MA 15800, Summer 2016 Lesson 25 Notes Solving a System of Equations by substitution (or elimination) Matrices. 2 A System of Equations
|
|
|
- Hortense Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MA 800, Summer 06 Lesson Notes Solving a Sstem of Equations b substitution (or elimination) Matrices Consider the graphs of the two equations below. A Sstem of Equations From our mathematics eperience, ou probabl know that the first equation represents a parabola and the second equation represents a line. If the graphs of these two equations intersect, the ordered pair(s) is(are) called the solution(s) of the sstem of equations. Below are the graphs of both equations with the two solutions shown. The graph of the first equation, the parabola, is in black and the graph of the second equation, the line, is in red (, ) (, ) The ordered pairs above not onl represent the points where the graphs of the two equations intersect, the are also the onl ordered pairs that satisf both equations. In other words, the are the onl ordered pairs that make both equations true when the variables and are replaced. Using the point (, ): Using the point (, ) ( ) () ( ) A solution to a sstem of two equations makes both equations true. Hint: Before solving a sstem of equations alwas think about how man solutions there ma be. For eample: A line and a parabola could intersect at two points (as above) or onl one point or at no points (empt set).
2 Substitution Method:. Solve one of the equations for one variable in terms of the other variable.. Substitute the epression found in step one into the other equation, obtaining an equation of one variable.. Solve for this variable.. Back-substitute into the simplest equation to find the remaining variable(s).. Check each ordered pair in the given sstem E : Solve the sstem below. Write the solution(s) as ordered pair(s). Verif the solution b graphing each equation. I will solve the first equation for and substitute that epression for in the second equation. ( ) 7 ( ) Solution: (, ) Computerized graph: Intersection of the two lines is the solution First equation s graph is in black; the second equation s graph is in red. Intersection of the two lines is (, -) **Note: When using the substitution method and both variables drop out when solving and a false statement, such as =, results, there is no solution. In other words, the graphs of these two equations do not intersect and there are no ordered pair that will satisf both equations.**
3 Solve the following sstems of equations using the substitution method. E : Note: When solving this sstem of equations, the quadratic equation will be used. 0 Substitute the for the in the bottom equation. 0 I will use the quadratic formula to solve. ()() 8 () There are no real solutions to this equation. Therefore, this sstem of equations has NO SOLUTION. Verif b graphing that the graphs of these two equations do not intersect. If there is no solution, the graphs of the two equations will not intersect. Below are the graphs of both equations. The top equation is in black; it is a parabola opening right. The bottom equation, a line, is in red
4 With a sstem of two linear equations, the elimination method ma be used.. If necessar, multipl one of the equations b a non-zero constant so that the coefficients of one of the variables are opposites.. Add the two equations together and solve for one variable.. Back-substitute to find the remaining variable.. Check our ordered pair in both equations. E : Solve, using the elimination method. 6 The coefficients of the s are alread opposites. I will add the two equations and solve for. 6 7 Back-substitute in the first equation and solve for. Solution: (, ) The graph below verifies that the solution (intersection of the two lines) is (, ). The first equation is in black and the second in red
5 We have discussed that there is no solution if both variables drop out and a false statement results. When using the elimination method, if both variables drop out and a true statement results ( =, 0 = 0, etc.), then there are an infinite number of solutions. This result indicates that the two equations represent the same line. The solution is written in the form {(, ) equation of line}. Do not write all real numbers. Solutions are ordered pairs, not numbers. Graphicall, this means that the equations represent the same line. E. Solve using the substitution method. Substitue for in the other equation. () As seen above, both variables were eliminated and a false statement resulted. This indicates that there is NO SOLUTION and the graph would be parallel lines. The graph of the lines is seen below. The black line is the first equation; red is the second E : Solve using the elimination method. 6 ( 6) Add the two equations together: 0 0 As seen above, both variables were eliminated but a TRUE statement resulted. This indicates that there are an INFINITE number of solutions because the two equations are the same line. {(, ) } or The solution would be written {(, ) 6} or {(, )} 8
6 Characteristics of a Sstem of Linear Equations in Variable Graphs Number of Solutions Classification Nonparallel Lines One Consistent and Independent Sstem Same Lines Infinite Consistent and Dependent Sstem Parallel Lines No Solution Inconsistent Sstem E : Classif the following sstems of linear equations as consistent and independent, consistent and dependent, or inconsistent. 7 c d a) b) 9 c d (7 ) 8 7( 9) 6 a) 9 There is a solution. Therefore the sstem is consistent and independent. Graph of sstem: First equation is in black, second in red b) First I will 'clear' the denominators in the equations. 6( c d ) c d 0 (c d 0) ( c d ) c d (c d ) c6d 60 9c 6d 9 c c 6
