A Functional Quantum Programming Language
|
|
|
- Francis Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Functional Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin supported by EPSRC grant GR/S30818/01 A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.1/??
2 Alternative title What you always wanted to know about quantum computation but never dared to ask. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.2/??
3 Another alternative title Quantum programming for the lazy functional programmer A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.3/??
4 Background A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
5 Background Simulation of quantum systems is expensive: Exponential time to simulate polynomial circuits. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
6 Background Simulation of quantum systems is expensive: Exponential time to simulate polynomial circuits. Feynman: Can we exploit this fact to perform computations more efficiently? A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
7 Background Simulation of quantum systems is expensive: Exponential time to simulate polynomial circuits. Feynman: Can we exploit this fact to perform computations more efficiently? Shor: Factorisation in quantum polynomial time. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
8 Background Simulation of quantum systems is expensive: Exponential time to simulate polynomial circuits. Feynman: Can we exploit this fact to perform computations more efficiently? Shor: Factorisation in quantum polynomial time. Grover: Blind search in A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
9 Background Simulation of quantum systems is expensive: Exponential time to simulate polynomial circuits. Feynman: Can we exploit this fact to perform computations more efficiently? Shor: Factorisation in quantum polynomial time. Grover: Blind search in Can we build a quantum computer? A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
10 Background Simulation of quantum systems is expensive: Exponential time to simulate polynomial circuits. Feynman: Can we exploit this fact to perform computations more efficiently? Shor: Factorisation in quantum polynomial time. Grover: Blind search in Can we build a quantum computer? yes We can run quantum algorithms. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
11 Background Simulation of quantum systems is expensive: Exponential time to simulate polynomial circuits. Feynman: Can we exploit this fact to perform computations more efficiently? Shor: Factorisation in quantum polynomial time. Grover: Blind search in Can we build a quantum computer? yes We can run quantum algorithms. no Nature is classical after all! A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
12 Background Simulation of quantum systems is expensive: Exponential time to simulate polynomial circuits. Feynman: Can we exploit this fact to perform computations more efficiently? Shor: Factorisation in quantum polynomial time. Grover: Blind search in Can we build a quantum computer? yes We can run quantum algorithms. no Nature is classical after all! Assumption: Nature is fair... A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.4/??
13 The quantum software crisis A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.5/??
14 The quantum software crisis Quantum algorithms are usually presented using the circuit model. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.5/??
15 The quantum software crisis Quantum algorithms are usually presented using the circuit model. Nielsen and Chuang, p.7, Coming up with good quantum algorithms is hard. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.5/??
16 The quantum software crisis Quantum algorithms are usually presented using the circuit model. Nielsen and Chuang, p.7, Coming up with good quantum algorithms is hard. Richard Josza, QPL 2004: We need to develop quantum thinking! A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.5/??
17 QML A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.6/??
18 QML QML: a first-order functional language for quantum computations on finite types. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.6/??
19 QML QML: a first-order functional language for quantum computations on finite types. Quantum control and quantum data. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.6/??
20 QML QML: a first-order functional language for quantum computations on finite types. Quantum control and quantum data. Design guided by semantics A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.6/??
21 QML QML: a first-order functional language for quantum computations on finite types. Quantum control and quantum data. Design guided by semantics Analogy with classical computation Finite classical computations Finite quantum computations A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.6/??
22 QML QML: a first-order functional language for quantum computations on finite types. Quantum control and quantum data. Design guided by semantics Analogy with classical computation Finite classical computations Finite quantum computations Important issue: control of decoherence A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.6/??
23 QML QML: a first-order functional language for quantum computations on finite types. Quantum control and quantum data. Design guided by semantics Analogy with classical computation Finite classical computations Finite quantum computations Important issue: control of decoherence Compiler under construction (Jonathan) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.6/??
24 Example: Hadamard operation A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.7/??
25 Example: Hadamard operation Matrix A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.7/??
26 Example: Hadamard operation Matrix QML * " &(') % $#!" * " &(') #!" +, A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.7/??
27 Something we know well... A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.8/??
28 Something we know well... Classical computations on finite types. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.8/??
29 Something we know well... Classical computations on finite types. Quantum mechanics is time-reversible... A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.8/??
30 Something we know well... Classical computations on finite types. Quantum mechanics is time-reversible hence quantum computation is based on reversible operations. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.8/??
31 Something we know well... Classical computations on finite types. Quantum mechanics is time-reversible hence quantum computation is based on reversible operations. However: Newtonian mechanics, Maxwellian electrodynamics are also time-reversible... A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.8/??
32 Something we know well... Classical computations on finite types. Quantum mechanics is time-reversible hence quantum computation is based on reversible operations. However: Newtonian mechanics, Maxwellian electrodynamics are also time-reversible hence classical computation should be based on reversible operations. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.8/??
33 Classical computation ( ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.9/??
34 0 1 - /. 2 Classical computation ( ) Given finite sets (input) and (output): A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.9/??
35 / Classical computation ( ) Given finite sets (input) and (output): a finite set of initial heaps, an initial heap 354 a finite set of garbage states, a bijection,, A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.9/??
36 Composing computations A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.10/??
37 Composing computations 9 8 A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.10/??
38 Extensional equality A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.11/??
39 6 4: < 8 $ : ; Extensional equality A classical computation induces a function U by % ; 3 ; 6 =?> U A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.11/??
40 6 4: < 8 $ : ; Extensional equality A classical computation induces a function U by % ; 3 ; 6 =?> U We say that two computations are extensionally equivalent, if they give rise to the same function. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.11/??
41 % $ % $ % $ : G : G Extensional equality... Theorem: U U U A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.12/??
42 % $ % $ % $ : G : G Extensional equality... Theorem: U U U Hence, classical computations upto extensional equality give rise to the category. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.12/??
43 % $ % $ % $ : G : G 4 Extensional equality... Theorem: U U U Hence, classical computations upto extensional equality give rise to the category. Theorem: Any function on finite sets ;can be realized by a computation. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.12/??
44 % $ % $ % $ : G : G 4 Extensional equality... Theorem: U U U Hence, classical computations upto extensional equality give rise to the category. Theorem: Any function on finite sets ;can be realized by a computation. Translation for Category Theoreticans: U is full and faithful. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.12/??
45 % $ 4 ; % $ L ; Example : function HJI HKI A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.13/??
46 $ % $ 4 ; L ; % Example : function HJI HKI computation /NMO A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.13/??
47 % $ ; % $ ; Example : function P 4 P A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.14/??
48 % $ ; % $ ; R Q Q Q T % $ 4 T ; ; % $ % $ T % $ % $ T Example : function A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.14/?? P 4 P computation S $ % S ; S ; U ; ;
49 Classical vs quantum A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
50 Classical vs quantum classical ( ) quantum ( ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
51 Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets ) quantum ( ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
52 Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
53 Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets bijections ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
54 Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets bijections ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces unitary operators ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
55 V Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets bijections cartesian product ( ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces unitary operators ) ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
56 W V Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets bijections cartesian product ( ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces unitary operators ) tensor product ( ) ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
57 W V Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets bijections cartesian product ( functions ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces unitary operators ) tensor product ( ) ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
58 W V Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets bijections cartesian product ( functions ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces unitary operators ) tensor product ( ) superoperators ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
59 W V Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets bijections cartesian product ( functions projections ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces unitary operators ) tensor product ( ) superoperators ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
60 W V Classical vs quantum classical ( finite sets bijections cartesian product ( functions projections ) quantum ( finite dimensional Hilbert spaces unitary operators ) tensor product ( ) superoperators partial trace ) A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.15/??
61 X, classically P G HDI A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.16/??
62 X Q R Q, classically P G HDI S /NMO /ZY A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.16/??
63 X Q R [ Q, classically P G HDI S /NMO /ZY A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.16/??
64 X Q R Q, quantum S /]MO /\Y A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.17/??
65 X Q _ S # R * _ # Q, quantum S /]MO /\Y input: I ^ I ^ A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.17/??
66 X R Q Q # _ S # # S # A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.17/??, quantum S /]MO /\Y * _ I ^ I ^ input: * _ I * _ I output:
67 X R Q Q # _ S # # S # A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.17/??, quantum S /]MO /\Y * _ I ^ I ^ input: * _ I * _ I output: Decoherence!
