Quasiconformal maps and the mapping theorem
|
|
|
- Lynette Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4 Quasiconformal maps and the mapping theorem Quasiconformal maps form a branch of complex analysis. I found the subject difficult to learn, mainly because I had a hard time appreciating how smooth the maps are. They are somehow rather magical, with properties that seem contradictory. They are smooth enough that much of calculus holds: the chain rule and the integral formulas for lengths and areas. They are rough enough that conjugating by them can change derivatives at fixed points. They are homeomorphisms, but have an affine structure: there are barycenters of quasiconformal mappings, and canonical straight lines joining pairs. Our treatment is somewhat different from the standard one: it is strongly colored by a prejudice in favor of soft analysis wherever possible. Thuswe avoid the words almost everywhere when we can, and more generally we avoid evaluating functions unless they are continuous: measurable functions should appear only under integral signs. Distributions are in, differentiability a.e. is out. Differential forms are in, densities are out. Approximations by C functions are in, absolute continuity on lines is out. 4. Two analytic definitions There are several possible definitions of quasiconformal mappings, and it is not so easy to see that they are equivalent. In this section we will give the best definition for our present purposes; in Section 4.5 we will give another and will propose three more in exercises. The great virtue of Definition 4.. below is that it is well adapted to the proof of the mapping theorem, Theorem However, it has drawbacks: although inverses and compositions of quasiconformal maps are quasiconformal, this does not follow easily from this analytic definition. Nor does this definition make it easy to check whether various explicit mappings are quasiconformal. Remark Definition 4.. involves distributional partial derivatives, often called weak derivatives. I dislike this misleading name, which suggests that a weak derivative carries inadequate information. Exactly the opposite is true: distributional derivatives carry all the information that a derivative
2 Chapter 4. Quasiconformal mappings should carry, unlike derivatives almost everywhere, which often overlook essential features. See Example 4..8 for a striking illustration. Definition 4.. (Quasiconformal map: first analytic definition) Let U, V be open subsets of C, take K, and set k := (K )/(K +), so that 0 k<. A mapping f : U V is K-quasiconformal if it is a homeomorphism whose distributional partial derivatives are in L loc (locally in L ) and satisfy f z k f z 4.. in L loc, i.e., almost everywhere. A map is quasiconformal if it is K-quasiconformal for some K. Definition 4.. (Quasiconformal constant) The smallest K such that f is K-quasiconformal is called the quasiconformal constant of f, denoted K(f). The quasiconformal constant is sometimes called the quasiconformal norm and sometimes the quasiconformal dilatation. The constant K measures how near a mapping is to being conformal, i.e., analytic; the closer K is to, the more nearly conformal a K-quasiconformal map is. This is not the only possible definition of what is means to be nearly conformal, but it is the most useful one, because good theorems are available for it. The meaning of inequality 4.. is best understood if f C (U). Then the derivative [Df(z 0 )] is an R-linear map, given by the Jacobian matrix, but it is easier to use complex notation: [Df(z 0 )](u) = f z (z 0)u + f z (z 0)ū. 4.. If we write a real linear transformation T : C C as T (u) =au + bū, so that a = T T u and b = ū, then we will see below that the determinant and norm of T are given by the important formulas det T = a b, T = a + b Remark 4..3 It follows from equation 4..3 that if T preserves orientation, then T ū < T T u, and if T reverses orientation, then ū > T u. (If the two sides are equal, then T is not an isomorphism, since it is neither orientation preserving nor orientation reversing.)
3 4. Two analytic definitions 3 Both formulas follow from computing the inverse image of the unit circle, i.e., from computing the real curve of equation T (u) =. Write u := re iθ, a := a e iα, and b := b e iβ The equation T (u) = becomes in polar coordinates ( ( a + b ) cos θ + α β ) + i( a b ) sin This is the equation of an ellipse, with minor axis at polar angle β α of semi-length major axis at polar angle β α + π ( θ + α β of semi-length ) = r a + b, and a b. This is illustrated in Figure 4... In particular, T = a + b (the inverse of the semi-length of the minor axis), and det T = a b (up to sign, the ratio of the area of the unit circle to the area of its preimage). a b a + b z 0 β α f f(z 0 ) V U T=[Df(z 0 )] Tu = au+bū Figure 4.. If f is K-quasiconformal and of class C (so that its derivative exists), then its derivative at z 0 takes the the ellipse on the left to the unit circle on the right. Finally, the ratio of the axes of the ellipse is a + b a b +k =K k Now set a := f z (z 0), b := f z (z 0) and write equation 4.. in the form [Df(z 0 )]u = au + bū. Then if f C (U) isk-quasiconformal, the condition 0 k< in Definition 4.. implies that det[df(z 0 )] is everywhere positive, so that f preserves orientation; see Remark 4..3.