7 There is a solution (variables were not eliminated). Therefore the sstem is consistent and independent and the graph would be two nonparallel lines. Below is a graph of both lines. d c ( ) 8 c) 07 Variables were eliminated and a false statement resulted. This sstem has no solution. The graph would be two parallel lines. Solve each sstem of equations. If it is a linear sstem, describe its classification. 6 E 6: I will solve the second equation for and substitute that epression for the in the first equation. ( ) (6) 0 0 or , 6 (0) Solutions: (, 0), The first equation is a circle and the second is a line. The graphs are shown on the net page. 7
8 (, 6 ) (,0) E 7: I will substitute the epression for from the bottom equation for the in the top equation. 8 0 (8) 0 0 or The top equation is a parabola. The bottom equation is a cubic curve. Both are graphed below. 8 (0 ) 0 Solutions: (0,0),, ( 8, 8 ) 0.00 (0,0)
9 We have solved applied problems where onl one equation of one variable was used. Sometimes writing two equations in two variables can be used to solve applied problems. E 8: The price of admission to a high school pla was $ for students and $.0 for nonstudents. If 0 tickets were sold for a total of $.0, how man of each kind of tickets were purchased? Let = the number of student tickets sold Let = the number of nonstudent tickets sold One equation: + = 0 Another equation: +. =. I will use the elimination method, multipling the first equation b then adding so the terms are eliminated. ( 0) student tickets and 7 nonstudent tickets E 9: A rancher is preparing an oat-cornmeal miture for livestock. Each ounce of oats provided grams of protein and 8 grams of carbohdrates. An ounce of cornmeal provides grams of protein and grams of carbohdrates. How man ounces of each can be used to meet the nutritional goals of 00 grams of protein and 0 grams of carbohdrates per feeding? Let a = number of ounces of oats Let b = number of ounces of cornmeal One equation: a + b = 00 Second equation: 8a + b = 0 I will use the elimination method, multipling the first equation b 8 and leaving the second equation as is. 8(a b 00) a b 600 8a b 0 8a b 0 a 80 a 0 ab00 (0) b b 00 b 0 b 0 0 ounces of oats and 0 ounces of cornmeal 9
10 E 0: Solve the following sstem. ( ) ( ) 0 ( ) ( ) 0 ( ) ( ) ( ) 0 0 or 0 0 Substitute in top equation. 0 Solutions: (0,), (, ) Both solutions check in both equations. The top equation is a circle with the center at (, ) and a radius length 0. The bottom equation is a line. Both are graphed below and the solutions ma be seen. (0, ) (, )
14.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 86 Chapter 1 Sstems of Equations and Matrices 1.1 Sstems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of equations in two variables. Use the method of elimination
86 Chapter 1 Sstems of Equations and Matrices 1.1 Sstems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of equations in two variables. Use the method of elimination
Unit 12 Study Notes 1 Systems of Equations
 You should learn to: Unit Stud Notes Sstems of Equations. Solve sstems of equations b substitution.. Solve sstems of equations b graphing (calculator). 3. Solve sstems of equations b elimination. 4. Solve
You should learn to: Unit Stud Notes Sstems of Equations. Solve sstems of equations b substitution.. Solve sstems of equations b graphing (calculator). 3. Solve sstems of equations b elimination. 4. Solve
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
12.1 Systems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination
 . Sstems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination Sstems of two linear equations in two variables A sstem of equations is a collection of two or more equations. A solution of a sstem in two variables
. Sstems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination Sstems of two linear equations in two variables A sstem of equations is a collection of two or more equations. A solution of a sstem in two variables
10.3 Solving Nonlinear Systems of Equations
 60 CHAPTER 0 Conic Sections Identif whether each equation, when graphed, will be a parabola, circle, ellipse, or hperbola. Then graph each equation.. - 7 + - =. = +. = + + 6. + 9 =. 9-9 = 6. 6 - = 7. 6
60 CHAPTER 0 Conic Sections Identif whether each equation, when graphed, will be a parabola, circle, ellipse, or hperbola. Then graph each equation.. - 7 + - =. = +. = + + 6. + 9 =. 9-9 = 6. 6 - = 7. 6
PRINCIPLES OF MATHEMATICS 11 Chapter 2 Quadratic Functions Lesson 1 Graphs of Quadratic Functions (2.1) where a, b, and c are constants and a 0
 PRINCIPLES OF MATHEMATICS 11 Chapter Quadratic Functions Lesson 1 Graphs of Quadratic Functions (.1) Date A. QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS A quadratic function is an equation that can be written in the following
PRINCIPLES OF MATHEMATICS 11 Chapter Quadratic Functions Lesson 1 Graphs of Quadratic Functions (.1) Date A. QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS A quadratic function is an equation that can be written in the following
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 4.. 4..4 Students have been solving equations even before Algebra. Now the focus on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions,
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 4.. 4..4 Students have been solving equations even before Algebra. Now the focus on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions,
1. Solutions to Systems of Linear Equations. Determine whether the ordered pairs are solutions to the system. x y 6. 3x y 2
 78 Chapter Sstems of Linear Equations Section. Concepts. Solutions to Sstems of Linear Equations. Dependent and Inconsistent Sstems of Linear Equations. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Solving
78 Chapter Sstems of Linear Equations Section. Concepts. Solutions to Sstems of Linear Equations. Dependent and Inconsistent Sstems of Linear Equations. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Solving
13.1 2X2 Systems of Equations
 . X Sstems of Equations In this section we want to spend some time reviewing sstems of equations. Recall there are two basic techniques we use for solving a sstem of equations: Elimination and Substitution.
