An extremal problem for a class of entire functions
|
|
|
- Roderick McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An extremal problem for a class of entire functions Alexandre Eremenko and Peter Yuditskii May 29, 28 Abstract Soi f est une fonction entière de type exponentielle donc le diagramme indicatrice est contenu dans l interval [ iσ, iσ], σ >. Alors de densité superieure de zeros de f ne dépasse pas cσ ou c est le solution d équation Cette borne est exacte. log( c c) = 1 + c 2. We consider the class E σ, σ > of entire functions of exponential type whose indicator diagram is contained in a segment [ iσ, iσ], which means that h(θ) := lim sup r + log f(re iθ ) r σ sin θ, θ π. (1) An alternative characterization of such functions follows from a theorem of Pólya [6]: f(z) = 1 F (ζ)e iζz dζ, 2π γ where F is an analytic function in C\[ σ, σ], F ( ) =, and γ is a closed contour going once around the segment [ σ, σ]. In other words, the class of Supported by NSF grant DMS Supported by Austrrian Fund FWF P2413-N18. 1
2 entire functions satisfying (1) consists of Fourier transforms of hyperfunctions supported by [ σ, σ], see, for example, [2] and [3]. Let n(r) be the number of zeros of f in the disc {z : z r}, counting multiplicity. We are interested in the upper density D = lim sup r If f satisfies the additional condition n(r) r. (2) log + f(x) 1 + x 2 dx <, (3) π then the limit (density) in (2) exists and equals (2π) 1 h(θ)dθ. For example, if f(z) = sin σz, then f E σ and D = 2σ/π.6366σ. The existence of the limit follows from a theorem of Levinson [5, 6]. Much more precise information about n(r) under the condition (3) is contained in the theorem of Beurling and Malliavin [1]. In the general case, the density might not exist as was shown by examples in [4, 1]. Moreover, it is possible that D > 2σ/π, see [2]. An easy estimate using Jensen s formula gives D 2eσ/π 1.735σ. This estimate is exact in the larger class of entire functions satisfying the condition h(θ) σ, but it is not exact in E σ. In this paper we find the best possible upper estimate for the upper density of zeros of functions in E σ. Theorem. The upper density of zeros of a function f E σ does not exceed cσ where c is the unique solution of the equation log( c c) = 1 + c 2, on (, + ). (4) For every σ > there exist entire functions f E σ such that D = cσ. Proof. Without loss of generality we assume that σ = 1. Moreover, it is enough to consider only even functions. To make a function f even we replace it by f(z)f( z), which results in multiplication of both the indicator h and the upper density D by the same factor of 2. Let t n + be such sequence that lim n(t n )/t n = D. Consider the sequence of subharmonic functions v n (z) = t 1 n log f(t n z). Compactness 2 π
3 Principle for subharmonic functions [3, Theorem ] implies that one can choose a subsequence that converges in D (Schwartz s distributions). The limit function v is subharmonic in the plane, and satisfies v(z) Im z, z C, and v() =. (5) Let µ be the Riesz measure of this function. We have to show that µ({z : z 1}) c. (6) First we reduce the problem to the case that the Riesz measure µ is supported by the real line. We have v(z) = 1 log 2 1 z2 ζ 2 dµ ζ. Let us compare this with v (z) = 1 2 log 1 z2 dµ t, where µ is the radial projection of the measure µ: it is supported on [, + ) and µ (a, b) = µ({z : a < z < b}), a < b. It is easy to see that t 2 v (z) σ Im z, z C, and v () = (7) with some σ >. We claim that one can choose σ 1 in (7). Let σ be the smallest number for which (7) holds. Then, by the subharmonic version of the theorem of Levinson mentioned above (see, for example, [9]), the limit exists in D and thus where 1 lim r r r lim r r 1 v (rz) = σ Im z n v (t) 1 π dt = lim v (re iθ )dθ = 2σ /π, t r 2πr π n v (r) = µ [, r] = µ{z : z r}. (8) Similar limits exist for v, and we have n v = n v, from which we conclude that σ 1. 3
4 From now on we assume that v is harmonic in the upper and lower halfplanes, and that v(iy) y, y +. (9) Let u be the harmonic function in the upper half-plane such that φ = u + iv is analytic, and φ() =. Then φ is a conformal map of the upper half-plane onto some region G of the form G = {x + iy : y > g(x)}, (1) where g is an even upper semi-continuous function, g() =. Moreover, which follows from (9), and φ(iy) iy, as y +, (11) φ( z) = φ(z), (12) because both the region G and the normalization of φ are symmetric with respect to the imaginary axis. Finally we have For all these facts we refer to [7]. µ([, x]) = 2 u(x). (13) π Remark. The function Re φ(x) = u(x) might be discontinuous for x R. We agree to understand u(x) as the limit from the right u(x+) which always exists since u is increasing. Inequality (5) implies that v(x), thus g(x), in other words, G contains the upper half-plane. Thus we obtain the following extremal problem: Among all univalent analytic functions φ satisfying (12) and mapping the upper half-plane onto regions of the form (1) with g, g() = and satisfying φ() = and (11), maximize Re φ(1). We claim that the extremal function g for this problem is {, < x < πc/2, g (x) =, otherwise, where c > 1 is the solution of equation (4). The corresponding region is shown in Fig. 1. For the extremal function we have φ (1) = πc/2 i. 4
5 Figure 1: Extremal Region To prove the claim, we fist notice that for a given G the mapping function is uniquely defined. Let a = φ(1), and b = Re a. Next we show that making g smaller on the interval (, b) results in increasing Re φ(1) and making g larger on the interval (b, + ) also results in increasing Re φ(1). The proofs of both statements are similar. Suppose that g 1 g, g 1 g, and g 1 (x) = g(x) outside of the two intervals p < x < q, where < p < q < b. Let G 1 be the region above the graph of g 1, and φ 1 the corresponding mapping function normalized in the same way as g. Then G G 1, and the conformal map φ 1 1 φ is defined in the upper half-plane and maps it into itself. We have φ 1 1 φ(x) = x + 2x w(t) t 2 x 2 dt, where w is a non-negative function supported on some interval inside (, 1). Putting x = 1 we obtain φ 1 1 (a) = w(t) t 2 1 dt, so φ 1 1 (a) < 1, that is Re φ 1 (1) > b. This proves our claim. It remains to compute the constant b in the extremal domain. We recall that φ (1) = b i and assume that b = φ (k) for some k > 1. Here φ is the extremal mapping function. Then by the Schwarz Christoffel formula we have φ (z) = 1 z 2 ζ k 2 dζ. (14) 2 ζ 1 To find k, we use the condition that Im p.v. k 2 ζ k 2 dζ =. ζ 1 5
