Phononic Crystals. J.H. Page
|
|
|
- Avis Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phononic Crystals J.H. Page University of Manitoba with Suxia Yang and M.L. Cowan at U of M, Ping Sheng and C.T. Chan at HKUST, & Zhengyou Liu at Wuhan University. We study ultrasonic waves in complex (strongly scattering) media. Random media: - ballistic and diffusive wave transport - new ultrasound scattering techniques (DSS & DAWS) Ordered media (phononic crystals): - ultrasound tunneling - focusing effects For more info and papers, see
2 Outline: Phononic Crystals Motivation: Why study phononic crystals? (acoustic and elastic analogues of photonic crystals): Wave phenomena in 3D phononic crystals (experiments and theory) : - our crystals and the experimental setup - spectral gaps - ultrasound tunneling - near field imaging - focusing effects Possible applications - lenses and filters? - sound insulation? y (cm) 4 Conclusions x (cm) 2 4-4
3 PHONONIC CRYSTALS e.g. ordered arrays of mm-sized beads in a liquid or solid matrix acoustic and elastic analogues of photonic crystals. Why study phononic crystals? richer physics? scattering contrast, v may be easier to achieve complete spectral gaps longitudinal + transverse modes novel wave phenomena? ultrasonic techniques have some advantages measure the field not the intensity pulsed techniques are easy good theory is available - e.g. Multiple Scattering Theory for elastic and acoustic waves. [Kafesaki and Economou, PRB 6, (1999); Liu et al. PRB 62, 2446 (2); Psarobas et al., Phys. Rev. B 62, 278 (2)] relatively few experiments have been performed on 3D systems (unlike 2D). new applications?
4 Questions: Can complete spectral gaps be readily achieved? How do waves travel through phononic band gaps? No propagating mode Tunneling? How long does it take? Can phononic crystals be used to focus ultrasound?
5 Our 3D Phononic Crystals: Close-packed periodic arrays of spherical beads surrounded by a liquid or solid matrix: hcp arrays of stainless steel balls in water fcc arrays of tungsten carbide balls in water fcc arrays of tungsten carbide beads in epoxy For all these crystals: very high contrast scatterers Z ball /Z matrix 3 to 6 very monodisperse spheres: diameter d =.8.6 mm very high quality crystals: produced by a manual assembly technique using a hexagonal template.
6 for hcp: ABAB layer sequence. (slabs with c-axis layers) for fcc: ABCABC layer sequence. ( [111]-axis layers) A C C C B B B B C C C B B B C Schematic graph shows how the beads are packed in a FCC crystal along the [111] direction. Beads A are on the bottom layer, B the second and C the third. The sequence is ABCABC... Material parameters for our phononic crystals made from tungsten carbide beads in water Scatterers:.8-mm-diameter tungsten carbide beads = 13.8 kg/m 3 v L v T = 6.65 km/s = 3.23 km/s Matrix: water = 1. kg/m 3 v L = 1.49 km/s
7 Experimental setup Ultrasound Detecting Transducer Compare transmitted pulses with reference pulses to measure: Sample Sample Holder y 2 L Close-up of sample phase velocity: v p () = L/( + 2n) ( = phase delay) group velocity: Planar input pulse (far field; large y 1 ) y 1 Ultrasound Generating Transducer v g () = L/t peak (t peak = peak delay time) transmission coefficient: A trans () / A ref (FFT ratio)
8 Multiple Scattering Theory Multiple scattering theory (MST) for acoustic and elastic waves -- ideally suited to spherical scatterers. (cf. KKR theory) [Liu et al. PRB 62, 2446 (2) ] Band-structure: calculate elastic Mie scattering of waves from all the scatterers in the crystal, and solve the resulting secular equation for the eigenfrequencies. Transmission: calculate the transmission through a multi-layer sample with thickness L using a layer MST. Q Q I IV (1) (1) 1 Q Transmitted wave III II Q (1) (1) I Q IV Q (2) (2) 2 III Q II Q (2) (2) Q Q I IV (12) (12) T( L, ) A( L, )exp[ i( L, )] A normalized amplitude (transmission coefficient) cumulative phase relative to the incident wave. Phase velocity Group velocity v v p g ( ) L / ( ) d dk d L d 12 Q III II Q (12) (12)
9 hcp bandstructure: stainless steel spheres in water 1..8 a / 2 v w K M A L H K a lattice constant sound velocity in water. v w WAVEVECTOR Very small complete gap
10 Fcc bandstructure: tunsgsten carbide beads in water a/2 v w X U a lattice constant v sound velocity in water. w Complete gap: centre 19 % L WAVE VECTOR X Reciprocal lattice W K
11 Fcc bandstructure and transmission: tunsgsten carbide beads in epoxy Layer Sample FREQUENCY (MHz) An even bigger complete gap! centre 9 %.5.5. X U L X WAVE VECTOR U K..1.11E-31E-41E-51E-61E-71E-8 TRANSMISSION COEFFICIENT
12 FCC tungsten carbide beads in water: Input and transmitted pulses near the lowest band gap, k [111] INPUT PULSE 1. TRANSMITTED PULSE 6-layer sample.8 NORMALIZED FIELD TIME (s) -.8
13 FCC tungsten carbide beads in water: Fourier Spectrum of these input and transmitted pulses near the -1. lowest band gap NORMALIZED FIELD INPUT PULSE TRANSMITTED PULSE 6-layer sample TIME (s) -.8 NORMALIZED AMPLITUDE 1. INPUT TRANSMITTED FREQUENCY (MHz)
14 Transmission coefficient AMPLITUDE TRANSMISSION COEFFICIENT E-3 6 LAYER: DATA THEORY 12 LAYER: DATA THEORY FREQUENCY (MHz)
15 Cumulative Phase and the Phase Velocity CUMULATIVE PHASE (rad) EXPERIMENT THEORY Use these data to compute the dispersion curve, versus k = /v p, and compare with the bandstructure calculation PHASE VELOCITY (km/s) EXPERIMENT THEORY FREQUENCY (MHz)
16 Fcc bandstructure: tunsgsten carbide beads in water The black symbols show experimental data from phase velocity measurements a/2 v w X U a lattice constant v sound velocity in water. w Complete gap: centre 19 % L WAVE VECTOR X Reciprocal lattice W K
17 Measuring the group velocity: Digitally filtered input and transmitted pulses (bandwidth.5 MHz) for a 12-layer phononic crystal in the middle of the gap, compared with the pulse transmitted through the same thickness of water. 1 INPUT NORMALIZED FIELD THROUGH WATER x1 THROUGH SAMPLE -1 x TIME (s)
18 Frequency dependence of the group velocity for a 5-layer sample. GROUP VELOCITY (km/s) THEORY FIT EXPERIMENT FREQUENCY (MHz)
19 Group Velocity versus sample thickness in the middle of the gap D Theory Group Velocity Theory Data VELOCITY (km/s) 8 4 v bead = v water = SAMPLE THICKNESS (mm) The group velocity increases linearly with thickness! tunneling. Yang et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 1431 (22)
20 Effect of absorption - the two-modes model Simple physical picture: Absorption cuts off the long scattering paths destructive interference is incomplete. Effectively, absorption introduces a small additional component having a real wave vector inside the gap. Two-modes model: (Dominant) Tunneling mode (constant tunneling time) + Propagation mode (constant velocity) Group velocity becomes v g L L L 2l 2 2l 1 b ae a a e L L ta L L 2la 2 2lb 2la 2 2lb L v ae 1a e ae 1a e b where L is the thickness, a is the coupling coefficient, t a and l a are the tunneling time and tunneling length, v b is the group velocity of the propagating mode and l b is its decay length.