. X Sstems of Equations In this section we want to spend some time reviewing sstems of equations. Recall there are two basic techniques we use for solving a sstem of equations: Elimination and Substitution.
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 3.. 3..4 In this course, one focus is on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions, students are able to solve equations
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 3.. 3..4 In this course, one focus is on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions, students are able to solve equations
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 5 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the equation. 1. + =. = 3 3. 5 + = 10. 3 = 5. 3 = 6. 3 + = 1 Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution. 7. a 3 > 8. c 9. d 5 < 3 10. 8 3r 5 r
Name Date Chapter 5 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the equation. 1. + =. = 3 3. 5 + = 10. 3 = 5. 3 = 6. 3 + = 1 Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution. 7. a 3 > 8. c 9. d 5 < 3 10. 8 3r 5 r
Chapter 6: Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 6: Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 6-1: Solving Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Identif solutions of sstems of linear equation in two variables. Solve sstems of linear equation in two variables
Chapter 6: Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 6-1: Solving Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Identif solutions of sstems of linear equation in two variables. Solve sstems of linear equation in two variables
RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS through
 RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS 11.1.2 through 11.1. Relations and Functions establish a correspondence between the input values (usuall ) and the output values (usuall ) according to the particular relation or
RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS 11.1.2 through 11.1. Relations and Functions establish a correspondence between the input values (usuall ) and the output values (usuall ) according to the particular relation or
Math098 Practice Final Test
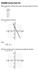 Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
MATH 115: Review for Chapter 6
 MATH 115: Review for Chapter 6 In order to prepare for our test on Chapter 6, ou need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics: I SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS CONTAINING
MATH 115: Review for Chapter 6 In order to prepare for our test on Chapter 6, ou need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics: I SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS CONTAINING
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions
 Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Systems of Linear and Quadratic Equations. Check Skills You ll Need. y x. Solve by Graphing. Solve the following system by graphing.
 NY- Learning Standards for Mathematics A.A. Solve a sstem of one linear and one quadratic equation in two variables, where onl factoring is required. A.G.9 Solve sstems of linear and quadratic equations
NY- Learning Standards for Mathematics A.A. Solve a sstem of one linear and one quadratic equation in two variables, where onl factoring is required. A.G.9 Solve sstems of linear and quadratic equations
M practice SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 M101 7.1-7.3 practice SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the sstem b substitution. 1) - 2 = -16 2-2 = -22 1) 2) 4-5 = 8 9 + 3 = 75
M101 7.1-7.3 practice SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the sstem b substitution. 1) - 2 = -16 2-2 = -22 1) 2) 4-5 = 8 9 + 3 = 75
8.7 Systems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities
 8.7 Sstems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities 67 8.7 Sstems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities In this section, we stud sstems of non-linear equations and inequalities. Unlike the sstems of
8.7 Sstems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities 67 8.7 Sstems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities In this section, we stud sstems of non-linear equations and inequalities. Unlike the sstems of
Essential Question How can you solve a nonlinear system of equations?
 .5 Solving Nonlinear Sstems Essential Question Essential Question How can ou solve a nonlinear sstem of equations? Solving Nonlinear Sstems of Equations Work with a partner. Match each sstem with its graph.
.5 Solving Nonlinear Sstems Essential Question Essential Question How can ou solve a nonlinear sstem of equations? Solving Nonlinear Sstems of Equations Work with a partner. Match each sstem with its graph.
LESSON #42 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART 2 COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations. The Method of Substitution. Equation 1 Equation 2. Check (2, 1) in Equation 1 and Equation 2: 2x y 5?
 3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
Chapter 5: Systems of Equations
 Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
The Elimination Method
 The Elimination Method The elimination method is sometimes called the addition method. It involves the process of eliminating a variable through addition. It is the final method of solving a sstem that
The Elimination Method The elimination method is sometimes called the addition method. It involves the process of eliminating a variable through addition. It is the final method of solving a sstem that
5.2 Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems
 Name Class Date 5. Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem composed of a linear equation in two variables and a quadratic equation in two variables? Resource Locker
Name Class Date 5. Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem composed of a linear equation in two variables and a quadratic equation in two variables? Resource Locker
Fair Game Review. Chapter 9. Find the square root(s) ± Find the side length of the square. 7. Simplify Simplify 63.
 Name Date Chapter 9 Find the square root(s). Fair Game Review... 9. ±. Find the side length of the square.. s. s s Area = 9 ft s Area = 0. m 7. Simplif 0. 8. Simplif. 9. Simplif 08. 0. Simplif 88. Copright
Name Date Chapter 9 Find the square root(s). Fair Game Review... 9. ±. Find the side length of the square.. s. s s Area = 9 ft s Area = 0. m 7. Simplif 0. 8. Simplif. 9. Simplif 08. 0. Simplif 88. Copright
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
10.4 Nonlinear Inequalities and Systems of Inequalities. OBJECTIVES 1 Graph a Nonlinear Inequality. 2 Graph a System of Nonlinear Inequalities.