68 Control of decoherence A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.18/??
69 Control of decoherence QML is based on strict linear logic A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.18/??
70 T Control of decoherence QML is based on strict linear logic Contraction is implicit and realized by. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.18/??
71 T Control of decoherence QML is based on strict linear logic Contraction is implicit and realized by Weakening is explicit and leads to decoherence.. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.18/??
72 QML overview A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.19/??
73 # # a ` a ` ` QML overview Types A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.19/??
74 # # a ` a ` # b d % $ c L ; # c c b % m QML overview Types ` Terms # c b + b # % $# % $# + c b ; c e f ' # b egf * l L e f ' # c e f b(k,j #ih * l L e f ' # c e f b(k,j #ih * c % #$n $ # A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.19/??
75 l b c c c h l b c c c,j h * l * l A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.20/?? Qbits % $ egf " & ') % $ egf '!" +, e f ' # c e f,j +, e f ' # c e f
76 QML overview... A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.21/??
77 o ` o ` QML overview... Typing judgements pq pq programs strict programs A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.21/??
78 o ` o ` p o o ` ` s s r o r s s r o r ` ` QML overview... Typing judgements Semantics pq pq programs strict programs q pq s 4 r q s 4 r q A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.21/??
79 ; & " o q x w pq o ` a pt ` Q pvu a t y{z Q A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.22/?? The let-rule
80 ; & " o q x w o ƒ ƒ ˆ C pq o ` a pt ` Q pvu a t y{z Q A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.22/?? The let-rule ~}
81 on contexts A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.23/??
82 ; Š 4Q R ` Q % ; dom if ` Q % ; A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.23/?? on contexts o $ ` Q ` Q o ; o $ ` Q o ;
83 ; Š 4Q R o o C ` Q % ; dom if ` Q % ; A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.23/?? on contexts o $ ` Q ` Q o ; o $ ` Q o ; ~}
84 Another source of decoherence A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.24/??
85 b Ž Œ Another source of decoherence mentions b Ž Œ " &(') +, " & ') b Ž Œ A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.24/??
86 b Ž Œ Ž Œ Œ Another source of decoherence mentions b " &(') +, & ') " b Ž but doesn t use it. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.24/??
87 b Ž Œ Ž Œ Œ Another source of decoherence mentions b " &(') +, & ') " b Ž but doesn t use it. Hence, it has to measure it! A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.24/??
88 -elim A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.25/??
89 œ š œ µ «ª œ š ž Ÿ ²ž ³ ² ± A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.25/?? -elim W
90 œ š œ µ «ª œ š œ Æ ˆ ƒ 2 ž Ÿ ²ž ³ ² ±» / º¹  /½¼¾ ÁÀ ÉËÊ Ç È /ÄÅ 2ÍÅ A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.25/?? -elim W W ƒ 1 Äà 1 Å À 1 ¾ Ì
91 -elim decoherence-free A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.26/??
92 œ š œ µ «ª Ï œ š -elim decoherence-free Î Ï Ð ž Ï ž Ï Ñ ²ž ³ ² ± Î W A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.26/??
93 œ š œ µ «ª Ï œ š œ ƒ Ö Æ ˆ 2 -elim decoherence-free Î Ï Ð ž Ï ž Ï Ñ ²ž ³ ² ± Î W W» /Ä º¹ ƒ 1 Äà À / ¾ ÁÓ Â /½¼Ò ÇØÈ ÇØÈ /ÕÔ 1 Ô 2ÙÔ Ó 1 Ò Ì A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.26/??
94 G Ú A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.27/??
95 b Ž Œ b Ž Œ " & ') +, " & ') A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.27/?? l l G Ú
96 b Ž Œ b Ž Œ w w G Ú l " & ') +, " & ') l This program has a type error, because. xüý Û xdüý Û A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.27/??
97 b Ž Œ b Ž Œ w w G Ú l " & ') +, " & ') l This program has a type error, because. xüý Û xdüý Û b ßÞ " & ') +,!" b ßÞ A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.27/??
98 b Ž Œ b Ž Œ w w w G Ú l " & ') +, " & ') l This program has a type error, because. xüý Û xdüý Û b ßÞ " & ') +,!" b ßÞ This program typechecks, because. xdüý Û w â àáá u Û A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.27/??
99 Conclusions A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.28/??
100 Conclusions Our semantic ideas proved useful when designing a quantum programming language, analogous concepts are modelled by the same syntactic constructs. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.28/??
101 Conclusions Our semantic ideas proved useful when designing a quantum programming language, analogous concepts are modelled by the same syntactic constructs. Our analysis also highlights the differences between classical and quantum programming. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.28/??
102 Conclusions Our semantic ideas proved useful when designing a quantum programming language, analogous concepts are modelled by the same syntactic constructs. Our analysis also highlights the differences between classical and quantum programming. Quantum programming introduces the problem of control of decoherence, which we address by making forgetting variables explicit and by having different if-then-else constructs. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.28/??
103 Further work A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.29/??
104 Further work We have to analyze more quantum programs to evaluate the practical usefulness of our approach. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.29/??
105 Further work We have to analyze more quantum programs to evaluate the practical usefulness of our approach. Are we able to come up with completely new algorithms using QML? A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.29/??
106 Further work We have to analyze more quantum programs to evaluate the practical usefulness of our approach. Are we able to come up with completely new algorithms using QML? How to deal with higher order programs? A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.29/??
107 Further work We have to analyze more quantum programs to evaluate the practical usefulness of our approach. Are we able to come up with completely new algorithms using QML? How to deal with higher order programs? How to deal with infinite datatypes? A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.29/??
108 Further work We have to analyze more quantum programs to evaluate the practical usefulness of our approach. Are we able to come up with completely new algorithms using QML? How to deal with higher order programs? How to deal with infinite datatypes? Investigate the similarities/differences between FCC and FQC from a categorical point of view. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.29/??