21 The effect of absorption: Fits of the two-modes model to 1 D theory and to our data for 3 D phononic crystals (dashed curves) D Theory Group Velocity Theory Data VELOCITY (km/s) 8 4 v bead =6.655 v water SAMPLE THICKNESS (mm)
22 Add: the phase velocity in the middle of the gap for the same sample thicknesses D Theory Group Velocity Theory Data VELOCITY (km/s) 8 4 v bead =6.655 v water Phase Velocity Theory Data SAMPLE THICKNESS (mm)
23 Electron tunneling through a barrier V Schrodinger equ. 2 2 d ( V E) ( x) 2 2mdx Boundary conditions ( ) ( ); ( ) ( ) ( L ) ( L ); ( L ) ( L ) Incident wave Transmitted wave x V V x L x L From the transmitted phase at large large L, find arctan 2 2 V v p L vg L V V Barrier: Both phase and group velocities increase with L. Band gap: Group velocity increases while the phase velocity is constant.
24 Tunneling Time water TRANSIT TIME (s) 1 Phononic crystals Experiment Theory Tungsten carbide SAMPLE THICKNESS (mm) 8 1 Magnitude of the tunneling time: t tunnel ~ 1 / gap (also true for light and electrons!)
25 Question: Is ultrasound tunneling dispersionless? Some general points about pulse propagation in dispersive media: Incident pulse at x = Fourier transform: x, t etexpi t Pulse after traveling a distance x, 1 x x t exp Eo expikx 2l e k 1 k o pulse envelope E() is F.T. of e(t) extinction length, dk d k 2 o o 2! 2 o d o d o 2 t E e s a l l l scattering absorption Expand the wave vector k() in a Taylor series about the central frequency o : o inverse group velocity group velocity dispersion (GVD)
26 Pulse at (x,t) becomes x o 2le E o exp i dk d o x exp i 2 d k d o x o o xt, exp exp ikx 1 o x exp exp ikox exp iot E exp i dk d x exp i d k d x 2 2l o e x x x exp exp io t t et exp i dkd x 2 2le vp v o g convolution attenuation peak travels at the group velocity of the central frequency carrier frequency oscillations travel at v p = o /k o GVD changes the width symmetrically Good approximation, so long as the pulse bandwidth is sufficiently narrow that: higher order terms in k() expansion are negligible frequency dependence of l e is not important.
27 Frequency dependence of the wave vector, the inverse group velocity and the group velocity dispersion near the band gap in a 5 layer tungsten carbide/water crystal. [c.f. measurements near the band edge in photonic crystals by Imhof et al. PRL 83, 2942 (1999)] 2 d 2 k/d 2 dk/d -2 2 Data Theory 1 5 k f (MHz)
28 Pulse broadening (a) just above the band gap, (b) in the middle of the gap and (c) just below the band gap (bandwidth.2 MHz). Very weak dispersion in the gap, despite very strong scattering and a large variation in v p with f = 1.2 MHz Shifted Reference Sample NORMALIZED AMPLITUDE 1 1. f =.972 MHz Shifted Reference Sample 1 f =.744 MHz Shifted Reference 6.14 Sample TIME (s)
NATO ASI on Photonic Crystals and Light Localization, Crete, June 19-30, 2000 ACOUSTIC BAND GAP MATERIALS
 NATO ASI on Photonic Crystals and Light Localization, Crete, June 19-30, 2000 ACOUSTIC BAND GAP MATERIALS J.H. Page 1, A.L. Goertzen 1,*, Suxia Yang 1,2, Zhengyou Liu 2,3, C.T. Chan 2 and Ping Sheng 2
NATO ASI on Photonic Crystals and Light Localization, Crete, June 19-30, 2000 ACOUSTIC BAND GAP MATERIALS J.H. Page 1, A.L. Goertzen 1,*, Suxia Yang 1,2, Zhengyou Liu 2,3, C.T. Chan 2 and Ping Sheng 2
Negative refraction of ultrasonic waves in 2D phononic crystals.