 Section 0. Nonlinear Inequalities and Sstems of Inequalities 6 CONCEPT EXTENSIONS For the eercises below, see the Concept Check in this section.. Without graphing, how can ou tell that the graph of + =
Section 0. Nonlinear Inequalities and Sstems of Inequalities 6 CONCEPT EXTENSIONS For the eercises below, see the Concept Check in this section.. Without graphing, how can ou tell that the graph of + =
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
Math 121. Practice Questions Chapters 2 and 3 Fall Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint.
 Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
8.4. If we let x denote the number of gallons pumped, then the price y in dollars can $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.
 8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
9-1. The Function with Equation y = ax 2. Vocabulary. Graphing y = x 2. Lesson
 Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
UNIT 5. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS
 3º ESO. Definitions UNIT 5. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS A linear equation with two unknowns is an equation with two unknowns having both of them degree one. Eamples. 3 + 5 and + 6 9. The standard form for these
3º ESO. Definitions UNIT 5. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS A linear equation with two unknowns is an equation with two unknowns having both of them degree one. Eamples. 3 + 5 and + 6 9. The standard form for these
2. Bunny Slope:, Medium Trail: 4. 58; The starting height of the trail is 58 meters ; The length of the trail is 1450 meters.
 ...7 Start Thinking! For use before Lesson.7 Sample answer: If ou need to write the equation of a line given the slope and a point on the line, ou can find the -intercept (either graphicall or algebraicall).
...7 Start Thinking! For use before Lesson.7 Sample answer: If ou need to write the equation of a line given the slope and a point on the line, ou can find the -intercept (either graphicall or algebraicall).
12x y (4) 2x y (4) 5x y is the same as
 Name: Unit #6 Review Quadratic Algebra Date: 1. When 6 is multiplied b the result is 0 1 () 9 1 () 9 1 () 1 0. When is multiplied b the result is 10 6 1 () 7 1 () 7 () 10 6. Written without negative eponents
Name: Unit #6 Review Quadratic Algebra Date: 1. When 6 is multiplied b the result is 0 1 () 9 1 () 9 1 () 1 0. When is multiplied b the result is 10 6 1 () 7 1 () 7 () 10 6. Written without negative eponents
15.4 Equation of a Circle
 Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
One Solution Two Solutions Three Solutions Four Solutions. Since both equations equal y we can set them equal Combine like terms Factor Solve for x
 Algebra Notes Quadratic Systems Name: Block: Date: Last class we discussed linear systems. The only possibilities we had we 1 solution, no solution or infinite solutions. With quadratic systems we have
Algebra Notes Quadratic Systems Name: Block: Date: Last class we discussed linear systems. The only possibilities we had we 1 solution, no solution or infinite solutions. With quadratic systems we have
Algebra I. Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176. Slide 3 / 176. Slide 4 / 176. Slide 6 / 176. Slide 5 / 176. System of Linear Equations.
 Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176 Algebra I Sstem of Linear Equations 21-11-2 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 176 Slide 4 / 176 Table of Contents Solving Sstems b Graphing Solving Sstems b Substitution Solving Sstems
Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176 Algebra I Sstem of Linear Equations 21-11-2 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 176 Slide 4 / 176 Table of Contents Solving Sstems b Graphing Solving Sstems b Substitution Solving Sstems
Module 3, Section 4 Analytic Geometry II
 Principles of Mathematics 11 Section, Introduction 01 Introduction, Section Analtic Geometr II As the lesson titles show, this section etends what ou have learned about Analtic Geometr to several related
Principles of Mathematics 11 Section, Introduction 01 Introduction, Section Analtic Geometr II As the lesson titles show, this section etends what ou have learned about Analtic Geometr to several related
7.5 Solve Special Types of
 75 Solve Special Tpes of Linear Sstems Goal p Identif the number of of a linear sstem Your Notes VOCABULARY Inconsistent sstem Consistent dependent sstem Eample A linear sstem with no Show that the linear
75 Solve Special Tpes of Linear Sstems Goal p Identif the number of of a linear sstem Your Notes VOCABULARY Inconsistent sstem Consistent dependent sstem Eample A linear sstem with no Show that the linear
10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 Name Class Date 10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of quadratic functions and cubic functions, and how can ou find them? Resource
Name Class Date 10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of quadratic functions and cubic functions, and how can ou find them? Resource
Chapter 13. Overview. The Quadratic Formula. Overview. The Quadratic Formula. The Quadratic Formula. Lewinter & Widulski 1. The Quadratic Formula
 Chapter 13 Overview Some More Math Before You Go The Quadratic Formula The iscriminant Multiplication of Binomials F.O.I.L. Factoring Zero factor propert Graphing Parabolas The Ais of Smmetr, Verte and
Chapter 13 Overview Some More Math Before You Go The Quadratic Formula The iscriminant Multiplication of Binomials F.O.I.L. Factoring Zero factor propert Graphing Parabolas The Ais of Smmetr, Verte and
Berkeley City College Precalculus - Math 1 - Chapter 11. Name
 Berkele Cit College Precalculus - Math 1 - Chapter 11 Homework 7 Due: Sstems of Equations Name Verif that the values of the variables listed are solutions of the sstem of equations. 1) 3 + = -3 + 3 = 1)
Berkele Cit College Precalculus - Math 1 - Chapter 11 Homework 7 Due: Sstems of Equations Name Verif that the values of the variables listed are solutions of the sstem of equations. 1) 3 + = -3 + 3 = 1)
Equations for Some Hyperbolas
 Lesson 1-6 Lesson 1-6 BIG IDEA From the geometric defi nition of a hperbola, an equation for an hperbola smmetric to the - and -aes can be found. The edges of the silhouettes of each of the towers pictured