109 The end Thank you for your attention. A Functional Quantum Programming Language p.30/??
Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language
 MGS Xmas 04 p.1/?? Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin supported
MGS Xmas 04 p.1/?? Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin supported
Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language
 Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin Towards ahigh LevelQuantum Programming
Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin Towards ahigh LevelQuantum Programming
A functional quantum programming language
 A functional quantum programming language Thorsten Altenkirch and Jonathan Grattage School of Computer Science and IT, Nottingham University email: {txa,jjg}@cs.nott.ac.uk Abstract. We introduce the language
A functional quantum programming language Thorsten Altenkirch and Jonathan Grattage School of Computer Science and IT, Nottingham University email: {txa,jjg}@cs.nott.ac.uk Abstract. We introduce the language
arxiv:quant-ph/ v5 19 Apr 2005
 A functional quantum programming language arxiv:quant-ph/0409065v5 19 Apr 2005 Thorsten Altenkirch and Jonathan Grattage School of Computer Science and IT, Nottingham University email: {txa,jjg}@cs.nott.ac.uk
A functional quantum programming language arxiv:quant-ph/0409065v5 19 Apr 2005 Thorsten Altenkirch and Jonathan Grattage School of Computer Science and IT, Nottingham University email: {txa,jjg}@cs.nott.ac.uk
 ! " # $! % & '! , ) ( + - (. ) ( ) * + / 0 1 2 3 0 / 4 5 / 6 0 ; 8 7 < = 7 > 8 7 8 9 : Œ Š ž P P h ˆ Š ˆ Œ ˆ Š ˆ Ž Ž Ý Ü Ý Ü Ý Ž Ý ê ç è ± ¹ ¼ ¹ ä ± ¹ w ç ¹ è ¼ è Œ ¹ ± ¹ è ¹ è ä ç w ¹ ã ¼ ¹ ä ¹ ¼ ¹ ±
! " # $! % & '! , ) ( + - (. ) ( ) * + / 0 1 2 3 0 / 4 5 / 6 0 ; 8 7 < = 7 > 8 7 8 9 : Œ Š ž P P h ˆ Š ˆ Œ ˆ Š ˆ Ž Ž Ý Ü Ý Ü Ý Ž Ý ê ç è ± ¹ ¼ ¹ ä ± ¹ w ç ¹ è ¼ è Œ ¹ ± ¹ è ¹ è ä ç w ¹ ã ¼ ¹ ä ¹ ¼ ¹ ±
Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations Spring 2015 Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees Marek Fiser Purdue University
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations Spring 2015 Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees Marek Fiser Purdue University
LA PRISE DE CALAIS. çoys, çoys, har - dis. çoys, dis. tons, mantz, tons, Gas. c est. à ce. C est à ce. coup, c est à ce
 > ƒ? @ Z [ \ _ ' µ `. l 1 2 3 z Æ Ñ 6 = Ð l sl (~131 1606) rn % & +, l r s s, r 7 nr ss r r s s s, r s, r! " # $ s s ( ) r * s, / 0 s, r 4 r r 9;: < 10 r mnz, rz, r ns, 1 s ; j;k ns, q r s { } ~ l r mnz,
> ƒ? @ Z [ \ _ ' µ `. l 1 2 3 z Æ Ñ 6 = Ð l sl (~131 1606) rn % & +, l r s s, r 7 nr ss r r s s s, r s, r! " # $ s s ( ) r * s, / 0 s, r 4 r r 9;: < 10 r mnz, rz, r ns, 1 s ; j;k ns, q r s { } ~ l r mnz,
Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory
 Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory p. 1/21 Decision Making:
Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory p. 1/21 Decision Making:
An Introduction to Optimal Control Applied to Disease Models
 An Introduction to Optimal Control Applied to Disease Models Suzanne Lenhart University of Tennessee, Knoxville Departments of Mathematics Lecture1 p.1/37 Example Number of cancer cells at time (exponential
An Introduction to Optimal Control Applied to Disease Models Suzanne Lenhart University of Tennessee, Knoxville Departments of Mathematics Lecture1 p.1/37 Example Number of cancer cells at time (exponential
Quantum Effects. Juliana K. Vizzotto 1 Thorsten Altenkirch 2. Amr Sabry January Yale CS Colloquium Page 1
 Quantum Effects Juliana K. Vizzotto 1 Thorsten Altenkirch 2 Amr Sabry 3 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul 2 The University of Nottingham 3 Indiana University 2 January 25 Yale CS Colloquium Page
Quantum Effects Juliana K. Vizzotto 1 Thorsten Altenkirch 2 Amr Sabry 3 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul 2 The University of Nottingham 3 Indiana University 2 January 25 Yale CS Colloquium Page
" #$ P UTS W U X [ZY \ Z _ `a \ dfe ih j mlk n p q sr t u s q e ps s t x q s y i_z { U U z W } y ~ y x t i e l US T { d ƒ ƒ ƒ j s q e uˆ ps i ˆ p q y
 " #$ +. 0. + 4 6 4 : + 4 ; 6 4 < = =@ = = =@ = =@ " #$ P UTS W U X [ZY \ Z _ `a \ dfe ih j mlk n p q sr t u s q e ps s t x q s y i_z { U U z W } y ~ y x t i e l US T { d ƒ ƒ ƒ j s q e uˆ ps i ˆ p q y h
" #$ +. 0. + 4 6 4 : + 4 ; 6 4 < = =@ = = =@ = =@ " #$ P UTS W U X [ZY \ Z _ `a \ dfe ih j mlk n p q sr t u s q e ps s t x q s y i_z { U U z W } y ~ y x t i e l US T { d ƒ ƒ ƒ j s q e uˆ ps i ˆ p q y h
An Example file... log.txt
 # ' ' Start of fie & %$ " 1 - : 5? ;., B - ( * * B - ( * * F I / 0. )- +, * ( ) 8 8 7 /. 6 )- +, 5 5 3 2( 7 7 +, 6 6 9( 3 5( ) 7-0 +, => - +< ( ) )- +, 7 / +, 5 9 (. 6 )- 0 * D>. C )- +, (A :, C 0 )- +,
# ' ' Start of fie & %$ " 1 - : 5? ;., B - ( * * B - ( * * F I / 0. )- +, * ( ) 8 8 7 /. 6 )- +, 5 5 3 2( 7 7 +, 6 6 9( 3 5( ) 7-0 +, => - +< ( ) )- +, 7 / +, 5 9 (. 6 )- 0 * D>. C )- +, (A :, C 0 )- +,
Principal Secretary to Government Haryana, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh.
 1 From To Principal Secretary to Government Haryana, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh. The Director General, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh. Memo No. Misc-2339
1 From To Principal Secretary to Government Haryana, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh. The Director General, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh. Memo No. Misc-2339
ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA
 P r a ž s k á v y s o k á š k o l a p s y c h o s o c i á l n í c h s t u d i í ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA N a t á l i a S l o b o d n í k o v á v e d ú c i p r á c e : P h D r. M a r t i n S t r o u
P r a ž s k á v y s o k á š k o l a p s y c h o s o c i á l n í c h s t u d i í ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA N a t á l i a S l o b o d n í k o v á v e d ú c i p r á c e : P h D r. M a r t i n S t r o u
Optimal Control of PDEs
 Optimal Control of PDEs Suzanne Lenhart University of Tennessee, Knoville Department of Mathematics Lecture1 p.1/36 Outline 1. Idea of diffusion PDE 2. Motivating Eample 3. Big picture of optimal control
Optimal Control of PDEs Suzanne Lenhart University of Tennessee, Knoville Department of Mathematics Lecture1 p.1/36 Outline 1. Idea of diffusion PDE 2. Motivating Eample 3. Big picture of optimal control
Constructive Decision Theory
 Constructive Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Constructive Decision Theory p. 1/2 Savage s Approach Savage s approach to decision
Constructive Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Constructive Decision Theory p. 1/2 Savage s Approach Savage s approach to decision
General Neoclassical Closure Theory: Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator
 General Neoclassical Closure Theory: Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator E. D. Held eheld@cc.usu.edu Utah State University General Neoclassical Closure Theory:Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator
General Neoclassical Closure Theory: Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator E. D. Held eheld@cc.usu.edu Utah State University General Neoclassical Closure Theory:Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator
Planning for Reactive Behaviors in Hide and Seek
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Center for Human Modeling and Simulation Department of Computer & Information Science May 1995 Planning for Reactive Behaviors in Hide and Seek Michael B. Moore
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Center for Human Modeling and Simulation Department of Computer & Information Science May 1995 Planning for Reactive Behaviors in Hide and Seek Michael B. Moore
Max. Input Power (W) Input Current (Arms) Dimming. Enclosure
 Product Overview XI025100V036NM1M Input Voltage (Vac) Output Power (W) Output Voltage Range (V) Output urrent (A) Efficiency@ Max Load and 70 ase Max ase Temp. ( ) Input urrent (Arms) Max. Input Power
Product Overview XI025100V036NM1M Input Voltage (Vac) Output Power (W) Output Voltage Range (V) Output urrent (A) Efficiency@ Max Load and 70 ase Max ase Temp. ( ) Input urrent (Arms) Max. Input Power
New BaBar Results on Rare Leptonic B Decays
 New BaBar Results on Rare Leptonic B Decays Valerie Halyo Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) FPCP 22 valerieh@slac.stanford.edu 1 Table of Contents Motivation to look for and Analysis Strategy Measurement
New BaBar Results on Rare Leptonic B Decays Valerie Halyo Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) FPCP 22 valerieh@slac.stanford.edu 1 Table of Contents Motivation to look for and Analysis Strategy Measurement
OC330C. Wiring Diagram. Recommended PKH- P35 / P50 GALH PKA- RP35 / RP50. Remarks (Drawing No.) No. Parts No. Parts Name Specifications
 G G " # $ % & " ' ( ) $ * " # $ % & " ( + ) $ * " # C % " ' ( ) $ * C " # C % " ( + ) $ * C D ; E @ F @ 9 = H I J ; @ = : @ A > B ; : K 9 L 9 M N O D K P D N O Q P D R S > T ; U V > = : W X Y J > E ; Z
G G " # $ % & " ' ( ) $ * " # $ % & " ( + ) $ * " # C % " ' ( ) $ * C " # C % " ( + ) $ * C D ; E @ F @ 9 = H I J ; @ = : @ A > B ; : K 9 L 9 M N O D K P D N O Q P D R S > T ; U V > = : W X Y J > E ; Z
The University of Bath School of Management is one of the oldest established management schools in Britain. It enjoys an international reputation for
 The University of Bath School of Management is one of the oldest established management schools in Britain. It enjoys an international reputation for the quality of its teaching and research. Its mission
The University of Bath School of Management is one of the oldest established management schools in Britain. It enjoys an international reputation for the quality of its teaching and research. Its mission
Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory
 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date: 16 December 2015
Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date: 16 December 2015
QUESTIONS ON QUARKONIUM PRODUCTION IN NUCLEAR COLLISIONS
 International Workshop Quarkonium Working Group QUESTIONS ON QUARKONIUM PRODUCTION IN NUCLEAR COLLISIONS ALBERTO POLLERI TU München and ECT* Trento CERN - November 2002 Outline What do we know for sure?