6 Denoting c = k 2 1 and evaluating the integral, we obtain log( c c) = 1 + c 2. Finally the jump of the real part of the integral in (14) occurs at the poiunt 1 and has magnitude π k 2 1 = πc. This completes the proof of the upper estimate in Theorem 1. To construct an example showing that this estimate can be attained, we follow the construction in [2, Sect.9-1]. The role of the subharmonic function u 1 there is played now by our extremal function v = Im φ. References [1] A. Beurling and P. Malliavin, On Fourier transforms of measures with compact support, Acta math., 118 (1967) [2] A. Eremenko and D. Novikov, oscillation of Fourier intergals with a spectral gap, J. Math. pures appl., 83 (24) 3, [3] L. Hörmander, Analysis of linear partial differential operators, vol. I, II, Springer, Berlin [4] P. Kahane and L. Rubel, On Weierstrass products of zero type on the real axis, Illinois Math. J., 4 (196) [5] P. Koosis, Leçons sur le theorémè de Beurling et Malliavin, Publ. CRM, Montréal, [6] B. Levin, Distribution of zeros of entire functions, AMS, Providence, RI, 198. [7] B. Levin, Subharmonic majorants and some applications, in the book: Complex analysis, Birkhauser, Basel, P [8] B. Levin, The connection of a majorant with a conformal mapping. II (Russian) teor. Funktsii Funk. Anal. i Prilozhen. 52 (1989), English translation in: J. Soviet Math., 52 (199), no 5, [9] V. Matsaev and M. Sodin, Distribution of Hilbert transforms of measures, Geom and Funct. Anal., 1 (2) 1,
7 [1] C. Roumieu, Sur quelques extensions de la notion de distributiion, Ann. Sci. Ecole Norm. Super., 77 (196) Purdue University West Lafayette IN 4797 USA J. Kepler University Linz A 44 Austria 7
Classification: Mathematics. Title: Oscillation of functions with a spectral gap. Authors and author affiliation: A. Eremenko ( ) and D.
 Classification: Mathematics. Title: Oscillation of functions with a spectral gap Authors and author affiliation: A. Eremenko ( ) and D. Novikov ( ) Department of Mathematics ( ) Purdue University West
Classification: Mathematics. Title: Oscillation of functions with a spectral gap Authors and author affiliation: A. Eremenko ( ) and D. Novikov ( ) Department of Mathematics ( ) Purdue University West
Zeros and coefficients
 Zeros and coefficients Alexandre Eremenko 0.28.205 Abstract Asymptotic distribution of zeros of sequences of analytic functions is studied. Let f n be a sequence of analytic functions in a region D in
Zeros and coefficients Alexandre Eremenko 0.28.205 Abstract Asymptotic distribution of zeros of sequences of analytic functions is studied. Let f n be a sequence of analytic functions in a region D in
Exceptional values in holomorphic families of entire functions
 Exceptional values in holomorphic families of entire functions Alexandre Eremenko March 4, 2005 In 1926, Julia [5] studied singularities of implicit functions defined by equations f(z, w) =0,wheref is
Exceptional values in holomorphic families of entire functions Alexandre Eremenko March 4, 2005 In 1926, Julia [5] studied singularities of implicit functions defined by equations f(z, w) =0,wheref is
SHARP ESTIMATES FOR HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS ON THE UNIT BALL OF C n
 SHARP ESTIMATES FOR HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS ON THE UNIT BALL OF C n ADAM OSȨKOWSKI Abstract. Let S n denote the unit sphere in C n. The purpose the paper is to establish sharp L log L estimates for H and
SHARP ESTIMATES FOR HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS ON THE UNIT BALL OF C n ADAM OSȨKOWSKI Abstract. Let S n denote the unit sphere in C n. The purpose the paper is to establish sharp L log L estimates for H and
Radially distributed values and normal families, II
 Radially distributed values and normal families, II Walter Bergweiler and Alexandre Eremenko Dedicated to Larry Zalcman Abstract We consider the family of all functions holomorphic in the unit disk for
Radially distributed values and normal families, II Walter Bergweiler and Alexandre Eremenko Dedicated to Larry Zalcman Abstract We consider the family of all functions holomorphic in the unit disk for
A Picard type theorem for holomorphic curves
 A Picard type theorem for holomorphic curves A. Eremenko Let P m be complex projective space of dimension m, π : C m+1 \{0} P m the standard projection and M P m a closed subset (with respect to the usual
A Picard type theorem for holomorphic curves A. Eremenko Let P m be complex projective space of dimension m, π : C m+1 \{0} P m the standard projection and M P m a closed subset (with respect to the usual
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
A SOLUTION TO SHEIL-SMALL S HARMONIC MAPPING PROBLEM FOR POLYGONS. 1. Introduction
 A SOLUTION TO SHEIL-SMALL S HARMONIC MAPPING PROLEM FOR POLYGONS DAOUD SHOUTY, ERIK LUNDERG, AND ALLEN WEITSMAN Abstract. The problem of mapping the interior of a Jordan polygon univalently by the Poisson
A SOLUTION TO SHEIL-SMALL S HARMONIC MAPPING PROLEM FOR POLYGONS DAOUD SHOUTY, ERIK LUNDERG, AND ALLEN WEITSMAN Abstract. The problem of mapping the interior of a Jordan polygon univalently by the Poisson
ASYMPTOTIC MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 27, 2002, 249 255 ASYMPTOTIC MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE Boris Korenblum University at Albany, Department of Mathematics and Statistics Albany, NY 12222,
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 27, 2002, 249 255 ASYMPTOTIC MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE Boris Korenblum University at Albany, Department of Mathematics and Statistics Albany, NY 12222,
Exceptional values in holomorphic families of entire functions
 Exceptional values in holomorphic families of entire functions Alexandre Eremenko March 21, 2005 In 1926, Julia [5] studied singularities of implicit functions defined by equations f(z, w) =0,wheref is
Exceptional values in holomorphic families of entire functions Alexandre Eremenko March 21, 2005 In 1926, Julia [5] studied singularities of implicit functions defined by equations f(z, w) =0,wheref is
Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 2012 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file)
 Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 212 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file) February 9, 212 16. Prove: If u is a complex-valued harmonic function, then the real and the imaginary parts
Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 212 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file) February 9, 212 16. Prove: If u is a complex-valued harmonic function, then the real and the imaginary parts
Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett/
 (February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
(February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
Homework 27. Homework 28. Homework 29. Homework 30. Prof. Girardi, Math 703, Fall 2012 Homework: Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by
 Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 220A - Fall Final Exam Solutions
 Math 22A - Fall 216 - Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are
Math 22A - Fall 216 - Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are
Electrostatic skeletons
 Electrostatic skeletons Alexandre Eremenko, Erik Lundberg, and Koushik Ramachandran September 21, 2013 Dedicated to the memory of Andrei Gonchar and Herbert Stahl Abstract Let u be the equilibrium potential
Electrostatic skeletons Alexandre Eremenko, Erik Lundberg, and Koushik Ramachandran September 21, 2013 Dedicated to the memory of Andrei Gonchar and Herbert Stahl Abstract Let u be the equilibrium potential
The result above is known as the Riemann mapping theorem. We will prove it using basic theory of normal families. We start this lecture with that.
 Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Conformal maps. Lent 2019 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor. A star means optional and not necessarily harder.
 Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Rudin Real and Complex Analysis - Harmonic Functions
 Rudin Real and Complex Analysis - Harmonic Functions Aaron Lou December 2018 1 Notes 1.1 The Cauchy-Riemann Equations 11.1: The Operators and Suppose f is a complex function defined in a plane open set
Rudin Real and Complex Analysis - Harmonic Functions Aaron Lou December 2018 1 Notes 1.1 The Cauchy-Riemann Equations 11.1: The Operators and Suppose f is a complex function defined in a plane open set
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS
 ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS Daoud Bshouty, Dept. of Mathematics, Technion Inst. of Technology, 3200 Haifa, Israel, and Allen Weitsman, Dept. of Mathematics, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, IN 47907
ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS Daoud Bshouty, Dept. of Mathematics, Technion Inst. of Technology, 3200 Haifa, Israel, and Allen Weitsman, Dept. of Mathematics, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, IN 47907
INTEGRAL MEANS AND COEFFICIENT ESTIMATES ON PLANAR HARMONIC MAPPINGS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 37 69 79 INTEGRAL MEANS AND COEFFICIENT ESTIMATES ON PLANAR HARMONIC MAPPINGS Shaolin Chen Saminathan Ponnusamy and Xiantao Wang Hunan Normal University
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 37 69 79 INTEGRAL MEANS AND COEFFICIENT ESTIMATES ON PLANAR HARMONIC MAPPINGS Shaolin Chen Saminathan Ponnusamy and Xiantao Wang Hunan Normal University
Moment Inequalities for Equilibrium Measures in the Plane
 Pure and Applied Mathematics Quarterly Volume 7, Number 1 (Special Issue: In honor of Frederick W. Gehring) 47 82, 2011 Moment Inequalities for Equilibrium Measures in the Plane A. Baernstein II, R. S.
Pure and Applied Mathematics Quarterly Volume 7, Number 1 (Special Issue: In honor of Frederick W. Gehring) 47 82, 2011 Moment Inequalities for Equilibrium Measures in the Plane A. Baernstein II, R. S.
Composition Operators with Multivalent Symbol
 Composition Operators with Multivalent Symbol Rebecca G. Wahl University of South Dakota, Vermillion, South Dakota 57069 March 10, 007 Abstract If ϕ is an analytic map of the unit disk D into itself, the
Composition Operators with Multivalent Symbol Rebecca G. Wahl University of South Dakota, Vermillion, South Dakota 57069 March 10, 007 Abstract If ϕ is an analytic map of the unit disk D into itself, the
POSITIVE LYAPUNOV EXPONENT OF DISCRETE ANALYTIC JACOBI OPERATOR
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 17 17, No. 39, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu POSITIVE LYAPUNOV EXPONENT OF DISCRETE ANALYTIC JACOBI
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 17 17, No. 39, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu POSITIVE LYAPUNOV EXPONENT OF DISCRETE ANALYTIC JACOBI
On the pits effect of Littlewood and Offord
 On the pits effect of Littlewood and Offord Alexandre Eremenko and Iossif Ostrovskii October 13, 2007 Abstract Asymptotic behaviour of the entire functions f(z) = e 2πinαn z n /n!, with real α n is studied.
On the pits effect of Littlewood and Offord Alexandre Eremenko and Iossif Ostrovskii October 13, 2007 Abstract Asymptotic behaviour of the entire functions f(z) = e 2πinαn z n /n!, with real α n is studied.
