Electricity and Magnetism Gauss s Law
|
|
|
- Catherine Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrcty and Magnetsm Gauss s Law Ampère s Law Lana Sherdan De Anza College Mar 1, 2018
2 Last tme magnetc feld of a movng charge magnetc feld of a current the Bot-Savart law magnetc feld around a straght wre
3 Overvew Gauss s Law for magnetsm Ampère s Law B-feld outsde and nsde a wre Solenods
4 B-Feld around a wre revsted Usng the Bot-Savart law we found that the feld around an nfntely long straght wre, carryng a current I was: at a dstance a from the wre. B = µ 0I 2πa Is the another way we could have solved ths problem? When we had an nfnte lne of charge, there was a law we could use to fnd the E-feld...
5 B-Feld around a wre revsted Usng the Bot-Savart law we found that the feld around an nfntely long straght wre, carryng a current I was: at a dstance a from the wre. B = µ 0I 2πa Is the another way we could have solved ths problem? When we had an nfnte lne of charge, there was a law we could use to fnd the E-feld... Gauss s law. Could we use somethng smlar here?
6 Gauss s Law for Magnetc Felds Gauss s Law for Electrc felds: Φ E = E da = q enc ɛ 0 The electrc flux through a closed surface s equal to the charge enclosed by the surface, dvded by ɛ 0. There s a smlar expresson for magnetc flux! Frst we must defne magnetc flux, Φ B.
7 (30.18) Magnetc Flux Defnton of magnetc flux feld B S that makes an case s (30.19), then u and the he plane as n Fgure axmum value). weber Magnetc (Wb); 1 Wb flux 5 plane s a agnetc to the plane. B S u S d A Fgure The magnetc flux through an area element da s S B? d S A 5 B da cos u, where d S A s a vector perpendcular to the surface. The magnetc flux of a magnetc feld through a surface A s Φ B = B da da S Unts: Tm 2 If the surface s a flat plane and B s unform, that just reduces to: Φ B = B A
8 Gauss s Law for Magnetc Felds Gauss s Law for magnetc felds.: B da = 0 Where the ntegral s taken over a closed surface A. We can nterpret t as an asserton that magnetc monopoles do not exst. In dfferental form: B = 0 The magnetc feld has no sources or snks. (It s dvergence-free ; we can wrte B = a, where a s the vector potental.)
9 Gauss s Law for Magnetc Felds 32-3 INDUCED MAGNETIC FIELDS B da = PART 3 re complcated than does not enclose the Fg encloses no x through t s zero. nly the north pole of l S. However, a south ce because magnetc lke one pece of the encloses a magnetc Surface II N B Surface I S tom faces and curved B of the unform and and B are arbtrary of the magnetc flux
10 B-Feld around a wre revsted Gauss s law wll not help us fnd the strength of the B-feld around the wre: the flux through any closed surface wll be zero. Another law can.
11 Ampère s Law dstrbuton of currents due to a For current-length constant currents (magnetostatcs): the elements.agan we However, f the dstrbe s law to fnd the mag- B ds = µ 0 I enc n be derved from the André-Mare Ampère wever, the law actually The lne ntegral of the magnetc feld around a closed loop s proportonal to the current that flows through the loop. 1 (29-14) product B : ds : s to be. The current enc s the ts ntegral, let us frst The fgure shows cross 2,and 3 ether drectly p lyng n the plane of The counterclockwse en drecton of ntegra- Amperan loop Only the currents encrcled by the loop are used n Ampere's law. Drecton of ntegraton Fg Ampere s law appled to an 1 That s, the current arbtrary thatamperan flows through loop that anyencrcles surface two bounded by the loop. ds θ B
12 772 Ampère s Law CHAPTER 29 MAGNETIC FIELDS DUE T Ths s how to assgn a sgn to a current used n Ampere's law Drecton of ntegraton drecton of Fg , th are perpend current s n be n that pl In Fg The sca Thus, Ampe We can now Fg A rght-hand rule for of the Ampe A current through Ampere s thelaw, loop to determne the general the drecton sgns forof your we can nte outstretched currents thumbencrcled s assgned by aan plus Amperan sgn, andloop. a current generally around the e n the opposte The stuaton drecton sthat assgned of Fg. a mnus sgn. When w
13 Queston CHECKPOINT 2 The fgure here shows three equal currents shows (two three parallel equaland currents one antparal- (two parallel and one The (29-19) fgure here antparallel) and lel) four and Amperan loops. Rank the loops accordng to the magntude of four Amperan loops. Rank the loops s law gves us B accordng ds alongto each, the magntude greatest frst. of B : ds : along each, greatest frst. a (29-20) b ortonal to r, at Eqs c d A a, b, c, d B d, b, c, a C (a and b), d, c D d, (a and c), b 1 Hallday, Resnck, Walker, page 773.
14 Queston CHECKPOINT 2 The fgure here shows three equal currents shows (two three parallel equaland currents one antparal- (two parallel and one The (29-19) fgure here antparallel) and lel) four and Amperan loops. Rank the loops accordng to the magntude of four Amperan loops. Rank the loops s law gves us B accordng ds alongto each, the magntude greatest frst. of B : ds : along each, greatest frst. a (29-20) b ortonal to r, at Eqs c d A a, b, c, d B d, b, c, a C (a and b), d, c D d, (a and c), b 1 Hallday, Resnck, Walker, page 773.
15 Ampère s Law and the Magnetc Feld from a Current Outsde a wre All of the current s You mght Suppose we want encrcled to know and the magntude thus all of the magnetc feldntude at a B o dstance r outsde s used a wre. n Usng Ampere's Ampère s law. Law? s that the ntegraton of an encr Amperan We can Wre r loop surface the stuato the ntegra m B 0 ( 1 2 ), We sh ( θ = 0) allow us to ds 3 Fg Usng Ampere s law to fnd the magnetc feld that a current produces outsde a long straght wre of crcular cross Magnetc Fgure 29-
16 Ampère s Law and the Magnetc Feld from a Current All of the Outsde current s a wre encrcled and thus all s used n Ampere's law. Wre surface r Amperan loop ( θ = 0) Fg Usng Ampere s law to fnd the magnetc feld that a current produces outsde a long straght wre of crcular cross secton.the Amperan loop s a concentrc crcle that les outsde the wre. ds B (Current 3 s not encrcled by the loop.) We can then rewrte B cos ds 0( 1 2 ). You mght wonder why, snce current 3 contrbutes to the ntude B on the left sde of Eq , t s not needed on the s that the contrbutons of current 3 to the magnetc feld ca ntegraton n Eq s made around the full loop. In contr of an encrcled current to the magnetc feld do not cancel ou We cannot solve Eq for the magntude B of the mag Ampère s Law: the stuaton of Fg we do not have enough nformaton the ntegral. However, we do know the outcome of the ntegrat m 0 ( 1 2 ), the value of whch s set by the net current passng th We shall now apply B Ampere s ds = µ 0 law I enc to two stuatons n w allow us to smplfy and solve the ntegral, hence to fnd the m Magnetc Feld Outsde a Long Straght Wre wth Cu To fnd the B-feld at a dstancefgure r from the shows wre s a long straght centerwre choose that carres a curren page. Equaton 29-4 tells us that the magnetc feld B : produc crcular path of radus r. the same magntude at all ponts that are the same dsta By cylndrcal symmetry, everywhere along the crcle B ds s constant.