International Workshop Quarkonium Working Group QUESTIONS ON QUARKONIUM PRODUCTION IN NUCLEAR COLLISIONS ALBERTO POLLERI TU München and ECT* Trento CERN - November 2002 Outline What do we know for sure?
1. Allstate Group Critical Illness Claim Form: When filing Critical Illness claim, please be sure to include the following:
 Dear Policyholder, Per your recent request, enclosed you will find the following forms: 1. Allstate Group Critical Illness Claim Form: When filing Critical Illness claim, please be sure to include the
Dear Policyholder, Per your recent request, enclosed you will find the following forms: 1. Allstate Group Critical Illness Claim Form: When filing Critical Illness claim, please be sure to include the
4.3 Laplace Transform in Linear System Analysis
 4.3 Laplace Transform in Linear System Analysis The main goal in analysis of any dynamic system is to find its response to a given input. The system response in general has two components: zero-state response
4.3 Laplace Transform in Linear System Analysis The main goal in analysis of any dynamic system is to find its response to a given input. The system response in general has two components: zero-state response
Manifold Regularization
 Manifold Regularization Vikas Sindhwani Department of Computer Science University of Chicago Joint Work with Mikhail Belkin and Partha Niyogi TTI-C Talk September 14, 24 p.1 The Problem of Learning is
Manifold Regularization Vikas Sindhwani Department of Computer Science University of Chicago Joint Work with Mikhail Belkin and Partha Niyogi TTI-C Talk September 14, 24 p.1 The Problem of Learning is
A Beamforming Method for Blind Calibration of Time-Interleaved A/D Converters
 A Beamforming Method for Blind Calibration of Time-nterleaved A/D Converters Bernard C. Levy University of California, Davis Joint wor with Steve Huang September 30, 200 Outline 1 Motivation Problem Formulation
A Beamforming Method for Blind Calibration of Time-nterleaved A/D Converters Bernard C. Levy University of California, Davis Joint wor with Steve Huang September 30, 200 Outline 1 Motivation Problem Formulation
Connection equations with stream variables are generated in a model when using the # $ % () operator or the & ' %
 7 9 9 7 The two basic variable types in a connector potential (or across) variable and flow (or through) variable are not sufficient to describe in a numerically sound way the bi-directional flow of matter
7 9 9 7 The two basic variable types in a connector potential (or across) variable and flow (or through) variable are not sufficient to describe in a numerically sound way the bi-directional flow of matter
AN IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHM FOR ARMAX SYSTEMS
 AN IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHM FOR ARMAX SYSTEMS First the X, then the AR, finally the MA Jan C. Willems, K.U. Leuven Workshop on Observation and Estimation Ben Gurion University, July 3, 2004 p./2 Joint
AN IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHM FOR ARMAX SYSTEMS First the X, then the AR, finally the MA Jan C. Willems, K.U. Leuven Workshop on Observation and Estimation Ben Gurion University, July 3, 2004 p./2 Joint
B œ c " " ã B œ c 8 8. such that substituting these values for the B 3 's will make all the equations true
 System of Linear Equations variables Ð unknowns Ñ B" ß B# ß ÞÞÞ ß B8 Æ Æ Æ + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, "" " "# # "8 8 " + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, #" " ## # #8 8 # ã + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, 3" " 3# # 38 8 3 ã + 7" B" + 7# B#
System of Linear Equations variables Ð unknowns Ñ B" ß B# ß ÞÞÞ ß B8 Æ Æ Æ + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, "" " "# # "8 8 " + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, #" " ## # #8 8 # ã + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, 3" " 3# # 38 8 3 ã + 7" B" + 7# B#
A functional quantum programming language. by Jonathan James Grattage, BSc (Hons)
 A functional quantum programming language by Jonathan James Grattage, BSc (Hons) Thesis submitted to The University of Nottingham for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, September 2006 Abstract This thesis
A functional quantum programming language by Jonathan James Grattage, BSc (Hons) Thesis submitted to The University of Nottingham for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, September 2006 Abstract This thesis
- Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? - Quantum Programming Languages. By : Amanda Cieslak and Ahmana Tarin
 - Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? - Quantum Programming Languages By : Amanda Cieslak and Ahmana Tarin Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? there are only a few problems for which quantum
- Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? - Quantum Programming Languages By : Amanda Cieslak and Ahmana Tarin Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? there are only a few problems for which quantum
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 REDCLIFF MUNICIPAL PLANNING COMMISSION FOR COMMENT/DISCUSSION DATE: TOPIC: April 27 th, 2018 Bylaw 1860/2018, proposed amendments to the Land Use Bylaw regarding cannabis
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 REDCLIFF MUNICIPAL PLANNING COMMISSION FOR COMMENT/DISCUSSION DATE: TOPIC: April 27 th, 2018 Bylaw 1860/2018, proposed amendments to the Land Use Bylaw regarding cannabis
Loop parallelization using compiler analysis
 Loop parallelization using compiler analysis Which of these loops is parallel? How can we determine this automatically using compiler analysis? Organization of a Modern Compiler Source Program Front-end
Loop parallelization using compiler analysis Which of these loops is parallel? How can we determine this automatically using compiler analysis? Organization of a Modern Compiler Source Program Front-end
Vectors. Teaching Learning Point. Ç, where OP. l m n
 Vectors 9 Teaching Learning Point l A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called is called a vector. l A directed line segment represents a vector and is denoted y AB Å or a Æ. l Position
Vectors 9 Teaching Learning Point l A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called is called a vector. l A directed line segment represents a vector and is denoted y AB Å or a Æ. l Position
Vector analysis. 1 Scalars and vectors. Fields. Coordinate systems 1. 2 The operator The gradient, divergence, curl, and Laplacian...
 Vector analysis Abstract These notes present some background material on vector analysis. Except for the material related to proving vector identities (including Einstein s summation convention and the
Vector analysis Abstract These notes present some background material on vector analysis. Except for the material related to proving vector identities (including Einstein s summation convention and the
Damping Ring Requirements for 3 TeV CLIC
 Damping Ring Requirements for 3 TeV CLIC Quantity Symbol Value Bunch population N b 9 4.1 10 No. of bunches/train k bt 154 Repetition frequency f r 100 Hz Horizontal emittance γε x 7 4.5 10 m Vertical
Damping Ring Requirements for 3 TeV CLIC Quantity Symbol Value Bunch population N b 9 4.1 10 No. of bunches/train k bt 154 Repetition frequency f r 100 Hz Horizontal emittance γε x 7 4.5 10 m Vertical
SOLAR MORTEC INDUSTRIES.
 SOLAR MORTEC INDUSTRIES www.mortecindustries.com.au Wind Regions Region A Callytharra Springs Gascoyne Junction Green Head Kununurra Lord Howe Island Morawa Toowoomba Wittanoom Bourke Region B Adelaide
SOLAR MORTEC INDUSTRIES www.mortecindustries.com.au Wind Regions Region A Callytharra Springs Gascoyne Junction Green Head Kununurra Lord Howe Island Morawa Toowoomba Wittanoom Bourke Region B Adelaide
Obtain from theory/experiment a value for the absorbtion cross-section. Calculate the number of atoms/ions/molecules giving rise to the line.