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Remarks on the Rademacher-Menshov Theorem
 Remarks on the Rademacher-Menshov Theorem Christopher Meaney Abstract We describe Salem s proof of the Rademacher-Menshov Theorem, which shows that one constant works for all orthogonal expansions in all
Remarks on the Rademacher-Menshov Theorem Christopher Meaney Abstract We describe Salem s proof of the Rademacher-Menshov Theorem, which shows that one constant works for all orthogonal expansions in all
Weak Subordination for Convex Univalent Harmonic Functions
 Weak Subordination for Convex Univalent Harmonic Functions Stacey Muir Abstract For two complex-valued harmonic functions f and F defined in the open unit disk with f() = F () =, we say f is weakly subordinate
Weak Subordination for Convex Univalent Harmonic Functions Stacey Muir Abstract For two complex-valued harmonic functions f and F defined in the open unit disk with f() = F () =, we say f is weakly subordinate
1. The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions.
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
ON THE NORM OF THE OPERATOR ai + bh ON L p (R)
 ON THE NOM OF THE OPEATO ai + bh ON L p () YONG DING, LOUKAS GAFAKOS, AND KAI ZHU 1 Abstract We provide a direct proof of the following theorem of Kalton, Hollenbeck, and Verbitsky [7]: let H be the Hilbert
ON THE NOM OF THE OPEATO ai + bh ON L p () YONG DING, LOUKAS GAFAKOS, AND KAI ZHU 1 Abstract We provide a direct proof of the following theorem of Kalton, Hollenbeck, and Verbitsky [7]: let H be the Hilbert
SHARP INEQUALITIES FOR LINEAR COMBINATIONS OF ORTHOGONAL MARTINGALES
 SHARP INEQUALITIES FOR LINEAR COMBINATIONS OF ORTHOGONAL MARTINGALES YONG DING, LOUKAS GRAFAKOS, AND KAI ZHU 1 Abstract. For any two real-valued continuous-path martingales X = {X t } t 0 Y = {Y t } t
SHARP INEQUALITIES FOR LINEAR COMBINATIONS OF ORTHOGONAL MARTINGALES YONG DING, LOUKAS GRAFAKOS, AND KAI ZHU 1 Abstract. For any two real-valued continuous-path martingales X = {X t } t 0 Y = {Y t } t
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016](/thumbs/88/117506527.jpg) B. N. Khabibullin, N. R. Tamindarova SUBHARMONIC TEST FUNCTIONS AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF ZERO SETS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS arxiv:1606.06714v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016 Abstract. Let m, n 1 are integers and
B. N. Khabibullin, N. R. Tamindarova SUBHARMONIC TEST FUNCTIONS AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF ZERO SETS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS arxiv:1606.06714v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016 Abstract. Let m, n 1 are integers and
MATH 452. SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, (10 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic.
 MATH 45 SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, 06. (0 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic. Because f is holomorphic, u and v satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations:
MATH 45 SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, 06. (0 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic. Because f is holomorphic, u and v satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations:
Linear independence of exponentials on the real line
 Linear independence of exponentials on the real line Alexandre Eremenko August 25, 2013 The following question was asked on Math Overflow. Let (λ n ) be a sequence of complex numbers tending to infinity.
Linear independence of exponentials on the real line Alexandre Eremenko August 25, 2013 The following question was asked on Math Overflow. Let (λ n ) be a sequence of complex numbers tending to infinity.
Electrostatic skeletons
 arxiv:1309.5483v3 [math.ap] 17 Nov 2013 Electrostatic skeletons Alexandre Eremenko, Erik Lundberg, and Koushik Ramachandran October 18, 2018 Dedicated to the memory of Andrei Gonchar and Herbert Stahl
arxiv:1309.5483v3 [math.ap] 17 Nov 2013 Electrostatic skeletons Alexandre Eremenko, Erik Lundberg, and Koushik Ramachandran October 18, 2018 Dedicated to the memory of Andrei Gonchar and Herbert Stahl
Math 417 Midterm Exam Solutions Friday, July 9, 2010
 Math 417 Midterm Exam Solutions Friday, July 9, 010 Solve any 4 of Problems 1 6 and 1 of Problems 7 8. Write your solutions in the booklet provided. If you attempt more than 5 problems, you must clearly
Math 417 Midterm Exam Solutions Friday, July 9, 010 Solve any 4 of Problems 1 6 and 1 of Problems 7 8. Write your solutions in the booklet provided. If you attempt more than 5 problems, you must clearly
BOUNDARY CORRESPONDENCE UNDER QUASICONFORMAL HARMONIC DIFFEO- MORPHISMS OF A HALF-PLANE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 3, 25, 159 165 BOUNDARY CORRESPONDENCE UNDER QUASICONFORMAL HARMONIC DIFFEO- MORPHISMS OF A HALF-PLANE David Kalaj and Miroslav Pavlović Prirodno-matematički
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 3, 25, 159 165 BOUNDARY CORRESPONDENCE UNDER QUASICONFORMAL HARMONIC DIFFEO- MORPHISMS OF A HALF-PLANE David Kalaj and Miroslav Pavlović Prirodno-matematički
ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS. C φ 2 e = lim sup w 1
 ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS PEKKA NIEMINEN AND EERO SAKSMAN Abstract. We give a negative answer to a conjecture of J. E. Shapiro concerning compactness of the dierence of
ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS PEKKA NIEMINEN AND EERO SAKSMAN Abstract. We give a negative answer to a conjecture of J. E. Shapiro concerning compactness of the dierence of
First fundamental Theorem of Nevanlinna Theory MAT 205B
 First fundamental Theorem of Nevanlinna Theory Ojesh Koul June 0, 208 The theory aims to describe the value distribution of meromorphic functions by looking at various formulae connecting the values of
First fundamental Theorem of Nevanlinna Theory Ojesh Koul June 0, 208 The theory aims to describe the value distribution of meromorphic functions by looking at various formulae connecting the values of