17 Ampère s Law and the Magnetc Feld from a Current All of the Outsde current s a wre encrcled and thus all s used n Ampere's law. Wre surface r Amperan loop ( θ = 0) Fg Usng Ampere s law to fnd the magnetc feld that a current produces outsde a long straght wre of crcular cross secton.the Amperan loop s a concentrc crcle that les outsde the wre. ds B (Current 3 s not encrcled by the loop.) We can then rewrte B cos ds 0( 1 2 ). You mght wonder why, snce current 3 contrbutes to the ntude B on the left sde of Eq , t s not needed on the s that the contrbutons of current 3 to the magnetc feld ca ntegraton n Eq s made around the full loop. In contr of an encrcled current to the magnetc feld do not cancel ou We cannot solve Eq for the magntude B of the mag Ampère s Law: the stuaton of Fg we do not have enough nformaton the ntegral. However, we do know the outcome of the ntegrat m 0 ( 1 2 ), the value of whch s set by the net current passng th We shall now apply B Ampere s ds = µ 0 law I enc to two stuatons n w allow us to smplfy and solve the ntegral, hence to fnd the m Magnetc Feld Outsde a Long Straght Wre wth Cu To fnd the B-feld at a dstancefgure r from the shows wre s a long straght centerwre choose that carres a curren page. Equaton 29-4 tells us that the magnetc feld B : produc crcular path of radus r. the same magntude at all ponts that are the same dsta By cylndrcal symmetry, everywhere along the crcle B ds s constant. The magnetc feld lnes must form a closed loop B ds = B ds.
18 Ampère s Law and All of the the current Magnetc s Feld from a Current Outsde encrcled a wreand thus all s used n Ampere's law. Wre surface r ds Amperan loop B ( θ = 0) You mght wonder w ntude B on the left s s that the contrbuto ntegraton n Eq. 29- of an encrcled curren We cannot solve E the stuaton of Fg. 29 the ntegral. However, m 0 ( 1 2 ), the value of We shall now app allow us to smplfy a And agan we get Fg Usng Ampere s law to fnd the magnetc feld that a current produces outsde a long B straght ds = wre µ 0 Iof enc crcular cross secton. The Amperan loop s a concentrc crcle that les outsde the wre. B(2πr) = µ 0 I B = µ 0I 2πr Magnetc Feld Ou Fgure shows a page. Equaton 29-4 t the same magntude
19 Ampère s Law and the Magnetc Feld from a Current Insde a wre PART 3 We can also use Ampère s Law n another context, where usng the 773 Bot-Savart Law s harder AMPERE S LAW he wre. We can take advanmpere s law (Eqs and lar Amperan loop of radus same magntude B at every se, so that ds : has the drec- Eq by notng that B : s as s ds :. Thus, B : and ds : are oop, and we shall arbtrarly between ds : and B : s 0, so omes B(2 r). ment lengths ds around the e 2pr of the loop. urrent of Fg The rght ve Only the current encrcled by the loop s used n Ampere's law. Fg Usng Ampere s law to fnd the magnetc feld that a current produces nsde a long straght wre of crcular cross secton.the current s unformly dstrbuted over the cross secton of the wre and emerges from the page.an Amperan loop s drawn nsde the wre. B r R ds Wre surface Amperan loop Now we place the Amperan loop nsde the wre. We stll have B ds = 2πrB, but now the current that flows through the loop s reduced.
20 Ampère s Law and the Magnetc Feld from a Current Insde a wre n- d us ry c- s re ly so e We stll have B ds = 2πrB, but now the current that flow through the loop s reduced. PART AMPERE S LAW 773 Assumng the wre has unform resstvty, I enc : Only the current encrcled by the loop s used n Ampere's law. Fg Usng Ampere s law to fnd the magnetc feld that a current produces nsde a long straght wre of crcular cross B r R ds Wre surface Amperan loop
21 Ampère s Law and the Magnetc Feld from a Current Insde a wre n- d us ry c- s re ly so e We stll have B ds = 2πrB, but now the current that flow through the loop s reduced. PART AMPERE S LAW 773 Assumng the wre has unform resstvty, I enc : Only the current encrcled by the loop s used n Ampere's law. Fg Usng Ampere s law to fnd the magnetc feld that a current produces nsde a long straght wre of crcular cross B r R ds Wre surface Amperan loop I enc = πr 2 πr 2 I = r 2 R 2 I Ampére s Law B ds = 2πrB = µ 0 r 2 R 2 I So, B = µ 0I r 2πR 2 = µ ( 0I r ) 2πR R
22 Ampère s Law For constant currents (magnetostatcs): B ds = µ 0 I enc The lne ntegral of the magnetc feld around a closed loop s proportonal to the current that flows through the loop. Later we wll extend ths law to deal wth the stuaton where the felds / currents are changng.
23 Solenods Addtonal examples, vdeo solenod A helcal col of tghtly wound wre that can carry a current. turn Fg A solenod carryng current Soleno Magnetc Feld o We now turn our useful. It concerns wound helcal col that the length of t Fgure sh The solenod s ma A sngle complete loop of wre n a solenod. Ths solenod has 10 turns, means t has 10 complete loops.
24 unform, we start wth a thn rng and then sum (va ntegraton) the rcled area. Magnetc Feld nsde and around a solenod P e central axs of a e turns are shown, as are the solenod. Each turn pror the solenod s axs, the s drected along the axs. ng magnetc feld. Outsde feld there s very weak. Each turn of wre locally has a crcular magnetc feld around t. The felds from all the wres add together to create very dense feld lnes nsde the solenod.