 Negative refraction of ultrasonic waves in 2D phononic crystals. Alexey Sukhovich 1, John Page 1, Zhengyou Liu 2, Maria Kafesaki 3 1 University of Manitoba, Canada; 2 Wuhan University, China; 3 IESL-FORTH,
Negative refraction of ultrasonic waves in 2D phononic crystals. Alexey Sukhovich 1, John Page 1, Zhengyou Liu 2, Maria Kafesaki 3 1 University of Manitoba, Canada; 2 Wuhan University, China; 3 IESL-FORTH,
Full Band Gap and Defects States in Solid-in-Solid Three Dimensional Phononic Crystals
 1 Full Band Gap and Defects States in Solid-in-Solid Three Dimensional Phononic Crystals Ke Sun and Z Yang 1 Department of Physics, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clearwater Bay, Kowloon,
1 Full Band Gap and Defects States in Solid-in-Solid Three Dimensional Phononic Crystals Ke Sun and Z Yang 1 Department of Physics, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clearwater Bay, Kowloon,
Ultrasonic wave transport in strongly scattering media
 Ultrasonic wave transport in strongly scattering media J. H. Page Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Manitoba Winnipeg, MB Canada R3T 2N2 Summary. Ultrasonic experiments are well suited
Ultrasonic wave transport in strongly scattering media J. H. Page Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Manitoba Winnipeg, MB Canada R3T 2N2 Summary. Ultrasonic experiments are well suited
Negative-refraction imaging with two-dimensional phononic crystals
 Negative-refraction imaging with two-dimensional phononic crystals Manzhu Ke, Zhengyou Liu,* Chunyin Qiu, Wengang Wang, and Jing Shi Department of Physics, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, People s Republic
Negative-refraction imaging with two-dimensional phononic crystals Manzhu Ke, Zhengyou Liu,* Chunyin Qiu, Wengang Wang, and Jing Shi Department of Physics, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, People s Republic
Chapter 4 2D 3D Phononic Crystals
 Chapter 4 2D 3D Phononic Crystals A. Sukhovich, J.H. Page, J.O. Vasseur, J.F. Robillard, N. Swinteck, and Pierre A. Deymier Abstract This chapter presents a comprehensive description of the properties
Chapter 4 2D 3D Phononic Crystals A. Sukhovich, J.H. Page, J.O. Vasseur, J.F. Robillard, N. Swinteck, and Pierre A. Deymier Abstract This chapter presents a comprehensive description of the properties
Theoretical study of subwavelength imaging by. acoustic metamaterial slabs
 Theoretical study of subwavelength imaging by acoustic metamaterial slabs Ke Deng,2, Yiqun Ding, Zhaojian He, Heping Zhao 2, Jing Shi, and Zhengyou Liu,a) Key Lab of Acoustic and Photonic materials and
Theoretical study of subwavelength imaging by acoustic metamaterial slabs Ke Deng,2, Yiqun Ding, Zhaojian He, Heping Zhao 2, Jing Shi, and Zhengyou Liu,a) Key Lab of Acoustic and Photonic materials and
Phononic Crystals: Towards the Full Control of Elastic Waves propagation OUTLINE
 Phononic Crystals: Towards the Full Control of Elastic Waves propagation José Sánchez-Dehesa Wave Phenomena Group, Department of Electronic Engineering, Polytechnic University of Valencia, SPAIN. OUTLINE
Phononic Crystals: Towards the Full Control of Elastic Waves propagation José Sánchez-Dehesa Wave Phenomena Group, Department of Electronic Engineering, Polytechnic University of Valencia, SPAIN. OUTLINE
Research on sound absorbing mechanism and the preparation of new backing material for ultrasound transducers
 Research on sound absorbing mechanism and the preparation of new backing material for ultrasound transducers Guofeng Bai a) Xiujuan Zhang b) Fusheng Sui c) Jun Yang d) Key Laboratory of Noise and Vibration
Research on sound absorbing mechanism and the preparation of new backing material for ultrasound transducers Guofeng Bai a) Xiujuan Zhang b) Fusheng Sui c) Jun Yang d) Key Laboratory of Noise and Vibration
Acoustic Velocity, Impedance, Reflection, Transmission, Attenuation, and Acoustic Etalons
 Acoustic Velocity, Impedance, Reflection, Transmission, Attenuation, and Acoustic Etalons Acoustic Velocity The equation of motion in a solid is (1) T = ρ 2 u t 2 (1) where T is the stress tensor, ρ is
Acoustic Velocity, Impedance, Reflection, Transmission, Attenuation, and Acoustic Etalons Acoustic Velocity The equation of motion in a solid is (1) T = ρ 2 u t 2 (1) where T is the stress tensor, ρ is
Miao Boya and An Yu Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing , People s Republic of China
 Localization in an acoustic cavitation cloud Miao Boya and An Yu Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, People s Republic of China Using a nonlinear sound wave equation for a bubbly
Localization in an acoustic cavitation cloud Miao Boya and An Yu Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, People s Republic of China Using a nonlinear sound wave equation for a bubbly
On the study of elastic wave scattering and Rayleigh wave velocity measurement of concrete with steel bar
 NDT&E International 33 (2000) 401 407 www.elsevier.com/locate/ndteint On the study of elastic wave scattering and Rayleigh wave velocity measurement of concrete with steel bar T.-T. Wu*, J.-H. Sun, J.-H.
NDT&E International 33 (2000) 401 407 www.elsevier.com/locate/ndteint On the study of elastic wave scattering and Rayleigh wave velocity measurement of concrete with steel bar T.-T. Wu*, J.-H. Sun, J.-H.
Sonic Crystals: Fundamentals, characterization and experimental techniques
 Sonic Crystals: Fundamentals, characterization and experimental techniques A. C e b r e c o s 1 L a u m, L e M a n s U n i v e r s i t é, C N R S, A v. O. M e s s i a e n, 7 2 0 8 5, L e M a n s Collaborators
Sonic Crystals: Fundamentals, characterization and experimental techniques A. C e b r e c o s 1 L a u m, L e M a n s U n i v e r s i t é, C N R S, A v. O. M e s s i a e n, 7 2 0 8 5, L e M a n s Collaborators
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium with thickness L. Supplementary Figure Measurement of
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium with thickness L. Supplementary Figure Measurement of
Acoustic pressure characteristic analysis in cavity of 2-D phononic crystal
 Journal of Engineering Technology and Education, Vol. 9, No. June 1, pp. 115-11 Acoustic pressure characteristic analysis in cavity of -D phononic crystal Jia-Yi Yeh 1, Jiun-Yeu Chen 1 Department of Information
Journal of Engineering Technology and Education, Vol. 9, No. June 1, pp. 115-11 Acoustic pressure characteristic analysis in cavity of -D phononic crystal Jia-Yi Yeh 1, Jiun-Yeu Chen 1 Department of Information
Anderson localization of ultrasound in three dimensions
 International School of Physics Enrico Fermi Course CLXXIII "Nano Optics and Atomics: Transport of Light and Matter Waves Varenna, June 23 rd to July 3 rd, 29 Anderson localization of ultrasound in three
International School of Physics Enrico Fermi Course CLXXIII "Nano Optics and Atomics: Transport of Light and Matter Waves Varenna, June 23 rd to July 3 rd, 29 Anderson localization of ultrasound in three
Recurrent scattering and memory effect at the Anderson transition
 Recurrent scattering and memory effect at the Anderson transition Alexandre Aubry Institut Langevin CNRS UMR 7587, ESPCI ParisTech Paris, France Collaborators: John Page, Laura Cobus (University of Manitoba,
Recurrent scattering and memory effect at the Anderson transition Alexandre Aubry Institut Langevin CNRS UMR 7587, ESPCI ParisTech Paris, France Collaborators: John Page, Laura Cobus (University of Manitoba,
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Physical Acoustics Session 2pPA: Material Characterization 2pPA10. Frequency-resolved
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Physical Acoustics Session 2pPA: Material Characterization 2pPA10. Frequency-resolved
Acoustic metamaterials in nanoscale
 Acoustic metamaterials in nanoscale Dr. Ari Salmi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 12.2.2014 1 Revisit to resonances Matemaattis-luonnontieteellinen tiedekunta / Henkilön nimi / Esityksen nimi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto
Acoustic metamaterials in nanoscale Dr. Ari Salmi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 12.2.2014 1 Revisit to resonances Matemaattis-luonnontieteellinen tiedekunta / Henkilön nimi / Esityksen nimi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto
Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Doppler echocardiography. History: - Langevin developed sonar.