 Line Emission Observations of spectral lines offer the possibility of determining a wealth of information about an astronomical source. A usual plan of attack is :- Identify the line. Obtain from theory/experiment
Line Emission Observations of spectral lines offer the possibility of determining a wealth of information about an astronomical source. A usual plan of attack is :- Identify the line. Obtain from theory/experiment
Complex Analysis. PH 503 Course TM. Charudatt Kadolkar Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Complex Analysis PH 503 Course TM Charudatt Kadolkar Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati ii Copyright 2000 by Charudatt Kadolkar Preface Preface Head These notes were prepared during the lectures
Complex Analysis PH 503 Course TM Charudatt Kadolkar Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati ii Copyright 2000 by Charudatt Kadolkar Preface Preface Head These notes were prepared during the lectures
Quantum data and control made easier
 QPL 006 Preliminary Version Quantum data and control made easier Michael Lampis 1, Kyriakos G. Ginis 3 Nikolaos S. Papaspyrou 4 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Technical University
QPL 006 Preliminary Version Quantum data and control made easier Michael Lampis 1, Kyriakos G. Ginis 3 Nikolaos S. Papaspyrou 4 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Technical University
Orthogonality and Algebraic Lambda-Calculus
 Orthogonality and Algebraic Lambda-Calculus Benoît Valiron March 28, 2010 Abstract Directly encoding lambda-terms on quantum strings while keeping a quantum interpretation is a hard task. As shown by van
Orthogonality and Algebraic Lambda-Calculus Benoît Valiron March 28, 2010 Abstract Directly encoding lambda-terms on quantum strings while keeping a quantum interpretation is a hard task. As shown by van
: œ Ö: =? À =ß> real numbers. œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example,! is translated to :)
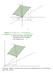 â SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö =? > @ À =ß> real numbers : SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö: =? > @ À =ß> real numbers œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example, is translated to :) á In general: Adding a vector :
â SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö =? > @ À =ß> real numbers : SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö: =? > @ À =ß> real numbers œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example, is translated to :) á In general: Adding a vector :
$%! & (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 +7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 A BDC EF G H I EJ KL N G H I. ] ^ _ ` _ ^ a b=c o e f p a q i h f i a j k e i l _ ^ m=c n ^
![$%! & (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 +7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 A BDC EF G H I EJ KL N G H I. ] ^ _ ` _ ^ a b=c o e f p a q i h f i a j k e i l _ ^ m=c n ^ $%! & (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 +7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 A BDC EF G H I EJ KL N G H I. ] ^ _ ` _ ^ a b=c o e f p a q i h f i a j k e i l _ ^ m=c n ^](/thumbs/92/108125918.jpg) ! #" $%! & ' ( ) ) (, -. / ( 0 1#2 ' ( ) ) (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 ;=? @ A BDC EF G H I EJ KL M @C N G H I OPQ ;=R F L EI E G H A S T U S V@C N G H IDW G Q G XYU Z A [ H R C \ G ] ^ _ `
! #" $%! & ' ( ) ) (, -. / ( 0 1#2 ' ( ) ) (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 ;=? @ A BDC EF G H I EJ KL M @C N G H I OPQ ;=R F L EI E G H A S T U S V@C N G H IDW G Q G XYU Z A [ H R C \ G ] ^ _ `
More advanced codes 0 1 ( , 1 1 (
 p. 1/24 More advanced codes The Shor code was the first general-purpose quantum error-correcting code, but since then many others have been discovered. An important example, discovered independently of
p. 1/24 More advanced codes The Shor code was the first general-purpose quantum error-correcting code, but since then many others have been discovered. An important example, discovered independently of
Transformation Rules for Designing CNOT-based Quantum Circuits
 Transformation Rules for Designing CNOT-based Quantum Circuits Kazuo Iwama Sch. of Inform., Kyoto Univ. QCI, ERATO, JST iwama@kuis.kyoto-u.ac.jp Yahiko Kambayashi Sch. of Inform., Kyoto Univ. yahiko@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Transformation Rules for Designing CNOT-based Quantum Circuits Kazuo Iwama Sch. of Inform., Kyoto Univ. QCI, ERATO, JST iwama@kuis.kyoto-u.ac.jp Yahiko Kambayashi Sch. of Inform., Kyoto Univ. yahiko@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp
 n P! " # $ % & % & ' ( ) * + % $, $ -. $ -..! " # ) & % $/ $ - 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 8 7 9 9 : 3 ; 1 7 < 9 : 5 = > : 9? @ A B C D E F G HI J G H K D L M N O P Q R S T U V M Q P W X X Y W X X Z [ Y \ ] M
n P! " # $ % & % & ' ( ) * + % $, $ -. $ -..! " # ) & % $/ $ - 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 8 7 9 9 : 3 ; 1 7 < 9 : 5 = > : 9? @ A B C D E F G HI J G H K D L M N O P Q R S T U V M Q P W X X Y W X X Z [ Y \ ] M
Cairns Hospital: Suspected Acute Coronary Syndrome Pathways. DO NOT USE if a non cardiac cause for the chest pain can be diagnosed
 Cairns Hospital: Suspected Acute Coronary Syndrome Pathways DO NOT USE if a non cardiac cause for the chest pain can be diagnosed Clinical pathways never replace clinical judgement. Care outlined on this
Cairns Hospital: Suspected Acute Coronary Syndrome Pathways DO NOT USE if a non cardiac cause for the chest pain can be diagnosed Clinical pathways never replace clinical judgement. Care outlined on this
Books. Book Collection Editor. Editor. Name Name Company. Title "SA" A tree pattern. A database instance
 "! # #%$ $ $ & & & # ( # ) $ + $, -. 0 1 1 1 2430 5 6 78 9 =?
"! # #%$ $ $ & & & # ( # ) $ + $, -. 0 1 1 1 2430 5 6 78 9 =?
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants Teaching-Learning Points A matri is an ordered rectanguar arra (arrangement) of numbers and encosed b capita bracket [ ]. These numbers are caed eements of the matri. Matri is
Matrices and Determinants Teaching-Learning Points A matri is an ordered rectanguar arra (arrangement) of numbers and encosed b capita bracket [ ]. These numbers are caed eements of the matri. Matri is
Type Systems for Quantum Computation
 Type Systems for Quantum Computation Bill Zorn Abstract Type systems are useful to programmers for a variety of reasons. In the classical world, they help us to define interfaces between separate pieces
Type Systems for Quantum Computation Bill Zorn Abstract Type systems are useful to programmers for a variety of reasons. In the classical world, they help us to define interfaces between separate pieces
Relation Between the Growth Twin and the Morphology of a Czochralski Silicon Single Crystal
 Korean J. Crystallography Vol. 11, No. 4, pp.207~211, 2000 LG, Relation Between the Growth Twin and the Morphology of a Czochralski Silicon Single Crystal Bong Mo Park LG Siltron Inc., 283, Imsoo-dong,
Korean J. Crystallography Vol. 11, No. 4, pp.207~211, 2000 LG, Relation Between the Growth Twin and the Morphology of a Czochralski Silicon Single Crystal Bong Mo Park LG Siltron Inc., 283, Imsoo-dong,
MARKET AREA UPDATE Report as of: 1Q 2Q 3Q 4Q
 Year: 2013 Market Area (Cit, State): Greater Portland, OR MARKET AREA UPDATE Report as of: 1Q 2Q 3Q 4Q Provided b (Compan / Companies): Coldwell Banker Seal, Archibald Relocation, Prudential Northwest
Year: 2013 Market Area (Cit, State): Greater Portland, OR MARKET AREA UPDATE Report as of: 1Q 2Q 3Q 4Q Provided b (Compan / Companies): Coldwell Banker Seal, Archibald Relocation, Prudential Northwest
Pharmacological and genomic profiling identifies NF-κB targeted treatment strategies for mantle cell lymphoma
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Med. 0, 87 9 (014) Pharmacoogica and genomic profiing identifies NF-κB targeted treatment strategies for mante ce ymphoma Rami Raha, Mareie Fric, Rodrigo Romero, Joshua M Korn, Robert
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Med. 0, 87 9 (014) Pharmacoogica and genomic profiing identifies NF-κB targeted treatment strategies for mante ce ymphoma Rami Raha, Mareie Fric, Rodrigo Romero, Joshua M Korn, Robert
Front-end. Organization of a Modern Compiler. Middle1. Middle2. Back-end. converted to control flow) Representation
 register allocation instruction selection Code Low-level intermediate Representation Back-end Assembly array references converted into low level operations, loops converted to control flow Middle2 Low-level
register allocation instruction selection Code Low-level intermediate Representation Back-end Assembly array references converted into low level operations, loops converted to control flow Middle2 Low-level
Juan Juan Salon. EH National Bank. Sandwich Shop Nail Design. OSKA Beverly. Chase Bank. Marina Rinaldi. Orogold. Mariposa.