25 Magnetc Feld of a solenod IELDS DUE TO CURRENTS P 2 P 1 Fg Magnetc feld lnes for a real solenod of fnte length. The feld s strong and unform at nteror ponts such as P 1 but relatvely weak at external ponts such as P 2. The wres on opposte sdes (top and bottom n the pcture) have currents n opposte drectons. The felds add up between them, vdual turns (wndngs) that make up the solenod. For ponts very close to a turn, but cancel out outsde of them. the wre behaves magnetcally almost lke a long straght wre, and the lnes of B : there are almost concentrc crcles. Fgure suggests that the feld tends to cancel between adjacent turns. It also suggests that, at ponts nsde the solenod :
26 apply Ampere s law, Magnetc Feld of an deal solenod In an deal solenod B : ds : (wth 0 enc, nfnte length) the feld(29-21) outsde s small (and perpendcular to the Amp. loop) and nsde s unform. enod (Smlar of Fg , to a where capactor!) B : s unform wthn the solenod and usng the rectangular Amperan loop abcda. We wrte B : ds : as Can use an Amperan loop to fnd the B-feld nsde: d h c B ds = µ 0 I enc B a b plcaton of Ampere s law to a secton of a long deal solenod carryng mperan loop s the rectangle abcda.
27 apply Ampere s law, Magnetc Feld of an deal solenod In an deal solenod B : ds : (wth 0 enc, nfnte length) the feld(29-21) outsde s small (and perpendcular to the Amp. loop) and nsde s unform. enod (Smlar of Fg , to a where capactor!) B : s unform wthn the solenod and usng the rectangular Amperan loop abcda. We wrte B : ds : as Can use an Amperan loop to fnd the B-feld nsde: d h c B ds = µ 0 I enc B a b plcaton Here, of Ampere s supposelaw there to a secton are n of turns a long per deal unt solenod lengthcarryng the solenod, mperan then loop Is enc the = rectangle Inh abcda. Bh = µ 0 Inh Insde an deal solenod: B = µ 0 In
28 he torod, drected as shown n Fg b.Let u Torods A torod s a solenod wrapped nto a torus (donut) shape. (a) The two ends of the solenod are wrapped around an attached to each other. g (a) A torod carryng a current.(b) A orzontal cross secton of the torod. The nteror agnetc feld (nsde the bracelet-shaped tube) can be und by applyng Ampere s law wth the Amperan
29 w and the symmetry of the bracelet. ee Magnetc that the lnes Feld of B : form n aconcentrc Torod crcles nsde n Fg b.Let us choose a concentrc crcle of Cross secton through a torod: Amperan loop ng a current.(b) A rod. The nteror t-shaped tube) can be wth the Amperan We can use the Amperan loop shown to fnd the feld nsde the torod s loop. (b) r B
30 y descrbe as a (hollow) solenod that rmng a sort of hollow bracelet. What nsde the hollow of the bracelet)? We metry of the bracelet. es of B : Suppose form concentrc the torod crcles has nsde N turns..let us choose a concentrc crcle of Magnetc Feld n a Torod Amperan loop B ds = µ 0 I enc b) A r can be ran (b) r B B(2πr) = µ 0 NI Insde a torod: s B = µ 0IN 2πr Ths s not ndependent of the radus! The feld s stronger closer to the nsde: t s not unform.
31 Summary Forces on parallel wres Gauss s Law for magnetsm Ampère s Law Solenods 3rd Test Frday, Mar 9. Homework Collected homework 3, posted onlne, due on Monday, Mar 5. Serway & Jewett: PREVIOUS: Ch 30, Problems: 3, 5, 9, 13, 19 NEW: Ch 30, Problems: 21, 25, 31, 33, 34, 47
Electricity and Magnetism Review Faraday s Law
 Electrcty and Magnetsm Revew Faraday s Law Lana Sherdan De Anza College Dec 3, 2015 Overvew Faraday s law Lenz s law magnetc feld from a movng charge Gauss s law Remnder: (30.18) Magnetc Flux feld S that
Electrcty and Magnetsm Revew Faraday s Law Lana Sherdan De Anza College Dec 3, 2015 Overvew Faraday s law Lenz s law magnetc feld from a movng charge Gauss s law Remnder: (30.18) Magnetc Flux feld S that
Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 121 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetic Fields (Currents) Y&F Chapter 28, Sec. 1-7
 Electrcty and Magnetsm - Physcs 11 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetc Felds (Currents) Y&F Chapter 8, Sec. 1-7 Magnetc felds are due to currents The Bot-Savart Law Calculatng feld at the centers of current
Electrcty and Magnetsm - Physcs 11 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetc Felds (Currents) Y&F Chapter 8, Sec. 1-7 Magnetc felds are due to currents The Bot-Savart Law Calculatng feld at the centers of current
Electricity and Magnetism. Motional EMF Faraday s Law
 Electricity and Magnetism Ampère s Law Motional EMF Faraday s Law Lana heridan De Anza College Nov 19, 2015 Last time magnetic fields from moving charges magnetic fields around current-carrying wires forces
Electricity and Magnetism Ampère s Law Motional EMF Faraday s Law Lana heridan De Anza College Nov 19, 2015 Last time magnetic fields from moving charges magnetic fields around current-carrying wires forces
Fields, Charges, and Field Lines
 Felds, Charges, and Feld Lnes Electrc charges create electrc felds. (Gauss Law) Electrc feld lnes begn on + charges and end on - charges. Lke charges repel, oppostes attract. Start wth same dea for magnetc
Felds, Charges, and Feld Lnes Electrc charges create electrc felds. (Gauss Law) Electrc feld lnes begn on + charges and end on - charges. Lke charges repel, oppostes attract. Start wth same dea for magnetc
PHYS 1101 Practice problem set 12, Chapter 32: 21, 22, 24, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 12, 32, 38, 44, 49, 76
 PHYS 1101 Practce problem set 1, Chapter 3: 1,, 4, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 1, 3, 38, 44, 49, 76 3.1. Vsualze: Please reer to Fgure Ex3.1. Solve: Because B s n the same drecton as the ntegraton path s
PHYS 1101 Practce problem set 1, Chapter 3: 1,, 4, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 1, 3, 38, 44, 49, 76 3.1. Vsualze: Please reer to Fgure Ex3.1. Solve: Because B s n the same drecton as the ntegraton path s
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 6/Page 1
 PES 110 Sprng 014, Spender Lecture 6/Page 1 Lecture today: Chapter 1) Electrc feld due to charge dstrbutons -> charged rod -> charged rng We ntroduced the electrc feld, E. I defned t as an nvsble aura
PES 110 Sprng 014, Spender Lecture 6/Page 1 Lecture today: Chapter 1) Electrc feld due to charge dstrbutons -> charged rod -> charged rng We ntroduced the electrc feld, E. I defned t as an nvsble aura
Physics 114 Exam 3 Spring Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS
 CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS We defne a conductor as a materal n whch charges are free to move over macroscopc dstances.e., they can leave ther nucle and move around the materal. An nsulator s anythng else.
CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS We defne a conductor as a materal n whch charges are free to move over macroscopc dstances.e., they can leave ther nucle and move around the materal. An nsulator s anythng else.