4 4 Chapter 4. Quasiconformal mappings This gives the explanation we were after: a K-quasiconformal mapping of class C is an orientation-preserving diffeomorphism whose derivative maps infinitesimal circles to infinitesimal ellipses with eccentricity at most K (i.e., the ratio of the lengths of the axes of the ellipses is bounded by K). Sometimes we know f : U V in real terms: f(x + iy) =u(x, y)+iv(x, y) Computing the operator norm [Df] is then a bit unpleasant; the easy thing to compute is ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) [Df] u u v v := x y x y Exercise 4..4 Show that K(x + iy)+ K(x+iy) = [Df(x, y)] Jac f(x, y) Note that if U, V C are open and f : U V is a continuous map whose distributional derivatives are locally in L, then Jac f = f z f z and [Df] ( f = z + f z ) 4..0 are locally in L. Thus Definition 4.. can be restated as follows: Definition 4..5 (Quasiconformal map: nd analytic definition) Let U, V be open subsets of C and take K. A map f : U V is K-quasiconformal if. it is a homeomorphism,. its distributional partial derivatives are locally in L, and 3. its distributional partial derivatives satisfy Jac f [Df] locally in L. 4.. K Note that f is necessarily orientation preserving, since the Jacobian is positive by part 3. Inequalities 4.. and 4.. would not make sense if distributional partial derivatives were simply distributions. They would make sense if the derivatives were only required to exist a.e. and to be in L. Some authors mistakenly use this definition of quasiconformal mapping. It is not a useful definition, because the resulting maps do not have the desired properties. In particular, Weyl s lemma would be false, as shown in Example 4..8.
5 4. Two analytic definitions 5 Theorem in 4..6 (Weyl s lemma) If U C is open, and f : U C is a distribution in U satisfying f/ z =0, then f is an analytic function on U. Proof Choose r>0, let D r (z) be the disc of radius r centered at z, and let ϕ ɛ be a family of test functions with support in D r (0) and tending to the delta function as ɛ 0. Then the convolutions f ɛ = f ϕ ɛ are C functions on U r := { z U D r (z) U }, and the f ɛ satisfy f ɛ / z =0. (This is not true for the function of Example It is essential that it is the distributional derivative that vanishes.) Therefore each f ɛ is an analytic function on U r. We want to show that the f ɛ converge uniformly on compact subsets as ɛ 0; for this we need a slight variation on the Cauchy integral formula. Choose r <r and a C function η with support in (r,r ) with r η(r) dr =. Then the equation r f ɛ (z) = πi r π r 0 f ɛ (z 0 + re iθ ) z (z 0 + re iθ η(r) dθ dr 4.. ) is true in the disc of radius r around any point z 0 U r+r. In equation 4.., for each fixed z, the distribution f ɛ is evaluated on the fixed test η(r) function z (z 0 + re iθ, so it converges as ɛ 0, giving f a value at ) every point. Since the test functions vary continuously as functions of z, the function f is continuous. Using an appropriate variant of the Cauchy integral formula, it is not much harder to show that the derivative exists and is continuous. Corollary in 4..7 A -quasiconformal mapping is analytic, in fact, it is a conformal mapping, since it is a homeomorphism. Proof A -quasiconformal mapping satisfies equation 4.. with k = 0, i.e., it satisfies the hypothesis of Weyl s lemma. The following example shows how badly behaved a homeomorphism can be when it is only differentiable almost everywhere, with the derivatives satisfying inequalities 4.. and 4... This example should be kept in mind throughout this chapter. In some sense the whole chapter is a fight against it: we are constantly worried that some part of the distributional derivative is hiding in a set of measure 0. Example 4..8 (A homeomorphism of R that is not quasiconformal) Let the function η : R R be the standard devil s staircase : the unique nondecreasing function such that
Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation
 Chapter 7 Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation 7. Linear distortion Assume that f(x + iy) =u(x + iy)+iv(x + iy) be a (real) linear map from C C that is orientation preserving. Let z = x + iy and
Chapter 7 Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation 7. Linear distortion Assume that f(x + iy) =u(x + iy)+iv(x + iy) be a (real) linear map from C C that is orientation preserving. Let z = x + iy and
Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings
 Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings Antti Rasila Helsinki University of Technology antti.rasila@tkk.fi (Mainly based on P. Duren s book Harmonic mappings in the plane) Helsinki Analysis Seminar,
Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings Antti Rasila Helsinki University of Technology antti.rasila@tkk.fi (Mainly based on P. Duren s book Harmonic mappings in the plane) Helsinki Analysis Seminar,
(x 1, y 1 ) = (x 2, y 2 ) if and only if x 1 = x 2 and y 1 = y 2.