 ( ) X é X é Q Ó / 8 ( ) Q / ( ) ( ) : ( ) : 44-3-8999 433 4 z 78-19 941, #115 Z 385-194 77-51 76-51 74-7777, 75-5 47-55 74-8141 74-5115 78-3344 73-3 14 81-4 86-784 78-33 551-888 j 48-4 61-35 z/ zz / 138
( ) X é X é Q Ó / 8 ( ) Q / ( ) ( ) : ( ) : 44-3-8999 433 4 z 78-19 941, #115 Z 385-194 77-51 76-51 74-7777, 75-5 47-55 74-8141 74-5115 78-3344 73-3 14 81-4 86-784 78-33 551-888 j 48-4 61-35 z/ zz / 138
February 17, 2015 REQUEST FOR PROPOSALS. For Columbus Metropolitan Library. Issued by: Purchasing Division 96 S. Grant Ave. Columbus, OH 43215
 F 7, 05 RQU FOR PROPOL P/B & O RFP L 5-006 F L : P D 96 G, OH 435 D : 3, 05 N :00 N (, O L ) W D, P P D, F D : (64) 849-034; F: (64) 849-34 @ RQU FOR PROPOL NRUON L ( L L ) R P ( RFP ) P B P N L 5-006
F 7, 05 RQU FOR PROPOL P/B & O RFP L 5-006 F L : P D 96 G, OH 435 D : 3, 05 N :00 N (, O L ) W D, P P D, F D : (64) 849-034; F: (64) 849-34 @ RQU FOR PROPOL NRUON L ( L L ) R P ( RFP ) P B P N L 5-006
Optimal data-independent point locations for RBF interpolation
 Optimal dataindependent point locations for RF interpolation S De Marchi, R Schaback and H Wendland Università di Verona (Italy), Universität Göttingen (Germany) Metodi di Approssimazione: lezione dell
Optimal dataindependent point locations for RF interpolation S De Marchi, R Schaback and H Wendland Università di Verona (Italy), Universität Göttingen (Germany) Metodi di Approssimazione: lezione dell
Optimization of a parallel 3d-FFT with non-blocking collective operations
 Optimization of a parallel 3d-FFT with non-blocking collective operations Chair of Computer Architecture Technical University of Chemnitz Département de Physique Théorique et Appliquée Commissariat à l
Optimization of a parallel 3d-FFT with non-blocking collective operations Chair of Computer Architecture Technical University of Chemnitz Département de Physique Théorique et Appliquée Commissariat à l
ALTER TABLE Employee ADD ( Mname VARCHAR2(20), Birthday DATE );
 !! "# $ % & '( ) # * +, - # $ "# $ % & '( ) # *.! / 0 "# "1 "& # 2 3 & 4 4 "# $ % & '( ) # *!! "# $ % & # * 1 3 - "# 1 * #! ) & 3 / 5 6 7 8 9 ALTER ; ? @ A B C D E F G H I A = @ A J > K L ; ?
!! "# $ % & '( ) # * +, - # $ "# $ % & '( ) # *.! / 0 "# "1 "& # 2 3 & 4 4 "# $ % & '( ) # *!! "# $ % & # * 1 3 - "# 1 * #! ) & 3 / 5 6 7 8 9 ALTER ; ? @ A B C D E F G H I A = @ A J > K L ; ?
PART IV LIVESTOCK, POULTRY AND FISH PRODUCTION
 ! " $#%(' ) PART IV LIVSTOCK, POULTRY AND FISH PRODUCTION Table (93) MAIN GROUPS OF ANIMAL PRODUCTS Production 1000 M.T Numbers 1000 Head Type 2012 Numbers Cattle 54164.5 53434.6 Buffaloes 4304.51 4292.51
! " $#%(' ) PART IV LIVSTOCK, POULTRY AND FISH PRODUCTION Table (93) MAIN GROUPS OF ANIMAL PRODUCTS Production 1000 M.T Numbers 1000 Head Type 2012 Numbers Cattle 54164.5 53434.6 Buffaloes 4304.51 4292.51
Symbols and dingbats. A 41 Α a 61 α À K cb ➋ à esc. Á g e7 á esc. Â e e5 â. Ã L cc ➌ ã esc ~ Ä esc : ä esc : Å esc * å esc *
 Note: Although every effort ws tken to get complete nd ccurte tble, the uhtor cn not be held responsible for ny errors. Vrious sources hd to be consulted nd MIF hd to be exmined to get s much informtion
Note: Although every effort ws tken to get complete nd ccurte tble, the uhtor cn not be held responsible for ny errors. Vrious sources hd to be consulted nd MIF hd to be exmined to get s much informtion
UNIQUE FJORDS AND THE ROYAL CAPITALS UNIQUE FJORDS & THE NORTH CAPE & UNIQUE NORTHERN CAPITALS
 Q J j,. Y j, q.. Q J & j,. & x x. Q x q. ø. 2019 :. q - j Q J & 11 Y j,.. j,, q j q. : 10 x. 3 x - 1..,,. 1-10 ( ). / 2-10. : 02-06.19-12.06.19 23.06.19-03.07.19 30.06.19-10.07.19 07.07.19-17.07.19 14.07.19-24.07.19
Q J j,. Y j, q.. Q J & j,. & x x. Q x q. ø. 2019 :. q - j Q J & 11 Y j,.. j,, q j q. : 10 x. 3 x - 1..,,. 1-10 ( ). / 2-10. : 02-06.19-12.06.19 23.06.19-03.07.19 30.06.19-10.07.19 07.07.19-17.07.19 14.07.19-24.07.19
1. CALL TO ORDER 2. ROLL CALL 3. PLEDGE OF ALLEGIANCE 4. ORAL COMMUNICATIONS (NON-ACTION ITEM) 5. APPROVAL OF AGENDA 6. EWA SEJPA INTEGRATION PROPOSAL
 SPECIAL MEETING AGENDA SAN ELIJO JOINT POWERS AUTHORITY (SEJPA) TUESDAY JULY 12, 2016 AT 8:30 AM ENCINA WATER POLLUTION CONTROL FACILITY (EWA) BOARD MEETING ROOM 6200 AVENIDA ENCINAS CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA
SPECIAL MEETING AGENDA SAN ELIJO JOINT POWERS AUTHORITY (SEJPA) TUESDAY JULY 12, 2016 AT 8:30 AM ENCINA WATER POLLUTION CONTROL FACILITY (EWA) BOARD MEETING ROOM 6200 AVENIDA ENCINAS CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA
Harlean. User s Guide
 Harlean User s Guide font faq HOW TO INSTALL YOUR FONT You will receive your files as a zipped folder. For instructions on how to unzip your folder, visit LauraWorthingtonType.com/faqs/. Your font is available
Harlean User s Guide font faq HOW TO INSTALL YOUR FONT You will receive your files as a zipped folder. For instructions on how to unzip your folder, visit LauraWorthingtonType.com/faqs/. Your font is available
Rarefied Gas FlowThroughan Orifice at Finite Pressure Ratio
 Rarefied Gas FlowThroughan Orifice at Finite Pressure Ratio Felix Sharipov Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal do Paraná Caixa Postal 90, 85-990 Curitiba, Brazil Email: sharipov@fisica.ufpr.br;
Rarefied Gas FlowThroughan Orifice at Finite Pressure Ratio Felix Sharipov Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal do Paraná Caixa Postal 90, 85-990 Curitiba, Brazil Email: sharipov@fisica.ufpr.br;
LEAD IN DRINKING WATER REPORT
 181 US Hwy 46 Mine Hill, NJ 07803 (908) 654-8068 (800) 783-0567 Fax 908-654-8069 LEAD IN DRINKING WATER REPORT Performed At: Montrose School 356 Clark St., South Orange, NJ 07079 Performed For: South Orange
181 US Hwy 46 Mine Hill, NJ 07803 (908) 654-8068 (800) 783-0567 Fax 908-654-8069 LEAD IN DRINKING WATER REPORT Performed At: Montrose School 356 Clark St., South Orange, NJ 07079 Performed For: South Orange
TELEMATICS LINK LEADS
 EEAICS I EADS UI CD PHOE VOICE AV PREIU I EADS REQ E E A + A + I A + I E B + E + I B + E + I B + E + H B + I D + UI CD PHOE VOICE AV PREIU I EADS REQ D + D + D + I C + C + C + C + I G G + I G + I G + H
EEAICS I EADS UI CD PHOE VOICE AV PREIU I EADS REQ E E A + A + I A + I E B + E + I B + E + I B + E + H B + I D + UI CD PHOE VOICE AV PREIU I EADS REQ D + D + D + I C + C + C + C + I G G + I G + I G + H
Quantum Recursion and Second Quantisation Basic Ideas and Examples
 Quantum Recursion and Second Quantisation Basic Ideas and Examples Mingsheng Ying University of Technology, Sydney, Australia and Tsinghua University, China Happy Birthday Prakash! Happy Birthday Prakash!