Lesson 1-6 Lesson 1-6 BIG IDEA From the geometric defi nition of a hperbola, an equation for an hperbola smmetric to the - and -aes can be found. The edges of the silhouettes of each of the towers pictured
APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation
 APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation Rotation of Aes Invariants Under Rotation After rotation of the - and -aes counterclockwise through an angle, the rotated aes are denoted as the
APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation Rotation of Aes Invariants Under Rotation After rotation of the - and -aes counterclockwise through an angle, the rotated aes are denoted as the
Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems
 36 LESSON Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems UNDERSTAND A sstem of two or more equations can include linear and nonlinear equations. In a linear-quadratic sstem, there is one linear equation and one quadratic
36 LESSON Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems UNDERSTAND A sstem of two or more equations can include linear and nonlinear equations. In a linear-quadratic sstem, there is one linear equation and one quadratic
Chapter 11. Systems of Equations Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing
 Chapter 11 Sstems of Equations 11.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Learning Objectives: A. Decide whether an ordered pair is a solution of a sstem of linear equations. B. Solve a sstem of
Chapter 11 Sstems of Equations 11.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Learning Objectives: A. Decide whether an ordered pair is a solution of a sstem of linear equations. B. Solve a sstem of
7.1 Guided Practice (p. 401) 1. to find an ordered pair that satisfies each of the equations in the system. solution of the system.
 CHAPTER 7 Think and Discuss (p. 9). 6,00,000 units. 0,00,000 6,00,000 4,400,000 renters Skill Review (p. 96) 9r 4r 6r. 8.. 0.d.d d 4. w 4 w 4 w 4 w 4 w. 6. 7 g g 9 g 7 g 6 g 0 7 8 40 40 40 7. 6 8. 8 9....
CHAPTER 7 Think and Discuss (p. 9). 6,00,000 units. 0,00,000 6,00,000 4,400,000 renters Skill Review (p. 96) 9r 4r 6r. 8.. 0.d.d d 4. w 4 w 4 w 4 w 4 w. 6. 7 g g 9 g 7 g 6 g 0 7 8 40 40 40 7. 6 8. 8 9....
Solve each system by graphing. Check your solution. y =-3x x + y = 5 y =-7
 Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
Section 5.1: Functions
 Objective: Identif functions and use correct notation to evaluate functions at numerical and variable values. A relationship is a matching of elements between two sets with the first set called the domain
Objective: Identif functions and use correct notation to evaluate functions at numerical and variable values. A relationship is a matching of elements between two sets with the first set called the domain
Course 15 Numbers and Their Properties
 Course Numbers and Their Properties KEY Module: Objective: Rules for Eponents and Radicals To practice appling rules for eponents when the eponents are rational numbers Name: Date: Fill in the blanks.
Course Numbers and Their Properties KEY Module: Objective: Rules for Eponents and Radicals To practice appling rules for eponents when the eponents are rational numbers Name: Date: Fill in the blanks.
Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 7 7. Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations 7. Two-Variable Linear Sstems 7.3 Multivariable Linear Sstems 7. Partial Fractions 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 7.6 Linear
Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 7 7. Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations 7. Two-Variable Linear Sstems 7.3 Multivariable Linear Sstems 7. Partial Fractions 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 7.6 Linear
Keira Godwin. Time Allotment: 13 days. Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to:
 Keira Godwin Time Allotment: 3 das Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: o Simplif comple rational fractions. o Solve comple rational fractional equations. o Solve quadratic
Keira Godwin Time Allotment: 3 das Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: o Simplif comple rational fractions. o Solve comple rational fractional equations. o Solve quadratic
AQA Level 2 Further mathematics Number & algebra. Section 3: Functions and their graphs
 AQA Level Further mathematics Number & algebra Section : Functions and their graphs Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on: The language of functions Gradients The equation of a straight
AQA Level Further mathematics Number & algebra Section : Functions and their graphs Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on: The language of functions Gradients The equation of a straight
Mth Quadratic functions and quadratic equations
 Mth 0 - Quadratic functions and quadratic equations Name Find the product. 1) 8a3(2a3 + 2 + 12a) 2) ( + 4)( + 6) 3) (3p - 1)(9p2 + 3p + 1) 4) (32 + 4-4)(2-3 + 3) ) (4a - 7)2 Factor completel. 6) 92-4 7)
Mth 0 - Quadratic functions and quadratic equations Name Find the product. 1) 8a3(2a3 + 2 + 12a) 2) ( + 4)( + 6) 3) (3p - 1)(9p2 + 3p + 1) 4) (32 + 4-4)(2-3 + 3) ) (4a - 7)2 Factor completel. 6) 92-4 7)
Chapter 9 Rational Expressions and Equations Lesson 9-1 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Pages
 Chapter 9 Rational Epressions and Equations Lesson 9- Multipling and Dividing Rational Epressions Pages 76 78. Sample answer: 3. Never; solving the equation using cross products leads to 5 0, which is
Chapter 9 Rational Epressions and Equations Lesson 9- Multipling and Dividing Rational Epressions Pages 76 78. Sample answer: 3. Never; solving the equation using cross products leads to 5 0, which is
HCC-SE MATH DEPT. 1 Revised Fall 2008
 FINAL EXAM REVIEW ITEMS Math : College Algebra Find the -intercepts and an -intercepts. ) f() = + 7-0 ) = Name ) Select the equation that describes the graph. Solve the equation and epress the solution
FINAL EXAM REVIEW ITEMS Math : College Algebra Find the -intercepts and an -intercepts. ) f() = + 7-0 ) = Name ) Select the equation that describes the graph. Solve the equation and epress the solution
Demonstrate solution methods for systems of linear equations. Show that a system of equations can be represented in matrix-vector form.