 1 Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging History: - Langevin developed sonar. - 1940s development of pulse-echo. - 1950s development of mode A and B. - 1957 development of continuous wave
1 Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging History: - Langevin developed sonar. - 1940s development of pulse-echo. - 1950s development of mode A and B. - 1957 development of continuous wave
Metamaterials with tunable dynamic properties
 Metamaterials with tunable dynamic properties Varvara Kouznetsova Marc Geers 6 October 2015 Mechanics of Materials Project aim development of new generation mechanical metamaterials with adaptive, tunable
Metamaterials with tunable dynamic properties Varvara Kouznetsova Marc Geers 6 October 2015 Mechanics of Materials Project aim development of new generation mechanical metamaterials with adaptive, tunable
Band gaps in a phononic crystal constituted by cylindrical dots on a homogeneous plate
 Band gaps in a phononic crystal constituted by cylindrical dots on a homogeneous plate B. Djafari-Rouhani, Y. Pennec, H. Larabi, J. Vasseur and A.-C. Hladky IEN, UR CNRS 852, avenue Poincaré, BP 669, 59652
Band gaps in a phononic crystal constituted by cylindrical dots on a homogeneous plate B. Djafari-Rouhani, Y. Pennec, H. Larabi, J. Vasseur and A.-C. Hladky IEN, UR CNRS 852, avenue Poincaré, BP 669, 59652
MODELING OF ACOUSTIC PROCESSES IN SOLIDS BASED ON PARTICLE INTERACTION
 MATEC Web of Conferences 55, 44 (8) IME&T 7 https://doi.org/.5/matecconf/85544 MODELING OF ACOUSTIC PROCESSES IN SOLIDS BASED ON PARTICLE INTERACTION Angela Kuzovova,, Timur Muksunov Tomsk State University,
MATEC Web of Conferences 55, 44 (8) IME&T 7 https://doi.org/.5/matecconf/85544 MODELING OF ACOUSTIC PROCESSES IN SOLIDS BASED ON PARTICLE INTERACTION Angela Kuzovova,, Timur Muksunov Tomsk State University,
Band gaps and the electromechanical coupling coefficient of a surface acoustic wave in a two-dimensional piezoelectric phononic crystal
 Band gaps and the electromechanical coupling coefficient of a surface acoustic wave in a two-dimensional piezoelectric phononic crystal Tsung-Tsong Wu* Zin-Chen Hsu and Zi-ui Huang Institute of Applied
Band gaps and the electromechanical coupling coefficient of a surface acoustic wave in a two-dimensional piezoelectric phononic crystal Tsung-Tsong Wu* Zin-Chen Hsu and Zi-ui Huang Institute of Applied
Attenuation and dispersion
 Attenuation and dispersion! Mechanisms: Absorption (inelastic); Scattering (elastic).! Mathematical descriptions! Measurement! Frequency dependence! Dispersion, its relation to attenuation Reading: Sheriff
Attenuation and dispersion! Mechanisms: Absorption (inelastic); Scattering (elastic).! Mathematical descriptions! Measurement! Frequency dependence! Dispersion, its relation to attenuation Reading: Sheriff
10. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
 1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence
1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence
Sound wave bends as it hits an interface at an oblique angle. 4. Reflection. Sound wave bounces back to probe
 : Ultrasound imaging and x-rays 1. How does ultrasound imaging work?. What is ionizing electromagnetic radiation? Definition of ionizing radiation 3. How are x-rays produced? Bremsstrahlung Auger electron
: Ultrasound imaging and x-rays 1. How does ultrasound imaging work?. What is ionizing electromagnetic radiation? Definition of ionizing radiation 3. How are x-rays produced? Bremsstrahlung Auger electron
RESONANCE-COUPLING EFFECT ON BROAD BAND GAP FORMATION AND SOUND ABSORPTION IN LOCALLY RESONANT SONIC METAMATERIALS WITH WOODPILE STRUCTURE
 RESONANCE-COUPLING EFFECT ON BROAD BAND GAP FORMATION AND SOUND ABSORPTION IN LOCALLY RESONANT SONIC METAMATERIALS WITH WOODPILE STRUCTURE Wang Yuren Key Laboratory of Microgravity, Institute of Mechanics,
RESONANCE-COUPLING EFFECT ON BROAD BAND GAP FORMATION AND SOUND ABSORPTION IN LOCALLY RESONANT SONIC METAMATERIALS WITH WOODPILE STRUCTURE Wang Yuren Key Laboratory of Microgravity, Institute of Mechanics,
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications
 6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 5: Specific Heat of Lattice Waves Outline Review Lecture 4 3-D Elastic Continuum 3-D Lattice Waves Lattice Density of Modes Specific Heat of Lattice Specific
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 5: Specific Heat of Lattice Waves Outline Review Lecture 4 3-D Elastic Continuum 3-D Lattice Waves Lattice Density of Modes Specific Heat of Lattice Specific
Lecture 4 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 4, Slide 1
 ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Left-handed materials: Transfer matrix method studies
 Left-handed materials: Transfer matrix method studies Peter Markos and C. M. Soukoulis Outline of Talk What are Metamaterials? An Example: Left-handed Materials Results of the transfer matrix method Negative
Left-handed materials: Transfer matrix method studies Peter Markos and C. M. Soukoulis Outline of Talk What are Metamaterials? An Example: Left-handed Materials Results of the transfer matrix method Negative
Nanoscale Energy Conversion and Information Processing Devices - NanoNice - Photoacoustic response in mesoscopic systems
 Nanoscale Energy Conversion and Information Processing Devices - NanoNice - Photoacoustic response in mesoscopic systems Photonics group W. Claeys, S. Dilhair, S. Grauby, JM. Rampnoux, L. Patino Lopez,
Nanoscale Energy Conversion and Information Processing Devices - NanoNice - Photoacoustic response in mesoscopic systems Photonics group W. Claeys, S. Dilhair, S. Grauby, JM. Rampnoux, L. Patino Lopez,
Electromagnetic fields and waves
 Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy
 Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy Paul T. Callaghan Department of Physics and Biophysics Massey University New Zealand CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD CONTENTS 1 PRINCIPLES OF IMAGING 1 1.1 Introduction
Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy Paul T. Callaghan Department of Physics and Biophysics Massey University New Zealand CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD CONTENTS 1 PRINCIPLES OF IMAGING 1 1.1 Introduction
Surface and bulk acoustic waves in two-dimensional phononic crystal consisting of materials with general anisotropy
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 69, 094301 2004 Surface and bulk acoustic waves in two-dimensional phononic crystal consisting of materials with general anisotropy Tsung-Tsong Wu,* Zi-Gui Huang, and S. Lin Ultrasonics