1.1. Introduction. An entire function F is said to have exponential type zero if
 PÓLYA SEQUENCES, TOEPLITZ KERNELS AND GAP THEOREMS MISHKO MITKOVSKI AND ALEXEI POLTORATSKI Abstract. A separated sequence Λ on the real line is called a Pólya sequence if any entire function of zero exponential
PÓLYA SEQUENCES, TOEPLITZ KERNELS AND GAP THEOREMS MISHKO MITKOVSKI AND ALEXEI POLTORATSKI Abstract. A separated sequence Λ on the real line is called a Pólya sequence if any entire function of zero exponential
Deficiency And Relative Deficiency Of E-Valued Meromorphic Functions
 Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 323, -8 c ISSN 67-25 Available free at mirror sites of http://www.math.nthu.edu.tw/ amen/ Deficiency And Relative Deficiency Of E-Valued Meromorphic Functions Zhaojun Wu, Zuxing
Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 323, -8 c ISSN 67-25 Available free at mirror sites of http://www.math.nthu.edu.tw/ amen/ Deficiency And Relative Deficiency Of E-Valued Meromorphic Functions Zhaojun Wu, Zuxing
A related space that will play a distinguished role in our space is the Hardy space H (D)
 Lecture : he Hardy Space on the isc In this first lecture we will focus on the Hardy space H (). We will have a crash course on the necessary theory for the Hardy space. Part of the reason for first introducing
Lecture : he Hardy Space on the isc In this first lecture we will focus on the Hardy space H (). We will have a crash course on the necessary theory for the Hardy space. Part of the reason for first introducing
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis. A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India. and. V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India
 NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 20 Complex Analysis Module: 10:
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 20 Complex Analysis Module: 10:
ENTIRE FUNCTIONS AND COMPLETENESS PROBLEMS. Lecture 3
 ENTIRE FUNCTIONS AND COMPLETENESS PROBLEMS A. POLTORATSKI Lecture 3 A version of the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle formulated in terms of Harmonic Analysis claims that a non-zero measure (distribution)
ENTIRE FUNCTIONS AND COMPLETENESS PROBLEMS A. POLTORATSKI Lecture 3 A version of the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle formulated in terms of Harmonic Analysis claims that a non-zero measure (distribution)
Advanced Calculus Math 127B, Winter 2005 Solutions: Final. nx2 1 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x
 . Define f n, g n : [, ] R by f n (x) = Advanced Calculus Math 27B, Winter 25 Solutions: Final nx2 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x 2 + n 2 x. 2 Show that the sequences (f n ), (g n ) converge pointwise on [, ],
. Define f n, g n : [, ] R by f n (x) = Advanced Calculus Math 27B, Winter 25 Solutions: Final nx2 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x 2 + n 2 x. 2 Show that the sequences (f n ), (g n ) converge pointwise on [, ],
On an uniqueness theorem for characteristic functions
 ISSN 392-53 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 207, Vol. 22, No. 3, 42 420 https://doi.org/0.5388/na.207.3.9 On an uniqueness theorem for characteristic functions Saulius Norvidas Institute of
ISSN 392-53 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 207, Vol. 22, No. 3, 42 420 https://doi.org/0.5388/na.207.3.9 On an uniqueness theorem for characteristic functions Saulius Norvidas Institute of
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
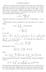 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES PHILIP FOTH 1. Cauchy s Formula and Cauchy s Theorem 1. Suppose that γ is a piecewise smooth positively ( counterclockwise ) oriented simple closed
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES PHILIP FOTH 1. Cauchy s Formula and Cauchy s Theorem 1. Suppose that γ is a piecewise smooth positively ( counterclockwise ) oriented simple closed
MATH 185: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. and g b (z) = eπz/2 1
 MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/0 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. Consider the functions defined y g a (z) = eiπz/2 e iπz/2 + Show that g a maps the set to D(0, ) while g maps the set and g (z) = eπz/2 e
MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/0 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. Consider the functions defined y g a (z) = eiπz/2 e iπz/2 + Show that g a maps the set to D(0, ) while g maps the set and g (z) = eπz/2 e
The heat equation for the Hermite operator on the Heisenberg group
 Hokkaido Mathematical Journal Vol. 34 (2005) p. 393 404 The heat equation for the Hermite operator on the Heisenberg group M. W. Wong (Received August 5, 2003) Abstract. We give a formula for the one-parameter
Hokkaido Mathematical Journal Vol. 34 (2005) p. 393 404 The heat equation for the Hermite operator on the Heisenberg group M. W. Wong (Received August 5, 2003) Abstract. We give a formula for the one-parameter
On lower bounds of exponential frames
 On lower bounds of exponential frames Alexander M. Lindner Abstract Lower frame bounds for sequences of exponentials are obtained in a special version of Avdonin s theorem on 1/4 in the mean (1974) and
On lower bounds of exponential frames Alexander M. Lindner Abstract Lower frame bounds for sequences of exponentials are obtained in a special version of Avdonin s theorem on 1/4 in the mean (1974) and
arxiv: v2 [math.fa] 17 May 2016
![arxiv: v2 [math.fa] 17 May 2016 arxiv: v2 [math.fa] 17 May 2016](/thumbs/92/108418866.jpg) ESTIMATES ON SINGULAR VALUES OF FUNCTIONS OF PERTURBED OPERATORS arxiv:1605.03931v2 [math.fa] 17 May 2016 QINBO LIU DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS, MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY EAST LANSING, MI 48824, USA Abstract.
ESTIMATES ON SINGULAR VALUES OF FUNCTIONS OF PERTURBED OPERATORS arxiv:1605.03931v2 [math.fa] 17 May 2016 QINBO LIU DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS, MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY EAST LANSING, MI 48824, USA Abstract.