 Chapter Linear lgebra Objective Demonstrate solution methods for sstems of linear equations. Show that a sstem of equations can be represented in matri-vector form. 4 Flowrates in kmol/hr Figure.: Two
Chapter Linear lgebra Objective Demonstrate solution methods for sstems of linear equations. Show that a sstem of equations can be represented in matri-vector form. 4 Flowrates in kmol/hr Figure.: Two
Chapter Start Thinking! For use before Activity 6.1. For use before Activity Start Thinking! For use before Lesson
 . Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
. Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
Algebra 2 Semester Exam Review
 Algebra Semester Eam Review 7 Graph the numbers,,,, and 0 on a number line Identif the propert shown rs rs r when r and s Evaluate What is the value of k k when k? Simplif the epression 7 7 Solve the equation
Algebra Semester Eam Review 7 Graph the numbers,,,, and 0 on a number line Identif the propert shown rs rs r when r and s Evaluate What is the value of k k when k? Simplif the epression 7 7 Solve the equation
Northwest High School s Algebra 2/Honors Algebra 2
 Northwest High School s Algebra /Honors Algebra Summer Review Packet 0 DUE Frida, September, 0 Student Name This packet has been designed to help ou review various mathematical topics that will be necessar
Northwest High School s Algebra /Honors Algebra Summer Review Packet 0 DUE Frida, September, 0 Student Name This packet has been designed to help ou review various mathematical topics that will be necessar
Lesson 12: Systems of Linear Equations
 Our final lesson involves the study of systems of linear equations. In this lesson, we examine the relationship between two distinct linear equations. Specifically, we are looking for the point where the
Our final lesson involves the study of systems of linear equations. In this lesson, we examine the relationship between two distinct linear equations. Specifically, we are looking for the point where the
Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 7. Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations 7. Two-Variable Linear Sstems 7.3 Multivariable Linear Sstems 7. Partial Fractions 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 7.6 Linear
Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 7. Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations 7. Two-Variable Linear Sstems 7.3 Multivariable Linear Sstems 7. Partial Fractions 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 7.6 Linear
11.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Math RE - Calculus I Functions Page 1 of 10. Topics of Functions used in Calculus
 Math 0-03-RE - Calculus I Functions Page of 0 Definition of a function f() : Topics of Functions used in Calculus A function = f() is a relation between variables and such that for ever value onl one value.
Math 0-03-RE - Calculus I Functions Page of 0 Definition of a function f() : Topics of Functions used in Calculus A function = f() is a relation between variables and such that for ever value onl one value.
For questions 5-8, solve each inequality and graph the solution set. You must show work for full credit. (2 pts each)
 Alg Midterm Review Practice Level 1 C 1. Find the opposite and the reciprocal of 0. a. 0, 1 b. 0, 1 0 0 c. 0, 1 0 d. 0, 1 0 For questions -, insert , or = to make the sentence true. (1pt each) A. 5
Alg Midterm Review Practice Level 1 C 1. Find the opposite and the reciprocal of 0. a. 0, 1 b. 0, 1 0 0 c. 0, 1 0 d. 0, 1 0 For questions -, insert , or = to make the sentence true. (1pt each) A. 5
Pure Core 1. Revision Notes
 Pure Core Revision Notes Ma 06 Pure Core Algebra... Indices... Rules of indices... Surds... 4 Simplifing surds... 4 Rationalising the denominator... 4 Quadratic functions... 5 Completing the square....
Pure Core Revision Notes Ma 06 Pure Core Algebra... Indices... Rules of indices... Surds... 4 Simplifing surds... 4 Rationalising the denominator... 4 Quadratic functions... 5 Completing the square....