 1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping
 Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
1. Bounded linear maps. A linear map T : E F of real Banach
 DIFFERENTIABLE MAPS 1. Bounded linear maps. A linear map T : E F of real Banach spaces E, F is bounded if M > 0 so that for all v E: T v M v. If v r T v C for some positive constants r, C, then T is bounded:
DIFFERENTIABLE MAPS 1. Bounded linear maps. A linear map T : E F of real Banach spaces E, F is bounded if M > 0 so that for all v E: T v M v. If v r T v C for some positive constants r, C, then T is bounded:
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
= 2 x y 2. (1)
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
Homework 27. Homework 28. Homework 29. Homework 30. Prof. Girardi, Math 703, Fall 2012 Homework: Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by
 Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Complex Analysis Homework 9: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges
Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C. 1.1 Holomorphic Functions
 11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C 1.1 Holomorphic Functions A domain Ω in the complex plane C is a connected, open subset of C. Let z o Ω and f a map f : Ω C. We say that f is real differentiable at z o if there
11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C 1.1 Holomorphic Functions A domain Ω in the complex plane C is a connected, open subset of C. Let z o Ω and f a map f : Ω C. We say that f is real differentiable at z o if there
7.2 Conformal mappings
 7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
Solutions for Problem Set #4 due October 10, 2003 Dustin Cartwright
 Solutions for Problem Set #4 due October 1, 3 Dustin Cartwright (B&N 4.3) Evaluate C f where f(z) 1/z as in Example, and C is given by z(t) sin t + i cos t, t π. Why is the result different from that of
Solutions for Problem Set #4 due October 1, 3 Dustin Cartwright (B&N 4.3) Evaluate C f where f(z) 1/z as in Example, and C is given by z(t) sin t + i cos t, t π. Why is the result different from that of
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Analysis II: The Implicit and Inverse Function Theorems
 Analysis II: The Implicit and Inverse Function Theorems Jesse Ratzkin November 17, 2009 Let f : R n R m be C 1. When is the zero set Z = {x R n : f(x) = 0} the graph of another function? When is Z nicely
Analysis II: The Implicit and Inverse Function Theorems Jesse Ratzkin November 17, 2009 Let f : R n R m be C 1. When is the zero set Z = {x R n : f(x) = 0} the graph of another function? When is Z nicely
Part III. 10 Topological Space Basics. Topological Spaces
 Part III 10 Topological Space Basics Topological Spaces Using the metric space results above as motivation we will axiomatize the notion of being an open set to more general settings. Definition 10.1.
Part III 10 Topological Space Basics Topological Spaces Using the metric space results above as motivation we will axiomatize the notion of being an open set to more general settings. Definition 10.1.
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010
 An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Complex Differentials and the Stokes, Goursat and Cauchy Theorems
 Complex Differentials and the Stokes, Goursat and Cauchy Theorems Benjamin McKay June 21, 2001 1 Stokes theorem Theorem 1 (Stokes) f(x, y) dx + g(x, y) dy = U ( g y f ) dx dy x where U is a region of the
Complex Differentials and the Stokes, Goursat and Cauchy Theorems Benjamin McKay June 21, 2001 1 Stokes theorem Theorem 1 (Stokes) f(x, y) dx + g(x, y) dy = U ( g y f ) dx dy x where U is a region of the
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
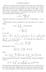 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
TEICHMÜLLER SPACE MATTHEW WOOLF
 TEICHMÜLLER SPACE MATTHEW WOOLF Abstract. It is a well-known fact that every Riemann surface with negative Euler characteristic admits a hyperbolic metric. But this metric is by no means unique indeed,
TEICHMÜLLER SPACE MATTHEW WOOLF Abstract. It is a well-known fact that every Riemann surface with negative Euler characteristic admits a hyperbolic metric. But this metric is by no means unique indeed,
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
LECTURE-15 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS
 LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
26.2. Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping 26.2 Introduction In this Section we consider two important features of complex functions. The Cauchy-Riemann equations provide a necessary and sufficient
Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping 26.2 Introduction In this Section we consider two important features of complex functions. The Cauchy-Riemann equations provide a necessary and sufficient
be the set of complex valued 2π-periodic functions f on R such that
 . Fourier series. Definition.. Given a real number P, we say a complex valued function f on R is P -periodic if f(x + P ) f(x) for all x R. We let be the set of complex valued -periodic functions f on
. Fourier series. Definition.. Given a real number P, we say a complex valued function f on R is P -periodic if f(x + P ) f(x) for all x R. We let be the set of complex valued -periodic functions f on
SMSTC (2017/18) Geometry and Topology 2.