Heinz Type Inequalities for Poisson Integrals
 Comput. Methods Funct. Theory (14 14:19 36 DOI 1.17/s4315-14-47-1 Heinz Type Inequalities for Poisson Integrals Dariusz Partyka Ken-ichi Sakan Received: 7 September 13 / Revised: 8 October 13 / Accepted:
Comput. Methods Funct. Theory (14 14:19 36 DOI 1.17/s4315-14-47-1 Heinz Type Inequalities for Poisson Integrals Dariusz Partyka Ken-ichi Sakan Received: 7 September 13 / Revised: 8 October 13 / Accepted:
SETS OF UNIQUENESS FOR DIRICHLET TYPE SPACES
 SES OF UNIQUENESS FOR DIRICHLE YPE SPACES KARIM KELLAY Abstract. We study the uniqueness sets on the unit circle for weighted Dirichlet spaces.. Introduction Let D be the open unit disk in the complex
SES OF UNIQUENESS FOR DIRICHLE YPE SPACES KARIM KELLAY Abstract. We study the uniqueness sets on the unit circle for weighted Dirichlet spaces.. Introduction Let D be the open unit disk in the complex
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
A TECHNIQUE OF BEURLING FOR LOWER ORDER
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 34, 29, 379 386 A TECHNIQUE OF BEURLING FOR LOWER ORDER P. C. Fenton and John Rossi University of Otago, Department of Mathematics and Statistics
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 34, 29, 379 386 A TECHNIQUE OF BEURLING FOR LOWER ORDER P. C. Fenton and John Rossi University of Otago, Department of Mathematics and Statistics
Numerical Range in C*-Algebras
 Journal of Mathematical Extension Vol. 6, No. 2, (2012), 91-98 Numerical Range in C*-Algebras M. T. Heydari Yasouj University Abstract. Let A be a C*-algebra with unit 1 and let S be the state space of
Journal of Mathematical Extension Vol. 6, No. 2, (2012), 91-98 Numerical Range in C*-Algebras M. T. Heydari Yasouj University Abstract. Let A be a C*-algebra with unit 1 and let S be the state space of
Non-real zeroes of real entire functions and their derivatives
 Non-real zeroes of real entire functions and their derivatives Daniel A. Nicks Abstract A real entire function belongs to the Laguerre-Pólya class LP if it is the limit of a sequence of real polynomials
Non-real zeroes of real entire functions and their derivatives Daniel A. Nicks Abstract A real entire function belongs to the Laguerre-Pólya class LP if it is the limit of a sequence of real polynomials
FREE PROBABILITY AND RANDOM MATRICES
 FEE POBABILITY AND ANDOM MATICES Lecture 4: Free Harmonic Analysis, October 4, 007 The Cauchy Transform. Let C + = {z C Im(z > 0} denote the complex upper half plane, and C = {z Im(z < 0} denote the lower
FEE POBABILITY AND ANDOM MATICES Lecture 4: Free Harmonic Analysis, October 4, 007 The Cauchy Transform. Let C + = {z C Im(z > 0} denote the complex upper half plane, and C = {z Im(z < 0} denote the lower
RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM
 RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM VED V. DATAR Recall that two domains are called conformally equivalent if there exists a holomorphic bijection from one to the other. This automatically implies that there is an
RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM VED V. DATAR Recall that two domains are called conformally equivalent if there exists a holomorphic bijection from one to the other. This automatically implies that there is an
3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations
 Summer School Normal Families in Complex Analysis Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg May 22 29, 2015 3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations Aimo Hinkkanen University of Illinois at Urbana
Summer School Normal Families in Complex Analysis Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg May 22 29, 2015 3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations Aimo Hinkkanen University of Illinois at Urbana
APPLICATION OF A RIESZ-TYPE FORMULA TO WEIGHTED BERGMAN SPACES
 PROCEEINGS OF HE AMERICAN MAHEMAICAL SOCIEY Volume 131, Number 1, Pages 155 164 S 000-99390)06491- Article electronically published on May 13, 00 APPLICAION OF A RIESZ-YPE FORMULA O WEIGHE BERGMAN SPACES
PROCEEINGS OF HE AMERICAN MAHEMAICAL SOCIEY Volume 131, Number 1, Pages 155 164 S 000-99390)06491- Article electronically published on May 13, 00 APPLICAION OF A RIESZ-YPE FORMULA O WEIGHE BERGMAN SPACES
BLOWUP THEORY FOR THE CRITICAL NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS REVISITED
 BLOWUP THEORY FOR THE CRITICAL NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS REVISITED TAOUFIK HMIDI AND SAHBI KERAANI Abstract. In this note we prove a refined version of compactness lemma adapted to the blowup analysis
BLOWUP THEORY FOR THE CRITICAL NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS REVISITED TAOUFIK HMIDI AND SAHBI KERAANI Abstract. In this note we prove a refined version of compactness lemma adapted to the blowup analysis
ON THE AREA FUNCTION FOR H ( σ p ), 1 p 2. OSCAR BLASCO. Presented by A. PELCZYNSKI
 ON THE AREA FUNCTION FOR H σ p ), 1 p. by OSCAR BLASCO Presented by A. PELCZYNSKI SUMMARY: It is shown that the inequality π f z) daz) dθ C f 1 holds for Hardy spaces of function taking values in the Schatten
ON THE AREA FUNCTION FOR H σ p ), 1 p. by OSCAR BLASCO Presented by A. PELCZYNSKI SUMMARY: It is shown that the inequality π f z) daz) dθ C f 1 holds for Hardy spaces of function taking values in the Schatten
Complex Analysis for F2
 Institutionen för Matematik KTH Stanislav Smirnov stas@math.kth.se Complex Analysis for F2 Projects September 2002 Suggested projects ask you to prove a few important and difficult theorems in complex
Institutionen för Matematik KTH Stanislav Smirnov stas@math.kth.se Complex Analysis for F2 Projects September 2002 Suggested projects ask you to prove a few important and difficult theorems in complex
Part IB. Further Analysis. Year
 Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
On the Bank Laine conjecture
 On the Bank Laine conjecture Walter Bergweiler and Alexandre Eremenko Abstract We resolve a question of Bank and Laine on the zeros of solutions of w + Aw = 0 where A is an entire function of finite order.
On the Bank Laine conjecture Walter Bergweiler and Alexandre Eremenko Abstract We resolve a question of Bank and Laine on the zeros of solutions of w + Aw = 0 where A is an entire function of finite order.
Mathematical MCQ for international students admitted to École polytechnique
 Mathematical MCQ for international students admitted to École polytechnique This multiple-choice questionnaire is intended for international students admitted to the first year of the engineering program
Mathematical MCQ for international students admitted to École polytechnique This multiple-choice questionnaire is intended for international students admitted to the first year of the engineering program
Complex Variables. Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit.
 Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
On the Bank Laine conjecture
 J. Eur. Math. Soc. 19, 1899 199 c European Mathematical Society 217 DOI 1.4171/JEMS/78 Walter Bergweiler Alexandre Eremenko On the Bank Laine conjecture Received August 11, 214 and in revised form March
J. Eur. Math. Soc. 19, 1899 199 c European Mathematical Society 217 DOI 1.4171/JEMS/78 Walter Bergweiler Alexandre Eremenko On the Bank Laine conjecture Received August 11, 214 and in revised form March
Local semiconvexity of Kantorovich potentials on non-compact manifolds
 Local semiconvexity of Kantorovich potentials on non-compact manifolds Alessio Figalli, Nicola Gigli Abstract We prove that any Kantorovich potential for the cost function c = d / on a Riemannian manifold
Local semiconvexity of Kantorovich potentials on non-compact manifolds Alessio Figalli, Nicola Gigli Abstract We prove that any Kantorovich potential for the cost function c = d / on a Riemannian manifold
On multiple points of meromorphic functions
 On multiple points of meromorphic functions Jim Langley and Dan Shea Abstract We establish lower bounds for the number of zeros of the logarithmic derivative of a meromorphic function of small growth with
On multiple points of meromorphic functions Jim Langley and Dan Shea Abstract We establish lower bounds for the number of zeros of the logarithmic derivative of a meromorphic function of small growth with
HOMEOMORPHISMS OF BOUNDED VARIATION
 HOMEOMORPHISMS OF BOUNDED VARIATION STANISLAV HENCL, PEKKA KOSKELA AND JANI ONNINEN Abstract. We show that the inverse of a planar homeomorphism of bounded variation is also of bounded variation. In higher
HOMEOMORPHISMS OF BOUNDED VARIATION STANISLAV HENCL, PEKKA KOSKELA AND JANI ONNINEN Abstract. We show that the inverse of a planar homeomorphism of bounded variation is also of bounded variation. In higher
Vectors in Function Spaces
 Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
BLOCH SPACE AND THE NORM OF THE BERGMAN PROJECTION
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 38, 2013, 849 853 BLOCH SPACE AN THE NORM OF THE BERGMAN PROJECTION Antti Perälä University of Helsinki, epartment of Mathematics and Statistics
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 38, 2013, 849 853 BLOCH SPACE AN THE NORM OF THE BERGMAN PROJECTION Antti Perälä University of Helsinki, epartment of Mathematics and Statistics
Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains
 Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains Ken-ichi Sakan (Osaka City Univ., Japan) Dariusz Partyka (The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Poland)
Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains Ken-ichi Sakan (Osaka City Univ., Japan) Dariusz Partyka (The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Poland)
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
Entire functions, PT-symmetry and Voros s quantization scheme
 Entire functions, PT-symmetry and Voros s quantization scheme Alexandre Eremenko January 19, 2017 Abstract In this paper, A. Avila s theorem on convergence of the exact quantization scheme of A. Voros
Entire functions, PT-symmetry and Voros s quantization scheme Alexandre Eremenko January 19, 2017 Abstract In this paper, A. Avila s theorem on convergence of the exact quantization scheme of A. Voros
Generating Starlike and Convex Univalent Functions
 M a t h e m a t i c a B a l k a n i c a New Series Vol. 9, 2005, Fasc. 3-4 Generating Starlike and Convex Univalent Functions Vanessa Bertoni, Dimitar K. Dimitrov 2 Presented by P.Kenderov We generate
M a t h e m a t i c a B a l k a n i c a New Series Vol. 9, 2005, Fasc. 3-4 Generating Starlike and Convex Univalent Functions Vanessa Bertoni, Dimitar K. Dimitrov 2 Presented by P.Kenderov We generate
MORE NOTES FOR MATH 823, FALL 2007
 MORE NOTES FOR MATH 83, FALL 007 Prop 1.1 Prop 1. Lemma 1.3 1. The Siegel upper half space 1.1. The Siegel upper half space and its Bergman kernel. The Siegel upper half space is the domain { U n+1 z C
MORE NOTES FOR MATH 83, FALL 007 Prop 1.1 Prop 1. Lemma 1.3 1. The Siegel upper half space 1.1. The Siegel upper half space and its Bergman kernel. The Siegel upper half space is the domain { U n+1 z C
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions
 Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
A Tilt at TILFs. Rod Nillsen University of Wollongong. This talk is dedicated to Gary H. Meisters
 A Tilt at TILFs Rod Nillsen University of Wollongong This talk is dedicated to Gary H. Meisters Abstract In this talk I will endeavour to give an overview of some aspects of the theory of Translation Invariant
A Tilt at TILFs Rod Nillsen University of Wollongong This talk is dedicated to Gary H. Meisters Abstract In this talk I will endeavour to give an overview of some aspects of the theory of Translation Invariant
GROWTH OF SOLUTIONS TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR HOMOGENEOUS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS IN ANGULAR DOMAINS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol 200(200), No 64, pp 7 ISSN: 072-669 URL: http://ejdemathtxstateedu or http://ejdemathuntedu ftp ejdemathtxstateedu GROWTH OF SOLUTIONS TO HIGHER ORDER
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol 200(200), No 64, pp 7 ISSN: 072-669 URL: http://ejdemathtxstateedu or http://ejdemathuntedu ftp ejdemathtxstateedu GROWTH OF SOLUTIONS TO HIGHER ORDER
Fundamental Solution
 Fundamental Solution onsider the following generic equation: Lu(X) = f(x). (1) Here X = (r, t) is the space-time coordinate (if either space or time coordinate is absent, then X t, or X r, respectively);
Fundamental Solution onsider the following generic equation: Lu(X) = f(x). (1) Here X = (r, t) is the space-time coordinate (if either space or time coordinate is absent, then X t, or X r, respectively);
3 (Due ). Let A X consist of points (x, y) such that either x or y is a rational number. Is A measurable? What is its Lebesgue measure?
