCASD. Self-study Packet. Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets):
 Math League SCASD Meet #4 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : Properties of Circles 3. Number Theory: Modular Arithmetic,
Math League SCASD Meet #4 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : Properties of Circles 3. Number Theory: Modular Arithmetic,
The GED math test gives you a page of math formulas that
 Math Smart 643 The GED Math Formulas The GED math test gives you a page of math formulas that you can use on the test, but just seeing the formulas doesn t do you any good. The important thing is understanding
Math Smart 643 The GED Math Formulas The GED math test gives you a page of math formulas that you can use on the test, but just seeing the formulas doesn t do you any good. The important thing is understanding
Section 3.2 Applications of Radian Measure
 Section. Applications of Radian Measure 07 (continued) 88. 80 radians = = 0 5 5 80 radians = = 00 7 5 = 5 radian s 0 = 0 radian s = radian 80 89. (a) In hours, the hour hand will rotate twice around the
Section. Applications of Radian Measure 07 (continued) 88. 80 radians = = 0 5 5 80 radians = = 00 7 5 = 5 radian s 0 = 0 radian s = radian 80 89. (a) In hours, the hour hand will rotate twice around the
10.1 circles and circumference 2017 ink.notebook. March 13, Page 91. Page 92. Page 90. Ch 10 Circles Circles and Circumference.
 Page 90 Page 91 Page 92 Ch 10 Circles 10.1 Circles and Circumference Lesson Objectives Page 93 Standards Lesson Notes Page 94 10.1 Circles and Circumference Press the tabs to view details. 1 Lesson Objectives
Page 90 Page 91 Page 92 Ch 10 Circles 10.1 Circles and Circumference Lesson Objectives Page 93 Standards Lesson Notes Page 94 10.1 Circles and Circumference Press the tabs to view details. 1 Lesson Objectives
Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2
 Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 Number Use standard form, expressed in standard notation and on a calculator display Calculate with standard form Convert between ordinary and standard form representations
Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 Number Use standard form, expressed in standard notation and on a calculator display Calculate with standard form Convert between ordinary and standard form representations
Example 1 Give the degree measure of the angle shown on the circle.
 Section 5. Angles 307 Section 5. Angles Because many applications involving circles also involve q rotation of the circle, it is natural to introduce a measure for the rotation, or angle, between two rays
Section 5. Angles 307 Section 5. Angles Because many applications involving circles also involve q rotation of the circle, it is natural to introduce a measure for the rotation, or angle, between two rays
Geometry Unit 8 - Notes Perimeter and Area
 Geometry Unit 8 - Notes Perimeter and Area Syllabus Objective: 8. - The student will formulate strategies for finding the perimeter or area of various geometric figures. Review terms: ) area ) perimeter
Geometry Unit 8 - Notes Perimeter and Area Syllabus Objective: 8. - The student will formulate strategies for finding the perimeter or area of various geometric figures. Review terms: ) area ) perimeter
For use only in [your school] Summer 2012 IGCSE-F1-02f-01 Fractions-Addition Addition and Subtraction of Fractions (Without Calculator)
![For use only in [your school] Summer 2012 IGCSE-F1-02f-01 Fractions-Addition Addition and Subtraction of Fractions (Without Calculator) For use only in [your school] Summer 2012 IGCSE-F1-02f-01 Fractions-Addition Addition and Subtraction of Fractions (Without Calculator)](/thumbs/74/71282758.jpg) IGCSE-F1-0f-01 Fractions-Addition Addition and Subtraction of Fractions (Without Calculator) 1. Calculate the following, showing all you working clearly (leave your answers as improper fractions where
IGCSE-F1-0f-01 Fractions-Addition Addition and Subtraction of Fractions (Without Calculator) 1. Calculate the following, showing all you working clearly (leave your answers as improper fractions where
Chapter 7 Sect. 2. A pythagorean triple is a set of three nonzero whole numbers a, b, and c, that satisfy the equation a 2 + b 2 = c 2.