 SMSTC (2017/18) Geometry and Topology 2 Lecture 1: Differentiable Functions and Manifolds in R n Lecturer: Diletta Martinelli (Notes by Bernd Schroers) a wwwsmstcacuk 11 General remarks In this lecture
SMSTC (2017/18) Geometry and Topology 2 Lecture 1: Differentiable Functions and Manifolds in R n Lecturer: Diletta Martinelli (Notes by Bernd Schroers) a wwwsmstcacuk 11 General remarks In this lecture
f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ
![f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ](/thumbs/87/95570641.jpg) Remarks. 1. So far we have seen that holomorphic is equivalent to analytic. Thus, if f is complex differentiable in an open set, then it is infinitely many times complex differentiable in that set. This
Remarks. 1. So far we have seen that holomorphic is equivalent to analytic. Thus, if f is complex differentiable in an open set, then it is infinitely many times complex differentiable in that set. This
Conformal Mappings. Chapter Schwarz Lemma
 Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
The result above is known as the Riemann mapping theorem. We will prove it using basic theory of normal families. We start this lecture with that.
 Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
g(x) = P (y) Proof. This is true for n = 0. Assume by the inductive hypothesis that g (n) (0) = 0 for some n. Compute g (n) (h) g (n) (0)
 Mollifiers and Smooth Functions We say a function f from C is C (or simply smooth) if all its derivatives to every order exist at every point of. For f : C, we say f is C if all partial derivatives to
Mollifiers and Smooth Functions We say a function f from C is C (or simply smooth) if all its derivatives to every order exist at every point of. For f : C, we say f is C if all partial derivatives to
Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r
![Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r](/thumbs/77/75527144.jpg) 2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY Multivariable Calculus, a refresher
 DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY Multivariable Calculus, a refresher 1 Preliminaries In this section I collect some results from multivariable calculus that play an important role in the course. If you don t know
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY Multivariable Calculus, a refresher 1 Preliminaries In this section I collect some results from multivariable calculus that play an important role in the course. If you don t know
Definition We say that a topological manifold X is C p if there is an atlas such that the transition functions are C p.
 13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
u xx + u yy = 0. (5.1)
 Chapter 5 Laplace Equation The following equation is called Laplace equation in two independent variables x, y: The non-homogeneous problem u xx + u yy =. (5.1) u xx + u yy = F, (5.) where F is a function
Chapter 5 Laplace Equation The following equation is called Laplace equation in two independent variables x, y: The non-homogeneous problem u xx + u yy =. (5.1) u xx + u yy = F, (5.) where F is a function
Several variables. x 1 x 2. x n
 Several variables Often we have not only one, but several variables in a problem The issues that come up are somewhat more complex than for one variable Let us first start with vector spaces and linear
Several variables Often we have not only one, but several variables in a problem The issues that come up are somewhat more complex than for one variable Let us first start with vector spaces and linear
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 11
 MAT389 Fall 216, Problem Set 11 Improper integrals 11.1 In each of the following cases, establish the convergence of the given integral and calculate its value. i) x 2 x 2 + 1) 2 ii) x x 2 + 1)x 2 + 2x
MAT389 Fall 216, Problem Set 11 Improper integrals 11.1 In each of the following cases, establish the convergence of the given integral and calculate its value. i) x 2 x 2 + 1) 2 ii) x x 2 + 1)x 2 + 2x
LECTURE Itineraries We start with a simple example of a dynamical system obtained by iterating the quadratic polynomial
 LECTURE. Itineraries We start with a simple example of a dynamical system obtained by iterating the quadratic polynomial f λ : R R x λx( x), where λ [, 4). Starting with the critical point x 0 := /2, we
LECTURE. Itineraries We start with a simple example of a dynamical system obtained by iterating the quadratic polynomial f λ : R R x λx( x), where λ [, 4). Starting with the critical point x 0 := /2, we
Part IB. Further Analysis. Year
 Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION
 POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
Final Exam Solutions June 10, 2004
 Math 0400: Analysis in R n II Spring 004 Section 55 P. Achar Final Exam Solutions June 10, 004 Total points: 00 There are three blank pages for scratch work at the end of the exam. Time it: hours 1. True
Math 0400: Analysis in R n II Spring 004 Section 55 P. Achar Final Exam Solutions June 10, 004 Total points: 00 There are three blank pages for scratch work at the end of the exam. Time it: hours 1. True
Analysis IV : Assignment 3 Solutions John Toth, Winter ,...). In particular for every fixed m N the sequence (u (n)
 Analysis IV : Assignment 3 Solutions John Toth, Winter 203 Exercise (l 2 (Z), 2 ) is a complete and separable Hilbert space. Proof Let {u (n) } n N be a Cauchy sequence. Say u (n) = (..., u 2, (n) u (n),
Analysis IV : Assignment 3 Solutions John Toth, Winter 203 Exercise (l 2 (Z), 2 ) is a complete and separable Hilbert space. Proof Let {u (n) } n N be a Cauchy sequence. Say u (n) = (..., u 2, (n) u (n),
Taylor and Laurent Series
 Chapter 4 Taylor and Laurent Series 4.. Taylor Series 4... Taylor Series for Holomorphic Functions. In Real Analysis, the Taylor series of a given function f : R R is given by: f (x + f (x (x x + f (x
Chapter 4 Taylor and Laurent Series 4.. Taylor Series 4... Taylor Series for Holomorphic Functions. In Real Analysis, the Taylor series of a given function f : R R is given by: f (x + f (x (x x + f (x
IV. Conformal Maps. 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability. 2. Automorphisms of the Riemann sphere: Möbius transformations
 MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
Notes on Complex Analysis
 Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Conformal maps. Lent 2019 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor. A star means optional and not necessarily harder.
 Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Complex Variables. Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit.
 Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
MAT 544 Problem Set 2 Solutions
 MAT 544 Problem Set 2 Solutions Problems. Problem 1 A metric space is separable if it contains a dense subset which is finite or countably infinite. Prove that every totally bounded metric space X is separable.
MAT 544 Problem Set 2 Solutions Problems. Problem 1 A metric space is separable if it contains a dense subset which is finite or countably infinite. Prove that every totally bounded metric space X is separable.
Poisson Image Editing
 Poisson Image Editing Sébastien Boisgérault, Mines ParisTech, under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 November 28, 2017 Contents Introduction 1 Modelling the Problem 2 Harmonic Functions 5 The irichlet Problem 8 Harmonic/Fourier
Poisson Image Editing Sébastien Boisgérault, Mines ParisTech, under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 November 28, 2017 Contents Introduction 1 Modelling the Problem 2 Harmonic Functions 5 The irichlet Problem 8 Harmonic/Fourier
u = (u, v) = y The velocity field described by ψ automatically satisfies the incompressibility condition, and it should be noted that
 18.354J Nonlinear Dynamics II: Continuum Systems Lecture 1 9 Spring 2015 19 Stream functions and conformal maps There is a useful device for thinking about two dimensional flows, called the stream function
18.354J Nonlinear Dynamics II: Continuum Systems Lecture 1 9 Spring 2015 19 Stream functions and conformal maps There is a useful device for thinking about two dimensional flows, called the stream function
Introduction to Topology
 Introduction to Topology Randall R. Holmes Auburn University Typeset by AMS-TEX Chapter 1. Metric Spaces 1. Definition and Examples. As the course progresses we will need to review some basic notions about
Introduction to Topology Randall R. Holmes Auburn University Typeset by AMS-TEX Chapter 1. Metric Spaces 1. Definition and Examples. As the course progresses we will need to review some basic notions about
Junior Seminar: Hyperbolic Geometry Lecture Notes
 Junior Seminar: Hyperbolic Geometry Lecture Notes Tim Campion January 20, 2010 1 Motivation Our first construction is very similar in spirit to an analogous one in Euclidean space. The group of isometries
Junior Seminar: Hyperbolic Geometry Lecture Notes Tim Campion January 20, 2010 1 Motivation Our first construction is very similar in spirit to an analogous one in Euclidean space. The group of isometries
Differential Topology Solution Set #2
 Differential Topology Solution Set #2 Select Solutions 1. Show that X compact implies that any smooth map f : X Y is proper. Recall that a space is called compact if, for every cover {U } by open sets
Differential Topology Solution Set #2 Select Solutions 1. Show that X compact implies that any smooth map f : X Y is proper. Recall that a space is called compact if, for every cover {U } by open sets
SPRING 2008: POLYNOMIAL IMAGES OF CIRCLES
 18.821 SPRING 28: POLYNOMIAL IMAGES OF CIRCLES JUSTIN CURRY, MICHAEL FORBES, MATTHEW GORDON Abstract. This paper considers the effect of complex polynomial maps on circles of various radii. Several phenomena
18.821 SPRING 28: POLYNOMIAL IMAGES OF CIRCLES JUSTIN CURRY, MICHAEL FORBES, MATTHEW GORDON Abstract. This paper considers the effect of complex polynomial maps on circles of various radii. Several phenomena
Course 212: Academic Year Section 1: Metric Spaces
 Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps
 1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps Last updated: April 14, 2011. 1.1 Examples and definitions Roughly, manifolds are sets where one can introduce coordinates. An n-dimensional manifold is a set
1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps Last updated: April 14, 2011. 1.1 Examples and definitions Roughly, manifolds are sets where one can introduce coordinates. An n-dimensional manifold is a set
III.2. Analytic Functions
 III.2. Analytic Functions 1 III.2. Analytic Functions Recall. When you hear analytic function, think power series representation! Definition. If G is an open set in C and f : G C, then f is differentiable