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutions Fall 2016 Solution:
 PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
PHYSICS - CLUTCH 1E CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
Physics 4B. Question and 3 tie (clockwise), then 2 and 5 tie (zero), then 4 and 6 tie (counterclockwise) B i. ( T / s) = 1.74 V.
 Physcs 4 Solutons to Chapter 3 HW Chapter 3: Questons:, 4, 1 Problems:, 15, 19, 7, 33, 41, 45, 54, 65 Queston 3-1 and 3 te (clockwse), then and 5 te (zero), then 4 and 6 te (counterclockwse) Queston 3-4
Physcs 4 Solutons to Chapter 3 HW Chapter 3: Questons:, 4, 1 Problems:, 15, 19, 7, 33, 41, 45, 54, 65 Queston 3-1 and 3 te (clockwse), then and 5 te (zero), then 4 and 6 te (counterclockwse) Queston 3-4
ˆ (0.10 m) E ( N m /C ) 36 ˆj ( j C m)
 7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
MAGNETISM MAGNETIC DIPOLES
 MAGNETISM We now turn to magnetsm. Ths has actually been used for longer than electrcty. People were usng compasses to sal around the Medterranean Sea several hundred years BC. However t was not understood
MAGNETISM We now turn to magnetsm. Ths has actually been used for longer than electrcty. People were usng compasses to sal around the Medterranean Sea several hundred years BC. However t was not understood
(b) This is about one-sixth the magnitude of the Earth s field. It will affect the compass reading.
 Chapter 9 (a) The magntude of the magnetc feld due to the current n the wre, at a pont a dstance r from the wre, s gven by r Wth r = ft = 6 m, we have c4 T m AhbAg 6 33 T 33 T m b g (b) Ths s about one-sxth
Chapter 9 (a) The magntude of the magnetc feld due to the current n the wre, at a pont a dstance r from the wre, s gven by r Wth r = ft = 6 m, we have c4 T m AhbAg 6 33 T 33 T m b g (b) Ths s about one-sxth
N S. 4/4/2006 Magnetic Fields ( F.Robilliard) 1
 y F N +q + θ S v x z 4/4/6 Magnetc Felds ( F.obllard) 1 4/4/6 Magnetc Felds ( F.obllard) Introducton: It has been known, snce antquty, that when certan peces of rock are hung by a thread, from ther centre
y F N +q + θ S v x z 4/4/6 Magnetc Felds ( F.obllard) 1 4/4/6 Magnetc Felds ( F.obllard) Introducton: It has been known, snce antquty, that when certan peces of rock are hung by a thread, from ther centre
Spring 2002 Lecture #13
 44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
VEKTORANALYS GAUSS THEOREM STOKES THEOREM. and. Kursvecka 3. Kapitel 6 7 Sidor 51 82
 VEKTORANAY Kursvecka 3 GAU THEOREM and TOKE THEOREM Kaptel 6 7 dor 51 82 TARGET PROBEM Do magnetc monopoles est? EECTRIC FIED MAGNETIC FIED N +? 1 TARGET PROBEM et s consder some EECTRIC CHARGE 2 - + +
VEKTORANAY Kursvecka 3 GAU THEOREM and TOKE THEOREM Kaptel 6 7 dor 51 82 TARGET PROBEM Do magnetc monopoles est? EECTRIC FIED MAGNETIC FIED N +? 1 TARGET PROBEM et s consder some EECTRIC CHARGE 2 - + +
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
kq r 2 2kQ 2kQ (A) (B) (C) (D)
 PHYS 1202W MULTIPL CHOIC QUSTIONS QUIZ #1 Answer the followng multple choce questons on the bubble sheet. Choose the best answer, 5 pts each. MC1 An uncharged metal sphere wll (A) be repelled by a charged
PHYS 1202W MULTIPL CHOIC QUSTIONS QUIZ #1 Answer the followng multple choce questons on the bubble sheet. Choose the best answer, 5 pts each. MC1 An uncharged metal sphere wll (A) be repelled by a charged
Physics 1202: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda
 Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
From Biot-Savart Law to Divergence of B (1)
 From Bot-Savart Law to Dvergence of B (1) Let s prove that Bot-Savart gves us B (r ) = 0 for an arbtrary current densty. Frst take the dvergence of both sdes of Bot-Savart. The dervatve s wth respect to
From Bot-Savart Law to Dvergence of B (1) Let s prove that Bot-Savart gves us B (r ) = 0 for an arbtrary current densty. Frst take the dvergence of both sdes of Bot-Savart. The dervatve s wth respect to
Rotational Dynamics. Physics 1425 Lecture 19. Michael Fowler, UVa
 Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
1 Matrix representations of canonical matrices
 1 Matrx representatons of canoncal matrces 2-d rotaton around the orgn: ( ) cos θ sn θ R 0 = sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the x-axs: R x = 1 0 0 0 cos θ sn θ 0 sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the y-axs:
1 Matrx representatons of canoncal matrces 2-d rotaton around the orgn: ( ) cos θ sn θ R 0 = sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the x-axs: R x = 1 0 0 0 cos θ sn θ 0 sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the y-axs:
Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Inclusion II
 ME340B Elastcty of Mcroscopc Structures Stanford Unversty Wnter 004 Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Incluson II Chrs Wenberger and We Ca c All rghts reserved January 6, 004 Contents 1 Incluson energy n an nfnte
ME340B Elastcty of Mcroscopc Structures Stanford Unversty Wnter 004 Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Incluson II Chrs Wenberger and We Ca c All rghts reserved January 6, 004 Contents 1 Incluson energy n an nfnte
Physics Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 12 - Inductance, RL Circuits. Y&F Chapter 30, Sect 1-4
 Physcs - lectrcty and Magnetsm ecture - Inductance, Crcuts Y&F Chapter 30, Sect - 4 Inductors and Inductance Self-Inductance Crcuts Current Growth Crcuts Current Decay nergy Stored n a Magnetc Feld nergy
Physcs - lectrcty and Magnetsm ecture - Inductance, Crcuts Y&F Chapter 30, Sect - 4 Inductors and Inductance Self-Inductance Crcuts Current Growth Crcuts Current Decay nergy Stored n a Magnetc Feld nergy
VEKTORANALYS. GAUSS s THEOREM and STOKES s THEOREM. Kursvecka 3. Kapitel 6-7 Sidor 51-82
 VEKTORANAY Kursvecka 3 GAU s THEOREM and TOKE s THEOREM Kaptel 6-7 dor 51-82 TARGET PROBEM EECTRIC FIED MAGNETIC FIED N + Magnetc monopoles do not est n nature. How can we epress ths nformaton for E and
VEKTORANAY Kursvecka 3 GAU s THEOREM and TOKE s THEOREM Kaptel 6-7 dor 51-82 TARGET PROBEM EECTRIC FIED MAGNETIC FIED N + Magnetc monopoles do not est n nature. How can we epress ths nformaton for E and
b mg (b) This is about one-sixth the magnitude of the Earth s field. It will affect the compass reading.