 MA 645-4A (Real Analysis), Dr. Chernov Homework assignment 1 (Due ). Show that the open disk x 2 + y 2 < 1 is a countable union of planar elementary sets. Show that the closed disk x 2 + y 2 1 is a countable
MA 645-4A (Real Analysis), Dr. Chernov Homework assignment 1 (Due ). Show that the open disk x 2 + y 2 < 1 is a countable union of planar elementary sets. Show that the closed disk x 2 + y 2 1 is a countable
SHARP INEQUALITIES FOR HILBERT TRANSFORM IN A VECTOR-VALUED SETTING
 SHARP INEQUALIIES FOR HILBER RANSFORM IN A VECOR-VALUED SEING ADAM OSȨKOWSKI Abstract. he paper is devoted to the study of the periodic Hilbert transform H in the vector valued setting. Precisely, for
SHARP INEQUALIIES FOR HILBER RANSFORM IN A VECOR-VALUED SEING ADAM OSȨKOWSKI Abstract. he paper is devoted to the study of the periodic Hilbert transform H in the vector valued setting. Precisely, for
HARMONIC FUNCTIONS. x 2 + 2
 HARMONIC FUNCTIONS DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. Harmonic functions 1 1.1. Use of Harmonic mappings 1 1.2. Harmonic functions and holomorphicity 2 1.3. Harmonic
HARMONIC FUNCTIONS DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. Harmonic functions 1 1.1. Use of Harmonic mappings 1 1.2. Harmonic functions and holomorphicity 2 1.3. Harmonic
1 Orthonormal sets in Hilbert space
 Math 857 Fall 15 1 Orthonormal sets in Hilbert space Let S H. We denote by [S] the span of S, i.e., the set of all linear combinations of elements from S. A set {u α : α A} is called orthonormal, if u
Math 857 Fall 15 1 Orthonormal sets in Hilbert space Let S H. We denote by [S] the span of S, i.e., the set of all linear combinations of elements from S. A set {u α : α A} is called orthonormal, if u
Title: Localized self-adjointness of Schrödinger-type operators on Riemannian manifolds. Proposed running head: Schrödinger-type operators on
 Title: Localized self-adjointness of Schrödinger-type operators on Riemannian manifolds. Proposed running head: Schrödinger-type operators on manifolds. Author: Ognjen Milatovic Department Address: Department
Title: Localized self-adjointness of Schrödinger-type operators on Riemannian manifolds. Proposed running head: Schrödinger-type operators on manifolds. Author: Ognjen Milatovic Department Address: Department
VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS
 VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS JIE XIAO AND KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. The classical integral means of a holomorphic function f in the unit disk are defined by [ 1/p 1 2π f(re iθ ) dθ] p, r < 1.
VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS JIE XIAO AND KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. The classical integral means of a holomorphic function f in the unit disk are defined by [ 1/p 1 2π f(re iθ ) dθ] p, r < 1.
APPROXIMATION OF MOORE-PENROSE INVERSE OF A CLOSED OPERATOR BY A SEQUENCE OF FINITE RANK OUTER INVERSES
 APPROXIMATION OF MOORE-PENROSE INVERSE OF A CLOSED OPERATOR BY A SEQUENCE OF FINITE RANK OUTER INVERSES S. H. KULKARNI AND G. RAMESH Abstract. Let T be a densely defined closed linear operator between
APPROXIMATION OF MOORE-PENROSE INVERSE OF A CLOSED OPERATOR BY A SEQUENCE OF FINITE RANK OUTER INVERSES S. H. KULKARNI AND G. RAMESH Abstract. Let T be a densely defined closed linear operator between
POINTWISE MULTIPLIERS FROM WEIGHTED BERGMAN SPACES AND HARDY SPACES TO WEIGHTED BERGMAN SPACES
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 29, 24, 139 15 POINTWISE MULTIPLIERS FROM WEIGHTE BERGMAN SPACES AN HARY SPACES TO WEIGHTE BERGMAN SPACES Ruhan Zhao University of Toledo, epartment
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 29, 24, 139 15 POINTWISE MULTIPLIERS FROM WEIGHTE BERGMAN SPACES AN HARY SPACES TO WEIGHTE BERGMAN SPACES Ruhan Zhao University of Toledo, epartment
On the smoothness of the conjugacy between circle maps with a break
 On the smoothness of the conjugacy between circle maps with a break Konstantin Khanin and Saša Kocić 2 Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada M5S 2E4 2 Department of Mathematics,
On the smoothness of the conjugacy between circle maps with a break Konstantin Khanin and Saša Kocić 2 Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada M5S 2E4 2 Department of Mathematics,
On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a Boundary Point
 Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 261, 649 664 (2001) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2001.7564, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 261, 649 664 (2001) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2001.7564, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a
ELLIPTIC PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS EXERCISES I (HARMONIC FUNCTIONS)
 ELLIPTIC PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS EXERCISES I (HARMONIC FUNCTIONS) MATANIA BEN-ARTZI. BOOKS [CH] R. Courant and D. Hilbert, Methods of Mathematical Physics, Vol. Interscience Publ. 962. II, [E] L.
ELLIPTIC PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS EXERCISES I (HARMONIC FUNCTIONS) MATANIA BEN-ARTZI. BOOKS [CH] R. Courant and D. Hilbert, Methods of Mathematical Physics, Vol. Interscience Publ. 962. II, [E] L.
ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY. [ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY] Authors: Oliver Knill: jan 2003 Literature: T. Ransford, Potential theory in the complex plane.
![ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY. [ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY] Authors: Oliver Knill: jan 2003 Literature: T. Ransford, Potential theory in the complex plane. ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY. [ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY] Authors: Oliver Knill: jan 2003 Literature: T. Ransford, Potential theory in the complex plane.](/thumbs/78/77015579.jpg) ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY [ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY] Authors: Oliver Knill: jan 2003 Literature: T. Ransford, Potential theory in the complex plane. Analytic [Analytic] Let D C be an open set. A continuous
ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY [ENTRY POTENTIAL THEORY] Authors: Oliver Knill: jan 2003 Literature: T. Ransford, Potential theory in the complex plane. Analytic [Analytic] Let D C be an open set. A continuous
Subharmonic functions
 Subharmonic functions N.A. 07 Upper semicontinuous functions. Let (X, d) be a metric space. A function f : X R { } is upper semicontinuous (u.s.c.) if lim inf f(y) f(x) x X. y x A function g is lower semicontinuous
Subharmonic functions N.A. 07 Upper semicontinuous functions. Let (X, d) be a metric space. A function f : X R { } is upper semicontinuous (u.s.c.) if lim inf f(y) f(x) x X. y x A function g is lower semicontinuous