III.2. Analytic Functions 1 III.2. Analytic Functions Recall. When you hear analytic function, think power series representation! Definition. If G is an open set in C and f : G C, then f is differentiable
4 Countability axioms
 4 COUNTABILITY AXIOMS 4 Countability axioms Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space X is said to be first countable if for any x X, there is a countable basis for the neighborhoods of x. X is said
4 COUNTABILITY AXIOMS 4 Countability axioms Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space X is said to be first countable if for any x X, there is a countable basis for the neighborhoods of x. X is said
Subharmonic functions
 Subharmonic functions N.A. 07 Upper semicontinuous functions. Let (X, d) be a metric space. A function f : X R { } is upper semicontinuous (u.s.c.) if lim inf f(y) f(x) x X. y x A function g is lower semicontinuous
Subharmonic functions N.A. 07 Upper semicontinuous functions. Let (X, d) be a metric space. A function f : X R { } is upper semicontinuous (u.s.c.) if lim inf f(y) f(x) x X. y x A function g is lower semicontinuous
Part V. 17 Introduction: What are measures and why measurable sets. Lebesgue Integration Theory
 Part V 7 Introduction: What are measures and why measurable sets Lebesgue Integration Theory Definition 7. (Preliminary). A measure on a set is a function :2 [ ] such that. () = 2. If { } = is a finite
Part V 7 Introduction: What are measures and why measurable sets Lebesgue Integration Theory Definition 7. (Preliminary). A measure on a set is a function :2 [ ] such that. () = 2. If { } = is a finite
KUIPER S THEOREM ON CONFORMALLY FLAT MANIFOLDS
 KUIPER S THEOREM ON CONFORMALLY FLAT MANIFOLDS RALPH HOWARD DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA COLUMBIA, S.C. 29208, USA HOWARD@MATH.SC.EDU 1. Introduction These are notes to that show
KUIPER S THEOREM ON CONFORMALLY FLAT MANIFOLDS RALPH HOWARD DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA COLUMBIA, S.C. 29208, USA HOWARD@MATH.SC.EDU 1. Introduction These are notes to that show
THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM
 THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM W. PATRICK HOOPER The implicit function theorem is the following result: Theorem 1. Let f be a C 1 function from a neighborhood of a point a R n into R n. Suppose A = Df(a)
THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM W. PATRICK HOOPER The implicit function theorem is the following result: Theorem 1. Let f be a C 1 function from a neighborhood of a point a R n into R n. Suppose A = Df(a)
(FALL 2011) 225A - DIFFERENTIAL TOPOLOGY FINAL < HOPF DEGREE THEOREM >
 (FALL 2011) 225A - DIFFERENTIAL TOPOLOGY FINAL < HOPF DEGREE THEOREM > GEUNHO GIM 1. Without loss of generality, we can assume that x = z = 0. Let A = df 0. By regularity at 0, A is a linear isomorphism.
(FALL 2011) 225A - DIFFERENTIAL TOPOLOGY FINAL < HOPF DEGREE THEOREM > GEUNHO GIM 1. Without loss of generality, we can assume that x = z = 0. Let A = df 0. By regularity at 0, A is a linear isomorphism.
Integration in the Complex Plane (Zill & Wright Chapter 18)
 Integration in the omplex Plane Zill & Wright hapter 18) 116-4-: omplex Variables Fall 11 ontents 1 ontour Integrals 1.1 Definition and Properties............................. 1. Evaluation.....................................
Integration in the omplex Plane Zill & Wright hapter 18) 116-4-: omplex Variables Fall 11 ontents 1 ontour Integrals 1.1 Definition and Properties............................. 1. Evaluation.....................................
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION TUTORIAL 2 ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION TUTORIAL ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION CONTENTS Function of a Function Differentiation of a Sum Differentiation of a Proct Differentiation of a Quotient Turning Points
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION TUTORIAL ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION CONTENTS Function of a Function Differentiation of a Sum Differentiation of a Proct Differentiation of a Quotient Turning Points