Quantum Recursion and Second Quantisation Basic Ideas and Examples Mingsheng Ying University of Technology, Sydney, Australia and Tsinghua University, China Happy Birthday Prakash! Happy Birthday Prakash!
A General Procedure to Design Good Codes at a Target BER
 A General Procedure to Design Good odes at a Target BER Speaker: Xiao Ma 1 maxiao@mail.sysu.edu.cn Joint work with: hulong Liang 1, Qiutao Zhuang 1, and Baoming Bai 2 1 Dept. Electronics and omm. Eng.,
A General Procedure to Design Good odes at a Target BER Speaker: Xiao Ma 1 maxiao@mail.sysu.edu.cn Joint work with: hulong Liang 1, Qiutao Zhuang 1, and Baoming Bai 2 1 Dept. Electronics and omm. Eng.,
U ight. User s Guide
 Samantha Uight Regular Bold User s Guide font faq HOW TO INSTALL YOUR FONT You will receive your files as a zipped folder. For instructions on how to unzip your folder, visit LauraWorthingtonType.com/faqs/.
Samantha Uight Regular Bold User s Guide font faq HOW TO INSTALL YOUR FONT You will receive your files as a zipped folder. For instructions on how to unzip your folder, visit LauraWorthingtonType.com/faqs/.
Quantum Computing. Thorsten Altenkirch
 Quantum Computing Thorsten Altenkirch Is Computation universal? Alonzo Church - calculus Alan Turing Turing machines computable functions The Church-Turing thesis All computational formalisms define the
Quantum Computing Thorsten Altenkirch Is Computation universal? Alonzo Church - calculus Alan Turing Turing machines computable functions The Church-Turing thesis All computational formalisms define the
New method for solving nonlinear sum of ratios problem based on simplicial bisection
 V Ù â ð f 33 3 Vol33, No3 2013 3 Systems Engineering Theory & Practice Mar, 2013 : 1000-6788(2013)03-0742-06 : O2112!"#$%&')(*)+),-))/0)1)23)45 : A 687:9 1, ;:= 2 (1?@ACBEDCFHCFEIJKLCFFM, NCO 453007;
V Ù â ð f 33 3 Vol33, No3 2013 3 Systems Engineering Theory & Practice Mar, 2013 : 1000-6788(2013)03-0742-06 : O2112!"#$%&')(*)+),-))/0)1)23)45 : A 687:9 1, ;:= 2 (1?@ACBEDCFHCFEIJKLCFFM, NCO 453007;
F O R SOCI AL WORK RESE ARCH
 7 TH EUROPE AN CONFERENCE F O R SOCI AL WORK RESE ARCH C h a l l e n g e s i n s o c i a l w o r k r e s e a r c h c o n f l i c t s, b a r r i e r s a n d p o s s i b i l i t i e s i n r e l a t i o n
7 TH EUROPE AN CONFERENCE F O R SOCI AL WORK RESE ARCH C h a l l e n g e s i n s o c i a l w o r k r e s e a r c h c o n f l i c t s, b a r r i e r s a n d p o s s i b i l i t i e s i n r e l a t i o n
First-principles calculations of insulators in a. finite electric field
 Université de Liège First-principles calculations of insulators in a finite electric field M. Veithen, I. Souza, J. Íñiguez, D. Vanderbilt, K. M. Rabe and h. Ghosez Supported by: FNRS Belgium, VW Stiftung,
Université de Liège First-principles calculations of insulators in a finite electric field M. Veithen, I. Souza, J. Íñiguez, D. Vanderbilt, K. M. Rabe and h. Ghosez Supported by: FNRS Belgium, VW Stiftung,
ALGEBRAIC THEORIES IN MONOIDAL CATEGORIES
 ALGEBRAIC THEORIES IN MONOIDAL CATEGORIES LUCA MAURI ABSTRACT. We define a monoidal semantics for algebraic theories. The basis for the definition is provided by the analysis of the structural rules in
ALGEBRAIC THEORIES IN MONOIDAL CATEGORIES LUCA MAURI ABSTRACT. We define a monoidal semantics for algebraic theories. The basis for the definition is provided by the analysis of the structural rules in
The incident energy per unit area on the electron is given by the Poynting vector, '
 ' ' # Thompson Scattering Consider a beam of radiation moving in the direction, and being scattered by an electron through an angle in the plane. The electron experiences the following electric fields
' ' # Thompson Scattering Consider a beam of radiation moving in the direction, and being scattered by an electron through an angle in the plane. The electron experiences the following electric fields
SCOTT PLUMMER ASHTON ANTONETTI
 2742 A E E E, UE, AAAMA 3802 231 EE AEA 38,000-cre dversfed federl cmus 41,000 emloyees wth 72+ dfferent gences UE roosed 80-cre mster-lnned develoment 20 home stes 3,000F of vllgestyle retl 100,000 E
2742 A E E E, UE, AAAMA 3802 231 EE AEA 38,000-cre dversfed federl cmus 41,000 emloyees wth 72+ dfferent gences UE roosed 80-cre mster-lnned develoment 20 home stes 3,000F of vllgestyle retl 100,000 E
Byung-Soo Choi.
 Grover Search and its Applications Bung-Soo Choi bschoi3@gmail.com Contents Basics of Quantum Computation General Properties of Grover Search Idea Analsis Weight Decision Smmetric To Weights Asmmetric
Grover Search and its Applications Bung-Soo Choi bschoi3@gmail.com Contents Basics of Quantum Computation General Properties of Grover Search Idea Analsis Weight Decision Smmetric To Weights Asmmetric
A Proposal for Requirement Engineering
 A Proposal for Requirement Engineering Fumio Negoro The Institute of Computer Based Software Methodology and Technology 3-11-3 Takanawa, Minato-ku, Tokyo 108-0074, Japan f-negoro@lyee.co.jp http://www.lyee.co.jp
A Proposal for Requirement Engineering Fumio Negoro The Institute of Computer Based Software Methodology and Technology 3-11-3 Takanawa, Minato-ku, Tokyo 108-0074, Japan f-negoro@lyee.co.jp http://www.lyee.co.jp
A Language for Task Orchestration and its Semantic Properties
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCES A Language for Task Orchestration and its Semantic Properties David Kitchin, William Cook and Jayadev Misra Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCES A Language for Task Orchestration and its Semantic Properties David Kitchin, William Cook and Jayadev Misra Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin
Towards a numerical solution of the "1/2 vs. 3/2" puzzle
 Towards a numerical solution of the /2 s 3/2 puzzle Benoît Blossier DESY Zeuthen Motiations Hea Quark Effectie Theor Theoretical expectations Experimental measurements umerical computation of Conclusion
Towards a numerical solution of the /2 s 3/2 puzzle Benoît Blossier DESY Zeuthen Motiations Hea Quark Effectie Theor Theoretical expectations Experimental measurements umerical computation of Conclusion
Reversible and Quantum computing. Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016
 Reversible and Quantum computing Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016 Reversible computing A process is said to be logically reversible if the transition function that maps old computational states to
Reversible and Quantum computing Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016 Reversible computing A process is said to be logically reversible if the transition function that maps old computational states to
Estimation of Retention Factors of Nucleotides by Buffer Concentrations in RP-HPLC
 HWAHAK KONGHAK Vol. 38, No. 5, October, 2000, pp. 626-632 (Journal of the Korean Institute of Chemical Engineers) RP-HPLC Nucleotides (2000 2 1, 2000 4 1 ) Estimation of Retention Factors of Nucleotides
HWAHAK KONGHAK Vol. 38, No. 5, October, 2000, pp. 626-632 (Journal of the Korean Institute of Chemical Engineers) RP-HPLC Nucleotides (2000 2 1, 2000 4 1 ) Estimation of Retention Factors of Nucleotides
A Study on Dental Health Awareness of High School Students
 Journal of Dental Hygiene Science Vol. 3, No. 1,. 23~ 31 (2003), 1 Su-Min Yoo and Geum-Sun Ahn 1 Deartment of Dental Hygiene, Dong-u College 1 Deartment of Dental Hygiene, Kyung Bok College In this research,
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science Vol. 3, No. 1,. 23~ 31 (2003), 1 Su-Min Yoo and Geum-Sun Ahn 1 Deartment of Dental Hygiene, Dong-u College 1 Deartment of Dental Hygiene, Kyung Bok College In this research,
6. Convert 5021 centimeters to kilometers. 7. How many seconds are in a leap year? 8. Convert the speed 5.30 m/s to km/h.