 Chapter 9 1 (a) The magntude of the magnetc feld due to the current n the wre, at a pont a dstance r from the wre, s gven by μ p r Wth r ft 61 m, we have c4p 1-7 TmA hb1ag p61 b mg 6 33 1 T 33 μ T (b)
Chapter 9 1 (a) The magntude of the magnetc feld due to the current n the wre, at a pont a dstance r from the wre, s gven by μ p r Wth r ft 61 m, we have c4p 1-7 TmA hb1ag p61 b mg 6 33 1 T 33 μ T (b)
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 4
 Topcs: 8.0 (E&M) Lecture 4 More applcatons of vector calculus to electrostatcs: Laplacan: Posson and Laplace equaton url: concept and applcatons to electrostatcs Introducton to conductors Last tme Electrc
Topcs: 8.0 (E&M) Lecture 4 More applcatons of vector calculus to electrostatcs: Laplacan: Posson and Laplace equaton url: concept and applcatons to electrostatcs Introducton to conductors Last tme Electrc
Physics 114 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Solutions. Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Moments of Inertia. and reminds us of the analogous equation for linear momentum p= mv, which is of the form. The kinetic energy of the body is.
 Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Section 8.1 Exercises
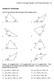 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Chapter 18 MAGNETIC FIELDS
 Ch. 18--Magnetc Felds Chapter 18 MAGNETIC FIELDS A.) A Small Matter of Specal Relatvty: 1.) Assume we have a partcle of charge q movng wth an ntal velocty v q parallel to a currentcarryng wre as shown
Ch. 18--Magnetc Felds Chapter 18 MAGNETIC FIELDS A.) A Small Matter of Specal Relatvty: 1.) Assume we have a partcle of charge q movng wth an ntal velocty v q parallel to a currentcarryng wre as shown
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Newtonian Mechanics
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Newtonan Mechancs Quck Revew of Newtonan Mechancs Basc Descrpton: -An dealzed pont partcle or a system of pont partcles n an nertal reference frame [Rgd bodes (ch. 5 later)]
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Newtonan Mechancs Quck Revew of Newtonan Mechancs Basc Descrpton: -An dealzed pont partcle or a system of pont partcles n an nertal reference frame [Rgd bodes (ch. 5 later)]
This model contains two bonds per unit cell (one along the x-direction and the other along y). So we can rewrite the Hamiltonian as:
 1 Problem set #1 1.1. A one-band model on a square lattce Fg. 1 Consder a square lattce wth only nearest-neghbor hoppngs (as shown n the fgure above): H t, j a a j (1.1) where,j stands for nearest neghbors
1 Problem set #1 1.1. A one-band model on a square lattce Fg. 1 Consder a square lattce wth only nearest-neghbor hoppngs (as shown n the fgure above): H t, j a a j (1.1) where,j stands for nearest neghbors
Inductance Calculation for Conductors of Arbitrary Shape
 CRYO/02/028 Aprl 5, 2002 Inductance Calculaton for Conductors of Arbtrary Shape L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Internal Summary In ths note we descrbe a method for the numercal calculaton of nductances among conductors
CRYO/02/028 Aprl 5, 2002 Inductance Calculaton for Conductors of Arbtrary Shape L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Internal Summary In ths note we descrbe a method for the numercal calculaton of nductances among conductors
Celestial Mechanics. Basic Orbits. Why circles? Tycho Brahe. PHY celestial-mechanics - J. Hedberg
 PHY 454 - celestal-mechancs - J. Hedberg - 207 Celestal Mechancs. Basc Orbts. Why crcles? 2. Tycho Brahe 3. Kepler 4. 3 laws of orbtng bodes 2. Newtonan Mechancs 3. Newton's Laws. Law of Gravtaton 2. The
PHY 454 - celestal-mechancs - J. Hedberg - 207 Celestal Mechancs. Basc Orbts. Why crcles? 2. Tycho Brahe 3. Kepler 4. 3 laws of orbtng bodes 2. Newtonan Mechancs 3. Newton's Laws. Law of Gravtaton 2. The
Phys102 General Physics II
 Electrc Potental/Energy Phys0 General Physcs II Electrc Potental Topcs Electrc potental energy and electrc potental Equpotental Surace Calculaton o potental rom eld Potental rom a pont charge Potental
Electrc Potental/Energy Phys0 General Physcs II Electrc Potental Topcs Electrc potental energy and electrc potental Equpotental Surace Calculaton o potental rom eld Potental rom a pont charge Potental
A Quantum Gauss-Bonnet Theorem
 A Quantum Gauss-Bonnet Theorem Tyler Fresen November 13, 2014 Curvature n the plane Let Γ be a smooth curve wth orentaton n R 2, parametrzed by arc length. The curvature k of Γ s ± Γ, where the sgn s postve
A Quantum Gauss-Bonnet Theorem Tyler Fresen November 13, 2014 Curvature n the plane Let Γ be a smooth curve wth orentaton n R 2, parametrzed by arc length. The curvature k of Γ s ± Γ, where the sgn s postve
I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Fall 2012 Fnal Exam Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
ME 270 Fall 2012 Fnal Exam Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
Conservation of Angular Momentum = "Spin"
 Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
Solutions to Practice Problems
 Phys A Solutons to Practce Probles hapter Inucton an Maxwell s uatons (a) At t s, the ef has a agntue of t ag t Wb s t Wb s Wb s t Wb s V t 5 (a) Table - gves the resstvty of copper Thus, L A 8 9 5 (b)
Phys A Solutons to Practce Probles hapter Inucton an Maxwell s uatons (a) At t s, the ef has a agntue of t ag t Wb s t Wb s Wb s t Wb s V t 5 (a) Table - gves the resstvty of copper Thus, L A 8 9 5 (b)
HO 40 Solutions ( ) ˆ. j, and B v. F m x 10-3 kg = i + ( 4.19 x 10 4 m/s)ˆ. (( )ˆ i + ( 4.19 x 10 4 m/s )ˆ j ) ( 1.40 T )ˆ k.
 .) m.8 x -3 g, q. x -8 C, ( 3. x 5 m/)ˆ, and (.85 T)ˆ The magnetc force : F q (. x -8 C) ( 3. x 5 m/)ˆ (.85 T)ˆ F.98 x -3 N F ma ( ˆ ˆ ) (.98 x -3 N) ˆ o a HO 4 Soluton F m (.98 x -3 N)ˆ.8 x -3 g.65 m.98
.) m.8 x -3 g, q. x -8 C, ( 3. x 5 m/)ˆ, and (.85 T)ˆ The magnetc force : F q (. x -8 C) ( 3. x 5 m/)ˆ (.85 T)ˆ F.98 x -3 N F ma ( ˆ ˆ ) (.98 x -3 N) ˆ o a HO 4 Soluton F m (.98 x -3 N)ˆ.8 x -3 g.65 m.98
Announcements. Lecture #2
 Announcements Lectures wll be n 4 LeConte begnnng Frday 8/29 Addtonal dscusson TA Denns Chang (Sectons 101, 105) Offce hours: Mo 2-3 PM; Th 5-6 PM Lab sectons begn Tuesday 9/2 Read Experment #1 onlne Download
Announcements Lectures wll be n 4 LeConte begnnng Frday 8/29 Addtonal dscusson TA Denns Chang (Sectons 101, 105) Offce hours: Mo 2-3 PM; Th 5-6 PM Lab sectons begn Tuesday 9/2 Read Experment #1 onlne Download
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec during recitations. If you have taken the post test, don t come to recitation!
 Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
EMF induced in a coil by moving a bar magnet. Induced EMF: Faraday s Law. Induction and Oscillations. Electromagnetic Induction.
 Inducton and Oscllatons Ch. 3: Faraday s Law Ch. 3: AC Crcuts Induced EMF: Faraday s Law Tme-dependent B creates nduced E In partcular: A changng magnetc flux creates an emf n a crcut: Ammeter or voltmeter.
Inducton and Oscllatons Ch. 3: Faraday s Law Ch. 3: AC Crcuts Induced EMF: Faraday s Law Tme-dependent B creates nduced E In partcular: A changng magnetc flux creates an emf n a crcut: Ammeter or voltmeter.
Section 8.3 Polar Form of Complex Numbers
 80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 11
 Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Inductor = (coil of wire)
 A student n 1120 emaled me to ask how much extra he should expect to pay on hs electrc bll when he strngs up a standard 1-strand box of ccle holday lghts outsde hs house. (total, cumulatve cost)? Try to
A student n 1120 emaled me to ask how much extra he should expect to pay on hs electrc bll when he strngs up a standard 1-strand box of ccle holday lghts outsde hs house. (total, cumulatve cost)? Try to
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
 COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
Thermodynamics Second Law Entropy
 Thermodynamcs Second Law Entropy Lana Sherdan De Anza College May 8, 2018 Last tme the Boltzmann dstrbuton (dstrbuton of energes) the Maxwell-Boltzmann dstrbuton (dstrbuton of speeds) the Second Law of
Thermodynamcs Second Law Entropy Lana Sherdan De Anza College May 8, 2018 Last tme the Boltzmann dstrbuton (dstrbuton of energes) the Maxwell-Boltzmann dstrbuton (dstrbuton of speeds) the Second Law of
Math1110 (Spring 2009) Prelim 3 - Solutions
 Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Equpotental Surfaces and Lnes Physcs for Scentsts & Engneers 2 Sprng Semester 2005 Lecture 9 January 25, 2005 Physcs for Scentsts&Engneers 2 1 When an electrc feld s present, the electrc potental has a
Equpotental Surfaces and Lnes Physcs for Scentsts & Engneers 2 Sprng Semester 2005 Lecture 9 January 25, 2005 Physcs for Scentsts&Engneers 2 1 When an electrc feld s present, the electrc potental has a
Physics 4B. A positive value is obtained, so the current is counterclockwise around the circuit.
 Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
AERODYNAMICS I LECTURE 6 AERODYNAMICS OF A WING FUNDAMENTALS OF THE LIFTING-LINE THEORY
 LECTURE 6 AERODYNAMICS OF A WING FUNDAMENTALS OF THE LIFTING-LINE THEORY The Bot-Savart Law The velocty nduced by the sngular vortex lne wth the crculaton can be determned by means of the Bot- Savart formula
LECTURE 6 AERODYNAMICS OF A WING FUNDAMENTALS OF THE LIFTING-LINE THEORY The Bot-Savart Law The velocty nduced by the sngular vortex lne wth the crculaton can be determned by means of the Bot- Savart formula
Lecture 12: Discrete Laplacian
 Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Chapter 2: Electric Energy and Capacitance
 Chapter : Electrc Energy and Capactance Potental One goal of physcs s to dentfy basc forces n our world, such as the electrc force as studed n the prevous lectures. Expermentally, we dscovered that the
Chapter : Electrc Energy and Capactance Potental One goal of physcs s to dentfy basc forces n our world, such as the electrc force as studed n the prevous lectures. Expermentally, we dscovered that the
Electric Potential Energy & Potential. Electric Potential Energy. Potential Energy. Potential Energy. Example: Charge launcher
 Electrc & Electrc Gravtatonal Increases as you move farther from Earth mgh Sprng Increases as you ncrease sprng extenson/comp resson Δ Increases or decreases as you move farther from the charge U ncreases
Electrc & Electrc Gravtatonal Increases as you move farther from Earth mgh Sprng Increases as you ncrease sprng extenson/comp resson Δ Increases or decreases as you move farther from the charge U ncreases
One Dimension Again. Chapter Fourteen
 hapter Fourteen One Dmenson Agan 4 Scalar Lne Integrals Now we agan consder the dea of the ntegral n one dmenson When we were ntroduced to the ntegral back n elementary school, we consdered only functons
hapter Fourteen One Dmenson Agan 4 Scalar Lne Integrals Now we agan consder the dea of the ntegral n one dmenson When we were ntroduced to the ntegral back n elementary school, we consdered only functons
Physics 2A Chapter 3 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Chapter 3. r r. Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Revisited
 Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Spin-rotation coupling of the angularly accelerated rigid body
 Spn-rotaton couplng of the angularly accelerated rgd body Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 E-mal: louaelzen@gmal.com November 1, 2017 All Rghts Reserved. Abstract Ths paper s
Spn-rotaton couplng of the angularly accelerated rgd body Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 E-mal: louaelzen@gmal.com November 1, 2017 All Rghts Reserved. Abstract Ths paper s
Waveguides and resonant cavities
 Wavegudes and resonant cavtes February 8, 014 Essentally, a wavegude s a conductng tube of unform cross-secton and a cavty s a wavegude wth end caps. The dmensons of the gude or cavty are chosen to transmt,
Wavegudes and resonant cavtes February 8, 014 Essentally, a wavegude s a conductng tube of unform cross-secton and a cavty s a wavegude wth end caps. The dmensons of the gude or cavty are chosen to transmt,
A particle in a state of uniform motion remain in that state of motion unless acted upon by external force.
 The fundamental prncples of classcal mechancs were lad down by Galleo and Newton n the 16th and 17th centures. In 1686, Newton wrote the Prncpa where he gave us three laws of moton, one law of gravty,
The fundamental prncples of classcal mechancs were lad down by Galleo and Newton n the 16th and 17th centures. In 1686, Newton wrote the Prncpa where he gave us three laws of moton, one law of gravty,
Dr. Fritz Wilhelm, Physics 230 E:\Excel files\230 lecture\ch26 capacitance.docx 1 of 13 Last saved: 12/27/2008; 8:40 PM. Homework: See website.
 Dr. Frtz Wlhelm, Physcs 3 E:\Excel fles\3 lecture\ch6 capactance.docx of 3 Last saved: /7/8; 8:4 PM Homework: See webste. Table of ontents: h.6. Defnton of apactance, 6. alculatng apactance, 6.a Parallel
Dr. Frtz Wlhelm, Physcs 3 E:\Excel fles\3 lecture\ch6 capactance.docx of 3 Last saved: /7/8; 8:4 PM Homework: See webste. Table of ontents: h.6. Defnton of apactance, 6. alculatng apactance, 6.a Parallel
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. Principle of Virtual Work-1
 P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
measurement and the charge the electric field will be calculated using E =. The direction of the field will be the . But, so
 THE ELECTRIC FIELD 6 Conceptual Questons 6.. A tny, postve test charge wll be placed at the pont n space and the force wll be measured. From the force F measurement and the charge the electrc feld wll
THE ELECTRIC FIELD 6 Conceptual Questons 6.. A tny, postve test charge wll be placed at the pont n space and the force wll be measured. From the force F measurement and the charge the electrc feld wll
MTH 263 Practice Test #1 Spring 1999
 Pat Ross MTH 6 Practce Test # Sprng 999 Name. Fnd the area of the regon bounded by the graph r =acos (θ). Observe: Ths s a crcle of radus a, for r =acos (θ) r =a ³ x r r =ax x + y =ax x ax + y =0 x ax
Pat Ross MTH 6 Practce Test # Sprng 999 Name. Fnd the area of the regon bounded by the graph r =acos (θ). Observe: Ths s a crcle of radus a, for r =acos (θ) r =a ³ x r r =ax x + y =ax x ax + y =0 x ax
MAGNUM - A Fortran Library for the Calculation of Magnetic Configurations
 CRYO/6/34 September, 3, 6 MAGNUM - A Fortran Lbrary for the Calculaton of Magnetc Confguratons L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Keywords: P. Bruzzone, M. Calv, J. Lster, C. Marnucc (EPFL/CRPP), A. Portone (EFDA-
CRYO/6/34 September, 3, 6 MAGNUM - A Fortran Lbrary for the Calculaton of Magnetc Confguratons L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Keywords: P. Bruzzone, M. Calv, J. Lster, C. Marnucc (EPFL/CRPP), A. Portone (EFDA-
CHAPTER 10 ROTATIONAL MOTION
 CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
Electricity and Magnetism Force on Parallel Wires
 Electricity and Magnetism Force on Parallel Wires Lana Sheridan De Anza College Mar 2, 2018 Last time Gauss s Law for magnetic fields Ampère s Law magnetic field around a straight wire solenoids Overview
Electricity and Magnetism Force on Parallel Wires Lana Sheridan De Anza College Mar 2, 2018 Last time Gauss s Law for magnetic fields Ampère s Law magnetic field around a straight wire solenoids Overview
Magnetic Field Around The New 400kV OH Power Transmission Lines In Libya
 ECENT ADVANCES n ENEGY & ENVIONMENT Magnetc Feld Around The New kv OH Power Transmsson Lnes In Lbya JAMAL M. EHTAIBA * SAYEH M. ELHABASHI ** Organzaton for Development of Admnstratve Centers, ODAC MISUATA
ECENT ADVANCES n ENEGY & ENVIONMENT Magnetc Feld Around The New kv OH Power Transmsson Lnes In Lbya JAMAL M. EHTAIBA * SAYEH M. ELHABASHI ** Organzaton for Development of Admnstratve Centers, ODAC MISUATA
Complex Variables. Chapter 18 Integration in the Complex Plane. March 12, 2013 Lecturer: Shih-Yuan Chen
 omplex Varables hapter 8 Integraton n the omplex Plane March, Lecturer: Shh-Yuan hen Except where otherwse noted, content s lcensed under a BY-N-SA. TW Lcense. ontents ontour ntegrals auchy-goursat theorem
omplex Varables hapter 8 Integraton n the omplex Plane March, Lecturer: Shh-Yuan hen Except where otherwse noted, content s lcensed under a BY-N-SA. TW Lcense. ontents ontour ntegrals auchy-goursat theorem
Lecture 3: Probability Distributions
 Lecture 3: Probablty Dstrbutons Random Varables Let us begn by defnng a sample space as a set of outcomes from an experment. We denote ths by S. A random varable s a functon whch maps outcomes nto the
Lecture 3: Probablty Dstrbutons Random Varables Let us begn by defnng a sample space as a set of outcomes from an experment. We denote ths by S. A random varable s a functon whch maps outcomes nto the
8.1 Arc Length. What is the length of a curve? How can we approximate it? We could do it following the pattern we ve used before
 .1 Arc Length hat s the length of a curve? How can we approxmate t? e could do t followng the pattern we ve used before Use a sequence of ncreasngly short segments to approxmate the curve: As the segments
.1 Arc Length hat s the length of a curve? How can we approxmate t? e could do t followng the pattern we ve used before Use a sequence of ncreasngly short segments to approxmate the curve: As the segments
Scattering by a perfectly conducting infinite cylinder
 Scatterng by a perfectly conductng nfnte cylnder Reeber that ths s the full soluton everywhere. We are actually nterested n the scatterng n the far feld lt. We agan use the asyptotc relatonshp exp exp
Scatterng by a perfectly conductng nfnte cylnder Reeber that ths s the full soluton everywhere. We are actually nterested n the scatterng n the far feld lt. We agan use the asyptotc relatonshp exp exp
Physics 181. Particle Systems
 Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Chapter 31. Induction and Magnetic Moment
 Chapter 31 Inducton and Magnetc Moment CHAPTER 31 INDUCTION AND MAG- NETIC MOMENT In ths chapter we dscuss several applcatons of Faraday s law and the Lorentz force law. The frst s to the nductor whch
Chapter 31 Inducton and Magnetc Moment CHAPTER 31 INDUCTION AND MAG- NETIC MOMENT In ths chapter we dscuss several applcatons of Faraday s law and the Lorentz force law. The frst s to the nductor whch
Introduction to circuit analysis. Classification of Materials
 Introducton to crcut analyss OUTLINE Electrcal quanttes Charge Current Voltage Power The deal basc crcut element Sgn conventons Current versus voltage (I-V) graph Readng: 1.2, 1.3,1.6 Lecture 2, Slde 1
Introducton to crcut analyss OUTLINE Electrcal quanttes Charge Current Voltage Power The deal basc crcut element Sgn conventons Current versus voltage (I-V) graph Readng: 1.2, 1.3,1.6 Lecture 2, Slde 1
Stanford University CS359G: Graph Partitioning and Expanders Handout 4 Luca Trevisan January 13, 2011
 Stanford Unversty CS359G: Graph Parttonng and Expanders Handout 4 Luca Trevsan January 3, 0 Lecture 4 In whch we prove the dffcult drecton of Cheeger s nequalty. As n the past lectures, consder an undrected
Stanford Unversty CS359G: Graph Parttonng and Expanders Handout 4 Luca Trevsan January 3, 0 Lecture 4 In whch we prove the dffcult drecton of Cheeger s nequalty. As n the past lectures, consder an undrected
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name and Secton: (Crcle Your Secton) Sectons:
Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name and Secton: (Crcle Your Secton) Sectons:
Chapter Twelve. Integration. We now turn our attention to the idea of an integral in dimensions higher than one. Consider a real-valued function f : D
 Chapter Twelve Integraton 12.1 Introducton We now turn our attenton to the dea of an ntegral n dmensons hgher than one. Consder a real-valued functon f : R, where the doman s a nce closed subset of Eucldean
Chapter Twelve Integraton 12.1 Introducton We now turn our attenton to the dea of an ntegral n dmensons hgher than one. Consder a real-valued functon f : R, where the doman s a nce closed subset of Eucldean
Physics 2113 Lecture 14: WED 18 FEB
 Physcs 2113 Jonathan Dowlng Physcs 2113 Lecture 14: WED 18 FEB Electrc Potental II Danger! Electrc Potental Energy, Unts : Electrc Potental Potental Energy = U = [J] = Joules Electrc Potental = V = U/q
Physcs 2113 Jonathan Dowlng Physcs 2113 Lecture 14: WED 18 FEB Electrc Potental II Danger! Electrc Potental Energy, Unts : Electrc Potental Potental Energy = U = [J] = Joules Electrc Potental = V = U/q
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Confirmation of Gauss s law
 Gauss s law Consder charge n a generc surface urround charge wth sphercal surface 1 concentrc to charge Consder cone of sold angle dω from charge to surface through the lttle sphere Electrc flu through
Gauss s law Consder charge n a generc surface urround charge wth sphercal surface 1 concentrc to charge Consder cone of sold angle dω from charge to surface through the lttle sphere Electrc flu through
Sections begin this week. Cancelled Sections: Th Labs begin this week. Attend your only second lab slot this week.
 Announcements Sectons begn ths week Cancelled Sectons: Th 122. Labs begn ths week. Attend your only second lab slot ths week. Cancelled labs: ThF 25. Please check your Lab secton. Homework #1 onlne Due
Announcements Sectons begn ths week Cancelled Sectons: Th 122. Labs begn ths week. Attend your only second lab slot ths week. Cancelled labs: ThF 25. Please check your Lab secton. Homework #1 onlne Due
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
Physics 53. Rotational Motion 3. Sir, I have found you an argument, but I am not obliged to find you an understanding.
 Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
Structure and Drive Paul A. Jensen Copyright July 20, 2003
 Structure and Drve Paul A. Jensen Copyrght July 20, 2003 A system s made up of several operatons wth flow passng between them. The structure of the system descrbes the flow paths from nputs to outputs.
Structure and Drve Paul A. Jensen Copyrght July 20, 2003 A system s made up of several operatons wth flow passng between them. The structure of the system descrbes the flow paths from nputs to outputs.
SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
 CHAPTER SEVEN SYSTES OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL OTION 7.1 Introducton 7.2 Centre of mass 7.3 oton of centre of mass 7.4 Lnear momentum of a system of partcles 7.5 Vector product of two vectors 7.6 Angular
CHAPTER SEVEN SYSTES OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL OTION 7.1 Introducton 7.2 Centre of mass 7.3 oton of centre of mass 7.4 Lnear momentum of a system of partcles 7.5 Vector product of two vectors 7.6 Angular
JEE ADVANCE : 2015 P1 PHASE TEST 4 ( )
 I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y IN D IA JEE ADVANCE : 5 P PHASE TEST (.8.7) ANSWER KEY PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS Q.No. Answer Key Q.No. Answer Key Q.No. Answer Key. () () (). () () (). (9) () (). () ()
I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y IN D IA JEE ADVANCE : 5 P PHASE TEST (.8.7) ANSWER KEY PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS Q.No. Answer Key Q.No. Answer Key Q.No. Answer Key. () () (). () () (). (9) () (). () ()
Advanced Circuits Topics - Part 1 by Dr. Colton (Fall 2017)
 Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
Module 1 : The equation of continuity. Lecture 1: Equation of Continuity
 1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
CHAPTER 14 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY
 CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
3.1 Expectation of Functions of Several Random Variables. )' be a k-dimensional discrete or continuous random vector, with joint PMF p (, E X E X1 E X
 Statstcs 1: Probablty Theory II 37 3 EPECTATION OF SEVERAL RANDOM VARIABLES As n Probablty Theory I, the nterest n most stuatons les not on the actual dstrbuton of a random vector, but rather on a number
Statstcs 1: Probablty Theory II 37 3 EPECTATION OF SEVERAL RANDOM VARIABLES As n Probablty Theory I, the nterest n most stuatons les not on the actual dstrbuton of a random vector, but rather on a number
So far: simple (planar) geometries
 Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
FE REVIEW OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 8/25/2010
 FE REVEW OPERATONAL AMPLFERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 1 The Op-amp 2 An op-amp has two nputs and one output. Note the op-amp below. The termnal labeled l wth the (-) sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth
FE REVEW OPERATONAL AMPLFERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 1 The Op-amp 2 An op-amp has two nputs and one output. Note the op-amp below. The termnal labeled l wth the (-) sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth
Lecture #4 Capacitors and Inductors Energy Stored in C and L Equivalent Circuits Thevenin Norton
 EES ntro. electroncs for S Sprng 003 Lecture : 0/03/03 A.R. Neureuther Verson Date 0/0/03 EES ntroducton to Electroncs for omputer Scence Andrew R. Neureuther Lecture # apactors and nductors Energy Stored
EES ntro. electroncs for S Sprng 003 Lecture : 0/03/03 A.R. Neureuther Verson Date 0/0/03 EES ntroducton to Electroncs for omputer Scence Andrew R. Neureuther Lecture # apactors and nductors Energy Stored