Math 3201 UNIT 5: Polynomial Functions NOTES. Characteristics of Graphs and Equations of Polynomials Functions
 1 Math 301 UNIT 5: Polnomial Functions NOTES Section 5.1 and 5.: Characteristics of Graphs and Equations of Polnomials Functions What is a polnomial function? Polnomial Function: - A function that contains
1 Math 301 UNIT 5: Polnomial Functions NOTES Section 5.1 and 5.: Characteristics of Graphs and Equations of Polnomials Functions What is a polnomial function? Polnomial Function: - A function that contains
Name Class Date. Solving by Graphing and Algebraically
 Name Class Date 16-4 Nonlinear Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? To estimate the solution to a sstem
Name Class Date 16-4 Nonlinear Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? To estimate the solution to a sstem
f(x) = 2x 2 + 2x - 4
 4-1 Graphing Quadratic Functions What You ll Learn Scan the tet under the Now heading. List two things ou will learn about in the lesson. 1. Active Vocabular 2. New Vocabular Label each bo with the terms
4-1 Graphing Quadratic Functions What You ll Learn Scan the tet under the Now heading. List two things ou will learn about in the lesson. 1. Active Vocabular 2. New Vocabular Label each bo with the terms
Ch 3 Alg 2 Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Systems of Equations
 Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Mt. Douglas Secondary
 Foundations of Math 11 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 57.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation A linear equation means the equation of a straight line, and can be written in one of two forms.
Foundations of Math 11 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 57.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation A linear equation means the equation of a straight line, and can be written in one of two forms.
Systems of Equations and Inequalities. College Algebra
 Systems of Equations and Inequalities College Algebra System of Linear Equations There are three types of systems of linear equations in two variables, and three types of solutions. 1. An independent system
Systems of Equations and Inequalities College Algebra System of Linear Equations There are three types of systems of linear equations in two variables, and three types of solutions. 1. An independent system
What if both of the variables cancel out?
 Name:. Solving Sstems of Equations Algebraicall Lesson Essential Question: How do ou solve a sstem of equations algebraicall? SUBSTITUTION ELIMINATION Definition- Definition- - = -6 + = - - = -6 + = -
Name:. Solving Sstems of Equations Algebraicall Lesson Essential Question: How do ou solve a sstem of equations algebraicall? SUBSTITUTION ELIMINATION Definition- Definition- - = -6 + = - - = -6 + = -
UNCORRECTED SAMPLE PAGES. 3Quadratics. Chapter 3. Objectives
 Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
 Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15)
 MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15) Date: Chapter Goals: Identif solutions to an equation. Solve an equation for one variable in terms of another. What is a function? Understand
MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15) Date: Chapter Goals: Identif solutions to an equation. Solve an equation for one variable in terms of another. What is a function? Understand
QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW
 Name: Date: QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW Linear and eponential functions are used throughout mathematics and science due to their simplicit and applicabilit. Quadratic functions comprise another ver important
Name: Date: QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW Linear and eponential functions are used throughout mathematics and science due to their simplicit and applicabilit. Quadratic functions comprise another ver important
A Preview of College Algebra CHAPTER
 hal9_ch_-9.qd //9 : PM Page A Preview of College Algebra CHAPTER Chapter Outline. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Using Augmented Matrices. Sstems of Linear Equations in Three Variables. Horizontal
hal9_ch_-9.qd //9 : PM Page A Preview of College Algebra CHAPTER Chapter Outline. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Using Augmented Matrices. Sstems of Linear Equations in Three Variables. Horizontal
Using Intercept Form
 8.5 Using Intercept Form Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of f () = a( p)( q)? Using Zeros to Write Functions Work with a partner. Each graph represents a function of
8.5 Using Intercept Form Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of f () = a( p)( q)? Using Zeros to Write Functions Work with a partner. Each graph represents a function of
McKinney High School AP Calculus Summer Packet
 McKinne High School AP Calculus Summer Packet (for students entering AP Calculus AB or AP Calculus BC) Name:. This packet is to be handed in to our Calculus teacher the first week of school.. ALL work
McKinne High School AP Calculus Summer Packet (for students entering AP Calculus AB or AP Calculus BC) Name:. This packet is to be handed in to our Calculus teacher the first week of school.. ALL work
( 7, 3) means x = 7 and y = 3. ( 7, 3) works in both equations so. Section 5 1: Solving a System of Linear Equations by Graphing
 Section 5 : Solving a Sstem of Linear Equations b Graphing What is a sstem of Linear Equations? A sstem of linear equations is a list of two or more linear equations that each represents the graph of a
Section 5 : Solving a Sstem of Linear Equations b Graphing What is a sstem of Linear Equations? A sstem of linear equations is a list of two or more linear equations that each represents the graph of a
Mathematics. Polynomials and Quadratics. hsn.uk.net. Higher. Contents. Polynomials and Quadratics 1. CfE Edition
 Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
Rev Name Date. Solve each of the following equations for y by isolating the square and using the square root property.
 Rev 8-8-3 Name Date TI-8 GC 3 Using GC to Graph Parabolae that are Not Functions of Objectives: Recall the square root propert Practice solving a quadratic equation f Graph the two parts of a hizontal
Rev 8-8-3 Name Date TI-8 GC 3 Using GC to Graph Parabolae that are Not Functions of Objectives: Recall the square root propert Practice solving a quadratic equation f Graph the two parts of a hizontal
Name Class Date. Solving Special Systems by Graphing. Does this linear system have a solution? Use the graph to explain.
 Name Class Date 5 Solving Special Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How do ou solve sstems with no or infinitel man solutions? 1 A-REI.3.6 EXAMPLE Solving Special Sstems b Graphing Use the graph
Name Class Date 5 Solving Special Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How do ou solve sstems with no or infinitel man solutions? 1 A-REI.3.6 EXAMPLE Solving Special Sstems b Graphing Use the graph
KEY IDEAS. Chapter 1 Function Transformations. 1.1 Horizontal and Vertical Translations Pre-Calculus 12 Student Workbook MHR 1
 Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
Graph the linear system and estimate the solution. Then check the solution algebraically.