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 69, 094301 2004 Surface and bulk acoustic waves in two-dimensional phononic crystal consisting of materials with general anisotropy Tsung-Tsong Wu,* Zi-Gui Huang, and S. Lin Ultrasonics
Method for retrieving effective properties of locally resonant acoustic metamaterials
 Method for retrieving effective properties of locally resonant acoustic metamaterials Vladimir Fokin, Muralidhar Ambati, Cheng Sun, and Xiang Zhang* Nano-scale Science and Engineering Center, University
Method for retrieving effective properties of locally resonant acoustic metamaterials Vladimir Fokin, Muralidhar Ambati, Cheng Sun, and Xiang Zhang* Nano-scale Science and Engineering Center, University
Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization Serena De Paolis *, Francesca Lionetto and Alfonso Maffezzoli
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization Serena De Paolis *, Francesca Lionetto and Alfonso Maffezzoli
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5 detector sample X-ray source monochromator David Ritchie http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home QCMP Lent/Easter 2019 5.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5 detector sample X-ray source monochromator David Ritchie http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home QCMP Lent/Easter 2019 5.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical
Diffusing acoustic wave spectroscopy
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 65, 066605 Diffusing acoustic wave spectroscopy M. L. Cowan, 1 I. P. Jones, 1, * J. H. Page, 1,2, and D. A. Weitz 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manitoba,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 65, 066605 Diffusing acoustic wave spectroscopy M. L. Cowan, 1 I. P. Jones, 1, * J. H. Page, 1,2, and D. A. Weitz 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manitoba,
Shear waves in solid-state materials
 Shear waves in solid-state materials TEAS Related topics Ultrasonic transmission measurement, propagation of ultrasound waves, ultrasound wave modes, shear waves, longitudinal and transverse waves, modulus
Shear waves in solid-state materials TEAS Related topics Ultrasonic transmission measurement, propagation of ultrasound waves, ultrasound wave modes, shear waves, longitudinal and transverse waves, modulus
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 9.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 9.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Time Evolution in Diffusion and Quantum Mechanics. Paul Hughes & Daniel Martin
 Time Evolution in Diffusion and Quantum Mechanics Paul Hughes & Daniel Martin April 29, 2005 Abstract The Diffusion and Time dependent Schrödinger equations were solved using both a Fourier based method
Time Evolution in Diffusion and Quantum Mechanics Paul Hughes & Daniel Martin April 29, 2005 Abstract The Diffusion and Time dependent Schrödinger equations were solved using both a Fourier based method
Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts. Christian Ratsch
 Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts Christian Ratsch Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics and Department of Mathematics, UCLA Motivation There are 10 20 atoms in 1 mm 3
Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts Christian Ratsch Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics and Department of Mathematics, UCLA Motivation There are 10 20 atoms in 1 mm 3
Band structure and transmission of 3D chiral sonic crystals
 Band structure and transmission of 3D chiral sonic crystals R. Pico, V. Romero-Garcia, V. Sanchez-Morcillo, A. Cebrecos and L.M. Garcia-Raffi Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Paranimf 1, 46730 Gandia,
Band structure and transmission of 3D chiral sonic crystals R. Pico, V. Romero-Garcia, V. Sanchez-Morcillo, A. Cebrecos and L.M. Garcia-Raffi Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Paranimf 1, 46730 Gandia,
Guided Acoustic Wave Brillouin Scattering (GAWBS) in Photonic Crystal Fibers (PCFs)
 Guided Acoustic Wave Brillouin Scattering (GAWBS) in Photonic Crystal Fibers (PCFs) FRISNO-9 Dominique Elser 15/02/2007 GAWBS Theory Thermally excited acoustic fiber vibrations at certain resonance frequencies
Guided Acoustic Wave Brillouin Scattering (GAWBS) in Photonic Crystal Fibers (PCFs) FRISNO-9 Dominique Elser 15/02/2007 GAWBS Theory Thermally excited acoustic fiber vibrations at certain resonance frequencies
Hot Topics in Physical Acoustics
 Hot Topics in Physical Acoustics J.R. (Josh) Gladden Dept. of Physics and Astronomy University of ASA Fall Meeting November 12, 2008 Outline Sound waves in the early universe Nature of sound in a hot plasma
Hot Topics in Physical Acoustics J.R. (Josh) Gladden Dept. of Physics and Astronomy University of ASA Fall Meeting November 12, 2008 Outline Sound waves in the early universe Nature of sound in a hot plasma
Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a).
 7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
Today s menu. Last lecture. Ultrasonic measurement systems. What is Ultrasound (cont d...)? What is ultrasound?
 Last lecture Measurement of volume flow rate Differential pressure flowmeters Mechanical flowmeters Vortex flowmeters Measurement of mass flow Measurement of tricky flows" Today s menu Ultrasonic measurement
Last lecture Measurement of volume flow rate Differential pressure flowmeters Mechanical flowmeters Vortex flowmeters Measurement of mass flow Measurement of tricky flows" Today s menu Ultrasonic measurement
'l John 3-f. Paee. you Liu sics anc[ Teclino{ogy Wufian University, Cliina. Suxia Ya!!B_~ 'l!{tysics ana.'astronomy anitoba, Canac[a
 'l 0 1 5 3rd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON PHONONIC CRYSTALS/ METAMATERIALS, PHONON TRANSPORT & PHONON COUPLING May 31-June 5, 2015 - Paris, France eyart~ 11niv Sclioo( of John 3-f. Paee 'l!{tysics ana.'astronomy
'l 0 1 5 3rd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON PHONONIC CRYSTALS/ METAMATERIALS, PHONON TRANSPORT & PHONON COUPLING May 31-June 5, 2015 - Paris, France eyart~ 11niv Sclioo( of John 3-f. Paee 'l!{tysics ana.'astronomy
Modelling and Simulation of Acoustic Wave Propagation in. Locally Resonant Sonic Materials
 Special session: Ultrasonic Modelling INVITED PAPER Version 1, 06/04/2003 Modelling and Simulation of Acoustic Wave Propagation in Locally Resonant Sonic Materials M. Hirsekorn a, P. P. Delsanto a, N.
Special session: Ultrasonic Modelling INVITED PAPER Version 1, 06/04/2003 Modelling and Simulation of Acoustic Wave Propagation in Locally Resonant Sonic Materials M. Hirsekorn a, P. P. Delsanto a, N.
Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors
 Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors Frank Ceballos 1, Ming-Gang Ju 2 Samuel D. Lane 1, Xiao Cheng Zeng 2 & Hui Zhao 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors Frank Ceballos 1, Ming-Gang Ju 2 Samuel D. Lane 1, Xiao Cheng Zeng 2 & Hui Zhao 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Decoherence in molecular magnets: Fe 8 and Mn 12
 Decoherence in molecular magnets: Fe 8 and Mn 12 I.S. Tupitsyn (with P.C.E. Stamp) Pacific Institute of Theoretical Physics (UBC, Vancouver) Early 7-s: Fast magnetic relaxation in rare-earth systems (Dy
Decoherence in molecular magnets: Fe 8 and Mn 12 I.S. Tupitsyn (with P.C.E. Stamp) Pacific Institute of Theoretical Physics (UBC, Vancouver) Early 7-s: Fast magnetic relaxation in rare-earth systems (Dy
Quantum Optics in Photonic Crystals. Peter Lodahl Dept. of Communications, Optics & Materials (COM) Technical University of Denmark
 Quantum Optics in Photonic Crystals Peter Lodahl Dept. of Communications, Optics & Materials (COM) Technical University of Denmark Acknowledgements AMOLF Institute Amsterdam / University of Twente Ivan
Quantum Optics in Photonic Crystals Peter Lodahl Dept. of Communications, Optics & Materials (COM) Technical University of Denmark Acknowledgements AMOLF Institute Amsterdam / University of Twente Ivan
Spatio-Temporal Characterization of Bio-acoustic Scatterers in Complex Media
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of Bio-acoustic Scatterers in Complex Media Karim G. Sabra, School of Mechanical Engineering,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of Bio-acoustic Scatterers in Complex Media Karim G. Sabra, School of Mechanical Engineering,
Nanoacoustics II Lecture #2 More on generation and pick-up of phonons
 Nanoacoustics II Lecture #2 More on generation and pick-up of phonons Dr. Ari Salmi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 26.3.2018 1 Last lecture key points Coherent acoustic phonons = sound at nanoscale Incoherent
Nanoacoustics II Lecture #2 More on generation and pick-up of phonons Dr. Ari Salmi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 26.3.2018 1 Last lecture key points Coherent acoustic phonons = sound at nanoscale Incoherent
The structure of laser pulses
 1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
(2) A two-dimensional solid has an electron energy band of the form, . [1]
![(2) A two-dimensional solid has an electron energy band of the form, . [1] (2) A two-dimensional solid has an electron energy band of the form, . [1]](/thumbs/96/128751828.jpg) (1) The figure shows a two-dimensional periodic lattice, containing A atoms (white) and B atoms (black). The section of lattice shown makes a 3a 4a rectangle, as shown (measured from A atom to A atom).
(1) The figure shows a two-dimensional periodic lattice, containing A atoms (white) and B atoms (black). The section of lattice shown makes a 3a 4a rectangle, as shown (measured from A atom to A atom).
Large omnidirectional band gaps in metallodielectric photonic crystals
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME, NUMBER 16 15 OCTOBER 1996-II Large omnidirectional band gaps in metallodielectric photonic crystals Shanhui Fan, Pierre R. Villeneuve, and J. D. Joannopoulos Department of Physics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME, NUMBER 16 15 OCTOBER 1996-II Large omnidirectional band gaps in metallodielectric photonic crystals Shanhui Fan, Pierre R. Villeneuve, and J. D. Joannopoulos Department of Physics,
Effects of self-steepening and self-frequency shifting on short-pulse splitting in dispersive nonlinear media
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A VOLUME 57, NUMBER 6 JUNE 1998 Effects of self-steepening and self-frequency shifting on short-pulse splitting in dispersive nonlinear media Marek Trippenbach and Y. B. Band Departments
PHYSICAL REVIEW A VOLUME 57, NUMBER 6 JUNE 1998 Effects of self-steepening and self-frequency shifting on short-pulse splitting in dispersive nonlinear media Marek Trippenbach and Y. B. Band Departments
Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016. Lecture 11, MLZ is a cooperation between:
 Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016 Lecture 11, 11.1.2016 MLZ is a cooperation between: Organization Exam (after winter term) Registration: via TUM-Online between 16.11.2015 15.1.2015 Email: sebastian.muehlbauer@frm2.tum.de
Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016 Lecture 11, 11.1.2016 MLZ is a cooperation between: Organization Exam (after winter term) Registration: via TUM-Online between 16.11.2015 15.1.2015 Email: sebastian.muehlbauer@frm2.tum.de
Design and Control of Advanced Functional Systems with Non- Conventional Material Properties
 Design and Control of Advanced Functional Systems with Non- Conventional Material Properties Dr Simon Pope Department of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering The University of Sheffield s.a.pope@sheffield.ac.uk
Design and Control of Advanced Functional Systems with Non- Conventional Material Properties Dr Simon Pope Department of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering The University of Sheffield s.a.pope@sheffield.ac.uk
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Ultrasonic particle and cell separation and size sorting
 SMR.1670-25 INTRODUCTION TO MICROFLUIDICS 8-26 August 2005 Ultrasonic Particle and Cell Separation and Size Sorting in Micro-channels V. Steinberg Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel Ultrasonic particle
SMR.1670-25 INTRODUCTION TO MICROFLUIDICS 8-26 August 2005 Ultrasonic Particle and Cell Separation and Size Sorting in Micro-channels V. Steinberg Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel Ultrasonic particle
6th NDT in Progress Lamb waves in an anisotropic plate of a single crystal silicon wafer
 6th NDT in Progress 2011 International Workshop of NDT Experts, Prague, 10-12 Oct 2011 Lamb waves in an anisotropic plate of a single crystal silicon wafer Young-Kyu PARK 1, Young H. KIM 1 1 Applied Acoustics
6th NDT in Progress 2011 International Workshop of NDT Experts, Prague, 10-12 Oct 2011 Lamb waves in an anisotropic plate of a single crystal silicon wafer Young-Kyu PARK 1, Young H. KIM 1 1 Applied Acoustics
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers. David Miller
 Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers David Miller Wavepackets Wavepackets Group velocity Group velocity Consider two waves at different frequencies 1 and 2 and suppose that the wave velocity
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers David Miller Wavepackets Wavepackets Group velocity Group velocity Consider two waves at different frequencies 1 and 2 and suppose that the wave velocity
Optical Fiber Signal Degradation
 Optical Fiber Signal Degradation Effects Pulse Spreading Dispersion (Distortion) Causes the optical pulses to broaden as they travel along a fiber Overlap between neighboring pulses creates errors Resulting
Optical Fiber Signal Degradation Effects Pulse Spreading Dispersion (Distortion) Causes the optical pulses to broaden as they travel along a fiber Overlap between neighboring pulses creates errors Resulting
Today s menu. Last lecture. Measurement of volume flow rate. Measurement of volume flow rate (cont d...) Differential pressure flow meters
 Last lecture Analog-to-digital conversion (Ch. 1.1). Introduction to flow measurement systems (Ch. 12.1). Today s menu Measurement of volume flow rate Differential pressure flowmeters Mechanical flowmeters
Last lecture Analog-to-digital conversion (Ch. 1.1). Introduction to flow measurement systems (Ch. 12.1). Today s menu Measurement of volume flow rate Differential pressure flowmeters Mechanical flowmeters
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.017.65 Imaging exciton-polariton transport in MoSe waveguides F. Hu 1,, Y. Luan 1,, M. E. Scott 3, J.