 % " ' ) 2 3 1 2 3 + + 4 2 3 L L CHAPTER A Physics Toolkit Practice Problems Mathematics and Physics pages page 5 For each problem, give the rewritten equation you would use and the answer. 1. A lightbulb
% " ' ) 2 3 1 2 3 + + 4 2 3 L L CHAPTER A Physics Toolkit Practice Problems Mathematics and Physics pages page 5 For each problem, give the rewritten equation you would use and the answer. 1. A lightbulb
Quantum Recursion and Second Quantisation
 Quantum Recursion and Second Quantisation Mingsheng Ying State Key Laboratory of Computer Science Outline 1. Introduction 2. Recursive Programming 3. Classical Recursion in Quantum Programming 4. Quantum
Quantum Recursion and Second Quantisation Mingsheng Ying State Key Laboratory of Computer Science Outline 1. Introduction 2. Recursive Programming 3. Classical Recursion in Quantum Programming 4. Quantum
Emefcy Group Limited (ASX : EMC) ASX Appendix 4D Half Year Report and Interim Financial Statements for the six months ended 30 June 2016
 Emefcy Group Limited (ASX EMC) ASX Appendix D Half Year Report and Interim Financial Statements for the six months ended June 6 Melbourne Australia and Caesarea Israel 6 August 6 he Company s ASX Appendix
Emefcy Group Limited (ASX EMC) ASX Appendix D Half Year Report and Interim Financial Statements for the six months ended June 6 Melbourne Australia and Caesarea Israel 6 August 6 he Company s ASX Appendix
Quantum Programming. Juliana K. Vizzotto 1 and Amr Sabry 2. 8 November Yale CS Colloquium Page 1. 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul
 Quantum Programming Juliana K. Vizzotto 1 and Amr Sabry 2 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul 2 IU Computer Science Department 8 November 2004 Yale CS Colloquium Page 1 Quantum mechanics It is a
Quantum Programming Juliana K. Vizzotto 1 and Amr Sabry 2 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul 2 IU Computer Science Department 8 November 2004 Yale CS Colloquium Page 1 Quantum mechanics It is a
Continuing Education and Workforce Training Course Schedule Winter / Spring 2010
 Continuing Education and Workforce Training Course Schedule Winter / Spring 2010 www.southeastmn.edu/training Creating the Solution that Fits! Information Information Registration Registration via our
Continuing Education and Workforce Training Course Schedule Winter / Spring 2010 www.southeastmn.edu/training Creating the Solution that Fits! Information Information Registration Registration via our
Port Vintage. Foundry: Onrepeat Types Website: Designer: João Oliveira INTRO PORT VINTAGE REGULAR
 Port Vintage Foundry: Onrepeat Types Website: http://www.onrepeat.net Designer: João Oliveira Email: hi@onrepeat.net 2 3 63 115 131 139 INTRO PORT VINTAGE REGULAR PORT VINTAGE DECORATED PORT VINTAGE ORNAMENTS
Port Vintage Foundry: Onrepeat Types Website: http://www.onrepeat.net Designer: João Oliveira Email: hi@onrepeat.net 2 3 63 115 131 139 INTRO PORT VINTAGE REGULAR PORT VINTAGE DECORATED PORT VINTAGE ORNAMENTS
Some emission processes are intrinsically polarised e.g. synchrotron radiation.
 Polarisation Some emission processes are intrinsically polarised e.g. synchrotron radiation. B e linearly polarised emission circularly polarised emission Scattering processes can either increase or decrease
Polarisation Some emission processes are intrinsically polarised e.g. synchrotron radiation. B e linearly polarised emission circularly polarised emission Scattering processes can either increase or decrease
SECTION A - EMPLOYEE DETAILS Termination date Employee number Contract/ Department SECTION C - STANDARD DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR ALL TERMINATIONS
 UNITRANS SA TERMINATION CHECKLIST NOTES: 1. This form applies to all terminations and needs to be submitted along with the required supplementary documentation to the HR Department within the following
UNITRANS SA TERMINATION CHECKLIST NOTES: 1. This form applies to all terminations and needs to be submitted along with the required supplementary documentation to the HR Department within the following
Adorn. sans condensed Smooth. v22622x
 s Adorn f t sans condensed Smooth 9 0 u v22622x user s guide PART OF THE ADORN POMANDER SMOOTH COLLECTION v O P E N T Y P E FAQ : For information on how to access the swashes and alternates, visit LauraWorthingtonType.com/faqs
s Adorn f t sans condensed Smooth 9 0 u v22622x user s guide PART OF THE ADORN POMANDER SMOOTH COLLECTION v O P E N T Y P E FAQ : For information on how to access the swashes and alternates, visit LauraWorthingtonType.com/faqs
Errata list, Nielsen & Chuang. rrata/errata.html
 Errata list, Nielsen & Chuang http://www.michaelnielsen.org/qcqi/errata/e rrata/errata.html Part II, Nielsen & Chuang Quantum circuits (Ch 4) SK Quantum algorithms (Ch 5 & 6) Göran Johansson Physical realisation
Errata list, Nielsen & Chuang http://www.michaelnielsen.org/qcqi/errata/e rrata/errata.html Part II, Nielsen & Chuang Quantum circuits (Ch 4) SK Quantum algorithms (Ch 5 & 6) Göran Johansson Physical realisation
 abosaleh @hotmail.com www.islamselect.com/secret ا ضاءة ١ تقدیم ٢ ` _ h g f e d cb a â á à ß Þ «ª µ ³ ² ± ٣ ٤ ٥ ٦ مقدمە ٧ ٨ ~ } { z y x w ٩ ١٠ the Secret DVD the Secret New Thought Movement ١١ ١٢ the Secret
abosaleh @hotmail.com www.islamselect.com/secret ا ضاءة ١ تقدیم ٢ ` _ h g f e d cb a â á à ß Þ «ª µ ³ ² ± ٣ ٤ ٥ ٦ مقدمە ٧ ٨ ~ } { z y x w ٩ ١٠ the Secret DVD the Secret New Thought Movement ١١ ١٢ the Secret
Æ Å not every column in E is a pivot column (so EB œ! has at least one free variable) Æ Å E has linearly dependent columns
 ßÞÞÞß @ is linearly independent if B" @" B# @# ÞÞÞ B: @: œ! has only the trivial solution EB œ! has only the trivial solution Ðwhere E œ Ò@ @ ÞÞÞ@ ÓÑ every column in E is a pivot column E has linearly
ßÞÞÞß @ is linearly independent if B" @" B# @# ÞÞÞ B: @: œ! has only the trivial solution EB œ! has only the trivial solution Ðwhere E œ Ò@ @ ÞÞÞ@ ÓÑ every column in E is a pivot column E has linearly
Regression and Correlation
 1 Topic 6 Regression and Correlation Contents 6.1 Introduction...................................... 2 6.2 Correlation...................................... 3 6.2.1 Definition...................................
1 Topic 6 Regression and Correlation Contents 6.1 Introduction...................................... 2 6.2 Correlation...................................... 3 6.2.1 Definition...................................
THE ANALYSIS OF THE CONVECTIVE-CONDUCTIVE HEAT TRANSFER IN THE BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS. Zbynek Svoboda
 THE NLSIS OF THE CONECTIE-CONDUCTIE HET TRNSFER IN THE BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS Zbynek Soboda Czech Technical Uniersity in Prague Faculty of Ciil Engineering 166 29 Prague 6 - Czech Republic BSTRCT The numerical
THE NLSIS OF THE CONECTIE-CONDUCTIE HET TRNSFER IN THE BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS Zbynek Soboda Czech Technical Uniersity in Prague Faculty of Ciil Engineering 166 29 Prague 6 - Czech Republic BSTRCT The numerical