 Chapter 7 Sect. 2 The well-known right triangle relationship called the Pythagorean Theorem is named for Pythagoras, a Greek mathematician who lived in the sixth century b.c. We now know that the Babylonians,
Chapter 7 Sect. 2 The well-known right triangle relationship called the Pythagorean Theorem is named for Pythagoras, a Greek mathematician who lived in the sixth century b.c. We now know that the Babylonians,
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle.
 Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Finding the Midpoint of a Line To work out the midpoint of line we need to find the halfway point Midpoint
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Finding the Midpoint of a Line To work out the midpoint of line we need to find the halfway point Midpoint
The following document was developed by Learning Materials Production, OTEN, DET.
 NOTE CAREFULLY The following document was developed y Learning Materials Production, OTEN, DET. This material does not contain any 3 rd party copyright items. Consequently, you may use this material in
NOTE CAREFULLY The following document was developed y Learning Materials Production, OTEN, DET. This material does not contain any 3 rd party copyright items. Consequently, you may use this material in
Preparing for the CSET. Sample Book. Mathematics
 Preparing for the CSET Sample Book Mathematics by Jeff Matthew Dave Zylstra Preparing for the CSET Sample Book Mathematics We at CSETMath want to thank you for interest in Preparing for the CSET - Mathematics.
Preparing for the CSET Sample Book Mathematics by Jeff Matthew Dave Zylstra Preparing for the CSET Sample Book Mathematics We at CSETMath want to thank you for interest in Preparing for the CSET - Mathematics.
P2 GCSE Maths best-guess paper 2018
 P2 GCSE Maths best-guess paper 2018 Name: Class: Date: Time: 90 minutes Marks: 80 marks This is a predicted paper based on topics that have already come up in P1 Comments: This is a best guess paper and
P2 GCSE Maths best-guess paper 2018 Name: Class: Date: Time: 90 minutes Marks: 80 marks This is a predicted paper based on topics that have already come up in P1 Comments: This is a best guess paper and
RAVEN S CORE MATHEMATICS GRADE 8
 RAVEN S CORE MATHEMATICS GRADE 8 MODIFIED PROGRAM (Designed for the Western Provinces and the Territories) STUDENT GUIDE AND RESOURCE BOOK The Key to Student Success One of a series of publications by
RAVEN S CORE MATHEMATICS GRADE 8 MODIFIED PROGRAM (Designed for the Western Provinces and the Territories) STUDENT GUIDE AND RESOURCE BOOK The Key to Student Success One of a series of publications by
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 17/18/19 October, Angles & Circles
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 17/18/19 October, 2017 Angles & Circles Introduction Circles are an important
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 17/18/19 October, 2017 Angles & Circles Introduction Circles are an important
Answers Investigation 1
 Applications. a. () + () + = tiles b. Possible epressions: + + ( + ) + ( + ) ( + ) + + ( + ) c. See part (b) for some epressions; eplanations will vary. Students might draw sketches. For eample: + + (
Applications. a. () + () + = tiles b. Possible epressions: + + ( + ) + ( + ) ( + ) + + ( + ) c. See part (b) for some epressions; eplanations will vary. Students might draw sketches. For eample: + + (
Wheels Radius / Distance Traveled
 Mechanics Teacher Note to the teacher On these pages, students will learn about the relationships between wheel radius, diameter, circumference, revolutions and distance. Students will use formulas relating
Mechanics Teacher Note to the teacher On these pages, students will learn about the relationships between wheel radius, diameter, circumference, revolutions and distance. Students will use formulas relating
( ) = 28. 2r = d 2 = = r d = r. 2 = r or 1. Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 33! page 1. Lesson 33 Formulas for Circles
 Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 33! page 1 Lesson 33 Formulas for Circles What is a Circle? Everyone knows what a circle looks like. A sprinkler line rotates around a center pivot, forming circles of irrigated
Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 33! page 1 Lesson 33 Formulas for Circles What is a Circle? Everyone knows what a circle looks like. A sprinkler line rotates around a center pivot, forming circles of irrigated
Circle Theorems. Angles at the circumference are equal. The angle in a semi-circle is x The angle at the centre. Cyclic Quadrilateral
 The angle in a semi-circle is 90 0 Angles at the circumference are equal. A B They must come from the same arc. Look out for a diameter. 2x Cyclic Quadrilateral Opposite angles add up to 180 0 A They must
The angle in a semi-circle is 90 0 Angles at the circumference are equal. A B They must come from the same arc. Look out for a diameter. 2x Cyclic Quadrilateral Opposite angles add up to 180 0 A They must
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry
 Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
Regents Exam Questions by Topic Page 1 ANGLES: Arc Length NAME:
 Regents Exam Questions by Topic Page 1 1. 010725b As shown in the accompanying diagram, a dial in the shape of a semicircle has a radius of 4 centimeters. Find the measure of, in radians, when the pointer
Regents Exam Questions by Topic Page 1 1. 010725b As shown in the accompanying diagram, a dial in the shape of a semicircle has a radius of 4 centimeters. Find the measure of, in radians, when the pointer
Math is Cool Masters
 Sponsored by: GENIE Industries 7 th Grade November 19, 2005 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round
Sponsored by: GENIE Industries 7 th Grade November 19, 2005 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round
AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES Introduction
 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 3 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 1 1.1 Introduction You are already familiar with some methods of finding perimeters and areas of simple plane figures such as rectangles, squares, parallelograms,
AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 3 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES 1 1.1 Introduction You are already familiar with some methods of finding perimeters and areas of simple plane figures such as rectangles, squares, parallelograms,
Circles Unit Test. Secondary Math II
 Circles Unit Test Secondary Math II 1. Which pair of circles described are congruent to each other? Circle M has a radius of 6 m; Circle N has a diameter of 10 m. Circle J has a circumference of in; Circle
Circles Unit Test Secondary Math II 1. Which pair of circles described are congruent to each other? Circle M has a radius of 6 m; Circle N has a diameter of 10 m. Circle J has a circumference of in; Circle
Assignment Assigned Date Due Date Grade 6.7 Worksheet
 Geometry Unit 6: Packet 2 CIRCLES This is a packet containing the homework and some classwork for the second half of unit 6. You will turn in completed assignments by their designated due date. If you
Geometry Unit 6: Packet 2 CIRCLES This is a packet containing the homework and some classwork for the second half of unit 6. You will turn in completed assignments by their designated due date. If you
Downloaded from AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES
 AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES #,&#,&#!#'&*(#6$&#)(,,#&()!,&&!!&###&#%#&#&.,.&#$#*&.*- 1. In the adjoining figure ABC right angled triangle right angled at A. Semi circles are drawn on the sides of the triangle
AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES #,&#,&#!#'&*(#6$&#)(,,#&()!,&&!!&###&#%#&#&.,.&#$#*&.*- 1. In the adjoining figure ABC right angled triangle right angled at A. Semi circles are drawn on the sides of the triangle
Date: Math 7 Final Exam Review Name:
 Specific Outcome Achievement Indicators Chapter Got it?? the Solve a given problem involving the addition of two or more decimal numbers. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals
Specific Outcome Achievement Indicators Chapter Got it?? the Solve a given problem involving the addition of two or more decimal numbers. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals
Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA123 exams.