MORE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOREM
 MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
1. The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions.
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
DECOMPOSING DIFFEOMORPHISMS OF THE SPHERE. inf{d Y (f(x), f(y)) : d X (x, y) r} H
 DECOMPOSING DIFFEOMORPHISMS OF THE SPHERE ALASTAIR FLETCHER, VLADIMIR MARKOVIC 1. Introduction 1.1. Background. A bi-lipschitz homeomorphism f : X Y between metric spaces is a mapping f such that f and
DECOMPOSING DIFFEOMORPHISMS OF THE SPHERE ALASTAIR FLETCHER, VLADIMIR MARKOVIC 1. Introduction 1.1. Background. A bi-lipschitz homeomorphism f : X Y between metric spaces is a mapping f such that f and
= F (b) F (a) F (x i ) F (x i+1 ). a x 0 x 1 x n b i
 Real Analysis Problem 1. If F : R R is a monotone function, show that F T V ([a,b]) = F (b) F (a) for any interval [a, b], and that F has bounded variation on R if and only if it is bounded. Here F T V
Real Analysis Problem 1. If F : R R is a monotone function, show that F T V ([a,b]) = F (b) F (a) for any interval [a, b], and that F has bounded variation on R if and only if it is bounded. Here F T V
NOTES ON THE REGULARITY OF QUASICONFORMAL HOMEOMORPHISMS
 NOTES ON THE REGULARITY OF QUASICONFORMAL HOMEOMORPHISMS CLARK BUTLER. Introduction The purpose of these notes is to give a self-contained proof of the following theorem, Theorem.. Let f : S n S n be a
NOTES ON THE REGULARITY OF QUASICONFORMAL HOMEOMORPHISMS CLARK BUTLER. Introduction The purpose of these notes is to give a self-contained proof of the following theorem, Theorem.. Let f : S n S n be a
(z 0 ) = lim. = lim. = f. Similarly along a vertical line, we fix x = x 0 and vary y. Setting z = x 0 + iy, we get. = lim. = i f
 . Holomorphic Harmonic Functions Basic notation. Considering C as R, with coordinates x y, z = x + iy denotes the stard complex coordinate, in the usual way. Definition.1. Let f : U C be a complex valued
. Holomorphic Harmonic Functions Basic notation. Considering C as R, with coordinates x y, z = x + iy denotes the stard complex coordinate, in the usual way. Definition.1. Let f : U C be a complex valued
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping. 1 Conformality. 1.1 Preservation of angle. 1.2 Length and area. MATH-GA Complex Variables
 Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
Complex Analysis Math 185A, Winter 2010 Final: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Math Homework 2
 Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Implicit Functions, Curves and Surfaces
 Chapter 11 Implicit Functions, Curves and Surfaces 11.1 Implicit Function Theorem Motivation. In many problems, objects or quantities of interest can only be described indirectly or implicitly. It is then
Chapter 11 Implicit Functions, Curves and Surfaces 11.1 Implicit Function Theorem Motivation. In many problems, objects or quantities of interest can only be described indirectly or implicitly. It is then
MATH8811: COMPLEX ANALYSIS
 MATH8811: COMPLEX ANALYSIS DAWEI CHEN Contents 1. Classical Topics 2 1.1. Complex numbers 2 1.2. Differentiability 2 1.3. Cauchy-Riemann Equations 3 1.4. The Riemann Sphere 4 1.5. Möbius transformations
MATH8811: COMPLEX ANALYSIS DAWEI CHEN Contents 1. Classical Topics 2 1.1. Complex numbers 2 1.2. Differentiability 2 1.3. Cauchy-Riemann Equations 3 1.4. The Riemann Sphere 4 1.5. Möbius transformations
Part IB Geometry. Theorems. Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2016
 Part IB Geometry Theorems Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IB Geometry Theorems Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Problem 1A. Suppose that f is a continuous real function on [0, 1]. Prove that
![Problem 1A. Suppose that f is a continuous real function on [0, 1]. Prove that Problem 1A. Suppose that f is a continuous real function on [0, 1]. Prove that](/thumbs/73/68962001.jpg) Problem 1A. Suppose that f is a continuous real function on [, 1]. Prove that lim α α + x α 1 f(x)dx = f(). Solution: This is obvious for f a constant, so by subtracting f() from both sides we can assume
Problem 1A. Suppose that f is a continuous real function on [, 1]. Prove that lim α α + x α 1 f(x)dx = f(). Solution: This is obvious for f a constant, so by subtracting f() from both sides we can assume
Metric Spaces and Topology
 Chapter 2 Metric Spaces and Topology From an engineering perspective, the most important way to construct a topology on a set is to define the topology in terms of a metric on the set. This approach underlies
Chapter 2 Metric Spaces and Topology From an engineering perspective, the most important way to construct a topology on a set is to define the topology in terms of a metric on the set. This approach underlies
Lebesgue Integration: A non-rigorous introduction. What is wrong with Riemann integration?