 (Chapters and ) A. Linear Sstems (pp. 6 0). Solve a Sstem b Graphing Vocabular Solution For a sstem of linear equations in two variables, an ordered pair (x, ) that satisfies each equation. Consistent
(Chapters and ) A. Linear Sstems (pp. 6 0). Solve a Sstem b Graphing Vocabular Solution For a sstem of linear equations in two variables, an ordered pair (x, ) that satisfies each equation. Consistent
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
SECOND-DEGREE INEQUALITIES
 60 (-40) Chapter Nonlinear Sstems and the Conic Sections 0 0 4 FIGURE FOR EXERCISE GETTING MORE INVOLVED. Cooperative learning. Let (, ) be an arbitrar point on an ellipse with foci (c, 0) and ( c, 0)
60 (-40) Chapter Nonlinear Sstems and the Conic Sections 0 0 4 FIGURE FOR EXERCISE GETTING MORE INVOLVED. Cooperative learning. Let (, ) be an arbitrar point on an ellipse with foci (c, 0) and ( c, 0)
MTH 112 Practice Test 3 Sections 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 1.9, 7.4, 7.5, 8.1, 8.2
 MTH 112 Practice Test 3 Sections 3.3, 3., 3., 1.9, 7., 7., 8.1, 8.2 Use properties of logarithms to epand the logarithmic epression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic epressions
MTH 112 Practice Test 3 Sections 3.3, 3., 3., 1.9, 7., 7., 8.1, 8.2 Use properties of logarithms to epand the logarithmic epression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic epressions
What You ll Learn Identify direct variation. Use direct variation to solve problems.
 AM_S_C_L_3.indd Page // 3: PM s-user /Volumes//GO/CORE_READING/TENNESSEE/ANCILLARY... Proportionalit and Linear Relationships Teach the Concept Lesson - Direct Variation Interactive Stud Guide See pages
AM_S_C_L_3.indd Page // 3: PM s-user /Volumes//GO/CORE_READING/TENNESSEE/ANCILLARY... Proportionalit and Linear Relationships Teach the Concept Lesson - Direct Variation Interactive Stud Guide See pages
Unit 3 NOTES Honors Common Core Math 2 1. Day 1: Properties of Exponents
 Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math Da : Properties of Eponents Warm-Up: Before we begin toda s lesson, how much do ou remember about eponents? Use epanded form to write the rules for the eponents. OBJECTIVE
Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math Da : Properties of Eponents Warm-Up: Before we begin toda s lesson, how much do ou remember about eponents? Use epanded form to write the rules for the eponents. OBJECTIVE
Solve each system by substitution or elimination. Check your solutions. b.
 Algebra: 10.3.1: Intersect or Intercept? Name Solutions Block Date Bell Work: a. = 4 2 3 = 3 2 3(4 ) = 3 2 12 + 3 = 3 5 12 = 3 5 = 15 Solve each sstem b substitution or elimination. Check our solutions.
Algebra: 10.3.1: Intersect or Intercept? Name Solutions Block Date Bell Work: a. = 4 2 3 = 3 2 3(4 ) = 3 2 12 + 3 = 3 5 12 = 3 5 = 15 Solve each sstem b substitution or elimination. Check our solutions.
Higher. Polynomials and Quadratics. Polynomials and Quadratics 1
 Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
Name: Richard Montgomery High School Department of Mathematics. Summer Math Packet. for students entering. Algebra 2/Trig*
 Name: Richard Montgomer High School Department of Mathematics Summer Math Packet for students entering Algebra 2/Trig* For the following courses: AAF, Honors Algebra 2, Algebra 2 (Please go the RM website
Name: Richard Montgomer High School Department of Mathematics Summer Math Packet for students entering Algebra 2/Trig* For the following courses: AAF, Honors Algebra 2, Algebra 2 (Please go the RM website
Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents
 Math 1400 - Mano Table of Contents - Review - page 1 of 2 Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus is one of the Marquette Core Courses for Mathematical
Math 1400 - Mano Table of Contents - Review - page 1 of 2 Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus is one of the Marquette Core Courses for Mathematical
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
+ = + + = x = + = + = 36x
 Ch 5 Alg L Homework Worksheets Computation Worksheet #1: You should be able to do these without a calculator! A) Addition (Subtraction = add the opposite of) B) Multiplication (Division = multipl b the
Ch 5 Alg L Homework Worksheets Computation Worksheet #1: You should be able to do these without a calculator! A) Addition (Subtraction = add the opposite of) B) Multiplication (Division = multipl b the
Cubic and quartic functions
 3 Cubic and quartic functions 3A Epanding 3B Long division of polnomials 3C Polnomial values 3D The remainder and factor theorems 3E Factorising polnomials 3F Sum and difference of two cubes 3G Solving
3 Cubic and quartic functions 3A Epanding 3B Long division of polnomials 3C Polnomial values 3D The remainder and factor theorems 3E Factorising polnomials 3F Sum and difference of two cubes 3G Solving