 Word problems Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA3 exams. Max-min problems []. A field has the shape of a rectangle with
Word problems Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA3 exams. Max-min problems []. A field has the shape of a rectangle with
AP Physics 1 Lesson 15.a Rotational Kinematics Graphical Analysis and Kinematic Equation Use. Name. Date. Period. Engage
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 15.a Rotational Kinematics Graphical Analysis and Kinematic Equation Use Name Outcomes Date Interpret graphical evidence of angular motion (uniform speed & uniform acceleration). Apply
AP Physics 1 Lesson 15.a Rotational Kinematics Graphical Analysis and Kinematic Equation Use Name Outcomes Date Interpret graphical evidence of angular motion (uniform speed & uniform acceleration). Apply
High School Math Contest
 High School Math Contest University of South Carolina February 4th, 017 Problem 1. If (x y) = 11 and (x + y) = 169, what is xy? (a) 11 (b) 1 (c) 1 (d) 4 (e) 48 Problem. Suppose the function g(x) = f(x)
High School Math Contest University of South Carolina February 4th, 017 Problem 1. If (x y) = 11 and (x + y) = 169, what is xy? (a) 11 (b) 1 (c) 1 (d) 4 (e) 48 Problem. Suppose the function g(x) = f(x)
High School Math Contest
 High School Math Contest University of South Carolina February th, 017 Problem 1. If (x y) = 11 and (x + y) = 169, what is xy? (a) 11 (b) 1 (c) 1 (d) (e) 8 Solution: Note that xy = (x + y) (x y) = 169
High School Math Contest University of South Carolina February th, 017 Problem 1. If (x y) = 11 and (x + y) = 169, what is xy? (a) 11 (b) 1 (c) 1 (d) (e) 8 Solution: Note that xy = (x + y) (x y) = 169
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 2: Methods 2 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Tuesday 21 June 2011 Morning
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 2: Methods 2 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Tuesday 21 June 2011 Morning
Eureka Math. Grade, Module. Student _B Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Eureka Math Grade, Module Student _B Contains Sprint and Fluency,, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. All rights reserved. No part
A Story of Eureka Math Grade, Module Student _B Contains Sprint and Fluency,, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. All rights reserved. No part
End Of Term 2 Revision Sheet
 Egyptian British International School Math Department Name:. Year (8..) End Of Term 2 Revision Sheet * Answer The following questions after revising your classwork copybook, course book, homework book
Egyptian British International School Math Department Name:. Year (8..) End Of Term 2 Revision Sheet * Answer The following questions after revising your classwork copybook, course book, homework book
Math 5 Trigonometry Review Sheet for Chapter 5
 Math 5 Trigonometry Review Sheet for Chapter 5 Key Ideas: Def: Radian measure of an angle is the ratio of arclength subtended s by that central angle to the radius of the circle: θ s= rθ r 180 = π radians.
Math 5 Trigonometry Review Sheet for Chapter 5 Key Ideas: Def: Radian measure of an angle is the ratio of arclength subtended s by that central angle to the radius of the circle: θ s= rθ r 180 = π radians.
The shaded shape has an area of 3 hexagons and a perimeter of 14 cm.
 1 Here is a grid of regular hexagons. The shaded shape has an area of 3 hexagons and a perimeter of 14 cm. Draw another shape on the grid which has an area of 4 hexagons and a perimeter of 14 cm. 1 mark
1 Here is a grid of regular hexagons. The shaded shape has an area of 3 hexagons and a perimeter of 14 cm. Draw another shape on the grid which has an area of 4 hexagons and a perimeter of 14 cm. 1 mark
Mental Math 5 th Grade
 Mental Math 5 th Grade 1. If a faucet drips three-hundred and four times in sixteen minutes, how many drips, on average, occurred each minute? 2. What is the radius of a circle with a circumference of
Mental Math 5 th Grade 1. If a faucet drips three-hundred and four times in sixteen minutes, how many drips, on average, occurred each minute? 2. What is the radius of a circle with a circumference of
New Rochelle High School Geometry Summer Assignment
 NAME - New Rochelle High School Geometry Summer Assignment To all Geometry students, This assignment will help you refresh some of the necessary math skills you will need to be successful in Geometry and
NAME - New Rochelle High School Geometry Summer Assignment To all Geometry students, This assignment will help you refresh some of the necessary math skills you will need to be successful in Geometry and
2. Which numbers below are perfect squares? Explain how you know. b) 0.004
 Grade 9 Math Final Eam Review Unit 1 Outcomes Determine the square root of positive rational numbers that are perfect squares. o Determine whether or not a given rational number is a square number and
Grade 9 Math Final Eam Review Unit 1 Outcomes Determine the square root of positive rational numbers that are perfect squares. o Determine whether or not a given rational number is a square number and
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 G8_U6_Final 7/4/05 8:52 AM Page 236 What is a circle? Where do you see circles? What do you know about a circle? What might be useful to know about a circle? What You ll Learn Measure the radius, diameter,
G8_U6_Final 7/4/05 8:52 AM Page 236 What is a circle? Where do you see circles? What do you know about a circle? What might be useful to know about a circle? What You ll Learn Measure the radius, diameter,
Sect 10.1 Angles and Triangles
 175 Sect 10.1 Angles and Triangles Objective 1: Converting Angle Units Each degree can be divided into 60 minutes, denoted 60', and each minute can be divided into 60 seconds, denoted 60". Hence, 1 = 60'
175 Sect 10.1 Angles and Triangles Objective 1: Converting Angle Units Each degree can be divided into 60 minutes, denoted 60', and each minute can be divided into 60 seconds, denoted 60". Hence, 1 = 60'
Practice Problems (/7/teachers /3/practice_problems.html)
 (http://openupresources.org)menu Close OUR Curriculum (http://openupresources.org) Professional Development (http://openupresources.org/illustrative-mathematics-professional-development) Implementation
(http://openupresources.org)menu Close OUR Curriculum (http://openupresources.org) Professional Development (http://openupresources.org/illustrative-mathematics-professional-development) Implementation
Day 1. Mental Arithmetic Questions. 1. What number is five cubed? 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle?
 Mental Arithmetic Questions 1. What number is five cubed? KS3 MATHEMATICS 10 4 10 Level 6 Questions Day 1 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle? 3. Jenny and Mark share
Mental Arithmetic Questions 1. What number is five cubed? KS3 MATHEMATICS 10 4 10 Level 6 Questions Day 1 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle? 3. Jenny and Mark share
Recognise the Equation of a Circle. Solve Problems about Circles Centred at O. Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes
 1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216)
 LESSON Name 1 Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216) You already know how to change a percent to a fraction. Rewrite the percent as a fraction with a denominator of 100 and reduce. 25% = 25 100 = 1 5%
LESSON Name 1 Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216) You already know how to change a percent to a fraction. Rewrite the percent as a fraction with a denominator of 100 and reduce. 25% = 25 100 = 1 5%
UNIT 6. BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle. The Circle
 UNIT 6 BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle The Circle 1 Questions How are perimeter and area related? How are the areas of polygons and circles
UNIT 6 BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle The Circle 1 Questions How are perimeter and area related? How are the areas of polygons and circles
Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1. Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know
 Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1 Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole Numbers and Decimals Measures, perimeter area and volume Expressions and formulae Indices
Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1 Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole Numbers and Decimals Measures, perimeter area and volume Expressions and formulae Indices
SAT SHEET (calculators allowed)
 . If! 15 = 15! x, then x = A) -0 B) -15 C) 0 D) 15 E) 0 4. A dozen roses cost $15.60 and the cost of one rose and one lily together cost $4.50. What is the cost of one lily? A) $1.0 B) $.0 C) $5.80 D)
. If! 15 = 15! x, then x = A) -0 B) -15 C) 0 D) 15 E) 0 4. A dozen roses cost $15.60 and the cost of one rose and one lily together cost $4.50. What is the cost of one lily? A) $1.0 B) $.0 C) $5.80 D)
April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
 11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
UNIT 13 Areas: CSEC Revision Test
 Area of square 64 cm (4 marks) MEP Jamaica: STRAND E : 1. The shaded square has sides of length 1 cm. It is enlarged a number of times as shown. Complete the table. Length of side of square 1 cm cm 3 cm
Area of square 64 cm (4 marks) MEP Jamaica: STRAND E : 1. The shaded square has sides of length 1 cm. It is enlarged a number of times as shown. Complete the table. Length of side of square 1 cm cm 3 cm
Around the corner. Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h
 Around the corner Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h Exploration 1 (Piano) You have to move a heavy piano through a 1 meter wide corridor with a right-angled corner in it. The figure
Around the corner Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h Exploration 1 (Piano) You have to move a heavy piano through a 1 meter wide corridor with a right-angled corner in it. The figure
Crash Course: Uniform Circular Motion. Our next test will be the week of Nov 27 Dec 1 and will cover projectiles and circular motion.
 Curriculum Outcomes Circular Motion (8 hours) describe uniform circular motion using algebraic and vector analysis (325 12) explain quantitatively circular motion using Newton s laws (325 13) Crash Course:
Curriculum Outcomes Circular Motion (8 hours) describe uniform circular motion using algebraic and vector analysis (325 12) explain quantitatively circular motion using Newton s laws (325 13) Crash Course:
Unit 3, Lesson 2: Exploring Circles
 Unit 3, Lesson 2: Exploring Circles Lesson Goals Describe the characteristics that make something a circle. Be introduced to the terms diameter, center, radius, and circumference. Required Materials rulers
Unit 3, Lesson 2: Exploring Circles Lesson Goals Describe the characteristics that make something a circle. Be introduced to the terms diameter, center, radius, and circumference. Required Materials rulers
End Of Term 2 Revision Sheet
 Egyptian British International School Math Department Name:. Year (8..) End Of Term 2 Revision Sheet * Answer The following questions after revising your classwork copybook, course book, homework book
Egyptian British International School Math Department Name:. Year (8..) End Of Term 2 Revision Sheet * Answer The following questions after revising your classwork copybook, course book, homework book
Geometric Formulas (page 474) Name
 LESSON 91 Geometric Formulas (page 474) Name Figure Perimeter Area Square P = 4s A = s 2 Rectangle P = 2I + 2w A = Iw Parallelogram P = 2b + 2s A = bh Triangle P = s 1 + s 2 + s 3 A = 1_ 2 bh Teacher Note:
LESSON 91 Geometric Formulas (page 474) Name Figure Perimeter Area Square P = 4s A = s 2 Rectangle P = 2I + 2w A = Iw Parallelogram P = 2b + 2s A = bh Triangle P = s 1 + s 2 + s 3 A = 1_ 2 bh Teacher Note:
YEAR 9 MATHS SEMESTER 1 EXAM REVISION BOOKLET 2018
 YEAR 9 MATHS SEMESTER 1 EXAM REVISION BOOKLET 2018 Topics Examined Chapter 12 Measurement (Exercises 12.2 12.7; 6.2-6.3) o Unit Conversions o Perimeter, Area, Total Surface Area, Volume and Capacity of
YEAR 9 MATHS SEMESTER 1 EXAM REVISION BOOKLET 2018 Topics Examined Chapter 12 Measurement (Exercises 12.2 12.7; 6.2-6.3) o Unit Conversions o Perimeter, Area, Total Surface Area, Volume and Capacity of
Math-2A. Lesson 10-3: Area of: -Triangles -rectangles -circles -trapezoids and Surface Area of: -Rectangular Prisms
 Math-A Lesson 10-3: Area of: -Triangles -rectangles -circles -trapezoids and Surface Area of: -Rectangular Prisms Describe the idea of area. Area attempts to answer the question how big is it? The area
Math-A Lesson 10-3: Area of: -Triangles -rectangles -circles -trapezoids and Surface Area of: -Rectangular Prisms Describe the idea of area. Area attempts to answer the question how big is it? The area
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
SAMPLE EXAMINATION PAPER FORM 3
 THE G C SCHOOL OF CAREERS MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT SCHOOL YEAR 2017-2018 SAMPLE EXAMINATION PAPER FORM 3 Name: INFORMATION TO CANDIDATES Full marks may be obtained for answers to ALL questions. This paper
THE G C SCHOOL OF CAREERS MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT SCHOOL YEAR 2017-2018 SAMPLE EXAMINATION PAPER FORM 3 Name: INFORMATION TO CANDIDATES Full marks may be obtained for answers to ALL questions. This paper
Key Stage 3 Subject: Maths Foundation Year: Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Topic/Module: Geometry
 Subject: Foundation Topic/Module: Geometry Time Geometry 1 234 Metric Units Angles/Polygons Bearings Transformations watch Clips N21 N7 N7 N7 N7 N7, R2, 112 112 G10, 46 G16, 122 G14 G13, G17, 45, 121 G23
Subject: Foundation Topic/Module: Geometry Time Geometry 1 234 Metric Units Angles/Polygons Bearings Transformations watch Clips N21 N7 N7 N7 N7 N7, R2, 112 112 G10, 46 G16, 122 G14 G13, G17, 45, 121 G23
University of Houston High School Mathematics Contest Geometry Exam Spring 2015
 University of Houston High School Mathematics Contest Geometry Exam Spring 2015 Note that diagrams may not be drawn to scale. 1. A pool has a 4 foot wide sidewalk around it. If the pool is 28 feet long
University of Houston High School Mathematics Contest Geometry Exam Spring 2015 Note that diagrams may not be drawn to scale. 1. A pool has a 4 foot wide sidewalk around it. If the pool is 28 feet long
Math is Cool Masters
 8th Grade November 19, 2005 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round any answers unless stated otherwise.
8th Grade November 19, 2005 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round any answers unless stated otherwise.
BLoCK 4 ~ ratios, rates And PerCents
 BLoCK 4 ~ ratios, rates And PerCents circles and similarity Lesson 20 ParTs of circles ------------------------------------------------------ 114 Explore! What Is It? Lesson 21 circumference of a circle
BLoCK 4 ~ ratios, rates And PerCents circles and similarity Lesson 20 ParTs of circles ------------------------------------------------------ 114 Explore! What Is It? Lesson 21 circumference of a circle
1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet
 1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet Name: School: Grade: 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10a 5 10b 6 10c TOTAL: GEOMETRY Question One. [3 points] Quadrilateral ALEX, pictured below (but not necessarily
1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet Name: School: Grade: 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10a 5 10b 6 10c TOTAL: GEOMETRY Question One. [3 points] Quadrilateral ALEX, pictured below (but not necessarily
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 1. The diagram above shows the sector OA of a circle with centre O, radius 9 cm and angle 0.7 radians. Find the length of the arc A. Find the area of the sector OA. The line AC shown in the diagram above
1. The diagram above shows the sector OA of a circle with centre O, radius 9 cm and angle 0.7 radians. Find the length of the arc A. Find the area of the sector OA. The line AC shown in the diagram above
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Two: Solving Equations
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Two: Solving Equations Properties of Real Numbers Syllabus Objective: (.1) The student will evaluate expressions using properties of addition and multiplication, and the distributive
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Two: Solving Equations Properties of Real Numbers Syllabus Objective: (.1) The student will evaluate expressions using properties of addition and multiplication, and the distributive
Student s Name Course Name Mathematics Grade 7. General Outcome: Develop number sense. Strand: Number. R D C Changed Outcome/achievement indicator
 Strand: Number Specific Outcomes It is expected that students will: 1. Determine and explain why a number is divisible by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 or 10, and why a number cannot be divided by 0. [C, R] 2. Demonstrate
Strand: Number Specific Outcomes It is expected that students will: 1. Determine and explain why a number is divisible by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 or 10, and why a number cannot be divided by 0. [C, R] 2. Demonstrate