 Lebesgue Integration: A non-rigorous introduction What is wrong with Riemann integration? xample. Let f(x) = { 0 for x Q 1 for x / Q. The upper integral is 1, while the lower integral is 0. Yet, the function
Lebesgue Integration: A non-rigorous introduction What is wrong with Riemann integration? xample. Let f(x) = { 0 for x Q 1 for x / Q. The upper integral is 1, while the lower integral is 0. Yet, the function
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE
 MATH 3: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE Recall the Residue Theorem: Let be a simple closed loop, traversed counterclockwise. Let f be a function that is analytic on and meromorphic inside. Then
MATH 3: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE Recall the Residue Theorem: Let be a simple closed loop, traversed counterclockwise. Let f be a function that is analytic on and meromorphic inside. Then
Sobolev spaces. May 18
 Sobolev spaces May 18 2015 1 Weak derivatives The purpose of these notes is to give a very basic introduction to Sobolev spaces. More extensive treatments can e.g. be found in the classical references
Sobolev spaces May 18 2015 1 Weak derivatives The purpose of these notes is to give a very basic introduction to Sobolev spaces. More extensive treatments can e.g. be found in the classical references
Metric spaces and metrizability
 1 Motivation Metric spaces and metrizability By this point in the course, this section should not need much in the way of motivation. From the very beginning, we have talked about R n usual and how relatively
1 Motivation Metric spaces and metrizability By this point in the course, this section should not need much in the way of motivation. From the very beginning, we have talked about R n usual and how relatively
2. Metric Spaces. 2.1 Definitions etc.
 2. Metric Spaces 2.1 Definitions etc. The procedure in Section for regarding R as a topological space may be generalized to many other sets in which there is some kind of distance (formally, sets with
2. Metric Spaces 2.1 Definitions etc. The procedure in Section for regarding R as a topological space may be generalized to many other sets in which there is some kind of distance (formally, sets with
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions
 Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 204 Cauchy and Runge Under the Same Roof. These notes can be used as an alternative to Section 5.5 of Chapter 2 in the textbook. They assume the theorem on winding numbers of the
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 204 Cauchy and Runge Under the Same Roof. These notes can be used as an alternative to Section 5.5 of Chapter 2 in the textbook. They assume the theorem on winding numbers of the
DIFFERENTIABLE CONJUGACY NEAR COMPACT INVARIANT MANIFOLDS
 DIFFERENTIABLE CONJUGACY NEAR COMPACT INVARIANT MANIFOLDS CLARK ROBINSON 0. Introduction In this paper 1, we show how the differentiable linearization of a diffeomorphism near a hyperbolic fixed point
DIFFERENTIABLE CONJUGACY NEAR COMPACT INVARIANT MANIFOLDS CLARK ROBINSON 0. Introduction In this paper 1, we show how the differentiable linearization of a diffeomorphism near a hyperbolic fixed point
8 Nonlinear change of variables
 Tel Aviv University, 206 Analysis-III 98 8 Nonlinear change of variables 8a Introduction....................... 98 8b Examples......................... 00 8c Measure 0 is preserved................. 02
Tel Aviv University, 206 Analysis-III 98 8 Nonlinear change of variables 8a Introduction....................... 98 8b Examples......................... 00 8c Measure 0 is preserved................. 02
Complex Analysis Important Concepts
 Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
COMPLEX VARIETIES AND THE ANALYTIC TOPOLOGY
 COMPLEX VARIETIES AND THE ANALYTIC TOPOLOGY BRIAN OSSERMAN Classical algebraic geometers studied algebraic varieties over the complex numbers. In this setting, they didn t have to worry about the Zariski
COMPLEX VARIETIES AND THE ANALYTIC TOPOLOGY BRIAN OSSERMAN Classical algebraic geometers studied algebraic varieties over the complex numbers. In this setting, they didn t have to worry about the Zariski
Synopsis of Complex Analysis. Ryan D. Reece
 Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Measurable functions are approximately nice, even if look terrible.
 Tel Aviv University, 2015 Functions of real variables 74 7 Approximation 7a A terrible integrable function........... 74 7b Approximation of sets................ 76 7c Approximation of functions............
Tel Aviv University, 2015 Functions of real variables 74 7 Approximation 7a A terrible integrable function........... 74 7b Approximation of sets................ 76 7c Approximation of functions............
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
Part II. Riemann Surfaces. Year
 Part II Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 96 Paper 2, Section II 23F State the uniformisation theorem. List without proof the Riemann surfaces which are uniformised
Part II Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 96 Paper 2, Section II 23F State the uniformisation theorem. List without proof the Riemann surfaces which are uniformised
Properties of Analytic Functions
 Properties of Analytic Functions Generalizing Results to Analytic Functions In the last few sections, we completely described entire functions through the use of everywhere convergent power series. Our
Properties of Analytic Functions Generalizing Results to Analytic Functions In the last few sections, we completely described entire functions through the use of everywhere convergent power series. Our
Math 520a - Final take home exam - solutions
 Math 52a - Final take home exam - solutions 1. Let f(z) be entire. Prove that f has finite order if and only if f has finite order and that when they have finite order their orders are the same. Solution:
Math 52a - Final take home exam - solutions 1. Let f(z) be entire. Prove that f has finite order if and only if f has finite order and that when they have finite order their orders are the same. Solution:
