What is a Force? Free-Body diagrams. Contact vs. At-a-Distance 11/28/2016. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
|
|
|
- Katrina Park
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object A change in the object s direction A deformation of the object s shape Newton s Laws of motion focus on the first 2 possibilities Units for Force: Newton (N) 1 N = 1 kg m s -2 Contact vs. At-a-Distance Contact Forces: Those forces which require a physical contact between two objects At-a-Distance Forces: Those forces which are exerted on objects even when there is no contact between them: Gravitational force Electrostatic force Magnetic force A Field is used to explain how at-a-distance forces act. Free-Body diagrams Step 1: draw a dot to represent the object upon which the forces are being exerted Step 2: draw vectors to indicate the strength and the direction of each force acting on the object (label these vectors clearly!) F friction F normal F push F g 1
2 Equilibrium Why Free-body diagrams? Main purpose is to give us a visual indication of the Net Force Net Force: The vector sum of all forces acting on an object Balanced Forces: when the net force is equal to zero, the forces acting on an object are said to be Balanced, and the object is in Equilibrium Occurs when the Net Force (Vector sum) is equal to zero Two Categories of equilibrium: Translational equilibrium: Occurs when the object is already at rest, and remains at rest Dynamic equilibrium: Occurs when the object is moving, and remains moving at a constant velocity Newton s 1 st Law of Motion An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue its state of uniform motion until an outside net force acts on it. So what does this mean??? Objects are in a state of equilibrium as long as they do not experience a net force If a body is at rest, it will remain so If a body is moving, it will continue to move in a straight line at a constant velocity Inertia An object s tendency to remain in its current state of motion (or state of rest) Inertia is a qualitative property It is directly related to an object s mass, but Inertia itself does NOT have a value The more massive an object is, the more difficult it is to change its state of motion. 2
3 Newton s 2 nd law of motion So what happens if the forces acting on an object are NOT balanced? Net force 0 N The net force on a body is proportional to that body s acceleration and is in the same direction as the acceleration Mathematically speaking: F net m a Common Forces: Weight (F g ) Depends on the strength of the gravitational field Weight is the force that is required to make a mass accelerate at the local acceleration due to gravity Here on Earth s surfaced: the weight of a mass is the force required to accelerate an object at 9.81 m s -2 towards the center of the Earth. F g m g What is the weight of a ball with a mass of 275 g? F g = m g F g = kg 9.81 m s 2 F g = N F g = m g 87.5N = m 9.81 m s 2 m=8.92 kg Tension (F T ) The force that arises in an inelastic object as a result of it being stretched Created when two forces are applied in opposite directions at the ends of a string (or rope, or chain, or wire ) Example: A lamp (m = 15.0 kg) is hung from the ceiling by a strong cord. What is the tension in the cord? F T = F g F T = m g F T = 15.0 kg 9.81 m s 2 F T = N 3
4 Examples of Normal Force: Normal Force (F N ) A force directed perpendicularly away from a surface Generally considered a support force, as it often has at least some component acting opposite the weight of an object. Example: the force you feel pushing up from the floor on your feet is the normal force exerted by the floor. Friction (F f ) A force that acts between two surfaces that are in contact with each other, and opposite to the direction an object is sliding or wants to slide. Static Friction The friction between two surfaces that are at rest relative to each other Dynamic Friction The friction between two surfaces that are sliding relative to each other Coefficient of Friction (m) A ratio of the frictional force to the normal force acting on an object resting or sliding across a surface. Unitless value Surfaces that experience less friction generally have smaller coefficients Coefficient of static friction: m s Coefficient of dynamic (kinetic) friction: m d or m k F f = μ F N 4
5 Sample Problem: A 53.0 kg box is pushed along a surface with a horizontal force of 275 N. If the box accelerates at a rate of 3.25 m s -2, what is the force of friction acting on the box? What is the coefficient of dynamic friction between the box and the floor? 5
Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass: Section 5.1
Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass: Section 5.1
Physics B Newton s Laws AP Review Packet
 Force A force is a push or pull on an object. Forces cause an object to accelerate To speed up To slow down To change direction Unit: Newton (SI system) Newton s First Law The Law of Inertia. A body in
Force A force is a push or pull on an object. Forces cause an object to accelerate To speed up To slow down To change direction Unit: Newton (SI system) Newton s First Law The Law of Inertia. A body in
Forces and Newton s Laws Notes
 Forces and Newton s Laws Notes Force An action exerted on an object which can change the motion of the object. The SI unit for force is the Newton (N) o N = (kg m)/s 2 o Pound is also a measure of force
Forces and Newton s Laws Notes Force An action exerted on an object which can change the motion of the object. The SI unit for force is the Newton (N) o N = (kg m)/s 2 o Pound is also a measure of force
Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Physics I Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass:
Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Physics I Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass:
Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: b) c)
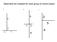 Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: a) b) c) 8 8 2 5-3 3 7-3 2-8 -8 a) 11 8 3 4 Magnitude 11.7 Direction: 70 degrees North of East -3 7 b) 8-3 2-8 1 Magnitude: 1 Direction: West c)
Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: a) b) c) 8 8 2 5-3 3 7-3 2-8 -8 a) 11 8 3 4 Magnitude 11.7 Direction: 70 degrees North of East -3 7 b) 8-3 2-8 1 Magnitude: 1 Direction: West c)
Chapter 4 Force and Motion
 Chapter 4 Force and Motion Units of Chapter 4 The Concepts of Force and Net Force Inertia and Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion More on Newton s Laws:
Chapter 4 Force and Motion Units of Chapter 4 The Concepts of Force and Net Force Inertia and Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion More on Newton s Laws:
Chapter 5. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The Laws of Motion The description of an object in motion included its position, velocity, and acceleration. There was no consideration of what might influence that motion.
Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The Laws of Motion The description of an object in motion included its position, velocity, and acceleration. There was no consideration of what might influence that motion.
The Concept of Force Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames Mass Newton s Second Law The Gravitational Force and Weight Newton s Third Law Analysis
 The Laws of Motion The Concept of Force Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames Mass Newton s Second Law The Gravitational Force and Weight Newton s Third Law Analysis Models using Newton s Second Law Forces
The Laws of Motion The Concept of Force Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames Mass Newton s Second Law The Gravitational Force and Weight Newton s Third Law Analysis Models using Newton s Second Law Forces
variable Formula S or v SI variable Formula S or v SI 4. How is a Newton defined? What does a Newton equal in pounds?
 Newton s Laws 1 1. Define mass variable Formula S or v SI 2. Define inertia, how is inertia related to mass 3. What is a Force? variable Formula S or v SI 4. How is a Newton defined? What does a Newton
Newton s Laws 1 1. Define mass variable Formula S or v SI 2. Define inertia, how is inertia related to mass 3. What is a Force? variable Formula S or v SI 4. How is a Newton defined? What does a Newton
Chapter 5. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The Laws of Motion The description of an object in There was no consideration of what might influence that motion. Two main factors need to be addressed to answer questions
Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The Laws of Motion The description of an object in There was no consideration of what might influence that motion. Two main factors need to be addressed to answer questions
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion Units of Chapter 4 Force Newton s First Law of Motion Mass Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion Weight the Force of Gravity; and the Normal
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion Units of Chapter 4 Force Newton s First Law of Motion Mass Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion Weight the Force of Gravity; and the Normal
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 5 Force and Motion Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Force Forces are what cause any change in the velocity of an object The net force is the vector sum of all the
Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 5 Force and Motion Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Force Forces are what cause any change in the velocity of an object The net force is the vector sum of all the
(a) On the dots below that represent the students, draw and label free-body diagrams showing the forces on Student A and on Student B.
 2003 B1. (15 points) A rope of negligible mass passes over a pulley of negligible mass attached to the ceiling, as shown above. One end of the rope is held by Student A of mass 70 kg, who is at rest on
2003 B1. (15 points) A rope of negligible mass passes over a pulley of negligible mass attached to the ceiling, as shown above. One end of the rope is held by Student A of mass 70 kg, who is at rest on
Chapter 4. The Laws of Motion. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Dr. Armen Kocharian Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical
Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Dr. Armen Kocharian Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical
Chapter 5. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion Sir Isaac Newton 1642 1727 Formulated basic laws of mechanics Discovered Law of Universal Gravitation Invented form of calculus Many observations dealing with light and optics
Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion Sir Isaac Newton 1642 1727 Formulated basic laws of mechanics Discovered Law of Universal Gravitation Invented form of calculus Many observations dealing with light and optics
Lecture Outline Chapter 6. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 6 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 6 Applications of Newton s Laws Units of Chapter 6 Frictional Forces Strings and Springs Translational Equilibrium Connected Objects
Lecture Outline Chapter 6 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 6 Applications of Newton s Laws Units of Chapter 6 Frictional Forces Strings and Springs Translational Equilibrium Connected Objects
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapter 5 Force and Motion Chapter Goal: To establish a connection between force and motion. Slide 5-2 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-3 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-4 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-5 Chapter 5 Preview
Chapter 5 Force and Motion Chapter Goal: To establish a connection between force and motion. Slide 5-2 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-3 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-4 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-5 Chapter 5 Preview
The Laws of Motion. Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples
 The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes. Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life.
 Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes Name: Section 4-1: Force What is force? Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life. Give an example of a situation where an object
Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes Name: Section 4-1: Force What is force? Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life. Give an example of a situation where an object
Chapter 5. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The astronaut orbiting the Earth in the Figure is preparing to dock with a Westar VI satellite. The satellite is in a circular orbit 700 km above the Earth's surface, where
Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The astronaut orbiting the Earth in the Figure is preparing to dock with a Westar VI satellite. The satellite is in a circular orbit 700 km above the Earth's surface, where
AP Mechanics Summer Assignment
 2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
Chapter 3, Problem 28. Agenda. Forces. Contact and Field Forces. Fundamental Forces. External and Internal Forces 2/6/14
 Agenda Today: Homework Quiz, Chapter 4 (Newton s Laws) Thursday: Applying Newton s Laws Start reading Chapter 5 Chapter 3, Problem 28 A ball with a horizontal speed of 1.25 m/s rolls off a bench 1.00 m
Agenda Today: Homework Quiz, Chapter 4 (Newton s Laws) Thursday: Applying Newton s Laws Start reading Chapter 5 Chapter 3, Problem 28 A ball with a horizontal speed of 1.25 m/s rolls off a bench 1.00 m
Dynamic equilibrium: object moves with constant velocity in a straight line. = 0, a x = i
 Dynamic equilibrium: object moves with constant velocity in a straight line. We note that F net a s are both vector quantities, so in terms of their components, (F net ) x = i (F i ) x = 0, a x = i (a
Dynamic equilibrium: object moves with constant velocity in a straight line. We note that F net a s are both vector quantities, so in terms of their components, (F net ) x = i (F i ) x = 0, a x = i (a
Chapter 3 The Laws of motion. The Laws of motion
 Chapter 3 The Laws of motion The Laws of motion The Concept of Force. Newton s First Law. Newton s Second Law. Newton s Third Law. Some Applications of Newton s Laws. 1 5.1 The Concept of Force Force:
Chapter 3 The Laws of motion The Laws of motion The Concept of Force. Newton s First Law. Newton s Second Law. Newton s Third Law. Some Applications of Newton s Laws. 1 5.1 The Concept of Force Force:
Chapter 4. Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion. That is, describing why objects move
 Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal orce, Tension, riction ree-body
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal orce, Tension, riction ree-body
Section /07/2013. PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow. Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs.
 PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs. 116-133 Section 5.1 A force is a push or a pull What is a force? What is a force? A force
PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs. 116-133 Section 5.1 A force is a push or a pull What is a force? What is a force? A force
3/10/2019. What Is a Force? What Is a Force? Tactics: Drawing Force Vectors
 What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Quiz 3 4.7 The Gravitational Force Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Quiz 3 4.7 The Gravitational Force Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other
I. AXN/RXN W.S. In the example below, the action-reaction pair is shown by the arrows (vectors), and the action-reaction described in words.
 I. AXN/RXN W.S. In the example below, the action-reaction pair is shown by the arrows (vectors), and the action-reaction described in words. 1. For the remaining situations, discuss with your neighbor
I. AXN/RXN W.S. In the example below, the action-reaction pair is shown by the arrows (vectors), and the action-reaction described in words. 1. For the remaining situations, discuss with your neighbor
Applying Newton s Laws
 Applying Newton s Laws Free Body Diagrams Draw and label the forces acting on the object. Examples of forces: weight, normal force, air resistance, friction, applied forces (like a push or pull) Velocity
Applying Newton s Laws Free Body Diagrams Draw and label the forces acting on the object. Examples of forces: weight, normal force, air resistance, friction, applied forces (like a push or pull) Velocity
What Is a Force? Slide Pearson Education, Inc.
 What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
Lecture 6. > Forces. > Newton's Laws. > Normal Force, Weight. (Source: Serway; Giancoli) Villacorta-DLSUM-BIOPHY1-L Term01
 Lecture 6 > Forces > Newton's Laws > Normal Force, Weight (Source: Serway; Giancoli) 1 Dynamics > Knowing the initial conditions of moving objects can predict the future motion of the said objects. > In
Lecture 6 > Forces > Newton's Laws > Normal Force, Weight (Source: Serway; Giancoli) 1 Dynamics > Knowing the initial conditions of moving objects can predict the future motion of the said objects. > In
Chapter 4: Newton's Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Lecture Chapter 4: Newton's Laws of Motion Goals for Chapter 4 To understand force either directly or as the net force of multiple components. To study and apply Newton's first law. To study
Chapter 4 Lecture Chapter 4: Newton's Laws of Motion Goals for Chapter 4 To understand force either directly or as the net force of multiple components. To study and apply Newton's first law. To study
1N the force that a 100g bar of chocolate exerts on your hand.
 Forces: - - > cause change in motions Newton's first law = law of inertia In absence of a net external force acting upon it, a body will either remain at rest or continue in its rectilinear uniform motion.
Forces: - - > cause change in motions Newton's first law = law of inertia In absence of a net external force acting upon it, a body will either remain at rest or continue in its rectilinear uniform motion.
Chapter 4. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not
Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not
Physics A - PHY 2048C
 Physics A - PHY 2048C Mass & Weight, Force, and Friction 10/04/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions 1 Did you read Chapters 6.1-6.6? 2 In your own words: What
Physics A - PHY 2048C Mass & Weight, Force, and Friction 10/04/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions 1 Did you read Chapters 6.1-6.6? 2 In your own words: What
PHYSICS. Chapter 5 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
You may use g = 10 m/s 2, sin 60 = 0.87, and cos 60 = 0.50.
 1. A child pulls a 15kg sled containing a 5kg dog along a straight path on a horizontal surface. He exerts a force of a 55N on the sled at an angle of 20º above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction
1. A child pulls a 15kg sled containing a 5kg dog along a straight path on a horizontal surface. He exerts a force of a 55N on the sled at an angle of 20º above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Forces. Isaac Newton stated 3 laws that deal with forces and describe motion. Backbone of Physics
 FORCES Forces Isaac Newton stated 3 laws that deal with forces and describe motion. Backbone of Physics Inertia Tendency of an object to remain in the same state of motion. Resists a change in motion.
FORCES Forces Isaac Newton stated 3 laws that deal with forces and describe motion. Backbone of Physics Inertia Tendency of an object to remain in the same state of motion. Resists a change in motion.
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued 4.9 Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface forces can act on the objects. The component of this force acting
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued 4.9 Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface forces can act on the objects. The component of this force acting
Forces. 3. The graph given shows the weight of three objects on planet X as a function of their mass. A. 0 N. B. between 0 N and 12 N C.
 Name: Date: 1. When a 12-newton horizontal force is applied to a box on a horizontal tabletop, the box remains at rest. The force of static friction acting on the box is 3. The graph given shows the weight
Name: Date: 1. When a 12-newton horizontal force is applied to a box on a horizontal tabletop, the box remains at rest. The force of static friction acting on the box is 3. The graph given shows the weight
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT STATIC EQUILIBRIUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 33 OPEN ENDED / 80 TOTAL / 113 NAME: 1. State the condition for translational equilibrium. A. ΣF = 0 B. ΣF
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT STATIC EQUILIBRIUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 33 OPEN ENDED / 80 TOTAL / 113 NAME: 1. State the condition for translational equilibrium. A. ΣF = 0 B. ΣF
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Force and Mass Units of Chapter 5 Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion The Vector Nature of Forces: Forces in Two Dimensions
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Force and Mass Units of Chapter 5 Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion The Vector Nature of Forces: Forces in Two Dimensions
Physics Mechanics. Lecture 11 Newton s Laws - part 2
 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 11 Newton s Laws - part 2 Newton s Second Law of Motion An object may have several forces acting on it; the acceleration is due to the net force: Newton s Second Law of
Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 11 Newton s Laws - part 2 Newton s Second Law of Motion An object may have several forces acting on it; the acceleration is due to the net force: Newton s Second Law of
General Physics I Spring Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 General Physics I Spring 2011 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion 1 Forces and Interactions The central concept in understanding why things move is force. If a tractor pushes or pulls a trailer, the tractor
General Physics I Spring 2011 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion 1 Forces and Interactions The central concept in understanding why things move is force. If a tractor pushes or pulls a trailer, the tractor
Newton s 3 rd Law. The Nature of Force. Matthew W. Milligan
 Newton s 3 rd Law The Nature of Force Forces Dynamics I. Laws of Motion: 1 & 2 - inertia, force, mass - weight II. Law 3 - interaction & nature of force - types of force: normal, friction - air resistance,
Newton s 3 rd Law The Nature of Force Forces Dynamics I. Laws of Motion: 1 & 2 - inertia, force, mass - weight II. Law 3 - interaction & nature of force - types of force: normal, friction - air resistance,
3. What type of force is the woman applying to cart in the illustration below?
 Name: Forces and Motion STUDY GUIDE Directions: Answer the following questions. 1. What is a force? a. A type of energy b. The rate at which an object performs work c. A push or a pull d. An object that
Name: Forces and Motion STUDY GUIDE Directions: Answer the following questions. 1. What is a force? a. A type of energy b. The rate at which an object performs work c. A push or a pull d. An object that
A force is a push or a pull.
 A force is a push or a pull. Contact forces arise from physical contact. Action at adistance forces do not require contact and include gravity and electrical forces. 1 Force is a vector [F]=[Newton]=[N]
A force is a push or a pull. Contact forces arise from physical contact. Action at adistance forces do not require contact and include gravity and electrical forces. 1 Force is a vector [F]=[Newton]=[N]
Topic: Force PHYSICS 231
 Topic: Force PHYSICS 231 Current Assignments Homework Set 2 due this Thursday, Jan 27, 11 pm Reading for next week: Chapters 10.1-6,10.10,8.3 2/1/11 Physics 231 Spring 2011 2 Key Concepts: Force Free body
Topic: Force PHYSICS 231 Current Assignments Homework Set 2 due this Thursday, Jan 27, 11 pm Reading for next week: Chapters 10.1-6,10.10,8.3 2/1/11 Physics 231 Spring 2011 2 Key Concepts: Force Free body
Newton s Laws. A force is simply a push or a pull. Forces are vectors; they have both size and direction.
 Newton s Laws Newton s first law: An object will stay at rest or in a state of uniform motion with constant velocity, in a straight line, unless acted upon by an external force. In other words, the bodies
Newton s Laws Newton s first law: An object will stay at rest or in a state of uniform motion with constant velocity, in a straight line, unless acted upon by an external force. In other words, the bodies
Chapter Test A. Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion. Assessment
 Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. c 2. d 3. d 4. c 5. c 6. c 7. c 8. b 9. d 10. d 11. c 12. a 13. d 14. d 15. b 16. d 17. c 18.
Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. c 2. d 3. d 4. c 5. c 6. c 7. c 8. b 9. d 10. d 11. c 12. a 13. d 14. d 15. b 16. d 17. c 18.
Chapter 4 NEWTONS LAWS. Newton s 3 Laws Force Diagrams Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces
 Chapter 4 NEWTONS LAWS Newton s 3 Laws Force Diagrams Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces Force: a push or a pull Measured in Newton Vector Quantity Contact Force: applied by direct contact Field Force:
Chapter 4 NEWTONS LAWS Newton s 3 Laws Force Diagrams Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces Force: a push or a pull Measured in Newton Vector Quantity Contact Force: applied by direct contact Field Force:
UNIT XX: DYNAMICS AND NEWTON S LAWS. DYNAMICS is the branch of mechanics concerned with the forces that cause motions of bodies
 I. Definition of FORCE UNIT XX: DYNAMICS AND NEWTON S LAWS DYNAMICS is the branch of mechanics concerned with the forces that cause motions of bodies FORCE is a quantitative interaction between two (or
I. Definition of FORCE UNIT XX: DYNAMICS AND NEWTON S LAWS DYNAMICS is the branch of mechanics concerned with the forces that cause motions of bodies FORCE is a quantitative interaction between two (or
Dynamics; Newton s Laws of Motion
 Dynamics; Newton s Laws of Motion Force A force is any kind of push or pull on an object. An object at rest needs a force to get it moving; a moving object needs a force to change its velocity. The magnitude
Dynamics; Newton s Laws of Motion Force A force is any kind of push or pull on an object. An object at rest needs a force to get it moving; a moving object needs a force to change its velocity. The magnitude
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Newtonian Mechanics Mass Mass is an intrinsic characteristic of a body The mass of a body is the characteristic that relates a force on the body to the resulting acceleration.
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Newtonian Mechanics Mass Mass is an intrinsic characteristic of a body The mass of a body is the characteristic that relates a force on the body to the resulting acceleration.
POGIL: Newton s First Law of Motion and Statics. Part 1: Net Force Model: Read the following carefully and study the diagrams that follow.
 POGIL: Newton s First Law of Motion and Statics Name Purpose: To become familiar with the forces acting on an object at rest Part 1: Net Force Model: Read the following carefully and study the diagrams
POGIL: Newton s First Law of Motion and Statics Name Purpose: To become familiar with the forces acting on an object at rest Part 1: Net Force Model: Read the following carefully and study the diagrams
Circular Motion. A car is traveling around a curve at a steady 45 mph. Is the car accelerating? A. Yes B. No
 Circular Motion A car is traveling around a curve at a steady 45 mph. Is the car accelerating? A. Yes B. No Circular Motion A car is traveling around a curve at a steady 45 mph. Which vector shows the
Circular Motion A car is traveling around a curve at a steady 45 mph. Is the car accelerating? A. Yes B. No Circular Motion A car is traveling around a curve at a steady 45 mph. Which vector shows the
Isaac Newton ( ) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity
 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Isaac Newton (1642-1727) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
PHYSICS. Chapter 5 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare It s not what happens to you that determines how far you will
Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare It s not what happens to you that determines how far you will
Newton s First Law. Newton s Second Law 9/29/11
 Newton s First Law Any object remains at constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. AND In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. Constant velocity could mean
Newton s First Law Any object remains at constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. AND In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. Constant velocity could mean
UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES. Objectives. To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law
 UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES Objectives To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law To be able to determine the object that is exerting a particular force To understand
UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES Objectives To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law To be able to determine the object that is exerting a particular force To understand
Chap. 4: Newton s Law of Motion
 Chap. 4: Newton s Law of Motion And Chap.5 Applying Newton s Laws (more examples) Force; Newton s 3 Laws; Mass and Weight Free-body Diagram (1D) Free-body Diagram (1D, 2 Bodies) Free-body Diagram (2D)
Chap. 4: Newton s Law of Motion And Chap.5 Applying Newton s Laws (more examples) Force; Newton s 3 Laws; Mass and Weight Free-body Diagram (1D) Free-body Diagram (1D, 2 Bodies) Free-body Diagram (2D)
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Force. The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object.
 Force The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object. Forces do not always give rise to motion. Forces can be equal and opposite. Force is a vector
Force The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object. Forces do not always give rise to motion. Forces can be equal and opposite. Force is a vector
Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium
 Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter: Two Mechanical Equilibrium Big Idea / Key Concepts Student Outcomes 2.1: Force 2.2: Mechanical Equilibrium 2.3: Support Force 2.4: Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter: Two Mechanical Equilibrium Big Idea / Key Concepts Student Outcomes 2.1: Force 2.2: Mechanical Equilibrium 2.3: Support Force 2.4: Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Chapter 4. The Laws of Motion. 1. Force. 2. Newton s Laws. 3. Applications. 4. Friction
 Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion 1. Force 2. Newton s Laws 3. Applications 4. Friction 1 Classical Mechanics What is classical Mechanics? Under what conditions can I use it? 2 Sir Isaac Newton 1642 1727 Formulated
Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion 1. Force 2. Newton s Laws 3. Applications 4. Friction 1 Classical Mechanics What is classical Mechanics? Under what conditions can I use it? 2 Sir Isaac Newton 1642 1727 Formulated
Forces and Motion Forces Gravity Net Forces Free Body Diagrams
 Forces and Motion Forces Gravity Net Forces Free Body Diagrams Misc. 200 200 200 200 200 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 FINAL JEOPARDY Go To Score
Forces and Motion Forces Gravity Net Forces Free Body Diagrams Misc. 200 200 200 200 200 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 FINAL JEOPARDY Go To Score
iat is the minimum coe cient of static friction necessary to keep the top block from slipping on " % e bottom block?
 1. Which one ofthe following terms is used to indicate the natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at a constant speed along a straight line? A) force B) acceleration C) equilibrium
1. Which one ofthe following terms is used to indicate the natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at a constant speed along a straight line? A) force B) acceleration C) equilibrium
Newton s Laws Student Success Sheets (SSS)
 --- Newton s Laws unit student success sheets--- Page 1 Newton s Laws Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-PS2-1 HS-PS2-2 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Physics Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
--- Newton s Laws unit student success sheets--- Page 1 Newton s Laws Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-PS2-1 HS-PS2-2 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Physics Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Engage I 1. What do you think about this design? If the car were to suddenly stop, what would happen to the child? Why?
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 4.a Nature of Forces Outcomes Define force. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion. Describe inertia and describe its relationship to mass. Draw free-body diagrams to represent
AP Physics 1 Lesson 4.a Nature of Forces Outcomes Define force. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion. Describe inertia and describe its relationship to mass. Draw free-body diagrams to represent
PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section V
 PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section V Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 2.5 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section V Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 2.5 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
FORCE. Definition: Combining Forces (Resultant Force)
 1 FORCE Definition: A force is either push or pull. A Force is a vector quantity that means it has magnitude and direction. Force is measured in a unit called Newtons (N). Some examples of forces are:
1 FORCE Definition: A force is either push or pull. A Force is a vector quantity that means it has magnitude and direction. Force is measured in a unit called Newtons (N). Some examples of forces are:
Unit 2 Forces. Fundamental Forces
 Lesson14.notebook July 10, 2013 Unit 2 Forces Fundamental Forces Today's goal: I can identify/name applied forces and draw appropriate free body diagrams (FBD's). There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
Lesson14.notebook July 10, 2013 Unit 2 Forces Fundamental Forces Today's goal: I can identify/name applied forces and draw appropriate free body diagrams (FBD's). There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
Welcome to Forces an anticipation guide A force is defined as a push or a pull When answering the following true or false statements, offer a
 Welcome to Forces an anticipation guide A force is defined as a push or a pull When answering the following true or false statements, offer a real-life example that justifies your answer. You haven t answered
Welcome to Forces an anticipation guide A force is defined as a push or a pull When answering the following true or false statements, offer a real-life example that justifies your answer. You haven t answered
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion
 Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Problem Set 2
 8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1. Stacked Blocks Problem Set 2 Consider two blocks that are resting one on top of the other. The lower block has mass m 2 = 4.8
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1. Stacked Blocks Problem Set 2 Consider two blocks that are resting one on top of the other. The lower block has mass m 2 = 4.8
Chapter Four Holt Physics. Forces and the Laws of Motion
 Chapter Four Holt Physics Forces and the Laws of Motion Physics Force and the study of dynamics 1.Forces - a. Force - a push or a pull. It can change the motion of an object; start or stop movement; and,
Chapter Four Holt Physics Forces and the Laws of Motion Physics Force and the study of dynamics 1.Forces - a. Force - a push or a pull. It can change the motion of an object; start or stop movement; and,
Can You Snap a Card Out From Under a Coin?
 Can You Snap a Card Out From Under a Coin? 1. Balance half of a 3 x 5 index card on the tip of an index finger. 2. Place a penny on the card, just above your fingertip. 3. Give the card a quick horizontal
Can You Snap a Card Out From Under a Coin? 1. Balance half of a 3 x 5 index card on the tip of an index finger. 2. Place a penny on the card, just above your fingertip. 3. Give the card a quick horizontal
Solution of HW4. and m 2
 Solution of HW4 9. REASONING AND SOLUION he magnitude of the gravitational force between any two of the particles is given by Newton's law of universal gravitation: F = Gm 1 m / r where m 1 and m are the
Solution of HW4 9. REASONING AND SOLUION he magnitude of the gravitational force between any two of the particles is given by Newton's law of universal gravitation: F = Gm 1 m / r where m 1 and m are the
Chapter 7 Newton s Third Law
 Chapter 7 Newton s Third Law Chapter Goal: To use Newton s third law to understand interacting objects. Slide 7-2 Chapter 7 Preview Slide 7-3 Chapter 7 Preview Slide 7-4 Chapter 7 Preview Slide 7-6 Chapter
Chapter 7 Newton s Third Law Chapter Goal: To use Newton s third law to understand interacting objects. Slide 7-2 Chapter 7 Preview Slide 7-3 Chapter 7 Preview Slide 7-4 Chapter 7 Preview Slide 7-6 Chapter
Written homework #5 due on Monday Online homework #5 due on Tuesday. Answer keys posted on course web site SPARK grades uploaded Average = 74.
 Homework Written homework #5 due on Monday Online homework #5 due on Tuesday Exam 1 Answer keys posted on course web site SPARK grades uploaded Average = 74.3% 1 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
Homework Written homework #5 due on Monday Online homework #5 due on Tuesday Exam 1 Answer keys posted on course web site SPARK grades uploaded Average = 74.3% 1 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
An Introduction to Forces Forces-part 1. Forces are Interactions
 An Introduction to Forces Forces-part 1 PHYS& 114: Eyres Forces are Interactions A force is an interaction between 2 objects Touching At a distance See the Fundamental Particle Chart (http://www.cpepphysics.org/images/2014-fund-chart.jpg)
An Introduction to Forces Forces-part 1 PHYS& 114: Eyres Forces are Interactions A force is an interaction between 2 objects Touching At a distance See the Fundamental Particle Chart (http://www.cpepphysics.org/images/2014-fund-chart.jpg)
The magnitude of this force is a scalar quantity called weight.
 Everyday Forces has direction The gravitational force (F g ) exerted on the ball by Earth is a vector directed toward the center of the earth. The magnitude of this force is a scalar quantity called weight.
Everyday Forces has direction The gravitational force (F g ) exerted on the ball by Earth is a vector directed toward the center of the earth. The magnitude of this force is a scalar quantity called weight.
Find the acceleration of the train B Find the distance traveled during this 20 s? C D
 75 A train with a mass of 25000 kg increases its speed from 10 m/s to 25 m/s in 20 seconds. Assume that the acceleration is constant and that you can neglect friction. A Find the acceleration of the train
75 A train with a mass of 25000 kg increases its speed from 10 m/s to 25 m/s in 20 seconds. Assume that the acceleration is constant and that you can neglect friction. A Find the acceleration of the train
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Q2. A book whose mass is 2 kg rests on a table. Find the magnitude of the force exerted by the table on the book.
 AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics
 1 Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics In this unit you will extend your study of forces. In particular, we will examine force as a vector quantity; this will involve solving problems where forces must be
1 Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics In this unit you will extend your study of forces. In particular, we will examine force as a vector quantity; this will involve solving problems where forces must be
The Concept of Force. field forces d) The gravitational force of attraction between two objects. f) Force a bar magnet exerts on a piece of iron.
 Lecture 3 The Laws of Motion OUTLINE 5.1 The Concept of Force 5.2 Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames 5.3 Mass 5.4 Newton s Second Law 5.5 The Gravitational Force and Weight 5.6 Newton s Third Law 5.8
Lecture 3 The Laws of Motion OUTLINE 5.1 The Concept of Force 5.2 Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames 5.3 Mass 5.4 Newton s Second Law 5.5 The Gravitational Force and Weight 5.6 Newton s Third Law 5.8
PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents: 1 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting a gun firing a bullet horizontally. 2 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting an arrow at a monkey in a tree.
PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents: 1 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting a gun firing a bullet horizontally. 2 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting an arrow at a monkey in a tree.
General Physics I Spring Applying Newton s Laws
 General Physics I Spring 2011 pplying Newton s Laws 1 Friction When you push horizontally on a heavy box at rest on a horizontal floor with a steadily increasing force, the box will remain at rest initially,
General Physics I Spring 2011 pplying Newton s Laws 1 Friction When you push horizontally on a heavy box at rest on a horizontal floor with a steadily increasing force, the box will remain at rest initially,
Fraser Heights Secondary Physics 11 Mr. Wu Practice Test (Dynamics)
 Fraser Heights Secondary Physics 11 Mr. Wu Practice Test (Dynamics) Instructions: Pick the best answer available for Part A. Show all your work for each question in Part B Part A: Multiple-Choice 1. Inertia
Fraser Heights Secondary Physics 11 Mr. Wu Practice Test (Dynamics) Instructions: Pick the best answer available for Part A. Show all your work for each question in Part B Part A: Multiple-Choice 1. Inertia
Chapter 4. Forces in One Dimension
 Chapter 4 Forces in One Dimension Chapter 4 Forces in One Dimension In this chapter you will: *VD Note Use Newton s laws to solve problems. Determine the magnitude and direction of the net force that causes
Chapter 4 Forces in One Dimension Chapter 4 Forces in One Dimension In this chapter you will: *VD Note Use Newton s laws to solve problems. Determine the magnitude and direction of the net force that causes
Section 1 Changes in Motion. Chapter 4. Preview. Objectives Force Force Diagrams
 Section 1 Changes in Motion Preview Objectives Force Force Diagrams Section 1 Changes in Motion Objectives Describe how force affects the motion of an object. Interpret and construct free body diagrams.
Section 1 Changes in Motion Preview Objectives Force Force Diagrams Section 1 Changes in Motion Objectives Describe how force affects the motion of an object. Interpret and construct free body diagrams.
Physics I (Navitas) EXAM #2 Spring 2015
 95.141 Physics I (Navitas) EXAM #2 Spring 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning each
95.141 Physics I (Navitas) EXAM #2 Spring 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning each
AP Physics I Summer Work
 AP Physics I Summer Work 2018 (20 points) Please complete the following set of questions and word problems. Answers will be reviewed in depth during the first week of class followed by an assessment based
AP Physics I Summer Work 2018 (20 points) Please complete the following set of questions and word problems. Answers will be reviewed in depth during the first week of class followed by an assessment based
Webreview practice test. Forces (again)
 Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview 4.3 - practice test. Forces (again) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 5.0-kg mass is suspended
Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview 4.3 - practice test. Forces (again) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 5.0-kg mass is suspended
Work. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 6/3/14. Define the joule in terms of force and distance.
 Objectives Define the joule in terms of force and. State the connection between work and energy. Apply the work equation to calculate work, force, or. 1. How is the joule composed of the units for force
Objectives Define the joule in terms of force and. State the connection between work and energy. Apply the work equation to calculate work, force, or. 1. How is the joule composed of the units for force