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.017.65 Imaging exciton-polariton transport in MoSe waveguides F. Hu 1,, Y. Luan 1,, M. E. Scott 3, J.
Lecture 11 - Phonons II - Thermal Prop. Continued
 Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization. Yuri S. Kivshar
 Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia St. Petersburg University of Information Technologies,
Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia St. Petersburg University of Information Technologies,
ANALYSIS OF FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS ON NON-INVASIVE ULTRASONIC-DOPPLER FLOW MEASUREMENT FOR METAL PIPES
 4th International Symposium on Ultrasonic Doppler Method for Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Engineering Sapporo, 6.-8. September, 2004 ANALYSIS OF FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS ON NON-INVASIVE ULTRASONIC-DOPPLER
4th International Symposium on Ultrasonic Doppler Method for Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Engineering Sapporo, 6.-8. September, 2004 ANALYSIS OF FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS ON NON-INVASIVE ULTRASONIC-DOPPLER
Lecture #8 Non-linear phononics
 Lecture #8 Non-linear phononics Dr. Ari Salmi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 10.4.2018 1 Last lecture High pressure phononics can give insight into phase transitions in materials SASER can be used to generate
Lecture #8 Non-linear phononics Dr. Ari Salmi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 10.4.2018 1 Last lecture High pressure phononics can give insight into phase transitions in materials SASER can be used to generate
Structure of Biological Materials
 ELEC ENG 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Notes for Lecture #19 Monday, November 22, 2010 6.5 Nuclear medicine imaging Nuclear imaging produces images of the distribution of radiopharmaceuticals
ELEC ENG 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Notes for Lecture #19 Monday, November 22, 2010 6.5 Nuclear medicine imaging Nuclear imaging produces images of the distribution of radiopharmaceuticals
The Physics of Doppler Ultrasound. HET408 Medical Imaging
 The Physics of Doppler Ultrasound HET408 Medical Imaging 1 The Doppler Principle The basis of Doppler ultrasonography is the fact that reflected/scattered ultrasonic waves from a moving interface will
The Physics of Doppler Ultrasound HET408 Medical Imaging 1 The Doppler Principle The basis of Doppler ultrasonography is the fact that reflected/scattered ultrasonic waves from a moving interface will
A PDMS-based broadband acoustic impedance matched material for underwater applications. R.-M. Guillermic, M. Lanoy, A. Strybulevych, J.H.
 A PDMS-based broadband acoustic impedance matched material for underwater applications R.-M. Guillermic, M. Lanoy, A. Strybulevych, J.H. Page Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of Manitoba,
A PDMS-based broadband acoustic impedance matched material for underwater applications R.-M. Guillermic, M. Lanoy, A. Strybulevych, J.H. Page Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of Manitoba,
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Optical Imaging Chapter 5 Light Scattering
 Optical Imaging Chapter 5 Light Scattering Gabriel Popescu University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Beckman Institute Quantitative Light Imaging Laboratory http://light.ece.uiuc.edu Principles of Optical
Optical Imaging Chapter 5 Light Scattering Gabriel Popescu University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Beckman Institute Quantitative Light Imaging Laboratory http://light.ece.uiuc.edu Principles of Optical
Transient, planar, nonlinear acoustical holography for reconstructing acoustic pressure and particle velocity fields a
 Denver, Colorado NOISE-CON 013 013 August 6-8 Transient, planar, nonlinear acoustical holography for reconstructing acoustic pressure and particle velocity fields a Yaying Niu * Yong-Joe Kim Noise and
Denver, Colorado NOISE-CON 013 013 August 6-8 Transient, planar, nonlinear acoustical holography for reconstructing acoustic pressure and particle velocity fields a Yaying Niu * Yong-Joe Kim Noise and
Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy
 Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy Michael Krall Elements of Nanophotonics Associated Seminar Recent Progress in Nanooptics & Photonics May 07, 2009 Outline Single molecule
Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy Michael Krall Elements of Nanophotonics Associated Seminar Recent Progress in Nanooptics & Photonics May 07, 2009 Outline Single molecule
introduction of thermal transport
 Subgroup meeting 2010.12.07 introduction of thermal transport members: 王虹之. 盧孟珮 introduction of thermal transport Phonon effect Electron effect Lattice vibration phonon Debye model of lattice vibration
Subgroup meeting 2010.12.07 introduction of thermal transport members: 王虹之. 盧孟珮 introduction of thermal transport Phonon effect Electron effect Lattice vibration phonon Debye model of lattice vibration
Chapter 2 Fundamental Properties of Phononic Crystal
 Chapter 2 Fundamental Properties of Phononic Crystal Yan Pennec and Bahram Djafari-Rouhani 2.1 Introduction to the Concept of Phononic Crystals and Their Band Structures The control and manipulation of
Chapter 2 Fundamental Properties of Phononic Crystal Yan Pennec and Bahram Djafari-Rouhani 2.1 Introduction to the Concept of Phononic Crystals and Their Band Structures The control and manipulation of
A small object is placed a distance 2.0 cm from a thin convex lens. The focal length of the lens is 5.0 cm.
 TC [66 marks] This question is about a converging (convex) lens. A small object is placed a distance 2.0 cm from a thin convex lens. The focal length of the lens is 5.0 cm. (i) Deduce the magnification
TC [66 marks] This question is about a converging (convex) lens. A small object is placed a distance 2.0 cm from a thin convex lens. The focal length of the lens is 5.0 cm. (i) Deduce the magnification
Concepts in Surface Physics
 M.-C. Desjonqueres D. Spanjaard Concepts in Surface Physics Second Edition With 257 Figures Springer 1. Introduction................................. 1 2. Thermodynamical and Statistical Properties of
M.-C. Desjonqueres D. Spanjaard Concepts in Surface Physics Second Edition With 257 Figures Springer 1. Introduction................................. 1 2. Thermodynamical and Statistical Properties of
B 2 P 2, which implies that g B should be
 Enhanced Summary of G.P. Agrawal Nonlinear Fiber Optics (3rd ed) Chapter 9 on SBS Stimulated Brillouin scattering is a nonlinear three-wave interaction between a forward-going laser pump beam P, a forward-going
Enhanced Summary of G.P. Agrawal Nonlinear Fiber Optics (3rd ed) Chapter 9 on SBS Stimulated Brillouin scattering is a nonlinear three-wave interaction between a forward-going laser pump beam P, a forward-going
Focusing Ultrasound with Acoustic Metamaterial Network
 Focusing Ultrasound with Acoustic Metamaterial etwork Shu Zhang, Leilei Yin and icholas Fang Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana- Champaign, USA We present
Focusing Ultrasound with Acoustic Metamaterial etwork Shu Zhang, Leilei Yin and icholas Fang Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana- Champaign, USA We present
Today: 5 July 2008 ٢
 Anderson localization M. Reza Rahimi Tabar IPM 5 July 2008 ١ Today: 5 July 2008 ٢ Short History of Anderson Localization ٣ Publication 1) F. Shahbazi, etal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 165505 (2005) 2) A. Esmailpour,
Anderson localization M. Reza Rahimi Tabar IPM 5 July 2008 ١ Today: 5 July 2008 ٢ Short History of Anderson Localization ٣ Publication 1) F. Shahbazi, etal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 165505 (2005) 2) A. Esmailpour,
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310
 Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
Nondestructive Determination of Elastic Constants of Thin Plates Based on PVDF Focusing Ultrasound Transducers and Lamb Wave Measurements
 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Nondestructive Determination of Elastic Constants of Thin Plates Based on PVDF Focusing Ultrasound Transducers and Lamb
17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Nondestructive Determination of Elastic Constants of Thin Plates Based on PVDF Focusing Ultrasound Transducers and Lamb
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications
 6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 29: Electron-phonon Scattering Outline Bloch Electron Scattering Deformation Potential Scattering LCAO Estimation of Deformation Potential Matrix Element
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 29: Electron-phonon Scattering Outline Bloch Electron Scattering Deformation Potential Scattering LCAO Estimation of Deformation Potential Matrix Element
Two-dimensional ternary locally resonant phononic crystals with a comblike coating
 Two-dimensional ternary locally resonant phononic crystals with a comblike coating Yan-Feng Wang, Yue-Sheng Wang,*, and Litian Wang Institute of Engineering Mechanics, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing,
Two-dimensional ternary locally resonant phononic crystals with a comblike coating Yan-Feng Wang, Yue-Sheng Wang,*, and Litian Wang Institute of Engineering Mechanics, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing,
Module 40: Tunneling Lecture 40: Step potentials
 Module 40: Tunneling Lecture 40: Step potentials V E I II III 0 x a Figure 40.1: A particle of energy E is incident on a step potential of hight V > E as shown in Figure 40.1. The step potential extends
Module 40: Tunneling Lecture 40: Step potentials V E I II III 0 x a Figure 40.1: A particle of energy E is incident on a step potential of hight V > E as shown in Figure 40.1. The step potential extends
Main Notation Used in This Book
 Main Notation Used in This Book z Direction normal to the surface x,y Directions in the plane of the surface Used to describe a component parallel to the interface plane xoz Plane of incidence j Label
Main Notation Used in This Book z Direction normal to the surface x,y Directions in the plane of the surface Used to describe a component parallel to the interface plane xoz Plane of incidence j Label
Nonlinear Electrodynamics and Optics of Graphene
 Nonlinear Electrodynamics and Optics of Graphene S. A. Mikhailov and N. A. Savostianova University of Augsburg, Institute of Physics, Universitätsstr. 1, 86159 Augsburg, Germany E-mail: sergey.mikhailov@physik.uni-augsburg.de
Nonlinear Electrodynamics and Optics of Graphene S. A. Mikhailov and N. A. Savostianova University of Augsburg, Institute of Physics, Universitätsstr. 1, 86159 Augsburg, Germany E-mail: sergey.mikhailov@physik.uni-augsburg.de
Nondifractive propagation of light in photonic crystals
 Nondifractive propagation of light in photonic crystals Kestutis Staliunas (1) and Ramon Herrero () (1) ICREA, Departament de Fisica i Enginyeria Nuclear, Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya, Colom 11,
Nondifractive propagation of light in photonic crystals Kestutis Staliunas (1) and Ramon Herrero () (1) ICREA, Departament de Fisica i Enginyeria Nuclear, Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya, Colom 11,
MPIP-Mainz. FORTH Heraklion. T.Still,W.Cheng,N.Gomopoulos G.F G.F. Sculpture by E.Sempere (Madrid)
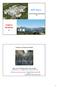 MPIP-Mainz T.Still,W.Cheng,N.Gomopoulos G.F FORTH Heraklion G.F Sculpture by E.Sempere (Madrid) Cubic arrays of hollow stainless-steel cylinders [diameter: 2.9 cm and lattice constant:a=0 cm] Minimum sound
MPIP-Mainz T.Still,W.Cheng,N.Gomopoulos G.F FORTH Heraklion G.F Sculpture by E.Sempere (Madrid) Cubic arrays of hollow stainless-steel cylinders [diameter: 2.9 cm and lattice constant:a=0 cm] Minimum sound
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications
 6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 19: Motion of Electronic Wavepackets Outline Review of Last Time Detailed Look at the Translation Operator Electronic Wavepackets Effective Mass Theorem
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 19: Motion of Electronic Wavepackets Outline Review of Last Time Detailed Look at the Translation Operator Electronic Wavepackets Effective Mass Theorem
Light Propagation in Free Space
 Intro Light Propagation in Free Space Helmholtz Equation 1-D Propagation Plane waves Plane wave propagation Light Propagation in Free Space 3-D Propagation Spherical Waves Huygen s Principle Each point
Intro Light Propagation in Free Space Helmholtz Equation 1-D Propagation Plane waves Plane wave propagation Light Propagation in Free Space 3-D Propagation Spherical Waves Huygen s Principle Each point
Lecture 10: Surface Plasmon Excitation. 5 nm
 Excitation Lecture 10: Surface Plasmon Excitation 5 nm Summary The dispersion relation for surface plasmons Useful for describing plasmon excitation & propagation This lecture: p sp Coupling light to surface
Excitation Lecture 10: Surface Plasmon Excitation 5 nm Summary The dispersion relation for surface plasmons Useful for describing plasmon excitation & propagation This lecture: p sp Coupling light to surface
D. BARD DIVISION OF ENGINEERING ACOUSTICS, LUND UNIVERSITY
 Transmission, Reflections, Eigenfrequencies, Eigenmodes Tranversal and Bending waves D. BARD DIVISION OF ENGINEERING ACOUSTICS, LUND UNIVERSITY Outline Introduction Types of waves Eigenfrequencies & Eigenmodes
Transmission, Reflections, Eigenfrequencies, Eigenmodes Tranversal and Bending waves D. BARD DIVISION OF ENGINEERING ACOUSTICS, LUND UNIVERSITY Outline Introduction Types of waves Eigenfrequencies & Eigenmodes
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Can be described by means of a classical sinusoidal wave model. Oscillating electric and magnetic field. (Wave model) wavelength,
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Can be described by means of a classical sinusoidal wave model. Oscillating electric and magnetic field. (Wave model) wavelength,
